mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
synced 2025-07-31 02:02:21 +06:00
Merge branch 'main' into add-aimv2-model
This commit is contained in:
commit
ab22ef60fa
36
.github/workflows/build-docker-images.yml
vendored
36
.github/workflows/build-docker-images.yml
vendored
@ -63,14 +63,14 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-all-latest-gpu-push-ci docker build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-all-latest-gpu-push-ci docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
latest-torch-deepspeed-docker:
|
||||
name: "Latest PyTorch + DeepSpeed"
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
group: aws-g4dn-2xlarge-cache
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
@ -99,7 +99,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER}}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu docker build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -140,7 +140,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu-push-ci docker build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu-push-ci docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -176,7 +176,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-doc-builder docker build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-doc-builder docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -214,7 +214,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-pytorch-gpudocker build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-pytorch-gpudocker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -223,19 +223,19 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
-
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
-
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
@ -263,7 +263,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu-push-ci build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu-push-ci build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -301,7 +301,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-tensorflow-gpu build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-tensorflow-gpu build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -310,19 +310,19 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
-
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
-
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
@ -350,7 +350,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -388,6 +388,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-quantization-latest-gpu build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-quantization-latest-gpu build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
nightly-torch-deepspeed-docker:
|
||||
name: "Nightly PyTorch + DeepSpeed"
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
group: aws-g4dn-2xlarge-cache
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
|
||||
20
.github/workflows/model_jobs.yml
vendored
20
.github/workflows/model_jobs.yml
vendored
@ -18,6 +18,10 @@ on:
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
report_name_prefix:
|
||||
required: false
|
||||
default: run_models_gpu
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
@ -116,23 +120,23 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -rsfE -v --make-reports=${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -rsfE -v --make-reports=${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run test
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
mkdir -p /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
echo "hello" > /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/hello.txt
|
||||
echo "${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
mkdir -p /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
echo "hello" > /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/hello.txt
|
||||
echo "${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
name: ${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/self-comment-ci.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/self-comment-ci.yml
vendored
@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
name: Get PR number
|
||||
# For security: only allow team members to run
|
||||
if: ${{ github.event.issue.state == 'open' && contains(fromJSON('["ydshieh", "ArthurZucker", "zucchini-nlp", "qubvel", "molbap", "gante", "LysandreJik", "Cyrilvallez", "Rocketknight1", "SunMarc", "muellerzr", "eustlb"]'), github.actor) && (startsWith(github.event.comment.body, 'run-slow') || startsWith(github.event.comment.body, 'run slow') || startsWith(github.event.comment.body, 'run_slow')) }}
|
||||
if: ${{ github.event.issue.state == 'open' && contains(fromJSON('["ydshieh", "ArthurZucker", "zucchini-nlp", "qubvel", "molbap", "gante", "LysandreJik", "Cyrilvallez", "Rocketknight1", "SunMarc", "muellerzr", "eustlb", "MekkCyber"]'), github.actor) && (startsWith(github.event.comment.body, 'run-slow') || startsWith(github.event.comment.body, 'run slow') || startsWith(github.event.comment.body, 'run_slow')) }}
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
PR_NUMBER: ${{ steps.set_pr_number.outputs.PR_NUMBER }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
|
||||
13
.github/workflows/self-scheduled-caller.yml
vendored
13
.github/workflows/self-scheduled-caller.yml
vendored
@ -54,12 +54,23 @@ jobs:
|
||||
ci_event: Daily CI
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
trainer-fsdp-ci:
|
||||
name: Trainer/FSDP CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-training"
|
||||
runner: daily-ci
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Daily CI
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
deepspeed-ci:
|
||||
name: DeepSpeed CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-deepspeed"
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-training"
|
||||
runner: daily-ci
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Daily CI
|
||||
|
||||
35
.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
vendored
35
.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
vendored
@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ env:
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
setup:
|
||||
if: contains(fromJSON('["run_models_gpu", "run_quantization_torch_gpu"]'), inputs.job)
|
||||
if: contains(fromJSON('["run_models_gpu", "run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu", "run_quantization_torch_gpu"]'), inputs.job)
|
||||
name: Setup
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
@ -77,12 +77,17 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- id: set-matrix
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_models_gpu' }}
|
||||
if: contains(fromJSON('["run_models_gpu", "run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu"]'), inputs.job)
|
||||
name: Identify models to test
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers/tests
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "folder_slices=$(python3 ../utils/split_model_tests.py --num_splits ${{ env.NUM_SLICES }})" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
echo "slice_ids=$(python3 -c 'd = list(range(${{ env.NUM_SLICES }})); print(d)')" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
if [ "${{ inputs.job }}" = "run_models_gpu" ]; then
|
||||
echo "folder_slices=$(python3 ../utils/split_model_tests.py --num_splits ${{ env.NUM_SLICES }})" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
echo "slice_ids=$(python3 -c 'd = list(range(${{ env.NUM_SLICES }})); print(d)')" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
elif [ "${{ inputs.job }}" = "run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu" ]; then
|
||||
echo "folder_slices=[['trainer'], ['fsdp']]" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
echo "slice_ids=[0, 1]" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
- id: set-matrix-quantization
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_quantization_torch_gpu' }}
|
||||
@ -113,6 +118,25 @@ jobs:
|
||||
docker: ${{ inputs.docker }}
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu:
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu' }}
|
||||
name: " "
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [aws-g4dn-2xlarge-cache, aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache]
|
||||
slice_id: [0, 1]
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/model_jobs.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
folder_slices: ${{ needs.setup.outputs.folder_slices }}
|
||||
machine_type: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}
|
||||
slice_id: ${{ matrix.slice_id }}
|
||||
runner: ${{ inputs.runner }}
|
||||
docker: ${{ inputs.docker }}
|
||||
report_name_prefix: run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_pipelines_torch_gpu:
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_pipelines_torch_gpu' }}
|
||||
name: PyTorch pipelines
|
||||
@ -382,7 +406,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set `machine_type` for report and artifact names
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
working-directory: ${{ inputs.working-directory-prefix }}/transformers
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.machine_type }}"
|
||||
@ -541,6 +565,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
needs: [
|
||||
setup,
|
||||
run_models_gpu,
|
||||
run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu,
|
||||
run_pipelines_torch_gpu,
|
||||
run_pipelines_tf_gpu,
|
||||
run_examples_gpu,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,13 +27,6 @@ These models require the `trust_remote_code=True` parameter to be set when using
|
||||
the content of the modeling files when using this argument. We recommend setting a revision in order to ensure you
|
||||
protect yourself from updates on the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tools
|
||||
|
||||
Through the `Agent` framework, remote tools can be downloaded to be used by the Agent. You're to specify these tools
|
||||
yourself, but please keep in mind that their code will be run on your machine if the Agent chooses to run them.
|
||||
|
||||
Please inspect the code of the tools before passing them to the Agent to protect your runtime and local setup.
|
||||
|
||||
## Reporting a Vulnerability
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to submit vulnerability reports to [security@huggingface.co](mailto:security@huggingface.co), where someone from the HF security team will review and recommend next steps. If reporting a vulnerability specific to open source, please note [Huntr](https://huntr.com) is a vulnerability disclosure program for open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,7 +66,6 @@ NOT_DEVICE_TESTS = {
|
||||
"ModelTester::test_pipeline_",
|
||||
"/repo_utils/",
|
||||
"/utils/",
|
||||
"/agents/",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# allow having multiple repository checkouts and not needing to remember to rerun
|
||||
@ -83,7 +82,6 @@ def pytest_configure(config):
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "is_pipeline_test: mark test to run only when pipelines are tested")
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "is_staging_test: mark test to run only in the staging environment")
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "accelerate_tests: mark test that require accelerate")
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "agent_tests: mark the agent tests that are run on their specific schedule")
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "not_device_test: mark the tests always running on cpu")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,6 +14,8 @@ ARG PYTORCH='2.6.0'
|
||||
ARG INTEL_TORCH_EXT='2.3.0'
|
||||
# Example: `cu102`, `cu113`, etc.
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu121'
|
||||
# Disable kernel mapping for now until all tests pass
|
||||
ENV DISABLE_KERNEL_MAPPING=1
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt update
|
||||
RUN apt install -y git libsndfile1-dev tesseract-ocr espeak-ng python3 python3-pip ffmpeg git-lfs
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
|
||||
# https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/frameworks/pytorch-release-notes/rel-23-11.html#rel-23-11
|
||||
FROM nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:23.11-py3
|
||||
# https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/frameworks/pytorch-release-notes/rel-24-08.html
|
||||
FROM nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:24.08-py3
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.2.0'
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.6.0'
|
||||
# Example: `cu102`, `cu113`, etc.
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu121'
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu126'
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt -y update
|
||||
RUN apt install -y libaio-dev
|
||||
@ -15,7 +15,8 @@ RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
RUN git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers && cd transformers && git checkout $REF
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir ./transformers[deepspeed-testing]
|
||||
# `datasets` requires pandas, pandas has some modules compiled with numpy=1.x causing errors
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir './transformers[deepspeed-testing]' 'pandas<2' 'numpy<2'
|
||||
|
||||
# Install latest release PyTorch
|
||||
# (PyTorch must be installed before pre-compiling any DeepSpeed c++/cuda ops.)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
||||
# https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/frameworks/pytorch-release-notes/rel-23-11.html#rel-23-11
|
||||
FROM nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:23.11-py3
|
||||
FROM nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:24.08-py3
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
# Example: `cu102`, `cu113`, etc.
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu121'
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu126'
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt -y update
|
||||
RUN apt install -y libaio-dev
|
||||
@ -21,7 +21,8 @@ RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y torch torchvision torchaudio
|
||||
# (https://www.deepspeed.ai/tutorials/advanced-install/#pre-install-deepspeed-ops)
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U --pre torch torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/$CUDA
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir ./transformers[deepspeed-testing]
|
||||
# `datasets` requires pandas, pandas has some modules compiled with numpy=1.x causing errors
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir './transformers[deepspeed-testing]' 'pandas<2' 'numpy<2'
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate@main#egg=accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,6 +12,8 @@ SHELL ["sh", "-lc"]
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.6.0'
|
||||
# Example: `cu102`, `cu113`, etc.
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu121'
|
||||
# Disable kernel mapping for quantization tests
|
||||
ENV DISABLE_KERNEL_MAPPING=1
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt update
|
||||
RUN apt install -y git libsndfile1-dev tesseract-ocr espeak-ng python3 python3-pip ffmpeg
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,8 +23,6 @@
|
||||
title: تحميل النماذج المخصصة وتدريبها باستخدام 🤗 PEFT
|
||||
- local: model_sharing
|
||||
title: مشاركة نموذجك
|
||||
- local: agents
|
||||
title: الوكلاء
|
||||
- local: llm_tutorial
|
||||
title: التوليد باستخدام LLMs
|
||||
- local: conversations
|
||||
@ -252,8 +250,6 @@
|
||||
title: أطر مفاهيمية
|
||||
# - sections:
|
||||
# - sections:
|
||||
# - local: main_classes/agent
|
||||
# title: الوكلاء والأدوات
|
||||
# - local: model_doc/auto
|
||||
# title: فئات يتم إنشاؤها ديناميكيًا
|
||||
# - local: main_classes/backbones
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,539 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# الوكلاء والأدوات
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
### ما هو الوكيل؟
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن للنظم اللغوية الكبيرة (LLMs) التي تم تدريبها على أداء [نمذجة اللغة السببية](./tasks/language_modeling.) التعامل مع مجموعة واسعة من المهام، ولكنها غالبًا ما تواجه صعوبات في المهام الأساسية مثل المنطق والحساب والبحث. وعندما يتم استدعاؤها في مجالات لا تؤدي فيها أداءً جيدًا، فإنها غالبًا ما تفشل في توليد الإجابة التي نتوقعها منها.
|
||||
|
||||
يتمثل أحد النهج للتغلب على هذا القصور في إنشاء "وكيل".
|
||||
|
||||
الوكيل هو نظام يستخدم LLM كمحرك له، ولديه حق الوصول إلى وظائف تسمى "أدوات".
|
||||
|
||||
هذه "الأدوات" هي وظائف لأداء مهمة، وتحتوي على جميع الأوصاف اللازمة للوكيل لاستخدامها بشكل صحيح.
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن برمجة الوكيل للقيام بما يلي:
|
||||
- وضع سلسلة من الإجراءات/الأدوات وتشغيلها جميعًا في نفس الوقت مثل [`CodeAgent`] على سبيل المثال
|
||||
- التخطيط للاجراءات/الأدوات وتنفيذها واحدة تلو الأخرى والانتظار حتى انتهاء كل إجراء قبل إطلاق التالي مثل [`ReactJsonAgent`] على سبيل المثال
|
||||
|
||||
### أنواع الوكلاء
|
||||
|
||||
#### الوكيل البرمجي (Code agent)
|
||||
|
||||
يتمتع هذا الوكيل يتبع خطوات محددة: أولًا، يخطط لسلسلة من الإجراءات التي يريد تنفيذها، ثم شفرة Python لتنفيذ جميع الإجراءات في نفس الوقت. وهو يتعامل بشكل أصلي مع أنواع مختلفة من المدخلات والمخرجات للأدوات التي يستخدمها، وبالتالي فهو الخيار الموصى به للمهام متعددة الوسائط.
|
||||
|
||||
#### وكلاء التفاعل
|
||||
|
||||
هذا هو الوكيل الذي يتم اللجوء إليه لحل مهام الاستدلال، حيث يجعل إطار ReAct ([Yao et al.، 2022](https://huggingface.co/papers/2210.03629)) من الكفاءة حقًا التفكير على أساس ملاحظاته السابقة.
|
||||
|
||||
نقوم بتنفيذ إصدارين من ReactJsonAgent:
|
||||
- [`ReactJsonAgent`] يقوم بتوليد استدعاءات الأدوات كـ JSON في إخراجها.
|
||||
- [`ReactCodeAgent`] هو نوع جديد من ReactJsonAgent يقوم بتوليد استدعاءات أدواته كمقاطع من التعليمات البرمجية، والتي تعمل بشكل جيد حقًا مع LLMs التي تتمتع بأداء قوي في البرمجة.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> اقرأ منشور المدونة [Open-source LLMs as LangChain Agents](https://huggingface.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents) لمعرفة المزيد عن وكيل ReAct.
|
||||
|
||||
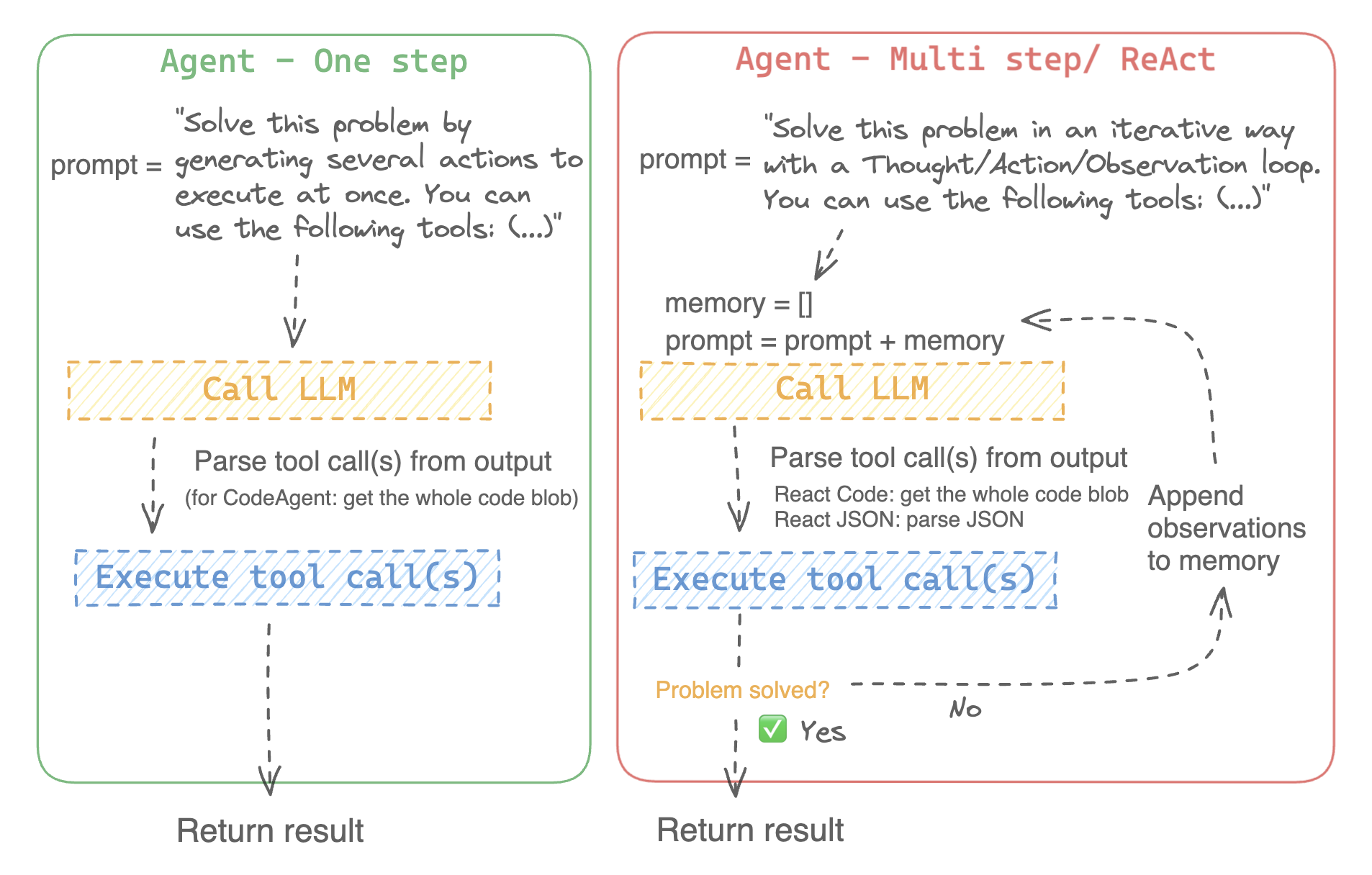
|
||||
|
||||
على سبيل المثال، إليك كيف يعمل وكيل ReAct Code طريقه من خلال السؤال التالي.
|
||||
|
||||
```py3
|
||||
>>> agent.run(
|
||||
... "How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?",
|
||||
... )
|
||||
=====New task=====
|
||||
How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?
|
||||
====Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
bert_blocks = search(query="number of blocks in BERT base encoder")
|
||||
print("BERT blocks:", bert_blocks)
|
||||
====
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
BERT blocks: twelve encoder blocks
|
||||
|
||||
====Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
attention_layer = search(query="number of layers in Attention is All You Need")
|
||||
print("Attention layers:", attention_layer)
|
||||
====
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
Attention layers: Encoder: The encoder is composed of a stack of N = 6 identical layers. Each layer has two sub-layers. The first is a multi-head self-attention mechanism, and the second is a simple, position- 2 Page 3 Figure 1: The Transformer - model architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
====Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
bert_blocks = 12
|
||||
attention_layers = 6
|
||||
diff = bert_blocks - attention_layers
|
||||
print("Difference in blocks:", diff)
|
||||
final_answer(diff)
|
||||
====
|
||||
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
Difference in blocks: 6
|
||||
|
||||
Final answer: 6
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### كيف يمكنني بناء وكيل؟
|
||||
|
||||
لتهيئة وكيل، تحتاج إلى هذه الوسائط:
|
||||
|
||||
- نموذج لغوي كبير (LLM) يشكل المحرك الأساسي للوكيل. الوكيل نفسه ليس النموذج اللغوي، بل هو برنامج يستخدم النموذج اللغوي كمحرك له.
|
||||
- موجه النظام (system prompt): هذه هي التعليمات التي يتم إعطاؤها للنموذج اللغوي لإنشاء مخرجاته.
|
||||
- صندوق أدوات (toolbox) يختار الوكيل منه الأدوات لتنفيذها
|
||||
- محلل (parser) لاستخراج الأدوات التي يجب استدعاؤها من مخرجات النموذج اللغوي LLM والأدوات التي يجب استخدامها
|
||||
|
||||
عند تهيئة نظام الوكيل، يتم استخدام سمات الأداة لإنشاء وصف للأداة، ثم يتم دمجها في موجه النظام الخاص `system_prompt` للوكيل لإعلامه بالأدوات التي يمكنه استخدامها ولماذا.
|
||||
|
||||
للبدء، يرجى تثبيت `agents` الإضافية لتثبيت جميع التبعيات الافتراضية.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers[agents]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
قم ببناء محرك LLM الخاص بك من خلال تعريف طريقة `llm_engine` التي تقبل قائمة من [الرسائل](./chat_templating.) وتعيد النص. يجب أن تقبل هذه الدالة القابلة للاستدعاء أيضًا معامل `stop` يشير إلى متى يجب التوقف عن التوليد.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import login, InferenceClient
|
||||
|
||||
login("<YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>")
|
||||
|
||||
client = InferenceClient(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
|
||||
def llm_engine(messages, stop_sequences=["Task"]) -> str:
|
||||
response = client.chat_completion(messages, stop=stop_sequences, max_tokens=1000)
|
||||
answer = response.choices[0].message.content
|
||||
return answer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك استخدام أي طريقة `llm_engine` طالما أنها:
|
||||
1. يتبع تنسيق [رسائل](./chat_templating.md) لإدخاله (`List [Dict [str، str]]`) ويعيد `str`
|
||||
2. يتوقف عن توليد المخراجات من التسلسلات التي تم تمريرها في معامل `stop`
|
||||
|
||||
أنت بحاجة أيضًا إلى معامل "الأدوات" الذي يقبل قائمة من "الأدوات". يمكنك توفير قائمة فارغة لـ "الأدوات"، ولكن استخدم صندوق الأدوات الافتراضي مع معامل اختياري `add_base_tools=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
الآن يمكنك إنشاء وكيل، مثل [`CodeAgent`], وتشغيله. ولتسهيل الأمر، نقدم أيضًا فئة [`HfEngine`] التي تستخدم `huggingface_hub.InferenceClient` بشكل مخفى.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent, HfEngine
|
||||
|
||||
llm_engine = HfEngine(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Could you translate this sentence from French, say it out loud and return the audio.",
|
||||
sentence="Où est la boulangerie la plus proche?",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
هذه الميزة ستكون مفيدة في حالة الحاجة الملحة! يمكنك حتى ترك معامل `llm_engine` غير محدد، وسيتم إنشاء [`HfEngine`] بشكل تلقائي.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Could you translate this sentence from French, say it out loud and give me the audio.",
|
||||
sentence="Où est la boulangerie la plus proche?",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لاحظ أننا استخدمنا معامل "sentence" إضافي: يمكنك تمرير النص كمعامل إضافي إلى النموذج.
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك أيضًا استخدام هذا للإشارة إلى مسار الملفات المحلية أو البعيدة للنموذج لاستخدامها:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Why does Mike not know many people in New York?", audio="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/recording.mp3")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
تم تحديد موجه النظام ومحلل المخرجات تلقائيًا، ولكن يمكنك فحصهما بسهولة عن طريق استدعاء `system_prompt_template` على وكيلك.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
print(agent.system_prompt_template)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
من المهم أن تشرح بأكبر قدر ممكن من الوضوح المهمة التي تريد تنفيذها.
|
||||
كل عملية [`~Agent.run`] مستقلة، وبما أن الوكيل مدعوم من LLM، فقد تؤدي الاختلافات الطفيفة في موجهك إلى نتائج مختلفة تمامًا.
|
||||
يمكنك أيضًا تشغيل وكيل بشكل متتالي لمهام مختلفة: في كل مرة يتم فيها إعادة تهيئة سمتي `agent.task` و`agent.logs`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### تنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية
|
||||
|
||||
يقوم مفسر Python بتنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية على مجموعة من المدخلات التي يتم تمريرها جنبًا إلى جنب مع أدواتك.
|
||||
يجب أن يكون هذا الأمر آمنًا لأن الوظائف الوحيدة التي يمكن استدعاؤها هي الأدوات التي قدمتها (خاصة إذا كانت أدوات من Hugging Face فقط) ووظيفة الطباعة، لذا فأنت مقيد بالفعل بما يمكن تنفيذه.
|
||||
|
||||
مفسر Python لا يسمح أيضًا باستدعاء دوال بشكل افتراضي خارج قائمة آمنة، لذا فإن جميع الهجمات الأكثر وضوحًا لا ينبغي أن تكون مشكلة.
|
||||
يمكنك أيضًا الإذن باستيرادات إضافية عن طريق تمرير الوحدات النمطية المصرح بها كقائمة من السلاسل في معامل `additional_authorized_imports` عند تهيئة [`ReactCodeAgent`] أو [`CodeAgent`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
>>> agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[], additional_authorized_imports=['requests', 'bs4'])
|
||||
>>> agent.run("Could you get me the title of the page at url 'https://huggingface.co/blog'?")
|
||||
|
||||
(...)
|
||||
'Hugging Face – Blog'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
سيتم إيقاف التنفيذ عند أي رمز يحاول تنفيذ عملية غير قانونية أو إذا كان هناك خطأ Python عادي في التعليمات البرمجية التي تم إنشاؤها بواسطة الوكيل.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> يمكن لـ LLM توليد شفرة برمجية عشوائية سيتم تنفيذها بعد ذلك: لا تقمب استدعاء أى دوال غير آمنة!
|
||||
|
||||
### موجه النظام
|
||||
|
||||
ينشئ الوكيل، أو بالأحرى LLM الذي يقود الوكيل، يولد مخرجات بناءً على موجه النظام. يمكن تخصيص موجه النظام وتصميمه للمهام المقصودة. على سبيل المثال، تحقق من موجه النظام لـ [`ReactCodeAgent`] (الإصدار أدناه مبسط قليلاً).
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
You will be given a task to solve as best you can.
|
||||
You have access to the following tools:
|
||||
<<tool_descriptions>>
|
||||
|
||||
To solve the task, you must plan forward to proceed in a series of steps, in a cycle of 'Thought:', 'Code:', and 'Observation:' sequences.
|
||||
|
||||
At each step, in the 'Thought:' sequence, you should first explain your reasoning towards solving the task, then the tools that you want to use.
|
||||
Then in the 'Code:' sequence, you should write the code in simple Python. The code sequence must end with '/End code' sequence.
|
||||
During each intermediate step, you can use 'print()' to save whatever important information you will then need.
|
||||
These print outputs will then be available in the 'Observation:' field, for using this information as input for the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
In the end you have to return a final answer using the `final_answer` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few examples using notional tools:
|
||||
---
|
||||
{examples}
|
||||
|
||||
Above example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. You only have access to those tools:
|
||||
<<tool_names>>
|
||||
You also can perform computations in the python code you generate.
|
||||
|
||||
Always provide a 'Thought:' and a 'Code:\n```py' sequence ending with '```<end_code>' sequence. You MUST provide at least the 'Code:' sequence to move forward.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to not perform too many operations in a single code block! You should split the task into intermediate code blocks.
|
||||
Print results at the end of each step to save the intermediate results. Then use final_answer() to return the final result.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to make sure that variables you use are all defined.
|
||||
|
||||
Now Begin!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يتضمن موجه النظام:
|
||||
- *مقدمة* تشرح كيف يجب أن يتصرف الوكيل والأدوات التي يجب عليه استخدامها.
|
||||
- وصف لجميع الأدوات التي يتم تحديدها بواسطة رمز `<<tool_descriptions>>` الذي يتم استبداله ديناميكيًا في وقت التشغيل بالأدوات التي يحددها المستخدم أو يختارها.
|
||||
- يأتي وصف الأداة من سمات الأداة، `name`، و`description`، و`inputs` و`output_type`، وقالب `jinja2` بسيط يمكنك تحسينه.
|
||||
- شكل المخرج المتوقع.
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك تحسين موجه النظام، على سبيل المثال، عن طريق إضافة شرح لتنسيق المخرجات.
|
||||
|
||||
للحصول على أقصى قدر من المرونة، يمكنك الكتابة فوق قالب موجه النظام بالكامل عن طريق تمرير موجه مخصص كمعامل إلى معلمة `system_prompt`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import ReactJsonAgent
|
||||
from transformers.agents import PythonInterpreterTool
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactJsonAgent(tools=[PythonInterpreterTool()], system_prompt="{your_custom_prompt}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> يرجى التأكد من تحديد سلسلة `<<tool_descriptions>>` في مكان ما في `template` حتى يكون الوكيل على علم
|
||||
بالأدوات المتاحة.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### فحص تشغيل الوكيل
|
||||
|
||||
فيما يلي بعض السمات المفيدة لفحص ما حدث بعد التشغيل:
|
||||
- تخزن `agent.logs` سجلات مفصلة للوكيل. في كل خطوة من تشغيل الوكيل، يتم تخزين كل شيء في قاموس إلحاقه بـ `agent.logs`.
|
||||
- تشغيل `agent.write_inner_memory_from_logs()` يخلق ذاكرة داخلية لسجلات الوكيل للنظام LLM لعرضها، كقائمة من رسائل الدردشة. تنتقل هذه الطريقة عبر كل خطوة من سجل الوكيل ولا تخزن سوى ما يهمها كرسالة: على سبيل المثال، سيحفظ موجه النظام والمهمة في رسائل منفصلة، ثم لكل خطوة سيخزن مخرج LLM كرسالة، ومخرج استدعاء الأداة كرسالة أخرى. استخدم هذا إذا كنت تريد عرضًا عامًا لما حدث - ولكن لن يتم نسخ كل سجل بواسطة هذه الطريقة.
|
||||
|
||||
## الأدوات
|
||||
|
||||
الأداة هي عبارة عن وظيفة أساسية يستخدمها الوكيل لتنفيذ مهمة محددة.
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك على سبيل المثال التحقق من [`PythonInterpreterTool`]: لديه اسم ووصف ووصف للمدخلات ونوع للمخرج، وطريقة `__call__` التي تقوم بتنفيذ المهمة المطلوبة.
|
||||
|
||||
عند تهيئة الوكيل، يتم استخدام سمات الأداة لتوليد وصف للأداة يتم تضمينه في موجه النظام الخاص بالوكيل. يتيح هذا للوكيل معرفة الأدوات التي يمكنه استخدامها ولماذا.
|
||||
|
||||
### صندوق الأدوات الافتراضي
|
||||
|
||||
يأتي Transformers مع صندوق أدوات افتراضي لتمكين الوكلاء، والذي يمكنك إضافته إلى وكيلك عند التهيئة باستخدام معامل `add_base_tools = True`:
|
||||
|
||||
- **الإجابة على أسئلة المستند**: الإجابة على سؤال حول المستند (مثل ملف PDF) بتنسيق صورة ([Donut](./model_doc/donut))
|
||||
- **الإجابة على أسئلة الصور**: الإجابة على سؤال حول صورة ([VILT](./model_doc/vilt))
|
||||
- **التحدث إلى النص**: قم بتفريغ الكلام إلى نص ([Whisper](./model_doc/whisper))
|
||||
- **النص إلى كلام**: تحويل النص إلى كلام ([SpeechT5](./model_doc/speecht5))
|
||||
- **الترجمة**: ترجمة جملة معينة من لغة المصدر إلى لغة الهدف.
|
||||
- **مفسر كود Python**: تشغيل كود Python الذي تم إنشاؤه بواسطة LLM في بيئة آمنة. لن يتم إضافة هذه الأداة إلى [`ReactJsonAgent`] إلا إذا استخدمت `add_base_tools=True`، نظرًا لأن الأدوات المستندة إلى التعليمات البرمجية يمكنها بالفعل تنفيذ كود Python
|
||||
لا تترجم النصوص الخاصة ولا الأكواد البرمجية ولا الروابط ولا رموز HTML وCSS:
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك استخدام أداة يدويًا عن طريق استدعاء دالة [`load_tool`] وتحديد مهمة لتنفيذها.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = load_tool("text-to-speech")
|
||||
audio = tool("This is a text to speech tool")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### إنشاء أداة جديدة
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك إنشاء أداتك الخاصة لتغطية حالات الاستخدام التي لا تغطيها الأدوات الافتراضية من Hugging Face.
|
||||
على سبيل المثال، دعنا نقوم بإنشاء أداة تعرض النموذج الأكثر تنزيلًا لمهمة معينة من Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
سوف نبدأ بالكود التالي.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
task = "text-classification"
|
||||
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
print(model.id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن تحويل هذه الشيفرة إلى فئة ترث من الفئة العليا [`Tool`].
|
||||
|
||||
تحتاج الأداة المخصصة إلى:
|
||||
|
||||
- اسم `name`، والتي تمثل اسم الأداة نفسها. عادةً ما يصف الاسم وظيفتها. بما أن الكود يعيد النموذج الأكثر تنزيلًا لمهمة ما، فلنسمها `model_download_counter`.
|
||||
- تستخدم خاصية `description` لملء موجه نظام الوكيل.
|
||||
- خاصية `inputs`، والتي هي عبارة عن قاموس بمفاتيح "type" و"description". يحتوي على معلومات تساعد المفسر Python على اتخاذ خيارات مستنيرة بشأن المدخلات.
|
||||
- خاصية `output_type`، والتي تحدد نوع المخرج.
|
||||
- طريقة `forward` والتي تحتوي على الكود الذي سيتم تنفيذه للحصول على النتيجة النهائية.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import Tool
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
class HFModelDownloadsTool(Tool):
|
||||
name = "model_download_counter"
|
||||
description = (
|
||||
"This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub. "
|
||||
"It returns the name of the checkpoint."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = {
|
||||
"task": {
|
||||
"type": "text",
|
||||
"description": "the task category (such as text-classification, depth-estimation, etc)",
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_type = "text"
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, task: str):
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
return model.id
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن بعد أن أصبحت فئة `HfModelDownloadsTool` المخصصة جاهزة، يمكنك حفظها في ملف باسم `model_downloads.py` واستيرادها للاستخدام.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from model_downloads import HFModelDownloadsTool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = HFModelDownloadsTool()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك أيضًا مشاركة أداتك المخصصة في Hub عن طريق استدعاء [`~Tool.push_to_hub`] على الأداة. تأكد من أنك قمت بإنشاء مستودع لها على Hub وأنك تستخدم رمز وصول للقراءة.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tool.push_to_hub("{your_username}/hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
قم بتحميل الأداة باستخدام دالة [`~Tool.load_tool`] ومررها إلى معلمة `tools` في الوكيل الخاص بك.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool, CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
model_download_tool = load_tool("m-ric/hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[model_download_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
ستحصل على ما يلي:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
======== New task ========
|
||||
Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?
|
||||
==== Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
most_downloaded_model = model_download_counter(task="text-to-video")
|
||||
print(f"The most downloaded model for the 'text-to-video' task is {most_downloaded_model}.")
|
||||
====
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
والناتج:
|
||||
|
||||
`"النموذج الأكثر تنزيلًا لمهمة `text-to-video` هو ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning."`
|
||||
|
||||
### إدارة صندوق أدوات الوكيل الخاص بك
|
||||
|
||||
إذا كنت قد قمت بتهيئة وكيل، فمن غير الملائم إعادة تهيئته من البداية لإضافة أداة جديدة ترغب في استخدامها. باستخدام مكتبة Transformers، يمكنك إدارة صندوق أدوات الوكيل بإضافة أو استبدال أداة موجودة.
|
||||
|
||||
دعنا نضيف الأداة `model_download_tool` إلى وكيل تم تهيئته مسبقًا باستخدام صندوق الأدوات الافتراضي.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
agent.toolbox.add_tool(model_download_tool)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن يمكننا الاستفادة من الأداة الجديدة وأداة تحويل النص إلى كلام السابقة:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Can you read out loud the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub and return the audio?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| **Audio** |
|
||||
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| <audio controls><source src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/damo.wav" type="audio/wav"/> |
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> احترس عند إضافة أدوات إلى وكيل يعمل بالفعل لأنه يمكن أن يؤثر على اختيار الأداة لصالح أداتك أو اختيار أداة أخرى غير المحددة بالفعل.
|
||||
|
||||
استخدم طريقة `agent.toolbox.update_tool()` لاستبدال أداة موجودة في صندوق أدوات الوكيل.
|
||||
هذا مفيد إذا كانت أداتك الجديدة بديلاً مباشرًا للأداة الموجودة لأن الوكيل يعرف بالفعل كيفية تنفيذ تلك المهمة المحددة.
|
||||
تأكد فقط من اتباع الأداة الجديدة لنفس واجهة برمجة التطبيقات (API) للأداة المستبدلة أو قم بتكييف قالب موجه النظام لضمان تحديث جميع الأمثلة التي تستخدم الأداة المستبدلة.
|
||||
|
||||
### استخدام مجموعة من الأدوات
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك الاستفادة من مجموعات الأدوات باستخدام كائن ToolCollection، مع تحديد مجموعة الأدوات التي تريد استخدامها.
|
||||
ثم قم بتمريرها كقائمة لتهيئة الوكيل الخاص بك، وبدء استخدامها!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ToolCollection, ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
image_tool_collection = ToolCollection(collection_slug="huggingface-tools/diffusion-tools-6630bb19a942c2306a2cdb6f")
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[*image_tool_collection.tools], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Please draw me a picture of rivers and lakes.")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لتسريع البداية، يتم تحميل الأدوات فقط إذا استدعاها الوكيل.
|
||||
|
||||
ستحصل على هذه الصورة:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png" />
|
||||
|
||||
### استخدام gradio-tools
|
||||
|
||||
[gradio-tools](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools) هي مكتبة قوية تتيح استخدام Hugging
|
||||
Face Spaces كأدوات. تدعم العديد من المساحات الموجودة بالإضافة إلى مساحات مخصصة.
|
||||
|
||||
تدعم مكتبة Transformers `gradio_tools` باستخدام طريقة [`Tool.from_gradio`] في الفئة. على سبيل المثال، دعنا نستخدم [`StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool`](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools/blob/main/gradio_tools/tools/prompt_generator.py) من مجموعة أدوات `gradio-tools` لتحسين المطالبات لإنشاء صور أفضل.
|
||||
|
||||
استورد وقم بتهيئة الأداة، ثم مررها إلى طريقة `Tool.from_gradio`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from gradio_tools import StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool
|
||||
from transformers import Tool, load_tool, CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
gradio_prompt_generator_tool = StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool()
|
||||
prompt_generator_tool = Tool.from_gradio(gradio_prompt_generator_tool)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن يمكنك استخدامه مثل أي أداة أخرى. على سبيل المثال، دعنا نحسن الموجه `a rabbit wearing a space suit`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
image_generation_tool = load_tool('huggingface-tools/text-to-image')
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[prompt_generator_tool, image_generation_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Improve this prompt, then generate an image of it.", prompt='A rabbit wearing a space suit'
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يستفيد النموذج بشكل كافٍ من الأداة:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
======== New task ========
|
||||
Improve this prompt, then generate an image of it.
|
||||
You have been provided with these initial arguments: {'prompt': 'A rabbit wearing a space suit'}.
|
||||
==== Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
improved_prompt = StableDiffusionPromptGenerator(query=prompt)
|
||||
while improved_prompt == "QUEUE_FULL":
|
||||
improved_prompt = StableDiffusionPromptGenerator(query=prompt)
|
||||
print(f"The improved prompt is {improved_prompt}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt=improved_prompt)
|
||||
====
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
قبل إنشاء الصورة أخيرًا:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rabbit_spacesuit_flux.webp" />
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> تتطلب gradio-tools إدخالات وإخراجات *نصية* حتى عند العمل مع طرائق مختلفة مثل كائنات الصور والصوت. الإدخالات والإخراجات الصورية والصوتية غير متوافقة حاليًا.
|
||||
|
||||
### استخدام أدوات LangChain
|
||||
|
||||
نحن نحب Langchain ونعتقد أنها تحتوي على مجموعة أدوات قوية للغاية.
|
||||
لاستيراد أداة من LangChain، استخدم الطريقة `from_langchain()`.
|
||||
|
||||
فيما يلي كيفية استخدامها لإعادة إنشاء نتيجة البحث في المقدمة باستخدام أداة بحث الويب LangChain.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.agents import load_tools
|
||||
from transformers import Tool, ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
search_tool = Tool.from_langchain(load_tools(["serpapi"])[0])
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[search_tool])
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## واجهة Gradio
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك الاستفادة من `gradio.Chatbot` لعرض أفكار الوكيل الخاص بك باستخدام `stream_to_gradio`، إليك مثال:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import gradio as gr
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
load_tool,
|
||||
ReactCodeAgent,
|
||||
HfEngine,
|
||||
stream_to_gradio,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Import tool from Hub
|
||||
image_generation_tool = load_tool("m-ric/text-to-image")
|
||||
|
||||
llm_engine = HfEngine("meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize the agent with the image generation tool
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[image_generation_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def interact_with_agent(task):
|
||||
messages = []
|
||||
messages.append(gr.ChatMessage(role="user", content=task))
|
||||
yield messages
|
||||
for msg in stream_to_gradio(agent, task):
|
||||
messages.append(msg)
|
||||
yield messages + [
|
||||
gr.ChatMessage(role="assistant", content="⏳ Task not finished yet!")
|
||||
]
|
||||
yield messages
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
|
||||
text_input = gr.Textbox(lines=1, label="Chat Message", value="Make me a picture of the Statue of Liberty.")
|
||||
submit = gr.Button("Run illustrator agent!")
|
||||
chatbot = gr.Chatbot(
|
||||
label="Agent",
|
||||
type="messages",
|
||||
avatar_images=(
|
||||
None,
|
||||
"https://em-content.zobj.net/source/twitter/53/robot-face_1f916.png",
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
submit.click(interact_with_agent, [text_input], [chatbot])
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
demo.launch()
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -674,29 +674,7 @@ use_cpu: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Tensor Parallelism with PyTorch 2">
|
||||
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
tp_config:
|
||||
tp_size: 4
|
||||
distributed_type: TP
|
||||
downcast_bf16: 'no'
|
||||
machine_rank: 0
|
||||
main_training_function: main
|
||||
mixed_precision: 'no'
|
||||
num_machines: 1
|
||||
num_processes: 4
|
||||
rdzv_backend: static
|
||||
same_network: true
|
||||
tpu_env: []
|
||||
tpu_use_cluster: false
|
||||
tpu_use_sudo: false
|
||||
use_cpu: false
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
يُعد أمر [`accelerate_launch`](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/package_reference/cli#accelerate-launch) هو الطريقة المُوصى بها لتشغيل نص البرمجى للتدريب على نظام موزع باستخدام Accelerate و [`Trainer`] مع المعلمات المحددة في `config_file.yaml`. يتم حفظ هذا الملف في مجلد ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت لـ Accelerate ويتم تحميله تلقائيًا عند تشغيل `accelerate_launch`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,8 +23,6 @@
|
||||
title: Laden und Trainieren von Adaptern mit 🤗 PEFT
|
||||
- local: model_sharing
|
||||
title: Ein Modell teilen
|
||||
- local: transformers_agents
|
||||
title: Agents
|
||||
- local: llm_tutorial
|
||||
title: Generation with LLMs
|
||||
title: Tutorials
|
||||
@ -39,4 +37,4 @@
|
||||
title: Testen
|
||||
- local: pr_checks
|
||||
title: Überprüfung einer Pull Request
|
||||
title: Contribute
|
||||
title: Contribute
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,323 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Transformers Agents
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers Agents ist eine experimentelle API, die jederzeit geändert werden kann. Die von den Agenten zurückgegebenen Ergebnisse
|
||||
zurückgegeben werden, können variieren, da sich die APIs oder die zugrunde liegenden Modelle ändern können.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers Version v4.29.0, die auf dem Konzept von *Tools* und *Agenten* aufbaut. Sie können damit spielen in
|
||||
[dieses Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1c7MHD-T1forUPGcC_jlwsIptOzpG3hSj).
|
||||
|
||||
Kurz gesagt, es bietet eine API für natürliche Sprache auf der Grundlage von Transformers: Wir definieren eine Reihe von kuratierten Tools und entwerfen einen
|
||||
Agenten, um natürliche Sprache zu interpretieren und diese Werkzeuge zu verwenden. Es ist von vornherein erweiterbar; wir haben einige relevante Tools kuratiert,
|
||||
aber wir werden Ihnen zeigen, wie das System einfach erweitert werden kann, um jedes von der Community entwickelte Tool zu verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
Beginnen wir mit einigen Beispielen dafür, was mit dieser neuen API erreicht werden kann. Sie ist besonders leistungsfähig, wenn es um
|
||||
Sie ist besonders leistungsstark, wenn es um multimodale Aufgaben geht. Lassen Sie uns also eine Runde drehen, um Bilder zu erzeugen und Text vorzulesen.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Caption the following image", image=image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| **Input** | **Output** |
|
||||
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------|
|
||||
| <img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/beaver.png" width=200> | A beaver is swimming in the water |
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Read the following text out loud", text=text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
| **Input** | **Output** |
|
||||
|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| A beaver is swimming in the water | <audio controls><source src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/tts_example.wav" type="audio/wav"> your browser does not support the audio element. </audio>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"In the following `document`, where will the TRRF Scientific Advisory Council Meeting take place?",
|
||||
document=document,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
| **Input** | **Output** |
|
||||
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------|
|
||||
| <img src="https://datasets-server.huggingface.co/assets/hf-internal-testing/example-documents/--/hf-internal-testing--example-documents/test/0/image/image.jpg" width=200> | ballroom foyer |
|
||||
|
||||
## Schnellstart
|
||||
|
||||
Bevor Sie `agent.run` verwenden können, müssen Sie einen Agenten instanziieren, der ein großes Sprachmodell (LLM) ist.
|
||||
Wir bieten Unterstützung für openAI-Modelle sowie für OpenSource-Alternativen von BigCode und OpenAssistant. Die openAI
|
||||
Modelle sind leistungsfähiger (erfordern aber einen openAI-API-Schlüssel, können also nicht kostenlos verwendet werden); Hugging Face
|
||||
bietet kostenlosen Zugang zu Endpunkten für BigCode- und OpenAssistant-Modelle.
|
||||
|
||||
To start with, please install the `agents` extras in order to install all default dependencies.
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers[agents]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Um openAI-Modelle zu verwenden, instanziieren Sie einen [`OpenAiAgent`], nachdem Sie die `openai`-Abhängigkeit installiert haben:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install openai
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import OpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = OpenAiAgent(model="text-davinci-003", api_key="<your_api_key>")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Um BigCode oder OpenAssistant zu verwenden, melden Sie sich zunächst an, um Zugriff auf die Inference API zu erhalten:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import login
|
||||
|
||||
login("<YOUR_TOKEN>")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dann instanziieren Sie den Agenten
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
# Starcoder
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder")
|
||||
# StarcoderBase
|
||||
# agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoderbase")
|
||||
# OpenAssistant
|
||||
# agent = HfAgent(url_endpoint="https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/OpenAssistant/oasst-sft-4-pythia-12b-epoch-3.5")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dies geschieht mit der Inferenz-API, die Hugging Face derzeit kostenlos zur Verfügung stellt. Wenn Sie Ihren eigenen Inferenz
|
||||
Endpunkt für dieses Modell (oder einen anderen) haben, können Sie die obige URL durch Ihren URL-Endpunkt ersetzen.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
StarCoder und OpenAssistant sind kostenlos und leisten bei einfachen Aufgaben bewundernswert gute Arbeit. Allerdings halten die Kontrollpunkte
|
||||
nicht, wenn es um komplexere Aufforderungen geht. Wenn Sie mit einem solchen Problem konfrontiert sind, empfehlen wir Ihnen, das OpenAI
|
||||
Modell auszuprobieren, das zwar leider nicht quelloffen ist, aber zur Zeit eine bessere Leistung erbringt.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Sie sind jetzt startklar! Lassen Sie uns in die beiden APIs eintauchen, die Ihnen jetzt zur Verfügung stehen.
|
||||
|
||||
### Einzelne Ausführung (run)
|
||||
|
||||
Die Methode der einmaligen Ausführung ist die Verwendung der [`~Agent.run`] Methode des Agenten:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes.")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
Es wählt automatisch das (oder die) Werkzeug(e) aus, das (die) für die von Ihnen gewünschte Aufgabe geeignet ist (sind) und führt es (sie) entsprechend aus. Es
|
||||
kann eine oder mehrere Aufgaben in der gleichen Anweisung ausführen (je komplexer Ihre Anweisung ist, desto wahrscheinlicher ist ein
|
||||
der Agent scheitern).
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of the sea then transform the picture to add an island")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/sea_and_island.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
<br/>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Jede [`~Agent.run`] Operation ist unabhängig, so dass Sie sie mehrmals hintereinander mit unterschiedlichen Aufgaben ausführen können.
|
||||
|
||||
Beachten Sie, dass Ihr `Agent` nur ein großsprachiges Modell ist, so dass kleine Variationen in Ihrer Eingabeaufforderung völlig unterschiedliche Ergebnisse liefern können.
|
||||
unterschiedliche Ergebnisse liefern. Es ist wichtig, dass Sie die Aufgabe, die Sie ausführen möchten, so genau wie möglich erklären. Wir gehen noch weiter ins Detail
|
||||
wie man gute Prompts schreibt [hier](custom_tools#writing-good-user-inputs).
