* docs: ko: model_doc/mistral.md * feat: nmt draft * fix: resolve suggestions Co-authored-by: Ahnjj_DEV <ahnjj.dev@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Chaewon Song <chaewon1019@ewhain.net> Co-authored-by: HyeokJun SHIN <96534680+jun048098@users.noreply.github.com> * fix: resolve suggestions * fix: resolve suggestions Co-authored-by: HyeokJun SHIN <96534680+jun048098@users.noreply.github.com> --------- Co-authored-by: Ahnjj_DEV <ahnjj.dev@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Chaewon Song <chaewon1019@ewhain.net> Co-authored-by: HyeokJun SHIN <96534680+jun048098@users.noreply.github.com>
12 KiB
Mistralmistral
개요overview
미스트랄은 Albert Jiang, Alexandre Sablayrolles, Arthur Mensch, Chris Bamford, Devendra Singh Chaplot, Diego de las Casas, Florian Bressand, Gianna Lengyel, Guillaume Lample, Lélio Renard Lavaud, Lucile Saulnier, Marie-Anne Lachaux, Pierre Stock, Teven Le Scao, Thibaut Lavril, Thomas Wang, Timothée Lacroix, William El Sayed가 작성한 이 블로그 포스트에서 소개되었습니다.
블로그 포스트의 서두는 다음과 같습니다:
미스트랄 AI팀은 현존하는 언어 모델 중 크기 대비 가장 강력한 미스트랄7B를 출시하게 되어 자랑스럽습니다.
미스트랄-7B는 mistral.ai에서 출시한 첫 번째 대규모 언어 모델(LLM)입니다.
아키텍처 세부사항architectural-details
미스트랄-7B는 다음과 같은 구조적 특징을 가진 디코더 전용 트랜스포머입니다:
- 슬라이딩 윈도우 어텐션: 8k 컨텍스트 길이와 고정 캐시 크기로 훈련되었으며, 이론상 128K 토큰의 어텐션 범위를 가집니다.
- GQA(Grouped Query Attention): 더 빠른 추론이 가능하고 더 작은 크기의 캐시를 사용합니다.
- 바이트 폴백(Byte-fallback) BPE 토크나이저: 문자들이 절대 어휘 목록 외의 토큰으로 매핑되지 않도록 보장합니다.
더 자세한 내용은 출시 블로그 포스트를 참조하세요.
라이선스license
미스트랄-7B는 아파치 2.0 라이선스로 출시되었습니다.
사용 팁usage-tips
미스트랄 AI팀은 다음 3가지 체크포인트를 공개했습니다:
- 기본 모델인 미스트랄-7B-v0.1은 인터넷 규모의 데이터에서 다음 토큰을 예측하도록 사전 훈련되었습니다.
- 지시 조정 모델인 미스트랄-7B-Instruct-v0.1은 지도 미세 조정(SFT)과 직접 선호도 최적화(DPO)를 사용한 채팅에 최적화된 기본 모델입니다.
- 개선된 지시 조정 모델인 미스트랄-7B-Instruct-v0.2는 v1을 개선한 버전입니다.
기본 모델은 다음과 같이 사용할 수 있습니다:
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1", device_map="auto")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
>>> prompt = "My favourite condiment is"
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer([prompt], return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
>>> model.to(device)
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs, max_new_tokens=100, do_sample=True)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids)[0]
"My favourite condiment is to ..."
지시 조정 모델은 다음과 같이 사용할 수 있습니다:
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2", device_map="auto")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2")
>>> messages = [
... {"role": "user", "content": "What is your favourite condiment?"},
... {"role": "assistant", "content": "Well, I'm quite partial to a good squeeze of fresh lemon juice. It adds just the right amount of zesty flavour to whatever I'm cooking up in the kitchen!"},
... {"role": "user", "content": "Do you have mayonnaise recipes?"}
... ]
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(model_inputs, max_new_tokens=100, do_sample=True)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids)[0]
"Mayonnaise can be made as follows: (...)"
지시 조정 모델은 입력이 올바른 형식으로 준비되도록 채팅 템플릿을 적용해야 합니다.
플래시 어텐션을 이용한 미스트랄 속도향상speeding-up-mistral-by-using-flash-attention
위의 코드 스니펫들은 어떤 최적화 기법도 사용하지 않은 추론 과정을 보여줍니다. 하지만 모델 내부에서 사용되는 어텐션 메커니즘의 더 빠른 구현인 플래시 어텐션2을 활용하면 모델의 속도를 크게 높일 수 있습니다.
