mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
synced 2025-07-30 17:52:35 +06:00
Migrate doc files to Markdown. (#24376)
* Rename index.mdx to index.md * With saved modifs * Address review comment * Treat all files * .mdx -> .md * Remove special char * Update utils/tests_fetcher.py Co-authored-by: Lysandre Debut <lysandre.debut@reseau.eseo.fr> --------- Co-authored-by: Lysandre Debut <lysandre.debut@reseau.eseo.fr>
This commit is contained in:
parent
b0513b013b
commit
eb849f6604
@ -480,7 +480,7 @@ doc_test_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
tests_to_run="$(cat pr_documentation_tests.txt)", # noqa
|
||||
pytest_options={"-doctest-modules": None, "doctest-glob": "*.mdx", "dist": "loadfile", "rvsA": None},
|
||||
pytest_options={"-doctest-modules": None, "doctest-glob": "*.md", "dist": "loadfile", "rvsA": None},
|
||||
command_timeout=1200, # test cannot run longer than 1200 seconds
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
20
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/i18n.md
vendored
20
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/i18n.md
vendored
@ -28,18 +28,18 @@ Some notes:
|
||||
|
||||
## Get Started section
|
||||
|
||||
- [ ] [index.mdx](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/index.mdx) https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/20180
|
||||
- [ ] [quicktour.mdx](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/quicktour.mdx) (waiting for initial PR to go through)
|
||||
- [ ] [installation.mdx](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/installation.mdx).
|
||||
- [ ] [index.md](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/index.md) https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/20180
|
||||
- [ ] [quicktour.md](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/quicktour.md) (waiting for initial PR to go through)
|
||||
- [ ] [installation.md](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/installation.md).
|
||||
|
||||
## Tutorial section
|
||||
- [ ] [pipeline_tutorial.mdx](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/pipeline_tutorial.mdx)
|
||||
- [ ] [autoclass_tutorial.mdx](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/master/docs/source/autoclass_tutorial.mdx)
|
||||
- [ ] [preprocessing.mdx](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/preprocessing.mdx)
|
||||
- [ ] [training.mdx](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/training.mdx)
|
||||
- [ ] [accelerate.mdx](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/accelerate.mdx)
|
||||
- [ ] [model_sharing.mdx](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/model_sharing.mdx)
|
||||
- [ ] [multilingual.mdx](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/multilingual.mdx)
|
||||
- [ ] [pipeline_tutorial.md](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/pipeline_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- [ ] [autoclass_tutorial.md](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/master/docs/source/autoclass_tutorial.md)
|
||||
- [ ] [preprocessing.md](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/preprocessing.md)
|
||||
- [ ] [training.md](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/training.md)
|
||||
- [ ] [accelerate.md](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/accelerate.md)
|
||||
- [ ] [model_sharing.md](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/model_sharing.md)
|
||||
- [ ] [multilingual.md](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/multilingual.md)
|
||||
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
Keep on adding more as you go 🔥
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/doctests.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/doctests.yml
vendored
@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run doctests
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports doc_tests_gpu --doctest-modules $(cat utils/documentation_tests.txt) -sv --doctest-continue-on-failure --doctest-glob="*.mdx"
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports doc_tests_gpu --doctest-modules $(cat utils/documentation_tests.txt) -sv --doctest-continue-on-failure --doctest-glob="*.md"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -81,7 +81,7 @@ The `preview` command only works with existing doc files. When you add a complet
|
||||
|
||||
## Adding a new element to the navigation bar
|
||||
|
||||
Accepted files are Markdown (.md or .mdx).
|
||||
Accepted files are Markdown (.md or .md).
|
||||
|
||||
Create a file with its extension and put it in the source directory. You can then link it to the toc-tree by putting
|
||||
the filename without the extension in the [`_toctree.yml`](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/_toctree.yml) file.
|
||||
@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ Sections that were moved:
|
||||
|
||||
Use the relative style to link to the new file so that the versioned docs continue to work.
|
||||
|
||||
For an example of a rich moved section set please see the very end of [the Trainer doc](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/main_classes/trainer.mdx).
|
||||
For an example of a rich moved section set please see the very end of [the Trainer doc](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/main_classes/trainer.md).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Writing Documentation - Specification
|
||||
@ -138,7 +138,7 @@ When translating, refer to the guide at [./TRANSLATING.md](https://github.com/hu
|
||||
|
||||
When adding a new model:
|
||||
|
||||
- Create a file `xxx.mdx` or under `./source/model_doc` (don't hesitate to copy an existing file as template).
|
||||
- Create a file `xxx.md` or under `./source/model_doc` (don't hesitate to copy an existing file as template).
|
||||
- Link that file in `./source/_toctree.yml`.
|
||||
- Write a short overview of the model:
|
||||
- Overview with paper & authors
|
||||
@ -386,7 +386,7 @@ pytest --doctest-modules src/transformers/models/wav2vec2/modeling_wav2vec2.py::
|
||||
You can test locally a given file with this command (here testing the quicktour):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pytest --doctest-modules docs/source/quicktour.mdx -sv --doctest-continue-on-failure --doctest-glob="*.mdx"
|
||||
pytest --doctest-modules docs/source/quicktour.md -sv --doctest-continue-on-failure --doctest-glob="*.md"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Writing doctests
|
||||
|
||||
136
docs/source/de/accelerate.md
Normal file
136
docs/source/de/accelerate.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Verteiltes Training mit 🤗 Accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
Da die Modelle immer größer werden, hat sich die Parallelität als Strategie zum Trainieren größerer Modelle auf begrenzter Hardware und zur Beschleunigung der Trainingsgeschwindigkeit um mehrere Größenordnungen erwiesen. Bei Hugging Face haben wir die Bibliothek [🤗 Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate) entwickelt, um Nutzern zu helfen, ein 🤗 Transformers-Modell auf jeder Art von verteiltem Setup zu trainieren, egal ob es sich um mehrere GPUs auf einer Maschine oder mehrere GPUs auf mehreren Maschinen handelt. In diesem Tutorial lernen Sie, wie Sie Ihre native PyTorch-Trainingsschleife anpassen, um das Training in einer verteilten Umgebung zu ermöglichen.
|
||||
|
||||
## Einrichtung
|
||||
|
||||
Beginnen Sie mit der Installation von 🤗 Accelerate:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install accelerate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dann importieren und erstellen Sie ein [`~accelerate.Accelerator`]-Objekt. Der [`~accelerate.Accelerator`] wird automatisch Ihre Art der verteilten Einrichtung erkennen und alle notwendigen Komponenten für das Training initialisieren. Sie müssen Ihr Modell nicht explizit auf einem Gerät platzieren.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
|
||||
>>> accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Vorbereiten auf die Beschleunigung
|
||||
|
||||
Der nächste Schritt ist die Übergabe aller relevanten Trainingsobjekte an die Methode [`~accelerate.Accelerator.prepare`]. Dazu gehören Ihre Trainings- und Evaluierungs-DataLoader, ein Modell und ein Optimierer:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
... train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Rückwärts
|
||||
|
||||
Die letzte Ergänzung besteht darin, das typische `loss.backward()` in der Trainingsschleife durch die 🤗 Accelerate-Methode [`~accelerate.Accelerator.backward`] zu ersetzen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> for epoch in range(num_epochs):
|
||||
... for batch in train_dataloader:
|
||||
... outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
... loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
... accelerator.backward(loss)
|
||||
|
||||
... optimizer.step()
|
||||
... lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
... optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
... progress_bar.update(1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wie Sie im folgenden Code sehen können, müssen Sie nur vier zusätzliche Codezeilen zu Ihrer Trainingsschleife hinzufügen, um verteiltes Training zu ermöglichen!
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
+ from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from transformers import AdamW, AutoModelForSequenceClassification, get_scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
+ accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(checkpoint, num_labels=2)
|
||||
optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=3e-5)
|
||||
|
||||
- device = torch.device("cuda") if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.device("cpu")
|
||||
- model.to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
+ train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
+ train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer
|
||||
+ )
|
||||
|
||||
num_epochs = 3
|
||||
num_training_steps = num_epochs * len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
|
||||
"linear",
|
||||
optimizer=optimizer,
|
||||
num_warmup_steps=0,
|
||||
num_training_steps=num_training_steps
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
progress_bar = tqdm(range(num_training_steps))
|
||||
|
||||
model.train()
|
||||
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
|
||||
for batch in train_dataloader:
|
||||
- batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
|
||||
outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
- loss.backward()
|
||||
+ accelerator.backward(loss)
|
||||
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
progress_bar.update(1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Trainieren
|
||||
|
||||
Sobald Sie die entsprechenden Codezeilen hinzugefügt haben, starten Sie Ihr Training in einem Skript oder einem Notebook wie Colaboratory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Trainieren mit einem Skript
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie Ihr Training mit einem Skript durchführen, führen Sie den folgenden Befehl aus, um eine Konfigurationsdatei zu erstellen und zu speichern:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dann starten Sie Ihr Training mit:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch train.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Trainieren mit einem Notebook
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Accelerate kann auch in einem Notebook laufen, wenn Sie planen, die TPUs von Colaboratory zu verwenden. Verpacken Sie den gesamten Code, der für das Training verantwortlich ist, in eine Funktion und übergeben Sie diese an [`~accelerate.notebook_launcher`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from accelerate import notebook_launcher
|
||||
|
||||
>>> notebook_launcher(training_function)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Informationen über 🤗 Accelerate und seine umfangreichen Funktionen finden Sie in der [Dokumentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate).
|
||||
@ -1,132 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Verteiltes Training mit 🤗 Accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
Da die Modelle immer größer werden, hat sich die Parallelität als Strategie zum Trainieren größerer Modelle auf begrenzter Hardware und zur Beschleunigung der Trainingsgeschwindigkeit um mehrere Größenordnungen erwiesen. Bei Hugging Face haben wir die Bibliothek [🤗 Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate) entwickelt, um Nutzern zu helfen, ein 🤗 Transformers-Modell auf jeder Art von verteiltem Setup zu trainieren, egal ob es sich um mehrere GPUs auf einer Maschine oder mehrere GPUs auf mehreren Maschinen handelt. In diesem Tutorial lernen Sie, wie Sie Ihre native PyTorch-Trainingsschleife anpassen, um das Training in einer verteilten Umgebung zu ermöglichen.
|
||||
|
||||
## Einrichtung
|
||||
|
||||
Beginnen Sie mit der Installation von 🤗 Accelerate:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install accelerate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dann importieren und erstellen Sie ein [`~accelerate.Accelerator`]-Objekt. Der [`~accelerate.Accelerator`] wird automatisch Ihre Art der verteilten Einrichtung erkennen und alle notwendigen Komponenten für das Training initialisieren. Sie müssen Ihr Modell nicht explizit auf einem Gerät platzieren.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
|
||||
>>> accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Vorbereiten auf die Beschleunigung
|
||||
|
||||
Der nächste Schritt ist die Übergabe aller relevanten Trainingsobjekte an die Methode [`~accelerate.Accelerator.prepare`]. Dazu gehören Ihre Trainings- und Evaluierungs-DataLoader, ein Modell und ein Optimierer:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
... train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Rückwärts
|
||||
|
||||
Die letzte Ergänzung besteht darin, das typische `loss.backward()` in der Trainingsschleife durch die 🤗 Accelerate-Methode [`~accelerate.Accelerator.backward`] zu ersetzen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> for epoch in range(num_epochs):
|
||||
... for batch in train_dataloader:
|
||||
... outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
... loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
... accelerator.backward(loss)
|
||||
|
||||
... optimizer.step()
|
||||
... lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
... optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
... progress_bar.update(1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wie Sie im folgenden Code sehen können, müssen Sie nur vier zusätzliche Codezeilen zu Ihrer Trainingsschleife hinzufügen, um verteiltes Training zu ermöglichen!