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie einen Status über Ausführungszeiten hinweg beibehalten oder dem Agenten Nicht-Text-Objekte übergeben möchten, können Sie dies tun, indem Sie
|
||||
Variablen, die der Agent verwenden soll. Sie könnten zum Beispiel das erste Bild von Flüssen und Seen erzeugen,
|
||||
und das Modell bitten, dieses Bild zu aktualisieren und eine Insel hinzuzufügen, indem Sie Folgendes tun:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
picture = agent.run("Generate a picture of rivers and lakes.")
|
||||
updated_picture = agent.run("Transform the image in `picture` to add an island to it.", picture=picture)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Dies kann hilfreich sein, wenn das Modell Ihre Anfrage nicht verstehen kann und die Werkzeuge verwechselt. Ein Beispiel wäre:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me the picture of a capybara swimming in the sea")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Hier könnte das Modell auf zwei Arten interpretieren:
|
||||
- Die Funktion `Text-zu-Bild` erzeugt ein Wasserschwein, das im Meer schwimmt.
|
||||
- Oder Sie lassen das `Text-zu-Bild` ein Wasserschwein erzeugen und verwenden dann das Werkzeug `Bildtransformation`, um es im Meer schwimmen zu lassen.
|
||||
|
||||
Falls Sie das erste Szenario erzwingen möchten, können Sie dies tun, indem Sie die Eingabeaufforderung als Argument übergeben:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of the `prompt`", prompt="a capybara swimming in the sea")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Chat-basierte Ausführung (Chat)
|
||||
|
||||
Der Agent verfügt auch über einen Chat-basierten Ansatz, der die Methode [`~Agent.chat`] verwendet:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.chat("Generate a picture of rivers and lakes")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.chat("Transform the picture so that there is a rock in there")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes_and_beaver.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
<br/>
|
||||
|
||||
Dies ist ein interessanter Ansatz, wenn Sie den Zustand über Anweisungen hinweg beibehalten möchten. Er ist besser für Experimente geeignet,
|
||||
eignet sich aber eher für einzelne Anweisungen als für komplexe Anweisungen (die die [`~Agent.run`]
|
||||
Methode besser verarbeiten kann).
|
||||
|
||||
Diese Methode kann auch Argumente entgegennehmen, wenn Sie Nicht-Text-Typen oder bestimmte Aufforderungen übergeben möchten.
|
||||
|
||||
### ⚠️ Fernausführung
|
||||
|
||||
Zu Demonstrationszwecken und damit es mit allen Setups verwendet werden kann, haben wir Remote-Executors für mehrere
|
||||
der Standard-Tools erstellt, auf die der Agent in dieser Version Zugriff hat. Diese werden erstellt mit
|
||||
[inference endpoints](https://huggingface.co/inference-endpoints).
|
||||
|
||||
Wir haben diese vorerst deaktiviert, aber um zu sehen, wie Sie selbst Remote Executors Tools einrichten können,
|
||||
empfehlen wir die Lektüre des [custom tool guide](./custom_tools).
|
||||
|
||||
### Was passiert hier? Was sind Tools und was sind Agenten?
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/diagram.png">
|
||||
|
||||
#### Agenten
|
||||
|
||||
Der "Agent" ist hier ein großes Sprachmodell, das wir auffordern, Zugang zu einem bestimmten Satz von Tools zu erhalten.
|
||||
|
||||
LLMs sind ziemlich gut darin, kleine Codeproben zu erzeugen. Diese API macht sich das zunutze, indem sie das
|
||||
LLM ein kleines Codebeispiel gibt, das eine Aufgabe mit einer Reihe von Werkzeugen ausführt. Diese Aufforderung wird dann ergänzt durch die
|
||||
Aufgabe, die Sie Ihrem Agenten geben, und die Beschreibung der Werkzeuge, die Sie ihm geben. Auf diese Weise erhält er Zugriff auf die Dokumentation der
|
||||
Tools, insbesondere die erwarteten Eingaben und Ausgaben, und kann den entsprechenden Code generieren.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tools
|
||||
|
||||
Tools sind sehr einfach: Sie bestehen aus einer einzigen Funktion mit einem Namen und einer Beschreibung. Wir verwenden dann die Beschreibungen dieser Tools
|
||||
um den Agenten aufzufordern. Anhand der Eingabeaufforderung zeigen wir dem Agenten, wie er die Tools nutzen kann, um das zu tun, was in der
|
||||
in der Abfrage angefordert wurde.
|
||||
|
||||
Dies geschieht mit brandneuen Tools und nicht mit Pipelines, denn der Agent schreibt besseren Code mit sehr atomaren Tools.
|
||||
Pipelines sind stärker refaktorisiert und fassen oft mehrere Aufgaben in einer einzigen zusammen. Tools sind dafür gedacht, sich auf
|
||||
eine einzige, sehr einfache Aufgabe konzentrieren.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Code-Ausführung?!
|
||||
|
||||
Dieser Code wird dann mit unserem kleinen Python-Interpreter auf den mit Ihren Tools übergebenen Eingaben ausgeführt.
|
||||
Wir hören Sie schon schreien "Willkürliche Codeausführung!", aber lassen Sie uns erklären, warum das nicht der Fall ist.
|
||||
|
||||
Die einzigen Funktionen, die aufgerufen werden können, sind die von Ihnen zur Verfügung gestellten Tools und die Druckfunktion, so dass Sie bereits eingeschränkt sind
|
||||
eingeschränkt, was ausgeführt werden kann. Sie sollten sicher sein, wenn es sich auf die Werkzeuge für das Umarmungsgesicht beschränkt.
|
||||
|
||||
Dann lassen wir keine Attributsuche oder Importe zu (die ohnehin nicht benötigt werden, um die
|
||||
Inputs/Outputs an eine kleine Gruppe von Funktionen), so dass alle offensichtlichen Angriffe (und Sie müssten den LLM
|
||||
dazu auffordern, sie auszugeben) kein Problem darstellen sollten. Wenn Sie auf Nummer sicher gehen wollen, können Sie die
|
||||
run()-Methode mit dem zusätzlichen Argument return_code=True ausführen. In diesem Fall gibt der Agent nur den auszuführenden Code
|
||||
zur Ausführung zurück und Sie können entscheiden, ob Sie ihn ausführen möchten oder nicht.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Ausführung bricht bei jeder Zeile ab, in der versucht wird, eine illegale Operation auszuführen, oder wenn ein regulärer Python-Fehler
|
||||
mit dem vom Agenten generierten Code.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ein kuratierter Satz von Tools
|
||||
|
||||
Wir haben eine Reihe von Tools identifiziert, die solche Agenten unterstützen können. Hier ist eine aktualisierte Liste der Tools, die wir integriert haben
|
||||
in `transformers` integriert haben:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Beantwortung von Fragen zu Dokumenten**: Beantworten Sie anhand eines Dokuments (z.B. PDF) im Bildformat eine Frage zu diesem Dokument ([Donut](./model_doc/donut))
|
||||
- Beantworten von Textfragen**: Geben Sie einen langen Text und eine Frage an, beantworten Sie die Frage im Text ([Flan-T5](./model_doc/flan-t5))
|
||||
- **Unbedingte Bildunterschriften**: Beschriften Sie das Bild! ([BLIP](./model_doc/blip))
|
||||
- **Bildfragebeantwortung**: Beantworten Sie bei einem Bild eine Frage zu diesem Bild ([VILT](./model_doc/vilt))
|
||||
- **Bildsegmentierung**: Geben Sie ein Bild und einen Prompt an und geben Sie die Segmentierungsmaske dieses Prompts aus ([CLIPSeg](./model_doc/clipseg))
|
||||
- **Sprache in Text**: Geben Sie eine Audioaufnahme einer sprechenden Person an und transkribieren Sie die Sprache in Text ([Whisper](./model_doc/whisper))
|
||||
- **Text in Sprache**: wandelt Text in Sprache um ([SpeechT5](./model_doc/speecht5))
|
||||
- **Zero-Shot-Textklassifizierung**: Ermitteln Sie anhand eines Textes und einer Liste von Bezeichnungen, welcher Bezeichnung der Text am ehesten entspricht ([BART](./model_doc/bart))
|
||||
- **Textzusammenfassung**: fassen Sie einen langen Text in einem oder wenigen Sätzen zusammen ([BART](./model_doc/bart))
|
||||
- **Übersetzung**: Übersetzen des Textes in eine bestimmte Sprache ([NLLB](./model_doc/nllb))
|
||||
|
||||
Diese Tools sind in Transformatoren integriert und können auch manuell verwendet werden, zum Beispiel:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = load_tool("text-to-speech")
|
||||
audio = tool("This is a text to speech tool")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Benutzerdefinierte Tools
|
||||
|
||||
Wir haben zwar eine Reihe von Tools identifiziert, sind aber der festen Überzeugung, dass der Hauptwert dieser Implementierung darin besteht
|
||||
die Möglichkeit, benutzerdefinierte Tools schnell zu erstellen und weiterzugeben.
|
||||
|
||||
Indem Sie den Code eines Tools in einen Hugging Face Space oder ein Modell-Repository stellen, können Sie das Tool
|
||||
direkt mit dem Agenten nutzen. Wir haben ein paar neue Funktionen hinzugefügt
|
||||
**transformers-agnostic** Tools zur [`huggingface-tools` Organisation](https://huggingface.co/huggingface-tools) hinzugefügt:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Text-Downloader**: zum Herunterladen eines Textes von einer Web-URL
|
||||
- **Text zu Bild**: erzeugt ein Bild nach einer Eingabeaufforderung und nutzt dabei stabile Diffusion
|
||||
- **Bildtransformation**: verändert ein Bild anhand eines Ausgangsbildes und einer Eingabeaufforderung, unter Ausnutzung der stabilen pix2pix-Diffusion
|
||||
- **Text zu Video**: Erzeugen eines kleinen Videos nach einer Eingabeaufforderung, unter Verwendung von damo-vilab
|
||||
|
||||
Das Text-zu-Bild-Tool, das wir von Anfang an verwendet haben, ist ein Remote-Tool, das sich in
|
||||
[*huggingface-tools/text-to-image*](https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface-tools/text-to-image)! Wir werden
|
||||
weiterhin solche Tools für diese und andere Organisationen veröffentlichen, um diese Implementierung weiter zu verbessern.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Agenten haben standardmäßig Zugriff auf die Tools, die sich auf [*huggingface-tools*](https://huggingface.co/huggingface-tools) befinden.
|
||||
Wie Sie Ihre eigenen Tools schreiben und freigeben können und wie Sie jedes benutzerdefinierte Tool, das sich auf dem Hub befindet, nutzen können, erklären wir in [folgender Anleitung](custom_tools).
|
||||
|
||||
### Code-Erzeugung
|
||||
|
||||
Bisher haben wir gezeigt, wie Sie die Agenten nutzen können, um Aktionen für Sie durchzuführen. Der Agent generiert jedoch nur Code
|
||||
den wir dann mit einem sehr eingeschränkten Python-Interpreter ausführen. Falls Sie den generierten Code in einer anderen Umgebung verwenden möchten
|
||||
einer anderen Umgebung verwenden möchten, können Sie den Agenten auffordern, den Code zusammen mit einer Tooldefinition und genauen Importen zurückzugeben.
|
||||
|
||||
Zum Beispiel die folgende Anweisung
|
||||
```python
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
gibt den folgenden Code zurück
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
image_generator = load_tool("huggingface-tools/text-to-image")
|
||||
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt="rivers and lakes")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
die Sie dann selbst ändern und ausführen können.
|
||||
@ -161,6 +161,8 @@
|
||||
sections:
|
||||
- local: quantization/overview
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: quantization/selecting
|
||||
title: Selecting a quantization method
|
||||
- local: quantization/aqlm
|
||||
title: AQLM
|
||||
- local: quantization/awq
|
||||
@ -306,8 +308,6 @@
|
||||
- isExpanded: false
|
||||
sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: main_classes/agent
|
||||
title: Agents and Tools
|
||||
- local: model_doc/auto
|
||||
title: Auto Classes
|
||||
- local: main_classes/backbones
|
||||
@ -461,6 +461,8 @@
|
||||
title: Gemma2
|
||||
- local: model_doc/glm
|
||||
title: GLM
|
||||
- local: model_doc/glm4
|
||||
title: glm4
|
||||
- local: model_doc/openai-gpt
|
||||
title: GPT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/gpt_neo
|
||||
@ -819,6 +821,8 @@
|
||||
title: EnCodec
|
||||
- local: model_doc/fastspeech2_conformer
|
||||
title: FastSpeech2Conformer
|
||||
- local: model_doc/granite_speech
|
||||
title: GraniteSpeech
|
||||
- local: model_doc/hubert
|
||||
title: Hubert
|
||||
- local: model_doc/mctct
|
||||
@ -1074,6 +1078,8 @@
|
||||
title: Utilities for Audio processing
|
||||
- local: internal/file_utils
|
||||
title: General Utilities
|
||||
- local: internal/import_utils
|
||||
title: Importing Utilities
|
||||
- local: internal/time_series_utils
|
||||
title: Utilities for Time Series
|
||||
title: Internal helpers
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,283 +15,4 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> Agents and tools are being spun out into the standalone [smolagents](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/index) library. These docs will be deprecated in the future!
|
||||
|
||||
# Agents
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
An agent is a system where a large language model (LLM) can execute more complex tasks through *planning* and using *tools*.
|
||||
|
||||
- Planning helps a LLM reason its way through a task by breaking it down into smaller subtasks. For example, [`CodeAgent`] plans a series of actions to take and then generates Python code to execute all the actions at once.
|
||||
|
||||
Another planning method is by self-reflection and refinement of its previous actions to improve its performance. The [`ReactJsonAgent`] is an example of this type of planning, and it's based on the [ReAct](https://hf.co/papers/2210.03629) framework. This agent plans and executes actions one at a time based on the feedback it receives from each action.
|
||||
|
||||
- Tools give a LLM access to external functions or APIs that it can use to help it complete a task. For example, [gradio-tools](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools) gives a LLM access to any of the [Gradio](https://www.gradio.app/) apps available on Hugging Face [Spaces](https://hf.co/spaces). These apps can be used for a wide range of tasks such as image generation, video generation, audio transcription, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
To use agents in Transformers, make sure you have the extra `agents` dependencies installed.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
!pip install transformers[agents]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create an agent instance (refer to the [Agents](./main_classes/agent#agents) API for supported agents in Transformers) and a list of tools available for it to use, then [`~ReactAgent.run`] the agent on your task. The example below demonstrates how a ReAct agent reasons through a task.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[])
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
======== New task ========
|
||||
How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?
|
||||
==== Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
bert_layers = 12 # BERT base encoder has 12 layers
|
||||
attention_layers = 6 # Encoder in Attention is All You Need has 6 layers
|
||||
layer_diff = bert_layers - attention_layers
|
||||
print("The difference in layers between BERT base encoder and Attention is All You Need is", layer_diff)
|
||||
====
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
The difference in layers between BERT base encoder and Attention is All You Need is 6
|
||||
|
||||
==== Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
final_answer("BERT base encoder has {} more layers than the encoder from Attention is All You Need.".format(layer_diff))
|
||||
====
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
>>> Final answer:
|
||||
BERT base encoder has 6 more layers than the encoder from Attention is All You Need.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will walk you through in more detail how to initialize an agent.
|
||||
|
||||
## LLM
|
||||
|
||||
An agent uses a LLM to plan and execute a task; it is the engine that powers the agent. To choose and build your own LLM engine, you need a method that:
|
||||
|
||||
1. the input uses the [chat template](./chat_templating) format, `List[Dict[str, str]]`, and it returns a string
|
||||
2. the LLM stops generating outputs when it encounters the sequences in `stop_sequences`
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
def llm_engine(messages, stop_sequences=["Task"]) -> str:
|
||||
response = client.chat_completion(messages, stop=stop_sequences, max_tokens=1000)
|
||||
answer = response.choices[0].message.content
|
||||
return answer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, initialize an engine to load a model. To run an agent locally, create a [`TransformersEngine`] to load a preinitialized [`Pipeline`].
|
||||
|
||||
However, you could also leverage Hugging Face's powerful inference infrastructure, [Inference API](https://hf.co/docs/api-inference/index) or [Inference Endpoints](https://hf.co/docs/inference-endpoints/index), to run your model. This is useful for loading larger models that are typically required for agentic behavior. In this case, load the [`HfApiEngine`] to run the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
The agent requires a list of tools it can use to complete a task. If you aren't using any additional tools, pass an empty list. The default tools provided by Transformers are loaded automatically, but you can optionally set `add_base_tools=True` to explicitly enable them.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="engine">
|
||||
<hfoption id="TransformersEngine">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, pipeline, TransformersEngine, CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct").to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline = pipeline("text-generation", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
llm_engine = TransformersEngine(pipeline)
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"What causes bread to rise?",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="HfApiEngine">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent, HfApiEngine
|
||||
|
||||
llm_engine = HfApiEngine(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Could you translate this sentence from French, say it out loud and return the audio.",
|
||||
sentence="Où est la boulangerie la plus proche?",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
The agent supports [constrained generation](https://hf.co/docs/text-generation-inference/conceptual/guidance) for generating outputs according to a specific structure with the `grammar` parameter. The `grammar` parameter should be specified in the `llm_engine` method or you can set it when initializing an agent.
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, an agent accepts additional inputs such as text and audio. In the [`HfApiEngine`] example above, the agent accepted a sentence to translate. But you could also pass a path to a local or remote file for the agent to access. The example below demonstrates how to pass a path to an audio file.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
agent.run("Why doesn't he know many people in New York?", audio="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/recording.mp3")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## System prompt
|
||||
|
||||
A system prompt describes how an agent should behave, a description of the available tools, and the expected output format.
|
||||
|
||||
Tools are defined by the `<<tool_descriptions>>` token which is dynamically replaced during runtime with the actual tool. The tool description is derived from the tool name, description, inputs, output type, and a Jinja2 template. Refer to the [Tools](./tools) guide for more information about how to describe tools.
|
||||
|
||||
The example below is the system prompt for [`ReactCodeAgent`].
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
You will be given a task to solve as best you can.
|
||||
You have access to the following tools:
|
||||
<<tool_descriptions>>
|
||||
|
||||
To solve the task, you must plan forward to proceed in a series of steps, in a cycle of 'Thought:', 'Code:', and 'Observation:' sequences.
|
||||
|
||||
At each step, in the 'Thought:' sequence, you should first explain your reasoning towards solving the task, then the tools that you want to use.
|
||||
Then in the 'Code:' sequence, you should write the code in simple Python. The code sequence must end with '/End code' sequence.
|
||||
During each intermediate step, you can use 'print()' to save whatever important information you will then need.
|
||||
These print outputs will then be available in the 'Observation:' field, for using this information as input for the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
In the end you have to return a final answer using the `final_answer` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few examples using notional tools:
|
||||
---
|
||||
{examples}
|
||||
|
||||
Above example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. You only have access to those tools:
|
||||
<<tool_names>>
|
||||
You also can perform computations in the python code you generate.
|
||||
|
||||
Always provide a 'Thought:' and a 'Code:\n```py' sequence ending with '```<end_code>' sequence. You MUST provide at least the 'Code:' sequence to move forward.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to not perform too many operations in a single code block! You should split the task into intermediate code blocks.
|
||||
Print results at the end of each step to save the intermediate results. Then use final_answer() to return the final result.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to make sure that variables you use are all defined.
|
||||
|
||||
Now Begin!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The system prompt can be tailored to the intended task. For example, you can add a better explanation of the output format or you can overwrite the system prompt template entirely with your own custom system prompt as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> If you're writing a custom system prompt, make sure to include `<<tool_descriptions>>` in the template so the agent is aware of the available tools.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ReactJsonAgent
|
||||
from transformers.agents import PythonInterpreterTool
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactJsonAgent(tools=[PythonInterpreterTool()], system_prompt="{your_custom_prompt}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Code execution
|
||||
|
||||
For safety, only the tools you provide (and the default Transformers tools) and the `print` function are executed. The interpreter doesn't allow importing modules that aren't on a safe list.
|
||||
|
||||
To import modules that aren't on the list, add them as a list to the `additional_authorized_imports` parameter when initializing an agent.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[], additional_authorized_imports=['requests', 'bs4'])
|
||||
agent.run("Could you get me the title of the page at url 'https://huggingface.co/blog'?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Code execution stops if a tool isn't on the safe list, it isn't authorized, or if the code generated by the agent returns a Python error.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> A LLM can generate any arbitrary code that can be executed, so don't add any unsafe imports!
|
||||
|
||||
## Multi-agent
|
||||
|
||||
[Multi-agent](https://hf.co/papers/2308.08155) refers to multiple agents working together to solve a task. Performance is typically better because each agent is specialized for a particular subtask.
|
||||
|
||||
Multi-agents are created through a [`ManagedAgent`] class, where a *manager agent* oversees how other agents work together. The manager agent requires an agent and their name and description. These are added to the manager agents system prompt which lets it know how to call and use them.
|
||||
|
||||
The multi-agent example below creates a web search agent that is managed by another [`ReactCodeAgent`].
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers.agents import ReactCodeAgent, HfApiEngine, DuckDuckGoSearchTool, ManagedAgent
|
||||
|
||||
llm_engine = HfApiEngine()
|
||||
web_agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool()], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
managed_web_agent = ManagedAgent(
|
||||
agent=web_agent,
|
||||
name="web_search",
|
||||
description="Runs web searches for you. Give it your query as an argument."
|
||||
)
|
||||
manager_agent = ReactCodeAgent(
|
||||
tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, managed_agents=[managed_web_agent]
|
||||
)
|
||||
manager_agent.run("Who is the CEO of Hugging Face?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Gradio integration
|
||||
|
||||
[Gradio](https://www.gradio.app/) is a library for quickly creating and sharing machine learning apps. The [gradio.Chatbot](https://www.gradio.app/docs/gradio/chatbot) supports chatting with a Transformers agent with the [`stream_to_gradio`] function.
|
||||
|
||||
Load a tool and LLM with an agent, and then create a Gradio app. The key is to use [`stream_to_gradio`] to stream the agents messages and display how it's reasoning through a task.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import gradio as gr
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
load_tool,
|
||||
ReactCodeAgent,
|
||||
HfApiEngine,
|
||||
stream_to_gradio,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Import tool from Hub
|
||||
image_generation_tool = load_tool("m-ric/text-to-image")
|
||||
llm_engine = HfApiEngine("meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize the agent with the image generation tool
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[image_generation_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
|
||||
def interact_with_agent(task):
|
||||
messages = []
|
||||
messages.append(gr.ChatMessage(role="user", content=task))
|
||||
yield messages
|
||||
for msg in stream_to_gradio(agent, task):
|
||||
messages.append(msg)
|
||||
yield messages + [
|
||||
gr.ChatMessage(role="assistant", content="⏳ Task not finished yet!")
|
||||
]
|
||||
yield messages
|
||||
|
||||
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
|
||||
text_input = gr.Textbox(lines=1, label="Chat Message", value="Make me a picture of the Statue of Liberty.")
|
||||
submit = gr.Button("Run illustrator agent!")
|
||||
chatbot = gr.Chatbot(
|
||||
label="Agent",
|
||||
type="messages",
|
||||
avatar_images=(
|
||||
None,
|
||||
"https://em-content.zobj.net/source/twitter/53/robot-face_1f916.png",
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
submit.click(interact_with_agent, [text_input], [chatbot])
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
demo.launch()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshoot
|
||||
|
||||
For a better idea of what is happening when you call an agent, it is always a good idea to check the system prompt template first.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
print(agent.system_prompt_template)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If the agent is behaving unexpectedly, remember to explain the task you want to perform as clearly as possible. Every [`~Agent.run`] is different and minor variations in your system prompt may yield completely different results.
|
||||
|
||||
To find out what happened after a run, check the following agent attributes.
|
||||
|
||||
- `agent.logs` stores the finegrained agent logs. At every step of the agents run, everything is stored in a dictionary and appended to `agent.logs`.
|
||||
- `agent.write_inner_memory_from_logs` only stores a high-level overview of the agents run. For example, at each step, it stores the LLM output as a message and the tool call output as a separate message. Not every detail from a step is transcripted by `write_inner_memory_from_logs`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Resources
|
||||
|
||||
Learn more about ReAct agents in the [Open-source LLMs as LangChain Agents](https://hf.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents) blog post.
|
||||
> Agents and tools were spun out into the standalone [smolagents](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/index) library. They were removed from `transformers` in v4.52.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -181,35 +181,6 @@ processed_chat = processor.apply_chat_template(
|
||||
print(processed_chat.keys())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="custom frame sampling">
|
||||
|
||||
Some models don't sample frames *uniformly* and require more complex logic to determine which frames to use. For example, the model may have an *adaptive frame selection* or if the model prioritizes *key moments* in a video rather than evenly spaced frames.
|
||||
|
||||
If a model has a different sampling strategy, you can write a function that customizes frame selection. The function should include the following requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
- Use the `sample_indices_fn` parameter to pass a callable function for sampling.
|
||||
- If provided, this function *overrides* the standard `num_frames` and `fps` parameters.
|
||||
- The function receives all the parameters passed to `load_video` and must return valid frame indices to sample from.
|
||||
|
||||
An example function is shown below. This gives you full control over frame selection, making the model more adaptable to different video scenarios.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
def sample_indices_fn(metadata, **kwargs):
|
||||
# samples only the first and the second frame
|
||||
return [0, 1]
|
||||
|
||||
processed_chat = processor.apply_chat_template(
|
||||
messages,
|
||||
add_generation_prompt=True,
|
||||
tokenize=True,
|
||||
return_dict=True,
|
||||
sample_indices_fn=sample_indices_fn,
|
||||
video_load_backend="decord",
|
||||
)
|
||||
print(processed_chat.keys())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="list of image frames">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
91
docs/source/en/internal/import_utils.md
Normal file
91
docs/source/en/internal/import_utils.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Import Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
This page goes through the transformers utilities to enable lazy and fast object import.
|
||||
While we strive for minimal dependencies, some models have specific dependencies requirements that cannot be
|
||||
worked around. We don't want for all users of `transformers` to have to install those dependencies to use other models,
|
||||
we therefore mark those as soft dependencies rather than hard dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
The transformers toolkit is not made to error-out on import of a model that has a specific dependency; instead, an
|
||||
object for which you are lacking a dependency will error-out when calling any method on it. As an example, if
|
||||
`torchvision` isn't installed, the fast image processors will not be available.
|
||||
|
||||
This object is still importable:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DetrImageProcessorFast
|
||||
>>> print(DetrImageProcessorFast)
|
||||
<class 'DetrImageProcessorFast'>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
However, no method can be called on that object:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> DetrImageProcessorFast.from_pretrained()
|
||||
ImportError:
|
||||
DetrImageProcessorFast requires the Torchvision library but it was not found in your environment. Checkout the instructions on the
|
||||
installation page: https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/ and follow the ones that match your environment.
|
||||
Please note that you may need to restart your runtime after installation.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let's see how to specify specific object dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
## Specifying Object Dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
### Filename-based
|
||||
|
||||
All objects under a given filename have an automatic dependency to the tool linked to the filename
|
||||
|
||||
**TensorFlow**: All files starting with `modeling_tf_` have an automatic TensorFlow dependency.
|
||||
|
||||
**Flax**: All files starting with `modeling_flax_` have an automatic Flax dependency
|
||||
|
||||
**PyTorch**: All files starting with `modeling_` and not valid with the above (TensorFlow and Flax) have an automatic
|
||||
PyTorch dependency
|
||||
|
||||
**Tokenizers**: All files starting with `tokenization_` and ending with `_fast` have an automatic `tokenizers` dependency
|
||||
|
||||
**Vision**: All files starting with `image_processing_` have an automatic dependency to the `vision` dependency group;
|
||||
at the time of writing, this only contains the `pillow` dependency.
|
||||
|
||||
**Vision + Torch + Torchvision**: All files starting with `image_processing_` and ending with `_fast` have an automatic
|
||||
dependency to `vision`, `torch`, and `torchvision`.
|
||||
|
||||
All of these automatic dependencies are added on top of the explicit dependencies that are detailed below.
|
||||
|
||||
### Explicit Object Dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
We add a method called `requires` that is used to explicitly specify the dependencies of a given object. As an
|
||||
example, the `Trainer` class has two hard dependencies: `torch` and `accelerate`. Here is how we specify these
|
||||
required dependencies:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from .utils.import_utils import requires
|
||||
|
||||
@requires(backends=("torch", "accelerate"))
|
||||
class Trainer:
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Backends that can be added here are all the backends that are available in the `import_utils.py` module.
|
||||
|
||||
## Methods
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.import_utils.define_import_structure
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.import_utils.requires
|
||||
@ -1,167 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Agents & Tools
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers Agents is an experimental API which is subject to change at any time. Results returned by the agents
|
||||
can vary as the APIs or underlying models are prone to change.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about agents and tools make sure to read the [introductory guide](../transformers_agents). This page
|
||||
contains the API docs for the underlying classes.
|
||||
|
||||
## Agents
|
||||
|
||||
We provide two types of agents, based on the main [`Agent`] class:
|
||||
- [`CodeAgent`] acts in one shot, generating code to solve the task, then executes it at once.
|
||||
- [`ReactAgent`] acts step by step, each step consisting of one thought, then one tool call and execution. It has two classes:
|
||||
- [`ReactJsonAgent`] writes its tool calls in JSON.
|
||||
- [`ReactCodeAgent`] writes its tool calls in Python code.
|
||||
|
||||
### Agent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Agent
|
||||
|
||||
### CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### React agents
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ReactAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ReactJsonAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### ManagedAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ManagedAgent
|
||||
|
||||
## Tools
|
||||
|
||||
### load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
### tool
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tool
|
||||
|
||||
### Tool
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Tool
|
||||
|
||||
### Toolbox
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Toolbox
|
||||
|
||||
### PipelineTool
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PipelineTool
|
||||
|
||||
### launch_gradio_demo
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] launch_gradio_demo
|
||||
|
||||
### stream_to_gradio
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] stream_to_gradio
|
||||
|
||||
### ToolCollection
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ToolCollection
|
||||
|
||||
## Engines
|
||||
|
||||
You're free to create and use your own engines to be usable by the Agents framework.
|
||||
These engines have the following specification:
|
||||
1. Follow the [messages format](../chat_templating.md) for its input (`List[Dict[str, str]]`) and return a string.
|
||||
2. Stop generating outputs *before* the sequences passed in the argument `stop_sequences`
|
||||
|
||||
### TransformersEngine
|
||||
|
||||
For convenience, we have added a `TransformersEngine` that implements the points above, taking a pre-initialized `Pipeline` as input.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, pipeline, TransformersEngine
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model_name = "HuggingFaceTB/SmolLM-135M-Instruct"
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pipe = pipeline("text-generation", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> engine = TransformersEngine(pipe)
|
||||
>>> engine([{"role": "user", "content": "Ok!"}], stop_sequences=["great"])
|
||||
|
||||
"What a "
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TransformersEngine
|
||||
|
||||
### HfApiEngine
|
||||
|
||||
The `HfApiEngine` is an engine that wraps an [HF Inference API](https://huggingface.co/docs/api-inference/index) client for the execution of the LLM.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import HfApiEngine
|
||||
|
||||
>>> messages = [
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "Hello, how are you?"},
|
||||
... {"role": "assistant", "content": "I'm doing great. How can I help you today?"},
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "No need to help, take it easy."},
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> HfApiEngine()(messages, stop_sequences=["conversation"])
|
||||
|
||||
"That's very kind of you to say! It's always nice to have a relaxed "
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HfApiEngine
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Agent Types
|
||||
|
||||
Agents can handle any type of object in-between tools; tools, being completely multimodal, can accept and return
|
||||
text, image, audio, video, among other types. In order to increase compatibility between tools, as well as to
|
||||
correctly render these returns in ipython (jupyter, colab, ipython notebooks, ...), we implement wrapper classes
|
||||
around these types.
|
||||
|
||||
The wrapped objects should continue behaving as initially; a text object should still behave as a string, an image
|
||||
object should still behave as a `PIL.Image`.
|
||||
|
||||
These types have three specific purposes:
|
||||
|
||||
- Calling `to_raw` on the type should return the underlying object
|
||||
- Calling `to_string` on the type should return the object as a string: that can be the string in case of an `AgentText`
|
||||
but will be the path of the serialized version of the object in other instances
|
||||
- Displaying it in an ipython kernel should display the object correctly
|
||||
|
||||
### AgentText
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.agents.agent_types.AgentText
|
||||
|
||||
### AgentImage
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.agents.agent_types.AgentImage
|
||||
|
||||
### AgentAudio
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.agents.agent_types.AgentAudio
|
||||
@ -88,6 +88,11 @@ The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/salesforce/BLIP).
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BlipTextModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## BlipTextLMHeadModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BlipTextLMHeadModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## BlipVisionModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BlipVisionModel
|
||||
@ -123,6 +128,11 @@ The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/salesforce/BLIP).
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFBlipTextModel
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
## TFBlipTextLMHeadModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFBlipTextLMHeadModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## TFBlipVisionModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFBlipVisionModel
|
||||
|
||||
@ -226,3 +226,8 @@ print(answer)
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DonutSwinModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## DonutSwinForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.DonutSwinForImageClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2025 The GLM & ZhipuAI team and The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
@ -14,13 +14,32 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# エージェントとツール
|
||||
# Glm4
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The Agents framework has significantly changed in version v4.41.0.
|
||||
This document has been removed as it was referencing an older API.
|
||||
To be released with the official model launch.
|
||||
|
||||
We eagerly welcome new contributions for the updated API.
|
||||
## Glm4Config
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Glm4Config
|
||||
|
||||
## Glm4Model
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Glm4Model
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## Glm4ForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Glm4ForCausalLM
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## Glm4ForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Glm4ForSequenceClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## Glm4ForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Glm4ForTokenClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
68
docs/source/en/model_doc/granite_speech.md
Normal file
68
docs/source/en/model_doc/granite_speech.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Granite Speech
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex flex-wrap space-x-1">
|
||||
<img alt="PyTorch" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/PyTorch-DE3412?style=flat&logo=pytorch&logoColor=white">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
The Granite Speech model is a multimodal language model, consisting of a speech encoder, speech projector, large language model, and LoRA adapter(s). More details regarding each component for the current (Granite 3.2 Speech) model architecture may be found below.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Speech Encoder: A [Conformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.08100) encoder trained with Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) on character-level targets on ASR corpora. The encoder uses block-attention and self-conditioned CTC from the middle layer.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Speech Projector: A query transformer (q-former) operating on the outputs of the last encoder block. The encoder and projector temporally downsample the audio features to be merged into the multimodal embeddings to be processed by the llm.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Large Language Model: The Granite Speech model leverages Granite LLMs, which were originally proposed in [this paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.13359).
|
||||
|
||||
4. LoRA adapter(s): The Granite Speech model contains a modality specific LoRA, which will be enabled when audio features are provided, and disabled otherwise.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Note that most of the aforementioned components are implemented generically to enable compatability and potential integration with other model architectures in transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [Alexander Brooks](https://huggingface.co/abrooks9944), [Avihu Dekel](https://huggingface.co/Avihu), and [George Saon](https://huggingface.co/gsaon).
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage tips
|
||||
- This model bundles its own LoRA adapter, which will be automatically loaded and enabled/disabled as needed during inference calls. Be sure to install [PEFT](https://github.com/huggingface/peft) to ensure the LoRA is correctly applied!
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- TODO (@alex-jw-brooks) Add an example here once the model compatible with the transformers implementation is released -->
|
||||
|
||||
## GraniteSpeechConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GraniteSpeechConfig
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## GraniteSpeechEncoderConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GraniteSpeechEncoderConfig
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## GraniteSpeechProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GraniteSpeechProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## GraniteSpeechFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GraniteSpeechFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## GraniteSpeechForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GraniteSpeechForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
135
docs/source/en/quantization/selecting.md
Normal file
135
docs/source/en/quantization/selecting.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Selecting a quantization method
|
||||
|
||||
There are many quantization methods available in Transformers for inference and fine-tuning. This guide helps you choose the most common and production-ready quantization techniques depending on your use case, and presents the advantages and disadvantages of each technique.
|
||||
|
||||
For a comprehensive overview of all supported methods and their features, refer back to the table in the [Overview](./overview).
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference
|
||||
|
||||
Consider the quantization methods below for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
| quantization method | use case |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
| bitsandbytes | ease of use and QLoRA fine-tuning on NVIDIA GPUs |
|
||||
| compressed-tensors | loading specific quantized formats (FP8, Sparse) |
|
||||
| GPTQModel or AWQ | good 4-bit accuracy with upfront calibration |
|
||||
| HQQ | fast on the fly quantization without calibration |
|
||||
| torchao | flexibility and fast inference with torch.compile |
|
||||
|
||||
### No Calibration Required (On-the-fly Quantization)
|
||||
|
||||
These methods are generally easier to use as they don't need a separate calibration dataset or step.
|
||||
|
||||
#### bitsandbytes
|
||||
|
||||
| Pros | Cons |
|
||||
|--------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| Very simple, no calibration dataset required for inference. | Primarily optimized for NVIDIA GPUs (CUDA). |
|
||||
| Good community support and widely adopted. | Inference speedup isn't guaranteed. |
|
||||
|
||||
See the [bitsandbytes documentation](./bitsandbytes) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
#### HQQ (Half-Quadratic Quantization)
|
||||
|
||||
| Pros | Cons |
|
||||
|----------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| Fast quantization process, no calibration data needed. | Accuracy can degrade significantly at bit depths <4-bit. |
|
||||
| Multiple backends for fast inference. | Inference speed may not match others unless using `torch.compile` or backends. |
|
||||
| Compatible with `torch.compile`. | |
|
||||
| Supports wide range of bit depths (8, 4, 3, 2, 1-bit). | |
|
||||
|
||||
See the [HQQ documentation](./hqq) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
#### torchao
|
||||
|
||||
| Pros | Cons |
|
||||
|----------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| Strong integration with `torch.compile` for potential speedups. | Newer library, ecosystem still evolving. |
|
||||
| Offers decent CPU quantization support. | Performance depends on `torch.compile` working well. |
|
||||
| Flexibility in quantization schemes (int8, int4, fp8). | 4-bit quantization (int4wo) may not match GPTQ/AWQ in accuracy. |
|
||||
|
||||
See the [torchao documentation](./torchao) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
### Calibration-based Quantization
|
||||
|
||||
These methods require an upfront calibration step using a dataset to potentially achieve higher accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
#### GPTQ/GPTQModel
|
||||
|
||||
Calibration for 8B model takes ~20 minutes on one A100 gpu.
|
||||
|
||||
| Pros | Cons |
|
||||
|----------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| Often achieves high accuracy. | Requires a calibration dataset and a separate calibration step. |
|
||||
| Can lead to inference speedups. | Possible to overfit on calibration data. |
|
||||
| Many pre-quantized GPTQ models on [Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?other=gptq). | |
|
||||
|
||||
See the [GPTQ documentation](./gptq) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
#### AWQ (Activation-aware Weight Quantization)
|
||||
|
||||
Calibration for 8B model takes ~10 minutes on one A100 gpu.
|
||||
|
||||
| Pros | Cons |
|
||||
|----------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| Often achieves high accuracy at 4-bit. (Sometimes surpasses GPTQ on specific tasks.) | Requires calibration if quantizing yourself. |
|
||||
| Can lead to inference speedups. | |
|
||||
| Shorter calibration time than GPTQ. | |
|
||||
| Many pre-quantized AWQ models on [Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?other=awq). | |
|
||||
|
||||
See the [AWQ documentation](./awq) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
### Loading Specific Formats
|
||||
|
||||
#### compressed-tensors
|
||||
|
||||
| Pros | Cons |
|
||||
|--------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| Supports flexible formats including FP8 and sparsity. | Primarily for loading pre-quantized models. |
|
||||
| | Doesn't perform quantization within Transformers directly. |
|
||||
|
||||
See the [compressed-tensors documentation](./compressed_tensors) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
## Fine-tuning
|
||||
|
||||
Consider the quantization method below during fine-tuning to save memory.
|
||||
|
||||
### bitsandbytes[[training]]
|
||||
|
||||
* **Description:** The standard method for QLoRA fine-tuning via PEFT.
|
||||
* **Pros:** Enables fine-tuning large models on consumer GPUs; widely supported and documented for PEFT.
|
||||
* **Cons:** Primarily for NVIDIA GPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
Other methods offer PEFT compatibility, though bitsandbytes is the most established and straightforward path for QLoRA.
|
||||
|
||||
See the [bitsandbytes documentation](./bitsandbytes#qlora) and [PEFT Docs](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/developer_guides/quantization#aqlm-quantization) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
## Research
|
||||
|
||||
Methods like [AQLM](./aqlm), [SpQR](./spqr), [VPTQ](./vptq), [HIGGS](./higgs), etc., push the boundaries of compression (< 2-bit) or explore novel techniques.
|
||||
|
||||
* Consider these if:
|
||||
* You need extreme compression (sub-4-bit).
|
||||
* You are conducting research or require state-of-the-art results from their respective papers.
|
||||
* You have significant compute resources available for potentially complex quantization procedures.
|
||||
We recommend consulting each methods documentation and associated papers carefully before choosing one for use in production.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Always benchmark the performance (accuracy and speed) of the quantized model on your specific task and hardware to ensure it meets your requirements. Refer to the individual documentation pages linked above for detailed usage instructions.
|
||||
@ -15,238 +15,4 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> Agents and tools are being spun out into the standalone [smolagents](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/index) library. These docs will be deprecated in the future!
|
||||
|
||||
# Tools
|
||||
|
||||
A tool is a function an agent can use to complete a task. Depending on your task, a tool can perform a web search, answer questions about a document, transcribe speech to text, and much more.
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers provides a default set of tools for agents. These include the tools mentioned above as well as image question answering, text-to-speech, translation, and a Python code interpreter that executes the Python code generated by a LLM in a secure environment.
|
||||
|
||||
Set `add_base_tools=True` to enable this default set of tools. The `tools` parameter is for adding additional tools. Leave the list empty if you aren't planning on adding any other tools to the toolbox.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You could also manually load a tool with [`load_tool`].
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool, ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
tool = load_tool("text-to-speech")
|
||||
audio = tool("This is a text-to-speech tool")
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[audio])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will help you learn how to create your own tools and manage an agents toolbox.
|
||||
|
||||
## Create a new tool
|
||||
|
||||
You can create any tool you can dream of to empower an agent. The example in this section creates a tool that returns the most downloaded model for a task from the Hub, and the code for it is shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
task = "text-classification"
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
print(model.id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are two ways you can create a tool, using a decorator or a superclass.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tool decorator
|
||||
|
||||
A fast and simple way to create a tool is to add the `@tool` decorator.
|
||||
|
||||
Convert the code above into a tool by wrapping it in a function and adding the `@tool` decorator. The function needs:
|
||||
|
||||
- A clear name that describes what the tool does, `model_download_counter`.
|
||||
- Type hints for the input and output (`str`).
|
||||
- A description that describes the tool in more detail and its arguments. This description is incorporated in the agents system prompt. It tells the agent *how* to use the tool, so try to make it as clear as possible!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import tool
|
||||
|
||||
@tool
|
||||
def model_download_counter(task: str) -> str:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This is a tool that returns the checkpoint name of the most downloaded model for a task from the Hugging Face Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
task: The task to retrieve the most downloaded model from.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
return model.id
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Pass the `model_download_counter` tool to the agents `tools` parameter to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[model_download_counter], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads on the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Tool superclass
|
||||
|
||||
Inheritance allows you to customize the [`Tool`] superclass or build a tool much more flexibly and comprehensively. This example will show you how to build the same `model_download_counter` tool as a [`Tool`] class.
|
||||
|
||||
The [`Tool`] class needs:
|
||||
|
||||
- A clear name that describes what the tool does, `model_download_counter`.
|
||||
- A description that describes the tool in more detail and its arguments. This description is incorporated in the agents system prompt. It tells the agent *how* to use the tool, so try to make it as clear as possible!
|
||||
- An `inputs` attribute that describes the input type. This is a dictionary with the keys, `type` and `description`.
|
||||
- An `outputs` attribute that describes the output type.
|
||||
- A `forward` method containing the code to be executed when the tool is called.
|
||||
|
||||
Write the following code below to a file named `model_download.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import Tool
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
class HFModelDownloadsTool(Tool):
|
||||
name = "model_download_counter"
|
||||
description = """
|
||||
This is a tool that returns the checkpoint name of the most downloaded model for a task from the Hugging Face Hub."""
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = {
|
||||
"task": {
|
||||
"type": "string",
|
||||
"description": "the task category (such as text-classification, depth-estimation, etc)",
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_type = "string"
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, task: str):
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
return model.id
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Import the tool from `model_download.py` and use [`load_tool`] to load it into the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from model_download import HFModelDownloadsTool
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool, CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
tool = HFModelDownloadsTool()
|
||||
model_counter = load_tool(tool)
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[model_counter], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Also consider sharing your tool to the Hub with [`~Tool.push_to_hub`] so that everyone can use it!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from model_download import HFModelDownloadsTool
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool, CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
tool = HFModelDownloadsTool()
|
||||
tool.push_to_hub("{your_username}/hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
model_counter = load_tool("m-ric/hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[model_counter], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Add and replace tools
|
||||
|
||||
Once an agent is initialized, add or replace its available tools without reinitializing the agent from scratch.
|
||||
|
||||
Use [`add_tool`] to add a tool to an existing agent.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
agent.toolbox.add_tool(model_download_counter)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can use the default text-to-speech tool to read aloud the most downloaded model for the text-to-video task.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Can you read out loud the name of the model that has the most downloads on the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub and return the audio?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> When adding tools to an agent that already works well, it can bias the agent towards your tool or a tool other than the one currently defined.
|
||||
|
||||
Use [`update_tool`] to replace an agents existing tool. This is useful if the new tool is a one-to-one replacement of the existing tool because the agent already knows how to perform the task. The new tool should follow the same API as the tool it replaced or the system prompt template should be adapted to ensure all examples using the replaced tool are updated.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.toolbox.update_tool(new_model_download_counter)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## ToolCollection
|
||||
|
||||
A [`ToolCollection`] is a collection of Hugging Face [Spaces](https://hf.co/spaces) that can be quickly loaded and used by an agent.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Learn more about creating collections on the Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a [`ToolCollection`] object and specify the `collection_slug` of the collection you want to use, and then pass it to the agent. To speed up the starting process, tools are only loaded if they're called by the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
The example loads a collection of image generation tools.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ToolCollection, ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
image_tool_collection = ToolCollection(collection_slug="")
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[*image_tool_collection], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Please draw me a picture of rivers and lakes."
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Tool integrations
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers supports tools from several other libraries, such as [gradio-tools](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools) and [LangChain](https://python.langchain.com/docs/introduction/).
|
||||
|
||||
### gradio-tools
|
||||
|
||||
gradio-tools is a library that enables [Gradio](https://www.gradio.app/) apps to be used as tools. With the wide variety of Gradio apps available, you can enhance your agent with a range of tools like generating images and videos or transcribing audio and summarizing it.
|
||||
|
||||
Import and instantiate a tool from gradio-tools, for example, the [StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools/blob/main/gradio_tools/tools/prompt_generator.py). This tool can help improve prompts to generate better images.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> gradio-tools require text inputs and outputs even when working with different modalities like images and audio, which are currently incompatible.
|
||||
|
||||
Use [`~Tool.from_gradio`] to load the prompt generator tool.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from gradio_tools import StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool
|
||||
from transformers import Tool, load_tool, CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
gradio_prompt_generator_tool = StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool()
|
||||
prompt_generator_tool = Tool.from_gradio(gradio_prompt_generator_tool)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now pass it to the agent along with a text-to-image tool.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image_generation_tool = load_tool("huggingface-tools/text-to-image")
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[prompt_generator_tool, image_generation_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Improve this prompt, then generate an image of it.", prompt="A rabbit wearing a space suit"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### LangChain
|
||||
|
||||
LangChain is a library for working with LLMs which includes agents and tools. Use the [`~Tool.from_langchain`] method to load any LangChain tool into an agent.
|
||||
|
||||
The example below demonstrates how to use LangChains web search tool.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from langchain.agents import load_tools
|
||||
from transformers import Tool, ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
search_tool = Tool.from_langchain(load_tools(["serpapi"])[0])
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[search_tool])
|
||||
agent.run("How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
> Agents and tools were spun out into the standalone [smolagents](https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/index) library. They were removed from `transformers` in v4.52.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -341,29 +341,9 @@ use_cpu: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Tensor parallelism with PyTorch 2">
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
tp_config:
|
||||
tp_size: 4
|
||||
distributed_type: TP
|
||||
downcast_bf16: 'no'
|
||||
machine_rank: 0
|
||||
main_training_function: main
|
||||
mixed_precision: 'no'
|
||||
num_machines: 1
|
||||
num_processes: 4
|
||||
rdzv_backend: static
|
||||
same_network: true
|
||||
tpu_env: []
|
||||
tpu_use_cluster: false
|
||||
tpu_use_sudo: false
|
||||
use_cpu: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Run [accelerate_launch](https://hf.co/docs/accelerate/package_reference/cli#accelerate-launch) to start training with the configurations set in `config_file.yaml`. This file is saved to the Accelerate cache folder and automatically loaded when you run `accelerate_launch`.
|
||||
|
||||
The example below launches the [run_glue.py](../../../examples/pytorch/text-classification/run_glue) script with the FSDP configuration shown earlier. Parameters from the `config_file.yaml` file can also be directly set in the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -363,29 +363,6 @@ use_cpu: false
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoption id="Tensor Parallelism with PyTorch 2">
|
||||
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
tp_config:
|
||||
tp_size: 4
|
||||
distributed_type: TP
|
||||
downcast_bf16: 'no'
|
||||
machine_rank: 0
|
||||
main_training_function: main
|
||||
mixed_precision: 'no'
|
||||
num_machines: 1
|
||||
num_processes: 4
|
||||
rdzv_backend: static
|
||||
same_network: true
|
||||
tpu_env: []
|
||||
tpu_use_cluster: false
|
||||
tpu_use_sudo: false
|
||||
use_cpu: false
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
El comando [`accelerate_launch`](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/package_reference/cli#accelerate-launch) es la forma recomendada de lanzar tu script de entrenamiento en un sistema distribuido con Accelerate y [`Trainer`] con los parámetros especificados en `config_file.yaml`. Este archivo se guarda en la carpeta de caché de Accelerate y se carga automáticamente cuando ejecutas `accelerate_launch`.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,8 +23,6 @@
|
||||
title: Chargement et entraînement des adaptateurs avec 🤗 PEFT
|
||||
- local: in_translation
|
||||
title: Partager un modèle
|
||||
- local: in_translation
|
||||
title: Agents
|
||||
- local: in_translation
|
||||
title: Génération avec LLMs
|
||||
title: Tutoriels
|
||||
@ -33,4 +31,4 @@
|
||||
title: Ce que 🤗 Transformers peut faire
|
||||
- local: tasks_explained
|
||||
title: Comment 🤗 Transformers résout ces tâches
|
||||
title: Guides conceptuels
|
||||
title: Guides conceptuels
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,8 +23,6 @@
|
||||
title: 🤗 PEFT を使用してアダプターをロードしてトレーニングする
|
||||
- local: model_sharing
|
||||
title: モデルを共有する
|
||||
- local: transformers_agents
|
||||
title: エージェント
|
||||
- local: llm_tutorial
|
||||
title: LLM を使用した生成
|
||||
title: Tutorials
|
||||
@ -119,8 +117,6 @@
|
||||
title: トーチスクリプトへのエクスポート
|
||||
- local: community
|
||||
title: コミュニティリソース
|
||||
- local: custom_tools
|
||||
title: カスタムツールとプロンプト
|
||||
- local: troubleshooting
|
||||
title: トラブルシューティング
|
||||
title: 開発者ガイド
|
||||
@ -200,8 +196,6 @@
|
||||
title: コンセプチュアルガイド
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: main_classes/agent
|
||||
title: エージェントとツール
|
||||
- local: model_doc/auto
|
||||
title: Auto Classes
|
||||
- local: main_classes/callback
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Custom Tools and Prompts
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
The Agents framework has significantly changed in version v4.41.0.
|
||||
This document has been removed as it was referencing an older API.
|
||||
|
||||
We eagerly welcome new contributions for the updated API.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
@ -1,282 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Transformers Agents
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers Agentsは、いつでも変更される可能性のある実験的なAPIです。エージェントが返す結果は、APIまたは基礎となるモデルが変更される可能性があるため、異なることがあります。
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformersバージョンv4.29.0は、*ツール*と*エージェント*のコンセプトを基に構築されています。この[colab](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1c7MHD-T1forUPGcC_jlwsIptOzpG3hSj)で試すことができます。
|
||||
|
||||
要するに、これはtransformersの上に自然言語APIを提供するものです:私たちは一連の厳選されたツールを定義し、自然言語を解釈し、これらのツールを使用するエージェントを設計します。これは設計上拡張可能です。私たちはいくつかの関連するツールを厳選しましたが、コミュニティによって開発された任意のツールを使用するためにシステムを簡単に拡張できる方法も示します。
|
||||
|
||||
この新しいAPIで何ができるかのいくつかの例から始めましょう。特に多モーダルなタスクに関して強力ですので、画像を生成したりテキストを読み上げたりするのに最適です。
|
||||
|
||||
上記のテキストの上に、日本語の翻訳を提供します。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Caption the following image", image=image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| **Input** | **Output** |
|
||||
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------|
|
||||
| <img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/beaver.png" width=200> | A beaver is swimming in the water |
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Read the following text out loud", text=text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
| **Input** | **Output** |
|
||||
|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| A beaver is swimming in the water | <audio controls><source src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/tts_example.wav" type="audio/wav"> your browser does not support the audio element. </audio>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"In the following `document`, where will the TRRF Scientific Advisory Council Meeting take place?",
|
||||
document=document,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
| **Input** | **Output** |
|
||||
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------|
|
||||
| <img src="https://datasets-server.huggingface.co/assets/hf-internal-testing/example-documents/--/hf-internal-testing--example-documents/test/0/image/image.jpg" width=200> | ballroom foyer |
|
||||
|
||||
## Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
`agent.run`を使用する前に、エージェントをインスタンス化する必要があります。エージェントは、大規模な言語モデル(LLM)です。
|
||||
OpenAIモデルとBigCode、OpenAssistantからのオープンソースの代替モデルをサポートしています。OpenAIモデルはパフォーマンスが優れていますが、OpenAIのAPIキーが必要であり、無料で使用することはできません。一方、Hugging FaceはBigCodeとOpenAssistantモデルのエンドポイントへの無料アクセスを提供しています。
|
||||
|
||||
まず、デフォルトの依存関係をすべてインストールするために`agents`のエクストラをインストールしてください。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers[agents]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
OpenAIモデルを使用するには、`openai`の依存関係をインストールした後、`OpenAiAgent`をインスタンス化します。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install openai
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import OpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = OpenAiAgent(model="text-davinci-003", api_key="<your_api_key>")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
BigCodeまたはOpenAssistantを使用するには、まずログインしてInference APIにアクセスしてください。
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import login
|
||||
|
||||
login("<YOUR_TOKEN>")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
次に、エージェントをインスタンス化してください。
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
# Starcoder
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder")
|
||||
# StarcoderBase
|
||||
# agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoderbase")
|
||||
# OpenAssistant
|
||||
# agent = HfAgent(url_endpoint="https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/OpenAssistant/oasst-sft-4-pythia-12b-epoch-3.5")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
これは、Hugging Faceが現在無料で提供している推論APIを使用しています。このモデル(または別のモデル)の独自の推論エンドポイントをお持ちの場合は、上記のURLエンドポイントをご自分のURLエンドポイントで置き換えることができます。
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
StarCoderとOpenAssistantは無料で利用でき、シンプルなタスクには非常に優れた性能を発揮します。ただし、より複雑なプロンプトを処理する際には、チェックポイントが十分でないことがあります。そのような場合には、現時点ではオープンソースではないものの、パフォーマンスが向上する可能性のあるOpenAIモデルを試してみることをお勧めします。
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
これで準備が整いました!これから、あなたが利用できる2つのAPIについて詳しく説明します。
|
||||
|
||||
### Single execution (run)
|
||||
|
||||
単一実行メソッドは、エージェントの [`~Agent.run`] メソッドを使用する場合です。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes.")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
これは、実行したいタスクに適したツール(またはツール)を自動的に選択し、適切に実行します。1つまたは複数のタスクを同じ命令で実行することができます(ただし、命令が複雑であるほど、エージェントが失敗する可能性が高くなります)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of the sea then transform the picture to add an island")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/sea_and_island.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
<br/>
|
||||
|
||||
[`~Agent.run`] 操作は独立して実行できますので、異なるタスクで何度も実行することができます。
|
||||
|
||||
注意点として、あなたの `agent` は単なる大規模な言語モデルであるため、プロンプトのわずかな変更でも完全に異なる結果が得られる可能性があります。したがって、実行したいタスクをできるだけ明確に説明することが重要です。良いプロンプトの書き方については、[こちら](custom_tools#writing-good-user-inputs) で詳しく説明しています。
|
||||
|
||||
実行ごとに状態を保持したり、テキスト以外のオブジェクトをエージェントに渡したりする場合は、エージェントが使用する変数を指定することができます。例えば、最初の川や湖の画像を生成し、その画像に島を追加するようにモデルに指示するには、次のように行うことができます:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
picture = agent.run("Generate a picture of rivers and lakes.")
