* udpaet * update * Update docs/source/ja/autoclass_tutorial.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * add codes workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml * Create preprocessing.md * added traning.md * Create Model_sharing.md * add quicktour.md * new * ll * Create benchmark.md * Create Tensorflow_model * add * add community.md * add create_a_model * create custom_model.md * create_custom_tools.md * create fast_tokenizers.md * create * add * Update docs/source/ja/_toctree.yml Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * md * add * commit * add * h * Update docs/source/ja/peft.md Co-authored-by: Younes Belkada <49240599+younesbelkada@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/_toctree.yml Co-authored-by: Younes Belkada <49240599+younesbelkada@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/_toctree.yml Co-authored-by: Younes Belkada <49240599+younesbelkada@users.noreply.github.com> * Suggested Update * add perf_train_gpu_one.md * added perf based MD files * Modify toctree.yml and Add transmartion to md codes * Add `serialization.md` and edit `_toctree.yml` * add task summary and tasks explained * Add and Modify files starting from T * Add testing.md * Create main_classes files * delete main_classes folder * Add toctree.yml * Update llm_tutorail.md * Update docs/source/ja/_toctree.yml Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update misspelled filenames * Update docs/source/ja/_toctree.yml Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/_toctree.yml * Update docs/source/ja/_toctree.yml * missplled file names inmrpovements * Update _toctree.yml * close tip block * close another tip block * Update docs/source/ja/quicktour.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/pipeline_tutorial.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/pipeline_tutorial.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/preprocessing.