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
+ from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from transformers import AdamW, AutoModelForSequenceClassification, get_scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
+ accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(checkpoint, num_labels=2)
|
||||
optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=3e-5)
|
||||
|
||||
- device = torch.device("cuda") if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.device("cpu")
|
||||
- model.to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
+ train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
+ train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer
|
||||
+ )
|
||||
|
||||
num_epochs = 3
|
||||
num_training_steps = num_epochs * len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
|
||||
"linear",
|
||||
optimizer=optimizer,
|
||||
num_warmup_steps=0,
|
||||
num_training_steps=num_training_steps
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
progress_bar = tqdm(range(num_training_steps))
|
||||
|
||||
model.train()
|
||||
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
|
||||
for batch in train_dataloader:
|
||||
- batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
|
||||
outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
- loss.backward()
|
||||
+ accelerator.backward(loss)
|
||||
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
progress_bar.update(1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Trainieren
|
||||
|
||||
Sobald Sie die entsprechenden Codezeilen hinzugefügt haben, starten Sie Ihr Training in einem Skript oder einem Notebook wie Colaboratory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Trainieren mit einem Skript
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie Ihr Training mit einem Skript durchführen, führen Sie den folgenden Befehl aus, um eine Konfigurationsdatei zu erstellen und zu speichern:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dann starten Sie Ihr Training mit:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch train.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Trainieren mit einem Notebook
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Accelerate kann auch in einem Notebook laufen, wenn Sie planen, die TPUs von Colaboratory zu verwenden. Verpacken Sie den gesamten Code, der für das Training verantwortlich ist, in eine Funktion und übergeben Sie diese an [`~accelerate.notebook_launcher`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from accelerate import notebook_launcher
|
||||
|
||||
>>> notebook_launcher(training_function)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Informationen über 🤗 Accelerate und seine umfangreichen Funktionen finden Sie in der [Dokumentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate).
|
||||
131
docs/source/de/autoclass_tutorial.md
Normal file
131
docs/source/de/autoclass_tutorial.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,131 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Vortrainierte Instanzen mit einer AutoClass laden
|
||||
|
||||
Bei so vielen verschiedenen Transformator-Architekturen kann es eine Herausforderung sein, eine für Ihren Checkpoint zu erstellen. Als Teil der 🤗 Transformers Kernphilosophie, die Bibliothek leicht, einfach und flexibel nutzbar zu machen, leitet eine `AutoClass` automatisch die richtige Architektur aus einem gegebenen Checkpoint ab und lädt sie. Mit der Methode `from_pretrained()` kann man schnell ein vortrainiertes Modell für eine beliebige Architektur laden, so dass man keine Zeit und Ressourcen aufwenden muss, um ein Modell von Grund auf zu trainieren. Die Erstellung dieser Art von Checkpoint-agnostischem Code bedeutet, dass Ihr Code, wenn er für einen Checkpoint funktioniert, auch mit einem anderen Checkpoint funktionieren wird - solange er für eine ähnliche Aufgabe trainiert wurde - selbst wenn die Architektur unterschiedlich ist.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Denken Sie daran, dass sich die Architektur auf das Skelett des Modells bezieht und die Checkpoints die Gewichte für eine bestimmte Architektur sind. Zum Beispiel ist [BERT](https://huggingface.co/bert-base-uncased) eine Architektur, während `bert-base-uncased` ein Checkpoint ist. Modell ist ein allgemeiner Begriff, der entweder Architektur oder Prüfpunkt bedeuten kann.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In dieser Anleitung lernen Sie, wie man:
|
||||
|
||||
* Einen vortrainierten Tokenizer lädt.
|
||||
* Einen vortrainierten Merkmalsextraktor lädt.
|
||||
* Einen vortrainierten Prozessor lädt.
|
||||
* Ein vortrainiertes Modell lädt.
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
Nahezu jede NLP-Aufgabe beginnt mit einem Tokenizer. Ein Tokenizer wandelt Ihre Eingabe in ein Format um, das vom Modell verarbeitet werden kann.
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie einen Tokenizer mit [`AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dann tokenisieren Sie Ihre Eingabe wie unten gezeigt:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> sequence = "In a hole in the ground there lived a hobbit."
|
||||
>>> print(tokenizer(sequence))
|
||||
{'input_ids': [101, 1999, 1037, 4920, 1999, 1996, 2598, 2045, 2973, 1037, 7570, 10322, 4183, 1012, 102],
|
||||
'token_type_ids': [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
'attention_mask': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
Für Audio- und Bildverarbeitungsaufgaben verarbeitet ein Merkmalsextraktor das Audiosignal oder Bild in das richtige Eingabeformat.
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie einen Merkmalsextraktor mit [`AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> feature_extractor = AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained(
|
||||
... "ehcalabres/wav2vec2-lg-xlsr-en-speech-emotion-recognition"
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
Multimodale Aufgaben erfordern einen Prozessor, der zwei Arten von Vorverarbeitungswerkzeugen kombiniert. Das Modell [LayoutLMV2](model_doc/layoutlmv2) beispielsweise benötigt einen Feature-Extraktor für Bilder und einen Tokenizer für Text; ein Prozessor kombiniert beide.
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie einen Prozessor mit [`AutoProcessor.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/layoutlmv2-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Mit den `AutoModelFor`-Klassen können Sie schließlich ein vortrainiertes Modell für eine bestimmte Aufgabe laden (siehe [hier](model_doc/auto) für eine vollständige Liste der verfügbaren Aufgaben). Laden Sie zum Beispiel ein Modell für die Sequenzklassifikation mit [`AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können denselben Prüfpunkt problemlos wiederverwenden, um eine Architektur für eine andere Aufgabe zu laden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForTokenClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Für PyTorch-Modelle verwendet die Methode `from_pretrained()` `torch.load()`, die intern `pickle` verwendet und als unsicher bekannt ist. Generell sollte man niemals ein Modell laden, das aus einer nicht vertrauenswürdigen Quelle stammen könnte, oder das manipuliert worden sein könnte. Dieses Sicherheitsrisiko wird für öffentliche Modelle, die auf dem Hugging Face Hub gehostet werden, teilweise gemildert, da diese bei jeder Übertragung [auf Malware](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security-malware) gescannt werden. Siehe die [Hub-Dokumentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security) für Best Practices wie [signierte Commit-Verifizierung](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security-gpg#signing-commits-with-gpg) mit GPG.
|
||||
|
||||
TensorFlow- und Flax-Checkpoints sind nicht betroffen und können in PyTorch-Architekturen mit den Kwargs `from_tf` und `from_flax` für die Methode `from_pretrained` geladen werden, um dieses Problem zu umgehen.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Im Allgemeinen empfehlen wir die Verwendung der Klasse "AutoTokenizer" und der Klasse "AutoModelFor", um trainierte Instanzen von Modellen zu laden. Dadurch wird sichergestellt, dass Sie jedes Mal die richtige Architektur laden. Im nächsten [Tutorial] (Vorverarbeitung) erfahren Sie, wie Sie Ihren neu geladenen Tokenizer, Feature Extractor und Prozessor verwenden, um einen Datensatz für die Feinabstimmung vorzuverarbeiten.
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Mit den Klassen `TFAutoModelFor` schließlich können Sie ein vortrainiertes Modell für eine bestimmte Aufgabe laden (siehe [hier](model_doc/auto) für eine vollständige Liste der verfügbaren Aufgaben). Laden Sie zum Beispiel ein Modell für die Sequenzklassifikation mit [`TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können denselben Prüfpunkt problemlos wiederverwenden, um eine Architektur für eine andere Aufgabe zu laden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = TFAutoModelForTokenClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Im Allgemeinen empfehlen wir, die Klasse "AutoTokenizer" und die Klasse "TFAutoModelFor" zu verwenden, um vortrainierte Instanzen von Modellen zu laden. Dadurch wird sichergestellt, dass Sie jedes Mal die richtige Architektur laden. Im nächsten [Tutorial] (Vorverarbeitung) erfahren Sie, wie Sie Ihren neu geladenen Tokenizer, Feature Extractor und Prozessor verwenden, um einen Datensatz für die Feinabstimmung vorzuverarbeiten.
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
@ -1,127 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Vortrainierte Instanzen mit einer AutoClass laden
|
||||
|
||||
Bei so vielen verschiedenen Transformator-Architekturen kann es eine Herausforderung sein, eine für Ihren Checkpoint zu erstellen. Als Teil der 🤗 Transformers Kernphilosophie, die Bibliothek leicht, einfach und flexibel nutzbar zu machen, leitet eine `AutoClass` automatisch die richtige Architektur aus einem gegebenen Checkpoint ab und lädt sie. Mit der Methode `from_pretrained()` kann man schnell ein vortrainiertes Modell für eine beliebige Architektur laden, so dass man keine Zeit und Ressourcen aufwenden muss, um ein Modell von Grund auf zu trainieren. Die Erstellung dieser Art von Checkpoint-agnostischem Code bedeutet, dass Ihr Code, wenn er für einen Checkpoint funktioniert, auch mit einem anderen Checkpoint funktionieren wird - solange er für eine ähnliche Aufgabe trainiert wurde - selbst wenn die Architektur unterschiedlich ist.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Denken Sie daran, dass sich die Architektur auf das Skelett des Modells bezieht und die Checkpoints die Gewichte für eine bestimmte Architektur sind. Zum Beispiel ist [BERT](https://huggingface.co/bert-base-uncased) eine Architektur, während `bert-base-uncased` ein Checkpoint ist. Modell ist ein allgemeiner Begriff, der entweder Architektur oder Prüfpunkt bedeuten kann.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In dieser Anleitung lernen Sie, wie man:
|
||||
|
||||
* Einen vortrainierten Tokenizer lädt.
|
||||
* Einen vortrainierten Merkmalsextraktor lädt.
|
||||
* Einen vortrainierten Prozessor lädt.
|
||||
* Ein vortrainiertes Modell lädt.
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
Nahezu jede NLP-Aufgabe beginnt mit einem Tokenizer. Ein Tokenizer wandelt Ihre Eingabe in ein Format um, das vom Modell verarbeitet werden kann.
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie einen Tokenizer mit [`AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dann tokenisieren Sie Ihre Eingabe wie unten gezeigt:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> sequence = "In a hole in the ground there lived a hobbit."
|
||||
>>> print(tokenizer(sequence))
|
||||
{'input_ids': [101, 1999, 1037, 4920, 1999, 1996, 2598, 2045, 2973, 1037, 7570, 10322, 4183, 1012, 102],
|
||||
'token_type_ids': [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
'attention_mask': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
Für Audio- und Bildverarbeitungsaufgaben verarbeitet ein Merkmalsextraktor das Audiosignal oder Bild in das richtige Eingabeformat.
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie einen Merkmalsextraktor mit [`AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> feature_extractor = AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained(
|
||||
... "ehcalabres/wav2vec2-lg-xlsr-en-speech-emotion-recognition"
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
Multimodale Aufgaben erfordern einen Prozessor, der zwei Arten von Vorverarbeitungswerkzeugen kombiniert. Das Modell [LayoutLMV2](model_doc/layoutlmv2) beispielsweise benötigt einen Feature-Extraktor für Bilder und einen Tokenizer für Text; ein Prozessor kombiniert beide.
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie einen Prozessor mit [`AutoProcessor.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/layoutlmv2-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Mit den `AutoModelFor`-Klassen können Sie schließlich ein vortrainiertes Modell für eine bestimmte Aufgabe laden (siehe [hier](model_doc/auto) für eine vollständige Liste der verfügbaren Aufgaben). Laden Sie zum Beispiel ein Modell für die Sequenzklassifikation mit [`AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können denselben Prüfpunkt problemlos wiederverwenden, um eine Architektur für eine andere Aufgabe zu laden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForTokenClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Für PyTorch-Modelle verwendet die Methode `from_pretrained()` `torch.load()`, die intern `pickle` verwendet und als unsicher bekannt ist. Generell sollte man niemals ein Modell laden, das aus einer nicht vertrauenswürdigen Quelle stammen könnte, oder das manipuliert worden sein könnte. Dieses Sicherheitsrisiko wird für öffentliche Modelle, die auf dem Hugging Face Hub gehostet werden, teilweise gemildert, da diese bei jeder Übertragung [auf Malware](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security-malware) gescannt werden. Siehe die [Hub-Dokumentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security) für Best Practices wie [signierte Commit-Verifizierung](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security-gpg#signing-commits-with-gpg) mit GPG.
|
||||
|
||||
TensorFlow- und Flax-Checkpoints sind nicht betroffen und können in PyTorch-Architekturen mit den Kwargs `from_tf` und `from_flax` für die Methode `from_pretrained` geladen werden, um dieses Problem zu umgehen.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Im Allgemeinen empfehlen wir die Verwendung der Klasse "AutoTokenizer" und der Klasse "AutoModelFor", um trainierte Instanzen von Modellen zu laden. Dadurch wird sichergestellt, dass Sie jedes Mal die richtige Architektur laden. Im nächsten [Tutorial] (Vorverarbeitung) erfahren Sie, wie Sie Ihren neu geladenen Tokenizer, Feature Extractor und Prozessor verwenden, um einen Datensatz für die Feinabstimmung vorzuverarbeiten.