|
||||
updated_picture = agent.run("Transform the image in `picture` to add an island to it.", picture=picture)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
これは、モデルがあなたのリクエストを理解できない場合や、ツールを混同する場合に役立つことがあります。例えば:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me the picture of a capybara swimming in the sea")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
ここでは、モデルは2つの方法で解釈できます:
|
||||
- `text-to-image`に海で泳ぐカピバラを生成させる
|
||||
- または、`text-to-image`でカピバラを生成し、それを海で泳がせるために`image-transformation`ツールを使用する
|
||||
|
||||
最初のシナリオを強制したい場合は、プロンプトを引数として渡すことができます:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of the `prompt`", prompt="a capybara swimming in the sea")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Chat-based execution (チャット)
|
||||
|
||||
エージェントは、[`~Agent.chat`] メソッドを使用することで、チャットベースのアプローチも可能です。
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.chat("Transform the picture so that there is a rock in there")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes_and_beaver.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
<br/>
|
||||
|
||||
これは、指示をまたいで状態を保持したい場合に便利なアプローチで、単一の指示に比べて複雑な指示を処理するのは難しいかもしれません(その場合は [`~Agent.run`] メソッドの方が適しています)。
|
||||
|
||||
このメソッドは、非テキスト型の引数や特定のプロンプトを渡したい場合にも使用できます。
|
||||
|
||||
### ⚠️ Remote execution
|
||||
|
||||
デモンストレーションの目的やすべてのセットアップで使用できるように、リリースのためにいくつかのデフォルトツール用のリモート実行ツールも作成しました。これらは [推論エンドポイント](https://huggingface.co/inference-endpoints) を使用して作成されます。
|
||||
|
||||
これらは現在オフになっていますが、リモート実行ツールを自分で設定する方法については、[カスタムツールガイド](./custom_tools) を読むことをお勧めします。
|
||||
|
||||
### What's happening here? What are tools, and what are agents?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Agents
|
||||
|
||||
ここでの「エージェント」とは、大規模な言語モデルのことであり、特定の一連のツールにアクセスできるようにプロンプトを設定しています。
|
||||
|
||||
LLM(大規模言語モデル)は、コードの小さなサンプルを生成するのにかなり優れており、このAPIは、エージェントに特定のツールセットを使用してタスクを実行するコードの小さなサンプルを生成させることに利用しています。このプロンプトは、エージェントにタスクとツールの説明を提供することで、エージェントが使用しているツールのドキュメントにアクセスし、関連するコードを生成できるようになります。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tools
|
||||
|
||||
ツールは非常に単純で、名前と説明からなる単一の関数です。それから、これらのツールの説明を使用してエージェントをプロンプトします。プロンプトを通じて、エージェントに、ツールを使用してクエリで要求されたタスクをどのように実行するかを示します。特に、ツールの期待される入力と出力を示します。
|
||||
|
||||
これは新しいツールを使用しており、パイプラインではなくツールを使用しています。なぜなら、エージェントは非常に原子的なツールでより良いコードを生成するからです。パイプラインはよりリファクタリングされ、しばしば複数のタスクを組み合わせています。ツールは非常に単純なタスクに焦点を当てることを意図しています。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Code-execution?!
|
||||
|
||||
このコードは、ツールとツールと一緒に渡される入力のセットで、当社の小規模なPythonインタープリタで実行されます。すでに提供されたツールとprint関数しか呼び出すことができないため、実行できることはすでに制限されています。Hugging Faceのツールに制限されているため、安全だと考えても問題ありません。
|
||||
|
||||
さらに、属性の検索やインポートは許可しておらず(それらは渡された入力/出力を処理するためには必要ないはずです)、最も明らかな攻撃は問題ありません(エージェントにそれらを出力するようにプロンプトする必要があります)。超安全な側に立ちたい場合は、追加の引数 return_code=True を指定して run() メソッドを実行できます。その場合、エージェントは実行するコードを返すだけで、実行するかどうかはあなた次第です。
|
||||
|
||||
実行は、違法な操作を試みる行またはエージェントが生成したコードに通常のPythonエラーがある場合に停止します。
|
||||
|
||||
### A curated set of tools
|
||||
|
||||
私たちは、このようなエージェントを強化できるツールのセットを特定します。以下は、`transformers`に統合されたツールの更新されたリストです:
|
||||
|
||||
- **ドキュメント質問応答**: 画像形式のドキュメント(PDFなど)が与えられた場合、このドキュメントに関する質問に回答します([Donut](./model_doc/donut))
|
||||
- **テキスト質問応答**: 長いテキストと質問が与えられた場合、テキスト内の質問に回答します([Flan-T5](./model_doc/flan-t5))
|
||||
- **無条件の画像キャプション**: 画像にキャプションを付けます!([BLIP](./model_doc/blip))
|
||||
- **画像質問応答**: 画像が与えられた場合、その画像に関する質問に回答します([VILT](./model_doc/vilt))
|
||||
- **画像セグメンテーション**: 画像とプロンプトが与えられた場合、そのプロンプトのセグメンテーションマスクを出力します([CLIPSeg](./model_doc/clipseg))
|
||||
- **音声からテキストへの変換**: 人の話し声のオーディオ録音が与えられた場合、その音声をテキストに転記します([Whisper](./model_doc/whisper))
|
||||
- **テキストから音声への変換**: テキストを音声に変換します([SpeechT5](./model_doc/speecht5))
|
||||
- **ゼロショットテキスト分類**: テキストとラベルのリストが与えられた場合、テキストが最も対応するラベルを識別します([BART](./model_doc/bart))
|
||||
- **テキスト要約**: 長いテキストを1つまたは数文に要約します([BART](./model_doc/bart))
|
||||
- **翻訳**: テキストを指定された言語に翻訳します([NLLB](./model_doc/nllb))
|
||||
|
||||
これらのツールはtransformersに統合されており、手動でも使用できます。たとえば、次のように使用できます:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = load_tool("text-to-speech")
|
||||
audio = tool("This is a text to speech tool")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom tools
|
||||
|
||||
私たちは、厳選されたツールのセットを特定する一方、この実装が提供する主要な価値は、カスタムツールを迅速に作成して共有できる能力だと強く信じています。
|
||||
|
||||
ツールのコードをHugging Face Spaceまたはモデルリポジトリにプッシュすることで、エージェントと直接連携してツールを活用できます。[`huggingface-tools` organization](https://huggingface.co/huggingface-tools)には、**transformers非依存**のいくつかのツールが追加されました:
|
||||
|
||||
- **テキストダウンローダー**: ウェブURLからテキストをダウンロードするためのツール
|
||||
- **テキストから画像へ**: プロンプトに従って画像を生成するためのツール。安定した拡散を活用します
|
||||
- **画像変換**: 初期画像とプロンプトを指定して画像を変更するためのツール。instruct pix2pixの安定した拡散を活用します
|
||||
- **テキストからビデオへ**: プロンプトに従って小さなビデオを生成するためのツール。damo-vilabを活用します
|
||||
|
||||
最初から使用しているテキストから画像へのツールは、[*huggingface-tools/text-to-image*](https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface-tools/text-to-image)にあるリモートツールです!今後も、この組織および他の組織にさらにこのようなツールをリリースし、この実装をさらに強化していきます。
|
||||
|
||||
エージェントはデフォルトで[`huggingface-tools`](https://huggingface.co/huggingface-tools)にあるツールにアクセスできます。
|
||||
ツールの作成と共有方法、またHubに存在するカスタムツールを活用する方法についての詳細は、[次のガイド](custom_tools)で説明しています。
|
||||
|
||||
### Code generation
|
||||
|
||||
これまで、エージェントを使用してあなたのためにアクションを実行する方法を示しました。ただし、エージェントはコードを生成するだけで、非常に制限されたPythonインタープリタを使用して実行します。生成されたコードを異なる環境で使用したい場合、エージェントにコードを返すように指示できます。ツールの定義と正確なインポートも含めて。
|
||||
|
||||
例えば、以下の命令:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
次のコードを返します
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
image_generator = load_tool("huggingface-tools/text-to-image")
|
||||
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt="rivers and lakes")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
その後、自分で変更して実行できます。
|
||||
@ -23,8 +23,6 @@
|
||||
title: 🤗 PEFT로 어댑터 로드 및 학습하기
|
||||
- local: model_sharing
|
||||
title: 만든 모델 공유하기
|
||||
- local: transformers_agents
|
||||
title: 에이전트
|
||||
- local: llm_tutorial
|
||||
title: 대규모 언어 모델로 생성하기
|
||||
- local: conversations
|
||||
@ -248,8 +246,6 @@
|
||||
title: (번역중) 개념 가이드
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: main_classes/agent
|
||||
title: 에이전트와 도구
|
||||
- local: model_doc/auto
|
||||
title: 자동 클래스
|
||||
- local: in_translation
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,134 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# 에이전트 & 도구 [[agents-tools]]
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers Agent는 실험 중인 API이므로 언제든지 변경될 수 있습니다.
|
||||
API나 기반 모델이 자주 업데이트되므로, 에이전트가 제공하는 결과물은 달라질 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
에이전트와 도구에 대해 더 알아보려면 [소개 가이드](../transformers_agents)를 꼭 읽어보세요.
|
||||
이 페이지에는 기본 클래스에 대한 API 문서가 포함되어 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
## 에이전트 [[agents]]
|
||||
|
||||
우리는 기본 [`Agent`] 클래스를 기반으로 두 가지 유형의 에이전트를 제공합니다:
|
||||
- [`CodeAgent`]는 한 번에 동작합니다. 작업을 해결하기 위해 코드를 생성한 다음, 바로 실행합니다.
|
||||
- [`ReactAgent`]는 단계별로 동작하며, 각 단계는 하나의 생각, 하나의 도구 호출 및 실행으로 구성됩니다. 이 에이전트에는 두 가지 클래스가 있습니다:
|
||||
- [`ReactJsonAgent`]는 도구 호출을 JSON으로 작성합니다.
|
||||
- [`ReactCodeAgent`]는 도구 호출을 Python 코드로 작성합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
### Agent [[agent]]
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Agent
|
||||
|
||||
### CodeAgent [[codeagent]]
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### React agents [[react-agents]]
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ReactAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ReactJsonAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
## Tools [[tools]]
|
||||
|
||||
### load_tool [[loadtool]]
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
### Tool [[tool]]
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Tool
|
||||
|
||||
### Toolbox [[toolbox]]
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Toolbox
|
||||
|
||||
### PipelineTool [[pipelinetool]]
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PipelineTool
|
||||
|
||||
### launch_gradio_demo [[launchgradiodemo]]
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] launch_gradio_demo
|
||||
|
||||
### ToolCollection [[toolcollection]]
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ToolCollection
|
||||
|
||||
## 엔진 [[engines]]
|
||||
|
||||
에이전트 프레임워크에서 사용할 수 있는 엔진을 자유롭게 만들고 사용할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
이 엔진들은 다음과 같은 사양을 가지고 있습니다:
|
||||
1. 입력(`List[Dict[str, str]]`)에 대한 [메시지 형식](../chat_templating.md)을 따르고 문자열을 반환해야 합니다.
|
||||
2. 인수 `stop_sequences`에 시퀀스가 전달되기 *전에* 출력을 생성하는 것을 중지해야 합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
### HfApiEngine [[HfApiEngine]]
|
||||
|
||||
편의를 위해, 위의 사항을 구현하고 대규모 언어 모델 실행을 위해 추론 엔드포인트를 사용하는 `HfApiEngine`을 추가했습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import HfApiEngine
|
||||
|
||||
>>> messages = [
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "Hello, how are you?"},
|
||||
... {"role": "assistant", "content": "I'm doing great. How can I help you today?"},
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "No need to help, take it easy."},
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> HfApiEngine()(messages, stop_sequences=["conversation"])
|
||||
|
||||
"That's very kind of you to say! It's always nice to have a relaxed "
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HfApiEngine
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 에이전트 유형 [[agent-types]]
|
||||
|
||||
에이전트는 도구 간의 모든 유형의 객체를 처리할 수 있습니다; 도구는 완전히 멀티모달이므로 텍스트, 이미지, 오디오, 비디오 등 다양한 유형을 수락하고 반환할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
도구 간의 호환성을 높이고 ipython (jupyter, colab, ipython 노트북, ...)에서 이러한
|
||||
반환 값을 올바르게 렌더링하기 위해 이러한 유형을 중심으로 래퍼 클래스를
|
||||
구현합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
래핑된 객체는 처음과 동일하게 작동해야 합니다; 텍스트 객체는 여전히 문자열로 작동해야 하며,
|
||||
이미지 객체는 여전히 `PIL.Image`로 작동해야 합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
이러한 유형에는 세 가지 특정 목적이 있습니다:
|
||||
|
||||
- `to_raw`를 호출하면 기본 객체가 반환되어야 합니다.
|
||||
- `to_string`을 호출하면 객체가 문자열로 반환되어야 합니다:
|
||||
`AgentText`의 경우 문자열이 될 수 있지만, 다른 경우에는 객체의 직렬화된 버전의 경로일 수 있습니다.
|
||||
- ipython 커널에서 표시할 때 객체가 올바르게 표시되어야 합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
### AgentText [[agenttext]]
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.agents.agent_types.AgentText
|
||||
|
||||
### AgentImage [[agentimage]]
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.agents.agent_types.AgentImage
|
||||
|
||||
### AgentAudio [[agentaudio]]
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.agents.agent_types.AgentAudio
|
||||
@ -549,29 +549,7 @@ use_cpu: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Tensor Parallelism with PyTorch 2">
|
||||
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
tp_config:
|
||||
tp_size: 4
|
||||
distributed_type: TP
|
||||
downcast_bf16: 'no'
|
||||
machine_rank: 0
|
||||
main_training_function: main
|
||||
mixed_precision: 'no'
|
||||
num_machines: 1
|
||||
num_processes: 4
|
||||
rdzv_backend: static
|
||||
same_network: true
|
||||
tpu_env: []
|
||||
tpu_use_cluster: false
|
||||
tpu_use_sudo: false
|
||||
use_cpu: false
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
[`accelerate_launch`](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/package_reference/cli#accelerate-launch) 명령은 Accelerate와 [`Trainer`]를 사용하여 분산 시스템에서 훈련 스크립트를 실행하는 권장 방법이며, `config_file.yaml`에 지정된 매개변수를 사용합니다. 이 파일은 Accelerate 캐시 폴더에 저장되며 `accelerate_launch`를 실행할 때 자동으로 로드됩니다.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,328 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Transformers Agent [[transformers-agent]]
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers Agent는 실험 중인 API로 언제든지 변경될 수 있습니다.
|
||||
API 또는 기반 모델이 변경되기 쉽기 때문에 에이전트가 반환하는 결과도 달라질 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers 버전 4.29.0.에서 *도구*와 *에이전트*라는 컨셉을 도입했습니다. [이 colab](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1c7MHD-T1forUPGcC_jlwsIptOzpG3hSj)에서 사용해볼 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
간단히 말하면, Agent는 트랜스포머 위에 자연어 API를 제공합니다.
|
||||
엄선된 도구 세트를 정의하고, 자연어를 해석하여 이러한 도구를 사용할 수 있는 에이전트를 설계했습니다.
|
||||
이 API는 확장이 가능하도록 설계 되었습니다.
|
||||
주요 도구를 선별해두었지만, 커뮤니티에서 개발한 모든 도구를 사용할 수 있도록 시스템을 쉽게 확장할 수 있는 방법도 보여드리겠습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
몇 가지 예를 통해 새로운 API로 무엇을 할 수 있는지 살펴보겠습니다.
|
||||
이 API는 특히 멀티모달 작업에서 강력하므로 이미지를 생성하고 텍스트를 소리내어 읽어보겠습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Caption the following image", image=image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| **Input** | **Output** |
|
||||
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------|
|
||||
| <img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/beaver.png" width=200> | A beaver is swimming in the water |
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Read the following text out loud", text=text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
| **Input** | **Output** |
|
||||
|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| A beaver is swimming in the water | <audio controls><source src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/tts_example.wav" type="audio/wav"> your browser does not support the audio element. </audio>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"In the following `document`, where will the TRRF Scientific Advisory Council Meeting take place?",
|
||||
document=document,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
| **Input** | **Output** |
|
||||
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------|
|
||||
| <img src="https://datasets-server.huggingface.co/assets/hf-internal-testing/example-documents/--/hf-internal-testing--example-documents/test/0/image/image.jpg" width=200> | ballroom foyer |
|
||||
|
||||
## 바로 시작하기 [[quickstart]]
|
||||
|
||||
`agent.run`을 사용하려면 먼저 대규모 언어 모델(LLM)인 에이전트를 인스턴스화해야 합니다.
|
||||
저희는 openAI 모델뿐만 아니라 BigCode 및 OpenAssistant의 오픈소스 대체 모델도 지원합니다.
|
||||
openAI 모델의 성능이 더 우수하지만(단, openAI API 키가 필요하므로 무료로 사용할 수 없음),
|
||||
Hugging Face는 BigCode와 OpenAssistant 모델의 엔드포인트에 대한 무료 액세스를 제공하고 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
우선 모든 기본 종속성을 설치하려면 `agents`를 추가로 설치하세요.
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers[agents]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
openAI 모델을 사용하려면 `openai` 종속성을 설치한 후 [`OpenAiAgent`]를 인스턴스화합니다:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install openai
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import OpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = OpenAiAgent(model="text-davinci-003", api_key="<your_api_key>")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
BigCode 또는 OpenAssistant를 사용하려면 먼저 로그인하여 Inference API에 액세스하세요:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import login
|
||||
|
||||
login("<YOUR_TOKEN>")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
그런 다음 에이전트를 인스턴스화합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
# Starcoder
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder")
|
||||
# StarcoderBase
|
||||
# agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoderbase")
|
||||
# OpenAssistant
|
||||
# agent = HfAgent(url_endpoint="https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/OpenAssistant/oasst-sft-4-pythia-12b-epoch-3.5")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
현재 Hugging Face에서 무료로 제공하는 추론 API를 사용하고 있습니다.
|
||||
이 모델에 대한 자체 추론 엔드포인트가 있는 경우(또는 다른 엔드포인트가 있는 경우) 위의 URL을 해당 URL 엔드포인트로 바꿀 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
StarCoder와 OpenAssistant는 무료로 사용할 수 있으며 간단한 작업에서 놀라울 정도로 잘 작동합니다.
|
||||
그러나 더 복잡한 프롬프트를 처리할 때는 체크포인트가 잘 작동하지 않습니다.
|
||||
이러한 문제가 발생하면 OpenAI 모델을 사용해 보시기 바랍니다. 아쉽게도 오픈소스는 아니지만 현재로서는 더 나은 성능을 제공합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
이제 준비가 완료되었습니다! 이제 자유롭게 사용할 수 있는 두 가지 API에 대해 자세히 알아보겠습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
### 단일 실행 (run) [[single-execution-(run)]]
|
||||
|
||||
단일 실행 방법은 에이전트의 [`~Agent.run`] 메소드를 사용하는 경우입니다:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes.")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
수행하려는 작업에 적합한 도구를 자동으로 선택하여 적절하게 실행합니다.
|
||||
동일한 명령어에서 하나 또는 여러 개의 작업을 수행할 수 있습니다
|
||||
(다만, 명령어가 복잡할수록 에이전트가 실패할 가능성이 높아집니다).
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of the sea then transform the picture to add an island")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/sea_and_island.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
<br/>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
모든 [`~Agent.run`] 작업은 독립적이므로 다른 작업으로 여러 번 연속해서 실행할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
`agent`는 큰 언어 모델일 뿐이므로 프롬프트에 약간의 변화를 주면 완전히 다른 결과가 나올 수 있다는 점에 유의하세요.
|
||||
수행하려는 작업을 최대한 명확하게 설명하는 것이 중요합니다.
|
||||
좋은 프롬프트를 작성하는 방법은 [여기](custom_tools#writing-good-user-inputs)에서 자세히 확인할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
여러 실행에 걸쳐 상태를 유지하거나 텍스트가 아닌 개체를 에이전트에게 전달하려는 경우에는 에이전트가 사용할 변수를 지정할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
예를 들어 강과 호수의 첫 번째 이미지를 생성한 뒤,
|
||||
모델이 해당 그림에 섬을 추가하도록 다음과 같이 요청할 수 있습니다:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
picture = agent.run("Generate a picture of rivers and lakes.")
|
||||
updated_picture = agent.run("Transform the image in `picture` to add an island to it.", picture=picture)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
이 방법은 모델이 요청을 이해하지 못하고 도구를 혼합할 때 유용할 수 있습니다. 예를 들면 다음과 같습니다:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me the picture of a capybara swimming in the sea")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
여기서 모델은 두 가지 방식으로 해석할 수 있습니다:
|
||||
- `text-to-image`이 바다에서 헤엄치는 카피바라를 생성하도록 합니다.
|
||||
- 또는 `text-to-image`이 카피바라를 생성한 다음 `image-transformation` 도구를 사용하여 바다에서 헤엄치도록 합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
첫 번째 시나리오를 강제로 실행하려면 프롬프트를 인수로 전달하여 실행할 수 있습니다:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of the `prompt`", prompt="a capybara swimming in the sea")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 대화 기반 실행 (chat) [[chat-based-execution-(chat)]]
|
||||
|
||||
에이전트는 [`~Agent.chat`] 메소드를 사용하는 대화 기반 접근 방식도 있습니다:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.chat("Generate a picture of rivers and lakes")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.chat("Transform the picture so that there is a rock in there")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes_and_beaver.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
<br/>
|
||||
|
||||
이 방식은 여러 명령어에 걸쳐 상태를 유지하고자 할 때 흥미로운 접근 방식입니다.
|
||||
실험용으로 더 좋지만 복잡한 명령어보다는
|
||||
단일 명령어([`~Agent.run`] 메소드가 더 잘 처리하는 명령어)에 훨씬 더 잘 작동하는 경향이 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
이 메소드는 텍스트가 아닌 유형이나 특정 프롬프트를 전달하려는 경우 인수를 받을 수도 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
### ⚠️ 원격 실행 [[remote-execution]]
|
||||
|
||||
데모 목적과 모든 설정에서 사용할 수 있도록
|
||||
에이전트가 접근할 수 있는 몇 가지 기본 도구에 대한 원격 실행기를 만들었습니다.
|
||||
이러한 도구는 [inference endpoints](https://huggingface.co/inference-endpoints)를 사용하여 만들어졌습니다.
|
||||
원격 실행기 도구를 직접 설정하는 방법을 보려면 [사용자 정의 도구 가이드](./custom_tools)를 읽어보시기 바랍니다.
|
||||
|
||||
원격 도구로 실행하려면 [`~Agent.run`] 또는 [`~Agent.chat`] 중 하나에 `remote=True`를 지정하기만 하면 됩니다.
|
||||
|
||||
예를 들어 다음 명령은 많은 RAM이나 GPU 없이도 모든 장치에서 효율적으로 실행할 수 있습니다:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes", remote=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[`~Agent.chat`]도 마찬가지입니다:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.chat("Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes", remote=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 여기서 무슨 일이 일어나는 거죠? 도구란 무엇이고, 에이전트란 무엇인가요? [[whats-happening-here-what-are-tools-and-what-are-agents]]
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/diagram.png">
|
||||
|
||||
#### 에이전트 [[agents]]
|
||||
|
||||
여기서 "에이전트"는 대규모 언어 모델이며, 특정 도구 모음에 접근할 수 있도록 프롬프트하고 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
LLM은 작은 코드 샘플을 생성하는 데 상당히 능숙하므로,
|
||||
이 장점을 활용해 도구 모음을 사용하여 작업을 수행하는 작은 코드 샘플을 제공하라는 메시지를 표시합니다.
|
||||
그런 다음 에이전트에게 제공하는 작업과 제공하는 도구에 대한 설명으로 이 프롬프트가 완료됩니다.
|
||||
이렇게 하면 사용 중인 도구들의 문서에 접근할 수 있으며, 해당 도구들의 입력과 출력을 예상하고, 관련된 코드를 생성할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 도구 [[tools]]
|
||||
|
||||
도구는 매우 간단합니다. 이름과 설명이 있는 단일 기능으로 구성되어 있습니다.
|
||||
그런 다음 이러한 도구의 설명을 사용하여 상담원에게 프롬프트를 표시합니다.
|
||||
이 프롬프트를 통해 상담원에게 쿼리에서 요청된 작업을 수행하기 위해 도구를 활용하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
|
||||
|
||||
에이전트가 매우 원자적인 도구를 사용하여 더 나은 코드를 작성하기 때문에 파이프라인이 아닌 완전히 새로운 도구를 사용합니다.
|
||||
파이프라인은 더 많이 리팩터링되며 종종 여러 작업을 하나로 결합합니다.
|
||||
도구는 하나의 매우 간단한 작업에만 집중하도록 되어 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 코드 실행?! [[code-execution]]
|
||||
|
||||
그런 다음 이 코드는 도구와 함께 전달된 입력 세트에 대해 작은 Python 인터프리터를 사용하여 실행됩니다.
|
||||
"임의 코드 실행이라니!"이라고 비명을 지르는 소리가 들리겠지만, 그렇지 않은 이유를 설명하겠습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
호출할 수 있는 함수는 제공한 도구와 인쇄 기능뿐이므로 이미 실행할 수 있는 기능이 제한되어 있습니다.
|
||||
Hugging Face 도구로 제한되어 있다면 안전할 것입니다.
|
||||
|
||||
그리고 어트리뷰트 조회나 가져오기를 허용하지 않으므로
|
||||
(어차피 작은 함수 집합에 입/출력을 전달할 때는 필요하지 않아야 합니다)
|
||||
가장 명백한 공격(어차피 LLM에 출력하라는 메시지를 표시해야 합니다)은 문제가 되지 않습니다.
|
||||
매우 안전하게 하고 싶다면 추가 인수 return_code=True를 사용하여 run() 메소드를 실행하면 됩니다.
|
||||
이 경우 에이전트가 실행할 코드를 반환하고 실행할지 여부를 결정할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
불법적인 연산을 수행하려고 하거나 에이전트가 생성한 코드에 일반적인 파이썬 오류가 있는 경우
|
||||
실행이 중지됩니다.
|
||||
|
||||
### 엄선된 도구 모음 [[a-curated-set-of-tools]]
|
||||
|
||||
저희는 이러한 에이전트들의 역량을 강화할 수 있는 일련의 도구를 확인하고 있습니다.
|
||||
다음은 연동된 도구의 최신 목록입니다:
|
||||
|
||||
- **문서 질문 답변**: 이미지 형식의 문서(예: PDF)가 주어지면 이 문서에 대한 질문에 답변합니다. ([Donut](./model_doc/donut))
|
||||
- **텍스트 질문 답변**: 긴 텍스트와 질문이 주어지면 텍스트에서 질문에 답변합니다. ([Flan-T5](./model_doc/flan-t5))
|
||||
- **무조건 이미지 캡셔닝**: 이미지에 캡션을 답니다! ([BLIP](./model_doc/blip))
|
||||
- **이미지 질문 답변**: 이미지가 주어지면 이 이미지에 대한 질문에 답변하기. ([VILT](./model_doc/vilt))
|
||||
- **이미지 분할**: 이미지와 프롬프트가 주어지면 해당 프롬프트의 분할 마스크를 출력합니다. ([CLIPSeg](./model_doc/clipseg))
|
||||
- **음성을 텍스트로 변환**: 사람이 말하는 오디오 녹음이 주어지면 음성을 텍스트로 변환합니다. ([Whisper](./model_doc/whisper))
|
||||
- **텍스트 음성 변환**: 텍스트를 음성으로 변환합니다. ([SpeechT5](./model_doc/speecht5))
|
||||
- **제로 샷(zero-shot) 텍스트 분류**: 텍스트와 레이블 목록이 주어지면 텍스트와 가장 관련 있는 레이블을 식별합니다. ([BART](./model_doc/bart))
|
||||
- **텍스트 요약**: 긴 텍스트를 한 문장 또는 몇 문장으로 요약합니다. ([BART](./model_doc/bart))
|
||||
- **번역**: 텍스트를 지정된 언어로 번역합니다. ([NLLB](./model_doc/nllb))
|
||||
|
||||
이러한 도구는 트랜스포머에 통합되어 있으며, 예를 들어 수동으로도 사용할 수 있습니다:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = load_tool("text-to-speech")
|
||||
audio = tool("This is a text to speech tool")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 사용자 정의 도구 [[custom-tools]]
|
||||
|
||||
엄선된 도구 세트도 있지만, 이 구현이 제공하는 가장 큰 가치는 사용자 지정 도구를 빠르게 만들고 공유할 수 있다는 점입니다.
|
||||
|
||||
도구의 코드를 Hugging Face Space나 모델 저장소에 푸시하면 에이전트에게 직접 도구를 활용할 수 있습니다. [`huggingface-tools` organization](https://huggingface.co/huggingface-tools)에 몇 가지 **트랜스포머에 구애받지 않는** 툴을 추가했습니다:
|
||||
|
||||
- **텍스트 다운로더**: 웹 URL에서 텍스트를 다운로드합니다.
|
||||
- **텍스트 이미지 변환**: 프롬프트에 따라 이미지를 생성하여 안정적인 확산을 활용합니다.
|
||||
- **이미지 변환**: 초기 이미지와 프롬프트가 주어진 이미지를 수정하고, 안정적인 확산을 활용하는 지시 픽셀 2 픽셀을 활용합니다.
|
||||
- **텍스트 비디오 변환**: 프롬프트에 따라 작은 비디오를 생성하며, damo-vilab을 활용합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
저희가 처음부터 사용하고 있는 텍스트-이미지 변환 도구는 [*huggingface-tools/text-to-image*](https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface-tools/text-to-image)에 있는 원격 도구입니다! 저희는 이 도구와 다른 조직에 이러한 도구를 계속 출시하여 이 구현을 더욱 강화할 것입니다.
|
||||
|
||||
에이전트는 기본적으로 [`huggingface-tools`](https://huggingface.co/huggingface-tools)에 있는 도구에 접근할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
[다음 가이드](custom_tools)에서 도구를 작성하고 공유하는 방법과 Hub에 있는 사용자 지정 도구를 활용하는 방법에 대해 설명합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
### 코드 생성[[code-generation]]
|
||||
|
||||
지금까지 에이전트를 사용하여 작업을 수행하는 방법을 보여드렸습니다. 하지만 에이전트는 매우 제한된 Python 인터프리터를 사용하여 실행할 코드만 생성하고 있습니다. 다른 설정에서 생성된 코드를 사용하려는 경우 에이전트에게 도구 정의 및 정확한 가져오기와 함께 코드를 반환하라는 메시지를 표시할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
예를 들어 다음 명령어는
|
||||
```python
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
다음 코드를 반환합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
image_generator = load_tool("huggingface-tools/text-to-image")
|
||||
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt="rivers and lakes")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
이 코드는 직접 수정하고 실행할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
@ -21,8 +21,6 @@
|
||||
title: Sediakan latihan yang diedarkan dengan 🤗 Accelerate
|
||||
- local: model_sharing
|
||||
title: Kongsi model anda
|
||||
- local: transformers_agents
|
||||
title: Ejen
|
||||
title: Tutorials
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
@ -179,8 +177,6 @@
|
||||
title: Panduan konsep
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: main_classes/agent
|
||||
title: Ejen dan Alat
|
||||
- local: model_doc/auto
|
||||
title: Kelas Auto
|
||||
- local: main_classes/callback
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,10 +23,6 @@
|
||||
title: 使用🤗 PEFT加载和训练adapters
|
||||
- local: model_sharing
|
||||
title: 分享您的模型
|
||||
- local: agents
|
||||
title: 智能体和工具
|
||||
- local: agents_advanced
|
||||
title: 智能体,超强版 - 多智能体、外部工具等
|
||||
- local: llm_tutorial
|
||||
title: 使用LLMs进行生成
|
||||
title: 教程
|
||||
@ -105,8 +101,6 @@
|
||||
title: 概念指南
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: main_classes/agent
|
||||
title: 智能体和工具
|
||||
- local: main_classes/callback
|
||||
title: Callbacks
|
||||
- local: main_classes/configuration
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,427 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
# 智能体和工具
|
||||
|
||||
[[在colab里打开]]
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是智能体 (Agent)?
|
||||
|
||||
大型语言模型(LLM)经过 [因果语言建模训练](./tasks/language_modeling) 可以应对各种任务,但在一些基本任务(如逻辑推理、计算和搜索)上常常表现不佳。当它们被用在自己不擅长的领域时,往往无法生成我们期望的答案。
|
||||
|
||||
为了解决这个问题,可以创建**智能体**.
|
||||
|
||||
智能体是一个系统,它使用 LLM 作为引擎,并且能够访问称为**工具**的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
这些**工具**是执行任务的函数,包含所有必要的描述信息,帮助智能体正确使用它们。
|
||||
|
||||
智能体可以被编程为:
|
||||
- 一次性设计一系列工具并同时执行它们,像 [`CodeAgent`]
|
||||
- 一次执行一个工具,并等待每个工具的结果后再启动下一个,像 [`ReactJsonAgent`]
|
||||
|
||||
### 智能体类型
|
||||
|
||||
#### 代码智能体
|
||||
|
||||
此智能体包含一个规划步骤,然后生成 Python 代码一次性执行所有任务。它原生支持处理不同输入和输出类型,因此推荐用于多模态任务。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 推理智能体
|
||||
|
||||
这是解决推理任务的首选代理,因为 ReAct 框架 ([Yao et al., 2022](https://huggingface.co/papers/2210.03629)) 使其在基于之前观察进行推理时非常高效。
|
||||
|
||||
我们实现了两种版本的 ReactJsonAgent:
|
||||
- [`ReactJsonAgent`] 将工具调用作为 JSON 格式输出。
|
||||
- [`ReactCodeAgent`] 是 ReactJsonAgent 的一种新型,生成工具调用的代码块,对于具备强大编程能力的 LLM 非常适用。
|
||||
|
||||
> [TIP]
|
||||
> 阅读 [Open-source LLMs as LangChain Agents](https://huggingface.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents) 博文,了解更多关于推理智能体的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
class="block dark:hidden"
|
||||
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/Agent_ManimCE.gif"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
<img
|
||||
class="hidden dark:block"
|
||||
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/Agent_ManimCE.gif"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
以下是一个推理代码智能体如何处理以下问题的示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```py3
|
||||
>>> agent.run(
|
||||
... "How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?",
|
||||
... )
|
||||
=====New task=====
|
||||
How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?
|
||||
====Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
bert_blocks = search(query="number of blocks in BERT base encoder")
|
||||
print("BERT blocks:", bert_blocks)
|
||||
====
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
BERT blocks: twelve encoder blocks
|
||||
|
||||
====Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
attention_layer = search(query="number of layers in Attention is All You Need")
|
||||
print("Attention layers:", attention_layer)
|
||||
====
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
Attention layers: Encoder: The encoder is composed of a stack of N = 6 identical layers. Each layer has two sub-layers. The first is a multi-head self-attention mechanism, and the second is a simple, position- 2 Page 3 Figure 1: The Transformer - model architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
====Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
bert_blocks = 12
|
||||
attention_layers = 6
|
||||
diff = bert_blocks - attention_layers
|
||||
print("Difference in blocks:", diff)
|
||||
final_answer(diff)
|
||||
====
|
||||
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
Difference in blocks: 6
|
||||
|
||||
Final answer: 6
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何构建智能体?
|
||||
|
||||
要初始化一个智能体,您需要以下参数:
|
||||
|
||||
- **一个 LLM** 来驱动智能体——智能体本身并不是 LLM,而是一个使用 LLM 作为引擎的程序。
|
||||
- **一个系统提示**:告诉 LLM 引擎应该如何生成输出。
|
||||
- **一个工具箱**,智能体可以从中选择工具执行。
|
||||
- **一个解析器**,从 LLM 输出中提取出哪些工具需要调用,以及使用哪些参数。
|
||||
|
||||
在智能体系统初始化时,工具属性将生成工具描述,并嵌入到智能体的系统提示中,告知智能体可以使用哪些工具,并且为什么使用它们。
|
||||
|
||||
**安装依赖**
|
||||
|
||||
首先,您需要安装**智能体**所需的额外依赖:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers[agents]
|
||||
```
|
||||
**创建LLM引擎**
|
||||
|
||||
定义一个 `llm_engine` 方法,该方法接受一系列[消息](./chat_templating)并返回文本。该 `callable` 还需要接受一个 `stop` 参数,用于指示何时停止生成输出。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import login, InferenceClient
|
||||
|
||||
login("<YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>")
|
||||
|
||||
client = InferenceClient(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
|
||||
def llm_engine(messages, stop_sequences=["Task"]) -> str:
|
||||
response = client.chat_completion(messages, stop=stop_sequences, max_tokens=1000)
|
||||
answer = response.choices[0].message.content
|
||||
return answer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您可以使用任何符合以下要求的 `llm_engine` 方法:
|
||||
1. [输入格式](./chat_templating)为 (`List[Dict[str, str]]`),并且返回一个字符串。
|
||||
2. 它在 `stop_sequences` 参数传递的序列处停止生成输出。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,`llm_engine` 还可以接受一个 `grammar` 参数。如果在智能体初始化时指定了 `grammar`,则该参数将传递给 `llm_engine` 的调用,以允许[受限生成](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/conceptual/guidance),以强制生成格式正确的智能体输出。
|
||||
|
||||
您还需要一个 `tools` 参数,它接受一个 `Tools` 列表 —— 可以是空列表。您也可以通过定义可选参数 `add_base_tools=True` 来将默认工具箱添加到工具列表中。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,您可以创建一个智能体,例如 [`CodeAgent`],并运行它。您还可以创建一个 [`TransformersEngine`],使用 `transformers` 在本地机器上运行预初始化的推理管道。 为了方便起见,由于智能体行为通常需要更强大的模型,例如 `Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct`,它们目前较难在本地运行,我们还提供了 [`HfApiEngine`] 类,它在底层初始化了一个 `huggingface_hub.InferenceClient`。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent, HfApiEngine
|
||||
|
||||
llm_engine = HfApiEngine(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Could you translate this sentence from French, say it out loud and return the audio.",
|
||||
sentence="Où est la boulangerie la plus proche?",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
当你急需某个东西时这将会很有用!
|
||||
您甚至可以将 `llm_engine` 参数留空,默认情况下会创建一个 [`HfApiEngine`]。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Could you translate this sentence from French, say it out loud and give me the audio.",
|
||||
sentence="Où est la boulangerie la plus proche?",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,我们使用了额外的 `sentence` 参数:您可以将文本作为附加参数传递给模型。
|
||||
|
||||
您还可以使用这个来指定本地或远程文件的路径供模型使用:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Why does Mike not know many people in New York?", audio="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/recording.mp3")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
系统提示和输出解析器会自动定义,但您可以通过调用智能体的 `system_prompt_template` 来轻松查看它们。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
print(agent.system_prompt_template)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
尽可能清楚地解释您要执行的任务非常重要。 每次 [`~Agent.run`] 操作都是独立的,并且由于智能体是由 LLM 驱动的,提示中的细微变化可能会导致完全不同的结果。
|
||||
您还可以连续运行多个任务,每次都会重新初始化智能体的 `agent.task` 和 `agent.logs` 属性。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 代码执行
|
||||
|
||||
Python 解释器在一组输入和工具上执行代码。 这应该是安全的,因为只能调用您提供的工具(特别是 Hugging Face 的工具)和 print 函数,因此您已经限制了可以执行的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
Python 解释器默认不允许导入不在安全列表中的模块,因此大多数明显的攻击问题应该不成问题。 您仍然可以通过在 [`ReactCodeAgent`] 或 [`CodeAgent`] 初始化时通过 `additional_authorized_imports` 参数传递一个授权的模块列表来授权额外的导入:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
>>> agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[], additional_authorized_imports=['requests', 'bs4'])
|
||||
>>> agent.run("Could you get me the title of the page at url 'https://huggingface.co/blog'?")
|
||||
|
||||
(...)
|
||||
'Hugging Face – Blog'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果有任何代码尝试执行非法操作,或者生成的代码出现常规 Python 错误,执行将停止。
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> 在使用大语言模型(LLM)生成代码时,生成的代码会被执行,避免导入或使用任何不安全的库或模块。
|
||||
|
||||
### 系统提示
|
||||
|
||||
智能体,或者说驱动智能体的 LLM,根据系统提示生成输出。系统提示可以定制并根据目标任务进行调整。例如,检查 [`ReactCodeAgent`] 的系统提示(以下版本经过简化)。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
You will be given a task to solve as best you can.
|
||||
You have access to the following tools:
|
||||
<<tool_descriptions>>
|
||||
|
||||
To solve the task, you must plan forward to proceed in a series of steps, in a cycle of 'Thought:', 'Code:', and 'Observation:' sequences.
|
||||
|
||||
At each step, in the 'Thought:' sequence, you should first explain your reasoning towards solving the task, then the tools that you want to use.
|
||||
Then in the 'Code:' sequence, you should write the code in simple Python. The code sequence must end with '/End code' sequence.
|
||||
During each intermediate step, you can use 'print()' to save whatever important information you will then need.
|
||||
These print outputs will then be available in the 'Observation:' field, for using this information as input for the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
In the end you have to return a final answer using the `final_answer` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few examples using notional tools:
|
||||
---
|
||||
{examples}
|
||||
|
||||
Above example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. You only have access to those tools:
|
||||
<<tool_names>>
|
||||
You also can perform computations in the python code you generate.
|
||||
|
||||
Always provide a 'Thought:' and a 'Code:\n```py' sequence ending with '```<end_code>' sequence. You MUST provide at least the 'Code:' sequence to move forward.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to not perform too many operations in a single code block! You should split the task into intermediate code blocks.
|
||||
Print results at the end of each step to save the intermediate results. Then use final_answer() to return the final result.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to make sure that variables you use are all defined.
|
||||
|
||||
Now Begin!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
系统提示包括:
|
||||
- 解释智能体应该如何工作以及工具的**介绍**。
|
||||
- 所有工具的描述由 `<<tool_descriptions>>` 标记在运行时动态替换,这样智能体就知道可以使用哪些工具及其用途。
|
||||
- 工具的描述来自工具的属性,`name`、`description`、`inputs` 和 `output_type`,以及一个简单的 `jinja2` 模板,您可以根据需要进行调整。
|
||||
- 期望的输出格式。
|
||||
|
||||
您可以通过向 `system_prompt` 参数传递自定义提示来最大程度地提高灵活性,从而覆盖整个系统提示模板。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import ReactJsonAgent
|
||||
from transformers.agents import PythonInterpreterTool
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactJsonAgent(tools=[PythonInterpreterTool()], system_prompt="{your_custom_prompt}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [WARNING]
|
||||
> 必须在`template`中定义 `<<tool_descriptions>>` 这个变量,以便智能体能够正确地识别并使用可用的工具
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 检查智能体的运行
|
||||
|
||||
以下是检查运行后发生了什么的一些有用属性:
|
||||
- `agent.logs` 存储了智能体的详细日志。每一步的所有内容都会存储在一个字典中,然后附加到 `agent.logs`。
|
||||
- 运行 `agent.write_inner_memory_from_logs()` 会从日志中创建智能体的内存,以便 LLM 查看,作为一系列聊天消息。此方法会遍历日志的每个步骤,只保存其感兴趣的消息:例如,它会单独保存系统提示和任务,然后为每个步骤保存 LLM 输出的消息,以及工具调用输出的消息。如果您想要更高层次的查看发生了什么,可以使用此方法 —— 但并不是每个日志都会被此方法转录。
|
||||
|
||||
## 工具
|
||||
|
||||
工具是智能体使用的基本功能。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,您可以检查 [`PythonInterpreterTool`]:它有一个名称、描述、输入描述、输出类型和 `__call__` 方法来执行该操作。
|
||||
|
||||
当智能体初始化时,工具属性会用来生成工具描述,然后将其嵌入到智能体的系统提示中,这让智能体知道可以使用哪些工具以及为什么使用它们。
|
||||
|
||||
### 默认工具箱
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers 提供了一个默认工具箱,用于增强智能体,您可以在初始化时通过 `add_base_tools=True` 参数将其添加到智能体中:
|
||||
|
||||
- **文档问答**:给定一个文档(如图像格式的 PDF),回答关于该文档的问题([Donut](./model_doc/donut))
|
||||
- **图像问答**:给定一张图片,回答关于该图像的问题([VILT](./model_doc/vilt))
|
||||
- **语音转文本**:给定一个人讲述的音频录音,将其转录为文本(Whisper)
|
||||
- **文本转语音**:将文本转换为语音([SpeechT5](./model_doc/speecht5))
|
||||
- **翻译**:将给定的句子从源语言翻译为目标语言
|
||||
- **DuckDuckGo 搜索**:使用 `DuckDuckGo` 浏览器进行网络搜索
|
||||
- **Python 代码解释器**:在安全环境中运行 LLM 生成的 Python 代码。只有在初始化 [`ReactJsonAgent`] 时将 `add_base_tools=True` 时,代码智能体才会添加此工具,因为基于代码的智能体已经能够原生执行 Python 代码
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
您可以通过调用 [`load_tool`] 函数来手动使用某个工具并执行任务。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = load_tool("text-to-speech")
|
||||
audio = tool("This is a text to speech tool")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建新工具
|
||||
|
||||
您可以为 `Hugging Face` 默认工具无法涵盖的用例创建自己的工具。
|
||||
例如,假设我们要创建一个返回在 `Hugging Face Hub` 上某个任务中下载次数最多的模型的工具。
|
||||
|
||||
您将从以下代码开始:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
task = "text-classification"
|
||||
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
print(model.id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这段代码可以很快转换为工具,只需将其包装成一个函数,并添加 `tool` 装饰器:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import tool
|
||||
|
||||
@tool
|
||||
def model_download_tool(task: str) -> str:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub.
|
||||
It returns the name of the checkpoint.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
task: The task for which
|
||||
"""
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter="text-classification", sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
return model.id
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
该函数需要:
|
||||
- 一个清晰的名称。名称通常描述工具的功能。由于代码返回某个任务中下载次数最多的模型,因此我们将其命名为 `model_download_tool`。
|
||||
- 对输入和输出进行类型提示
|
||||
- 描述,其中包括 "`Args`:" 部分,描述每个参数(这次不需要类型指示,它会从类型提示中获取)。
|
||||
|
||||
所有这些将自动嵌入到智能体的系统提示中,因此请尽量使它们尽可能清晰!
|
||||
|
||||
> [TIP]
|
||||
> 这个定义格式与 apply_chat_template 中使用的工具模式相同,唯一的区别是添加了 tool 装饰器:可以在我们的工具使用 API 中[了解更多](https://huggingface.co/blog/unified-tool-use#passing-tools-to-a-chat-template).
|
||||
|
||||
然后,您可以直接初始化您的智能体:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[model_download_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您将得到以下输出:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
======== New task ========
|
||||
Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?
|
||||
==== Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
most_downloaded_model = model_download_tool(task="text-to-video")
|
||||
print(f"The most downloaded model for the 'text-to-video' task is {most_downloaded_model}.")
|
||||
====
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
`"The most downloaded model for the 'text-to-video' task is ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning."`
|
||||
|
||||
### 管理智能体的工具箱
|
||||
|
||||
如果您已经初始化了一个智能体,但想添加一个新的工具,重新初始化智能体会很麻烦。借助 Transformers,您可以通过添加或替换工具来管理智能体的工具箱。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们将 `model_download_tool` 添加到一个仅初始化了默认工具箱的现有智能体中。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
agent.toolbox.add_tool(model_download_tool)
|
||||
```
|
||||
现在,我们可以同时使用新工具和之前的文本到语音工具:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Can you read out loud the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub and return the audio?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| **Audio** |
|
||||
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| <audio controls><source src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/damo.wav" type="audio/wav"/> |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> [WARNING]
|
||||
> 当向一个已经运行良好的代理添加工具时要小心,因为这可能会导致选择偏向你的工具,或者选择已经定义的工具之外的其他工具。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
使用 agent.toolbox.update_tool() 方法可以替换智能体工具箱中的现有工具。
|
||||
如果您的新工具完全替代了现有工具,这非常有用,因为智能体已经知道如何执行该特定任务。
|
||||
只需确保新工具遵循与替换工具相同的 API,或者调整系统提示模板,以确保所有使用替换工具的示例都得到更新。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用工具集合
|
||||
|
||||
您可以通过使用 ToolCollection 对象来利用工具集合,指定您想要使用的工具集合的 slug。
|
||||
然后将这些工具作为列表传递给智能体进行初始化,并开始使用它们!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ToolCollection, ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
image_tool_collection = ToolCollection(collection_slug="huggingface-tools/diffusion-tools-6630bb19a942c2306a2cdb6f")
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[*image_tool_collection.tools], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Please draw me a picture of rivers and lakes.")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为了加速启动,工具仅在智能体调用时加载。
|
||||
|
||||
这将生成如下图像:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png">
|
||||
@ -1,250 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
# 智能体,超强版 - 多智能体、外部工具等
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是智能体?
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> 如果你是 `transformers.agents` 的新手,请先阅读主文档 [智能体文档 ](./agents).
|
||||
在本页面中,我们将重点介绍 `transformers.agents` 的几种高级用法。
|
||||
|
||||
## 多智能体
|
||||
|
||||
多智能体功能是微软框架 [Autogen](https://huggingface.co/papers/2308.08155) 中引入的。
|
||||
它的意思是让多个智能体一起工作来解决任务,而不是只有一个智能体。
|
||||
经验表明,在大多数基准测试中,这种方法能带来更好的性能。之所以有更好的性能,原因很简单:对于许多任务,通常我们更愿意让多个单独的单元专注于子任务,而不是让一个系统做所有事情。这里,拥有不同工具集和记忆的多个智能体可以实现高效的专业化。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以轻松地用 `transformers.agents` 构建层次化的多智能体系统。
|
||||
|
||||
为此,需要将智能体封装在 [`ManagedAgent`] 对象中。这个对象需要 `agent`、`name` 和 `description` 这几个参数,这些信息会嵌入到管理智能体的系统提示中,帮助它知道如何调用这个管理的智能体,就像我们对工具所做的那样。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一个通过使用我们的 [`DuckDuckGoSearchTool`] 创建一个管理特定网络搜索智能体的示例:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers.agents import ReactCodeAgent, HfApiEngine, DuckDuckGoSearchTool, ManagedAgent
|
||||
|
||||
llm_engine = HfApiEngine()
|
||||
|
||||
web_agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool()], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
|
||||
managed_web_agent = ManagedAgent(
|
||||
agent=web_agent,
|
||||
name="web_search",
|
||||
description="Runs web searches for you. Give it your query as an argument."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
manager_agent = ReactCodeAgent(
|
||||
tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, managed_agents=[managed_web_agent]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
manager_agent.run("Who is the CEO of Hugging Face?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> 如果你想深入了解如何高效地实现多智能体系统,请查看 [how we pushed our multi-agent system to the top of the GAIA leaderboard](https://huggingface.co/blog/beating-gaia).
|
||||
|
||||
## 高级工具使用
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过子类化 Tool 来直接定义工具,并将其共享到 Hub
|
||||
|
||||
让我们再次使用主文档中的工具示例,我们已经实现了一个 `tool` 装饰器。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你需要添加一些变化,比如为工具自定义属性,可以按照更细粒度的方法构建工具:构建一个继承自 [`Tool`] 超类的类。
|
||||
|
||||
自定义工具需要:
|
||||
- `name` 属性:表示工具本身的名称,通常描述工具的作用。由于代码返回了针对任务下载量最多的模型,我们将其命名为 model_download_counter。
|
||||
- `description` 属性:用于填充智能体的系统提示。
|
||||
- `inputs` 属性:这是一个包含 "type" 和 "description" 键的字典。它包含了有助于 Python 解释器做出选择的输入信息。
|
||||
- `output_type` 属性:指定输出类型。
|
||||
- `forward` 方法:其中包含执行推理代码。
|
||||
|
||||
`inputs` 和 `output_type` 的类型应当是 [Pydantic 格式](https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/json_schema/#generating-json-schema)。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import Tool
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
class HFModelDownloadsTool(Tool):
|
||||
name = "model_download_counter"
|
||||
description = """
|
||||
This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub.
|
||||
It returns the name of the checkpoint."""
