* toctree * not-doctested.txt * collapse sections * feedback * update * rewrite get started sections * fixes * fix * loading models * fix * customize models * share * fix link * contribute part 1 * contribute pt 2 * fix toctree * tokenization pt 1 * Add new model (#32615) * v1 - working version * fix * fix * fix * fix * rename to correct name * fix title * fixup * rename files * fix * add copied from on tests * rename to `FalconMamba` everywhere and fix bugs * fix quantization + accelerate * fix copies * add `torch.compile` support * fix tests * fix tests and add slow tests * copies on config * merge the latest changes * fix tests * add few lines about instruct * Apply suggestions from code review Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com> * fix * fix tests --------- Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com> * "to be not" -> "not to be" (#32636) * "to be not" -> "not to be" * Update sam.md * Update trainer.py * Update modeling_utils.py * Update test_modeling_utils.py * Update test_modeling_utils.py * fix hfoption tag * tokenization pt. 2 * image processor * fix toctree * backbones * feature extractor * fix file name * processor * update not-doctested * update * make style * fix toctree * revision * make fixup * fix toctree * fix * make style * fix hfoption tag * pipeline * pipeline gradio * pipeline web server * add pipeline * fix toctree * not-doctested * prompting * llm optims * fix toctree * fixes * cache * text generation * fix * chat pipeline * chat stuff * xla * torch.compile * cpu inference * toctree * gpu inference * agents and tools * gguf/tiktoken * finetune * toctree * trainer * trainer pt 2 * optims * optimizers * accelerate * parallelism * fsdp * update * distributed cpu * hardware training * gpu training * gpu training 2 * peft * distrib debug * deepspeed 1 * deepspeed 2 * chat toctree * quant pt 1 * quant pt 2 * fix toctree * fix * fix * quant pt 3 * quant pt 4 * serialization * torchscript * scripts * tpu * review * model addition timeline * modular * more reviews * reviews * fix toctree * reviews reviews * continue reviews * more reviews * modular transformers * more review * zamba2 * fix * all frameworks * pytorch * supported model frameworks * flashattention * rm check_table * not-doctested.txt * rm check_support_list.py * feedback * updates/feedback * review * feedback * fix * update * feedback * updates * update --------- Co-authored-by: Younes Belkada <49240599+younesbelkada@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Quentin Gallouédec <45557362+qgallouedec@users.noreply.github.com>
6.5 KiB
VideoMAE


Overview
The VideoMAE model was proposed in VideoMAE: Masked Autoencoders are Data-Efficient Learners for Self-Supervised Video Pre-Training by Zhan Tong, Yibing Song, Jue Wang, Limin Wang. VideoMAE extends masked auto encoders (MAE) to video, claiming state-of-the-art performance on several video classification benchmarks.
The abstract from the paper is the following:
Pre-training video transformers on extra large-scale datasets is generally required to achieve premier performance on relatively small datasets. In this paper, we show that video masked autoencoders (VideoMAE) are data-efficient learners for self-supervised video pre-training (SSVP). We are inspired by the recent ImageMAE and propose customized video tube masking and reconstruction. These simple designs turn out to be effective for overcoming information leakage caused by the temporal correlation during video reconstruction. We obtain three important findings on SSVP: (1) An extremely high proportion of masking ratio (i.e., 90% to 95%) still yields favorable performance of VideoMAE. The temporally redundant video content enables higher masking ratio than that of images. (2) VideoMAE achieves impressive results on very small datasets (i.e., around 3k-4k videos) without using any extra data. This is partially ascribed to the challenging task of video reconstruction to enforce high-level structure learning. (3) VideoMAE shows that data quality is more important than data quantity for SSVP. Domain shift between pre-training and target datasets are important issues in SSVP. Notably, our VideoMAE with the vanilla ViT backbone can achieve 83.9% on Kinects-400, 75.3% on Something-Something V2, 90.8% on UCF101, and 61.1% on HMDB51 without using any extra data.