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Mit den Klassen `TFAutoModelFor` schließlich können Sie ein vortrainiertes Modell für eine bestimmte Aufgabe laden (siehe [hier](model_doc/auto) für eine vollständige Liste der verfügbaren Aufgaben). Laden Sie zum Beispiel ein Modell für die Sequenzklassifikation mit [`TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können denselben Prüfpunkt problemlos wiederverwenden, um eine Architektur für eine andere Aufgabe zu laden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = TFAutoModelForTokenClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Im Allgemeinen empfehlen wir, die Klasse "AutoTokenizer" und die Klasse "TFAutoModelFor" zu verwenden, um vortrainierte Instanzen von Modellen zu laden. Dadurch wird sichergestellt, dass Sie jedes Mal die richtige Architektur laden. Im nächsten [Tutorial] (Vorverarbeitung) erfahren Sie, wie Sie Ihren neu geladenen Tokenizer, Feature Extractor und Prozessor verwenden, um einen Datensatz für die Feinabstimmung vorzuverarbeiten.
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
333
docs/source/de/index.md
Normal file
333
docs/source/de/index.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,333 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
Maschinelles Lernen auf dem neuesten Stand der Technik für PyTorch, TensorFlow und JAX.
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers bietet APIs zum einfachen Herunterladen und Trainieren von vortrainierten Modellen auf dem neuesten Stand der Technik. Die Verwendung von vortrainierten Modellen kann Rechenkosten sparen und den CO2-Fußabdruck reduzieren und Zeit sparen, die für das Training eines Modells von Grund auf benötigt wird. Die Modelle können für verschiedene Modalitäten verwendet werden, wie z. B.:
|
||||
|
||||
* 📝 Text: Textklassifizierung, Informationsextrahierung, Beantwortung von Fragen, Zusammenfassung, Übersetzung und Texterstellung in über 100 Sprachen.
|
||||
* 🖼️ Bilder: Bildklassifizierung, Objekterkennung und Segmentierung.
|
||||
* 🗣️ Audio: Spracherkennung und Audioklassifizierung.
|
||||
* 🐙 Multimodal: Beantwortung von Tabellenfragen, optische Zeichenerkennung, Informationsextraktion aus gescannten Dokumenten, Videoklassifizierung und Beantwortung visueller Fragen.
|
||||
|
||||
Unsere Bibliothek unterstützt die nahtlose Integration von drei der beliebtesten Deep-Learning-Bibliotheken: [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/) und [JAX](https://jax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/). Trainieren Sie Ihr Modell in drei Codezeilen in einem Framework und laden Sie es zur Inferenz mit einem anderen.
|
||||
|
||||
Jede 🤗 Transformers-Architektur ist in einem eigenständigen Python-Modul definiert, so dass sie leicht für Forschung und Experimente angepasst werden kann.
|
||||
|
||||
## Wenn Sie auf der Suche nach individueller Unterstützung durch das Hugging Face-Team sind
|
||||
|
||||
<a target="_blank" href="https://huggingface.co/support">
|
||||
<img alt="HuggingFace Expert Acceleration Program" src="https://cdn-media.huggingface.co/marketing/transformers/new-support-improved.png" style="width: 100%; max-width: 600px; border: 1px solid #eee; border-radius: 4px; box-shadow: 0 1px 2px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Inhalt
|
||||
|
||||
Die Dokumentation ist in fünf Teile gegliedert:
|
||||
|
||||
- **GET STARTED** enthält eine kurze Tour und Installationsanweisungen, um mit 🤗 Transformers loszulegen.
|
||||
- **TUTORIALS** sind ein hervorragender Ausgangspunkt, wenn Sie neu in unserer Bibliothek sind. Dieser Abschnitt hilft Ihnen, die grundlegenden Fähigkeiten zu erlangen, die Sie benötigen, um mit 🤗 Transformers zu arbeiten.
|
||||
- **HOW-TO GUIDES** zeigen Ihnen, wie Sie ein bestimmtes Ziel erreichen können, z. B. die Feinabstimmung eines vortrainierten Modells für die Sprachmodellierung oder die Erstellung eines benutzerdefinierten Modellkopfs.
|
||||
- **KONZEPTUELLE ANLEITUNGEN** bietet weitere Diskussionen und Erklärungen zu den zugrunde liegenden Konzepten und Ideen hinter Modellen, Aufgaben und der Designphilosophie von 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
- **API** beschreibt jede Klasse und Funktion, gruppiert in:
|
||||
|
||||
- **MAIN CLASSES** für die Hauptklassen, die die wichtigsten APIs der Bibliothek darstellen.
|
||||
- MODELLE** für die Klassen und Funktionen, die zu jedem in der Bibliothek implementierten Modell gehören.
|
||||
- **INTERNAL HELPERS** für die Klassen und Funktionen, die wir intern verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Bibliothek enthält derzeit JAX-, PyTorch- und TensorFlow-Implementierungen, vortrainierte Modellgewichte, Nutzungsskripte und Konvertierungsprogramme für die folgenden Modelle.
|
||||
|
||||
### Unterstütze Modelle
|
||||
|
||||
<!--This list is updated automatically from the README with _make fix-copies_. Do not update manually! -->
|
||||
|
||||
1. **[ALBERT](model_doc/albert)** (from Google Research and the Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago) released with the paper [ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-supervised Learning of Language Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.11942), by Zhenzhong Lan, Mingda Chen, Sebastian Goodman, Kevin Gimpel, Piyush Sharma, Radu Soricut.
|
||||
1. **[ALIGN](model_doc/align)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Scaling Up Visual and Vision-Language Representation Learning With Noisy Text Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.05918) by Chao Jia, Yinfei Yang, Ye Xia, Yi-Ting Chen, Zarana Parekh, Hieu Pham, Quoc V. Le, Yunhsuan Sung, Zhen Li, Tom Duerig.
|
||||
1. **[BART](model_doc/bart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [BART: Denoising Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training for Natural Language Generation, Translation, and Comprehension](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.13461) by Mike Lewis, Yinhan Liu, Naman Goyal, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Omer Levy, Ves Stoyanov and Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[BARThez](model_doc/barthez)** (from École polytechnique) released with the paper [BARThez: a Skilled Pretrained French Sequence-to-Sequence Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.12321) by Moussa Kamal Eddine, Antoine J.-P. Tixier, Michalis Vazirgiannis.
|
||||
1. **[BARTpho](model_doc/bartpho)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [BARTpho: Pre-trained Sequence-to-Sequence Models for Vietnamese](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.09701) by Nguyen Luong Tran, Duong Minh Le and Dat Quoc Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[BEiT](model_doc/beit)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [BEiT: BERT Pre-Training of Image Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.08254) by Hangbo Bao, Li Dong, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[BERT](model_doc/bert)** (from Google) released with the paper [BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805) by Jacob Devlin, Ming-Wei Chang, Kenton Lee and Kristina Toutanova.
|
||||
1. **[BERT For Sequence Generation](model_doc/bert-generation)** (from Google) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[BERTweet](model_doc/bertweet)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [BERTweet: A pre-trained language model for English Tweets](https://aclanthology.org/2020.emnlp-demos.2/) by Dat Quoc Nguyen, Thanh Vu and Anh Tuan Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-Pegasus](model_doc/bigbird_pegasus)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-RoBERTa](model_doc/big_bird)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[Blenderbot](model_doc/blenderbot)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BlenderbotSmall](model_doc/blenderbot-small)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BLOOM](model_doc/bloom)** (from BigScience workshop) released by the [BigScience Workshop](https://bigscience.huggingface.co/).
|
||||
1. **[BORT](model_doc/bort)** (from Alexa) released with the paper [Optimal Subarchitecture Extraction For BERT](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.10499) by Adrian de Wynter and Daniel J. Perry.
|
||||
1. **[ByT5](model_doc/byt5)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [ByT5: Towards a token-free future with pre-trained byte-to-byte models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.13626) by Linting Xue, Aditya Barua, Noah Constant, Rami Al-Rfou, Sharan Narang, Mihir Kale, Adam Roberts, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[CamemBERT](model_doc/camembert)** (from Inria/Facebook/Sorbonne) released with the paper [CamemBERT: a Tasty French Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.03894) by Louis Martin*, Benjamin Muller*, Pedro Javier Ortiz Suárez*, Yoann Dupont, Laurent Romary, Éric Villemonte de la Clergerie, Djamé Seddah and Benoît Sagot.
|
||||
1. **[CANINE](model_doc/canine)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [CANINE: Pre-training an Efficient Tokenization-Free Encoder for Language Representation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06874) by Jonathan H. Clark, Dan Garrette, Iulia Turc, John Wieting.
|
||||
1. **[CLIP](model_doc/clip)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020) by Alec Radford, Jong Wook Kim, Chris Hallacy, Aditya Ramesh, Gabriel Goh, Sandhini Agarwal, Girish Sastry, Amanda Askell, Pamela Mishkin, Jack Clark, Gretchen Krueger, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[CodeGen](model_doc/codegen)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [A Conversational Paradigm for Program Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.13474) by Erik Nijkamp, Bo Pang, Hiroaki Hayashi, Lifu Tu, Huan Wang, Yingbo Zhou, Silvio Savarese, Caiming Xiong.
|
||||
1. **[ConvBERT](model_doc/convbert)** (from YituTech) released with the paper [ConvBERT: Improving BERT with Span-based Dynamic Convolution](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.02496) by Zihang Jiang, Weihao Yu, Daquan Zhou, Yunpeng Chen, Jiashi Feng, Shuicheng Yan.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXT](model_doc/convnext)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [A ConvNet for the 2020s](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545) by Zhuang Liu, Hanzi Mao, Chao-Yuan Wu, Christoph Feichtenhofer, Trevor Darrell, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXTV2](model_doc/convnextv2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [ConvNeXt V2: Co-designing and Scaling ConvNets with Masked Autoencoders](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.00808) by Sanghyun Woo, Shoubhik Debnath, Ronghang Hu, Xinlei Chen, Zhuang Liu, In So Kweon, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[CPM](model_doc/cpm)** (from Tsinghua University) released with the paper [CPM: A Large-scale Generative Chinese Pre-trained Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.00413) by Zhengyan Zhang, Xu Han, Hao Zhou, Pei Ke, Yuxian Gu, Deming Ye, Yujia Qin, Yusheng Su, Haozhe Ji, Jian Guan, Fanchao Qi, Xiaozhi Wang, Yanan Zheng, Guoyang Zeng, Huanqi Cao, Shengqi Chen, Daixuan Li, Zhenbo Sun, Zhiyuan Liu, Minlie Huang, Wentao Han, Jie Tang, Juanzi Li, Xiaoyan Zhu, Maosong Sun.
|
||||
1. **[CTRL](model_doc/ctrl)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [CTRL: A Conditional Transformer Language Model for Controllable Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.05858) by Nitish Shirish Keskar*, Bryan McCann*, Lav R. Varshney, Caiming Xiong and Richard Socher.
|
||||
1. **[CvT](model_doc/cvt)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [CvT: Introducing Convolutions to Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.15808) by Haiping Wu, Bin Xiao, Noel Codella, Mengchen Liu, Xiyang Dai, Lu Yuan, Lei Zhang.
|
||||
1. **[Data2Vec](model_doc/data2vec)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Data2Vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.03555) by Alexei Baevski, Wei-Ning Hsu, Qiantong Xu, Arun Babu, Jiatao Gu, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa](model_doc/deberta)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa-v2](model_doc/deberta-v2)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[Decision Transformer](model_doc/decision_transformer)** (from Berkeley/Facebook/Google) released with the paper [Decision Transformer: Reinforcement Learning via Sequence Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.01345) by Lili Chen, Kevin Lu, Aravind Rajeswaran, Kimin Lee, Aditya Grover, Michael Laskin, Pieter Abbeel, Aravind Srinivas, Igor Mordatch.