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = {
|
||||
"task": {
|
||||
"type": "string",
|
||||
"description": "the task category (such as text-classification, depth-estimation, etc)",
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_type = "string"
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, task: str):
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
return model.id
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在,自定义的 `HfModelDownloadsTool` 类已经准备好,可以将其保存到名为 `model_downloads.py` 的文件中,并导入使用。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from model_downloads import HFModelDownloadsTool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = HFModelDownloadsTool()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你还可以通过调用 [`~Tool.push_to_hub`] 将自定义工具推送到 Hub。确保你已经为该工具创建了一个仓库,并使用具有读取访问权限的许可。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tool.push_to_hub("{your_username}/hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
通过 [`~Tool.load_tool`] 函数加载工具,并将其传递给智能体的 tools 参数。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool, CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
model_download_tool = load_tool("m-ric/hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 将 Space 导入为工具 🚀
|
||||
|
||||
你可以直接通过 [`Tool.from_space`] 方法将 Hub 上的 Space 导入为工具!
|
||||
|
||||
只需要提供 Space 在 Hub 上的 ID、名称和描述,帮助智能体理解工具的作用。在幕后,这将使用 [`gradio-client`](https://pypi.org/project/gradio-client/) 库来调用 Space。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,下面是从 Hub 导入 `FLUX.1-dev` Space 并用其生成图像的示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
from transformers import Tool
|
||||
image_generation_tool = Tool.from_space(
|
||||
"black-forest-labs/FLUX.1-dev",
|
||||
name="image_generator",
|
||||
description="Generate an image from a prompt")
|
||||
image_generation_tool("A sunny beach")
|
||||
```
|
||||
看!这就是你生成的图像!🏖️
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/sunny_beach.webp">
|
||||
|
||||
然后,你可以像使用其他工具一样使用这个工具。例如,改进提示 `穿宇航服的兔子` 并生成其图像:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[image_generation_tool])
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Improve this prompt, then generate an image of it.", prompt='A rabbit wearing a space suit'
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
=== Agent thoughts:
|
||||
improved_prompt could be "A bright blue space suit wearing rabbit, on the surface of the moon, under a bright orange sunset, with the Earth visible in the background"
|
||||
Now that I have improved the prompt, I can use the image generator tool to generate an image based on this prompt.
|
||||
>>> Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt="A bright blue space suit wearing rabbit, on the surface of the moon, under a bright orange sunset, with the Earth visible in the background")
|
||||
final_answer(image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rabbit_spacesuit_flux.webp">
|
||||
|
||||
这真酷吧?🤩
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 gradio-tools
|
||||
|
||||
[gradio-tools](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools) 是一个强大的库,允许使用 Hugging Face Spaces 作为工具。它支持许多现有的 Spaces,也支持自定义 Spaces。
|
||||
|
||||
transformers 支持通过 [`Tool.from_gradio`] 方法使用 `gradio_tools`。例如,下面是如何使用来自 `gradio-tools` 工具包的 [`StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool`](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools/blob/main/gradio_tools/tools/prompt_generator.py) 来改进提示,以生成更好的图像:
|
||||
|
||||
导入和实例化工具,并将其传递给 `Tool.from_gradio` 方法:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from gradio_tools import StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool
|
||||
from transformers import Tool, load_tool, CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
gradio_prompt_generator_tool = StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool()
|
||||
prompt_generator_tool = Tool.from_gradio(gradio_prompt_generator_tool)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> gradio-tools 需要 **文本** 输入和输出,即使在处理像图像和音频这样的不同模态时也是如此。目前,图像和音频的输入输出与此不兼容。
|
||||
### 使用 LangChain 工具
|
||||
|
||||
我们很喜欢 LangChain,并认为它有一套非常有吸引力的工具。
|
||||
要从 LangChain 导入工具,可以使用 `from_langchain()` 方法。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,下面是如何使用它来重新创建上面介绍的搜索结果,使用一个 LangChain 网络搜索工具。该工具需要 `pip install google-search-results` 来正常工作。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.agents import load_tools
|
||||
from transformers import Tool, ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
search_tool = Tool.from_langchain(load_tools(["serpapi"])[0])
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[search_tool])
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) are in BERT base encoder compared to the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 在酷炫的 Gradio 界面中展示智能体运行
|
||||
|
||||
你可以利用 `gradio.Chatbot` 来展示智能体的思考过程,通过 `stream_to_gradio`,下面是一个示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import gradio as gr
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
load_tool,
|
||||
ReactCodeAgent,
|
||||
HfApiEngine,
|
||||
stream_to_gradio,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Import tool from Hub
|
||||
image_generation_tool = load_tool("m-ric/text-to-image")
|
||||
|
||||
llm_engine = HfApiEngine("meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize the agent with the image generation tool
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[image_generation_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def interact_with_agent(task):
|
||||
messages = []
|
||||
messages.append(gr.ChatMessage(role="user", content=task))
|
||||
yield messages
|
||||
for msg in stream_to_gradio(agent, task):
|
||||
messages.append(msg)
|
||||
yield messages + [
|
||||
gr.ChatMessage(role="assistant", content="⏳ Task not finished yet!")
|
||||
]
|
||||
yield messages
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
|
||||
text_input = gr.Textbox(lines=1, label="Chat Message", value="Make me a picture of the Statue of Liberty.")
|
||||
submit = gr.Button("Run illustrator agent!")
|
||||
chatbot = gr.Chatbot(
|
||||
label="Agent",
|
||||
type="messages",
|
||||
avatar_images=(
|
||||
None,
|
||||
"https://em-content.zobj.net/source/twitter/53/robot-face_1f916.png",
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
submit.click(interact_with_agent, [text_input], [chatbot])
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
demo.launch()
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Agents和工具
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
The Agents framework has significantly changed in version v4.41.0.
|
||||
This document has been removed as it was referencing an older API.
|
||||
|
||||
We eagerly welcome new contributions for the updated API.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
162
hubconf.py
162
hubconf.py
@ -1,162 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
SRC_DIR = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "src")
|
||||
sys.path.append(SRC_DIR)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
AutoConfig,
|
||||
AutoModel,
|
||||
AutoModelForCausalLM,
|
||||
AutoModelForMaskedLM,
|
||||
AutoModelForQuestionAnswering,
|
||||
AutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
AutoTokenizer,
|
||||
add_start_docstrings,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
dependencies = ["torch", "numpy", "tokenizers", "filelock", "requests", "tqdm", "regex", "sentencepiece", "sacremoses", "importlib_metadata", "huggingface_hub"]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@add_start_docstrings(AutoConfig.__doc__)
|
||||
def config(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
# Using torch.hub !
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
config = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'config', 'google-bert/bert-base-uncased') # Download configuration from huggingface.co and cache.
|
||||
config = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'config', './test/bert_saved_model/') # E.g. config (or model) was saved using `save_pretrained('./test/saved_model/')`
|
||||
config = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'config', './test/bert_saved_model/my_configuration.json')
|
||||
config = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'config', 'google-bert/bert-base-uncased', output_attentions=True, foo=False)
|
||||
assert config.output_attentions == True
|
||||
config, unused_kwargs = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'config', 'google-bert/bert-base-uncased', output_attentions=True, foo=False, return_unused_kwargs=True)
|
||||
assert config.output_attentions == True
|
||||
assert unused_kwargs == {'foo': False}
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
return AutoConfig.from_pretrained(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@add_start_docstrings(AutoTokenizer.__doc__)
|
||||
def tokenizer(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
# Using torch.hub !
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'tokenizer', 'google-bert/bert-base-uncased') # Download vocabulary from huggingface.co and cache.
|
||||
tokenizer = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'tokenizer', './test/bert_saved_model/') # E.g. tokenizer was saved using `save_pretrained('./test/saved_model/')`
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
return AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@add_start_docstrings(AutoModel.__doc__)
|
||||
def model(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
# Using torch.hub !
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'model', 'google-bert/bert-base-uncased') # Download model and configuration from huggingface.co and cache.
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'model', './test/bert_model/') # E.g. model was saved using `save_pretrained('./test/saved_model/')`
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'model', 'google-bert/bert-base-uncased', output_attentions=True) # Update configuration during loading
|
||||
assert model.config.output_attentions == True
|
||||
# Loading from a TF checkpoint file instead of a PyTorch model (slower)
|
||||
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained('./tf_model/bert_tf_model_config.json')
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'model', './tf_model/bert_tf_checkpoint.ckpt.index', from_tf=True, config=config)
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
return AutoModel.from_pretrained(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@add_start_docstrings(AutoModelForCausalLM.__doc__)
|
||||
def modelForCausalLM(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
# Using torch.hub !
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForCausalLM', 'openai-community/gpt2') # Download model and configuration from huggingface.co and cache.
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForCausalLM', './test/saved_model/') # E.g. model was saved using `save_pretrained('./test/saved_model/')`
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForCausalLM', 'openai-community/gpt2', output_attentions=True) # Update configuration during loading
|
||||
assert model.config.output_attentions == True
|
||||
# Loading from a TF checkpoint file instead of a PyTorch model (slower)
|
||||
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained('./tf_model/gpt_tf_model_config.json')
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForCausalLM', './tf_model/gpt_tf_checkpoint.ckpt.index', from_tf=True, config=config)
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@add_start_docstrings(AutoModelForMaskedLM.__doc__)
|
||||
def modelForMaskedLM(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
# Using torch.hub !
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForMaskedLM', 'google-bert/bert-base-uncased') # Download model and configuration from huggingface.co and cache.
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForMaskedLM', './test/bert_model/') # E.g. model was saved using `save_pretrained('./test/saved_model/')`
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForMaskedLM', 'google-bert/bert-base-uncased', output_attentions=True) # Update configuration during loading
|
||||
assert model.config.output_attentions == True
|
||||
# Loading from a TF checkpoint file instead of a PyTorch model (slower)
|
||||
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained('./tf_model/bert_tf_model_config.json')
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForMaskedLM', './tf_model/bert_tf_checkpoint.ckpt.index', from_tf=True, config=config)
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
return AutoModelForMaskedLM.from_pretrained(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@add_start_docstrings(AutoModelForSequenceClassification.__doc__)
|
||||
def modelForSequenceClassification(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
# Using torch.hub !
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForSequenceClassification', 'google-bert/bert-base-uncased') # Download model and configuration from huggingface.co and cache.
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForSequenceClassification', './test/bert_model/') # E.g. model was saved using `save_pretrained('./test/saved_model/')`
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForSequenceClassification', 'google-bert/bert-base-uncased', output_attentions=True) # Update configuration during loading
|
||||
assert model.config.output_attentions == True
|
||||
# Loading from a TF checkpoint file instead of a PyTorch model (slower)
|
||||
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained('./tf_model/bert_tf_model_config.json')
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForSequenceClassification', './tf_model/bert_tf_checkpoint.ckpt.index', from_tf=True, config=config)
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
return AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@add_start_docstrings(AutoModelForQuestionAnswering.__doc__)
|
||||
def modelForQuestionAnswering(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
# Using torch.hub !
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForQuestionAnswering', 'google-bert/bert-base-uncased') # Download model and configuration from huggingface.co and cache.
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForQuestionAnswering', './test/bert_model/') # E.g. model was saved using `save_pretrained('./test/saved_model/')`
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForQuestionAnswering', 'google-bert/bert-base-uncased', output_attentions=True) # Update configuration during loading
|
||||
assert model.config.output_attentions == True
|
||||
# Loading from a TF checkpoint file instead of a PyTorch model (slower)
|
||||
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained('./tf_model/bert_tf_model_config.json')
|
||||
model = torch.hub.load('huggingface/transformers', 'modelForQuestionAnswering', './tf_model/bert_tf_checkpoint.ckpt.index', from_tf=True, config=config)
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return AutoModelForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
6
setup.py
6
setup.py
@ -130,7 +130,7 @@ _deps = [
|
||||
# Keras pin - this is to make sure Keras 3 doesn't destroy us. Remove or change when we have proper support.
|
||||
"keras>2.9,<2.16",
|
||||
"keras-nlp>=0.3.1,<0.14.0", # keras-nlp 0.14 doesn't support keras 2, see pin on keras.
|
||||
"kernels>=0.3.2,<0.4",
|
||||
"kernels>=0.4.4,<0.5",
|
||||
"librosa",
|
||||
"natten>=0.14.6,<0.15.0",
|
||||
"nltk<=3.8.1",
|
||||
@ -431,10 +431,6 @@ extras["torchhub"] = deps_list(
|
||||
"tqdm",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
extras["agents"] = deps_list(
|
||||
"diffusers", "accelerate", "datasets", "torch", "sentencepiece", "opencv-python", "Pillow"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
extras["benchmark"] = deps_list("optimum-benchmark")
|
||||
|
||||
# when modifying the following list, make sure to update src/transformers/dependency_versions_check.py
|
||||
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -16,7 +16,6 @@ import math
|
||||
from collections import OrderedDict
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from packaging import version
|
||||
from torch import Tensor, nn
|
||||
|
||||
from .utils import logging
|
||||
@ -34,14 +33,6 @@ class PytorchGELUTanh(nn.Module):
|
||||
match due to rounding errors.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
if version.parse(torch.__version__) < version.parse("1.12.0"):
|
||||
raise ImportError(
|
||||
f"You are using torch=={torch.__version__}, but torch>=1.12.0 is required to use "
|
||||
"PytorchGELUTanh. Please upgrade torch."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:
|
||||
return nn.functional.gelu(input, approximate="tanh")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -145,10 +136,7 @@ class MishActivation(nn.Module):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
if version.parse(torch.__version__) < version.parse("1.9.0"):
|
||||
self.act = self._mish_python
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.act = nn.functional.mish
|
||||
self.act = nn.functional.mish
|
||||
|
||||
def _mish_python(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:
|
||||
return input * torch.tanh(nn.functional.softplus(input))
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
|
||||
|
||||
from ..utils import (
|
||||
OptionalDependencyNotAvailable,
|
||||
_LazyModule,
|
||||
is_torch_available,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
_import_structure = {
|
||||
"agents": ["Agent", "CodeAgent", "ManagedAgent", "ReactAgent", "ReactCodeAgent", "ReactJsonAgent", "Toolbox"],
|
||||
"llm_engine": ["HfApiEngine", "TransformersEngine"],
|
||||
"monitoring": ["stream_to_gradio"],
|
||||
"tools": ["PipelineTool", "Tool", "ToolCollection", "launch_gradio_demo", "load_tool", "tool"],
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if not is_torch_available():
|
||||
raise OptionalDependencyNotAvailable()
|
||||
except OptionalDependencyNotAvailable:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
_import_structure["default_tools"] = ["FinalAnswerTool", "PythonInterpreterTool"]
|
||||
_import_structure["document_question_answering"] = ["DocumentQuestionAnsweringTool"]
|
||||
_import_structure["image_question_answering"] = ["ImageQuestionAnsweringTool"]
|
||||
_import_structure["search"] = ["DuckDuckGoSearchTool", "VisitWebpageTool"]
|
||||
_import_structure["speech_to_text"] = ["SpeechToTextTool"]
|
||||
_import_structure["text_to_speech"] = ["TextToSpeechTool"]
|
||||
_import_structure["translation"] = ["TranslationTool"]
|
||||
|
||||
if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
from .agents import Agent, CodeAgent, ManagedAgent, ReactAgent, ReactCodeAgent, ReactJsonAgent, Toolbox
|
||||
from .llm_engine import HfApiEngine, TransformersEngine
|
||||
from .monitoring import stream_to_gradio
|
||||
from .tools import PipelineTool, Tool, ToolCollection, launch_gradio_demo, load_tool, tool
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if not is_torch_available():
|
||||
raise OptionalDependencyNotAvailable()
|
||||
except OptionalDependencyNotAvailable:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
from .default_tools import FinalAnswerTool, PythonInterpreterTool
|
||||
from .document_question_answering import DocumentQuestionAnsweringTool
|
||||
from .image_question_answering import ImageQuestionAnsweringTool
|
||||
from .search import DuckDuckGoSearchTool, VisitWebpageTool
|
||||
from .speech_to_text import SpeechToTextTool
|
||||
from .text_to_speech import TextToSpeechTool
|
||||
from .translation import TranslationTool
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
sys.modules[__name__] = _LazyModule(__name__, globals()["__file__"], _import_structure, module_spec=__spec__)
|
||||
@ -1,260 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 HuggingFace Inc.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import pathlib
|
||||
import tempfile
|
||||
import uuid
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from ..utils import is_soundfile_available, is_torch_available, is_vision_available, logging
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
if is_vision_available():
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from PIL.Image import Image as ImageType
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ImageType = object
|
||||
|
||||
if is_torch_available():
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torch import Tensor
|
||||
else:
|
||||
Tensor = object
|
||||
|
||||
if is_soundfile_available():
|
||||
import soundfile as sf
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AgentType:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Abstract class to be reimplemented to define types that can be returned by agents.
|
||||
|
||||
These objects serve three purposes:
|
||||
|
||||
- They behave as they were the type they're meant to be, e.g., a string for text, a PIL.Image for images
|
||||
- They can be stringified: str(object) in order to return a string defining the object
|
||||
- They should be displayed correctly in ipython notebooks/colab/jupyter
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, value):
|
||||
self._value = value
|
||||
|
||||
def __str__(self):
|
||||
return self.to_string()
|
||||
|
||||
def to_raw(self):
|
||||
logger.error(
|
||||
"This is a raw AgentType of unknown type. Display in notebooks and string conversion will be unreliable"
|
||||
)
|
||||
return self._value
|
||||
|
||||
def to_string(self) -> str:
|
||||
logger.error(
|
||||
"This is a raw AgentType of unknown type. Display in notebooks and string conversion will be unreliable"
|
||||
)
|
||||
return str(self._value)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AgentText(AgentType, str):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Text type returned by the agent. Behaves as a string.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def to_raw(self):
|
||||
return self._value
|
||||
|
||||
def to_string(self):
|
||||
return str(self._value)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AgentImage(AgentType, ImageType):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Image type returned by the agent. Behaves as a PIL.Image.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, value):
|
||||
AgentType.__init__(self, value)
|
||||
ImageType.__init__(self)
|
||||
|
||||
if not is_vision_available():
|
||||
raise ImportError("PIL must be installed in order to handle images.")
|
||||
|
||||
self._path = None
|
||||
self._raw = None
|
||||
self._tensor = None
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(value, ImageType):
|
||||
self._raw = value
|
||||
elif isinstance(value, (str, pathlib.Path)):
|
||||
self._path = value
|
||||
elif isinstance(value, torch.Tensor):
|
||||
self._tensor = value
|
||||
elif isinstance(value, np.ndarray):
|
||||
self._tensor = torch.from_numpy(value)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise TypeError(f"Unsupported type for {self.__class__.__name__}: {type(value)}")
|
||||
|
||||
def _ipython_display_(self, include=None, exclude=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Displays correctly this type in an ipython notebook (ipython, colab, jupyter, ...)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
from IPython.display import Image, display
|
||||
|
||||
display(Image(self.to_string()))
|
||||
|
||||
def to_raw(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the "raw" version of that object. In the case of an AgentImage, it is a PIL.Image.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if self._raw is not None:
|
||||
return self._raw
|
||||
|
||||
if self._path is not None:
|
||||
self._raw = Image.open(self._path)
|
||||
return self._raw
|
||||
|
||||
if self._tensor is not None:
|
||||
array = self._tensor.detach().cpu().numpy()
|
||||
return Image.fromarray((255 - array * 255).astype(np.uint8))
|
||||
|
||||
def to_string(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the stringified version of that object. In the case of an AgentImage, it is a path to the serialized
|
||||
version of the image.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if self._path is not None:
|
||||
return self._path
|
||||
|
||||
if self._raw is not None:
|
||||
directory = tempfile.mkdtemp()
|
||||
self._path = os.path.join(directory, str(uuid.uuid4()) + ".png")
|
||||
self._raw.save(self._path)
|
||||
return self._path
|
||||
|
||||
if self._tensor is not None:
|
||||
array = self._tensor.detach().cpu().numpy()
|
||||
|
||||
# There is likely simpler than load into image into save
|
||||
img = Image.fromarray((255 - array * 255).astype(np.uint8))
|
||||
|
||||
directory = tempfile.mkdtemp()
|
||||
self._path = os.path.join(directory, str(uuid.uuid4()) + ".png")
|
||||
|
||||
img.save(self._path)
|
||||
|
||||
return self._path
|
||||
|
||||
def save(self, output_bytes, format, **params):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Saves the image to a file.
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
output_bytes (bytes): The output bytes to save the image to.
|
||||
format (str): The format to use for the output image. The format is the same as in PIL.Image.save.
|
||||
**params: Additional parameters to pass to PIL.Image.save.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
img = self.to_raw()
|
||||
img.save(output_bytes, format, **params)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AgentAudio(AgentType, str):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Audio type returned by the agent.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, value, samplerate=16_000):
|
||||
super().__init__(value)
|
||||
|
||||
if not is_soundfile_available():
|
||||
raise ImportError("soundfile must be installed in order to handle audio.")
|
||||
|
||||
self._path = None
|
||||
self._tensor = None
|
||||
|
||||
self.samplerate = samplerate
|
||||
if isinstance(value, (str, pathlib.Path)):
|
||||
self._path = value
|
||||
elif is_torch_available() and isinstance(value, torch.Tensor):
|
||||
self._tensor = value
|
||||
elif isinstance(value, tuple):
|
||||
self.samplerate = value[0]
|
||||
if isinstance(value[1], np.ndarray):
|
||||
self._tensor = torch.from_numpy(value[1])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._tensor = torch.tensor(value[1])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported audio type: {type(value)}")
|
||||
|
||||
def _ipython_display_(self, include=None, exclude=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Displays correctly this type in an ipython notebook (ipython, colab, jupyter, ...)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
from IPython.display import Audio, display
|
||||
|
||||
display(Audio(self.to_string(), rate=self.samplerate))
|
||||
|
||||
def to_raw(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the "raw" version of that object. It is a `torch.Tensor` object.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if self._tensor is not None:
|
||||
return self._tensor
|
||||
|
||||
if self._path is not None:
|
||||
tensor, self.samplerate = sf.read(self._path)
|
||||
self._tensor = torch.tensor(tensor)
|
||||
return self._tensor
|
||||
|
||||
def to_string(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the stringified version of that object. In the case of an AgentAudio, it is a path to the serialized
|
||||
version of the audio.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if self._path is not None:
|
||||
return self._path
|
||||
|
||||
if self._tensor is not None:
|
||||
directory = tempfile.mkdtemp()
|
||||
self._path = os.path.join(directory, str(uuid.uuid4()) + ".wav")
|
||||
sf.write(self._path, self._tensor, samplerate=self.samplerate)
|
||||
return self._path
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
AGENT_TYPE_MAPPING = {"string": AgentText, "image": AgentImage, "audio": AgentAudio}
|
||||
INSTANCE_TYPE_MAPPING = {str: AgentText, ImageType: AgentImage}
|
||||
|
||||
if is_torch_available():
|
||||
INSTANCE_TYPE_MAPPING[Tensor] = AgentAudio
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def handle_agent_inputs(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
args = [(arg.to_raw() if isinstance(arg, AgentType) else arg) for arg in args]
|
||||
kwargs = {k: (v.to_raw() if isinstance(v, AgentType) else v) for k, v in kwargs.items()}
|
||||
return args, kwargs
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def handle_agent_outputs(output, output_type=None):
|
||||
if output_type in AGENT_TYPE_MAPPING:
|
||||
# If the class has defined outputs, we can map directly according to the class definition
|
||||
decoded_outputs = AGENT_TYPE_MAPPING[output_type](output)
|
||||
return decoded_outputs
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# If the class does not have defined output, then we map according to the type
|
||||
for _k, _v in INSTANCE_TYPE_MAPPING.items():
|
||||
if isinstance(output, _k):
|
||||
return _v(output)
|
||||
return output
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -1,187 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import importlib.util
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import math
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass
|
||||
from math import sqrt
|
||||
from typing import Dict
|
||||
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download, list_spaces
|
||||
|
||||
from ..utils import is_offline_mode
|
||||
from .python_interpreter import LIST_SAFE_MODULES, evaluate_python_code
|
||||
from .tools import TOOL_CONFIG_FILE, TOOL_MAPPING, Tool
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def custom_print(*args):
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
BASE_PYTHON_TOOLS = {
|
||||
"print": custom_print,
|
||||
"isinstance": isinstance,
|
||||
"range": range,
|
||||
"float": float,
|
||||
"int": int,
|
||||
"bool": bool,
|
||||
"str": str,
|
||||
"set": set,
|
||||
"list": list,
|
||||
"dict": dict,
|
||||
"tuple": tuple,
|
||||
"round": round,
|
||||
"ceil": math.ceil,
|
||||
"floor": math.floor,
|
||||
"log": math.log,
|
||||
"exp": math.exp,
|
||||
"sin": math.sin,
|
||||
"cos": math.cos,
|
||||
"tan": math.tan,
|
||||
"asin": math.asin,
|
||||
"acos": math.acos,
|
||||
"atan": math.atan,
|
||||
"atan2": math.atan2,
|
||||
"degrees": math.degrees,
|
||||
"radians": math.radians,
|
||||
"pow": math.pow,
|
||||
"sqrt": sqrt,
|
||||
"len": len,
|
||||
"sum": sum,
|
||||
"max": max,
|
||||
"min": min,
|
||||
"abs": abs,
|
||||
"enumerate": enumerate,
|
||||
"zip": zip,
|
||||
"reversed": reversed,
|
||||
"sorted": sorted,
|
||||
"all": all,
|
||||
"any": any,
|
||||
"map": map,
|
||||
"filter": filter,
|
||||
"ord": ord,
|
||||
"chr": chr,
|
||||
"next": next,
|
||||
"iter": iter,
|
||||
"divmod": divmod,
|
||||
"callable": callable,
|
||||
"getattr": getattr,
|
||||
"hasattr": hasattr,
|
||||
"setattr": setattr,
|
||||
"issubclass": issubclass,
|
||||
"type": type,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class PreTool:
|
||||
name: str
|
||||
inputs: Dict[str, str]
|
||||
output_type: type
|
||||
task: str
|
||||
description: str
|
||||
repo_id: str
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
HUGGINGFACE_DEFAULT_TOOLS_FROM_HUB = [
|
||||
"image-transformation",
|
||||
"text-to-image",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_remote_tools(logger, organization="huggingface-tools"):
|
||||
if is_offline_mode():
|
||||
logger.info("You are in offline mode, so remote tools are not available.")
|
||||
return {}
|
||||
|
||||
spaces = list_spaces(author=organization)
|
||||
tools = {}
|
||||
for space_info in spaces:
|
||||
repo_id = space_info.id
|
||||
resolved_config_file = hf_hub_download(repo_id, TOOL_CONFIG_FILE, repo_type="space")
|
||||
with open(resolved_config_file, encoding="utf-8") as reader:
|
||||
config = json.load(reader)
|
||||
task = repo_id.split("/")[-1]
|
||||
tools[config["name"]] = PreTool(
|
||||
task=task,
|
||||
description=config["description"],
|
||||
repo_id=repo_id,
|
||||
name=task,
|
||||
inputs=config["inputs"],
|
||||
output_type=config["output_type"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return tools
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def setup_default_tools(logger):
|
||||
default_tools = {}
|
||||
main_module = importlib.import_module("transformers")
|
||||
tools_module = main_module.agents
|
||||
|
||||
for task_name, tool_class_name in TOOL_MAPPING.items():
|
||||
tool_class = getattr(tools_module, tool_class_name)
|
||||
tool_instance = tool_class()
|
||||
default_tools[tool_class.name] = PreTool(
|
||||
name=tool_instance.name,
|
||||
inputs=tool_instance.inputs,
|
||||
output_type=tool_instance.output_type,
|
||||
task=task_name,
|
||||
description=tool_instance.description,
|
||||
repo_id=None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return default_tools
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PythonInterpreterTool(Tool):
|
||||
name = "python_interpreter"
|
||||
description = "This is a tool that evaluates python code. It can be used to perform calculations."
|
||||
|
||||
output_type = "string"
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, authorized_imports=None, **kwargs):
|
||||
if authorized_imports is None:
|
||||
self.authorized_imports = list(set(LIST_SAFE_MODULES))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.authorized_imports = list(set(LIST_SAFE_MODULES) | set(authorized_imports))
|
||||
self.inputs = {
|
||||
"code": {
|
||||
"type": "string",
|
||||
"description": (
|
||||
"The code snippet to evaluate. All variables used in this snippet must be defined in this same snippet, "
|
||||
f"else you will get an error. This code can only import the following python libraries: {authorized_imports}."
|
||||
),
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, code):
|
||||
output = str(
|
||||
evaluate_python_code(code, static_tools=BASE_PYTHON_TOOLS, authorized_imports=self.authorized_imports)
|
||||
)
|
||||
return output
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FinalAnswerTool(Tool):
|
||||
name = "final_answer"
|
||||
description = "Provides a final answer to the given problem."
|
||||
inputs = {"answer": {"type": "any", "description": "The final answer to the problem"}}
|
||||
output_type = "any"
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, answer):
|
||||
return answer
|
||||
@ -1,89 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import re
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from ..models.auto import AutoProcessor
|
||||
from ..models.vision_encoder_decoder import VisionEncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
from ..utils import is_vision_available
|
||||
from .tools import PipelineTool
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_vision_available():
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DocumentQuestionAnsweringTool(PipelineTool):
|
||||
default_checkpoint = "naver-clova-ix/donut-base-finetuned-docvqa"
|
||||
description = "This is a tool that answers a question about an document (pdf). It returns a string that contains the answer to the question."
|
||||
name = "document_qa"
|
||||
pre_processor_class = AutoProcessor
|
||||
model_class = VisionEncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = {
|
||||
"document": {
|
||||
"type": "image",
|
||||
"description": "The image containing the information. Can be a PIL Image or a string path to the image.",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"question": {"type": "string", "description": "The question in English"},
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_type = "string"
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
if not is_vision_available():
|
||||
raise ValueError("Pillow must be installed to use the DocumentQuestionAnsweringTool.")
|
||||
|
||||
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def encode(self, document: "Image", question: str):
|
||||
task_prompt = "<s_docvqa><s_question>{user_input}</s_question><s_answer>"
|
||||
prompt = task_prompt.replace("{user_input}", question)
|
||||
decoder_input_ids = self.pre_processor.tokenizer(
|
||||
prompt, add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors="pt"
|
||||
).input_ids
|
||||
if isinstance(document, str):
|
||||
img = Image.open(document).convert("RGB")
|
||||
img_array = np.array(img).transpose(2, 0, 1)
|
||||
document = torch.from_numpy(img_array)
|
||||
pixel_values = self.pre_processor(document, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
|
||||
|
||||
return {"decoder_input_ids": decoder_input_ids, "pixel_values": pixel_values}
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, inputs):
|
||||
return self.model.generate(
|
||||
inputs["pixel_values"].to(self.device),
|
||||
decoder_input_ids=inputs["decoder_input_ids"].to(self.device),
|
||||
max_length=self.model.decoder.config.max_position_embeddings,
|
||||
early_stopping=True,
|
||||
pad_token_id=self.pre_processor.tokenizer.pad_token_id,
|
||||
eos_token_id=self.pre_processor.tokenizer.eos_token_id,
|
||||
use_cache=True,
|
||||
num_beams=1,
|
||||
bad_words_ids=[[self.pre_processor.tokenizer.unk_token_id]],
|
||||
return_dict_in_generate=True,
|
||||
).sequences
|
||||
|
||||
def decode(self, outputs):
|
||||
sequence = self.pre_processor.batch_decode(outputs)[0]
|
||||
sequence = sequence.replace(self.pre_processor.tokenizer.eos_token, "")
|
||||
sequence = sequence.replace(self.pre_processor.tokenizer.pad_token, "")
|
||||
sequence = re.sub(r"<.*?>", "", sequence, count=1).strip() # remove first task start token
|
||||
sequence = self.pre_processor.token2json(sequence)
|
||||
|
||||
return sequence["answer"]
|
||||
@ -1,414 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
from .agents import BASE_PYTHON_TOOLS
|
||||
from .python_interpreter import InterpreterError, evaluate
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Fake tools for test
|
||||
def classifier(text, labels):
|
||||
return f"This is the classification of {text} along {labels}."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def translator(text, src_lang, tgt_lang):
|
||||
return f"This is the translation of {text} from {src_lang} to {tgt_lang}."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def speaker(text):
|
||||
return f"This is actually a sound reading {text}."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def transcriber(audio):
|
||||
if "sound" not in audio:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`audio` ({audio}) is not a sound.")
|
||||
return f"This is the transcribed text from {audio}."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def image_generator(prompt):
|
||||
return f"This is actually an image representing {prompt}."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def image_captioner(image):
|
||||
if "image" not in image:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`image` ({image}) is not an image.")
|
||||
return f"This is a description of {image}."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def image_transformer(image, prompt):
|
||||
if "image" not in image:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`image` ({image}) is not an image.")
|
||||
return f"This is a transformation of {image} according to {prompt}."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def question_answerer(text, question):
|
||||
return f"This is the answer to {question} from {text}."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def image_qa(image, question):
|
||||
if "image" not in image:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`image` ({image}) is not an image.")
|
||||
return f"This is the answer to {question} from {image}."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def text_downloader(url):
|
||||
return f"This is the content of {url}."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def summarizer(text):
|
||||
return f"This is a summary of {text}."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def video_generator(prompt, seconds=2):
|
||||
return f"A video of {prompt}"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def document_qa(image, question):
|
||||
return f"This is the answer to {question} from the document {image}."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def image_segmenter(image, prompt):
|
||||
return f"This is the mask of {prompt} in {image}"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
TEST_TOOLS = {
|
||||
"text_classifier": classifier,
|
||||
"translator": translator,
|
||||
"text_reader": speaker,
|
||||
"summarizer": summarizer,
|
||||
"transcriber": transcriber,
|
||||
"image_generator": image_generator,
|
||||
"image_captioner": image_captioner,
|
||||
"image_transformer": image_transformer,
|
||||
"text_qa": question_answerer,
|
||||
"text_downloader": text_downloader,
|
||||
"image_qa": image_qa,
|
||||
"video_generator": video_generator,
|
||||
"document_qa": document_qa,
|
||||
"image_segmenter": image_segmenter,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Problem:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A class regrouping all the information to solve a problem on which we will evaluate agents.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
task (`str` ou `list[str]`):
|
||||
One or several descriptions of the task to perform. If a list, it should contain variations on the
|
||||
phrasing, but for the same task.
|
||||
inputs (`list[str]` or `dict[str, str]`):
|
||||
The inputs that will be fed to the tools. For this testing environment, only strings are accepted as
|
||||
values. Pass along a dictionary when you want to specify the values of each inputs, or just the list of
|
||||
inputs expected (the value used will be `<<input_name>>` in this case).
|
||||
answer (`str` or `list[str]`):
|
||||
The theoretical answer (or list of possible valid answers) to the problem, as code.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, task, inputs, answer):
|
||||
self.task = task
|
||||
self.inputs = inputs
|
||||
self.answer = answer
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### The list of problems the agent will be evaluated on.
|
||||
EVALUATION_TASKS = [
|
||||
Problem(
|
||||
task=[
|
||||
"Is the following `text` (in Spanish) positive or negative?",
|
||||
"Is the text in the variable `text` (in Spanish) positive or negative?",
|
||||
"Translate the following `text` from Spanish to English then tell me if its positive or negative.",
|
||||
],
|
||||
inputs=["text"],
|
||||
answer="""text_classifier(translator(text, src_lang="Spanish", tgt_lang="English"), labels=["positive", "negative"])""",
|
||||
),
|
||||
Problem(
|
||||
task=[
|
||||
"Tell me out loud what the `image` contains.",
|
||||
"Describe the following `image` out loud.",
|
||||
"Find what is in the picture stored in `image` then read it out loud.",
|
||||
],
|
||||
inputs=["image"],
|
||||
answer=[
|
||||
"text_reader(image_captioner(image))",
|
||||
"text_reader(image_qa(image, question='What is in the image?'))",
|
||||
],
|
||||
),
|
||||
Problem(
|
||||
task=[
|
||||
"Generate an image from the text given in `text_input`. Then transform it according to the text in `prompt`.",
|
||||
"Use the following `text_input` to generate an image, then transform it by using the text in `prompt`.",
|
||||
],
|
||||
inputs=["text_input", "prompt"],
|
||||
answer="image_transformer(image_generator(text_input), prompt)",
|
||||
),
|
||||
Problem(
|
||||
task=[
|
||||
"Download the content of `url`, summarize it then generate an image from its content.",
|
||||
"Use a summary of the web page at `url` to generate an image.",
|
||||
"Summarize the content of the web page at `url`, and use the result to generate an image.",
|
||||
],
|
||||
inputs=["url"],
|
||||
answer="image_generator(summarizer(text_downloader(url)))",
|
||||
),
|
||||
Problem(
|
||||
task=[
|
||||
"Transform the following `image` using the prompt in `text`. The prompt is in Spanish.",
|
||||
"Use the text prompt in `text` (in Spanish) to transform the following `image`.",
|
||||
"Translate the `text` from Spanish to English then use it to transform the picture in `image`.",
|
||||
],
|
||||
inputs=["text", "image"],
|
||||
answer="image_transformer(image, translator(text, src_lang='Spanish', tgt_lang='English'))",
|
||||
),
|
||||
Problem(
|
||||
task=[
|
||||
"Download the content of `url`, summarize it then read it out loud to me.",
|
||||
"Read me a summary of the web page at `url`.",
|
||||
],
|
||||
inputs=["url"],
|
||||
answer="text_reader(summarizer(text_downloader(url)))",
|
||||
),
|
||||
Problem(
|
||||
task=[
|
||||
"Generate an image from the text given in `text_input`.",
|
||||
],
|
||||
inputs=["text_input"],
|
||||
answer="image_generator(text_input)",
|
||||
),
|
||||
Problem(
|
||||
task=[
|
||||
"Replace the beaver in the `image` by the `prompt`.",
|
||||
"Transform the `image` so that it contains the `prompt`.",
|
||||
"Use `prompt` to transform this `image`.",
|
||||
],
|
||||
inputs=["image", "prompt"],
|
||||
answer="image_transformer(image, prompt)",
|
||||
),
|
||||
Problem(
|
||||
task=[
|
||||
"Provide me the summary of the `text`, then read it to me before transcribing it and translating it in French.",
|
||||
"Summarize `text`, read it out loud then transcribe the audio and translate it in French.",
|
||||
"Read me a summary of the `text` out loud. Transcribe this and translate it in French.",
|
||||
],
|
||||
inputs=["text"],
|
||||
answer="translator(transcriber(text_reader(summarizer(text))), src_lang='English', tgt_lang='French')",
|
||||
),
|
||||
Problem(
|
||||
task=["Generate a video of the `prompt`", "Animate a `prompt`", "Make me a short video using `prompt`."],
|
||||
inputs={"prompt": "A lobster swimming"},
|
||||
answer="video_generator('A lobster swimming')",
|
||||
),
|
||||
Problem(
|
||||
task=[
|
||||
"Download the following file `url`, summarize it in a few words and generate a video from it."
|
||||
"Fetch the file at this `url`, summarize it, and create an animation out of it."
|
||||
],
|
||||
inputs=["url"],
|
||||
answer="video_generator(summarizer(text_downloader(url)))",
|
||||
),
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_theoretical_tools(agent_answer, theoretical_answer, code_answer):
|
||||
if not isinstance(theoretical_answer, list):
|
||||
return {name for name in TEST_TOOLS if name in code_answer}
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(agent_answer, dict):
|
||||
for one_answer, one_code in zip(theoretical_answer, code_answer):
|
||||
if one_answer in agent_answer.values():
|
||||
return {name for name in TEST_TOOLS if name in one_code}
|
||||
|
||||
for one_answer, one_code in zip(theoretical_answer, code_answer):
|
||||
if agent_answer == one_answer:
|
||||
return {name for name in TEST_TOOLS if name in one_code}
|
||||
|
||||
return {name for name in TEST_TOOLS if name in code_answer[0]}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_code(code, inputs=None, state=None, verbose=False, return_interpretor_error=False):
|
||||
tools = BASE_PYTHON_TOOLS.copy()
|
||||
for name, tool in TEST_TOOLS.items():
|
||||
if name not in code:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
tools[name] = tool
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(inputs, dict):
|
||||
inputs = inputs.copy()
|
||||
elif inputs is not None:
|
||||
inputs = {inp: f"<<{inp}>>" for inp in inputs}
|
||||
|
||||
if state is not None:
|
||||
state.update(inputs)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
state = inputs
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return evaluate(code, tools, state)
|
||||
except InterpreterError as e:
|
||||
return str(e)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
if verbose:
|
||||
print(e)
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def score_code(agent_answer, theoretical_answer, verbose: bool = False):
|
||||
if verbose:
|
||||
print(agent_answer, theoretical_answer)
|
||||
theoretical_answer = theoretical_answer if isinstance(theoretical_answer, list) else [theoretical_answer]
|
||||
|
||||
if agent_answer in theoretical_answer:
|
||||
if verbose:
|
||||
print("Perfect!")
|
||||
return 1
|
||||
elif isinstance(agent_answer, dict) and any(v in theoretical_answer for v in agent_answer.values()):
|
||||
if verbose:
|
||||
print("Almost perfect, result in state!")
|
||||
return 0.75
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if verbose:
|
||||
print("Result is not the right one but code executed.")
|
||||
return 0.3
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_one_result(code, agent_answer, theoretical_answer, answer, verbose=False):
|
||||
tools_in_code = {name for name in TEST_TOOLS if f"`{name}`" in code}
|
||||
theoretical_tools = get_theoretical_tools(agent_answer, theoretical_answer, answer)
|
||||
if tools_in_code == theoretical_tools:
|
||||
tool_selection_score = 1.0
|
||||
tool_selection_errors = None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
missing_tools = len(theoretical_tools - tools_in_code)
|
||||
unexpected_tools = len(tools_in_code - theoretical_tools)
|
||||
tool_selection_score = max(0, 1.0 - 0.25 * missing_tools - 0.25 * unexpected_tools)
|
||||
|
||||
tool_selection_errors = {
|
||||
"selected_tools": tools_in_code,
|
||||
"theoretical_tools": theoretical_tools,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
tools_in_code = {name for name in TEST_TOOLS if name in code}
|
||||
if tools_in_code == theoretical_tools:
|
||||
tool_used_score = 1.0
|
||||
tool_used_errors = None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
missing_tools = len(theoretical_tools - tools_in_code)
|
||||
unexpected_tools = len(tools_in_code - theoretical_tools)
|
||||
tool_used_score = max(0, 1.0 - 0.25 * missing_tools - 0.25 * unexpected_tools)
|
||||
|
||||
tool_used_errors = {
|
||||
"selected_tools": tools_in_code,
|
||||
"theoretical_tools": theoretical_tools,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
score = score_code(agent_answer, theoretical_answer, verbose=verbose)
|
||||
if score < 1.0:
|
||||
code_errors = {
|
||||
"code_produced": code,
|
||||
"evaluation": agent_answer,
|
||||
"theoretical_answer": theoretical_answer,
|
||||
}
|
||||
else:
|
||||
code_errors = None
|
||||
|
||||
return (tool_selection_score, tool_used_score, score), (tool_selection_errors, tool_used_errors, code_errors)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_agent(agent, batch_size=8, verbose=False, return_errors=False):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Evaluates a new agent on all `EVALUATION_TASKS`.
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent = NewOpenAiAgent(model="text-davinci-003", api_key=your_api_key)
|
||||
bads = new_evaluate_agent(agent)
|
||||
for bad in bads:
|
||||
print(bad)
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Sanity check
|
||||
agent_tools = set(agent.toolbox.keys())
|
||||
if agent_tools != set(TEST_TOOLS):
|
||||
missing_tools = set(TEST_TOOLS) - agent_tools
|
||||
unexpected_tools = set(agent_tools) - TEST_TOOLS
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Fix the test tools in the evaluate_agent module. Tools missing: {missing_tools}. Extra tools: {unexpected_tools}."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
eval_tasks = []
|
||||
eval_idx = []
|
||||
for idx, pb in enumerate(EVALUATION_TASKS):
|
||||
if isinstance(pb.task, list):
|
||||
eval_tasks.extend(pb.task)
|
||||
eval_idx.extend([idx] * len(pb.task))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
eval_tasks.append(pb.task)
|
||||
eval_idx.append(idx)
|
||||
|
||||
tool_selection_score = 0
|
||||
tool_used_score = 0
|
||||
code_score = 0
|
||||
|
||||
if return_errors:
|
||||
tool_selection_errors = {}
|
||||
tool_used_errors = {}
|
||||
code_errors = {}
|
||||
|
||||
for start_idx in range(0, len(eval_tasks), batch_size):
|
||||
end_idx = min(start_idx + batch_size, len(eval_tasks))
|
||||
batch_tasks = eval_tasks[start_idx:end_idx]
|
||||
|
||||
results = [agent.run(task, return_generated_code=True) for task in batch_tasks]
|
||||
|
||||
for idx, result in enumerate(results):
|
||||
problem = EVALUATION_TASKS[eval_idx[start_idx + idx]]
|
||||
if verbose:
|
||||
print(f"====Task {start_idx + idx}====\n{batch_tasks[idx]}\n")
|
||||
code = agent.extract_action(result, split_token="Answer:")
|
||||
|
||||
# Evaluate agent answer and code answer
|
||||
agent_answer = evaluate_code(code, problem.inputs, verbose=verbose)
|
||||
if isinstance(problem.answer, list):
|
||||
theoretical_answer = [evaluate_code(answer, problem.inputs) for answer in problem.answer]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
theoretical_answer = evaluate_code(problem.answer, problem.inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
scores, errors = evaluate_one_result(
|
||||
code, agent_answer, theoretical_answer, problem.answer, verbose=verbose
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tool_selection_score += scores[0]
|
||||
tool_used_score += scores[1]
|
||||
code_score += scores[2]
|
||||
|
||||
if return_errors:
|
||||
if errors[0] is not None:
|
||||
tool_selection_errors[batch_tasks[idx]] = errors[0]
|
||||
if errors[1] is not None:
|
||||
tool_used_errors[batch_tasks[idx]] = errors[1]
|
||||
if errors[2] is not None:
|
||||
code_errors[batch_tasks[idx]] = errors[2]
|
||||
|
||||
scores = {
|
||||
"tool selection score": 100 * (tool_selection_score / len(eval_tasks)),
|
||||
"tool used score": 100 * (tool_used_score / len(eval_tasks)),
|
||||
"code score": 100 * (code_score / len(eval_tasks)),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
if return_errors:
|
||||
return scores, tool_selection_errors, tool_used_errors, code_errors
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return scores
|
||||
@ -1,57 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
from ..models.auto import AutoModelForVisualQuestionAnswering, AutoProcessor
|
||||
from ..utils import requires_backends
|
||||
from .tools import PipelineTool
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ImageQuestionAnsweringTool(PipelineTool):
|
||||
default_checkpoint = "dandelin/vilt-b32-finetuned-vqa"
|
||||
description = (
|
||||
"This is a tool that answers a question about an image. It returns a text that is the answer to the question."
|
||||
)
|
||||
name = "image_qa"
|
||||
pre_processor_class = AutoProcessor
|
||||
model_class = AutoModelForVisualQuestionAnswering
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = {
|
||||
"image": {
|
||||
"type": "image",
|
||||
"description": "The image containing the information. Can be a PIL Image or a string path to the image.",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"question": {"type": "string", "description": "The question in English"},
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_type = "string"
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
requires_backends(self, ["vision"])
|
||||
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def encode(self, image: "Image", question: str):
|
||||
return self.pre_processor(image, question, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, inputs):
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
return self.model(**inputs).logits
|
||||
|
||||
def decode(self, outputs):
|
||||
idx = outputs.argmax(-1).item()
|
||||
return self.model.config.id2label[idx]
|
||||
@ -1,243 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
from copy import deepcopy
|
||||
from enum import Enum
|
||||
from typing import Dict, List, Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import InferenceClient
|
||||
from huggingface_hub.utils._deprecation import _deprecate_method
|
||||
|
||||
from .. import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
from ..pipelines.base import Pipeline
|
||||
from ..utils import logging
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class MessageRole(str, Enum):
|
||||
USER = "user"
|
||||
ASSISTANT = "assistant"
|
||||
SYSTEM = "system"
|
||||
TOOL_CALL = "tool-call"
|
||||
TOOL_RESPONSE = "tool-response"
|
||||
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def roles(cls):
|
||||
return [r.value for r in cls]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_clean_message_list(message_list: List[Dict[str, str]], role_conversions: Dict[str, str] = {}):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Subsequent messages with the same role will be concatenated to a single message.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
message_list (`List[Dict[str, str]]`): List of chat messages.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
final_message_list = []
|
||||
message_list = deepcopy(message_list) # Avoid modifying the original list
|
||||
for message in message_list:
|
||||
if not set(message.keys()) == {"role", "content"}:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Message should contain only 'role' and 'content' keys!")
|
||||
|
||||
role = message["role"]
|
||||
if role not in MessageRole.roles():
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Incorrect role {role}, only {MessageRole.roles()} are supported for now.")
|
||||
|
||||
if role in role_conversions:
|
||||
message["role"] = role_conversions[role]
|
||||
|
||||
if len(final_message_list) > 0 and message["role"] == final_message_list[-1]["role"]:
|
||||
final_message_list[-1]["content"] += "\n=======\n" + message["content"]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
final_message_list.append(message)
|
||||
return final_message_list
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
llama_role_conversions = {
|
||||
MessageRole.TOOL_RESPONSE: MessageRole.USER,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class HfEngine:
|
||||
@_deprecate_method(
|
||||
version="4.51.0",
|
||||
message="Switch to smolagents instead, with the same functionalities and similar API (https://huggingface.co/docs/smolagents/index)",
|
||||
)
|
||||
def __init__(self, model_id: Optional[str] = None):
|
||||
self.last_input_token_count = None
|
||||
self.last_output_token_count = None
|
||||
if model_id is None:
|
||||
model_id = "HuggingFaceTB/SmolLM2-1.7B-Instruct"
|
||||
logger.warning(f"Using default model for token counting: '{model_id}'")
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
logger.warning(f"Failed to load tokenizer for model {model_id}: {e}. Loading default tokenizer instead.")
|
||||
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("HuggingFaceTB/SmolLM2-1.7B-Instruct")
|
||||
|
||||
def get_token_counts(self):
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"input_token_count": self.last_input_token_count,
|
||||
"output_token_count": self.last_output_token_count,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def generate(
|
||||
self, messages: List[Dict[str, str]], stop_sequences: Optional[List[str]] = None, grammar: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
):
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(
|
||||
self, messages: List[Dict[str, str]], stop_sequences: Optional[List[str]] = None, grammar: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
) -> str:
|
||||
"""Process the input messages and return the model's response.
|
||||
|
||||
This method sends a list of messages to the Hugging Face Inference API, optionally with stop sequences and grammar customization.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters:
|
||||
messages (`List[Dict[str, str]]`):
|
||||
A list of message dictionaries to be processed. Each dictionary should have the structure `{"role": "user/system", "content": "message content"}`.
|
||||
stop_sequences (`List[str]`, *optional*):
|
||||
A list of strings that will stop the generation if encountered in the model's output.
|
||||
grammar (`str`, *optional*):
|
||||
The grammar or formatting structure to use in the model's response.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
`str`: The text content of the model's response.