먼저, 슬라이딩 윈도우 어텐션 기능을 포함하는 플래시 어텐션2의 최신 버전을 설치해야 합니다.
pip install -U flash-attn --no-build-isolation
하드웨어와 플래시 어텐션2의 호환여부를 확인하세요. 이에 대한 자세한 내용은 플래시 어텐션 저장소의 공식 문서에서 확인할 수 있습니다. 또한 모델을 반정밀도(예: torch.float16)로 불러와야합니다.
플래시 어텐션2를 사용하여 모델을 불러오고 실행하려면 아래 코드 스니펫을 참조하세요:
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1", torch_dtype=torch.float16, attn_implementation="flash_attention_2", device_map="auto")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
>>> prompt = "My favourite condiment is"
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer([prompt], return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
>>> model.to(device)
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs, max_new_tokens=100, do_sample=True)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids)[0]
"My favourite condiment is to (...)"
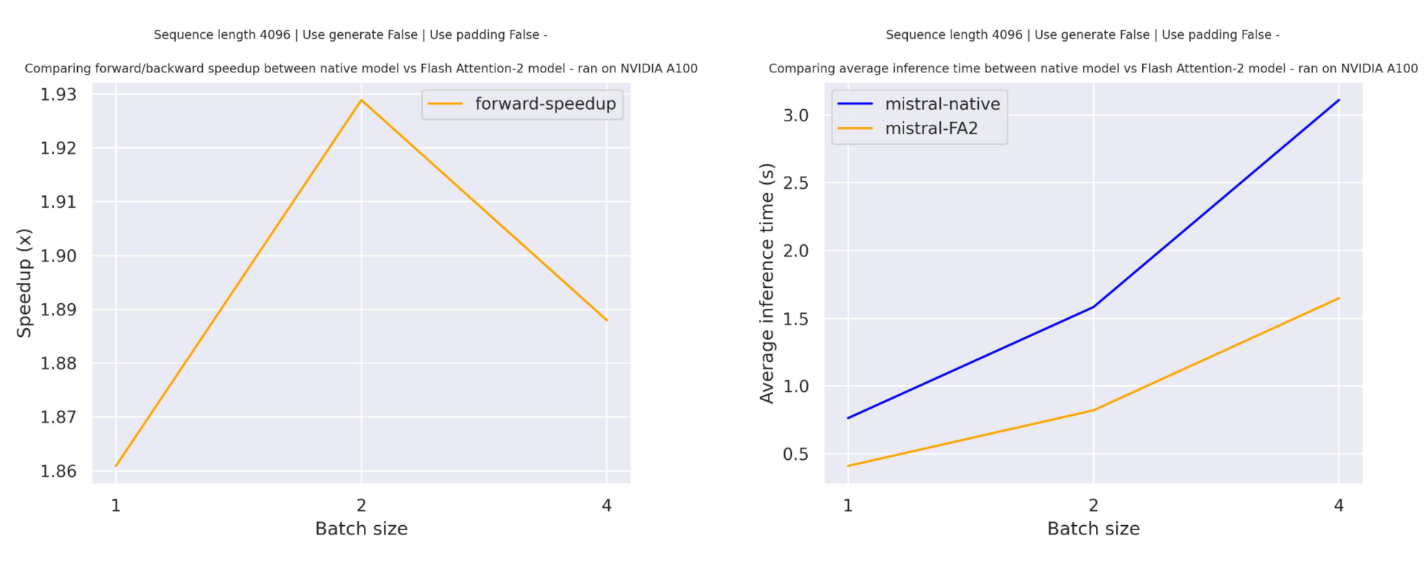
기대하는 속도 향상expected-speedups
다음은 mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1 체크포인트를 사용한 트랜스포머의 기본 구현과 플래시 어텐션2 버전 모델 사이의 순수 추론 시간을 비교한 예상 속도 향상 다이어그램입니다.
슬라이딩 윈도우 어텐션sliding-window-attention
현재 구현은 슬라이딩 윈도우 어텐션 메커니즘과 메모리 효율적인 캐시 관리 기능을 지원합니다. 슬라이딩 윈도우 어텐션을 활성화하려면, 슬라이딩 윈도우 어텐션과 호환되는flash-attn(>=2.3.0)버전을 사용하면 됩니다.