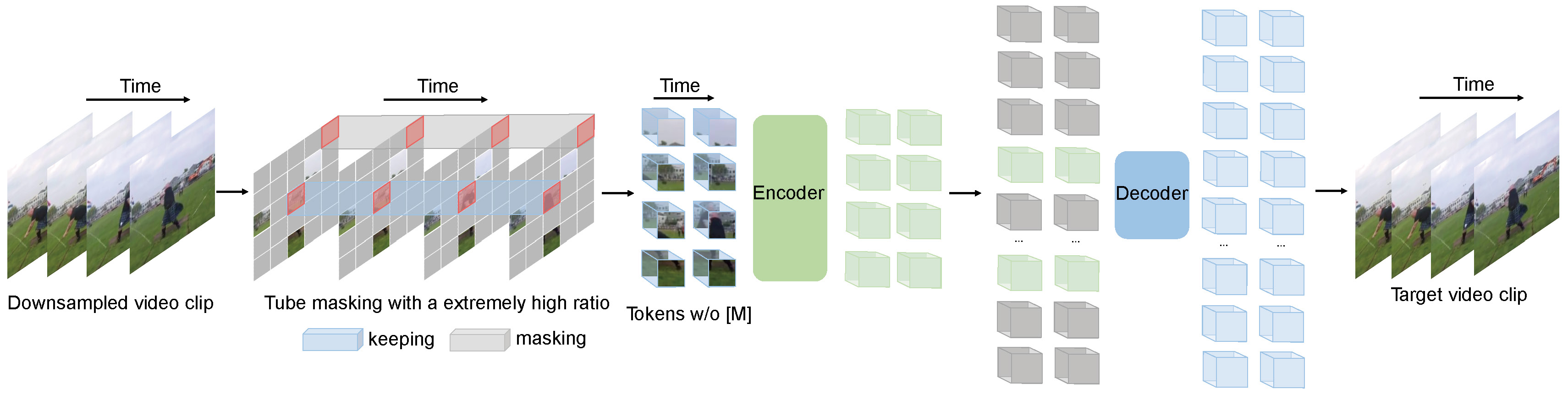
VideoMAE pre-training. Taken from the original paper.
This model was contributed by nielsr. The original code can be found here.
Using Scaled Dot Product Attention (SDPA)
PyTorch includes a native scaled dot-product attention (SDPA) operator as part of torch.nn.functional. This function
encompasses several implementations that can be applied depending on the inputs and the hardware in use. See the
official documentation
or the GPU Inference
page for more information.
SDPA is used by default for torch>=2.1.1 when an implementation is available, but you may also set
attn_implementation="sdpa" in from_pretrained() to explicitly request SDPA to be used.
from transformers import VideoMAEForVideoClassification
model = VideoMAEForVideoClassification.from_pretrained("MCG-NJU/videomae-base-finetuned-kinetics", attn_implementation="sdpa", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
...
For the best speedups, we recommend loading the model in half-precision (e.g. torch.float16 or torch.bfloat16).
On a local benchmark (A100-40GB, PyTorch 2.3.0, OS Ubuntu 22.04) with float32 and MCG-NJU/videomae-base-finetuned-kinetics model, we saw the following speedups during inference.
| Batch size | Average inference time (ms), eager mode | Average inference time (ms), sdpa model | Speed up, Sdpa / Eager (x) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 37 | 10 | 3.7 |
| 2 | 24 | 18 | 1.33 |
| 4 | 43 | 32 | 1.34 |
| 8 | 84 | 60 | 1.4 |
Resources
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with VideoMAE. If you're interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we'll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
Video classification
- A notebook that shows how to fine-tune a VideoMAE model on a custom dataset.
- Video classification task guide
- A 🤗 Space showing how to perform inference with a video classification model.
VideoMAEConfig
autodoc VideoMAEConfig
VideoMAEFeatureExtractor
autodoc VideoMAEFeatureExtractor - call
VideoMAEImageProcessor
autodoc VideoMAEImageProcessor - preprocess
VideoMAEModel
autodoc VideoMAEModel - forward
VideoMAEForPreTraining
VideoMAEForPreTraining includes the decoder on top for self-supervised pre-training.
autodoc transformers.VideoMAEForPreTraining - forward
VideoMAEForVideoClassification
autodoc transformers.VideoMAEForVideoClassification - forward