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> engine = HfApiEngine(
|
||||
... model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct",
|
||||
... token="your_hf_token_here",
|
||||
... max_tokens=2000
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> messages = [{"role": "user", "content": "Explain quantum mechanics in simple terms."}]
|
||||
>>> response = engine(messages, stop_sequences=["END"])
|
||||
>>> print(response)
|
||||
"Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that studies..."
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not isinstance(messages, List):
|
||||
raise ValueError("Messages should be a list of dictionaries with 'role' and 'content' keys.")
|
||||
if stop_sequences is None:
|
||||
stop_sequences = []
|
||||
response = self.generate(messages, stop_sequences, grammar)
|
||||
self.last_input_token_count = len(self.tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=True))
|
||||
self.last_output_token_count = len(self.tokenizer.encode(response))
|
||||
|
||||
# Remove stop sequences from LLM output
|
||||
for stop_seq in stop_sequences:
|
||||
if response[-len(stop_seq) :] == stop_seq:
|
||||
response = response[: -len(stop_seq)]
|
||||
return response
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class HfApiEngine(HfEngine):
|
||||
"""A class to interact with Hugging Face's Inference API for language model interaction.
|
||||
|
||||
This engine allows you to communicate with Hugging Face's models using the Inference API. It can be used in both serverless mode or with a dedicated endpoint, supporting features like stop sequences and grammar customization.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters:
|
||||
model (`str`, *optional*, defaults to `"meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct"`):
|
||||
The Hugging Face model ID to be used for inference. This can be a path or model identifier from the Hugging Face model hub.
|
||||
token (`str`, *optional*):
|
||||
Token used by the Hugging Face API for authentication.
|
||||
If not provided, the class will use the token stored in the Hugging Face CLI configuration.
|
||||
max_tokens (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 1500):
|
||||
The maximum number of tokens allowed in the output.
|
||||
timeout (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 120):
|
||||
Timeout for the API request, in seconds.
|
||||
|
||||
Raises:
|
||||
ValueError:
|
||||
If the model name is not provided.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
model: str = "meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct",
|
||||
token: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
max_tokens: Optional[int] = 1500,
|
||||
timeout: Optional[int] = 120,
|
||||
):
|
||||
super().__init__(model_id=model)
|
||||
self.model = model
|
||||
self.client = InferenceClient(self.model, token=token, timeout=timeout)
|
||||
self.max_tokens = max_tokens
|
||||
|
||||
def generate(
|
||||
self, messages: List[Dict[str, str]], stop_sequences: Optional[List[str]] = None, grammar: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
) -> str:
|
||||
# Get clean message list
|
||||
messages = get_clean_message_list(messages, role_conversions=llama_role_conversions)
|
||||
|
||||
# Send messages to the Hugging Face Inference API
|
||||
if grammar is not None:
|
||||
response = self.client.chat_completion(
|
||||
messages, stop=stop_sequences, max_tokens=self.max_tokens, response_format=grammar
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
response = self.client.chat_completion(messages, stop=stop_sequences, max_tokens=self.max_tokens)
|
||||
|
||||
response = response.choices[0].message.content
|
||||
return response
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TransformersEngine(HfEngine):
|
||||
"""This engine uses a pre-initialized local text-generation pipeline."""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, pipeline: Pipeline, model_id: Optional[str] = None):
|
||||
super().__init__(model_id)
|
||||
self.pipeline = pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
def generate(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
messages: List[Dict[str, str]],
|
||||
stop_sequences: Optional[List[str]] = None,
|
||||
grammar: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
max_length: int = 1500,
|
||||
) -> str:
|
||||
# Get clean message list
|
||||
messages = get_clean_message_list(messages, role_conversions=llama_role_conversions)
|
||||
|
||||
# Get LLM output
|
||||
if stop_sequences is not None and len(stop_sequences) > 0:
|
||||
stop_strings = stop_sequences
|
||||
else:
|
||||
stop_strings = None
|
||||
|
||||
output = self.pipeline(
|
||||
messages,
|
||||
stop_strings=stop_strings,
|
||||
max_length=max_length,
|
||||
tokenizer=self.pipeline.tokenizer,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
response = output[0]["generated_text"][-1]["content"]
|
||||
return response
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
DEFAULT_JSONAGENT_REGEX_GRAMMAR = {
|
||||
"type": "regex",
|
||||
"value": 'Thought: .+?\\nAction:\\n\\{\\n\\s{4}"action":\\s"[^"\\n]+",\\n\\s{4}"action_input":\\s"[^"\\n]+"\\n\\}\\n<end_action>',
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
DEFAULT_CODEAGENT_REGEX_GRAMMAR = {
|
||||
"type": "regex",
|
||||
"value": "Thought: .+?\\nCode:\\n```(?:py|python)?\\n(?:.|\\s)+?\\n```<end_action>",
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1,117 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
from ..utils import logging
|
||||
from .agent_types import AgentAudio, AgentImage, AgentText
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def pull_message(step_log: dict, test_mode: bool = True):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from gradio import ChatMessage
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
if test_mode:
|
||||
|
||||
class ChatMessage:
|
||||
def __init__(self, role, content, metadata=None):
|
||||
self.role = role
|
||||
self.content = content
|
||||
self.metadata = metadata
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ImportError("Gradio should be installed in order to launch a gradio demo.")
|
||||
|
||||
if step_log.get("rationale"):
|
||||
yield ChatMessage(role="assistant", content=step_log["rationale"])
|
||||
if step_log.get("tool_call"):
|
||||
used_code = step_log["tool_call"]["tool_name"] == "code interpreter"
|
||||
content = step_log["tool_call"]["tool_arguments"]
|
||||
if used_code:
|
||||
content = f"```py\n{content}\n```"
|
||||
yield ChatMessage(
|
||||
role="assistant",
|
||||
metadata={"title": f"🛠️ Used tool {step_log['tool_call']['tool_name']}"},
|
||||
content=str(content),
|
||||
)
|
||||
if step_log.get("observation"):
|
||||
yield ChatMessage(role="assistant", content=f"```\n{step_log['observation']}\n```")
|
||||
if step_log.get("error"):
|
||||
yield ChatMessage(
|
||||
role="assistant",
|
||||
content=str(step_log["error"]),
|
||||
metadata={"title": "💥 Error"},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def stream_to_gradio(agent, task: str, test_mode: bool = False, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""Runs an agent with the given task and streams the messages from the agent as gradio ChatMessages."""
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from gradio import ChatMessage
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
if test_mode:
|
||||
|
||||
class ChatMessage:
|
||||
def __init__(self, role, content, metadata=None):
|
||||
self.role = role
|
||||
self.content = content
|
||||
self.metadata = metadata
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ImportError("Gradio should be installed in order to launch a gradio demo.")
|
||||
|
||||
for step_log in agent.run(task, stream=True, **kwargs):
|
||||
if isinstance(step_log, dict):
|
||||
for message in pull_message(step_log, test_mode=test_mode):
|
||||
yield message
|
||||
|
||||
final_answer = step_log # Last log is the run's final_answer
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(final_answer, AgentText):
|
||||
yield ChatMessage(role="assistant", content=f"**Final answer:**\n```\n{final_answer.to_string()}\n```")
|
||||
elif isinstance(final_answer, AgentImage):
|
||||
yield ChatMessage(
|
||||
role="assistant",
|
||||
content={"path": final_answer.to_string(), "mime_type": "image/png"},
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif isinstance(final_answer, AgentAudio):
|
||||
yield ChatMessage(
|
||||
role="assistant",
|
||||
content={"path": final_answer.to_string(), "mime_type": "audio/wav"},
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
yield ChatMessage(role="assistant", content=str(final_answer))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Monitor:
|
||||
def __init__(self, tracked_llm_engine):
|
||||
self.step_durations = []
|
||||
self.tracked_llm_engine = tracked_llm_engine
|
||||
if getattr(self.tracked_llm_engine, "last_input_token_count", "Not found") != "Not found":
|
||||
self.total_input_token_count = 0
|
||||
self.total_output_token_count = 0
|
||||
|
||||
def update_metrics(self, step_log):
|
||||
step_duration = step_log["step_duration"]
|
||||
self.step_durations.append(step_duration)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Step {len(self.step_durations)}:")
|
||||
logger.info(f"- Time taken: {step_duration:.2f} seconds (valid only if step succeeded)")
|
||||
|
||||
if getattr(self.tracked_llm_engine, "last_input_token_count", None) is not None:
|
||||
self.total_input_token_count += self.tracked_llm_engine.last_input_token_count
|
||||
self.total_output_token_count += self.tracked_llm_engine.last_output_token_count
|
||||
logger.info(f"- Input tokens: {self.total_input_token_count}")
|
||||
logger.info(f"- Output tokens: {self.total_output_token_count}")
|
||||
@ -1,789 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import re
|
||||
|
||||
from ..utils import cached_file
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# docstyle-ignore
|
||||
CHAT_MESSAGE_PROMPT = """
|
||||
Human: <<task>>
|
||||
|
||||
Assistant: """
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
DEFAULT_PROMPTS_REPO = "huggingface-tools/default-prompts"
|
||||
PROMPT_FILES = {"chat": "chat_prompt_template.txt", "run": "run_prompt_template.txt"}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def download_prompt(prompt_or_repo_id, agent_name, mode="run"):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Downloads and caches the prompt from a repo and returns it contents (if necessary).
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if prompt_or_repo_id is None:
|
||||
prompt_or_repo_id = DEFAULT_PROMPTS_REPO
|
||||
|
||||
# prompt is considered a repo ID when it does not contain any kind of space
|
||||
if re.search("\\s", prompt_or_repo_id) is not None:
|
||||
return prompt_or_repo_id
|
||||
|
||||
prompt_file = cached_file(
|
||||
prompt_or_repo_id, PROMPT_FILES[mode], repo_type="dataset", user_agent={"agent": agent_name}
|
||||
)
|
||||
with open(prompt_file, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
|
||||
return f.read()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
DEFAULT_CODE_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """You will be given a task to solve, your job is to come up with a series of simple commands in Python that will perform the task.
|
||||
To help you, I will give you access to a set of tools that you can use. Each tool is a Python function and has a description explaining the task it performs, the inputs it expects and the outputs it returns.
|
||||
You should first explain which tool you will use to perform the task and for what reason, then write the code in Python.
|
||||
Each instruction in Python should be a simple assignment. You can print intermediate results if it makes sense to do so.
|
||||
In the end, use tool 'final_answer' to return your answer, its argument will be what gets returned.
|
||||
You can use imports in your code, but only from the following list of modules: <<authorized_imports>>
|
||||
Be sure to provide a 'Code:' token, else the run will fail.
|
||||
|
||||
Tools:
|
||||
<<tool_descriptions>>
|
||||
|
||||
Examples:
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task: "Answer the question in the variable `question` about the image stored in the variable `image`. The question is in French."
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I will use the following tools: `translator` to translate the question into English and then `image_qa` to answer the question on the input image.
|
||||
Code:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
translated_question = translator(question=question, src_lang="French", tgt_lang="English")
|
||||
print(f"The translated question is {translated_question}.")
|
||||
answer = image_qa(image=image, question=translated_question)
|
||||
final_answer(f"The answer is {answer}")
|
||||
```<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task: "Identify the oldest person in the `document` and create an image showcasing the result."
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I will use the following tools: `document_qa` to find the oldest person in the document, then `image_generator` to generate an image according to the answer.
|
||||
Code:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
answer = document_qa(document, question="What is the oldest person?")
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator(answer)
|
||||
final_answer(image)
|
||||
```<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task: "Generate an image using the text given in the variable `caption`."
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I will use the following tool: `image_generator` to generate an image.
|
||||
Code:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt=caption)
|
||||
final_answer(image)
|
||||
```<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task: "Summarize the text given in the variable `text` and read it out loud."
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I will use the following tools: `summarizer` to create a summary of the input text, then `text_reader` to read it out loud.
|
||||
Code:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
summarized_text = summarizer(text)
|
||||
print(f"Summary: {summarized_text}")
|
||||
audio_summary = text_reader(summarized_text)
|
||||
final_answer(audio_summary)
|
||||
```<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task: "Answer the question in the variable `question` about the text in the variable `text`. Use the answer to generate an image."
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I will use the following tools: `text_qa` to create the answer, then `image_generator` to generate an image according to the answer.
|
||||
Code:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
answer = text_qa(text=text, question=question)
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator(answer)
|
||||
final_answer(image)
|
||||
```<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task: "Caption the following `image`."
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I will use the following tool: `image_captioner` to generate a caption for the image.
|
||||
Code:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
caption = image_captioner(image)
|
||||
final_answer(caption)
|
||||
```<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
Above example were using tools that might not exist for you. You only have access to these Tools:
|
||||
<<tool_names>>
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to make sure that variables you use are all defined.
|
||||
Be sure to provide a 'Code:\n```' sequence before the code and '```<end_action>' after, else you will get an error.
|
||||
DO NOT pass the arguments as a dict as in 'answer = ask_search_agent({'query': "What is the place where James Bond lives?"})', but use the arguments directly as in 'answer = ask_search_agent(query="What is the place where James Bond lives?")'.
|
||||
|
||||
Now Begin! If you solve the task correctly, you will receive a reward of $1,000,000.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
DEFAULT_REACT_JSON_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """You are an expert assistant who can solve any task using JSON tool calls. You will be given a task to solve as best you can.
|
||||
To do so, you have been given access to the following tools: <<tool_names>>
|
||||
The way you use the tools is by specifying a json blob, ending with '<end_action>'.
|
||||
Specifically, this json should have an `action` key (name of the tool to use) and an `action_input` key (input to the tool).
|
||||
|
||||
The $ACTION_JSON_BLOB should only contain a SINGLE action, do NOT return a list of multiple actions. It should be formatted in json. Do not try to escape special characters. Here is the template of a valid $ACTION_JSON_BLOB:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": $TOOL_NAME,
|
||||
"action_input": $INPUT
|
||||
}<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to have the $INPUT as a dictionary in the right format for the tool you are using, and do not put variable names as input if you can find the right values.
|
||||
|
||||
You should ALWAYS use the following format:
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: you should always think about one action to take. Then use the action as follows:
|
||||
Action:
|
||||
$ACTION_JSON_BLOB
|
||||
Observation: the result of the action
|
||||
... (this Thought/Action/Observation can repeat N times, you should take several steps when needed. The $ACTION_JSON_BLOB must only use a SINGLE action at a time.)
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the result of the previous action as input for the next action.
|
||||
The observation will always be a string: it can represent a file, like "image_1.jpg".
|
||||
Then you can use it as input for the next action. You can do it for instance as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
Observation: "image_1.jpg"
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I need to transform the image that I received in the previous observation to make it green.
|
||||
Action:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": "image_transformer",
|
||||
"action_input": {"image": "image_1.jpg"}
|
||||
}<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
To provide the final answer to the task, use an action blob with "action": "final_answer" tool. It is the only way to complete the task, else you will be stuck on a loop. So your final output should look like this:
|
||||
Action:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": "final_answer",
|
||||
"action_input": {"answer": "insert your final answer here"}
|
||||
}<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few examples using notional tools:
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task: "Generate an image of the oldest person in this document."
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I will proceed step by step and use the following tools: `document_qa` to find the oldest person in the document, then `image_generator` to generate an image according to the answer.
|
||||
Action:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": "document_qa",
|
||||
"action_input": {"document": "document.pdf", "question": "Who is the oldest person mentioned?"}
|
||||
}<end_action>
|
||||
Observation: "The oldest person in the document is John Doe, a 55 year old lumberjack living in Newfoundland."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I will now generate an image showcasing the oldest person.
|
||||
Action:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": "image_generator",
|
||||
"action_input": {"prompt": "A portrait of John Doe, a 55-year-old man living in Canada."}
|
||||
}<end_action>
|
||||
Observation: "image.png"
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I will now return the generated image.
|
||||
Action:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": "final_answer",
|
||||
"action_input": "image.png"
|
||||
}<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task: "What is the result of the following operation: 5 + 3 + 1294.678?"
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I will use python code evaluator to compute the result of the operation and then return the final answer using the `final_answer` tool
|
||||
Action:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": "python_interpreter",
|
||||
"action_input": {"code": "5 + 3 + 1294.678"}
|
||||
}<end_action>
|
||||
Observation: 1302.678
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: Now that I know the result, I will now return it.
|
||||
Action:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": "final_answer",
|
||||
"action_input": "1302.678"
|
||||
}<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task: "Which city has the highest population , Guangzhou or Shanghai?"
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I need to get the populations for both cities and compare them: I will use the tool `search` to get the population of both cities.
|
||||
Action:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": "search",
|
||||
"action_input": "Population Guangzhou"
|
||||
}<end_action>
|
||||
Observation: ['Guangzhou has a population of 15 million inhabitants as of 2021.']
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: Now let's get the population of Shanghai using the tool 'search'.
|
||||
Action:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": "search",
|
||||
"action_input": "Population Shanghai"
|
||||
}
|
||||
Observation: '26 million (2019)'
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: Now I know that Shanghai has a larger population. Let's return the result.
|
||||
Action:
|
||||
{
|
||||
"action": "final_answer",
|
||||
"action_input": "Shanghai"
|
||||
}<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Above example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. You only have access to these tools:
|
||||
<<tool_descriptions>>
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the rules you should always follow to solve your task:
|
||||
1. ALWAYS provide a 'Thought:' sequence, and an 'Action:' sequence that ends with <end_action>, else you will fail.
|
||||
2. Always use the right arguments for the tools. Never use variable names in the 'action_input' field, use the value instead.
|
||||
3. Call a tool only when needed: do not call the search agent if you do not need information, try to solve the task yourself.
|
||||
4. Never re-do a tool call that you previously did with the exact same parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
Now Begin! If you solve the task correctly, you will receive a reward of $1,000,000.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
DEFAULT_REACT_CODE_SYSTEM_PROMPT = """You are an expert assistant who can solve any task using code blobs. You will be given a task to solve as best you can.
|
||||
To do so, you have been given access to a list of tools: these tools are basically Python functions which you can call with code.
|
||||
To solve the task, you must plan forward to proceed in a series of steps, in a cycle of 'Thought:', 'Code:', and 'Observation:' sequences.
|
||||
|
||||
At each step, in the 'Thought:' sequence, you should first explain your reasoning towards solving the task and the tools that you want to use.
|
||||
Then in the 'Code:' sequence, you should write the code in simple Python. The code sequence must end with '<end_action>' sequence.
|
||||
During each intermediate step, you can use 'print()' to save whatever important information you will then need.
|
||||
These print outputs will then appear in the 'Observation:' field, which will be available as input for the next step.
|
||||
In the end you have to return a final answer using the `final_answer` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few examples using notional tools:
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task: "Generate an image of the oldest person in this document."
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I will proceed step by step and use the following tools: `document_qa` to find the oldest person in the document, then `image_generator` to generate an image according to the answer.
|
||||
Code:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
answer = document_qa(document=document, question="Who is the oldest person mentioned?")
|
||||
print(answer)
|
||||
```<end_action>
|
||||
Observation: "The oldest person in the document is John Doe, a 55 year old lumberjack living in Newfoundland."
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I will now generate an image showcasing the oldest person.
|
||||
Code:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = image_generator("A portrait of John Doe, a 55-year-old man living in Canada.")
|
||||
final_answer(image)
|
||||
```<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task: "What is the result of the following operation: 5 + 3 + 1294.678?"
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I will use python code to compute the result of the operation and then return the final answer using the `final_answer` tool
|
||||
Code:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
result = 5 + 3 + 1294.678
|
||||
final_answer(result)
|
||||
```<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task: "Which city has the highest population: Guangzhou or Shanghai?"
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I need to get the populations for both cities and compare them: I will use the tool `search` to get the population of both cities.
|
||||
Code:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
population_guangzhou = search("Guangzhou population")
|
||||
print("Population Guangzhou:", population_guangzhou)
|
||||
population_shanghai = search("Shanghai population")
|
||||
print("Population Shanghai:", population_shanghai)
|
||||
```<end_action>
|
||||
Observation:
|
||||
Population Guangzhou: ['Guangzhou has a population of 15 million inhabitants as of 2021.']
|
||||
Population Shanghai: '26 million (2019)'
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: Now I know that Shanghai has the highest population.
|
||||
Code:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
final_answer("Shanghai")
|
||||
```<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task: "What is the current age of the pope, raised to the power 0.36?"
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I will use the tool `wiki` to get the age of the pope, then raise it to the power 0.36.
|
||||
Code:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pope_age = wiki(query="current pope age")
|
||||
print("Pope age:", pope_age)
|
||||
```<end_action>
|
||||
Observation:
|
||||
Pope age: "The pope Francis is currently 85 years old."
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I know that the pope is 85 years old. Let's compute the result using python code.
|
||||
Code:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pope_current_age = 85 ** 0.36
|
||||
final_answer(pope_current_age)
|
||||
```<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
Above example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. On top of performing computations in the Python code snippets that you create, you have access to these tools (and no other tool):
|
||||
|
||||
<<tool_descriptions>>
|
||||
|
||||
<<managed_agents_descriptions>>
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the rules you should always follow to solve your task:
|
||||
1. Always provide a 'Thought:' sequence, and a 'Code:\n```py' sequence ending with '```<end_action>' sequence, else you will fail.
|
||||
2. Use only variables that you have defined!
|
||||
3. Always use the right arguments for the tools. DO NOT pass the arguments as a dict as in 'answer = wiki({'query': "What is the place where James Bond lives?"})', but use the arguments directly as in 'answer = wiki(query="What is the place where James Bond lives?")'.
|
||||
4. Take care to not chain too many sequential tool calls in the same code block, especially when the output format is unpredictable. For instance, a call to search has an unpredictable return format, so do not have another tool call that depends on its output in the same block: rather output results with print() to use them in the next block.
|
||||
5. Call a tool only when needed, and never re-do a tool call that you previously did with the exact same parameters.
|
||||
6. Don't name any new variable with the same name as a tool: for instance don't name a variable 'final_answer'.
|
||||
7. Never create any notional variables in our code, as having these in your logs might derail you from the true variables.
|
||||
8. You can use imports in your code, but only from the following list of modules: <<authorized_imports>>
|
||||
9. The state persists between code executions: so if in one step you've created variables or imported modules, these will all persist.
|
||||
10. Don't give up! You're in charge of solving the task, not providing directions to solve it.
|
||||
|
||||
Now Begin! If you solve the task correctly, you will receive a reward of $1,000,000.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
SYSTEM_PROMPT_FACTS = """Below I will present you a task.
|
||||
|
||||
You will now build a comprehensive preparatory survey of which facts we have at our disposal and which ones we still need.
|
||||
To do so, you will have to read the task and identify things that must be discovered in order to successfully complete it.
|
||||
Don't make any assumptions. For each item, provide a thorough reasoning. Here is how you will structure this survey:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
### 1. Facts given in the task
|
||||
List here the specific facts given in the task that could help you (there might be nothing here).
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Facts to look up
|
||||
List here any facts that we may need to look up.
|
||||
Also list where to find each of these, for instance a website, a file... - maybe the task contains some sources that you should re-use here.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Facts to derive
|
||||
List here anything that we want to derive from the above by logical reasoning, for instance computation or simulation.
|
||||
|
||||
Keep in mind that "facts" will typically be specific names, dates, values, etc. Your answer should use the below headings:
|
||||
### 1. Facts given in the task
|
||||
### 2. Facts to look up
|
||||
### 3. Facts to derive
|
||||
Do not add anything else."""
|
||||
|
||||
SYSTEM_PROMPT_PLAN = """You are a world expert at making efficient plans to solve any task using a set of carefully crafted tools.
|
||||
|
||||
Now for the given task, develop a step-by-step high-level plan taking into account the above inputs and list of facts.
|
||||
This plan should involve individual tasks based on the available tools, that if executed correctly will yield the correct answer.
|
||||
Do not skip steps, do not add any superfluous steps. Only write the high-level plan, DO NOT DETAIL INDIVIDUAL TOOL CALLS.
|
||||
After writing the final step of the plan, write the '\n<end_plan>' tag and stop there."""
|
||||
|
||||
USER_PROMPT_PLAN = """
|
||||
Here is your task:
|
||||
|
||||
Task:
|
||||
```
|
||||
{task}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Your plan can leverage any of these tools:
|
||||
{tool_descriptions}
|
||||
|
||||
{managed_agents_descriptions}
|
||||
|
||||
List of facts that you know:
|
||||
```
|
||||
{answer_facts}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now begin! Write your plan below."""
|
||||
|
||||
SYSTEM_PROMPT_FACTS_UPDATE = """
|
||||
You are a world expert at gathering known and unknown facts based on a conversation.
|
||||
Below you will find a task, and ahistory of attempts made to solve the task. You will have to produce a list of these:
|
||||
### 1. Facts given in the task
|
||||
### 2. Facts that we have learned
|
||||
### 3. Facts still to look up
|
||||
### 4. Facts still to derive
|
||||
Find the task and history below."""
|
||||
|
||||
USER_PROMPT_FACTS_UPDATE = """Earlier we've built a list of facts.
|
||||
But since in your previous steps you may have learned useful new facts or invalidated some false ones.
|
||||
Please update your list of facts based on the previous history, and provide these headings:
|
||||
### 1. Facts given in the task
|
||||
### 2. Facts that we have learned
|
||||
### 3. Facts still to look up
|
||||
### 4. Facts still to derive
|
||||
|
||||
Now write your new list of facts below."""
|
||||
|
||||
SYSTEM_PROMPT_PLAN_UPDATE = """You are a world expert at making efficient plans to solve any task using a set of carefully crafted tools.
|
||||
|
||||
You have been given a task:
|
||||
```
|
||||
{task}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Find below the record of what has been tried so far to solve it. Then you will be asked to make an updated plan to solve the task.
|
||||
If the previous tries so far have met some success, you can make an updated plan based on these actions.
|
||||
If you are stalled, you can make a completely new plan starting from scratch.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
USER_PROMPT_PLAN_UPDATE = """You're still working towards solving this task:
|
||||
```
|
||||
{task}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You have access to these tools and only these:
|
||||
{tool_descriptions}
|
||||
|
||||
{managed_agents_descriptions}
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the up to date list of facts that you know:
|
||||
```
|
||||
{facts_update}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now for the given task, develop a step-by-step high-level plan taking into account the above inputs and list of facts.
|
||||
This plan should involve individual tasks based on the available tools, that if executed correctly will yield the correct answer.
|
||||
Beware that you have {remaining_steps} steps remaining.
|
||||
Do not skip steps, do not add any superfluous steps. Only write the high-level plan, DO NOT DETAIL INDIVIDUAL TOOL CALLS.
|
||||
After writing the final step of the plan, write the '\n<end_plan>' tag and stop there.
|
||||
|
||||
Now write your new plan below."""
|
||||
|
||||
SYSTEM_PROMPT_PLAN_STRUCTURED = """Output a step-by-step plan to solve the task using the given tools.
|
||||
This plan should involve individual tasks based on the available tools, that if executed correctly will yield the correct answer. Each step should be structured as follows:
|
||||
Step #n: {
|
||||
"description": <description of what the step does and its output>
|
||||
"tool": <tool to use>,
|
||||
"params": {
|
||||
<parameters to pass to the tool as a valid dict>
|
||||
}
|
||||
"output_var": <output variable name>
|
||||
}
|
||||
Each step must be necessary to reach the final answer. Steps should reuse outputs produced by earlier steps. The last step must be the final answer.
|
||||
|
||||
Below are some examples:
|
||||
|
||||
Example 1:
|
||||
------
|
||||
Inputs:
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task:
|
||||
How many encoder blocks were in the first attention-only ML architecture published?
|
||||
|
||||
[FACTS LIST]:
|
||||
### 1. Facts given in the task
|
||||
- The paper first introduced an attention-only ML architecture.
|
||||
- The specific information required is the page number where the number of encoder blocks is stated.
|
||||
- No local files are provided for access.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Facts to look up
|
||||
- The title and authors of the paper that first introduced an attention-only ML architecture.
|
||||
- Source: Online search (e.g., Google Scholar, arXiv, or other academic databases)
|
||||
- The full text of the identified paper.
|
||||
- Source: Online academic repositories (e.g., arXiv, journal websites)
|
||||
- The specific page number in the paper where the number of encoder blocks is mentioned.
|
||||
- Source: The content of the identified paper
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Facts to derive
|
||||
- By identifying the correct paper and locating the specific page, we will derive the page number where the number of encoder blocks is stated.
|
||||
- Logical steps: Identify the correct paper, access its content, search for the term "encoder blocks," and note the page number where this information is found.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[STEP 1 TOOL CALL]: {'tool_name': 'code interpreter', 'tool_arguments': '# Step 1: Identify the title and authors of the paper that first introduced an attention-only ML architecture.\nanswer = ask_search_agent(query="Can you find the title and authors of the paper that first introduced an attention-only machine learning architecture? Please provide the full citation.")\nprint(answer)'}
|
||||
[OUTPUT OF STEP 1] Observation: **Title**: Attention Is All You Need
|
||||
**Authors**: Ashish Vaswani, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N. Gomez, Lukasz Kaiser, Illia Polosukhin
|
||||
[STEP 2 TOOL CALL]: {'tool_name': 'code interpreter', 'tool_arguments': '# Step 1: Find the full text of the identified paper on arXiv\\npaper_url = "https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762.pdf"\\nprint(paper_url)'}
|
||||
[OUTPUT OF STEP 2] Observation: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762.pdf
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Output plan:
|
||||
---
|
||||
Step #1: {
|
||||
"description": "Open the PDF of the paper from the provided URL and search within the text of the paper for the mention of "encoder blocks"",
|
||||
"tool": "inspect_file_as_text",
|
||||
"params": {
|
||||
"file_path": "https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762.pdf",
|
||||
"question": "On which page is the number of encoder blocks mentioned?"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"output_var": "page_number"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Step #2: {
|
||||
"description": "Provide the final answer",
|
||||
"tool": "final_answer",
|
||||
"params": {
|
||||
"answer": "{page_number}"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"output_var": ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
------
|
||||
|
||||
Example 2:
|
||||
------
|
||||
Inputs:
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task:
|
||||
How many golf balls fits into a Boeing-747?
|
||||
|
||||
[FACTS LIST]:
|
||||
### 1. Facts given in the task
|
||||
- The task requires calculating the number of golf balls that fir into a Boeing-747
|
||||
### 2. Facts to look up
|
||||
- The volume of a golf ball
|
||||
- The volume of a Boeing-747
|
||||
### 3. Facts to derive
|
||||
- Once the volumes are known the final answer can be calculated
|
||||
---
|
||||
Output plan:
|
||||
---
|
||||
Step #1: {
|
||||
"description": "Find the volume of a Boeing-747",
|
||||
"tool": "web_search",
|
||||
"params": {
|
||||
"query": "What is the internal volume of a Boeing-747 in cubic meters?"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"output_var": "boeing_volume"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Step #2: {
|
||||
"description": "Find the volume of a standard golf ball",
|
||||
"tool": "ask_search_agent",
|
||||
"params": {
|
||||
"query": "What is the volume of a standard golf ball in cubic centimeters?"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"output_var": "golf_ball_volume"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Step #3: {
|
||||
"description": "Convert the volume of a golf ball from cubic centimeters to cubic meters. Calculate the number of golf balls that fit into the Boeing-747 by dividing the internal volume of the Boeing-747 by the volume of a golf ball.",
|
||||
"tool": "python_code",
|
||||
"params": {
|
||||
"code": "golf_ball_volume_m3 = golf_ball_volume / 1e6\nnumber_of_golf_balls = boeing_volume / golf_ball_volume_m3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"output_var": "number_of_golf_balls"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Step #4: {
|
||||
"description": "Provide the final answer",
|
||||
"tool": "final_answer",
|
||||
"params": {
|
||||
"answer": "{number_of_golf_balls}"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"output_var": ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
------
|
||||
Above example were using tools that might not exist for you.
|
||||
Your goal is to create a plan to solve the task."""
|
||||
|
||||
USER_PROMPT_PLAN_STRUCTURED = """
|
||||
Here are your inputs:
|
||||
|
||||
Task:
|
||||
```
|
||||
{task}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Your plan can leverage any of these tools:
|
||||
{tool_descriptions}
|
||||
These tools are Python functions which you can call with code. You also have access to a Python interpreter so you can run Python code.
|
||||
|
||||
List of facts that you know:
|
||||
```
|
||||
{answer_facts}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now for the given task, create a plan taking into account the list of facts.
|
||||
After writing the final step of the plan, write the '\n<end_plan>' tag and stop there. Output the plan only and nothing else."""
|
||||
|
||||
SYSTEM_PROMPT_PLAN_UPDATE_STRUCTURED = """Output a step-by-step plan to solve the task using the given tools.
|
||||
This plan should involve individual tasks based on the available tools, that if executed correctly will yield the correct answer. Each step should be structured as follows:
|
||||
Step #n: {{
|
||||
"description": <description of what the step does and its output>
|
||||
"tool": <tool to use>,
|
||||
"params": {{
|
||||
<parameters to pass to the tool as a valid dict>
|
||||
}}
|
||||
"output_var": <output variable name>
|
||||
}}
|
||||
Each step must be necessary to reach the final answer. Steps should reuse outputs produced by earlier steps. The last step must be the final answer.
|
||||
|
||||
Below are some examples:
|
||||
|
||||
Example 1:
|
||||
------
|
||||
Inputs:
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task:
|
||||
How many encoder blocks were in the first attention-only ML architecture published?
|
||||
|
||||
[FACTS LIST]:
|
||||
### 1. Facts given in the task
|
||||
- The paper first introduced an attention-only ML architecture.
|
||||
- The specific information required is the page number where the number of encoder blocks is stated.
|
||||
- No local files are provided for access.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Facts to look up
|
||||
- The title and authors of the paper that first introduced an attention-only ML architecture.
|
||||
- Source: Online search (e.g., Google Scholar, arXiv, or other academic databases)
|
||||
- The full text of the identified paper.
|
||||
- Source: Online academic repositories (e.g., arXiv, journal websites)
|
||||
- The specific page number in the paper where the number of encoder blocks is mentioned.
|
||||
- Source: The content of the identified paper
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Facts to derive
|
||||
- By identifying the correct paper and locating the specific page, we will derive the page number where the number of encoder blocks is stated.
|
||||
- Logical steps: Identify the correct paper, access its content, search for the term "encoder blocks," and note the page number where this information is found.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[STEP 1 TOOL CALL]: {{'tool_name': 'code interpreter', 'tool_arguments': '# Step 1: Identify the title and authors of the paper that first introduced an attention-only ML architecture.\nanswer = ask_search_agent(query="Can you find the title and authors of the paper that first introduced an attention-only machine learning architecture? Please provide the full citation.")\nprint(answer)'}}
|
||||
[OUTPUT OF STEP 1] Observation: **Title**: Attention Is All You Need
|
||||
**Authors**: Ashish Vaswani, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N. Gomez, Lukasz Kaiser, Illia Polosukhin
|
||||
[STEP 2 TOOL CALL]: {{'tool_name': 'code interpreter', 'tool_arguments': '# Step 1: Find the full text of the identified paper on arXiv\\npaper_url = "https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762.pdf"\\nprint(paper_url)'}}
|
||||
[OUTPUT OF STEP 2] Observation: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762.pdf
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
Output plan:
|
||||
---
|
||||
Step #1: {{
|
||||
"description": "Open the PDF of the paper from the provided URL and search within the text of the paper for the mention of "encoder blocks"",
|
||||
"tool": "inspect_file_as_text",
|
||||
"params": {{
|
||||
"file_path": "https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762.pdf",
|
||||
"question": "On which page is the number of encoder blocks mentioned?"
|
||||
}},
|
||||
"output_var": "page_number"
|
||||
}}
|
||||
|
||||
Step #2: {{
|
||||
"description": "Provide the final answer",
|
||||
"tool": "final_answer",
|
||||
"params": {{
|
||||
"answer": "{{page_number}}"
|
||||
}},
|
||||
"output_var": ""
|
||||
}}
|
||||
------
|
||||
|
||||
Example 2:
|
||||
------
|
||||
Inputs:
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task:
|
||||
How many golf balls fits into a Boeing-747?
|
||||
|
||||
[FACTS LIST]:
|
||||
### 1. Facts given in the task
|
||||
- The task requires calculating the number of golf balls that fir into a Boeing-747
|
||||
### 2. Facts to look up
|
||||
- The volume of a golf ball
|
||||
- The volume of a Boeing-747
|
||||
### 3. Facts to derive
|
||||
- Once the volumes are known the final answer can be calculated
|
||||
---
|
||||
Output plan:
|
||||
---
|
||||
Step #1: {{
|
||||
"description": "Find the volume of a Boeing-747",
|
||||
"tool": "web_search",
|
||||
"params": {{
|
||||
"query": "What is the internal volume of a Boeing-747 in cubic meters?"
|
||||
}},
|
||||
"output_var": "boeing_volume"
|
||||
}}
|
||||
|
||||
Step #2: {{
|
||||
"description": "Find the volume of a standard golf ball",
|
||||
"tool": "ask_search_agent",
|
||||
"params": {{
|
||||
"query": "What is the volume of a standard golf ball in cubic centimeters?"
|
||||
}},
|
||||
"output_var": "golf_ball_volume"
|
||||
}}
|
||||
|
||||
Step #3: {{
|
||||
"description": "Convert the volume of a golf ball from cubic centimeters to cubic meters. Calculate the number of golf balls that fit into the Boeing-747 by dividing the internal volume of the Boeing-747 by the volume of a golf ball.",
|
||||
"tool": "python_code",
|
||||
"params": {{
|
||||
"code": "golf_ball_volume_m3 = golf_ball_volume / 1e6\nnumber_of_golf_balls = boeing_volume / golf_ball_volume_m3"
|
||||
}},
|
||||
"output_var": "number_of_golf_balls"
|
||||
}}
|
||||
|
||||
Step #4: {{
|
||||
"description": "Provide the final answer",
|
||||
"tool": "final_answer",
|
||||
"params": {{
|
||||
"answer": "{{number_of_golf_balls}}"
|
||||
}},
|
||||
"output_var": ""
|
||||
}}
|
||||
------
|
||||
Above example were using tools that might not exist for you.
|
||||
Find below the record of what has been tried so far to solve it. Your goal is to create an updated plan to solve the task."""
|
||||
|
||||
USER_PROMPT_PLAN_UPDATE_STRUCTURED = """
|
||||
Here are your inputs:
|
||||
|
||||
Task:
|
||||
```
|
||||
{task}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Your plan can leverage any of these tools:
|
||||
{tool_descriptions}
|
||||
These tools are Python functions which you can call with code. You also have access to a Python interpreter so you can run Python code.
|
||||
|
||||
List of facts that you know:
|
||||
```
|
||||
{facts_update}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now for the given task, create a plan taking into account the above inputs and list of facts.
|
||||
Beware that you have {remaining_steps} steps remaining.
|
||||
After writing the final step of the plan, write the '\n<end_plan>' tag and stop there. Output the plan only and nothing else."""
|
||||
|
||||
PLAN_UPDATE_FINAL_PLAN_REDACTION = """I still need to solve the task I was given:
|
||||
```
|
||||
{task}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here is my new/updated plan of action to solve the task:
|
||||
```
|
||||
{plan_update}
|
||||
```"""
|
||||
|
||||
SUPPORTED_PLAN_TYPES = ["default", "structured"]
|
||||
|
||||
PROMPTS_FOR_INITIAL_PLAN = {
|
||||
"default": {"system": SYSTEM_PROMPT_PLAN, "user": USER_PROMPT_PLAN},
|
||||
"structured": {"system": SYSTEM_PROMPT_PLAN_STRUCTURED, "user": USER_PROMPT_PLAN_STRUCTURED},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
PROMPTS_FOR_PLAN_UPDATE = {
|
||||
"default": {"system": SYSTEM_PROMPT_PLAN_UPDATE, "user": USER_PROMPT_PLAN_UPDATE},
|
||||
"structured": {"system": SYSTEM_PROMPT_PLAN_UPDATE_STRUCTURED, "user": USER_PROMPT_PLAN_UPDATE_STRUCTURED},
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -1,908 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import ast
|
||||
import builtins
|
||||
import difflib
|
||||
from collections.abc import Mapping
|
||||
from importlib import import_module
|
||||
from typing import Any, Callable, Dict, List, Optional
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from ..utils import is_pandas_available
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_pandas_available():
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class InterpreterError(ValueError):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
An error raised when the interpreter cannot evaluate a Python expression, due to syntax error or unsupported
|
||||
operations.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ERRORS = {
|
||||
name: getattr(builtins, name)
|
||||
for name in dir(builtins)
|
||||
if isinstance(getattr(builtins, name), type) and issubclass(getattr(builtins, name), BaseException)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
LIST_SAFE_MODULES = [
|
||||
"random",
|
||||
"collections",
|
||||
"math",
|
||||
"time",
|
||||
"queue",
|
||||
"itertools",
|
||||
"re",
|
||||
"stat",
|
||||
"statistics",
|
||||
"unicodedata",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
PRINT_OUTPUTS, MAX_LEN_OUTPUT = "", 50000
|
||||
OPERATIONS_COUNT, MAX_OPERATIONS = 0, 10000000
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class BreakException(Exception):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ContinueException(Exception):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ReturnException(Exception):
|
||||
def __init__(self, value):
|
||||
self.value = value
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_iterable(obj):
|
||||
if isinstance(obj, list):
|
||||
return obj
|
||||
elif hasattr(obj, "__iter__"):
|
||||
return list(obj)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError("Object is not iterable")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_unaryop(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
operand = evaluate_ast(expression.operand, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
if isinstance(expression.op, ast.USub):
|
||||
return -operand
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression.op, ast.UAdd):
|
||||
return operand
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression.op, ast.Not):
|
||||
return not operand
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression.op, ast.Invert):
|
||||
return ~operand
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"Unary operation {expression.op.__class__.__name__} is not supported.")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_lambda(lambda_expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
args = [arg.arg for arg in lambda_expression.args.args]
|
||||
|
||||
def lambda_func(*values):
|
||||
new_state = state.copy()
|
||||
for arg, value in zip(args, values):
|
||||
new_state[arg] = value
|
||||
return evaluate_ast(lambda_expression.body, new_state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
|
||||
return lambda_func
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_while(while_loop, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
max_iterations = 1000
|
||||
iterations = 0
|
||||
while evaluate_ast(while_loop.test, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
for node in while_loop.body:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
evaluate_ast(node, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
except BreakException:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
except ContinueException:
|
||||
break
|
||||
iterations += 1
|
||||
if iterations > max_iterations:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"Maximum number of {max_iterations} iterations in While loop exceeded")
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def create_function(func_def, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
def new_func(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
func_state = state.copy()
|
||||
arg_names = [arg.arg for arg in func_def.args.args]
|
||||
default_values = [evaluate_ast(d, state, static_tools, custom_tools) for d in func_def.args.defaults]
|
||||
|
||||
# Apply default values
|
||||
defaults = dict(zip(arg_names[-len(default_values) :], default_values))
|
||||
|
||||
# Set positional arguments
|
||||
for name, value in zip(arg_names, args):
|
||||
func_state[name] = value
|
||||
|
||||
# # Set keyword arguments
|
||||
for name, value in kwargs.items():
|
||||
func_state[name] = value
|
||||
|
||||
# Handle variable arguments
|
||||
if func_def.args.vararg:
|
||||
vararg_name = func_def.args.vararg.arg
|
||||
func_state[vararg_name] = args
|
||||
|
||||
if func_def.args.kwarg:
|
||||
kwarg_name = func_def.args.kwarg.arg
|
||||
func_state[kwarg_name] = kwargs
|
||||
|
||||
# Set default values for arguments that were not provided
|
||||
for name, value in defaults.items():
|
||||
if name not in func_state:
|
||||
func_state[name] = value
|
||||
|
||||
# Update function state with self and __class__
|
||||
if func_def.args.args and func_def.args.args[0].arg == "self":
|
||||
if args:
|
||||
func_state["self"] = args[0]
|
||||
func_state["__class__"] = args[0].__class__
|
||||
|
||||
result = None
|
||||
try:
|
||||
for stmt in func_def.body:
|
||||
result = evaluate_ast(stmt, func_state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
except ReturnException as e:
|
||||
result = e.value
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
return new_func
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def create_class(class_name, class_bases, class_body):
|
||||
class_dict = {}
|
||||
for key, value in class_body.items():
|
||||
class_dict[key] = value
|
||||
return type(class_name, tuple(class_bases), class_dict)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_function_def(func_def, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
custom_tools[func_def.name] = create_function(func_def, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
return custom_tools[func_def.name]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_class_def(class_def, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
class_name = class_def.name
|
||||
bases = [evaluate_ast(base, state, static_tools, custom_tools) for base in class_def.bases]
|
||||
class_dict = {}
|
||||
|
||||
for stmt in class_def.body:
|
||||
if isinstance(stmt, ast.FunctionDef):
|
||||
class_dict[stmt.name] = evaluate_function_def(stmt, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(stmt, ast.Assign):
|
||||
for target in stmt.targets:
|
||||
if isinstance(target, ast.Name):
|
||||
class_dict[target.id] = evaluate_ast(stmt.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(target, ast.Attribute):
|
||||
class_dict[target.attr] = evaluate_ast(stmt.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"Unsupported statement in class body: {stmt.__class__.__name__}")
|
||||
|
||||
new_class = type(class_name, tuple(bases), class_dict)
|
||||
state[class_name] = new_class
|
||||
return new_class
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_augassign(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
# Helper function to get current value and set new value based on the target type
|
||||
def get_current_value(target):
|
||||
if isinstance(target, ast.Name):
|
||||
return state.get(target.id, 0)
|
||||
elif isinstance(target, ast.Subscript):
|
||||
obj = evaluate_ast(target.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
key = evaluate_ast(target.slice, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
return obj[key]
|
||||
elif isinstance(target, ast.Attribute):
|
||||
obj = evaluate_ast(target.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
return getattr(obj, target.attr)
|
||||
elif isinstance(target, ast.Tuple):
|
||||
return tuple(get_current_value(elt) for elt in target.elts)
|
||||
elif isinstance(target, ast.List):
|
||||
return [get_current_value(elt) for elt in target.elts]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError("AugAssign not supported for {type(target)} targets.")
|
||||
|
||||
current_value = get_current_value(expression.target)
|
||||
value_to_add = evaluate_ast(expression.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
|
||||
# Determine the operation and apply it
|
||||
if isinstance(expression.op, ast.Add):
|
||||
if isinstance(current_value, list):
|
||||
if not isinstance(value_to_add, list):
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"Cannot add non-list value {value_to_add} to a list.")
|
||||
updated_value = current_value + value_to_add
|
||||
else:
|
||||
updated_value = current_value + value_to_add
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression.op, ast.Sub):
|
||||
updated_value = current_value - value_to_add
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression.op, ast.Mult):
|
||||
updated_value = current_value * value_to_add
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression.op, ast.Div):
|
||||
updated_value = current_value / value_to_add
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression.op, ast.Mod):
|
||||
updated_value = current_value % value_to_add
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression.op, ast.Pow):
|
||||
updated_value = current_value**value_to_add
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression.op, ast.FloorDiv):
|
||||
updated_value = current_value // value_to_add
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression.op, ast.BitAnd):
|
||||
updated_value = current_value & value_to_add
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression.op, ast.BitOr):
|
||||
updated_value = current_value | value_to_add
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression.op, ast.BitXor):
|
||||
updated_value = current_value ^ value_to_add
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression.op, ast.LShift):
|
||||
updated_value = current_value << value_to_add
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression.op, ast.RShift):
|
||||
updated_value = current_value >> value_to_add
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"Operation {type(expression.op).__name__} is not supported.")
|
||||
|
||||
# Update the state
|
||||
set_value(expression.target, updated_value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
|
||||
return updated_value
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_boolop(node, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
if isinstance(node.op, ast.And):
|
||||
for value in node.values:
|
||||
if not evaluate_ast(value, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return True
|
||||
elif isinstance(node.op, ast.Or):
|
||||
for value in node.values:
|
||||
if evaluate_ast(value, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
return True
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_binop(binop, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
# Recursively evaluate the left and right operands
|
||||
left_val = evaluate_ast(binop.left, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
right_val = evaluate_ast(binop.right, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
|
||||
# Determine the operation based on the type of the operator in the BinOp
|
||||
if isinstance(binop.op, ast.Add):
|
||||
return left_val + right_val
|
||||
elif isinstance(binop.op, ast.Sub):
|
||||
return left_val - right_val
|
||||
elif isinstance(binop.op, ast.Mult):
|
||||
return left_val * right_val
|
||||
elif isinstance(binop.op, ast.Div):
|
||||
return left_val / right_val
|
||||
elif isinstance(binop.op, ast.Mod):
|
||||
return left_val % right_val
|
||||
elif isinstance(binop.op, ast.Pow):
|
||||
return left_val**right_val
|
||||
elif isinstance(binop.op, ast.FloorDiv):
|
||||
return left_val // right_val
|
||||
elif isinstance(binop.op, ast.BitAnd):
|
||||
return left_val & right_val
|
||||
elif isinstance(binop.op, ast.BitOr):
|
||||
return left_val | right_val
|
||||
elif isinstance(binop.op, ast.BitXor):
|
||||
return left_val ^ right_val
|
||||
elif isinstance(binop.op, ast.LShift):
|
||||
return left_val << right_val
|
||||
elif isinstance(binop.op, ast.RShift):
|
||||
return left_val >> right_val
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError(f"Binary operation {type(binop.op).__name__} is not implemented.")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_assign(assign, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
result = evaluate_ast(assign.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
if len(assign.targets) == 1:
|
||||
target = assign.targets[0]
|
||||
set_value(target, result, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if len(assign.targets) != len(result):
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"Assign failed: expected {len(result)} values but got {len(assign.targets)}.")
|
||||
expanded_values = []
|
||||
for tgt in assign.targets:
|
||||
if isinstance(tgt, ast.Starred):
|
||||
expanded_values.extend(result)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
expanded_values.append(result)
|
||||
for tgt, val in zip(assign.targets, expanded_values):
|
||||
set_value(tgt, val, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def set_value(target, value, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
if isinstance(target, ast.Name):
|
||||
if target.id in static_tools:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"Cannot assign to name '{target.id}': doing this would erase the existing tool!")
|
||||
state[target.id] = value
|
||||
elif isinstance(target, ast.Tuple):
|
||||
if not isinstance(value, tuple):
|
||||
if hasattr(value, "__iter__") and not isinstance(value, (str, bytes)):
|
||||
value = tuple(value)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError("Cannot unpack non-tuple value")
|
||||
if len(target.elts) != len(value):
|
||||
raise InterpreterError("Cannot unpack tuple of wrong size")
|
||||
for i, elem in enumerate(target.elts):
|
||||
set_value(elem, value[i], state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(target, ast.Subscript):
|
||||
obj = evaluate_ast(target.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
key = evaluate_ast(target.slice, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
obj[key] = value
|
||||
elif isinstance(target, ast.Attribute):
|
||||
obj = evaluate_ast(target.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
setattr(obj, target.attr, value)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_call(call, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
if not (isinstance(call.func, ast.Attribute) or isinstance(call.func, ast.Name)):
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"This is not a correct function: {call.func}).")