|
||||
1. **[DeiT](model_doc/deit)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.12877) by Hugo Touvron, Matthieu Cord, Matthijs Douze, Francisco Massa, Alexandre Sablayrolles, Hervé Jégou.
|
||||
1. **[DETR](model_doc/detr)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.12872) by Nicolas Carion, Francisco Massa, Gabriel Synnaeve, Nicolas Usunier, Alexander Kirillov, Sergey Zagoruyko.
|
||||
1. **[DialoGPT](model_doc/dialogpt)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [DialoGPT: Large-Scale Generative Pre-training for Conversational Response Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.00536) by Yizhe Zhang, Siqi Sun, Michel Galley, Yen-Chun Chen, Chris Brockett, Xiang Gao, Jianfeng Gao, Jingjing Liu, Bill Dolan.
|
||||
1. **[DistilBERT](model_doc/distilbert)** (from HuggingFace), released together with the paper [DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.01108) by Victor Sanh, Lysandre Debut and Thomas Wolf. The same method has been applied to compress GPT2 into [DistilGPT2](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation), RoBERTa into [DistilRoBERTa](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation), Multilingual BERT into [DistilmBERT](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation) and a German version of DistilBERT.
|
||||
1. **[DiT](model_doc/dit)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [DiT: Self-supervised Pre-training for Document Image Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.02378) by Junlong Li, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[DPR](model_doc/dpr)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Dense Passage Retrieval for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.04906) by Vladimir Karpukhin, Barlas Oğuz, Sewon Min, Patrick Lewis, Ledell Wu, Sergey Edunov, Danqi Chen, and Wen-tau Yih.
|
||||
1. **[DPT](master/model_doc/dpt)** (from Intel Labs) released with the paper [Vision Transformers for Dense Prediction](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13413) by René Ranftl, Alexey Bochkovskiy, Vladlen Koltun.
|
||||
1. **[EfficientNet](model_doc/efficientnet)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946) by Mingxing Tan and Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[ELECTRA](model_doc/electra)** (from Google Research/Stanford University) released with the paper [ELECTRA: Pre-training text encoders as discriminators rather than generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10555) by Kevin Clark, Minh-Thang Luong, Quoc V. Le, Christopher D. Manning.
|
||||
1. **[EncoderDecoder](model_doc/encoder-decoder)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[FlauBERT](model_doc/flaubert)** (from CNRS) released with the paper [FlauBERT: Unsupervised Language Model Pre-training for French](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.05372) by Hang Le, Loïc Vial, Jibril Frej, Vincent Segonne, Maximin Coavoux, Benjamin Lecouteux, Alexandre Allauzen, Benoît Crabbé, Laurent Besacier, Didier Schwab.
|
||||
1. **[FLAVA](model_doc/flava)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FLAVA: A Foundational Language And Vision Alignment Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.04482) by Amanpreet Singh, Ronghang Hu, Vedanuj Goswami, Guillaume Couairon, Wojciech Galuba, Marcus Rohrbach, and Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[FNet](model_doc/fnet)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [FNet: Mixing Tokens with Fourier Transforms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.03824) by James Lee-Thorp, Joshua Ainslie, Ilya Eckstein, Santiago Ontanon.
|
||||
1. **[Funnel Transformer](model_doc/funnel)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [Funnel-Transformer: Filtering out Sequential Redundancy for Efficient Language Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03236) by Zihang Dai, Guokun Lai, Yiming Yang, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[GLPN](model_doc/glpn)** (from KAIST) released with the paper [Global-Local Path Networks for Monocular Depth Estimation with Vertical CutDepth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.07436) by Doyeon Kim, Woonghyun Ga, Pyungwhan Ahn, Donggyu Joo, Sehwan Chun, Junmo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[GPT](model_doc/openai-gpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training](https://blog.openai.com/language-unsupervised/) by Alec Radford, Karthik Narasimhan, Tim Salimans and Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[GPT Neo](model_doc/gpt_neo)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [EleutherAI/gpt-neo](https://github.com/EleutherAI/gpt-neo) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Leo Gao, Phil Wang and Connor Leahy.
|
||||
1. **[GPT NeoX](model_doc/gpt_neox)** (from EleutherAI) released with the paper [GPT-NeoX-20B: An Open-Source Autoregressive Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06745) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Eric Hallahan, Quentin Anthony, Leo Gao, Laurence Golding, Horace He, Connor Leahy, Kyle McDonell, Jason Phang, Michael Pieler, USVSN Sai Prashanth, Shivanshu Purohit, Laria Reynolds, Jonathan Tow, Ben Wang, Samuel Weinbach
|
||||
1. **[GPT-2](model_doc/gpt2)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners](https://blog.openai.com/better-language-models/) by Alec Radford*, Jeffrey Wu*, Rewon Child, David Luan, Dario Amodei** and Ilya Sutskever**.
|
||||
1. **[GPT-J](model_doc/gptj)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax](https://github.com/kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax/) by Ben Wang and Aran Komatsuzaki.
|
||||
1. **[GPTSAN-japanese](model_doc/gptsan-japanese)** released in the repository [tanreinama/GPTSAN](https://github.com/tanreinama/GPTSAN/blob/main/report/model.md) by Toshiyuki Sakamoto(tanreinama).
|
||||
1. **[GroupViT](model_doc/groupvit)** (from UCSD, NVIDIA) released with the paper [GroupViT: Semantic Segmentation Emerges from Text Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.11094) by Jiarui Xu, Shalini De Mello, Sifei Liu, Wonmin Byeon, Thomas Breuel, Jan Kautz, Xiaolong Wang.
|
||||
1. **[Hubert](model_doc/hubert)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [HuBERT: Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning by Masked Prediction of Hidden Units](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.07447) by Wei-Ning Hsu, Benjamin Bolte, Yao-Hung Hubert Tsai, Kushal Lakhotia, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Abdelrahman Mohamed.
|
||||
1. **[I-BERT](model_doc/ibert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [I-BERT: Integer-only BERT Quantization](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.01321) by Sehoon Kim, Amir Gholami, Zhewei Yao, Michael W. Mahoney, Kurt Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[ImageGPT](model_doc/imagegpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Generative Pretraining from Pixels](https://openai.com/blog/image-gpt/) by Mark Chen, Alec Radford, Rewon Child, Jeffrey Wu, Heewoo Jun, David Luan, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLM](model_doc/layoutlm)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLM: Pre-training of Text and Layout for Document Image Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.13318) by Yiheng Xu, Minghao Li, Lei Cui, Shaohan Huang, Furu Wei, Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv2](model_doc/layoutlmv2)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv2: Multi-modal Pre-training for Visually-Rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.14740) by Yang Xu, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Furu Wei, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Wanxiang Che, Min Zhang, Lidong Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv3](model_doc/layoutlmv3)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv3: Pre-training for Document AI with Unified Text and Image Masking](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.08387) by Yupan Huang, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yutong Lu, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutXLM](model_doc/layoutxlm)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutXLM: Multimodal Pre-training for Multilingual Visually-rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.08836) by Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LED](model_doc/led)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LeViT](model_doc/levit)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [LeViT: A Vision Transformer in ConvNet's Clothing for Faster Inference](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01136) by Ben Graham, Alaaeldin El-Nouby, Hugo Touvron, Pierre Stock, Armand Joulin, Hervé Jégou, Matthijs Douze.
|
||||
1. **[Longformer](model_doc/longformer)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LongT5](model_doc/longt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [LongT5: Efficient Text-To-Text Transformer for Long Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.07916) by Mandy Guo, Joshua Ainslie, David Uthus, Santiago Ontanon, Jianmo Ni, Yun-Hsuan Sung, Yinfei Yang.
|
||||
1. **[LUKE](model_doc/luke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [LUKE: Deep Contextualized Entity Representations with Entity-aware Self-attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.01057) by Ikuya Yamada, Akari Asai, Hiroyuki Shindo, Hideaki Takeda, Yuji Matsumoto.
|
||||
1. **[LXMERT](model_doc/lxmert)** (from UNC Chapel Hill) released with the paper [LXMERT: Learning Cross-Modality Encoder Representations from Transformers for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.07490) by Hao Tan and Mohit Bansal.
|
||||
1. **[M-CTC-T](model_doc/mctct)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Pseudo-Labeling For Massively Multilingual Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.00161) by Loren Lugosch, Tatiana Likhomanenko, Gabriel Synnaeve, and Ronan Collobert.
|
||||
1. **[M2M100](model_doc/m2m_100)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Beyond English-Centric Multilingual Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11125) by Angela Fan, Shruti Bhosale, Holger Schwenk, Zhiyi Ma, Ahmed El-Kishky, Siddharth Goyal, Mandeep Baines, Onur Celebi, Guillaume Wenzek, Vishrav Chaudhary, Naman Goyal, Tom Birch, Vitaliy Liptchinsky, Sergey Edunov, Edouard Grave, Michael Auli, Armand Joulin.
|
||||
1. **[MarianMT](model_doc/marian)** Machine translation models trained using [OPUS](http://opus.nlpl.eu/) data by Jörg Tiedemann. The [Marian Framework](https://marian-nmt.github.io/) is being developed by the Microsoft Translator Team.
|
||||
1. **[Mask2Former](model_doc/mask2former)** (from FAIR and UIUC) released with the paper [Masked-attention Mask Transformer for Universal Image Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.01527) by Bowen Cheng, Ishan Misra, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov, Rohit Girdhar.
|
||||
1. **[MaskFormer](model_doc/maskformer)** (from Meta and UIUC) released with the paper [Per-Pixel Classification is Not All You Need for Semantic Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.06278) by Bowen Cheng, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov.
|
||||
1. **[mBART](model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08210) by Yinhan Liu, Jiatao Gu, Naman Goyal, Xian Li, Sergey Edunov, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[mBART-50](model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Translation with Extensible Multilingual Pretraining and Finetuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00401) by Yuqing Tang, Chau Tran, Xian Li, Peng-Jen Chen, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Jiatao Gu, Angela Fan.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-BERT](model_doc/megatron-bert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-GPT2](model_doc/megatron_gpt2)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[mLUKE](model_doc/mluke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [mLUKE: The Power of Entity Representations in Multilingual Pretrained Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.08151) by Ryokan Ri, Ikuya Yamada, and Yoshimasa Tsuruoka.
|
||||
1. **[MobileBERT](model_doc/mobilebert)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [MobileBERT: a Compact Task-Agnostic BERT for Resource-Limited Devices](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02984) by Zhiqing Sun, Hongkun Yu, Xiaodan Song, Renjie Liu, Yiming Yang, and Denny Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[MobileViT](model_doc/mobilevit)** (from Apple) released with the paper [MobileViT: Light-weight, General-purpose, and Mobile-friendly Vision Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.02178) by Sachin Mehta and Mohammad Rastegari.
|
||||
1. **[MPNet](model_doc/mpnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [MPNet: Masked and Permuted Pre-training for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09297) by Kaitao Song, Xu Tan, Tao Qin, Jianfeng Lu, Tie-Yan Liu.
|
||||
1. **[MT5](model_doc/mt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [mT5: A massively multilingual pre-trained text-to-text transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11934) by Linting Xue, Noah Constant, Adam Roberts, Mihir Kale, Rami Al-Rfou, Aditya Siddhant, Aditya Barua, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[MVP](model_doc/mvp)** (from RUC AI Box) released with the paper [MVP: Multi-task Supervised Pre-training for Natural Language Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.12131) by Tianyi Tang, Junyi Li, Wayne Xin Zhao and Ji-Rong Wen.
|
||||
1. **[Nezha](model_doc/nezha)** (from Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab) released with the paper [NEZHA: Neural Contextualized Representation for Chinese Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.00204) by Junqiu Wei, Xiaozhe Ren, Xiaoguang Li, Wenyong Huang, Yi Liao, Yasheng Wang, Jiashu Lin, Xin Jiang, Xiao Chen and Qun Liu.