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/peft.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/add_new_model.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/testing.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/task_summary.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/tasks_explained.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update glossary.md * Update docs/source/ja/transformers_agents.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/llm_tutorial.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/create_a_model.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/torchscript.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/benchmarks.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/troubleshooting.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/troubleshooting.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/troubleshooting.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update docs/source/ja/add_new_model.md Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> * Update perf_torch_compile.md * Update Year to default in en documentation * Final Update --------- Co-authored-by: Steven Liu <59462357+stevhliu@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Younes Belkada <49240599+younesbelkada@users.noreply.github.com>
9.5 KiB
Perplexity of fixed-length models
パープレキシティ(PPL)は言語モデルの評価に最も一般的な指標の1つです。深入りする前に、この指標は特に古典的な言語モデル(時にはオートレグレッシブまたは因果言語モデルとも呼ばれる)に適用され、BERTなどのマスクされた言語モデルには適していないことに注意すべきです(モデルの概要を参照してくださいモデルの概要)。
パープレキシティは、シーケンスの指数平均負の対数尤度として定義されます。トークン化されたシーケンス \(X = (x_0, x_1, \dots, x_t)\) がある場合、\(X\) のパープレキシティは次のように表されます。
\text{PPL}(X) = \exp \left\{ {-\frac{1}{t}\sum_i^t \log p_\theta (x_i|x_{<i}) } \right\}ここで、\(\log p_\theta (x_i|x_{<i})\) はモデルによる前のトークン \(x_{<i}\) に対する第iトークンの対数尤度です。直感的には、これはモデルがコーパス内の指定されたトークンの集合に対して一様に予測する能力の評価と考えることができます。重要なのは、これによってトークン化手法がモデルのパープレキシティに直接影響を与えるため、異なるモデルを比較する際には常に考慮すべきであるということです。