|
||||
if isinstance(call.func, ast.Attribute):
|
||||
obj = evaluate_ast(call.func.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
func_name = call.func.attr
|
||||
if not hasattr(obj, func_name):
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"Object {obj} has no attribute {func_name}")
|
||||
func = getattr(obj, func_name)
|
||||
|
||||
elif isinstance(call.func, ast.Name):
|
||||
func_name = call.func.id
|
||||
if func_name in state:
|
||||
func = state[func_name]
|
||||
elif func_name in static_tools:
|
||||
func = static_tools[func_name]
|
||||
elif func_name in custom_tools:
|
||||
func = custom_tools[func_name]
|
||||
elif func_name in ERRORS:
|
||||
func = ERRORS[func_name]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(
|
||||
f"It is not permitted to evaluate other functions than the provided tools or functions defined in previous code (tried to execute {call.func.id})."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
args = []
|
||||
for arg in call.args:
|
||||
if isinstance(arg, ast.Starred):
|
||||
args.extend(evaluate_ast(arg.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
args.append(evaluate_ast(arg, state, static_tools, custom_tools))
|
||||
|
||||
args = []
|
||||
for arg in call.args:
|
||||
if isinstance(arg, ast.Starred):
|
||||
unpacked = evaluate_ast(arg.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
if not hasattr(unpacked, "__iter__") or isinstance(unpacked, (str, bytes)):
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"Cannot unpack non-iterable value {unpacked}")
|
||||
args.extend(unpacked)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
args.append(evaluate_ast(arg, state, static_tools, custom_tools))
|
||||
|
||||
kwargs = {keyword.arg: evaluate_ast(keyword.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools) for keyword in call.keywords}
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(func, type) and len(func.__module__.split(".")) > 1: # Check for user-defined classes
|
||||
# Instantiate the class using its constructor
|
||||
obj = func.__new__(func) # Create a new instance of the class
|
||||
if hasattr(obj, "__init__"): # Check if the class has an __init__ method
|
||||
obj.__init__(*args, **kwargs) # Call the __init__ method correctly
|
||||
return obj
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if func_name == "super":
|
||||
if not args:
|
||||
if "__class__" in state and "self" in state:
|
||||
return super(state["__class__"], state["self"])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError("super() needs at least one argument")
|
||||
cls = args[0]
|
||||
if not isinstance(cls, type):
|
||||
raise InterpreterError("super() argument 1 must be type")
|
||||
if len(args) == 1:
|
||||
return super(cls)
|
||||
elif len(args) == 2:
|
||||
instance = args[1]
|
||||
return super(cls, instance)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError("super() takes at most 2 arguments")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if func_name == "print":
|
||||
output = " ".join(map(str, args))
|
||||
global PRINT_OUTPUTS
|
||||
PRINT_OUTPUTS += output + "\n"
|
||||
# cap the number of lines
|
||||
return None
|
||||
else: # Assume it's a callable object
|
||||
output = func(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
return output
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_subscript(subscript, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
index = evaluate_ast(subscript.slice, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
value = evaluate_ast(subscript.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(value, str) and isinstance(index, str):
|
||||
raise InterpreterError("You're trying to subscript a string with a string index, which is impossible")
|
||||
if isinstance(value, pd.core.indexing._LocIndexer):
|
||||
parent_object = value.obj
|
||||
return parent_object.loc[index]
|
||||
if isinstance(value, (pd.DataFrame, pd.Series, np.ndarray)):
|
||||
return value[index]
|
||||
elif isinstance(value, pd.core.groupby.generic.DataFrameGroupBy):
|
||||
return value[index]
|
||||
elif isinstance(index, slice):
|
||||
return value[index]
|
||||
elif isinstance(value, (list, tuple)):
|
||||
if not (-len(value) <= index < len(value)):
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"Index {index} out of bounds for list of length {len(value)}")
|
||||
return value[int(index)]
|
||||
elif isinstance(value, str):
|
||||
if not (-len(value) <= index < len(value)):
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"Index {index} out of bounds for string of length {len(value)}")
|
||||
return value[index]
|
||||
elif index in value:
|
||||
return value[index]
|
||||
elif isinstance(index, str) and isinstance(value, Mapping):
|
||||
close_matches = difflib.get_close_matches(index, list(value.keys()))
|
||||
if len(close_matches) > 0:
|
||||
return value[close_matches[0]]
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"Could not index {value} with '{index}'.")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_name(name, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
if name.id in state:
|
||||
return state[name.id]
|
||||
elif name.id in static_tools:
|
||||
return static_tools[name.id]
|
||||
elif name.id in ERRORS:
|
||||
return ERRORS[name.id]
|
||||
close_matches = difflib.get_close_matches(name.id, list(state.keys()))
|
||||
if len(close_matches) > 0:
|
||||
return state[close_matches[0]]
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"The variable `{name.id}` is not defined.")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_condition(condition, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
left = evaluate_ast(condition.left, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
comparators = [evaluate_ast(c, state, static_tools, custom_tools) for c in condition.comparators]
|
||||
ops = [type(op) for op in condition.ops]
|
||||
|
||||
result = True
|
||||
current_left = left
|
||||
|
||||
for op, comparator in zip(ops, comparators):
|
||||
if op == ast.Eq:
|
||||
current_result = current_left == comparator
|
||||
elif op == ast.NotEq:
|
||||
current_result = current_left != comparator
|
||||
elif op == ast.Lt:
|
||||
current_result = current_left < comparator
|
||||
elif op == ast.LtE:
|
||||
current_result = current_left <= comparator
|
||||
elif op == ast.Gt:
|
||||
current_result = current_left > comparator
|
||||
elif op == ast.GtE:
|
||||
current_result = current_left >= comparator
|
||||
elif op == ast.Is:
|
||||
current_result = current_left is comparator
|
||||
elif op == ast.IsNot:
|
||||
current_result = current_left is not comparator
|
||||
elif op == ast.In:
|
||||
current_result = current_left in comparator
|
||||
elif op == ast.NotIn:
|
||||
current_result = current_left not in comparator
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"Operator not supported: {op}")
|
||||
|
||||
result = result & current_result
|
||||
current_left = comparator
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(result, bool) and not result:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
return result if isinstance(result, (bool, pd.Series)) else result.all()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_if(if_statement, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
result = None
|
||||
test_result = evaluate_ast(if_statement.test, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
if test_result:
|
||||
for line in if_statement.body:
|
||||
line_result = evaluate_ast(line, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
if line_result is not None:
|
||||
result = line_result
|
||||
else:
|
||||
for line in if_statement.orelse:
|
||||
line_result = evaluate_ast(line, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
if line_result is not None:
|
||||
result = line_result
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_for(for_loop, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
result = None
|
||||
iterator = evaluate_ast(for_loop.iter, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
for counter in iterator:
|
||||
set_value(for_loop.target, counter, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
for node in for_loop.body:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
line_result = evaluate_ast(node, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
if line_result is not None:
|
||||
result = line_result
|
||||
except BreakException:
|
||||
break
|
||||
except ContinueException:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
else:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
break
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_listcomp(listcomp, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
def inner_evaluate(generators, index, current_state):
|
||||
if index >= len(generators):
|
||||
return [evaluate_ast(listcomp.elt, current_state, static_tools, custom_tools)]
|
||||
generator = generators[index]
|
||||
iter_value = evaluate_ast(generator.iter, current_state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
result = []
|
||||
for value in iter_value:
|
||||
new_state = current_state.copy()
|
||||
if isinstance(generator.target, ast.Tuple):
|
||||
for idx, elem in enumerate(generator.target.elts):
|
||||
new_state[elem.id] = value[idx]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
new_state[generator.target.id] = value
|
||||
if all(evaluate_ast(if_clause, new_state, static_tools, custom_tools) for if_clause in generator.ifs):
|
||||
result.extend(inner_evaluate(generators, index + 1, new_state))
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
return inner_evaluate(listcomp.generators, 0, state)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_try(try_node, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
for stmt in try_node.body:
|
||||
evaluate_ast(stmt, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
matched = False
|
||||
for handler in try_node.handlers:
|
||||
if handler.type is None or isinstance(e, evaluate_ast(handler.type, state, static_tools, custom_tools)):
|
||||
matched = True
|
||||
if handler.name:
|
||||
state[handler.name] = e
|
||||
for stmt in handler.body:
|
||||
evaluate_ast(stmt, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
break
|
||||
if not matched:
|
||||
raise e
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if try_node.orelse:
|
||||
for stmt in try_node.orelse:
|
||||
evaluate_ast(stmt, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
if try_node.finalbody:
|
||||
for stmt in try_node.finalbody:
|
||||
evaluate_ast(stmt, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_raise(raise_node, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
if raise_node.exc is not None:
|
||||
exc = evaluate_ast(raise_node.exc, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
exc = None
|
||||
if raise_node.cause is not None:
|
||||
cause = evaluate_ast(raise_node.cause, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cause = None
|
||||
if exc is not None:
|
||||
if cause is not None:
|
||||
raise exc from cause
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise exc
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError("Re-raise is not supported without an active exception")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_assert(assert_node, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
test_result = evaluate_ast(assert_node.test, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
if not test_result:
|
||||
if assert_node.msg:
|
||||
msg = evaluate_ast(assert_node.msg, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
raise AssertionError(msg)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Include the failing condition in the assertion message
|
||||
test_code = ast.unparse(assert_node.test)
|
||||
raise AssertionError(f"Assertion failed: {test_code}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_with(with_node, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
contexts = []
|
||||
for item in with_node.items:
|
||||
context_expr = evaluate_ast(item.context_expr, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
if item.optional_vars:
|
||||
state[item.optional_vars.id] = context_expr.__enter__()
|
||||
contexts.append(state[item.optional_vars.id])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
context_var = context_expr.__enter__()
|
||||
contexts.append(context_var)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
for stmt in with_node.body:
|
||||
evaluate_ast(stmt, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
for context in reversed(contexts):
|
||||
context.__exit__(type(e), e, e.__traceback__)
|
||||
raise
|
||||
else:
|
||||
for context in reversed(contexts):
|
||||
context.__exit__(None, None, None)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def import_modules(expression, state, authorized_imports):
|
||||
def check_module_authorized(module_name):
|
||||
module_path = module_name.split(".")
|
||||
module_subpaths = [".".join(module_path[:i]) for i in range(1, len(module_path) + 1)]
|
||||
return any(subpath in authorized_imports for subpath in module_subpaths)
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(expression, ast.Import):
|
||||
for alias in expression.names:
|
||||
if check_module_authorized(alias.name):
|
||||
module = import_module(alias.name)
|
||||
state[alias.asname or alias.name] = module
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(
|
||||
f"Import of {alias.name} is not allowed. Authorized imports are: {str(authorized_imports)}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
return None
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.ImportFrom):
|
||||
if check_module_authorized(expression.module):
|
||||
module = __import__(expression.module, fromlist=[alias.name for alias in expression.names])
|
||||
for alias in expression.names:
|
||||
state[alias.asname or alias.name] = getattr(module, alias.name)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"Import from {expression.module} is not allowed.")
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_dictcomp(dictcomp, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
result = {}
|
||||
for gen in dictcomp.generators:
|
||||
iter_value = evaluate_ast(gen.iter, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
for value in iter_value:
|
||||
new_state = state.copy()
|
||||
set_value(gen.target, value, new_state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
if all(evaluate_ast(if_clause, new_state, static_tools, custom_tools) for if_clause in gen.ifs):
|
||||
key = evaluate_ast(dictcomp.key, new_state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
val = evaluate_ast(dictcomp.value, new_state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
result[key] = val
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_ast(
|
||||
expression: ast.AST,
|
||||
state: Dict[str, Any],
|
||||
static_tools: Dict[str, Callable],
|
||||
custom_tools: Dict[str, Callable],
|
||||
authorized_imports: List[str] = LIST_SAFE_MODULES,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Evaluate an abstract syntax tree using the content of the variables stored in a state and only evaluating a given
|
||||
set of functions.
|
||||
|
||||
This function will recurse through the nodes of the tree provided.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
expression (`ast.AST`):
|
||||
The code to evaluate, as an abstract syntax tree.
|
||||
state (`Dict[str, Any]`):
|
||||
A dictionary mapping variable names to values. The `state` is updated if need be when the evaluation
|
||||
encounters assignments.
|
||||
static_tools (`Dict[str, Callable]`):
|
||||
Functions that may be called during the evaluation. Trying to change one of these static_tools will raise an error.
|
||||
custom_tools (`Dict[str, Callable]`):
|
||||
Functions that may be called during the evaluation. These static_tools can be overwritten.
|
||||
authorized_imports (`List[str]`):
|
||||
The list of modules that can be imported by the code. By default, only a few safe modules are allowed.
|
||||
Add more at your own risk!
|
||||
"""
|
||||
global OPERATIONS_COUNT
|
||||
if OPERATIONS_COUNT >= MAX_OPERATIONS:
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(
|
||||
f"Reached the max number of operations of {MAX_OPERATIONS}. Maybe there is an infinite loop somewhere in the code, or you're just asking too many calculations."
|
||||
)
|
||||
OPERATIONS_COUNT += 1
|
||||
if isinstance(expression, ast.Assign):
|
||||
# Assignment -> we evaluate the assignment which should update the state
|
||||
# We return the variable assigned as it may be used to determine the final result.
|
||||
return evaluate_assign(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.AugAssign):
|
||||
return evaluate_augassign(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Call):
|
||||
# Function call -> we return the value of the function call
|
||||
return evaluate_call(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Constant):
|
||||
# Constant -> just return the value
|
||||
return expression.value
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Tuple):
|
||||
return tuple(evaluate_ast(elt, state, static_tools, custom_tools) for elt in expression.elts)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, (ast.ListComp, ast.GeneratorExp)):
|
||||
return evaluate_listcomp(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.UnaryOp):
|
||||
return evaluate_unaryop(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Starred):
|
||||
return evaluate_ast(expression.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.BoolOp):
|
||||
# Boolean operation -> evaluate the operation
|
||||
return evaluate_boolop(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Break):
|
||||
raise BreakException()
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Continue):
|
||||
raise ContinueException()
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.BinOp):
|
||||
# Binary operation -> execute operation
|
||||
return evaluate_binop(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Compare):
|
||||
# Comparison -> evaluate the comparison
|
||||
return evaluate_condition(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Lambda):
|
||||
return evaluate_lambda(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.FunctionDef):
|
||||
return evaluate_function_def(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Dict):
|
||||
# Dict -> evaluate all keys and values
|
||||
keys = [evaluate_ast(k, state, static_tools, custom_tools) for k in expression.keys]
|
||||
values = [evaluate_ast(v, state, static_tools, custom_tools) for v in expression.values]
|
||||
return dict(zip(keys, values))
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Expr):
|
||||
# Expression -> evaluate the content
|
||||
return evaluate_ast(expression.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.For):
|
||||
# For loop -> execute the loop
|
||||
return evaluate_for(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.FormattedValue):
|
||||
# Formatted value (part of f-string) -> evaluate the content and return
|
||||
return evaluate_ast(expression.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.If):
|
||||
# If -> execute the right branch
|
||||
return evaluate_if(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif hasattr(ast, "Index") and isinstance(expression, ast.Index):
|
||||
return evaluate_ast(expression.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.JoinedStr):
|
||||
return "".join([str(evaluate_ast(v, state, static_tools, custom_tools)) for v in expression.values])
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.List):
|
||||
# List -> evaluate all elements
|
||||
return [evaluate_ast(elt, state, static_tools, custom_tools) for elt in expression.elts]
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Name):
|
||||
# Name -> pick up the value in the state
|
||||
return evaluate_name(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Subscript):
|
||||
# Subscript -> return the value of the indexing
|
||||
return evaluate_subscript(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.IfExp):
|
||||
test_val = evaluate_ast(expression.test, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
if test_val:
|
||||
return evaluate_ast(expression.body, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return evaluate_ast(expression.orelse, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Attribute):
|
||||
value = evaluate_ast(expression.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
return getattr(value, expression.attr)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Slice):
|
||||
return slice(
|
||||
evaluate_ast(expression.lower, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
if expression.lower is not None
|
||||
else None,
|
||||
evaluate_ast(expression.upper, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
if expression.upper is not None
|
||||
else None,
|
||||
evaluate_ast(expression.step, state, static_tools, custom_tools) if expression.step is not None else None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.DictComp):
|
||||
return evaluate_dictcomp(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.While):
|
||||
return evaluate_while(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, (ast.Import, ast.ImportFrom)):
|
||||
return import_modules(expression, state, authorized_imports)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.ClassDef):
|
||||
return evaluate_class_def(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Try):
|
||||
return evaluate_try(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Raise):
|
||||
return evaluate_raise(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Assert):
|
||||
return evaluate_assert(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.With):
|
||||
return evaluate_with(expression, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Set):
|
||||
return {evaluate_ast(elt, state, static_tools, custom_tools) for elt in expression.elts}
|
||||
elif isinstance(expression, ast.Return):
|
||||
raise ReturnException(
|
||||
evaluate_ast(expression.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools) if expression.value else None
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# For now we refuse anything else. Let's add things as we need them.
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(f"{expression.__class__.__name__} is not supported.")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def truncate_print_outputs(print_outputs: str, max_len_outputs: int = MAX_LEN_OUTPUT) -> str:
|
||||
if len(print_outputs) < max_len_outputs:
|
||||
return print_outputs
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return f"Print outputs:\n{print_outputs[:max_len_outputs]}\n_Print outputs have been truncated over the limit of {max_len_outputs} characters._\n"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluate_python_code(
|
||||
code: str,
|
||||
static_tools: Optional[Dict[str, Callable]] = None,
|
||||
custom_tools: Optional[Dict[str, Callable]] = None,
|
||||
state: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None,
|
||||
authorized_imports: List[str] = LIST_SAFE_MODULES,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Evaluate a python expression using the content of the variables stored in a state and only evaluating a given set
|
||||
of functions.
|
||||
|
||||
This function will recurse through the nodes of the tree provided.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
code (`str`):
|
||||
The code to evaluate.
|
||||
static_tools (`Dict[str, Callable]`):
|
||||
The functions that may be called during the evaluation.
|
||||
These tools cannot be overwritten in the code: any assignment to their name will raise an error.
|
||||
custom_tools (`Dict[str, Callable]`):
|
||||
The functions that may be called during the evaluation.
|
||||
These tools can be overwritten in the code: any assignment to their name will overwrite them.
|
||||
state (`Dict[str, Any]`):
|
||||
A dictionary mapping variable names to values. The `state` should contain the initial inputs but will be
|
||||
updated by this function to contain all variables as they are evaluated.
|
||||
The print outputs will be stored in the state under the key 'print_outputs'.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
try:
|
||||
expression = ast.parse(code)
|
||||
except SyntaxError as e:
|
||||
raise SyntaxError(f"The code generated by the agent is not valid.\n{e}")
|
||||
if state is None:
|
||||
state = {}
|
||||
if static_tools is None:
|
||||
static_tools = {}
|
||||
if custom_tools is None:
|
||||
custom_tools = {}
|
||||
result = None
|
||||
global PRINT_OUTPUTS
|
||||
PRINT_OUTPUTS = ""
|
||||
global OPERATIONS_COUNT
|
||||
OPERATIONS_COUNT = 0
|
||||
try:
|
||||
for node in expression.body:
|
||||
result = evaluate_ast(node, state, static_tools, custom_tools, authorized_imports)
|
||||
state["print_outputs"] = truncate_print_outputs(PRINT_OUTPUTS, max_len_outputs=MAX_LEN_OUTPUT)
|
||||
return result
|
||||
except InterpreterError as e:
|
||||
msg = truncate_print_outputs(PRINT_OUTPUTS, max_len_outputs=MAX_LEN_OUTPUT)
|
||||
msg += f"EXECUTION FAILED:\nEvaluation stopped at line '{ast.get_source_segment(code, node)}' because of the following error:\n{e}"
|
||||
raise InterpreterError(msg)
|
||||
@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import re
|
||||
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from requests.exceptions import RequestException
|
||||
|
||||
from .tools import Tool
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DuckDuckGoSearchTool(Tool):
|
||||
name = "web_search"
|
||||
description = """Perform a web search based on your query (think a Google search) then returns the top search results as a list of dict elements.
|
||||
Each result has keys 'title', 'href' and 'body'."""
|
||||
inputs = {"query": {"type": "string", "description": "The search query to perform."}}
|
||||
output_type = "any"
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, query: str) -> str:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from duckduckgo_search import DDGS
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
raise ImportError(
|
||||
"You must install package `duckduckgo_search` to run this tool: for instance run `pip install duckduckgo-search`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
results = DDGS().text(query, max_results=7)
|
||||
return results
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class VisitWebpageTool(Tool):
|
||||
name = "visit_webpage"
|
||||
description = "Visits a webpage at the given url and returns its content as a markdown string."
|
||||
inputs = {
|
||||
"url": {
|
||||
"type": "string",
|
||||
"description": "The url of the webpage to visit.",
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_type = "string"
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, url: str) -> str:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from markdownify import markdownify
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
raise ImportError(
|
||||
"You must install package `markdownify` to run this tool: for instance run `pip install markdownify`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# Send a GET request to the URL
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
response.raise_for_status() # Raise an exception for bad status codes
|
||||
|
||||
# Convert the HTML content to Markdown
|
||||
markdown_content = markdownify(response.text).strip()
|
||||
|
||||
# Remove multiple line breaks
|
||||
markdown_content = re.sub(r"\n{3,}", "\n\n", markdown_content)
|
||||
|
||||
return markdown_content
|
||||
|
||||
except RequestException as e:
|
||||
return f"Error fetching the webpage: {str(e)}"
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
return f"An unexpected error occurred: {str(e)}"
|
||||
@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from ..models.whisper import WhisperForConditionalGeneration, WhisperProcessor
|
||||
from .tools import PipelineTool
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class SpeechToTextTool(PipelineTool):
|
||||
default_checkpoint = "distil-whisper/distil-large-v3"
|
||||
description = "This is a tool that transcribes an audio into text. It returns the transcribed text."
|
||||
name = "transcriber"
|
||||
pre_processor_class = WhisperProcessor
|
||||
model_class = WhisperForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = {"audio": {"type": "audio", "description": "The audio to transcribe"}}
|
||||
output_type = "string"
|
||||
|
||||
def encode(self, audio):
|
||||
return self.pre_processor(audio, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, inputs):
|
||||
return self.model.generate(inputs["input_features"])
|
||||
|
||||
def decode(self, outputs):
|
||||
return self.pre_processor.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
|
||||
@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from ..models.speecht5 import SpeechT5ForTextToSpeech, SpeechT5HifiGan, SpeechT5Processor
|
||||
from ..utils import is_datasets_available
|
||||
from .tools import PipelineTool
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_datasets_available():
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TextToSpeechTool(PipelineTool):
|
||||
default_checkpoint = "microsoft/speecht5_tts"
|
||||
description = (
|
||||
"This is a tool that reads an English text out loud. It returns a waveform object containing the sound."
|
||||
)
|
||||
name = "text_to_speech"
|
||||
pre_processor_class = SpeechT5Processor
|
||||
model_class = SpeechT5ForTextToSpeech
|
||||
post_processor_class = SpeechT5HifiGan
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = {"text": {"type": "string", "description": "The text to read out loud (in English)"}}
|
||||
output_type = "audio"
|
||||
|
||||
def setup(self):
|
||||
if self.post_processor is None:
|
||||
self.post_processor = "microsoft/speecht5_hifigan"
|
||||
super().setup()
|
||||
|
||||
def encode(self, text, speaker_embeddings=None):
|
||||
inputs = self.pre_processor(text=text, return_tensors="pt", truncation=True)
|
||||
|
||||
if speaker_embeddings is None:
|
||||
if not is_datasets_available():
|
||||
raise ImportError("Datasets needs to be installed if not passing speaker embeddings.")
|
||||
|
||||
embeddings_dataset = load_dataset(
|
||||
"Matthijs/cmu-arctic-xvectors", split="validation", trust_remote_code=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
speaker_embeddings = torch.tensor(embeddings_dataset[7305]["xvector"]).unsqueeze(0)
|
||||
|
||||
return {"input_ids": inputs["input_ids"], "speaker_embeddings": speaker_embeddings}
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, inputs):
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
return self.model.generate_speech(**inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
def decode(self, outputs):
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
return self.post_processor(outputs).detach().cpu()
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -1,279 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
from ..models.auto import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
from .tools import PipelineTool
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
LANGUAGE_CODES = {
|
||||
"Acehnese Arabic": "ace_Arab",
|
||||
"Acehnese Latin": "ace_Latn",
|
||||
"Mesopotamian Arabic": "acm_Arab",
|
||||
"Ta'izzi-Adeni Arabic": "acq_Arab",
|
||||
"Tunisian Arabic": "aeb_Arab",
|
||||
"Afrikaans": "afr_Latn",
|
||||
"South Levantine Arabic": "ajp_Arab",
|
||||
"Akan": "aka_Latn",
|
||||
"Amharic": "amh_Ethi",
|
||||
"North Levantine Arabic": "apc_Arab",
|
||||
"Modern Standard Arabic": "arb_Arab",
|
||||
"Modern Standard Arabic Romanized": "arb_Latn",
|
||||
"Najdi Arabic": "ars_Arab",
|
||||
"Moroccan Arabic": "ary_Arab",
|
||||
"Egyptian Arabic": "arz_Arab",
|
||||
"Assamese": "asm_Beng",
|
||||
"Asturian": "ast_Latn",
|
||||
"Awadhi": "awa_Deva",
|
||||
"Central Aymara": "ayr_Latn",
|
||||
"South Azerbaijani": "azb_Arab",
|
||||
"North Azerbaijani": "azj_Latn",
|
||||
"Bashkir": "bak_Cyrl",
|
||||
"Bambara": "bam_Latn",
|
||||
"Balinese": "ban_Latn",
|
||||
"Belarusian": "bel_Cyrl",
|
||||
"Bemba": "bem_Latn",
|
||||
"Bengali": "ben_Beng",
|
||||
"Bhojpuri": "bho_Deva",
|
||||
"Banjar Arabic": "bjn_Arab",
|
||||
"Banjar Latin": "bjn_Latn",
|
||||
"Standard Tibetan": "bod_Tibt",
|
||||
"Bosnian": "bos_Latn",
|
||||
"Buginese": "bug_Latn",
|
||||
"Bulgarian": "bul_Cyrl",
|
||||
"Catalan": "cat_Latn",
|
||||
"Cebuano": "ceb_Latn",
|
||||
"Czech": "ces_Latn",
|
||||
"Chokwe": "cjk_Latn",
|
||||
"Central Kurdish": "ckb_Arab",
|
||||
"Crimean Tatar": "crh_Latn",
|
||||
"Welsh": "cym_Latn",
|
||||
"Danish": "dan_Latn",
|
||||
"German": "deu_Latn",
|
||||
"Southwestern Dinka": "dik_Latn",
|
||||
"Dyula": "dyu_Latn",
|
||||
"Dzongkha": "dzo_Tibt",
|
||||
"Greek": "ell_Grek",
|
||||
"English": "eng_Latn",
|
||||
"Esperanto": "epo_Latn",
|
||||
"Estonian": "est_Latn",
|
||||
"Basque": "eus_Latn",
|
||||
"Ewe": "ewe_Latn",
|
||||
"Faroese": "fao_Latn",
|
||||
"Fijian": "fij_Latn",
|
||||
"Finnish": "fin_Latn",
|
||||
"Fon": "fon_Latn",
|
||||
"French": "fra_Latn",
|
||||
"Friulian": "fur_Latn",
|
||||
"Nigerian Fulfulde": "fuv_Latn",
|
||||
"Scottish Gaelic": "gla_Latn",
|
||||
"Irish": "gle_Latn",
|
||||
"Galician": "glg_Latn",
|
||||
"Guarani": "grn_Latn",
|
||||
"Gujarati": "guj_Gujr",
|
||||
"Haitian Creole": "hat_Latn",
|
||||
"Hausa": "hau_Latn",
|
||||
"Hebrew": "heb_Hebr",
|
||||
"Hindi": "hin_Deva",
|
||||
"Chhattisgarhi": "hne_Deva",
|
||||
"Croatian": "hrv_Latn",
|
||||
"Hungarian": "hun_Latn",
|
||||
"Armenian": "hye_Armn",
|
||||
"Igbo": "ibo_Latn",
|
||||
"Ilocano": "ilo_Latn",
|
||||
"Indonesian": "ind_Latn",
|
||||
"Icelandic": "isl_Latn",
|
||||
"Italian": "ita_Latn",
|
||||
"Javanese": "jav_Latn",
|
||||
"Japanese": "jpn_Jpan",
|
||||
"Kabyle": "kab_Latn",
|
||||
"Jingpho": "kac_Latn",
|
||||
"Kamba": "kam_Latn",
|
||||
"Kannada": "kan_Knda",
|
||||
"Kashmiri Arabic": "kas_Arab",
|
||||
"Kashmiri Devanagari": "kas_Deva",
|
||||
"Georgian": "kat_Geor",
|
||||
"Central Kanuri Arabic": "knc_Arab",
|
||||
"Central Kanuri Latin": "knc_Latn",
|
||||
"Kazakh": "kaz_Cyrl",
|
||||
"Kabiyè": "kbp_Latn",
|
||||
"Kabuverdianu": "kea_Latn",
|
||||
"Khmer": "khm_Khmr",
|
||||
"Kikuyu": "kik_Latn",
|
||||
"Kinyarwanda": "kin_Latn",
|
||||
"Kyrgyz": "kir_Cyrl",
|
||||
"Kimbundu": "kmb_Latn",
|
||||
"Northern Kurdish": "kmr_Latn",
|
||||
"Kikongo": "kon_Latn",
|
||||
"Korean": "kor_Hang",
|
||||
"Lao": "lao_Laoo",
|
||||
"Ligurian": "lij_Latn",
|
||||
"Limburgish": "lim_Latn",
|
||||
"Lingala": "lin_Latn",
|
||||
"Lithuanian": "lit_Latn",
|
||||
"Lombard": "lmo_Latn",
|
||||
"Latgalian": "ltg_Latn",
|
||||
"Luxembourgish": "ltz_Latn",
|
||||
"Luba-Kasai": "lua_Latn",
|
||||
"Ganda": "lug_Latn",
|
||||
"Luo": "luo_Latn",
|
||||
"Mizo": "lus_Latn",
|
||||
"Standard Latvian": "lvs_Latn",
|
||||
"Magahi": "mag_Deva",
|
||||
"Maithili": "mai_Deva",
|
||||
"Malayalam": "mal_Mlym",
|
||||
"Marathi": "mar_Deva",
|
||||
"Minangkabau Arabic ": "min_Arab",
|
||||
"Minangkabau Latin": "min_Latn",
|
||||
"Macedonian": "mkd_Cyrl",
|
||||
"Plateau Malagasy": "plt_Latn",
|
||||
"Maltese": "mlt_Latn",
|
||||
"Meitei Bengali": "mni_Beng",
|
||||
"Halh Mongolian": "khk_Cyrl",
|
||||
"Mossi": "mos_Latn",
|
||||
"Maori": "mri_Latn",
|
||||
"Burmese": "mya_Mymr",
|
||||
"Dutch": "nld_Latn",
|
||||
"Norwegian Nynorsk": "nno_Latn",
|
||||
"Norwegian Bokmål": "nob_Latn",
|
||||
"Nepali": "npi_Deva",
|
||||
"Northern Sotho": "nso_Latn",
|
||||
"Nuer": "nus_Latn",
|
||||
"Nyanja": "nya_Latn",
|
||||
"Occitan": "oci_Latn",
|
||||
"West Central Oromo": "gaz_Latn",
|
||||
"Odia": "ory_Orya",
|
||||
"Pangasinan": "pag_Latn",
|
||||
"Eastern Panjabi": "pan_Guru",
|
||||
"Papiamento": "pap_Latn",
|
||||
"Western Persian": "pes_Arab",
|
||||
"Polish": "pol_Latn",
|
||||
"Portuguese": "por_Latn",
|
||||
"Dari": "prs_Arab",
|
||||
"Southern Pashto": "pbt_Arab",
|
||||
"Ayacucho Quechua": "quy_Latn",
|
||||
"Romanian": "ron_Latn",
|
||||
"Rundi": "run_Latn",
|
||||
"Russian": "rus_Cyrl",
|
||||
"Sango": "sag_Latn",
|
||||
"Sanskrit": "san_Deva",
|
||||
"Santali": "sat_Olck",
|
||||
"Sicilian": "scn_Latn",
|
||||
"Shan": "shn_Mymr",
|
||||
"Sinhala": "sin_Sinh",
|
||||
"Slovak": "slk_Latn",
|
||||
"Slovenian": "slv_Latn",
|
||||
"Samoan": "smo_Latn",
|
||||
"Shona": "sna_Latn",
|
||||
"Sindhi": "snd_Arab",
|
||||
"Somali": "som_Latn",
|
||||
"Southern Sotho": "sot_Latn",
|
||||
"Spanish": "spa_Latn",
|
||||
"Tosk Albanian": "als_Latn",
|
||||
"Sardinian": "srd_Latn",
|
||||
"Serbian": "srp_Cyrl",
|
||||
"Swati": "ssw_Latn",
|
||||
"Sundanese": "sun_Latn",
|
||||
"Swedish": "swe_Latn",
|
||||
"Swahili": "swh_Latn",
|
||||
"Silesian": "szl_Latn",
|
||||
"Tamil": "tam_Taml",
|
||||
"Tatar": "tat_Cyrl",
|
||||
"Telugu": "tel_Telu",
|
||||
"Tajik": "tgk_Cyrl",
|
||||
"Tagalog": "tgl_Latn",
|
||||
"Thai": "tha_Thai",
|
||||
"Tigrinya": "tir_Ethi",
|
||||
"Tamasheq Latin": "taq_Latn",
|
||||
"Tamasheq Tifinagh": "taq_Tfng",
|
||||
"Tok Pisin": "tpi_Latn",
|
||||
"Tswana": "tsn_Latn",
|
||||
"Tsonga": "tso_Latn",
|
||||
"Turkmen": "tuk_Latn",
|
||||
"Tumbuka": "tum_Latn",
|
||||
"Turkish": "tur_Latn",
|
||||
"Twi": "twi_Latn",
|
||||
"Central Atlas Tamazight": "tzm_Tfng",
|
||||
"Uyghur": "uig_Arab",
|
||||
"Ukrainian": "ukr_Cyrl",
|
||||
"Umbundu": "umb_Latn",
|
||||
"Urdu": "urd_Arab",
|
||||
"Northern Uzbek": "uzn_Latn",
|
||||
"Venetian": "vec_Latn",
|
||||
"Vietnamese": "vie_Latn",
|
||||
"Waray": "war_Latn",
|
||||
"Wolof": "wol_Latn",
|
||||
"Xhosa": "xho_Latn",
|
||||
"Eastern Yiddish": "ydd_Hebr",
|
||||
"Yoruba": "yor_Latn",
|
||||
"Yue Chinese": "yue_Hant",
|
||||
"Chinese Simplified": "zho_Hans",
|
||||
"Chinese Traditional": "zho_Hant",
|
||||
"Standard Malay": "zsm_Latn",
|
||||
"Zulu": "zul_Latn",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TranslationTool(PipelineTool):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers.agents import TranslationTool
|
||||
|
||||
translator = TranslationTool()
|
||||
translator("This is a super nice API!", src_lang="English", tgt_lang="French")
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
lang_to_code = LANGUAGE_CODES
|
||||
default_checkpoint = "facebook/nllb-200-distilled-600M"
|
||||
description = (
|
||||
"This is a tool that translates text from a language to another."
|
||||
f"Both `src_lang`and `tgt_lang` should belong to this list of languages: {list(lang_to_code.keys())}."
|
||||
)
|
||||
name = "translator"
|
||||
pre_processor_class = AutoTokenizer
|
||||
model_class = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = {
|
||||
"text": {"type": "string", "description": "The text to translate"},
|
||||
"src_lang": {
|
||||
"type": "string",
|
||||
"description": "The language of the text to translate. Written in plain English, such as 'Romanian', or 'Albanian'",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"tgt_lang": {
|
||||
"type": "string",
|
||||
"description": "The language for the desired output language. Written in plain English, such as 'Romanian', or 'Albanian'",
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_type = "string"
|
||||
|
||||
def encode(self, text, src_lang, tgt_lang):
|
||||
if src_lang not in self.lang_to_code:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"{src_lang} is not a supported language.")
|
||||
if tgt_lang not in self.lang_to_code:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"{tgt_lang} is not a supported language.")
|
||||
src_lang = self.lang_to_code[src_lang]
|
||||
tgt_lang = self.lang_to_code[tgt_lang]
|
||||
return self.pre_processor._build_translation_inputs(
|
||||
text, return_tensors="pt", src_lang=src_lang, tgt_lang=tgt_lang
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, inputs):
|
||||
return self.model.generate(**inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
def decode(self, outputs):
|
||||
return self.post_processor.decode(outputs[0].tolist(), skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
@ -1195,9 +1195,7 @@ class StaticCache(Cache):
|
||||
self.max_cache_len = config.max_position_embeddings if max_cache_len is None else max_cache_len
|
||||
|
||||
# Some model define a custom `head_dim` != config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads
|
||||
self.head_dim = (
|
||||
config.head_dim if hasattr(config, "head_dim") else config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.head_dim = getattr(config, "head_dim", None) or config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads
|
||||
|
||||
self._dtype = dtype
|
||||
self.num_key_value_heads = (
|
||||
@ -1611,9 +1609,10 @@ class EncoderDecoderCache(Cache):
|
||||
|
||||
class HybridCache(Cache):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Hybrid Cache class to be used with `torch.compile` for Gemma2 models that alternate between a local sliding window attention
|
||||
and global attention in every other layer. Under the hood, Hybrid Cache leverages ["SlidingWindowCache"] for sliding window attention
|
||||
and ["StaticCache"] for global attention. For more information, see the documentation of each subcomponeent cache class.
|
||||
Hybrid Cache class to be used with `torch.compile` for models that alternate between a local sliding window
|
||||
attention and global attention in every other layer (originally implemented for Gemma2).
|
||||
Under the hood, Hybrid Cache leverages ["SlidingWindowCache"] for sliding window attention and ["StaticCache"]
|
||||
for global attention.For more information, see the documentation of each subcomponent cache class.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters:
|
||||
config (`PretrainedConfig):
|
||||
@ -1813,9 +1812,11 @@ class HybridCache(Cache):
|
||||
|
||||
class HybridChunkedCache(Cache):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Hybrid Cache class to be used with `torch.compile` for Gemma2 models that alternate between a local sliding window attention
|
||||
and global attention in every other layer. Under the hood, Hybrid Cache leverages ["SlidingWindowCache"] for sliding window attention
|
||||
and ["StaticCache"] for global attention. For more information, see the documentation of each subcomponeent cache class.
|
||||
Hybrid Cache class to be used with `torch.compile` for models that alternate between a local sliding window
|
||||
attention and global attention in every other layer, with support for chunked attention (originally implemented
|
||||
for Llama4).
|
||||
Under the hood, Hybrid Cache leverages ["SlidingWindowCache"] for sliding window attention and ["StaticCache"]
|
||||
for global attention. For more information, see the documentation of each subcomponent cache class.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters:
|
||||
config (`PretrainedConfig):
|
||||
@ -1912,37 +1913,38 @@ class HybridChunkedCache(Cache):
|
||||
self.value_cache.append(new_layer_value_cache)
|
||||
|
||||
def _sliding_update(self, cache_position, layer_idx, key_states, value_states, k_out, v_out, max_cache_len):
|
||||
if cache_position.shape[0] > max_cache_len:
|
||||
cache_position = cache_position.clamp(0, max_cache_len - 1)
|
||||
k_out = key_states[:, :, -max_cache_len:, :]
|
||||
v_out = value_states[:, :, -max_cache_len:, :]
|
||||
# Assumption: caches are all zeros at this point, `+=` is equivalent to `=` but compile-friendly
|
||||
self.key_cache[layer_idx].zero_()
|
||||
self.value_cache[layer_idx].zero_()
|
||||
cumulative_length = self.cumulative_length[layer_idx]
|
||||
# Update it now that we saved the value above
|
||||
self.cumulative_length[layer_idx] += key_states.shape[-2]
|
||||
is_full = cumulative_length >= max_cache_len
|
||||
if is_full:
|
||||
full_key_states = torch.cat((k_out[:, :, 1:, :], key_states), dim=-2)
|
||||
full_value_states = torch.cat((v_out[:, :, 1:, :], value_states), dim=-2)
|
||||
# Fast decoding path -> here as the effective size is still sliding window, it is extremely important
|
||||
# to return `self.key_cache[layer_idx]` and `self.value_cache[layer_idx]`, as they have the fixed adress
|
||||
# in memory (the values are the same as the full states, but not the address!!)
|
||||
if key_states.shape[-2] == 1:
|
||||
self.key_cache[layer_idx].copy_(full_key_states)
|
||||
self.value_cache[layer_idx].copy_(full_value_states)
|
||||
return self.key_cache[layer_idx], self.value_cache[layer_idx]
|
||||
elif not is_full and cumulative_length + key_states.shape[2] > max_cache_len:
|
||||
# Fast prefill path, no need to cat() in this case (which creates a copy even if cating from 0 dim)
|
||||
if cumulative_length == 0:
|
||||
full_key_states = key_states
|
||||
full_value_states = value_states
|
||||
else:
|
||||
full_key_states = torch.cat((k_out[:, :, :cumulative_length, :], key_states), dim=-2)
|
||||
full_value_states = torch.cat((v_out[:, :, :cumulative_length, :], value_states), dim=-2)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.key_cache[layer_idx].index_copy_(2, cache_position, key_states)
|
||||
self.value_cache[layer_idx].index_copy_(2, cache_position, value_states)
|
||||
return self.key_cache[layer_idx], self.value_cache[layer_idx]
|
||||
|
||||
self.key_cache[layer_idx] += k_out
|
||||
self.value_cache[layer_idx] += v_out
|
||||
# we should return the whole states instead of k_out, v_out to take the whole prompt
|
||||
# into consideration when building kv cache instead of just throwing away tokens outside of the window
|
||||
return key_states, value_states
|
||||
|
||||
# otherwise we are decoding. Most efficient way to cat 1 token
|
||||
slicing = torch.ones(max_cache_len, dtype=torch.long, device=value_states.device).cumsum(0)
|
||||
cache_position = cache_position.clamp(0, max_cache_len - 1)
|
||||
to_shift = cache_position >= max_cache_len - 1
|
||||
indices = (slicing + to_shift[-1].int() - 1) % max_cache_len
|
||||
k_out = k_out[:, :, indices]
|
||||
v_out = v_out[:, :, indices]
|
||||
|
||||
k_out[:, :, cache_position] = key_states
|
||||
v_out[:, :, cache_position] = value_states
|
||||
# `_.zero()` followed by `+=` is equivalent `=`, but compile-friendly (without graph breaks due to assignment)
|
||||
self.key_cache[layer_idx].zero_()
|
||||
self.value_cache[layer_idx].zero_()
|
||||
|
||||
self.key_cache[layer_idx] += k_out
|
||||
self.value_cache[layer_idx] += v_out
|
||||
return k_out, v_out
|
||||
self.key_cache[layer_idx].copy_(full_key_states[:, :, -max_cache_len:, :])
|
||||
self.value_cache[layer_idx].copy_(full_value_states[:, :, -max_cache_len:, :])
|
||||
# we should return the whole states instead of k_out, v_out to take the whole prompt
|
||||
# into consideration when building kv cache instead of just throwing away tokens outside of the window
|
||||
return full_key_states, full_value_states
|
||||
|
||||
def _static_update(self, cache_position, layer_idx, key_states, value_states, k_out, v_out, max_cache_len):
|
||||
k_out[:, :, cache_position] = key_states
|
||||
@ -2009,6 +2011,118 @@ class HybridChunkedCache(Cache):
|
||||
self.cumulative_length = [0 for _ in range(len(self.cumulative_length))]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class OffloadedHybridCache(HybridChunkedCache):
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
config: PretrainedConfig,
|
||||
max_batch_size: int,
|
||||
max_cache_len: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
device: Union[torch.device, str, None] = None,
|
||||
dtype: torch.dtype = torch.bfloat16,
|
||||
offload_device: Union[str, torch.device] = torch.device("cpu"),
|
||||
layer_device_map: Optional[Dict[int, Union[str, torch.device, int]]] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
super().__init__(config, max_batch_size, max_cache_len, device, dtype, layer_device_map)
|
||||
self.offload_device = torch.device(offload_device)
|
||||
# Create new CUDA stream for parallel prefetching.
|
||||
self._prefetch_stream = torch.cuda.Stream() if torch._C._get_accelerator().type == "cuda" else None
|
||||
# Those will be dynamically created as the other layers (for TP)
|
||||
self.device_key_cache = None
|
||||
self.device_value_cache = None
|
||||
# This gives the index of which on-device full layer to use (we need 2 to avoid race conditions when prefetching)
|
||||
self.active_device_layer = 0
|
||||
|
||||
def initialise_cache_layer(self, layer_idx, key_states):
|
||||
"""Overriden to use the correct device if offloaded layer (and pin memory)."""
|
||||
if len(self.key_cache) > layer_idx:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
num_key_value_heads = key_states.shape[1]
|
||||
device = key_states.device if self.is_sliding[layer_idx] else self.offload_device
|
||||
pin_memory = not self.is_sliding[layer_idx]
|
||||
global_cache_shape = (self.max_batch_size, num_key_value_heads, self.max_cache_len, self.head_dim)
|
||||
sliding_cache_shape = (
|
||||
self.max_batch_size,
|
||||
num_key_value_heads,
|
||||
self.sliding_window,
|
||||
self.head_dim,
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Note: `mark_static_address` is used to tag the cache as an fixed data pointer, preventing cuda graph
|
||||
# breaks when updating the cache.
|
||||
cache_shape = sliding_cache_shape if self.is_sliding[layer_idx] else global_cache_shape
|
||||
new_layer_key_cache = torch.zeros(cache_shape, dtype=self._dtype, device=device, pin_memory=pin_memory)
|
||||
new_layer_value_cache = torch.zeros(cache_shape, dtype=self._dtype, device=device, pin_memory=pin_memory)
|
||||
torch._dynamo.mark_static_address(new_layer_key_cache)
|
||||
torch._dynamo.mark_static_address(new_layer_value_cache)
|
||||
self.key_cache.append(new_layer_key_cache)
|
||||
self.value_cache.append(new_layer_value_cache)
|
||||
|
||||
# Make sure to initialize the on-device layer if it does not already exist
|
||||
if self.device_key_cache is None and not self.is_sliding[layer_idx]:
|
||||
self.device_key_cache = []
|
||||
self.device_value_cache = []
|
||||
# We need 2 layers to avoid race conditions when prefetching the next one
|
||||
for _ in range(2):
|
||||
device_layer_key_cache = torch.zeros(cache_shape, dtype=self._dtype, device=key_states.device)
|
||||
device_layer_value_cache = torch.zeros(cache_shape, dtype=self._dtype, device=key_states.device)
|
||||
torch._dynamo.mark_static_address(new_layer_key_cache)
|
||||
torch._dynamo.mark_static_address(new_layer_value_cache)
|
||||
self.device_key_cache.append(device_layer_key_cache)
|
||||
self.device_value_cache.append(device_layer_value_cache)
|
||||
|
||||
def _static_update(self, cache_position, layer_idx, key_states, value_states, k_out, v_out, max_cache_len):
|
||||
# Wait for prefetch stream if needed
|
||||
if self._prefetch_stream is not None:
|
||||
torch.cuda.default_stream(key_states.device).wait_stream(self._prefetch_stream)
|
||||
|
||||
# Get correct on-device layer
|
||||
k_out = self.device_key_cache[self.active_device_layer]
|
||||
v_out = self.device_value_cache[self.active_device_layer]
|
||||
|
||||
# Let's prefetch the next layer as soon as possible
|
||||
self._prefetch_next_layer(layer_idx)
|
||||
|
||||
# Copy to on-device layer
|
||||
k_out[:, :, cache_position] = key_states
|
||||
v_out[:, :, cache_position] = value_states
|
||||
|
||||
# Copy to offloaded device
|
||||
self.key_cache[layer_idx][:, :, cache_position] = key_states.to(self.offload_device)
|
||||
self.value_cache[layer_idx][:, :, cache_position] = value_states.to(self.offload_device)
|
||||
|
||||
return k_out, v_out
|
||||
|
||||
def _prefetch_next_layer(self, layer_idx: int) -> None:
|
||||
"""Based on current layer_idx, prefetch next full layer to the device."""
|
||||
|
||||
# Switch the active layer
|
||||
self.active_device_layer = 0 if self.active_device_layer == 1 else 1
|
||||
|
||||
# Find the next non-sliding layer
|
||||
try:
|
||||
next_layer = layer_idx + 1 + self.is_sliding[layer_idx + 1 :].index(False)
|
||||
# In this case, we are at the last layer, and we go back to prefect the first one
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
next_layer = self.is_sliding.index(False)
|
||||
|
||||
# Alternate between two on-device caches.
|
||||
if self._prefetch_stream is not None:
|
||||
with torch.cuda.stream(self._prefetch_stream):
|
||||
self._prefetch_layer_in_context(next_layer)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._prefetch_layer_in_context(next_layer)
|
||||
|
||||
def _prefetch_layer_in_context(self, layer_idx: int) -> None:
|
||||
"""Performs the actual copy of the layer to device cache."""
|
||||
if len(self.key_cache) >= layer_idx:
|
||||
self.device_key_cache[self.active_device_layer].copy_(self.key_cache[layer_idx], non_blocking=True)
|
||||
self.device_value_cache[self.active_device_layer].copy_(self.value_cache[layer_idx], non_blocking=True)
|
||||
# The layer was not yet initialized
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.device_key_cache[self.active_device_layer].fill_(0.0)
|
||||
self.device_value_cache[self.active_device_layer].fill_(0.0)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class MambaCache:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Cache for mamba model which does not have attention mechanism and key value states.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -61,9 +61,10 @@ class PretrainedConfig(PushToHubMixin):
|
||||
|
||||
- **model_type** (`str`) -- An identifier for the model type, serialized into the JSON file, and used to recreate
|
||||
the correct object in [`~transformers.AutoConfig`].
|
||||
- **is_composition** (`bool`) -- Whether the config class is composed of multiple sub-configs. In this case the
|
||||
config has to be initialized from two or more configs of type [`~transformers.PretrainedConfig`] like:
|
||||
[`~transformers.EncoderDecoderConfig`] or [`~RagConfig`].
|
||||
- **has_no_defaults_at_init** (`bool`) -- Whether the config class can be initialized without providing input arguments.
|
||||
Some configurations requires inputs to be defined at init and have no default values, usually these are composite configs,
|
||||
(but not necessarily) such as [`~transformers.EncoderDecoderConfig`] or [`~RagConfig`]. They have to be initialized from
|
||||
two or more configs of type [`~transformers.PretrainedConfig`].
|
||||
- **keys_to_ignore_at_inference** (`List[str]`) -- A list of keys to ignore by default when looking at dictionary
|
||||
outputs of the model during inference.
|
||||
- **attribute_map** (`Dict[str, str]`) -- A dict that maps model specific attribute names to the standardized
|
||||
@ -193,7 +194,7 @@ class PretrainedConfig(PushToHubMixin):
|
||||
model_type: str = ""
|
||||
base_config_key: str = ""
|
||||
sub_configs: dict[str, "PretrainedConfig"] = {}
|
||||
is_composition: bool = False
|
||||
has_no_defaults_at_init: bool = False
|
||||
attribute_map: dict[str, str] = {}
|
||||
base_model_tp_plan: Optional[dict[str, Any]] = None
|
||||
base_model_pp_plan: Optional[dict[str, tuple[list[str]]]] = None
|
||||
@ -813,8 +814,8 @@ class PretrainedConfig(PushToHubMixin):
|
||||
# Get the default config dict (from a fresh PreTrainedConfig instance)
|
||||
default_config_dict = PretrainedConfig().to_dict()
|
||||
|
||||
# Get class-specific config dict if not part of a composition
|
||||
class_config_dict = self.__class__().to_dict() if not self.is_composition else {}
|
||||
# get class specific config dict
|
||||
class_config_dict = self.__class__().to_dict() if not self.has_no_defaults_at_init else {}
|
||||
|
||||
serializable_config_dict = {}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -122,7 +122,7 @@ class GlueDataset(Dataset):
|
||||
with FileLock(lock_path):
|
||||
if os.path.exists(cached_features_file) and not args.overwrite_cache:
|
||||
start = time.time()
|
||||
self.features = torch.load(cached_features_file)
|
||||
self.features = torch.load(cached_features_file, weights_only=True)
|
||||
logger.info(
|
||||
f"Loading features from cached file {cached_features_file} [took %.3f s]", time.time() - start
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ deps = {
|
||||
"kenlm@git+https://github.com/ydshieh/kenlm@78f664fb3dafe1468d868d71faf19534530698d5": "kenlm@git+https://github.com/ydshieh/kenlm@78f664fb3dafe1468d868d71faf19534530698d5",
|
||||
"keras": "keras>2.9,<2.16",
|
||||
"keras-nlp": "keras-nlp>=0.3.1,<0.14.0",
|
||||
"kernels": "kernels>=0.3.2,<0.4",
|
||||
"kernels": "kernels>=0.4.4,<0.5",
|
||||
"librosa": "librosa",
|
||||
"natten": "natten>=0.14.6,<0.15.0",
|
||||
"nltk": "nltk<=3.8.1",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,7 +19,9 @@ from typing import TYPE_CHECKING, Any, Dict, Optional, Tuple
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import torch.nn as nn
|
||||
|
||||
from ..pytorch_utils import prune_linear_layer
|
||||
from ..utils import is_sklearn_available
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,6 +38,8 @@ if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
from ..tokenization_utils_base import PreTrainedTokenizerBase
|
||||
from .configuration_utils import GenerationConfig
|
||||
|
||||
from ..utils.deprecation import deprecate_kwarg
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CandidateGenerator:
|
||||
"""Abstract base class for all candidate generators that can be applied during assisted generation."""
|
||||
@ -612,6 +616,63 @@ class AssistedCandidateGeneratorDifferentTokenizers(AssistedCandidateGenerator):
|
||||
return new_target_ids
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class _PruneReindexingLMHead(nn.Module):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A class to prune and reindex the language model head.
|
||||
|
||||
This class prunes the language model head to only include the specified token IDs and reindexes the logits
|
||||
to map back to the original vocabulary.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
original_lm_head (nn.Module): The original language model head.
|
||||
token_ids (list[int]): The list of token IDs to keep.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, original_lm_head, assistant_overlap_token_ids):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.pruned_lm_head = prune_linear_layer(original_lm_head, assistant_overlap_token_ids).to(
|
||||
original_lm_head.weight.dtype
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, hidden_states):
|
||||
pruned_logits = self.pruned_lm_head(hidden_states)
|
||||
return pruned_logits
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class _MapInputEmbedding(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, original_embedding: nn.Embedding, assistant_overlap_token_ids):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Wraps an existing embedding layer and remaps token IDs before lookup.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
original_embedding (nn.Embedding): Pre-trained or existing embedding layer.
|
||||
assistant_overlap_token_ids (dict): Mapping from original token IDs to new token IDs.
|
||||
Example: {old_id: new_id}
|
||||
"""
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.original_embedding = original_embedding
|
||||
self.weight = original_embedding.weight
|
||||
self.assistant_overlap_token_ids = assistant_overlap_token_ids
|
||||
self.map = False
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, input_ids: torch.LongTensor) -> torch.FloatTensor:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
input_ids (torch.LongTensor): Tensor of token IDs (batch_size, seq_len).