|
||||
1. **[NLLB](model_doc/nllb)** (from Meta) released with the paper [No Language Left Behind: Scaling Human-Centered Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.04672) by the NLLB team.
|
||||
1. **[Nyströmformer](model_doc/nystromformer)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [Nyströmformer: A Nyström-Based Algorithm for Approximating Self-Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03902) by Yunyang Xiong, Zhanpeng Zeng, Rudrasis Chakraborty, Mingxing Tan, Glenn Fung, Yin Li, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
1. **[OneFormer](model_doc/oneformer)** (from SHI Labs) released with the paper [OneFormer: One Transformer to Rule Universal Image Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06220) by Jitesh Jain, Jiachen Li, MangTik Chiu, Ali Hassani, Nikita Orlov, Humphrey Shi.
|
||||
1. **[OPT](master/model_doc/opt)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [OPT: Open Pre-trained Transformer Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.01068) by Susan Zhang, Stephen Roller, Naman Goyal, Mikel Artetxe, Moya Chen, Shuohui Chen et al.
|
||||
1. **[OWL-ViT](model_doc/owlvit)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Simple Open-Vocabulary Object Detection with Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.06230) by Matthias Minderer, Alexey Gritsenko, Austin Stone, Maxim Neumann, Dirk Weissenborn, Alexey Dosovitskiy, Aravindh Mahendran, Anurag Arnab, Mostafa Dehghani, Zhuoran Shen, Xiao Wang, Xiaohua Zhai, Thomas Kipf, and Neil Houlsby.
|
||||
1. **[Pegasus](model_doc/pegasus)** (from Google) released with the paper [PEGASUS: Pre-training with Extracted Gap-sentences for Abstractive Summarization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.08777) by Jingqing Zhang, Yao Zhao, Mohammad Saleh and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[Perceiver IO](model_doc/perceiver)** (from Deepmind) released with the paper [Perceiver IO: A General Architecture for Structured Inputs & Outputs](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.14795) by Andrew Jaegle, Sebastian Borgeaud, Jean-Baptiste Alayrac, Carl Doersch, Catalin Ionescu, David Ding, Skanda Koppula, Daniel Zoran, Andrew Brock, Evan Shelhamer, Olivier Hénaff, Matthew M. Botvinick, Andrew Zisserman, Oriol Vinyals, João Carreira.
|
||||
1. **[PhoBERT](model_doc/phobert)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [PhoBERT: Pre-trained language models for Vietnamese](https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.findings-emnlp.92/) by Dat Quoc Nguyen and Anh Tuan Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[PLBart](model_doc/plbart)** (from UCLA NLP) released with the paper [Unified Pre-training for Program Understanding and Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06333) by Wasi Uddin Ahmad, Saikat Chakraborty, Baishakhi Ray, Kai-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[PoolFormer](model_doc/poolformer)** (from Sea AI Labs) released with the paper [MetaFormer is Actually What You Need for Vision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.11418) by Yu, Weihao and Luo, Mi and Zhou, Pan and Si, Chenyang and Zhou, Yichen and Wang, Xinchao and Feng, Jiashi and Yan, Shuicheng.
|
||||
1. **[ProphetNet](model_doc/prophetnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [ProphetNet: Predicting Future N-gram for Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04063) by Yu Yan, Weizhen Qi, Yeyun Gong, Dayiheng Liu, Nan Duan, Jiusheng Chen, Ruofei Zhang and Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[QDQBert](model_doc/qdqbert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Integer Quantization for Deep Learning Inference: Principles and Empirical Evaluation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09602) by Hao Wu, Patrick Judd, Xiaojie Zhang, Mikhail Isaev and Paulius Micikevicius.
|
||||
1. **[RAG](model_doc/rag)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11401) by Patrick Lewis, Ethan Perez, Aleksandara Piktus, Fabio Petroni, Vladimir Karpukhin, Naman Goyal, Heinrich Küttler, Mike Lewis, Wen-tau Yih, Tim Rocktäschel, Sebastian Riedel, Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[REALM](model_doc/realm.html)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [REALM: Retrieval-Augmented Language Model Pre-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.08909) by Kelvin Guu, Kenton Lee, Zora Tung, Panupong Pasupat and Ming-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[Reformer](model_doc/reformer)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Reformer: The Efficient Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04451) by Nikita Kitaev, Łukasz Kaiser, Anselm Levskaya.
|
||||
1. **[RegNet](model_doc/regnet)** (from META Platforms) released with the paper [Designing Network Design Space](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.13678) by Ilija Radosavovic, Raj Prateek Kosaraju, Ross Girshick, Kaiming He, Piotr Dollár.
|
||||
1. **[RemBERT](model_doc/rembert)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Rethinking embedding coupling in pre-trained language models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.12821) by Hyung Won Chung, Thibault Févry, Henry Tsai, M. Johnson, Sebastian Ruder.
|
||||
1. **[ResNet](model_doc/resnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385) by Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun.
|
||||
1. **[RoBERTa](model_doc/roberta)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692) by Yinhan Liu, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Mandar Joshi, Danqi Chen, Omer Levy, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer, Veselin Stoyanov.
|
||||
1. **[RoFormer](model_doc/roformer)** (from ZhuiyiTechnology), released together with the paper [RoFormer: Enhanced Transformer with Rotary Position Embedding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.09864) by Jianlin Su and Yu Lu and Shengfeng Pan and Bo Wen and Yunfeng Liu.
|
||||
1. **[SegFormer](model_doc/segformer)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [SegFormer: Simple and Efficient Design for Semantic Segmentation with Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.15203) by Enze Xie, Wenhai Wang, Zhiding Yu, Anima Anandkumar, Jose M. Alvarez, Ping Luo.
|
||||
1. **[SEW](model_doc/sew)** (from ASAPP) released with the paper [Performance-Efficiency Trade-offs in Unsupervised Pre-training for Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.06870) by Felix Wu, Kwangyoun Kim, Jing Pan, Kyu Han, Kilian Q. Weinberger, Yoav Artzi.
|
||||
1. **[SEW-D](model_doc/sew_d)** (from ASAPP) released with the paper [Performance-Efficiency Trade-offs in Unsupervised Pre-training for Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.06870) by Felix Wu, Kwangyoun Kim, Jing Pan, Kyu Han, Kilian Q. Weinberger, Yoav Artzi.
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer](model_doc/speech_to_text)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [fairseq S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with fairseq](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer2](model_doc/speech_to_text_2)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [Large-Scale Self- and Semi-Supervised Learning for Speech Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.06678) by Changhan Wang, Anne Wu, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli, Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[Splinter](model_doc/splinter)** (from Tel Aviv University), released together with the paper [Few-Shot Question Answering by Pretraining Span Selection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.00438) by Ori Ram, Yuval Kirstain, Jonathan Berant, Amir Globerson, Omer Levy.
|
||||
1. **[SqueezeBERT](model_doc/squeezebert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [SqueezeBERT: What can computer vision teach NLP about efficient neural networks?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11316) by Forrest N. Iandola, Albert E. Shaw, Ravi Krishna, and Kurt W. Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[Swin Transformer](model_doc/swin)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14030) by Ze Liu, Yutong Lin, Yue Cao, Han Hu, Yixuan Wei, Zheng Zhang, Stephen Lin, Baining Guo.
|
||||
1. **[Swin Transformer V2](model_doc/swinv2)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [Swin Transformer V2: Scaling Up Capacity and Resolution](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09883) by Ze Liu, Han Hu, Yutong Lin, Zhuliang Yao, Zhenda Xie, Yixuan Wei, Jia Ning, Yue Cao, Zheng Zhang, Li Dong, Furu Wei, Baining Guo.
|
||||
1. **[T5](model_doc/t5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10683) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[T5v1.1](model_doc/t5v1.1)** (from Google AI) released in the repository [google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer](https://github.com/google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer/blob/main/released_checkpoints.md#t511) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[TAPAS](model_doc/tapas)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [TAPAS: Weakly Supervised Table Parsing via Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02349) by Jonathan Herzig, Paweł Krzysztof Nowak, Thomas Müller, Francesco Piccinno and Julian Martin Eisenschlos.
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](model_doc/tapex)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou.
|
||||
1. **[Trajectory Transformer](model_doc/trajectory_transformers)** (from the University of California at Berkeley) released with the paper [Offline Reinforcement Learning as One Big Sequence Modeling Problem](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.02039) by Michael Janner, Qiyang Li, Sergey Levine
|
||||
1. **[Transformer-XL](model_doc/transfo-xl)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860) by Zihang Dai*, Zhilin Yang*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Quoc V. Le, Ruslan Salakhutdinov.
|
||||
1. **[TrOCR](model_doc/trocr)** (from Microsoft), released together with the paper [TrOCR: Transformer-based Optical Character Recognition with Pre-trained Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.10282) by Minghao Li, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Zhoujun Li, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[UL2](model_doc/ul2)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Unifying Language Learning Paradigms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.05131v1) by Yi Tay, Mostafa Dehghani, Vinh Q. Tran, Xavier Garcia, Dara Bahri, Tal Schuster, Huaixiu Steven Zheng, Neil Houlsby, Donald Metzler
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeech](model_doc/unispeech)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.07597) by Chengyi Wang, Yu Wu, Yao Qian, Kenichi Kumatani, Shujie Liu, Furu Wei, Michael Zeng, Xuedong Huang.
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeechSat](model_doc/unispeech-sat)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UNISPEECH-SAT: UNIVERSAL SPEECH REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH SPEAKER AWARE PRE-TRAINING](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.05752) by Sanyuan Chen, Yu Wu, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Zhuo Chen, Shujie Liu, Jian Wu, Yao Qian, Furu Wei, Jinyu Li, Xiangzhan Yu.
|
||||
1. **[VAN](model_doc/van)** (from Tsinghua University and Nankai University) released with the paper [Visual Attention Network](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.09741) by Meng-Hao Guo, Cheng-Ze Lu, Zheng-Ning Liu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Shi-Min Hu.
|
||||
1. **[VideoMAE](model_doc/videomae)** (from Multimedia Computing Group, Nanjing University) released with the paper [VideoMAE: Masked Autoencoders are Data-Efficient Learners for Self-Supervised Video Pre-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.12602) by Zhan Tong, Yibing Song, Jue Wang, Limin Wang.
|
||||
1. **[ViLT](model_doc/vilt)** (from NAVER AI Lab/Kakao Enterprise/Kakao Brain) released with the paper [ViLT: Vision-and-Language Transformer Without Convolution or Region Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03334) by Wonjae Kim, Bokyung Son, Ildoo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[Vision Transformer (ViT)](model_doc/vit)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929) by Alexey Dosovitskiy, Lucas Beyer, Alexander Kolesnikov, Dirk Weissenborn, Xiaohua Zhai, Thomas Unterthiner, Mostafa Dehghani, Matthias Minderer, Georg Heigold, Sylvain Gelly, Jakob Uszkoreit, Neil Houlsby.
|
||||
1. **[VisualBERT](model_doc/visual_bert)** (from UCLA NLP) released with the paper [VisualBERT: A Simple and Performant Baseline for Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.03557) by Liunian Harold Li, Mark Yatskar, Da Yin, Cho-Jui Hsieh, Kai-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[ViTMAE](model_doc/vit_mae)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.06377) by Kaiming He, Xinlei Chen, Saining Xie, Yanghao Li, Piotr Dollár, Ross Girshick.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2](model_doc/wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [wav2vec 2.0: A Framework for Self-Supervised Learning of Speech Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11477) by Alexei Baevski, Henry Zhou, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2-Conformer](model_doc/wav2vec2-conformer)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FAIRSEQ S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with FAIRSEQ](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Sravya Popuri, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2Phoneme](model_doc/wav2vec2_phoneme)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Simple and Effective Zero-shot Cross-lingual Phoneme Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.11680) by Qiantong Xu, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[WavLM](model_doc/wavlm)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [WavLM: Large-Scale Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Full Stack Speech Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.13900) by Sanyuan Chen, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Yu Wu, Shujie Liu, Zhuo Chen, Jinyu Li, Naoyuki Kanda, Takuya Yoshioka, Xiong Xiao, Jian Wu, Long Zhou, Shuo Ren, Yanmin Qian, Yao Qian, Jian Wu, Michael Zeng, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[XGLM](model_doc/xglm)** (From Facebook AI) released with the paper [Few-shot Learning with Multilingual Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10668) by Xi Victoria Lin, Todor Mihaylov, Mikel Artetxe, Tianlu Wang, Shuohui Chen, Daniel Simig, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Shruti Bhosale, Jingfei Du, Ramakanth Pasunuru, Sam Shleifer, Punit Singh Koura, Vishrav Chaudhary, Brian O'Horo, Jeff Wang, Luke Zettlemoyer, Zornitsa Kozareva, Mona Diab, Veselin Stoyanov, Xian Li.