これはまた、データとモデルの予測との間の交差エントロピーの指数化と同等です。パープレキシティおよびビット・パー・キャラクター(BPC)とデータ圧縮との関係についての詳細な情報については、この素晴らしい The Gradient のブログ記事を参照してください。
Calculating PPL with fixed-length models
モデルのコンテキストサイズに制約がない場合、モデルのパープレキシティを評価するためには、シーケンスを自己回帰的に因子分解し、各ステップで前のサブシーケンスに条件を付けることで計算します。以下に示すように。
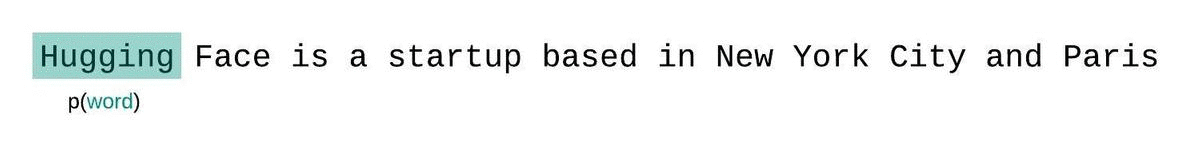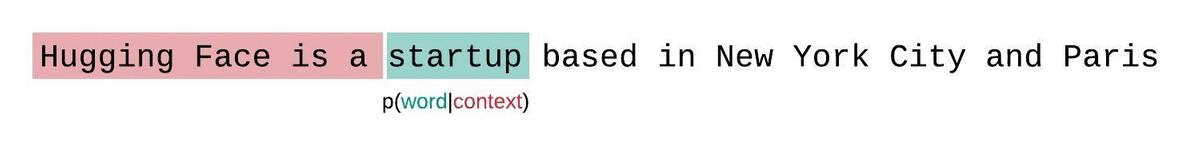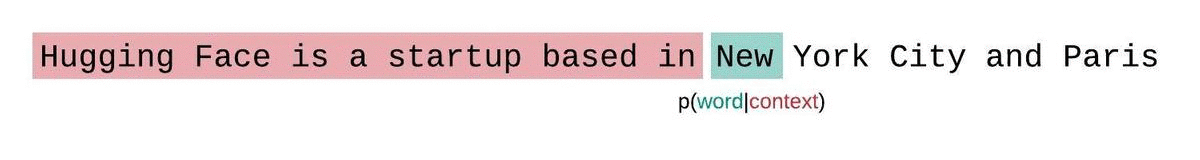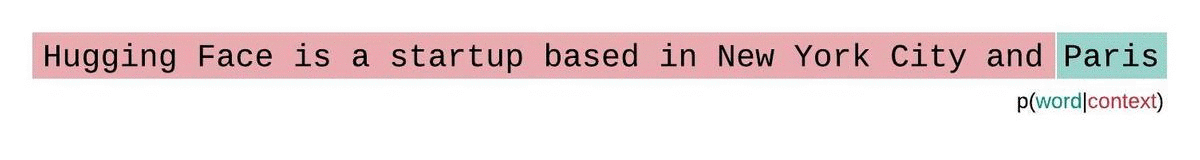
しかし、通常、近似モデルを使用する場合、モデルが処理できるトークン数に制約があります。例えば、最大のGPT-2のバージョンは1024トークンの固定長を持っているため、1024よりも大きい \(t\) に対して \(p_\theta(x_t|x_{<t})\) を直接計算することはできません。
代わりに、通常、シーケンスはモデルの最大入力サイズに等しいサブシーケンスに分割されます。モデルの最大入力サイズが \(k\) の場合、トークン \(x_t\) の尤度を近似するには、完全なコンテキストではなく、それを先行する \(k-1\) トークンにのみ条件を付けることがあります。シーケンスのモデルのパープレキシティを評価する際、誘惑的ですが非効率な方法は、シーケンスを分割し、各セグメントの分解対数尤度を独立に合算することです。
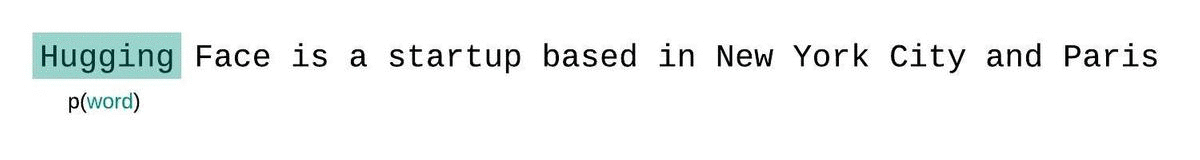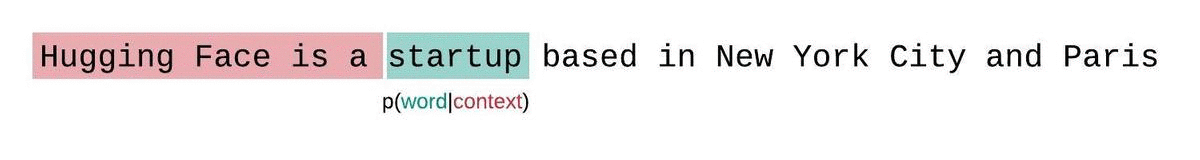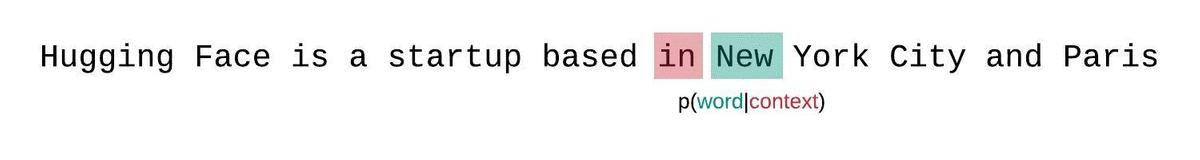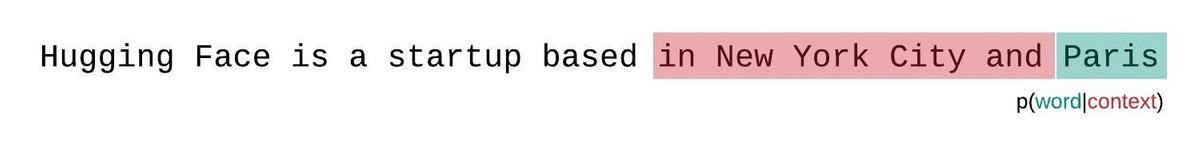
これは各セグメントのパープレキシティが1回のフォワードパスで計算できるため、計算が迅速ですが、通常、モデルはほとんどの予測ステップでコンテキストが少ないため、完全に因子分解されたパープレキシティの悪い近似となり、通常、より高い(悪い)PPLを返します。
代わりに、固定長モデルのPPLはスライディングウィンドウ戦略を用いて評価するべきです。これには、モデルが各予測ステップでより多くのコンテキストを持つように、コンテキストウィンドウを繰り返しスライドさせるという方法が含まれます。
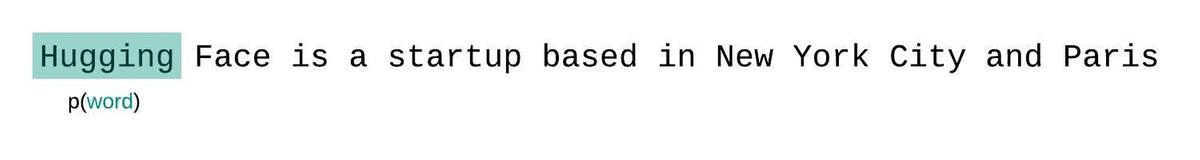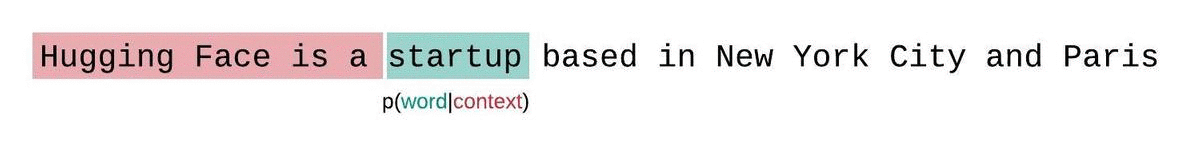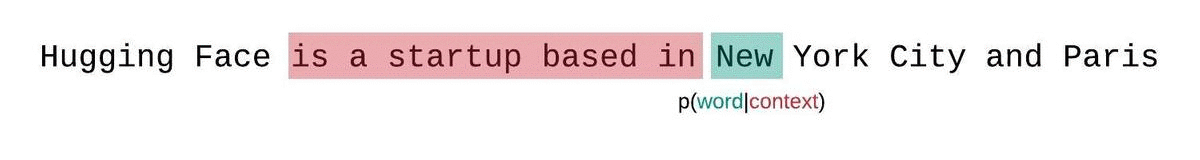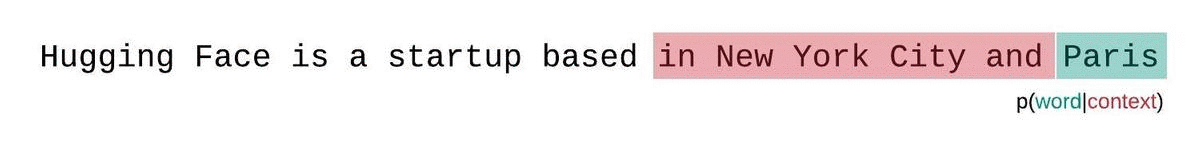
これはシーケンスの確率のより正確な分解に近いものであり、通常はより有利なスコアを生成します。欠点は、コーパス内の各トークンに対して別個の前方パスが必要です。実用的な妥協案は、1トークンずつスライドする代わりに、より大きなストライドでコンテキストを移動するストライド型のスライディングウィンドウを使用することです。これにより、計算がはるかに高速に進行できる一方で、モデルには各ステップで予測を行うための大きなコンテキストが提供されます。
Example: Calculating perplexity with GPT-2 in 🤗 Transformers
GPT-2を使用してこのプロセスをデモンストレーションしてみましょう。
from transformers import GPT2LMHeadModel, GPT2TokenizerFast
device = "cuda"
model_id = "gpt2-large"
model = GPT2LMHeadModel.from_pretrained(model_id).to(device)
tokenizer = GPT2TokenizerFast.from_pretrained(model_id)