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
torch.FloatTensor: Corresponding input embeddings.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if self.map:
|
||||
# Get the last item from input_ids
|
||||
my_input_ids = self.assistant_overlap_token_ids[input_ids[0, -1]].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.map = True
|
||||
my_input_ids = input_ids
|
||||
|
||||
return self.original_embedding(my_input_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AssistantToTargetTranslator:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Translates token ids and logits between assistant and target model vocabularies. This class is used to handle
|
||||
@ -625,36 +686,74 @@ class AssistantToTargetTranslator:
|
||||
The tokenizer used by the target (main) model.
|
||||
assistant_tokenizer (`PreTrainedTokenizerBase`):
|
||||
The tokenizer used by the assistant model.
|
||||
assistant_model_device (`str`, defaults to "cpu"):
|
||||
The device where the assistant model is located. Used for placing tensors.
|
||||
target_vocab_size (`int`, *optional*):
|
||||
target_vocab_size (`int`):
|
||||
The size of the target model's vocabulary. If not provided, will be inferred from the target tokenizer.
|
||||
assistant_model_device (str, optional): The device on which the assistant model is loaded.
|
||||
Defaults to "cpu".
|
||||
assistant_model_device (`str`, defaults to "cpu"): The device where the assistant model is located. Used for placing tensors.
|
||||
assistant_model (Optional[PreTrainedModel], optional): The assistant model to be used. Defaults to None for backward compatibility.
|
||||
assistant_prune_lm_head (bool): Whether to prune the assistant model's language model
|
||||
head to match the target vocabulary. This is only applicable if `assistant_model` is provided.
|
||||
Defaults to False for backward compatibility.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
FILTER_VALUE: float = -float("Inf") # The value used to filter out unmapped tokens in the logits.
|
||||
SUPPRESS_TOKEN_ID: int = -1 # The ID used to mark suppressed tokens in the mapping.
|
||||
|
||||
@deprecate_kwarg("assistant_model_device", version="4.53")
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
target_tokenizer: "PreTrainedTokenizerBase",
|
||||
assistant_tokenizer: "PreTrainedTokenizerBase",
|
||||
target_vocab_size: int, # required since target_vocab_size can be different from the length of target_tokenizer.get_vocab()
|
||||
assistant_model_device: str = "cpu",
|
||||
assistant_model: Optional["PreTrainedModel"] = None,
|
||||
assistant_prune_lm_head: bool = False,
|
||||
):
|
||||
self._target_tokenizer: "PreTrainedTokenizerBase" = target_tokenizer
|
||||
self._assistant_tokenizer: "PreTrainedTokenizerBase" = assistant_tokenizer
|
||||
self._assistant_model_device: str = assistant_model_device
|
||||
self._assistant_model_device: str = (
|
||||
assistant_model_device if assistant_model is None else assistant_model.device
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.target_vocab_size: int = target_vocab_size
|
||||
self._assistant_to_target_input_ids, self.target_to_assistant_input_ids = (
|
||||
self._get_assistant_to_target_input_ids()
|
||||
)
|
||||
self._suppress_input_ids: list[int] = self._get_suppress_input_ids()
|
||||
self.logits_processors: Optional[LogitsProcessorList] = None
|
||||
self.assistant_prune_lm_head = assistant_prune_lm_head and assistant_model is not None
|
||||
if len(self._suppress_input_ids) > 0:
|
||||
# len(self._suppress_input_ids) = 0 if the assistant vocab is a subset of the target vocab
|
||||
self.logits_processors = LogitsProcessorList(
|
||||
[SuppressTokensLogitsProcessor(self._get_suppress_input_ids(), self._assistant_model_device)]
|
||||
)
|
||||
# the assistant vocab is not a subset of the target vocab
|
||||
if self.assistant_prune_lm_head:
|
||||
self.assistant_overlap_token_ids = torch.tensor(
|
||||
list(self.target_to_assistant_input_ids.values()),
|
||||
dtype=torch.long,
|
||||
device=self._assistant_model_device,
|
||||
)
|
||||
original_lm_head = assistant_model.get_output_embeddings()
|
||||
pruned_lm_head = _PruneReindexingLMHead(original_lm_head, self.assistant_overlap_token_ids)
|
||||
del original_lm_head
|
||||
assistant_model.set_output_embeddings(pruned_lm_head)
|
||||
|
||||
original_input_embeddings = assistant_model.get_input_embeddings()
|
||||
map_input_embeddings = _MapInputEmbedding(original_input_embeddings, self.assistant_overlap_token_ids)
|
||||
del original_input_embeddings
|
||||
assistant_model.set_input_embeddings(map_input_embeddings)
|
||||
self.map_input_embeddings = map_input_embeddings
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.logits_processors = LogitsProcessorList(
|
||||
[SuppressTokensLogitsProcessor(self._get_suppress_input_ids(), self._assistant_model_device)]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def unmap_input_ids(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Disables the mapping of input ids despite the assistant pruning for the language model head being enabled.
|
||||
|
||||
This method is required for the first forward pass of `_MapInputEmbedding` where input ids are already in the assistant vocabulary space. By disabling the mapping, it ensures that the input ids are processed correctly without remapping.
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if self.assistant_prune_lm_head:
|
||||
self.map_input_embeddings.map = False
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_assistant_to_target_input_ids(self):
|
||||
target_vocab = self._target_tokenizer.get_vocab()
|
||||
@ -710,7 +809,12 @@ class AssistantToTargetTranslator:
|
||||
if num_new_tokens == 0:
|
||||
return target_input_ids
|
||||
else:
|
||||
transformed_slice = self._assistant_to_target_input_ids[assistant_candidate_ids[0, -num_new_tokens:]]
|
||||
# Get last `num_new_tokens` candidate IDs
|
||||
last_candidate_ids = assistant_candidate_ids[0, -num_new_tokens:]
|
||||
if self.assistant_prune_lm_head:
|
||||
# Map assistant IDs -> target input IDs
|
||||
last_candidate_ids = self.assistant_overlap_token_ids[last_candidate_ids]
|
||||
transformed_slice = self._assistant_to_target_input_ids[last_candidate_ids]
|
||||
return torch.cat((target_input_ids, transformed_slice.unsqueeze(0)), dim=1)
|
||||
|
||||
def get_target_logits(self, assistant_logits: torch.FloatTensor) -> torch.FloatTensor:
|
||||
@ -726,10 +830,12 @@ class AssistantToTargetTranslator:
|
||||
assistant_indices_mask = self._assistant_to_target_input_ids != self.SUPPRESS_TOKEN_ID
|
||||
# Exclude invalid indices
|
||||
target_logits_supported_indices = self._assistant_to_target_input_ids[assistant_indices_mask]
|
||||
valid_assistant_logits = assistant_logits[..., : self._assistant_to_target_input_ids.shape[0]]
|
||||
|
||||
target_logits[..., target_logits_supported_indices] = valid_assistant_logits[..., assistant_indices_mask]
|
||||
|
||||
if self.assistant_prune_lm_head:
|
||||
target_logits[..., target_logits_supported_indices] = assistant_logits
|
||||
else:
|
||||
valid_assistant_logits = assistant_logits[..., : self._assistant_to_target_input_ids.shape[0]]
|
||||
target_logits[..., target_logits_supported_indices] = valid_assistant_logits[..., assistant_indices_mask]
|
||||
return target_logits
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -742,12 +848,15 @@ class AssistantVocabTranslatorCache:
|
||||
_cache = weakref.WeakKeyDictionary()
|
||||
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
@deprecate_kwarg("assistant_model_device", version="4.53")
|
||||
def get_translator(
|
||||
cls,
|
||||
target_tokenizer: "PreTrainedTokenizerBase",
|
||||
assistant_tokenizer: "PreTrainedTokenizerBase",
|
||||
target_vocab_size: int,
|
||||
assistant_model_device: str = "cpu",
|
||||
assistant_model: Optional["PreTrainedModel"] = None,
|
||||
assistant_prune_lm_head: bool = False,
|
||||
) -> AssistantToTargetTranslator:
|
||||
assistant_dict = cls._cache.get(target_tokenizer)
|
||||
if assistant_dict is None:
|
||||
@ -757,7 +866,12 @@ class AssistantVocabTranslatorCache:
|
||||
mapping = assistant_dict.get(assistant_tokenizer)
|
||||
if mapping is None:
|
||||
mapping = AssistantToTargetTranslator(
|
||||
target_tokenizer, assistant_tokenizer, target_vocab_size, assistant_model_device
|
||||
target_tokenizer,
|
||||
assistant_tokenizer,
|
||||
target_vocab_size,
|
||||
assistant_model_device,
|
||||
assistant_model,
|
||||
assistant_prune_lm_head,
|
||||
)
|
||||
assistant_dict[assistant_tokenizer] = mapping
|
||||
|
||||
@ -894,7 +1008,7 @@ class UniversalSpeculativeDecodingGenerator(AssistedCandidateGeneratorDifferentT
|
||||
self._prev_assistant_ids = self._prev_assistant_ids[:, :-tokens_to_remove]
|
||||
assistant_input_ids = torch.cat([self._prev_assistant_ids, assistant_new_ids], dim=-1)
|
||||
assistant_input_ids = assistant_input_ids.to(dtype=torch.long)
|
||||
|
||||
self._atm_translator.unmap_input_ids()
|
||||
return assistant_input_ids, len(assistant_new_ids[0])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,6 +54,7 @@ if is_torch_available():
|
||||
HybridCache,
|
||||
HybridChunkedCache,
|
||||
MambaCache,
|
||||
OffloadedHybridCache,
|
||||
OffloadedStaticCache,
|
||||
QuantizedCacheConfig,
|
||||
QuantoQuantizedCache,
|
||||
@ -71,6 +72,8 @@ if is_torch_available():
|
||||
"sliding_window": SlidingWindowCache,
|
||||
"hybrid": HybridCache,
|
||||
"hybrid_chunked": HybridChunkedCache,
|
||||
"offloaded_hybrid": OffloadedHybridCache,
|
||||
"offloaded_hybrid_chunked": OffloadedHybridCache,
|
||||
"mamba": MambaCache,
|
||||
}
|
||||
QUANT_BACKEND_CLASSES_MAPPING = {"quanto": QuantoQuantizedCache, "HQQ": HQQQuantizedCache}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -33,7 +33,9 @@ from ..cache_utils import (
|
||||
Cache,
|
||||
DynamicCache,
|
||||
EncoderDecoderCache,
|
||||
HybridChunkedCache,
|
||||
OffloadedCache,
|
||||
OffloadedHybridCache,
|
||||
QuantizedCacheConfig,
|
||||
StaticCache,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -962,8 +964,14 @@ class GenerationMixin:
|
||||
elif different_tokenizers:
|
||||
if generation_config.do_sample is True:
|
||||
atm_translator = AssistantVocabTranslatorCache.get_translator(
|
||||
target_tokenizer, assistant_tokenizer, self.config.vocab_size, assistant_model.device
|
||||
target_tokenizer,
|
||||
assistant_tokenizer,
|
||||
self.config.vocab_size,
|
||||
assistant_model=assistant_model,
|
||||
assistant_prune_lm_head=True, # prune LM head of assistant model
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Since we prune the LM head, we cannot use the repetition penalty on the assistant model due to mismaches between token ids and logits index
|
||||
assistant_model.generation_config.repetition_penalty = None
|
||||
candidate_generator = UniversalSpeculativeDecodingGenerator(
|
||||
input_ids=input_ids,
|
||||
assistant_model=assistant_model,
|
||||
@ -1430,27 +1438,6 @@ class GenerationMixin:
|
||||
|
||||
return transition_scores
|
||||
|
||||
def _validate_model_class(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Confirms that the model class is compatible with generation. If not, raises an exception that points to the
|
||||
right class to use.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# TODO(joao): remove this function in v4.50, i.e. when we remove the inheritance of `GenerationMixin` from
|
||||
# `PreTrainedModel`. With that inheritance removed, all model classes inheriting from `GenerationMixin` can
|
||||
# safely call `GenerationMixin.generate`
|
||||
if not self.can_generate():
|
||||
terminations_with_generation_support = [
|
||||
"ForCausalLM",
|
||||
"ForConditionalGeneration",
|
||||
"ForSpeechSeq2Seq",
|
||||
"ForVision2Seq",
|
||||
]
|
||||
raise TypeError(
|
||||
f"The current model class ({self.__class__.__name__}) is not compatible with `.generate()`, as "
|
||||
"it doesn't have a language model head. Classes that support generation often end in one of these "
|
||||
f"names: {terminations_with_generation_support}."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def _validate_assistant(self, assistant_model, tokenizer, assistant_tokenizer):
|
||||
if assistant_model is None:
|
||||
return
|
||||
@ -1848,6 +1835,9 @@ class GenerationMixin:
|
||||
not hasattr(self, "_cache")
|
||||
or (not isinstance(cache_to_check, cache_cls))
|
||||
or cache_to_check.max_batch_size != batch_size
|
||||
or isinstance(
|
||||
cache_to_check, (HybridChunkedCache, OffloadedHybridCache)
|
||||
) # due to internal slicing, we always re-init
|
||||
)
|
||||
if cache_implementation != "mamba":
|
||||
need_new_cache = need_new_cache or cache_to_check.max_cache_len < max_cache_len
|
||||
@ -2213,7 +2203,6 @@ class GenerationMixin:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# 1. Handle `generation_config` and kwargs that might update it, and validate the `.generate()` call
|
||||
self._validate_model_class()
|
||||
tokenizer = kwargs.pop("tokenizer", None) # Pull this out first, we only use it for stopping criteria
|
||||
assistant_tokenizer = kwargs.pop("assistant_tokenizer", None) # only used for assisted generation
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,6 +22,7 @@ from .image_processing_base import BatchFeature, ImageProcessingMixin
|
||||
from .image_transforms import center_crop, normalize, rescale
|
||||
from .image_utils import ChannelDimension, get_image_size
|
||||
from .utils import logging
|
||||
from .utils.import_utils import requires
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
@ -33,6 +34,7 @@ INIT_SERVICE_KWARGS = [
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@requires(backends=("vision",))
|
||||
class BaseImageProcessor(ImageProcessingMixin):
|
||||
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
super().__init__(**kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -68,6 +68,8 @@ if is_torchvision_available():
|
||||
from torchvision.transforms.v2 import functional as F
|
||||
else:
|
||||
from torchvision.transforms import functional as F
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pil_torch_interpolation_mapping = None
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -689,8 +691,12 @@ class BaseImageProcessorFast(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
|
||||
# torch resize uses interpolation instead of resample
|
||||
resample = kwargs.pop("resample")
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if resample is an int before checking if it's an instance of PILImageResampling
|
||||
# because if pillow < 9.1.0, resample is an int and PILImageResampling is a module.
|
||||
# Checking PILImageResampling will fail with error `TypeError: isinstance() arg 2 must be a type or tuple of types`.
|
||||
kwargs["interpolation"] = (
|
||||
pil_torch_interpolation_mapping[resample] if isinstance(resample, (PILImageResampling, int)) else resample
|
||||
pil_torch_interpolation_mapping[resample] if isinstance(resample, (int, PILImageResampling)) else resample
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Pop kwargs that are not needed in _preprocess
|
||||
|
||||
@ -72,6 +72,8 @@ if is_vision_available():
|
||||
PILImageResampling.BICUBIC: InterpolationMode.BICUBIC,
|
||||
PILImageResampling.LANCZOS: InterpolationMode.LANCZOS,
|
||||
}
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pil_torch_interpolation_mapping = {}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ class FbgemmFp8Linear(torch.nn.Linear):
|
||||
# x_quantized and x_scale are not necessarily on the same device as x, this is an issue.
|
||||
# https://github.com/pytorch/FBGEMM/blob/e08af8539c391437f447173863df0f3f6f6f1855/fbgemm_gpu/experimental/gen_ai/src/quantize/quantize.cu#L1237C3-L1237C45
|
||||
x_quantized, x_scale = torch.ops.fbgemm.quantize_fp8_per_row(
|
||||
x.view(-1, x.shape[-1]), scale_ub=self.input_scale_ub
|
||||
x.view(-1, x.shape[-1]).contiguous(), scale_ub=self.input_scale_ub
|
||||
)
|
||||
# moving x_quantized, x_scale here creates glibberish output ... However, if we move the output, it works
|
||||
# x_quantized, x_scale = x_quantized.to(x.device), x_scale.to(x.device)
|
||||
@ -207,9 +207,6 @@ def _replace_with_fbgemm_fp8_linear(
|
||||
(key + "." in current_key_name_str) or (key == current_key_name_str) for key in modules_to_not_convert
|
||||
):
|
||||
with init_empty_weights(include_buffers=True):
|
||||
tp_plan[re.sub(r"\d+", "*", current_key_name_str + ".gate_up_proj_scale")] = tp_plan[
|
||||
re.sub(r"\d+", "*", current_key_name_str + ".gate_up_proj")
|
||||
]
|
||||
tp_plan[re.sub(r"\d+", "*", current_key_name_str + ".down_proj_scale")] = None
|
||||
model._modules[name] = FbgemmFp8Llama4TextExperts(
|
||||
config.text_config,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -29,6 +29,7 @@ Citation:
|
||||
from typing import Optional, Tuple, Union
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from packaging import version
|
||||
|
||||
from ..utils import is_torch_flex_attn_available
|
||||
from ..utils.import_utils import _torch_version
|
||||
@ -61,16 +62,17 @@ class WrappedFlexAttention:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Initialize or update the singleton instance.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not self._is_flex_compiled:
|
||||
if not self._is_flex_compiled or training != self.training:
|
||||
# In PyTorch 2.6.0, there's a known issue with flex attention compilation which may
|
||||
# cause errors. The suggested fix is to compile with "max-autotune-no-cudagraphs"
|
||||
# see https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/146260 for training
|
||||
if _torch_version == "2.6.0" and training:
|
||||
self.training = training
|
||||
if version.parse(_torch_version).base_version == "2.6.0" and training:
|
||||
self._compiled_flex_attention = torch.compile(
|
||||
flex_attention, dynamic=False, mode="max-autotune-no-cudagraphs"
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._compiled_flex_attention = torch.compile(flex_attention, dynamic=False)
|
||||
self._compiled_flex_attention = torch.compile(flex_attention)
|
||||
self._is_flex_compiled = True
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -204,6 +204,23 @@ GGUF_CONFIG_MAPPING = {
|
||||
"attention.head_count": "num_attention_heads",
|
||||
"attention.head_count_kv": "num_key_value_heads",
|
||||
"attention.layer_norm_rms_epsilon": "rms_norm_eps",
|
||||
"attention.sliding_window": "sliding_window",
|
||||
"vocab_size": "vocab_size",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"gemma3": {
|
||||
"context_length": "max_position_embeddings",
|
||||
"block_count": "num_hidden_layers",
|
||||
"feed_forward_length": "intermediate_size",
|
||||
"embedding_length": "hidden_size",
|
||||
"rope.dimension_count": None,
|
||||
"rope.freq_base": "rope_theta",
|
||||
# NOTE: Gemma3 has key_length==value_length==head_dim
|
||||
# See: https://github.com/ggml-org/llama.cpp/blob/fe5b78c89670b2f37ecb216306bed3e677b49d9f/convert_hf_to_gguf.py#L3495-L3496
|
||||
"attention.key_length": "head_dim",
|
||||
"attention.head_count": "num_attention_heads",
|
||||
"attention.head_count_kv": "num_key_value_heads",
|
||||
"attention.layer_norm_rms_epsilon": "rms_norm_eps",
|
||||
"attention.sliding_window": "sliding_window",
|
||||
"vocab_size": "vocab_size",
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -669,6 +686,7 @@ GGUF_TO_FAST_CONVERTERS = {
|
||||
"mamba": GGUFGPTConverter,
|
||||
"nemotron": GGUFGPTConverter,
|
||||
"gemma2": GGUFGemmaConverter,
|
||||
"gemma3_text": GGUFGemmaConverter,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -31,7 +31,27 @@ try:
|
||||
repo_id="kernels-community/deformable-detr",
|
||||
layer_name="MultiScaleDeformableAttention",
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"Llama4TextMoe": {
|
||||
"cuda": LayerRepository(
|
||||
# Move to kernels-community/moe once we release.
|
||||
repo_id="kernels-community/moe",
|
||||
layer_name="Llama4TextMoe",
|
||||
)
|
||||
},
|
||||
"RMSNorm": {
|
||||
"cuda": LayerRepository(
|
||||
repo_id="kernels-community/triton-layer-norm",
|
||||
layer_name="LlamaRMSNorm",
|
||||
revision="pure-layer-test",
|
||||
)
|
||||
},
|
||||
"MLP": {
|
||||
"cuda": LayerRepository(
|
||||
repo_id="medmekk/triton-llama-mlp",
|
||||
layer_name="TritonLlamaMLP",
|
||||
)
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
register_kernel_mapping(_KERNEL_MAPPING)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -219,7 +219,7 @@ class GatherParallel(TensorParallelLayer):
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def _prepare_input_fn(input_layouts, desired_input_layouts, mod, inputs, device_mesh):
|
||||
if isinstance(inputs[0], DTensor):
|
||||
if inputs and isinstance(inputs[0], DTensor):
|
||||
inputs = inputs[0].to_local()
|
||||
return inputs
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -145,6 +145,7 @@ LOSS_MAPPING = {
|
||||
"ForMaskedLM": ForMaskedLMLoss,
|
||||
"ForQuestionAnswering": ForQuestionAnsweringLoss,
|
||||
"ForSequenceClassification": ForSequenceClassificationLoss,
|
||||
"ForImageClassification": ForSequenceClassificationLoss,
|
||||
"ForTokenClassification": ForTokenClassification,
|
||||
"ForSegmentation": ForSegmentationLoss,
|
||||
"ForObjectDetection": ForObjectDetectionLoss,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ import re
|
||||
from contextlib import contextmanager
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers.utils.import_utils import export
|
||||
from transformers.utils.import_utils import requires
|
||||
|
||||
from .utils import is_torch_available
|
||||
|
||||
@ -225,7 +225,7 @@ def _attach_debugger_logic(model, class_name, debug_path: str):
|
||||
break # exit the loop after finding one (unsure, but should be just one call.)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@export(backends=("torch",))
|
||||
@requires(backends=("torch",))
|
||||
def model_addition_debugger(cls):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Model addition debugger - a model adder tracer
|
||||
@ -282,7 +282,7 @@ def model_addition_debugger(cls):
|
||||
return cls
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@export(backends=("torch",))
|
||||
@requires(backends=("torch",))
|
||||
@contextmanager
|
||||
def model_addition_debugger_context(model, debug_path: Optional[str] = None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -253,6 +253,7 @@ TENSOR_PROCESSORS = {
|
||||
"mamba": MambaTensorProcessor,
|
||||
"nemotron": NemotronTensorProcessor,
|
||||
"gemma2": Gemma2TensorProcessor,
|
||||
"gemma3": Gemma2TensorProcessor,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -292,6 +293,8 @@ def get_gguf_hf_weights_map(
|
||||
model_type = "command-r"
|
||||
elif model_type == "qwen2_moe":
|
||||
model_type = "qwen2moe"
|
||||
elif model_type == "gemma3_text":
|
||||
model_type = "gemma3"
|
||||
arch = None
|
||||
for key, value in MODEL_ARCH_NAMES.items():
|
||||
if value == model_type:
|
||||
@ -438,6 +441,10 @@ def load_gguf_checkpoint(gguf_checkpoint_path, return_tensors=False, model_to_lo
|
||||
if gguf_key in reader_keys:
|
||||
logger.info(f"Some keys were not parsed and added into account {gguf_key} | {value}")
|
||||
|
||||
# Gemma3 GGUF checkpoint only contains weights of text backbone
|
||||
if parsed_parameters["config"]["model_type"] == "gemma3":
|
||||
parsed_parameters["config"]["model_type"] = "gemma3_text"
|
||||
|
||||
# retrieve config vocab_size from tokenizer
|
||||
# Please refer to https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/32526 for more details
|
||||
if "vocab_size" not in parsed_parameters["config"]:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -121,7 +121,7 @@ def _compute_default_rope_parameters(
|
||||
elif config is not None:
|
||||
base = config.rope_theta
|
||||
partial_rotary_factor = config.partial_rotary_factor if hasattr(config, "partial_rotary_factor") else 1.0
|
||||
head_dim = getattr(config, "head_dim", config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads)
|
||||
head_dim = getattr(config, "head_dim", None) or config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads
|
||||
dim = int(head_dim * partial_rotary_factor)
|
||||
|
||||
attention_factor = 1.0 # Unused in this type of RoPE
|
||||
|
||||
@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ if is_torchao_available():
|
||||
from .activations import get_activation
|
||||
from .configuration_utils import PretrainedConfig
|
||||
from .dynamic_module_utils import custom_object_save
|
||||
from .generation import CompileConfig, GenerationConfig, GenerationMixin
|
||||
from .generation import CompileConfig, GenerationConfig
|
||||
from .integrations import PeftAdapterMixin, deepspeed_config, is_deepspeed_zero3_enabled
|
||||
from .integrations.accelerate import find_tied_parameters, init_empty_weights
|
||||
from .integrations.deepspeed import _load_state_dict_into_zero3_model, is_deepspeed_available
|
||||
@ -102,6 +102,7 @@ from .utils import (
|
||||
is_accelerate_available,
|
||||
is_bitsandbytes_available,
|
||||
is_flash_attn_2_available,
|
||||
is_kernels_available,
|
||||
is_offline_mode,
|
||||
is_optimum_available,
|
||||
is_peft_available,
|
||||
@ -157,6 +158,9 @@ if is_safetensors_available():
|
||||
if is_deepspeed_available():
|
||||
import deepspeed
|
||||
|
||||
if is_kernels_available():
|
||||
from kernels import get_kernel
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -298,24 +302,6 @@ def get_parameter_device(parameter: Union[nn.Module, "ModuleUtilsMixin"]):
|
||||
return first_tuple[1].device
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_first_parameter_dtype(parameter: Union[nn.Module, "ModuleUtilsMixin"]):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the first parameter dtype (can be non-floating) or asserts if none were found.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return next(parameter.parameters()).dtype
|
||||
except StopIteration:
|
||||
# For nn.DataParallel compatibility in PyTorch > 1.5
|
||||
|
||||
def find_tensor_attributes(module: nn.Module) -> List[Tuple[str, Tensor]]:
|
||||
tuples = [(k, v) for k, v in module.__dict__.items() if torch.is_tensor(v)]
|
||||
return tuples
|
||||
|
||||
gen = parameter._named_members(get_members_fn=find_tensor_attributes)
|
||||
first_tuple = next(gen)
|
||||
return first_tuple[1].dtype
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_parameter_dtype(parameter: Union[nn.Module, "ModuleUtilsMixin"]):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the first found floating dtype in parameters if there is one, otherwise returns the last dtype it found.
|
||||
@ -365,17 +351,6 @@ def get_parameter_dtype(parameter: Union[nn.Module, "ModuleUtilsMixin"]):
|
||||
return last_dtype
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_state_dict_float_dtype(state_dict):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the first found floating dtype in `state_dict` or asserts if none were found.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
for t in state_dict.values():
|
||||
if t.is_floating_point():
|
||||
return t.dtype
|
||||
|
||||
raise ValueError("couldn't find any floating point dtypes in state_dict")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_state_dict_dtype(state_dict):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the first found floating dtype in `state_dict` if there is one, otherwise returns the first dtype.
|
||||
@ -674,7 +649,10 @@ def _infer_parameter_dtype(
|
||||
try:
|
||||
old_param = model.get_parameter_or_buffer(param_name)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
if hf_quantizer is not None and hf_quantizer.quantization_config.quant_method == QuantizationMethod.HQQ:
|
||||
if hf_quantizer is not None and hf_quantizer.quantization_config.quant_method in {
|
||||
QuantizationMethod.HQQ,
|
||||
QuantizationMethod.QUARK,
|
||||
}:
|
||||
return True, None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise e
|
||||
@ -733,11 +711,12 @@ def _load_state_dict_into_meta_model(
|
||||
device_map_regex = "|".join([re.escape(k) for k in sorted(device_map.keys(), reverse=True)])
|
||||
|
||||
is_quantized = hf_quantizer is not None
|
||||
is_hqq_or_bnb = is_quantized and hf_quantizer.quantization_config.quant_method in [
|
||||
is_hqq_or_bnb_or_quark = is_quantized and hf_quantizer.quantization_config.quant_method in {
|
||||
QuantizationMethod.HQQ,
|
||||
QuantizationMethod.BITS_AND_BYTES,
|
||||
]
|
||||
is_meta_state_dict = shard_file.endswith(".safetensors") and not is_hqq_or_bnb
|
||||
QuantizationMethod.QUARK,
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_meta_state_dict = shard_file.endswith(".safetensors") and not is_hqq_or_bnb_or_quark
|
||||
file_pointer = None
|
||||
if is_meta_state_dict:
|
||||
file_pointer = safe_open(shard_file, framework="pt", device=tensor_device)
|
||||
@ -1525,7 +1504,6 @@ class ModuleUtilsMixin:
|
||||
seq_ids = torch.arange(seq_length, device=device)
|
||||
causal_mask = seq_ids[None, None, :].repeat(batch_size, seq_length, 1) <= seq_ids[None, :, None]
|
||||
# in case past_key_values are used we need to add a prefix ones mask to the causal mask
|
||||
# causal and attention masks must have same type with pytorch version < 1.3
|
||||
causal_mask = causal_mask.to(attention_mask.dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
if causal_mask.shape[1] < attention_mask.shape[1]:
|
||||
@ -1733,8 +1711,7 @@ class ModuleUtilsMixin:
|
||||
return 6 * self.estimate_tokens(input_dict) * self.num_parameters(exclude_embeddings=exclude_embeddings)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO (joao): remove `GenerationMixin` inheritance in v4.50
|
||||
class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMixin, PeftAdapterMixin):
|
||||
class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, PushToHubMixin, PeftAdapterMixin):
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
Base class for all models.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1814,6 +1791,9 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
# for example.
|
||||
_tp_plan = None
|
||||
|
||||
# tensor parallel degree to which model is sharded to.
|
||||
_tp_size = None
|
||||
|
||||
# A pipeline parallel plan specifying the layers which may not be present
|
||||
# on all ranks when PP is enabled. For top-level models, this attribute is
|
||||
# currently defined in respective model code. For base models, this
|
||||
@ -2054,6 +2034,35 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
' We recommend to just use `attn_implementation="flash_attention_2"` when loading the model.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(config._attn_implementation, str) and re.match(
|
||||
r"^[^/:]+/[^/:]+:[^/:]+$", config._attn_implementation
|
||||
):
|
||||
if not is_kernels_available():
|
||||
raise ValueError("kernels is not installed. Please install it with `pip install kernels`.")
|
||||
|
||||
# Extract repo_id and kernel_name from the string
|
||||
repo_id, kernel_name = config._attn_implementation.split(":")
|
||||
kernel_name = kernel_name.strip()
|
||||
repo_id = repo_id.strip()
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
kernel = get_kernel(repo_id)
|
||||
ALL_ATTENTION_FUNCTIONS.register(
|
||||
f"kernel_{repo_id.replace('/', '_')}", getattr(kernel, kernel_name)
|
||||
)
|
||||
config._attn_implementation = f"kernel_{repo_id.replace('/', '_')}"
|
||||
except FileNotFoundError as e:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"Could not find a kernel repository '{repo_id}' compatible with your devicein the hub: {e}. Using eager attention implementation instead."
|
||||
)
|
||||
config._attn_implementation = "eager"
|
||||
except AttributeError:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"the kernel function name or class specified in the attn_implementation argument is not valid. \
|
||||
Please check the documentation for the correct format, \
|
||||
and check that the kernel exports the class and the function correctly."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if (
|
||||
not isinstance(config._attn_implementation, dict)
|
||||
and config._attn_implementation not in ["eager"] + ALL_ATTENTION_FUNCTIONS.valid_keys()
|
||||
@ -2186,12 +2195,12 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if "PreTrainedModel" not in str(base) and base.can_generate():
|
||||
return True
|
||||
# BC: Detects whether `prepare_inputs_for_generation` has been overwritten in the model. Prior to v4.45, this
|
||||
# Detects whether `prepare_inputs_for_generation` has been overwritten in the model. Prior to v4.45, this
|
||||
# was how we detected whether a model could generate.
|
||||
if "GenerationMixin" not in str(cls.prepare_inputs_for_generation):
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
if hasattr(cls, "prepare_inputs_for_generation"): # implicit: doesn't inherit `GenerationMixin`
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"{cls.__name__} has generative capabilities, as `prepare_inputs_for_generation` is explicitly "
|
||||
"overwritten. However, it doesn't directly inherit from `GenerationMixin`. From 👉v4.50👈 onwards, "
|
||||
"defined. However, it doesn't directly inherit from `GenerationMixin`. From 👉v4.50👈 onwards, "
|
||||
"`PreTrainedModel` will NOT inherit from `GenerationMixin`, and this model will lose the ability "
|
||||
"to call `generate` and other related functions."
|
||||
"\n - If you're using `trust_remote_code=True`, you can get rid of this warning by loading the "
|
||||
@ -2201,7 +2210,6 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
"\n - If you are not the owner of the model architecture class, please contact the model code owner "
|
||||
"to update it."
|
||||
)
|
||||
return True
|
||||
# Otherwise, can't generate
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3876,6 +3884,8 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
A torch tensor parallel plan, see [here](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/TP_tutorial.html). Currently, it only accepts
|
||||
`tp_plan="auto"` to use predefined plan based on the model. Note that if you use it, you should launch your script accordingly with
|
||||
`torchrun [args] script.py`. This will be much faster than using a `device_map`, but has limitations.
|
||||
tp_size (`str`, *optional*):
|
||||
A torch tensor parallel degree. If not provided would default to world size.
|
||||
offload_folder (`str` or `os.PathLike`, *optional*):
|
||||
If the `device_map` contains any value `"disk"`, the folder where we will offload weights.
|
||||
offload_state_dict (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
@ -3972,6 +3982,7 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
generation_config = kwargs.pop("generation_config", None)
|
||||
gguf_file = kwargs.pop("gguf_file", None)
|
||||
tp_plan = kwargs.pop("tp_plan", None)
|
||||
tp_size = kwargs.pop("tp_size", None)
|
||||
key_mapping = kwargs.pop("key_mapping", None)
|
||||
# Not used anymore -- remove them from the kwargs
|
||||
_ = kwargs.pop("resume_download", None)
|
||||
@ -3984,7 +3995,8 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"`state_dict` cannot be passed together with a model name or a `gguf_file`. Use one of the two loading strategies."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if tp_size is not None and tp_plan is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("tp_plan has to be set when tp_size is passed.")
|
||||
if tp_plan is not None and tp_plan != "auto":
|
||||
# TODO: we can relax this check when we support taking tp_plan from a json file, for example.
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"tp_plan supports 'auto' only for now but got {tp_plan}.")
|
||||
@ -4020,6 +4032,9 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
elif device_type == "cpu":
|
||||
cpu_backend = "ccl" if int(os.environ.get("CCL_WORKER_COUNT", 0)) else "gloo"
|
||||
torch.distributed.init_process_group(cpu_backend, rank=rank, world_size=world_size)
|
||||
elif device_type == "xpu":
|
||||
torch.distributed.init_process_group("ccl", rank=rank, world_size=world_size)
|
||||
torch.xpu.set_device(int(os.environ["LOCAL_RANK"]))
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
raise EnvironmentError(
|
||||
@ -4028,7 +4043,10 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
) from e
|
||||
|
||||
# Get device with index assuming equal number of devices per host
|
||||
index = None if device_type == "cpu" else torch.cuda.current_device()
|
||||
if device_type == "xpu":
|
||||
index = torch.xpu.current_device()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
index = None if device_type == "cpu" else torch.cuda.current_device()
|
||||
tp_device = torch.device(device_type, index)
|
||||
|
||||
if index is not None and index > 0:
|
||||
@ -4038,9 +4056,10 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
sys.stderr = open(os.devnull, "w")
|
||||
# This is the easiest way to dispatch to the current process device
|
||||
device_map = tp_device
|
||||
# Assuming sharding the model onto the world
|
||||
world_size = torch.distributed.get_world_size()
|
||||
device_mesh = torch.distributed.init_device_mesh(tp_device.type, (world_size,))
|
||||
|
||||
# Assuming sharding the model onto the world when tp_size not provided
|
||||
tp_size = tp_size if tp_size is not None else torch.distributed.get_world_size()
|
||||
device_mesh = torch.distributed.init_device_mesh(tp_device.type, (tp_size,))
|
||||
|
||||
if use_auth_token is not None:
|
||||
warnings.warn(
|
||||
@ -4324,7 +4343,10 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
config = copy.deepcopy(config) # We do not want to modify the config inplace in from_pretrained.
|
||||
if not getattr(config, "_attn_implementation_autoset", False):
|
||||
config = cls._autoset_attn_implementation(
|
||||
config, use_flash_attention_2=use_flash_attention_2, torch_dtype=torch_dtype, device_map=device_map
|
||||
config,
|
||||
use_flash_attention_2=use_flash_attention_2,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch_dtype,
|
||||
device_map=device_map,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with ContextManagers(model_init_context):
|
||||
@ -4404,6 +4426,9 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
weights_only=weights_only,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# record tp degree the model sharded to
|
||||
model._tp_size = tp_size
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure token embedding weights are still tied if needed
|
||||
model.tie_weights()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -4487,7 +4512,6 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
elif from_flax:
|
||||
loading_info = None
|
||||
return model, loading_info
|
||||
|
||||
return model
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
@ -4612,11 +4636,15 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
):
|
||||
# Useful flags
|
||||
is_quantized = hf_quantizer is not None
|
||||
is_hqq = is_quantized and hf_quantizer.quantization_config.quant_method == QuantizationMethod.HQQ
|
||||
is_hqq_or_bnb = is_quantized and hf_quantizer.quantization_config.quant_method in [
|
||||
is_hqq_or_quark = is_quantized and hf_quantizer.quantization_config.quant_method in {
|
||||
QuantizationMethod.HQQ,
|
||||
QuantizationMethod.QUARK,
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_hqq_or_bnb_or_quark = is_quantized and hf_quantizer.quantization_config.quant_method in {
|
||||
QuantizationMethod.HQQ,
|
||||
QuantizationMethod.BITS_AND_BYTES,
|
||||
]
|
||||
QuantizationMethod.QUARK,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Get all the keys of the state dicts that we have to initialize the model
|
||||
if sharded_metadata is not None:
|
||||
@ -4778,7 +4806,7 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
expected_keys = hf_quantizer.update_expected_keys(model_to_load, expected_keys, checkpoint_keys)
|
||||
|
||||
# Warmup cuda to load the weights much faster on devices
|
||||
if device_map is not None and not is_hqq:
|
||||
if device_map is not None and not is_hqq_or_quark:
|
||||
expanded_device_map = expand_device_map(device_map, expected_keys)
|
||||
caching_allocator_warmup(model_to_load, expanded_device_map, factor=2 if hf_quantizer is None else 4)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -4792,7 +4820,7 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
map_location = "cpu"
|
||||
if (
|
||||
shard_file.endswith(".safetensors")
|
||||
and not is_hqq_or_bnb
|
||||
and not is_hqq_or_bnb_or_quark
|
||||
and not (is_deepspeed_zero3_enabled() and not is_quantized)
|
||||
):
|
||||
map_location = "meta"
|
||||
@ -5131,6 +5159,14 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
return True
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def tp_size(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the model's tensor parallelism degree.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# if None, the model didn't undergo tensor parallel sharding
|
||||
return self._tp_size
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def supports_pp_plan(self):
|
||||
if self._pp_plan is not None:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,316 +11,322 @@
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
|
||||
|
||||
from . import (
|
||||
aimv2,
|
||||
albert,
|
||||
align,
|
||||
altclip,
|
||||
aria,
|
||||
audio_spectrogram_transformer,
|
||||
auto,
|
||||
autoformer,
|
||||
aya_vision,
|
||||
bamba,
|
||||
bark,
|
||||
bart,
|
||||
barthez,
|
||||
bartpho,
|
||||
beit,
|
||||
bert,
|
||||
bert_generation,
|
||||
bert_japanese,
|
||||
bertweet,
|
||||
big_bird,
|
||||
bigbird_pegasus,
|
||||
biogpt,
|
||||
bit,
|
||||
blenderbot,
|
||||
blenderbot_small,
|
||||
blip,
|
||||
blip_2,
|
||||
bloom,
|
||||
bridgetower,
|
||||
bros,
|
||||
byt5,
|
||||
camembert,
|
||||
canine,
|
||||
chameleon,
|
||||
chinese_clip,
|
||||
clap,
|
||||
clip,
|
||||
clipseg,
|
||||
clvp,
|
||||
code_llama,
|
||||
codegen,
|
||||
cohere,
|
||||
cohere2,
|
||||
colpali,
|
||||
conditional_detr,
|
||||
convbert,
|
||||
convnext,
|
||||
convnextv2,
|
||||
cpm,
|
||||
cpmant,
|
||||
ctrl,
|
||||
cvt,
|
||||
dab_detr,
|
||||
dac,
|
||||
data2vec,
|
||||
dbrx,
|
||||
deberta,
|
||||
deberta_v2,
|
||||
decision_transformer,
|
||||
deepseek_v3,
|
||||
deformable_detr,
|
||||
deit,
|
||||
deprecated,
|
||||
depth_anything,
|
||||
depth_pro,
|
||||
detr,
|
||||
dialogpt,
|
||||
diffllama,
|
||||
dinat,
|
||||
dinov2,
|
||||
dinov2_with_registers,
|
||||
distilbert,
|
||||
dit,
|
||||
donut,
|
||||
dpr,
|
||||
dpt,
|
||||
efficientnet,
|
||||
electra,
|
||||
emu3,
|
||||
encodec,
|
||||
encoder_decoder,
|
||||
ernie,
|
||||
esm,
|
||||
falcon,
|
||||
falcon_mamba,
|
||||
fastspeech2_conformer,
|
||||
flaubert,
|
||||
flava,
|
||||
fnet,
|
||||
focalnet,
|
||||
fsmt,
|
||||
funnel,
|
||||
fuyu,
|
||||
gemma,
|
||||
gemma2,
|
||||
gemma3,
|
||||
git,
|
||||
glm,
|
||||
glpn,
|
||||
got_ocr2,
|
||||
gpt2,
|
||||
gpt_bigcode,
|
||||
gpt_neo,
|
||||
gpt_neox,
|
||||
gpt_neox_japanese,
|
||||
gpt_sw3,
|
||||
gptj,
|
||||
granite,
|
||||
granitemoe,
|
||||
granitemoeshared,
|
||||
grounding_dino,
|
||||
groupvit,
|
||||
helium,
|
||||
herbert,
|
||||
hiera,
|
||||
hubert,
|
||||
ibert,
|
||||
idefics,
|
||||
idefics2,
|
||||
idefics3,
|
||||
ijepa,
|
||||
imagegpt,
|
||||
informer,
|
||||
instructblip,
|
||||
instructblipvideo,
|
||||
jamba,
|
||||
jetmoe,
|
||||
kosmos2,
|
||||
layoutlm,
|
||||
layoutlmv2,
|
||||
layoutlmv3,
|
||||
layoutxlm,
|
||||
led,
|
||||
levit,
|
||||
lilt,
|
||||
llama,
|
||||
llama4,
|
||||
llava,
|
||||
llava_next,
|
||||
llava_next_video,
|
||||
llava_onevision,
|
||||
longformer,
|
||||
longt5,
|
||||
luke,
|
||||
lxmert,
|
||||
m2m_100,
|
||||
mamba,
|
||||
mamba2,
|
||||
marian,
|
||||
markuplm,
|
||||
mask2former,
|
||||
maskformer,
|
||||
mbart,
|
||||
mbart50,
|
||||
megatron_bert,
|
||||
megatron_gpt2,
|
||||
mgp_str,
|
||||
mimi,
|
||||
mistral,
|
||||
mistral3,
|
||||
mixtral,
|
||||
mllama,
|
||||
mluke,
|
||||
mobilebert,
|
||||
mobilenet_v1,
|
||||
mobilenet_v2,
|
||||
mobilevit,
|
||||
mobilevitv2,
|
||||
modernbert,
|
||||
moonshine,
|
||||
moshi,
|
||||
mpnet,
|
||||
mpt,
|
||||
mra,
|
||||
mt5,
|
||||
musicgen,
|
||||
musicgen_melody,
|
||||
mvp,
|
||||
myt5,
|
||||
nemotron,
|
||||
nllb,
|
||||
nllb_moe,
|
||||
nougat,
|
||||
nystromformer,
|
||||
olmo,
|
||||
olmo2,
|
||||
olmoe,
|
||||
omdet_turbo,
|
||||
oneformer,
|
||||
openai,
|
||||
opt,
|
||||
owlv2,
|
||||
owlvit,
|
||||
paligemma,
|
||||
patchtsmixer,
|
||||
patchtst,
|
||||
pegasus,
|
||||
pegasus_x,
|
||||
perceiver,
|
||||
persimmon,
|
||||
phi,
|
||||
phi3,
|
||||
phi4_multimodal,
|
||||
phimoe,
|
||||
phobert,
|
||||
pix2struct,
|
||||
pixtral,
|
||||
plbart,
|
||||
poolformer,
|
||||
pop2piano,
|
||||
prompt_depth_anything,
|
||||
prophetnet,
|
||||
pvt,
|
||||
pvt_v2,
|
||||
qwen2,
|
||||
qwen2_5_vl,
|
||||
qwen2_audio,
|
||||
qwen2_moe,
|
||||
qwen2_vl,
|
||||
qwen3,
|
||||
qwen3_moe,
|
||||
rag,
|
||||
recurrent_gemma,
|
||||
reformer,
|
||||
regnet,
|
||||
rembert,
|
||||
resnet,
|
||||
roberta,
|
||||
roberta_prelayernorm,
|
||||
roc_bert,
|
||||
roformer,
|
||||
rt_detr,
|
||||
rt_detr_v2,
|
||||
rwkv,
|
||||
sam,
|
||||
seamless_m4t,
|
||||
seamless_m4t_v2,
|
||||
segformer,
|
||||
seggpt,
|
||||
sew,
|
||||
sew_d,
|
||||
shieldgemma2,
|
||||
siglip,
|
||||
siglip2,
|
||||
smolvlm,
|
||||
speech_encoder_decoder,
|
||||
speech_to_text,
|
||||
speecht5,
|
||||
splinter,
|
||||
squeezebert,
|
||||
stablelm,
|
||||
starcoder2,
|
||||
superglue,
|
||||
superpoint,
|
||||
swiftformer,
|
||||
swin,
|
||||
swin2sr,
|
||||
swinv2,
|
||||
switch_transformers,
|
||||
t5,
|
||||
table_transformer,
|
||||
tapas,
|
||||
textnet,
|
||||
time_series_transformer,
|
||||
timesformer,
|
||||
timm_backbone,
|
||||
timm_wrapper,
|
||||
trocr,
|
||||
tvp,
|
||||
udop,
|
||||
umt5,
|
||||
unispeech,
|
||||
unispeech_sat,
|
||||
univnet,
|
||||
upernet,
|
||||
video_llava,
|
||||
videomae,
|
||||
vilt,
|
||||
vipllava,
|
||||
vision_encoder_decoder,
|
||||
vision_text_dual_encoder,
|
||||
visual_bert,
|
||||
vit,
|
||||
vit_mae,
|
||||
vit_msn,
|
||||
vitdet,
|
||||
vitmatte,
|
||||
vitpose,
|
||||
vitpose_backbone,
|
||||
vits,
|
||||
vivit,
|
||||
wav2vec2,
|
||||
wav2vec2_bert,
|
||||
wav2vec2_conformer,
|
||||
wav2vec2_phoneme,
|
||||
wav2vec2_with_lm,
|
||||
wavlm,
|
||||
whisper,
|
||||
x_clip,
|
||||
xglm,
|
||||
xlm,
|
||||
xlm_roberta,
|
||||
xlm_roberta_xl,
|
||||
xlnet,
|
||||
xmod,
|
||||
yolos,
|
||||
yoso,
|
||||
zamba,
|
||||
zamba2,
|
||||
zoedepth,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from ..utils import _LazyModule
|
||||
from ..utils.import_utils import define_import_structure
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
from .aimv2 import *
|
||||
from .albert import *
|
||||
from .align import *
|
||||
from .altclip import *
|
||||
from .aria import *
|
||||
from .audio_spectrogram_transformer import *
|
||||
from .auto import *
|
||||
from .autoformer import *
|
||||
from .aya_vision import *
|
||||
from .bamba import *
|
||||
from .bark import *
|
||||
from .bart import *
|
||||
from .barthez import *
|
||||
from .bartpho import *
|
||||
from .beit import *
|
||||
from .bert import *
|
||||
from .bert_generation import *
|
||||
from .bert_japanese import *
|
||||
from .bertweet import *
|
||||
from .big_bird import *
|
||||
from .bigbird_pegasus import *
|
||||
from .biogpt import *
|
||||
from .bit import *
|
||||
from .blenderbot import *
|
||||
from .blenderbot_small import *
|
||||
from .blip import *
|
||||
from .blip_2 import *
|
||||
from .bloom import *
|
||||
from .bridgetower import *
|
||||
from .bros import *
|
||||
from .byt5 import *
|
||||
from .camembert import *
|
||||
from .canine import *
|
||||
from .chameleon import *
|
||||
from .chinese_clip import *
|
||||
from .clap import *
|
||||
from .clip import *
|
||||
from .clipseg import *
|
||||
from .clvp import *
|
||||
from .code_llama import *
|
||||
from .codegen import *
|
||||
from .cohere import *
|
||||
from .cohere2 import *
|
||||
from .colpali import *
|
||||
from .conditional_detr import *
|
||||
from .convbert import *
|
||||
from .convnext import *
|
||||
from .convnextv2 import *
|
||||
from .cpm import *
|
||||
from .cpmant import *
|
||||
from .ctrl import *
|
||||
from .cvt import *
|
||||
from .dab_detr import *
|
||||
from .dac import *
|
||||
from .data2vec import *
|
||||
from .dbrx import *
|
||||
from .deberta import *
|
||||
from .deberta_v2 import *
|
||||
from .decision_transformer import *
|
||||
from .deformable_detr import *
|
||||
from .deit import *
|
||||
from .deprecated import *
|
||||
from .depth_anything import *
|
||||
from .depth_pro import *
|
||||
from .detr import *
|
||||
from .dialogpt import *
|
||||
from .diffllama import *
|
||||
from .dinat import *
|
||||
from .dinov2 import *
|
||||
from .dinov2_with_registers import *
|
||||
from .distilbert import *
|
||||
from .dit import *
|
||||
from .donut import *
|
||||
from .dpr import *
|
||||
from .dpt import *
|
||||
from .efficientnet import *
|
||||
from .electra import *
|
||||
from .emu3 import *
|
||||
from .encodec import *
|
||||
from .encoder_decoder import *
|
||||
from .ernie import *
|
||||
from .esm import *
|
||||
from .falcon import *
|
||||
from .falcon_mamba import *
|
||||
from .fastspeech2_conformer import *
|
||||
from .flaubert import *
|
||||
from .flava import *
|
||||
from .fnet import *
|
||||
from .focalnet import *
|
||||
from .fsmt import *
|
||||
from .funnel import *
|
||||
from .fuyu import *
|
||||
from .gemma import *
|
||||
from .gemma2 import *
|
||||
from .gemma3 import *
|
||||
from .git import *
|
||||
from .glm import *
|
||||
from .glm4 import *
|
||||
from .glpn import *
|
||||
from .got_ocr2 import *
|
||||
from .gpt2 import *
|
||||
from .gpt_bigcode import *
|
||||
from .gpt_neo import *
|
||||
from .gpt_neox import *
|
||||
from .gpt_neox_japanese import *
|
||||
from .gpt_sw3 import *
|
||||
from .gptj import *
|
||||
from .granite import *
|
||||
from .granite_speech import *
|
||||
from .granitemoe import *
|
||||
from .granitemoeshared import *
|
||||
from .grounding_dino import *
|
||||
from .groupvit import *
|
||||
from .helium import *
|
||||
from .herbert import *
|
||||
from .hiera import *
|
||||
from .hubert import *
|
||||
from .ibert import *
|
||||
from .idefics import *
|
||||
from .idefics2 import *
|
||||
from .idefics3 import *
|
||||
from .ijepa import *
|
||||
from .imagegpt import *
|
||||
from .informer import *
|
||||
from .instructblip import *
|
||||
from .instructblipvideo import *
|
||||
from .jamba import *
|
||||
from .jetmoe import *
|
||||
from .kosmos2 import *
|
||||
from .layoutlm import *
|
||||
from .layoutlmv2 import *
|
||||
from .layoutlmv3 import *
|
||||
from .layoutxlm import *
|
||||
from .led import *
|
||||
from .levit import *
|
||||
from .lilt import *
|
||||
from .llama import *
|
||||
from .llama4 import *
|
||||
from .llava import *
|
||||
from .llava_next import *
|
||||
from .llava_next_video import *
|
||||
from .llava_onevision import *
|
||||
from .longformer import *
|
||||
from .longt5 import *
|
||||
from .luke import *
|
||||
from .lxmert import *
|
||||
from .m2m_100 import *
|
||||
from .mamba import *
|
||||
from .mamba2 import *
|
||||
from .marian import *
|
||||
from .markuplm import *
|
||||
from .mask2former import *
|
||||
from .maskformer import *
|
||||
from .mbart import *
|
||||
from .mbart50 import *
|
||||
from .megatron_bert import *
|
||||
from .megatron_gpt2 import *
|
||||
from .mgp_str import *
|
||||
from .mimi import *
|
||||
from .mistral import *
|
||||
from .mistral3 import *
|
||||
from .mixtral import *
|
||||
from .mllama import *
|
||||
from .mluke import *
|
||||
from .mobilebert import *
|
||||
from .mobilenet_v1 import *
|
||||
from .mobilenet_v2 import *
|
||||
from .mobilevit import *
|
||||
from .mobilevitv2 import *
|
||||
from .modernbert import *
|
||||
from .moonshine import *
|
||||
from .moshi import *
|
||||
from .mpnet import *
|
||||
from .mpt import *
|
||||
from .mra import *
|
||||
from .mt5 import *
|
||||
from .musicgen import *
|
||||
from .musicgen_melody import *
|
||||
from .mvp import *
|
||||
from .myt5 import *
|
||||
from .nemotron import *
|
||||
from .nllb import *
|
||||
from .nllb_moe import *
|
||||
from .nougat import *
|
||||
from .nystromformer import *
|
||||
from .olmo import *
|
||||
from .olmo2 import *
|
||||
from .olmoe import *
|
||||
from .omdet_turbo import *
|
||||
from .oneformer import *
|
||||
from .openai import *
|
||||
from .opt import *
|
||||
from .owlv2 import *
|
||||
from .owlvit import *
|
||||
from .paligemma import *
|
||||
from .patchtsmixer import *
|
||||
from .patchtst import *
|
||||
from .pegasus import *
|
||||
from .pegasus_x import *
|
||||
from .perceiver import *
|
||||
from .persimmon import *
|
||||
from .phi import *
|
||||
from .phi3 import *
|
||||
from .phi4_multimodal import *
|
||||
from .phimoe import *
|
||||
from .phobert import *
|
||||
from .pix2struct import *
|
||||
from .pixtral import *
|
||||
from .plbart import *
|
||||
from .poolformer import *
|
||||
from .pop2piano import *
|
||||
from .prophetnet import *
|
||||
from .pvt import *
|
||||
from .pvt_v2 import *
|
||||
from .qwen2 import *
|
||||
from .qwen2_5_vl import *
|
||||
from .qwen2_audio import *
|
||||
from .qwen2_moe import *
|
||||
from .qwen2_vl import *
|
||||
from .rag import *
|
||||
from .recurrent_gemma import *
|
||||
from .reformer import *
|
||||
from .regnet import *
|
||||
from .rembert import *
|
||||
from .resnet import *
|
||||
from .roberta import *
|
||||
from .roberta_prelayernorm import *
|
||||
from .roc_bert import *
|
||||
from .roformer import *
|
||||
from .rt_detr import *
|
||||
from .rt_detr_v2 import *
|
||||
from .rwkv import *
|
||||
from .sam import *
|
||||
from .seamless_m4t import *
|
||||
from .seamless_m4t_v2 import *
|
||||
from .segformer import *
|
||||
from .seggpt import *
|
||||
from .sew import *
|
||||
from .sew_d import *
|
||||
from .siglip import *
|
||||
from .siglip2 import *
|
||||
from .smolvlm import *
|
||||
from .speech_encoder_decoder import *
|
||||
from .speech_to_text import *
|
||||
from .speecht5 import *
|
||||
from .splinter import *
|
||||
from .squeezebert import *
|
||||
from .stablelm import *
|
||||
from .starcoder2 import *
|
||||
from .superglue import *
|
||||
from .superpoint import *
|
||||
from .swiftformer import *
|
||||
from .swin import *
|
||||
from .swin2sr import *
|
||||
from .swinv2 import *
|
||||
from .switch_transformers import *
|
||||
from .t5 import *
|
||||
from .table_transformer import *
|
||||
from .tapas import *
|
||||
from .textnet import *
|
||||
from .time_series_transformer import *
|
||||
from .timesformer import *
|
||||
from .timm_backbone import *
|
||||
from .timm_wrapper import *
|
||||
from .trocr import *
|
||||
from .tvp import *
|
||||
from .udop import *
|
||||
from .umt5 import *
|
||||
from .unispeech import *
|
||||
from .unispeech_sat import *
|
||||
from .univnet import *
|
||||
from .upernet import *
|
||||
from .video_llava import *
|
||||
from .videomae import *
|
||||
from .vilt import *
|
||||
from .vipllava import *
|
||||
from .vision_encoder_decoder import *
|
||||
from .vision_text_dual_encoder import *
|
||||
from .visual_bert import *
|
||||
from .vit import *
|
||||
from .vit_mae import *
|
||||
from .vit_msn import *
|
||||
from .vitdet import *
|
||||
from .vitmatte import *
|
||||
from .vitpose import *
|
||||
from .vitpose_backbone import *
|
||||
from .vits import *
|
||||
from .vivit import *
|
||||
from .wav2vec2 import *
|
||||
from .wav2vec2_bert import *
|
||||
from .wav2vec2_conformer import *
|
||||
from .wav2vec2_phoneme import *
|
||||
from .wav2vec2_with_lm import *
|
||||
from .wavlm import *
|
||||
from .whisper import *
|
||||
from .x_clip import *
|
||||
from .xglm import *
|
||||
from .xlm import *
|
||||
from .xlm_roberta import *
|
||||
from .xlm_roberta_xl import *
|
||||
from .xlnet import *
|
||||
from .xmod import *
|
||||
from .yolos import *
|
||||
from .yoso import *
|
||||
from .zamba import *
|
||||
from .zamba2 import *
|
||||
from .zoedepth import *
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
_file = globals()["__file__"]
|
||||
sys.modules[__name__] = _LazyModule(__name__, _file, define_import_structure(_file), module_spec=__spec__)
|
||||
@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ import sentencepiece as spm
|
||||
|
||||
from ...tokenization_utils import AddedToken, PreTrainedTokenizer
|
||||
from ...utils import logging
|
||||
from ...utils.import_utils import export
|
||||
from ...utils.import_utils import requires
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ VOCAB_FILES_NAMES = {"vocab_file": "spiece.model"}
|
||||
SPIECE_UNDERLINE = "▁"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@export(backends=("sentencepiece",))
|
||||
@requires(backends=("sentencepiece",))
|
||||
class AlbertTokenizer(PreTrainedTokenizer):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Construct an ALBERT tokenizer. Based on [SentencePiece](https://github.com/google/sentencepiece).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -31,12 +31,16 @@ from ...image_utils import (
|
||||
PILImageResampling,
|
||||
get_image_size,
|
||||
infer_channel_dimension_format,
|
||||
is_scaled_image,
|
||||
make_flat_list_of_images,
|
||||
to_numpy_array,
|
||||
valid_images,
|
||||
validate_preprocess_arguments,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from ...utils import TensorType
|
||||
from ...utils import TensorType, logging
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def divide_to_patches(image: np.array, patch_size: int, input_data_format) -> List[np.array]:
|
||||
@ -104,6 +108,12 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
Whether to split the image.