또한 플래시 어텐션2 모델은 더 메모리 효율적인 캐시 슬라이싱 메커니즘을 사용합니다. 미스트랄 모델의 공식 구현에서 권장하는 롤링 캐시 메커니즘을 따라, 캐시 크기를 고정(self.config.sliding_window)으로 유지하고, padding_side="left"인 경우에만 배치 생성(batch generation)을 지원하며, 현재 토큰의 절대 위치를 사용해 위치 임베딩을 계산합니다.
양자화로 미스트랄 크기 줄이기shrinking-down-mistral-using-quantization
미스트랄 모델은 70억 개의 파라미터를 가지고 있어, 절반의 정밀도(float16)로 약 14GB의 GPU RAM이 필요합니다. 각 파라미터가 2바이트로 저장되기 때문입니다. 하지만 양자화를 사용하면 모델 크기를 줄일 수 있습니다. 모델을 4비트(즉, 파라미터당 반 바이트)로 양자화하면 약 3.5GB의 RAM만 필요합니다.
모델을 양자화하는 것은 quantization_config를 모델에 전달하는 것만큼 간단합니다. 아래에서는 BitsAndBytes 양자화를 사용하지만, 다른 양자화 방법은 이 페이지를 참고하세요:
>>> import torch
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig
>>> # specify how to quantize the model
>>> quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
... load_in_4bit=True,
... bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
... bnb_4bit_compute_dtype="torch.float16",
... )
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2", quantization_config=True, device_map="auto")
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2")
>>> prompt = "My favourite condiment is"
>>> messages = [
... {"role": "user", "content": "What is your favourite condiment?"},
... {"role": "assistant", "content": "Well, I'm quite partial to a good squeeze of fresh lemon juice. It adds just the right amount of zesty flavour to whatever I'm cooking up in the kitchen!"},
... {"role": "user", "content": "Do you have mayonnaise recipes?"}
... ]
>>> model_inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(model_inputs, max_new_tokens=100, do_sample=True)
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids)[0]
"The expected output"
이 모델은 Younes Belkada와 Arthur Zucker가 기여했습니다. 원본 코드는 이곳에서 확인할 수 있습니다.
리소스resources
미스트랄을 시작하는 데 도움이 되는 Hugging Face와 community 자료 목록(🌎로 표시됨) 입니다. 여기에 포함될 자료를 제출하고 싶으시다면 PR(Pull Request)를 열어주세요. 리뷰해 드리겠습니다! 자료는 기존 자료를 복제하는 대신 새로운 내용을 담고 있어야 합니다.
- 미스트랄-7B의 지도형 미세조정(SFT)을 수행하는 데모 노트북은 이곳에서 확인할 수 있습니다. 🌎
- 2024년에 Hugging Face 도구를 사용해 LLM을 미세 조정하는 방법에 대한 블로그 포스트. 🌎
- Hugging Face의 정렬(Alignment) 핸드북에는 미스트랄-7B를 사용한 지도형 미세 조정(SFT) 및 직접 선호 최적화(DPO)를 수행하기 위한 스크립트와 레시피가 포함되어 있습니다. 여기에는 단일 GPU에서 QLoRa 및 다중 GPU를 사용한 전체 미세 조정을 위한 스크립트가 포함되어 있습니다.
- 인과적 언어 모델링 작업 가이드
MistralConfigtransformers.MistralConfig
autodoc MistralConfig
MistralModeltransformers.MistralModel
autodoc MistralModel - forward
MistralForCausalLMtransformers.MistralForCausalLM
autodoc MistralForCausalLM - forward
MistralForSequenceClassificationtransformers.MistralForSequenceClassification
autodoc MistralForSequenceClassification - forward
MistralForTokenClassificationtransformers.MistralForTokenClassification
autodoc MistralForTokenClassification - forward
FlaxMistralModeltransformers.FlaxMistralModel
autodoc FlaxMistralModel - call
FlaxMistralForCausalLMtransformers.FlaxMistralForCausalLM
autodoc FlaxMistralForCausalLM - call
TFMistralModeltransformers.TFMistralModel
autodoc TFMistralModel - call
TFMistralForCausalLMtransformers.TFMistralForCausalLM
autodoc TFMistralForCausalLM - call
TFMistralForSequenceClassificationtransformers.TFMistralForSequenceClassification
autodoc TFMistralForSequenceClassification - call