WikiText-2データセットを読み込み、異なるスライディングウィンドウ戦略を使用してパープレキシティを評価します。このデータセットは小規模で、セット全体に対して単一のフォワードパスを実行するだけなので、データセット全体をメモリに読み込んでエンコードするだけで十分です。
from datasets import load_dataset
test = load_dataset("wikitext", "wikitext-2-raw-v1", split="test")
encodings = tokenizer("\n\n".join(test["text"]), return_tensors="pt")
🤗 Transformersを使用すると、単純にinput_idsをモデルのlabelsとして渡すことで、各トークンの平均負の対数尤度が損失として返されます。しかし、スライディングウィンドウのアプローチでは、各イテレーションでモデルに渡すトークンにオーバーラップがあります。私たちは、コンテキストとして扱っているトークンの対数尤度を損失に含めたくありません。そのため、これらの対象を -100 に設定して無視されるようにします。以下は、ストライドを 512 とした場合の例です。これにより、モデルは任意のトークンの条件付けの尤度を計算する際に、少なくともコンテキストとして 512 トークンを持つことになります(512 個の前のトークンが利用可能である場合)。
import torch
from tqdm import tqdm
max_length = model.config.n_positions
stride = 512
seq_len = encodings.input_ids.size(1)
nlls = []
prev_end_loc = 0
for begin_loc in tqdm(range(0, seq_len, stride)):
end_loc = min(begin_loc + max_length, seq_len)
trg_len = end_loc - prev_end_loc # may be different from stride on last loop
input_ids = encodings.input_ids[:, begin_loc:end_loc].to(device)
target_ids = input_ids.clone()
target_ids[:, :-trg_len] = -100
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(input_ids, labels=target_ids)
# loss is calculated using CrossEntropyLoss which averages over valid labels
# N.B. the model only calculates loss over trg_len - 1 labels, because it internally shifts the labels
# to the left by 1.
neg_log_likelihood = outputs.loss
nlls.append(neg_log_likelihood)
prev_end_loc = end_loc
if end_loc == seq_len:
break
ppl = torch.exp(torch.stack(nlls).mean())
ストライド長が最大入力長と同じ場合、上述の最適でないスライディングウィンドウ戦略と同等です。ストライドが小さいほど、モデルは各予測を行う際により多くのコンテキストを持つため、通常、報告される困難度(perplexity)が向上します。
上記のコードを stride = 1024 で実行すると、オーバーラップがない状態で、結果の困難度(perplexity)は 19.44 になります。これは GPT-2 の論文に報告された 19.93 とほぼ同等です。一方、stride = 512 を使用し、このようにストライディングウィンドウ戦略を採用すると、困難度(perplexity)が 16.45 に向上します。これはより好意的なスコアだけでなく、シーケンスの尤度の真の自己回帰分解により近い方法で計算されています。