|
||||
do_convert_rgb (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Whether to convert the image to RGB.
|
||||
do_rescale (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Whether to rescale the image by the specified scale `rescale_factor`. Can be overridden by `do_rescale` in
|
||||
the `preprocess` method.
|
||||
rescale_factor (`int` or `float`, *optional*, defaults to `1/255`):
|
||||
Scale factor to use if rescaling the image. Can be overridden by `rescale_factor` in the `preprocess`
|
||||
method.
|
||||
do_normalize (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Whether to normalize the image.
|
||||
resample (PILImageResampling, *optional*, defaults to `BICUBIC`):
|
||||
@ -121,6 +131,8 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
split_resolutions: Optional[List[Tuple[int, int]]] = None,
|
||||
split_image: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
do_convert_rgb: Optional[bool] = True,
|
||||
do_rescale: bool = True,
|
||||
rescale_factor: Union[int, float] = 1 / 255,
|
||||
do_normalize: Optional[bool] = True,
|
||||
resample: PILImageResampling = PILImageResampling.BICUBIC,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
@ -141,6 +153,8 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
split_resolutions = [(el[0] * 490, el[1] * 490) for el in split_resolutions]
|
||||
self.split_resolutions = split_resolutions
|
||||
self.do_convert_rgb = do_convert_rgb
|
||||
self.do_rescale = do_rescale
|
||||
self.rescale_factor = rescale_factor
|
||||
self.do_normalize = do_normalize
|
||||
self.resample = resample
|
||||
|
||||
@ -153,6 +167,8 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
min_image_size: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
split_image: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
do_convert_rgb: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
do_rescale: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
rescale_factor: Optional[float] = None,
|
||||
do_normalize: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
resample: PILImageResampling = None,
|
||||
return_tensors: Optional[Union[str, TensorType]] = "pt",
|
||||
@ -177,6 +193,10 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
Whether to split the image.
|
||||
do_convert_rgb (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `self.do_convert_rgb` (True)):
|
||||
Whether to convert the image to RGB.
|
||||
do_rescale (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `self.do_rescale`):
|
||||
Whether to rescale the image.
|
||||
rescale_factor (`float`, *optional*, defaults to `self.rescale_factor`):
|
||||
Rescale factor to rescale the image by if `do_rescale` is set to `True`.
|
||||
do_normalize (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `self.do_normalize` (True)):
|
||||
Whether to normalize the image.
|
||||
resample (PILImageResampling, *optional*, defaults to `self.resample` (BICUBIC)):
|
||||
@ -217,6 +237,8 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
min_image_size = min_image_size if min_image_size is not None else self.min_image_size
|
||||
split_image = split_image if split_image is not None else self.split_image
|
||||
do_convert_rgb = do_convert_rgb if do_convert_rgb is not None else self.do_convert_rgb
|
||||
do_rescale = do_rescale if do_rescale is not None else self.do_rescale
|
||||
rescale_factor = rescale_factor if rescale_factor is not None else self.rescale_factor
|
||||
do_normalize = do_normalize if do_normalize is not None else self.do_normalize
|
||||
resample = resample if resample is not None else self.resample
|
||||
|
||||
@ -236,6 +258,8 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
image_mean=image_mean,
|
||||
image_std=image_std,
|
||||
resample=resample,
|
||||
do_rescale=do_rescale,
|
||||
rescale_factor=rescale_factor,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if do_convert_rgb:
|
||||
@ -244,6 +268,12 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
# All transformations expect numpy arrays.
|
||||
images = [to_numpy_array(image) for image in images]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_rescale and is_scaled_image(images[0]):
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"It looks like you are trying to rescale already rescaled images. If the input"
|
||||
" images have pixel values between 0 and 1, set `do_rescale=False` to avoid rescaling them again."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if input_data_format is None:
|
||||
# We assume that all images have the same channel dimension format.
|
||||
input_data_format = infer_channel_dimension_format(images[0])
|
||||
@ -297,9 +327,14 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
pixel_mask[: new_size[0], : new_size[1]] = 1
|
||||
pixel_masks.append(pixel_mask)
|
||||
|
||||
if do_rescale:
|
||||
crop_image_padded = self.rescale(
|
||||
image=crop_image_padded, scale=rescale_factor, input_data_format=input_data_format
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if do_normalize:
|
||||
crop_image_padded = self.normalize(
|
||||
crop_image_padded / 255.0,
|
||||
crop_image_padded,
|
||||
self.image_mean,
|
||||
self.image_std,
|
||||
data_format=input_data_format,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,6 +25,7 @@ from typing import Callable, List, Optional, Tuple, Union
|
||||
from ...activations import ACT2FN
|
||||
from ...cache_utils import Cache, DynamicCache, StaticCache
|
||||
from ...generation import GenerationMixin
|
||||
from ...integrations import use_kernel_forward_from_hub
|
||||
from ...modeling_attn_mask_utils import AttentionMaskConverter
|
||||
from ...modeling_flash_attention_utils import FlashAttentionKwargs
|
||||
from ...modeling_outputs import BaseModelOutputWithPast, CausalLMOutputWithPast, ModelOutput
|
||||
@ -61,6 +62,7 @@ logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
_CONFIG_FOR_DOC = "AriaTextConfig"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@use_kernel_forward_from_hub("RMSNorm")
|
||||
class AriaTextRMSNorm(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, hidden_size, eps=1e-6):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -563,6 +565,7 @@ class AriaTextAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
key_states, value_states = past_key_value.update(key_states, value_states, self.layer_idx, cache_kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
attention_interface: Callable = eager_attention_forward
|
||||
|
||||
if self.config._attn_implementation != "eager":
|
||||
if self.config._attn_implementation == "sdpa" and kwargs.get("output_attentions", False):
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
@ -623,7 +626,6 @@ class AriaTextDecoderLayer(nn.Module):
|
||||
**kwargs: Unpack[FlashAttentionKwargs],
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, Optional[Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor]]]:
|
||||
residual = hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
hidden_states = self.input_layernorm(hidden_states)
|
||||
|
||||
# Self Attention
|
||||
@ -1037,7 +1039,7 @@ class AriaTextModel(AriaTextPreTrainedModel):
|
||||
if (
|
||||
self.config._attn_implementation == "sdpa"
|
||||
and attention_mask is not None
|
||||
and attention_mask.device.type in ["cuda", "xpu"]
|
||||
and attention_mask.device.type in ["cuda", "xpu", "npu"]
|
||||
and not output_attentions
|
||||
):
|
||||
# Attend to all tokens in fully masked rows in the causal_mask, for example the relevant first rows when
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,6 +28,7 @@ from ...image_utils import (
|
||||
PILImageResampling,
|
||||
get_image_size,
|
||||
infer_channel_dimension_format,
|
||||
is_scaled_image,
|
||||
make_flat_list_of_images,
|
||||
to_numpy_array,
|
||||
valid_images,
|
||||
@ -495,6 +496,12 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
Whether to split the image.
|
||||
do_convert_rgb (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Whether to convert the image to RGB.
|
||||
do_rescale (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Whether to rescale the image by the specified scale `rescale_factor`. Can be overridden by `do_rescale` in
|
||||
the `preprocess` method.
|
||||
rescale_factor (`int` or `float`, *optional*, defaults to `1/255`):
|
||||
Scale factor to use if rescaling the image. Can be overridden by `rescale_factor` in the `preprocess`
|
||||
method.
|
||||
do_normalize (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Whether to normalize the image.
|
||||
resample (PILImageResampling, *optional*, defaults to `BICUBIC`):
|
||||
@ -512,6 +519,8 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
split_resolutions: Optional[List[Tuple[int, int]]] = None,
|
||||
split_image: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
do_convert_rgb: Optional[bool] = True,
|
||||
do_rescale: bool = True,
|
||||
rescale_factor: Union[int, float] = 1 / 255,
|
||||
do_normalize: Optional[bool] = True,
|
||||
resample: PILImageResampling = PILImageResampling.BICUBIC,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
@ -532,6 +541,8 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
split_resolutions = [(el[0] * 490, el[1] * 490) for el in split_resolutions]
|
||||
self.split_resolutions = split_resolutions
|
||||
self.do_convert_rgb = do_convert_rgb
|
||||
self.do_rescale = do_rescale
|
||||
self.rescale_factor = rescale_factor
|
||||
self.do_normalize = do_normalize
|
||||
self.resample = resample
|
||||
|
||||
@ -544,6 +555,8 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
min_image_size: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
split_image: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
do_convert_rgb: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
do_rescale: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
rescale_factor: Optional[float] = None,
|
||||
do_normalize: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
resample: PILImageResampling = None,
|
||||
return_tensors: Optional[Union[str, TensorType]] = "pt",
|
||||
@ -568,6 +581,10 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
Whether to split the image.
|
||||
do_convert_rgb (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `self.do_convert_rgb` (True)):
|
||||
Whether to convert the image to RGB.
|
||||
do_rescale (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `self.do_rescale`):
|
||||
Whether to rescale the image.
|
||||
rescale_factor (`float`, *optional*, defaults to `self.rescale_factor`):
|
||||
Rescale factor to rescale the image by if `do_rescale` is set to `True`.
|
||||
do_normalize (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `self.do_normalize` (True)):
|
||||
Whether to normalize the image.
|
||||
resample (PILImageResampling, *optional*, defaults to `self.resample` (BICUBIC)):
|
||||
@ -608,6 +625,8 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
min_image_size = min_image_size if min_image_size is not None else self.min_image_size
|
||||
split_image = split_image if split_image is not None else self.split_image
|
||||
do_convert_rgb = do_convert_rgb if do_convert_rgb is not None else self.do_convert_rgb
|
||||
do_rescale = do_rescale if do_rescale is not None else self.do_rescale
|
||||
rescale_factor = rescale_factor if rescale_factor is not None else self.rescale_factor
|
||||
do_normalize = do_normalize if do_normalize is not None else self.do_normalize
|
||||
resample = resample if resample is not None else self.resample
|
||||
|
||||
@ -627,6 +646,8 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
image_mean=image_mean,
|
||||
image_std=image_std,
|
||||
resample=resample,
|
||||
do_rescale=do_rescale,
|
||||
rescale_factor=rescale_factor,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if do_convert_rgb:
|
||||
@ -635,6 +656,12 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
# All transformations expect numpy arrays.
|
||||
images = [to_numpy_array(image) for image in images]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_rescale and is_scaled_image(images[0]):
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"It looks like you are trying to rescale already rescaled images. If the input"
|
||||
" images have pixel values between 0 and 1, set `do_rescale=False` to avoid rescaling them again."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if input_data_format is None:
|
||||
# We assume that all images have the same channel dimension format.
|
||||
input_data_format = infer_channel_dimension_format(images[0])
|
||||
@ -688,9 +715,14 @@ class AriaImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
pixel_mask[: new_size[0], : new_size[1]] = 1
|
||||
pixel_masks.append(pixel_mask)
|
||||
|
||||
if do_rescale:
|
||||
crop_image_padded = self.rescale(
|
||||
image=crop_image_padded, scale=rescale_factor, input_data_format=input_data_format
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if do_normalize:
|
||||
crop_image_padded = self.normalize(
|
||||
crop_image_padded / 255.0,
|
||||
crop_image_padded,
|
||||
self.image_mean,
|
||||
self.image_std,
|
||||
data_format=input_data_format,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,399 +11,24 @@
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
|
||||
|
||||
from ...utils import (
|
||||
OptionalDependencyNotAvailable,
|
||||
_LazyModule,
|
||||
is_flax_available,
|
||||
is_tf_available,
|
||||
is_torch_available,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
_import_structure = {
|
||||
"auto_factory": ["get_values"],
|
||||
"configuration_auto": ["CONFIG_MAPPING", "MODEL_NAMES_MAPPING", "AutoConfig"],
|
||||
"feature_extraction_auto": ["FEATURE_EXTRACTOR_MAPPING", "AutoFeatureExtractor"],
|
||||
"image_processing_auto": ["IMAGE_PROCESSOR_MAPPING", "AutoImageProcessor"],
|
||||
"processing_auto": ["PROCESSOR_MAPPING", "AutoProcessor"],
|
||||
"tokenization_auto": ["TOKENIZER_MAPPING", "AutoTokenizer"],
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if not is_torch_available():
|
||||
raise OptionalDependencyNotAvailable()
|
||||
except OptionalDependencyNotAvailable:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
_import_structure["modeling_auto"] = [
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_FRAME_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_XVECTOR_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_BACKBONE_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_IMAGE_MODELING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_CTC_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_DOCUMENT_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_DEPTH_ESTIMATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_TO_IMAGE_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_KEYPOINT_DETECTION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_INSTANCE_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_MASKED_IMAGE_MODELING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_MASKED_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_MASK_GENERATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_MULTIPLE_CHOICE_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_NEXT_SENTENCE_PREDICTION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_OBJECT_DETECTION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_PRETRAINING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_SEMANTIC_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_SEQ_TO_SEQ_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_SEQUENCE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_SPEECH_SEQ_2_SEQ_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_TABLE_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_TEXT_ENCODING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_TEXT_TO_WAVEFORM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_TEXT_TO_SPECTROGRAM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_TOKEN_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_UNIVERSAL_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_VIDEO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_VISION_2_SEQ_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_RETRIEVAL_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_TEXT_TO_TEXT_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_VISUAL_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_WITH_LM_HEAD_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_ZERO_SHOT_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_ZERO_SHOT_OBJECT_DETECTION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_TIME_SERIES_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_TIME_SERIES_REGRESSION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"AutoModel",
|
||||
"AutoBackbone",
|
||||
"AutoModelForAudioClassification",
|
||||
"AutoModelForAudioFrameClassification",
|
||||
"AutoModelForAudioXVector",
|
||||
"AutoModelForCausalLM",
|
||||
"AutoModelForCTC",
|
||||
"AutoModelForDepthEstimation",
|
||||
"AutoModelForImageClassification",
|
||||
"AutoModelForImageSegmentation",
|
||||
"AutoModelForImageToImage",
|
||||
"AutoModelForInstanceSegmentation",
|
||||
"AutoModelForKeypointDetection",
|
||||
"AutoModelForMaskGeneration",
|
||||
"AutoModelForTextEncoding",
|
||||
"AutoModelForMaskedImageModeling",
|
||||
"AutoModelForMaskedLM",
|
||||
"AutoModelForMultipleChoice",
|
||||
"AutoModelForNextSentencePrediction",
|
||||
"AutoModelForObjectDetection",
|
||||
"AutoModelForPreTraining",
|
||||
"AutoModelForQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"AutoModelForSemanticSegmentation",
|
||||
"AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM",
|
||||
"AutoModelForSequenceClassification",
|
||||
"AutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq",
|
||||
"AutoModelForTableQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"AutoModelForTextToSpectrogram",
|
||||
"AutoModelForTextToWaveform",
|
||||
"AutoModelForTokenClassification",
|
||||
"AutoModelForUniversalSegmentation",
|
||||
"AutoModelForVideoClassification",
|
||||
"AutoModelForVision2Seq",
|
||||
"AutoModelForVisualQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"AutoModelForDocumentQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"AutoModelWithLMHead",
|
||||
"AutoModelForZeroShotImageClassification",
|
||||
"AutoModelForZeroShotObjectDetection",
|
||||
"AutoModelForImageTextToText",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if not is_tf_available():
|
||||
raise OptionalDependencyNotAvailable()
|
||||
except OptionalDependencyNotAvailable:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
_import_structure["modeling_tf_auto"] = [
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_MASK_GENERATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_MASKED_IMAGE_MODELING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_MASKED_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_MULTIPLE_CHOICE_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_NEXT_SENTENCE_PREDICTION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_PRETRAINING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_DOCUMENT_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_SEMANTIC_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_SEQ_TO_SEQ_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_SEQUENCE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_SPEECH_SEQ_2_SEQ_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_TABLE_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_TEXT_ENCODING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_TOKEN_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_VISION_2_SEQ_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_ZERO_SHOT_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_WITH_LM_HEAD_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TFAutoModel",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForAudioClassification",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForCausalLM",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForImageClassification",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForMaskedImageModeling",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForMaskedLM",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForMaskGeneration",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForMultipleChoice",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForNextSentencePrediction",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForPreTraining",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForDocumentQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForSemanticSegmentation",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForSeq2SeqLM",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForTableQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForTextEncoding",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForTokenClassification",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForVision2Seq",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForZeroShotImageClassification",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelWithLMHead",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if not is_flax_available():
|
||||
raise OptionalDependencyNotAvailable()
|
||||
except OptionalDependencyNotAvailable:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
_import_structure["modeling_flax_auto"] = [
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_MASKED_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_MULTIPLE_CHOICE_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_NEXT_SENTENCE_PREDICTION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_PRETRAINING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_SEQ_TO_SEQ_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_SEQUENCE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_SPEECH_SEQ_2_SEQ_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_TOKEN_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_VISION_2_SEQ_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModel",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForCausalLM",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForImageClassification",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForMaskedLM",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForMultipleChoice",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForNextSentencePrediction",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForPreTraining",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForSeq2SeqLM",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForSequenceClassification",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForTokenClassification",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForVision2Seq",
|
||||
]
|
||||
from ...utils import _LazyModule
|
||||
from ...utils.import_utils import define_import_structure
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
from .auto_factory import get_values
|
||||
from .configuration_auto import CONFIG_MAPPING, MODEL_NAMES_MAPPING, AutoConfig
|
||||
from .feature_extraction_auto import FEATURE_EXTRACTOR_MAPPING, AutoFeatureExtractor
|
||||
from .image_processing_auto import IMAGE_PROCESSOR_MAPPING, AutoImageProcessor
|
||||
from .processing_auto import PROCESSOR_MAPPING, AutoProcessor
|
||||
from .tokenization_auto import TOKENIZER_MAPPING, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if not is_torch_available():
|
||||
raise OptionalDependencyNotAvailable()
|
||||
except OptionalDependencyNotAvailable:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
from .modeling_auto import (
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_FRAME_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_XVECTOR_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_BACKBONE_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_IMAGE_MODELING_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_CTC_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_DEPTH_ESTIMATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_DOCUMENT_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_TEXT_TO_TEXT_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_TO_IMAGE_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_INSTANCE_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_KEYPOINT_DETECTION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_MASK_GENERATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_MASKED_IMAGE_MODELING_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_MASKED_LM_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_MULTIPLE_CHOICE_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_NEXT_SENTENCE_PREDICTION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_OBJECT_DETECTION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_PRETRAINING_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_RETRIEVAL_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_SEMANTIC_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_SEQ_TO_SEQ_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_SEQUENCE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_SPEECH_SEQ_2_SEQ_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_TABLE_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_TEXT_ENCODING_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_TEXT_TO_SPECTROGRAM_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_TEXT_TO_WAVEFORM_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_TIME_SERIES_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_TIME_SERIES_REGRESSION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_TOKEN_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_UNIVERSAL_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_VIDEO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_VISION_2_SEQ_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_VISUAL_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_ZERO_SHOT_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_ZERO_SHOT_OBJECT_DETECTION_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_MAPPING,
|
||||
MODEL_WITH_LM_HEAD_MAPPING,
|
||||
AutoBackbone,
|
||||
AutoModel,
|
||||
AutoModelForAudioClassification,
|
||||
AutoModelForAudioFrameClassification,
|
||||
AutoModelForAudioXVector,
|
||||
AutoModelForCausalLM,
|
||||
AutoModelForCTC,
|
||||
AutoModelForDepthEstimation,
|
||||
AutoModelForDocumentQuestionAnswering,
|
||||
AutoModelForImageClassification,
|
||||
AutoModelForImageSegmentation,
|
||||
AutoModelForImageTextToText,
|
||||
AutoModelForImageToImage,
|
||||
AutoModelForInstanceSegmentation,
|
||||
AutoModelForKeypointDetection,
|
||||
AutoModelForMaskedImageModeling,
|
||||
AutoModelForMaskedLM,
|
||||
AutoModelForMaskGeneration,
|
||||
AutoModelForMultipleChoice,
|
||||
AutoModelForNextSentencePrediction,
|
||||
AutoModelForObjectDetection,
|
||||
AutoModelForPreTraining,
|
||||
AutoModelForQuestionAnswering,
|
||||
AutoModelForSemanticSegmentation,
|
||||
AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM,
|
||||
AutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
AutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq,
|
||||
AutoModelForTableQuestionAnswering,
|
||||
AutoModelForTextEncoding,
|
||||
AutoModelForTextToSpectrogram,
|
||||
AutoModelForTextToWaveform,
|
||||
AutoModelForTokenClassification,
|
||||
AutoModelForUniversalSegmentation,
|
||||
AutoModelForVideoClassification,
|
||||
AutoModelForVision2Seq,
|
||||
AutoModelForVisualQuestionAnswering,
|
||||
AutoModelForZeroShotImageClassification,
|
||||
AutoModelForZeroShotObjectDetection,
|
||||
AutoModelWithLMHead,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if not is_tf_available():
|
||||
raise OptionalDependencyNotAvailable()
|
||||
except OptionalDependencyNotAvailable:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
from .modeling_tf_auto import (
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_DOCUMENT_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_MASK_GENERATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_MASKED_IMAGE_MODELING_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_MASKED_LM_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_MULTIPLE_CHOICE_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_NEXT_SENTENCE_PREDICTION_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_PRETRAINING_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_SEMANTIC_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_SEQ_TO_SEQ_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_SEQUENCE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_SPEECH_SEQ_2_SEQ_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_TABLE_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_TEXT_ENCODING_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_TOKEN_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_VISION_2_SEQ_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_FOR_ZERO_SHOT_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_MAPPING,
|
||||
TF_MODEL_WITH_LM_HEAD_MAPPING,
|
||||
TFAutoModel,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForAudioClassification,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForCausalLM,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForDocumentQuestionAnswering,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForImageClassification,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForMaskedImageModeling,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForMaskedLM,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForMaskGeneration,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForMultipleChoice,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForNextSentencePrediction,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForPreTraining,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForQuestionAnswering,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForSemanticSegmentation,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForSeq2SeqLM,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForTableQuestionAnswering,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForTextEncoding,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForTokenClassification,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForVision2Seq,
|
||||
TFAutoModelForZeroShotImageClassification,
|
||||
TFAutoModelWithLMHead,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if not is_flax_available():
|
||||
raise OptionalDependencyNotAvailable()
|
||||
except OptionalDependencyNotAvailable:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
from .modeling_flax_auto import (
|
||||
FLAX_MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
FLAX_MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING,
|
||||
FLAX_MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
FLAX_MODEL_FOR_MASKED_LM_MAPPING,
|
||||
FLAX_MODEL_FOR_MULTIPLE_CHOICE_MAPPING,
|
||||
FLAX_MODEL_FOR_NEXT_SENTENCE_PREDICTION_MAPPING,
|
||||
FLAX_MODEL_FOR_PRETRAINING_MAPPING,
|
||||
FLAX_MODEL_FOR_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING,
|
||||
FLAX_MODEL_FOR_SEQ_TO_SEQ_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING,
|
||||
FLAX_MODEL_FOR_SEQUENCE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
FLAX_MODEL_FOR_SPEECH_SEQ_2_SEQ_MAPPING,
|
||||
FLAX_MODEL_FOR_TOKEN_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING,
|
||||
FLAX_MODEL_FOR_VISION_2_SEQ_MAPPING,
|
||||
FLAX_MODEL_MAPPING,
|
||||
FlaxAutoModel,
|
||||
FlaxAutoModelForCausalLM,
|
||||
FlaxAutoModelForImageClassification,
|
||||
FlaxAutoModelForMaskedLM,
|
||||
FlaxAutoModelForMultipleChoice,
|
||||
FlaxAutoModelForNextSentencePrediction,
|
||||
FlaxAutoModelForPreTraining,
|
||||
FlaxAutoModelForQuestionAnswering,
|
||||
FlaxAutoModelForSeq2SeqLM,
|
||||
FlaxAutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
FlaxAutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq,
|
||||
FlaxAutoModelForTokenClassification,
|
||||
FlaxAutoModelForVision2Seq,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
from .auto_factory import *
|
||||
from .configuration_auto import *
|
||||
from .feature_extraction_auto import *
|
||||
from .image_processing_auto import *
|
||||
from .modeling_auto import *
|
||||
from .modeling_flax_auto import *
|
||||
from .modeling_tf_auto import *
|
||||
from .processing_auto import *
|
||||
from .tokenization_auto import *
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
sys.modules[__name__] = _LazyModule(__name__, globals()["__file__"], _import_structure, module_spec=__spec__)
|
||||
_file = globals()["__file__"]
|
||||
sys.modules[__name__] = _LazyModule(__name__, _file, define_import_structure(_file), module_spec=__spec__)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -730,8 +730,12 @@ def add_generation_mixin_to_remote_model(model_class):
|
||||
|
||||
# 3. Prior to v4.45, we could detect whether a model was `generate`-compatible if it had its own `generate` and/or
|
||||
# `prepare_inputs_for_generation` method.
|
||||
has_custom_generate = "GenerationMixin" not in str(getattr(model_class, "generate"))
|
||||
has_custom_prepare_inputs = "GenerationMixin" not in str(getattr(model_class, "prepare_inputs_for_generation"))
|
||||
has_custom_generate = hasattr(model_class, "generate") and "GenerationMixin" not in str(
|
||||
getattr(model_class, "generate")
|
||||
)
|
||||
has_custom_prepare_inputs = hasattr(model_class, "prepare_inputs_for_generation") and "GenerationMixin" not in str(
|
||||
getattr(model_class, "prepare_inputs_for_generation")
|
||||
)
|
||||
if has_custom_generate or has_custom_prepare_inputs:
|
||||
model_class_with_generation_mixin = type(
|
||||
model_class.__name__, (model_class, GenerationMixin), {**model_class.__dict__}
|
||||
@ -840,3 +844,6 @@ class _LazyAutoMapping(OrderedDict):
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"'{key}' is already used by a Transformers model.")
|
||||
|
||||
self._extra_content[key] = value
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = ["get_values"]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -132,6 +132,7 @@ CONFIG_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("gemma3_text", "Gemma3TextConfig"),
|
||||
("git", "GitConfig"),
|
||||
("glm", "GlmConfig"),
|
||||
("glm4", "Glm4Config"),
|
||||
("glpn", "GLPNConfig"),
|
||||
("got_ocr2", "GotOcr2Config"),
|
||||
("gpt-sw3", "GPT2Config"),
|
||||
@ -143,6 +144,7 @@ CONFIG_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("gptj", "GPTJConfig"),
|
||||
("gptsan-japanese", "GPTSanJapaneseConfig"),
|
||||
("granite", "GraniteConfig"),
|
||||
("granite_speech", "GraniteSpeechConfig"),
|
||||
("granitemoe", "GraniteMoeConfig"),
|
||||
("granitemoeshared", "GraniteMoeSharedConfig"),
|
||||
("granitevision", "LlavaNextConfig"),
|
||||
@ -482,6 +484,7 @@ MODEL_NAMES_MAPPING = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("gemma3_text", "Gemma3ForCausalLM"),
|
||||
("git", "GIT"),
|
||||
("glm", "GLM"),
|
||||
("glm4", "glm4"),
|
||||
("glpn", "GLPN"),
|
||||
("got_ocr2", "GOT-OCR2"),
|
||||
("gpt-sw3", "GPT-Sw3"),
|
||||
@ -493,6 +496,7 @@ MODEL_NAMES_MAPPING = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("gptj", "GPT-J"),
|
||||
("gptsan-japanese", "GPTSAN-japanese"),
|
||||
("granite", "Granite"),
|
||||
("granite_speech", "GraniteSpeech"),
|
||||
("granitemoe", "GraniteMoeMoe"),
|
||||
("granitemoeshared", "GraniteMoeSharedMoe"),
|
||||
("granitevision", "LLaVA-NeXT"),
|
||||
@ -1176,3 +1180,6 @@ class AutoConfig:
|
||||
"match!"
|
||||
)
|
||||
CONFIG_MAPPING.register(model_type, config, exist_ok=exist_ok)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = ["CONFIG_MAPPING", "MODEL_NAMES_MAPPING", "AutoConfig"]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -61,6 +61,7 @@ FEATURE_EXTRACTOR_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("encodec", "EncodecFeatureExtractor"),
|
||||
("flava", "FlavaFeatureExtractor"),
|
||||
("glpn", "GLPNFeatureExtractor"),
|
||||
("granite_speech", "GraniteSpeechFeatureExtractor"),
|
||||
("groupvit", "CLIPFeatureExtractor"),
|
||||
("hubert", "Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor"),
|
||||
("imagegpt", "ImageGPTFeatureExtractor"),
|
||||
@ -406,3 +407,6 @@ class AutoFeatureExtractor:
|
||||
feature_extractor_class ([`FeatureExtractorMixin`]): The feature extractor to register.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
FEATURE_EXTRACTOR_MAPPING.register(config_class, feature_extractor_class, exist_ok=exist_ok)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = ["FEATURE_EXTRACTOR_MAPPING", "AutoFeatureExtractor"]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,6 +36,7 @@ from ...utils import (
|
||||
is_vision_available,
|
||||
logging,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from ...utils.import_utils import requires
|
||||
from .auto_factory import _LazyAutoMapping
|
||||
from .configuration_auto import (
|
||||
CONFIG_MAPPING_NAMES,
|
||||
@ -324,6 +325,7 @@ def _warning_fast_image_processor_available(fast_class):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@requires(backends=("vision", "torchvision"))
|
||||
class AutoImageProcessor:
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
This is a generic image processor class that will be instantiated as one of the image processor classes of the
|
||||
@ -640,3 +642,6 @@ class AutoImageProcessor:
|
||||
IMAGE_PROCESSOR_MAPPING.register(
|
||||
config_class, (slow_image_processor_class, fast_image_processor_class), exist_ok=exist_ok
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = ["IMAGE_PROCESSOR_MAPPING", "AutoImageProcessor"]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -125,6 +125,7 @@ MODEL_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("gemma3_text", "Gemma3TextModel"),
|
||||
("git", "GitModel"),
|
||||
("glm", "GlmModel"),
|
||||
("glm4", "Glm4Model"),
|
||||
("glpn", "GLPNModel"),
|
||||
("got_ocr2", "GotOcr2ForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("gpt-sw3", "GPT2Model"),
|
||||
@ -535,6 +536,7 @@ MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("gemma3_text", "Gemma3ForCausalLM"),
|
||||
("git", "GitForCausalLM"),
|
||||
("glm", "GlmForCausalLM"),
|
||||
("glm4", "Glm4ForCausalLM"),
|
||||
("got_ocr2", "GotOcr2ForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("gpt-sw3", "GPT2LMHeadModel"),
|
||||
("gpt2", "GPT2LMHeadModel"),
|
||||
@ -708,6 +710,7 @@ MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("dinat", "DinatForImageClassification"),
|
||||
("dinov2", "Dinov2ForImageClassification"),
|
||||
("dinov2_with_registers", "Dinov2WithRegistersForImageClassification"),
|
||||
("donut-swin", "DonutSwinForImageClassification"),
|
||||
(
|
||||
"efficientformer",
|
||||
(
|
||||
@ -973,6 +976,7 @@ MODEL_FOR_SEQ_TO_SEQ_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("encoder-decoder", "EncoderDecoderModel"),
|
||||
("fsmt", "FSMTForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("gptsan-japanese", "GPTSanJapaneseForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("granite_speech", "GraniteSpeechForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("led", "LEDForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("longt5", "LongT5ForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("m2m_100", "M2M100ForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
@ -997,6 +1001,7 @@ MODEL_FOR_SEQ_TO_SEQ_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_SPEECH_SEQ_2_SEQ_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
[
|
||||
("granite_speech", "GraniteSpeechForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("moonshine", "MoonshineForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("pop2piano", "Pop2PianoForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("seamless_m4t", "SeamlessM4TForSpeechToText"),
|
||||
@ -1039,6 +1044,7 @@ MODEL_FOR_SEQUENCE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("gemma", "GemmaForSequenceClassification"),
|
||||
("gemma2", "Gemma2ForSequenceClassification"),
|
||||
("glm", "GlmForSequenceClassification"),
|
||||
("glm4", "Glm4ForSequenceClassification"),
|
||||
("gpt-sw3", "GPT2ForSequenceClassification"),
|
||||
("gpt2", "GPT2ForSequenceClassification"),
|
||||
("gpt_bigcode", "GPTBigCodeForSequenceClassification"),
|
||||
@ -1240,6 +1246,7 @@ MODEL_FOR_TOKEN_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("gemma", "GemmaForTokenClassification"),
|
||||
("gemma2", "Gemma2ForTokenClassification"),
|
||||
("glm", "GlmForTokenClassification"),
|
||||
("glm4", "Glm4ForTokenClassification"),
|
||||
("gpt-sw3", "GPT2ForTokenClassification"),
|
||||
("gpt2", "GPT2ForTokenClassification"),
|
||||
("gpt_bigcode", "GPTBigCodeForTokenClassification"),
|
||||
@ -1953,3 +1960,90 @@ class AutoModelWithLMHead(_AutoModelWithLMHead):
|
||||
FutureWarning,
|
||||
)
|
||||
return super().from_pretrained(pretrained_model_name_or_path, *model_args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = [
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_FRAME_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_XVECTOR_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_BACKBONE_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_IMAGE_MODELING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_CTC_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_DOCUMENT_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_DEPTH_ESTIMATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_TO_IMAGE_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_KEYPOINT_DETECTION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_INSTANCE_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_MASKED_IMAGE_MODELING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_MASKED_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_MASK_GENERATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_MULTIPLE_CHOICE_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_NEXT_SENTENCE_PREDICTION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_OBJECT_DETECTION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_PRETRAINING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_SEMANTIC_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_SEQ_TO_SEQ_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_SEQUENCE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_SPEECH_SEQ_2_SEQ_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_TABLE_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_TEXT_ENCODING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_TEXT_TO_WAVEFORM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_TEXT_TO_SPECTROGRAM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_TOKEN_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_UNIVERSAL_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_VIDEO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_VISION_2_SEQ_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_RETRIEVAL_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_TEXT_TO_TEXT_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_VISUAL_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_WITH_LM_HEAD_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_ZERO_SHOT_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_ZERO_SHOT_OBJECT_DETECTION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_TIME_SERIES_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"MODEL_FOR_TIME_SERIES_REGRESSION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"AutoModel",
|
||||
"AutoBackbone",
|
||||
"AutoModelForAudioClassification",
|
||||
"AutoModelForAudioFrameClassification",
|
||||
"AutoModelForAudioXVector",
|
||||
"AutoModelForCausalLM",
|
||||
"AutoModelForCTC",
|
||||
"AutoModelForDepthEstimation",
|
||||
"AutoModelForImageClassification",
|
||||
"AutoModelForImageSegmentation",
|
||||
"AutoModelForImageToImage",
|
||||
"AutoModelForInstanceSegmentation",
|
||||
"AutoModelForKeypointDetection",
|
||||
"AutoModelForMaskGeneration",
|
||||
"AutoModelForTextEncoding",
|
||||
"AutoModelForMaskedImageModeling",
|
||||
"AutoModelForMaskedLM",
|
||||
"AutoModelForMultipleChoice",
|
||||
"AutoModelForNextSentencePrediction",
|
||||
"AutoModelForObjectDetection",
|
||||
"AutoModelForPreTraining",
|
||||
"AutoModelForQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"AutoModelForSemanticSegmentation",
|
||||
"AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM",
|
||||
"AutoModelForSequenceClassification",
|
||||
"AutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq",
|
||||
"AutoModelForTableQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"AutoModelForTextToSpectrogram",
|
||||
"AutoModelForTextToWaveform",
|
||||
"AutoModelForTokenClassification",
|
||||
"AutoModelForUniversalSegmentation",
|
||||
"AutoModelForVideoClassification",
|
||||
"AutoModelForVision2Seq",
|
||||
"AutoModelForVisualQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"AutoModelForDocumentQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"AutoModelWithLMHead",
|
||||
"AutoModelForZeroShotImageClassification",
|
||||
"AutoModelForZeroShotObjectDetection",
|
||||
"AutoModelForImageTextToText",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -381,3 +381,33 @@ class FlaxAutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq(_BaseAutoModelClass):
|
||||
FlaxAutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq = auto_class_update(
|
||||
FlaxAutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq, head_doc="sequence-to-sequence speech-to-text modeling"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = [
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_MASKED_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_MULTIPLE_CHOICE_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_NEXT_SENTENCE_PREDICTION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_PRETRAINING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_SEQ_TO_SEQ_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_SEQUENCE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_SPEECH_SEQ_2_SEQ_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_TOKEN_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_FOR_VISION_2_SEQ_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FLAX_MODEL_MAPPING",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModel",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForCausalLM",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForImageClassification",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForMaskedLM",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForMultipleChoice",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForNextSentencePrediction",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForPreTraining",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForSeq2SeqLM",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForSequenceClassification",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForTokenClassification",
|
||||
"FlaxAutoModelForVision2Seq",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -726,3 +726,51 @@ class TFAutoModelWithLMHead(_TFAutoModelWithLMHead):
|
||||
FutureWarning,
|
||||
)
|
||||
return super().from_pretrained(pretrained_model_name_or_path, *model_args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = [
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_AUDIO_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_MASK_GENERATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_MASKED_IMAGE_MODELING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_MASKED_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_MULTIPLE_CHOICE_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_NEXT_SENTENCE_PREDICTION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_PRETRAINING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_DOCUMENT_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_SEMANTIC_SEGMENTATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_SEQ_TO_SEQ_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_SEQUENCE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_SPEECH_SEQ_2_SEQ_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_TABLE_QUESTION_ANSWERING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_TEXT_ENCODING_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_TOKEN_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_VISION_2_SEQ_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_FOR_ZERO_SHOT_IMAGE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TF_MODEL_WITH_LM_HEAD_MAPPING",
|
||||
"TFAutoModel",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForAudioClassification",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForCausalLM",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForImageClassification",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForMaskedImageModeling",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForMaskedLM",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForMaskGeneration",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForMultipleChoice",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForNextSentencePrediction",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForPreTraining",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForDocumentQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForSemanticSegmentation",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForSeq2SeqLM",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForSpeechSeq2Seq",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForTableQuestionAnswering",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForTextEncoding",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForTokenClassification",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForVision2Seq",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelForZeroShotImageClassification",
|
||||
"TFAutoModelWithLMHead",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,6 +66,7 @@ PROCESSOR_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("gemma3", "Gemma3Processor"),
|
||||
("git", "GitProcessor"),
|
||||
("got_ocr2", "GotOcr2Processor"),
|
||||
("granite_speech", "GraniteSpeechProcessor"),
|
||||
("grounding-dino", "GroundingDinoProcessor"),
|
||||
("groupvit", "CLIPProcessor"),
|
||||
("hubert", "Wav2Vec2Processor"),
|
||||
@ -389,3 +390,6 @@ class AutoProcessor:
|
||||
processor_class ([`ProcessorMixin`]): The processor to register.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
PROCESSOR_MAPPING.register(config_class, processor_class, exist_ok=exist_ok)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = ["PROCESSOR_MAPPING", "AutoProcessor"]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -245,6 +245,7 @@ else:
|
||||
),
|
||||
("git", ("BertTokenizer", "BertTokenizerFast" if is_tokenizers_available() else None)),
|
||||
("glm", (None, "PreTrainedTokenizerFast" if is_tokenizers_available() else None)),
|
||||
("glm4", (None, "PreTrainedTokenizerFast" if is_tokenizers_available() else None)),
|
||||
("gpt-sw3", ("GPTSw3Tokenizer" if is_sentencepiece_available() else None, None)),
|
||||
("gpt2", ("GPT2Tokenizer", "GPT2TokenizerFast" if is_tokenizers_available() else None)),
|
||||
("gpt_bigcode", ("GPT2Tokenizer", "GPT2TokenizerFast" if is_tokenizers_available() else None)),
|
||||
@ -1089,3 +1090,6 @@ class AutoTokenizer:
|
||||
fast_tokenizer_class = existing_fast
|
||||
|
||||
TOKENIZER_MAPPING.register(config_class, (slow_tokenizer_class, fast_tokenizer_class), exist_ok=exist_ok)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = ["TOKENIZER_MAPPING", "AutoTokenizer"]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,45 +13,15 @@
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
|
||||
|
||||
# rely on isort to merge the imports
|
||||
from ...utils import OptionalDependencyNotAvailable, _LazyModule, is_torch_available
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
_import_structure = {
|
||||
"configuration_autoformer": ["AutoformerConfig"],
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if not is_torch_available():
|
||||
raise OptionalDependencyNotAvailable()
|
||||
except OptionalDependencyNotAvailable:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
_import_structure["modeling_autoformer"] = [
|
||||
"AutoformerForPrediction",
|
||||
"AutoformerModel",
|
||||
"AutoformerPreTrainedModel",
|
||||
]
|
||||
from ...utils import _LazyModule
|
||||
from ...utils.import_utils import define_import_structure
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
from .configuration_autoformer import (
|
||||
AutoformerConfig,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if not is_torch_available():
|
||||
raise OptionalDependencyNotAvailable()
|
||||
except OptionalDependencyNotAvailable:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
else:
|
||||
from .modeling_autoformer import (
|
||||
AutoformerForPrediction,
|
||||
AutoformerModel,
|
||||
AutoformerPreTrainedModel,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
from .configuration_autoformer import *
|
||||
from .modeling_autoformer import *
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
sys.modules[__name__] = _LazyModule(__name__, globals()["__file__"], _import_structure, module_spec=__spec__)
|
||||
_file = globals()["__file__"]
|
||||
sys.modules[__name__] = _LazyModule(__name__, _file, define_import_structure(_file), module_spec=__spec__)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -240,3 +240,6 @@ class AutoformerConfig(PretrainedConfig):
|
||||
+ self.num_static_real_features
|
||||
+ self.input_size * 2 # the log1p(abs(loc)) and log(scale) features
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = ["AutoformerConfig"]
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user