|
||||
1. **[XLM](model_doc/xlm)** (from Facebook) released together with the paper [Cross-lingual Language Model Pretraining](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.07291) by Guillaume Lample and Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-ProphetNet](model_doc/xlm-prophetnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [ProphetNet: Predicting Future N-gram for Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04063) by Yu Yan, Weizhen Qi, Yeyun Gong, Dayiheng Liu, Nan Duan, Jiusheng Chen, Ruofei Zhang and Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-RoBERTa](model_doc/xlm-roberta)** (from Facebook AI), released together with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-lingual Representation Learning at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.02116) by Alexis Conneau*, Kartikay Khandelwal*, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Guillaume Wenzek, Francisco Guzmán, Edouard Grave, Myle Ott, Luke Zettlemoyer and Veselin Stoyanov.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-RoBERTa-XL](model_doc/xlm-roberta-xl)** (from Facebook AI), released together with the paper [Larger-Scale Transformers for Multilingual Masked Language Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.00572) by Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Myle Ott, Giri Anantharaman, Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-V](model_doc/xlm-v)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [XLM-V: Overcoming the Vocabulary Bottleneck in Multilingual Masked Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.10472) by Davis Liang, Hila Gonen, Yuning Mao, Rui Hou, Naman Goyal, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Luke Zettlemoyer, Madian Khabsa.
|
||||
1. **[XLNet](model_doc/xlnet)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [XLNet: Generalized Autoregressive Pretraining for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.08237) by Zhilin Yang*, Zihang Dai*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[XLS-R](model_doc/xls_r)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [XLS-R: Self-supervised Cross-lingual Speech Representation Learning at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09296) by Arun Babu, Changhan Wang, Andros Tjandra, Kushal Lakhotia, Qiantong Xu, Naman Goyal, Kritika Singh, Patrick von Platen, Yatharth Saraf, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Alexis Conneau, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[XLSR-Wav2Vec2](model_doc/xlsr_wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-Lingual Representation Learning For Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.13979) by Alexis Conneau, Alexei Baevski, Ronan Collobert, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[YOLOS](model_doc/yolos)** (from Huazhong University of Science & Technology) released with the paper [You Only Look at One Sequence: Rethinking Transformer in Vision through Object Detection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00666) by Yuxin Fang, Bencheng Liao, Xinggang Wang, Jiemin Fang, Jiyang Qi, Rui Wu, Jianwei Niu, Wenyu Liu.
|
||||
1. **[YOSO](model_doc/yoso)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [You Only Sample (Almost) Once: Linear Cost Self-Attention Via Bernoulli Sampling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09714) by Zhanpeng Zeng, Yunyang Xiong, Sathya N. Ravi, Shailesh Acharya, Glenn Fung, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Unterstützte Frameworks
|
||||
|
||||
Die folgende Tabelle zeigt die derzeitige Unterstützung in der Bibliothek für jedes dieser Modelle, unabhängig davon, ob sie einen Python
|
||||
Tokenizer haben (als "langsam" bezeichnet), ein "schneller" Tokenizer, der von der 🤗 Tokenizers Bibliothek unterstützt wird, ob sie Unterstützung in Jax (via
|
||||
Flax), PyTorch, und/oder TensorFlow haben.
|
||||
|
||||
<!--This table is updated automatically from the auto modules with _make fix-copies_. Do not update manually!-->
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Tokenizer slow | Tokenizer fast | PyTorch support | TensorFlow support | Flax Support |
|
||||
|:---------------------------:|:--------------:|:--------------:|:---------------:|:------------------:|:------------:|
|
||||
| ALBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BART | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BEiT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Bert Generation | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BigBird | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BigBird-Pegasus | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Blenderbot | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BlenderbotSmall | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BLOOM | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CamemBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CANINE | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CLIP | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| CodeGen | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ConvBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ConvNeXT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CTRL | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CvT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Data2VecAudio | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Data2VecText | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Data2VecVision | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeBERTa-v2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Decision Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeiT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DETR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DistilBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| DPR | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ELECTRA | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Encoder decoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| FairSeq Machine-Translation | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FlauBERT | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FLAVA | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FNet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Funnel Transformer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GLPN | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GPT Neo | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GPT NeoX | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GPT-J | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GroupViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Hubert | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| I-BERT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ImageGPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LayoutLM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LayoutLMv2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LayoutLMv3 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LED | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LeViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Longformer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LongT5 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| LUKE | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LXMERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| M-CTC-T | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| M2M100 | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Marian | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| MaskFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| mBART | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Megatron-BERT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MPNet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MT5 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| MVP | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Nezha | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Nyströmformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| OpenAI GPT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| OpenAI GPT-2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| OPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| OWL-ViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Pegasus | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Perceiver | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| PLBart | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| PoolFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ProphetNet | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| QDQBert | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RAG | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| REALM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Reformer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RegNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RemBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ResNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RetriBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RoBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RoFormer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| SegFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SEW | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SEW-D | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Speech Encoder decoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Speech2Text | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Speech2Text2 | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Splinter | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SqueezeBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Swin Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Swin Transformer V2 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| T5 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| TAPAS | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Trajectory Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Transformer-XL | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TrOCR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| UniSpeech | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| UniSpeechSat | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| VAN | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| VideoMAE | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ViLT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Vision Encoder decoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| VisionTextDualEncoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| VisualBERT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| ViTMAE | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Wav2Vec2 | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Wav2Vec2-Conformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| WavLM | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XGLM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| XLM | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLM-ProphetNet | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLM-RoBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| XLM-RoBERTa-XL | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLNet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| YOLOS | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| YOSO | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- End table-->
|
||||
@ -1,329 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
Maschinelles Lernen auf dem neuesten Stand der Technik für PyTorch, TensorFlow und JAX.
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers bietet APIs zum einfachen Herunterladen und Trainieren von vortrainierten Modellen auf dem neuesten Stand der Technik. Die Verwendung von vortrainierten Modellen kann Rechenkosten sparen und den CO2-Fußabdruck reduzieren und Zeit sparen, die für das Training eines Modells von Grund auf benötigt wird. Die Modelle können für verschiedene Modalitäten verwendet werden, wie z. B.:
|
||||
|
||||
* 📝 Text: Textklassifizierung, Informationsextrahierung, Beantwortung von Fragen, Zusammenfassung, Übersetzung und Texterstellung in über 100 Sprachen.
|
||||
* 🖼️ Bilder: Bildklassifizierung, Objekterkennung und Segmentierung.
|
||||
* 🗣️ Audio: Spracherkennung und Audioklassifizierung.
|
||||
* 🐙 Multimodal: Beantwortung von Tabellenfragen, optische Zeichenerkennung, Informationsextraktion aus gescannten Dokumenten, Videoklassifizierung und Beantwortung visueller Fragen.
|
||||
|
||||
Unsere Bibliothek unterstützt die nahtlose Integration von drei der beliebtesten Deep-Learning-Bibliotheken: [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/) und [JAX](https://jax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/). Trainieren Sie Ihr Modell in drei Codezeilen in einem Framework und laden Sie es zur Inferenz mit einem anderen.
|
||||
|
||||
Jede 🤗 Transformers-Architektur ist in einem eigenständigen Python-Modul definiert, so dass sie leicht für Forschung und Experimente angepasst werden kann.
|
||||
|
||||
## Wenn Sie auf der Suche nach individueller Unterstützung durch das Hugging Face-Team sind
|
||||
|
||||
<a target="_blank" href="https://huggingface.co/support">
|
||||
<img alt="HuggingFace Expert Acceleration Program" src="https://cdn-media.huggingface.co/marketing/transformers/new-support-improved.png" style="width: 100%; max-width: 600px; border: 1px solid #eee; border-radius: 4px; box-shadow: 0 1px 2px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Inhalt
|
||||
|
||||
Die Dokumentation ist in fünf Teile gegliedert:
|
||||
|
||||
- **GET STARTED** enthält eine kurze Tour und Installationsanweisungen, um mit 🤗 Transformers loszulegen.
|
||||
- **TUTORIALS** sind ein hervorragender Ausgangspunkt, wenn Sie neu in unserer Bibliothek sind. Dieser Abschnitt hilft Ihnen, die grundlegenden Fähigkeiten zu erlangen, die Sie benötigen, um mit 🤗 Transformers zu arbeiten.
|
||||
- **HOW-TO GUIDES** zeigen Ihnen, wie Sie ein bestimmtes Ziel erreichen können, z. B. die Feinabstimmung eines vortrainierten Modells für die Sprachmodellierung oder die Erstellung eines benutzerdefinierten Modellkopfs.
|
||||
- **KONZEPTUELLE ANLEITUNGEN** bietet weitere Diskussionen und Erklärungen zu den zugrunde liegenden Konzepten und Ideen hinter Modellen, Aufgaben und der Designphilosophie von 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
- **API** beschreibt jede Klasse und Funktion, gruppiert in:
|
||||
|
||||
- **MAIN CLASSES** für die Hauptklassen, die die wichtigsten APIs der Bibliothek darstellen.
|
||||
- MODELLE** für die Klassen und Funktionen, die zu jedem in der Bibliothek implementierten Modell gehören.
|
||||
- **INTERNAL HELPERS** für die Klassen und Funktionen, die wir intern verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Bibliothek enthält derzeit JAX-, PyTorch- und TensorFlow-Implementierungen, vortrainierte Modellgewichte, Nutzungsskripte und Konvertierungsprogramme für die folgenden Modelle.
|
||||
|
||||
### Unterstütze Modelle
|
||||
|
||||
<!--This list is updated automatically from the README with _make fix-copies_. Do not update manually! -->
|
||||
|
||||
1. **[ALBERT](model_doc/albert)** (from Google Research and the Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago) released with the paper [ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-supervised Learning of Language Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.11942), by Zhenzhong Lan, Mingda Chen, Sebastian Goodman, Kevin Gimpel, Piyush Sharma, Radu Soricut.
|
||||
1. **[ALIGN](model_doc/align)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Scaling Up Visual and Vision-Language Representation Learning With Noisy Text Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.05918) by Chao Jia, Yinfei Yang, Ye Xia, Yi-Ting Chen, Zarana Parekh, Hieu Pham, Quoc V. Le, Yunhsuan Sung, Zhen Li, Tom Duerig.
|
||||
1. **[BART](model_doc/bart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [BART: Denoising Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training for Natural Language Generation, Translation, and Comprehension](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.13461) by Mike Lewis, Yinhan Liu, Naman Goyal, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Omer Levy, Ves Stoyanov and Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[BARThez](model_doc/barthez)** (from École polytechnique) released with the paper [BARThez: a Skilled Pretrained French Sequence-to-Sequence Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.12321) by Moussa Kamal Eddine, Antoine J.-P. Tixier, Michalis Vazirgiannis.
|
||||
1. **[BARTpho](model_doc/bartpho)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [BARTpho: Pre-trained Sequence-to-Sequence Models for Vietnamese](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.09701) by Nguyen Luong Tran, Duong Minh Le and Dat Quoc Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[BEiT](model_doc/beit)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [BEiT: BERT Pre-Training of Image Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.08254) by Hangbo Bao, Li Dong, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[BERT](model_doc/bert)** (from Google) released with the paper [BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805) by Jacob Devlin, Ming-Wei Chang, Kenton Lee and Kristina Toutanova.
|
||||
1. **[BERT For Sequence Generation](model_doc/bert-generation)** (from Google) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[BERTweet](model_doc/bertweet)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [BERTweet: A pre-trained language model for English Tweets](https://aclanthology.org/2020.emnlp-demos.2/) by Dat Quoc Nguyen, Thanh Vu and Anh Tuan Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-Pegasus](model_doc/bigbird_pegasus)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-RoBERTa](model_doc/big_bird)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[Blenderbot](model_doc/blenderbot)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BlenderbotSmall](model_doc/blenderbot-small)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BLOOM](model_doc/bloom)** (from BigScience workshop) released by the [BigScience Workshop](https://bigscience.huggingface.co/).
|
||||
1. **[BORT](model_doc/bort)** (from Alexa) released with the paper [Optimal Subarchitecture Extraction For BERT](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.10499) by Adrian de Wynter and Daniel J. Perry.
|
||||
1. **[ByT5](model_doc/byt5)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [ByT5: Towards a token-free future with pre-trained byte-to-byte models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.13626) by Linting Xue, Aditya Barua, Noah Constant, Rami Al-Rfou, Sharan Narang, Mihir Kale, Adam Roberts, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[CamemBERT](model_doc/camembert)** (from Inria/Facebook/Sorbonne) released with the paper [CamemBERT: a Tasty French Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.03894) by Louis Martin*, Benjamin Muller*, Pedro Javier Ortiz Suárez*, Yoann Dupont, Laurent Romary, Éric Villemonte de la Clergerie, Djamé Seddah and Benoît Sagot.
|
||||
1. **[CANINE](model_doc/canine)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [CANINE: Pre-training an Efficient Tokenization-Free Encoder for Language Representation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06874) by Jonathan H. Clark, Dan Garrette, Iulia Turc, John Wieting.
|
||||
1. **[CLIP](model_doc/clip)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020) by Alec Radford, Jong Wook Kim, Chris Hallacy, Aditya Ramesh, Gabriel Goh, Sandhini Agarwal, Girish Sastry, Amanda Askell, Pamela Mishkin, Jack Clark, Gretchen Krueger, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[CodeGen](model_doc/codegen)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [A Conversational Paradigm for Program Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.13474) by Erik Nijkamp, Bo Pang, Hiroaki Hayashi, Lifu Tu, Huan Wang, Yingbo Zhou, Silvio Savarese, Caiming Xiong.
|
||||
1. **[ConvBERT](model_doc/convbert)** (from YituTech) released with the paper [ConvBERT: Improving BERT with Span-based Dynamic Convolution](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.02496) by Zihang Jiang, Weihao Yu, Daquan Zhou, Yunpeng Chen, Jiashi Feng, Shuicheng Yan.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXT](model_doc/convnext)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [A ConvNet for the 2020s](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545) by Zhuang Liu, Hanzi Mao, Chao-Yuan Wu, Christoph Feichtenhofer, Trevor Darrell, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXTV2](model_doc/convnextv2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [ConvNeXt V2: Co-designing and Scaling ConvNets with Masked Autoencoders](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.00808) by Sanghyun Woo, Shoubhik Debnath, Ronghang Hu, Xinlei Chen, Zhuang Liu, In So Kweon, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[CPM](model_doc/cpm)** (from Tsinghua University) released with the paper [CPM: A Large-scale Generative Chinese Pre-trained Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.00413) by Zhengyan Zhang, Xu Han, Hao Zhou, Pei Ke, Yuxian Gu, Deming Ye, Yujia Qin, Yusheng Su, Haozhe Ji, Jian Guan, Fanchao Qi, Xiaozhi Wang, Yanan Zheng, Guoyang Zeng, Huanqi Cao, Shengqi Chen, Daixuan Li, Zhenbo Sun, Zhiyuan Liu, Minlie Huang, Wentao Han, Jie Tang, Juanzi Li, Xiaoyan Zhu, Maosong Sun.
|
||||
1. **[CTRL](model_doc/ctrl)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [CTRL: A Conditional Transformer Language Model for Controllable Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.05858) by Nitish Shirish Keskar*, Bryan McCann*, Lav R. Varshney, Caiming Xiong and Richard Socher.
|
||||
1. **[CvT](model_doc/cvt)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [CvT: Introducing Convolutions to Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.15808) by Haiping Wu, Bin Xiao, Noel Codella, Mengchen Liu, Xiyang Dai, Lu Yuan, Lei Zhang.
|
||||
1. **[Data2Vec](model_doc/data2vec)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Data2Vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.03555) by Alexei Baevski, Wei-Ning Hsu, Qiantong Xu, Arun Babu, Jiatao Gu, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa](model_doc/deberta)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa-v2](model_doc/deberta-v2)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[Decision Transformer](model_doc/decision_transformer)** (from Berkeley/Facebook/Google) released with the paper [Decision Transformer: Reinforcement Learning via Sequence Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.01345) by Lili Chen, Kevin Lu, Aravind Rajeswaran, Kimin Lee, Aditya Grover, Michael Laskin, Pieter Abbeel, Aravind Srinivas, Igor Mordatch.
|
||||
1. **[DeiT](model_doc/deit)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.12877) by Hugo Touvron, Matthieu Cord, Matthijs Douze, Francisco Massa, Alexandre Sablayrolles, Hervé Jégou.
|
||||
1. **[DETR](model_doc/detr)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.12872) by Nicolas Carion, Francisco Massa, Gabriel Synnaeve, Nicolas Usunier, Alexander Kirillov, Sergey Zagoruyko.
|
||||
1. **[DialoGPT](model_doc/dialogpt)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [DialoGPT: Large-Scale Generative Pre-training for Conversational Response Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.00536) by Yizhe Zhang, Siqi Sun, Michel Galley, Yen-Chun Chen, Chris Brockett, Xiang Gao, Jianfeng Gao, Jingjing Liu, Bill Dolan.
|
||||
1. **[DistilBERT](model_doc/distilbert)** (from HuggingFace), released together with the paper [DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.01108) by Victor Sanh, Lysandre Debut and Thomas Wolf. The same method has been applied to compress GPT2 into [DistilGPT2](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation), RoBERTa into [DistilRoBERTa](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation), Multilingual BERT into [DistilmBERT](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation) and a German version of DistilBERT.
|
||||
1. **[DiT](model_doc/dit)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [DiT: Self-supervised Pre-training for Document Image Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.02378) by Junlong Li, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[DPR](model_doc/dpr)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Dense Passage Retrieval for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.04906) by Vladimir Karpukhin, Barlas Oğuz, Sewon Min, Patrick Lewis, Ledell Wu, Sergey Edunov, Danqi Chen, and Wen-tau Yih.
|
||||
1. **[DPT](master/model_doc/dpt)** (from Intel Labs) released with the paper [Vision Transformers for Dense Prediction](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13413) by René Ranftl, Alexey Bochkovskiy, Vladlen Koltun.
|
||||
1. **[EfficientNet](model_doc/efficientnet)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946) by Mingxing Tan and Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[ELECTRA](model_doc/electra)** (from Google Research/Stanford University) released with the paper [ELECTRA: Pre-training text encoders as discriminators rather than generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10555) by Kevin Clark, Minh-Thang Luong, Quoc V. Le, Christopher D. Manning.
|
||||
1. **[EncoderDecoder](model_doc/encoder-decoder)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[FlauBERT](model_doc/flaubert)** (from CNRS) released with the paper [FlauBERT: Unsupervised Language Model Pre-training for French](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.05372) by Hang Le, Loïc Vial, Jibril Frej, Vincent Segonne, Maximin Coavoux, Benjamin Lecouteux, Alexandre Allauzen, Benoît Crabbé, Laurent Besacier, Didier Schwab.
|
||||
1. **[FLAVA](model_doc/flava)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FLAVA: A Foundational Language And Vision Alignment Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.04482) by Amanpreet Singh, Ronghang Hu, Vedanuj Goswami, Guillaume Couairon, Wojciech Galuba, Marcus Rohrbach, and Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[FNet](model_doc/fnet)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [FNet: Mixing Tokens with Fourier Transforms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.03824) by James Lee-Thorp, Joshua Ainslie, Ilya Eckstein, Santiago Ontanon.
|
||||
1. **[Funnel Transformer](model_doc/funnel)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [Funnel-Transformer: Filtering out Sequential Redundancy for Efficient Language Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03236) by Zihang Dai, Guokun Lai, Yiming Yang, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[GLPN](model_doc/glpn)** (from KAIST) released with the paper [Global-Local Path Networks for Monocular Depth Estimation with Vertical CutDepth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.07436) by Doyeon Kim, Woonghyun Ga, Pyungwhan Ahn, Donggyu Joo, Sehwan Chun, Junmo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[GPT](model_doc/openai-gpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training](https://blog.openai.com/language-unsupervised/) by Alec Radford, Karthik Narasimhan, Tim Salimans and Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[GPT Neo](model_doc/gpt_neo)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [EleutherAI/gpt-neo](https://github.com/EleutherAI/gpt-neo) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Leo Gao, Phil Wang and Connor Leahy.
|
||||
1. **[GPT NeoX](model_doc/gpt_neox)** (from EleutherAI) released with the paper [GPT-NeoX-20B: An Open-Source Autoregressive Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06745) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Eric Hallahan, Quentin Anthony, Leo Gao, Laurence Golding, Horace He, Connor Leahy, Kyle McDonell, Jason Phang, Michael Pieler, USVSN Sai Prashanth, Shivanshu Purohit, Laria Reynolds, Jonathan Tow, Ben Wang, Samuel Weinbach
|
||||
1. **[GPT-2](model_doc/gpt2)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners](https://blog.openai.com/better-language-models/) by Alec Radford*, Jeffrey Wu*, Rewon Child, David Luan, Dario Amodei** and Ilya Sutskever**.
|
||||
1. **[GPT-J](model_doc/gptj)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax](https://github.com/kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax/) by Ben Wang and Aran Komatsuzaki.
|
||||
1. **[GPTSAN-japanese](model_doc/gptsan-japanese)** released in the repository [tanreinama/GPTSAN](https://github.com/tanreinama/GPTSAN/blob/main/report/model.md) by Toshiyuki Sakamoto(tanreinama).
|
||||
1. **[GroupViT](model_doc/groupvit)** (from UCSD, NVIDIA) released with the paper [GroupViT: Semantic Segmentation Emerges from Text Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.11094) by Jiarui Xu, Shalini De Mello, Sifei Liu, Wonmin Byeon, Thomas Breuel, Jan Kautz, Xiaolong Wang.
|
||||
1. **[Hubert](model_doc/hubert)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [HuBERT: Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning by Masked Prediction of Hidden Units](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.07447) by Wei-Ning Hsu, Benjamin Bolte, Yao-Hung Hubert Tsai, Kushal Lakhotia, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Abdelrahman Mohamed.
|
||||
1. **[I-BERT](model_doc/ibert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [I-BERT: Integer-only BERT Quantization](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.01321) by Sehoon Kim, Amir Gholami, Zhewei Yao, Michael W. Mahoney, Kurt Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[ImageGPT](model_doc/imagegpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Generative Pretraining from Pixels](https://openai.com/blog/image-gpt/) by Mark Chen, Alec Radford, Rewon Child, Jeffrey Wu, Heewoo Jun, David Luan, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLM](model_doc/layoutlm)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLM: Pre-training of Text and Layout for Document Image Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.13318) by Yiheng Xu, Minghao Li, Lei Cui, Shaohan Huang, Furu Wei, Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv2](model_doc/layoutlmv2)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv2: Multi-modal Pre-training for Visually-Rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.14740) by Yang Xu, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Furu Wei, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Wanxiang Che, Min Zhang, Lidong Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv3](model_doc/layoutlmv3)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv3: Pre-training for Document AI with Unified Text and Image Masking](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.08387) by Yupan Huang, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yutong Lu, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutXLM](model_doc/layoutxlm)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutXLM: Multimodal Pre-training for Multilingual Visually-rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.08836) by Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LED](model_doc/led)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LeViT](model_doc/levit)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [LeViT: A Vision Transformer in ConvNet's Clothing for Faster Inference](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01136) by Ben Graham, Alaaeldin El-Nouby, Hugo Touvron, Pierre Stock, Armand Joulin, Hervé Jégou, Matthijs Douze.
|
||||
1. **[Longformer](model_doc/longformer)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LongT5](model_doc/longt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [LongT5: Efficient Text-To-Text Transformer for Long Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.07916) by Mandy Guo, Joshua Ainslie, David Uthus, Santiago Ontanon, Jianmo Ni, Yun-Hsuan Sung, Yinfei Yang.
|
||||
1. **[LUKE](model_doc/luke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [LUKE: Deep Contextualized Entity Representations with Entity-aware Self-attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.01057) by Ikuya Yamada, Akari Asai, Hiroyuki Shindo, Hideaki Takeda, Yuji Matsumoto.
|
||||
1. **[LXMERT](model_doc/lxmert)** (from UNC Chapel Hill) released with the paper [LXMERT: Learning Cross-Modality Encoder Representations from Transformers for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.07490) by Hao Tan and Mohit Bansal.
|
||||
1. **[M-CTC-T](model_doc/mctct)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Pseudo-Labeling For Massively Multilingual Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.00161) by Loren Lugosch, Tatiana Likhomanenko, Gabriel Synnaeve, and Ronan Collobert.
|
||||
1. **[M2M100](model_doc/m2m_100)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Beyond English-Centric Multilingual Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11125) by Angela Fan, Shruti Bhosale, Holger Schwenk, Zhiyi Ma, Ahmed El-Kishky, Siddharth Goyal, Mandeep Baines, Onur Celebi, Guillaume Wenzek, Vishrav Chaudhary, Naman Goyal, Tom Birch, Vitaliy Liptchinsky, Sergey Edunov, Edouard Grave, Michael Auli, Armand Joulin.
|
||||
1. **[MarianMT](model_doc/marian)** Machine translation models trained using [OPUS](http://opus.nlpl.eu/) data by Jörg Tiedemann. The [Marian Framework](https://marian-nmt.github.io/) is being developed by the Microsoft Translator Team.
|
||||
1. **[Mask2Former](model_doc/mask2former)** (from FAIR and UIUC) released with the paper [Masked-attention Mask Transformer for Universal Image Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.01527) by Bowen Cheng, Ishan Misra, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov, Rohit Girdhar.
|
||||
1. **[MaskFormer](model_doc/maskformer)** (from Meta and UIUC) released with the paper [Per-Pixel Classification is Not All You Need for Semantic Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.06278) by Bowen Cheng, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov.
|
||||
1. **[mBART](model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08210) by Yinhan Liu, Jiatao Gu, Naman Goyal, Xian Li, Sergey Edunov, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[mBART-50](model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Translation with Extensible Multilingual Pretraining and Finetuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00401) by Yuqing Tang, Chau Tran, Xian Li, Peng-Jen Chen, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Jiatao Gu, Angela Fan.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-BERT](model_doc/megatron-bert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-GPT2](model_doc/megatron_gpt2)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[mLUKE](model_doc/mluke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [mLUKE: The Power of Entity Representations in Multilingual Pretrained Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.08151) by Ryokan Ri, Ikuya Yamada, and Yoshimasa Tsuruoka.
|
||||
1. **[MobileBERT](model_doc/mobilebert)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [MobileBERT: a Compact Task-Agnostic BERT for Resource-Limited Devices](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02984) by Zhiqing Sun, Hongkun Yu, Xiaodan Song, Renjie Liu, Yiming Yang, and Denny Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[MobileViT](model_doc/mobilevit)** (from Apple) released with the paper [MobileViT: Light-weight, General-purpose, and Mobile-friendly Vision Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.02178) by Sachin Mehta and Mohammad Rastegari.
|
||||
1. **[MPNet](model_doc/mpnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [MPNet: Masked and Permuted Pre-training for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09297) by Kaitao Song, Xu Tan, Tao Qin, Jianfeng Lu, Tie-Yan Liu.
|
||||
1. **[MT5](model_doc/mt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [mT5: A massively multilingual pre-trained text-to-text transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11934) by Linting Xue, Noah Constant, Adam Roberts, Mihir Kale, Rami Al-Rfou, Aditya Siddhant, Aditya Barua, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[MVP](model_doc/mvp)** (from RUC AI Box) released with the paper [MVP: Multi-task Supervised Pre-training for Natural Language Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.12131) by Tianyi Tang, Junyi Li, Wayne Xin Zhao and Ji-Rong Wen.
|
||||
1. **[Nezha](model_doc/nezha)** (from Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab) released with the paper [NEZHA: Neural Contextualized Representation for Chinese Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.00204) by Junqiu Wei, Xiaozhe Ren, Xiaoguang Li, Wenyong Huang, Yi Liao, Yasheng Wang, Jiashu Lin, Xin Jiang, Xiao Chen and Qun Liu.
|
||||
1. **[NLLB](model_doc/nllb)** (from Meta) released with the paper [No Language Left Behind: Scaling Human-Centered Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.04672) by the NLLB team.
|
||||
1. **[Nyströmformer](model_doc/nystromformer)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [Nyströmformer: A Nyström-Based Algorithm for Approximating Self-Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03902) by Yunyang Xiong, Zhanpeng Zeng, Rudrasis Chakraborty, Mingxing Tan, Glenn Fung, Yin Li, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
1. **[OneFormer](model_doc/oneformer)** (from SHI Labs) released with the paper [OneFormer: One Transformer to Rule Universal Image Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06220) by Jitesh Jain, Jiachen Li, MangTik Chiu, Ali Hassani, Nikita Orlov, Humphrey Shi.
|
||||
1. **[OPT](master/model_doc/opt)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [OPT: Open Pre-trained Transformer Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.01068) by Susan Zhang, Stephen Roller, Naman Goyal, Mikel Artetxe, Moya Chen, Shuohui Chen et al.
|
||||
1. **[OWL-ViT](model_doc/owlvit)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Simple Open-Vocabulary Object Detection with Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.06230) by Matthias Minderer, Alexey Gritsenko, Austin Stone, Maxim Neumann, Dirk Weissenborn, Alexey Dosovitskiy, Aravindh Mahendran, Anurag Arnab, Mostafa Dehghani, Zhuoran Shen, Xiao Wang, Xiaohua Zhai, Thomas Kipf, and Neil Houlsby.
|
||||
1. **[Pegasus](model_doc/pegasus)** (from Google) released with the paper [PEGASUS: Pre-training with Extracted Gap-sentences for Abstractive Summarization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.08777) by Jingqing Zhang, Yao Zhao, Mohammad Saleh and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[Perceiver IO](model_doc/perceiver)** (from Deepmind) released with the paper [Perceiver IO: A General Architecture for Structured Inputs & Outputs](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.14795) by Andrew Jaegle, Sebastian Borgeaud, Jean-Baptiste Alayrac, Carl Doersch, Catalin Ionescu, David Ding, Skanda Koppula, Daniel Zoran, Andrew Brock, Evan Shelhamer, Olivier Hénaff, Matthew M. Botvinick, Andrew Zisserman, Oriol Vinyals, João Carreira.
|
||||
1. **[PhoBERT](model_doc/phobert)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [PhoBERT: Pre-trained language models for Vietnamese](https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.findings-emnlp.92/) by Dat Quoc Nguyen and Anh Tuan Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[PLBart](model_doc/plbart)** (from UCLA NLP) released with the paper [Unified Pre-training for Program Understanding and Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06333) by Wasi Uddin Ahmad, Saikat Chakraborty, Baishakhi Ray, Kai-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[PoolFormer](model_doc/poolformer)** (from Sea AI Labs) released with the paper [MetaFormer is Actually What You Need for Vision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.11418) by Yu, Weihao and Luo, Mi and Zhou, Pan and Si, Chenyang and Zhou, Yichen and Wang, Xinchao and Feng, Jiashi and Yan, Shuicheng.
|
||||
1. **[ProphetNet](model_doc/prophetnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [ProphetNet: Predicting Future N-gram for Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04063) by Yu Yan, Weizhen Qi, Yeyun Gong, Dayiheng Liu, Nan Duan, Jiusheng Chen, Ruofei Zhang and Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[QDQBert](model_doc/qdqbert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Integer Quantization for Deep Learning Inference: Principles and Empirical Evaluation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09602) by Hao Wu, Patrick Judd, Xiaojie Zhang, Mikhail Isaev and Paulius Micikevicius.
|
||||
1. **[RAG](model_doc/rag)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11401) by Patrick Lewis, Ethan Perez, Aleksandara Piktus, Fabio Petroni, Vladimir Karpukhin, Naman Goyal, Heinrich Küttler, Mike Lewis, Wen-tau Yih, Tim Rocktäschel, Sebastian Riedel, Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[REALM](model_doc/realm.html)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [REALM: Retrieval-Augmented Language Model Pre-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.08909) by Kelvin Guu, Kenton Lee, Zora Tung, Panupong Pasupat and Ming-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[Reformer](model_doc/reformer)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Reformer: The Efficient Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04451) by Nikita Kitaev, Łukasz Kaiser, Anselm Levskaya.
|
||||
1. **[RegNet](model_doc/regnet)** (from META Platforms) released with the paper [Designing Network Design Space](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.13678) by Ilija Radosavovic, Raj Prateek Kosaraju, Ross Girshick, Kaiming He, Piotr Dollár.
|
||||
1. **[RemBERT](model_doc/rembert)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Rethinking embedding coupling in pre-trained language models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.12821) by Hyung Won Chung, Thibault Févry, Henry Tsai, M. Johnson, Sebastian Ruder.
|
||||
1. **[ResNet](model_doc/resnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385) by Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun.
|
||||
1. **[RoBERTa](model_doc/roberta)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692) by Yinhan Liu, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Mandar Joshi, Danqi Chen, Omer Levy, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer, Veselin Stoyanov.
|
||||
1. **[RoFormer](model_doc/roformer)** (from ZhuiyiTechnology), released together with the paper [RoFormer: Enhanced Transformer with Rotary Position Embedding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.09864) by Jianlin Su and Yu Lu and Shengfeng Pan and Bo Wen and Yunfeng Liu.
|
||||
1. **[SegFormer](model_doc/segformer)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [SegFormer: Simple and Efficient Design for Semantic Segmentation with Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.15203) by Enze Xie, Wenhai Wang, Zhiding Yu, Anima Anandkumar, Jose M. Alvarez, Ping Luo.
|
||||
1. **[SEW](model_doc/sew)** (from ASAPP) released with the paper [Performance-Efficiency Trade-offs in Unsupervised Pre-training for Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.06870) by Felix Wu, Kwangyoun Kim, Jing Pan, Kyu Han, Kilian Q. Weinberger, Yoav Artzi.
|
||||
1. **[SEW-D](model_doc/sew_d)** (from ASAPP) released with the paper [Performance-Efficiency Trade-offs in Unsupervised Pre-training for Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.06870) by Felix Wu, Kwangyoun Kim, Jing Pan, Kyu Han, Kilian Q. Weinberger, Yoav Artzi.
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer](model_doc/speech_to_text)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [fairseq S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with fairseq](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer2](model_doc/speech_to_text_2)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [Large-Scale Self- and Semi-Supervised Learning for Speech Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.06678) by Changhan Wang, Anne Wu, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli, Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[Splinter](model_doc/splinter)** (from Tel Aviv University), released together with the paper [Few-Shot Question Answering by Pretraining Span Selection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.00438) by Ori Ram, Yuval Kirstain, Jonathan Berant, Amir Globerson, Omer Levy.
|
||||
1. **[SqueezeBERT](model_doc/squeezebert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [SqueezeBERT: What can computer vision teach NLP about efficient neural networks?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11316) by Forrest N. Iandola, Albert E. Shaw, Ravi Krishna, and Kurt W. Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[Swin Transformer](model_doc/swin)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14030) by Ze Liu, Yutong Lin, Yue Cao, Han Hu, Yixuan Wei, Zheng Zhang, Stephen Lin, Baining Guo.
|
||||
1. **[Swin Transformer V2](model_doc/swinv2)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [Swin Transformer V2: Scaling Up Capacity and Resolution](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09883) by Ze Liu, Han Hu, Yutong Lin, Zhuliang Yao, Zhenda Xie, Yixuan Wei, Jia Ning, Yue Cao, Zheng Zhang, Li Dong, Furu Wei, Baining Guo.
|
||||
1. **[T5](model_doc/t5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10683) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[T5v1.1](model_doc/t5v1.1)** (from Google AI) released in the repository [google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer](https://github.com/google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer/blob/main/released_checkpoints.md#t511) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[TAPAS](model_doc/tapas)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [TAPAS: Weakly Supervised Table Parsing via Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02349) by Jonathan Herzig, Paweł Krzysztof Nowak, Thomas Müller, Francesco Piccinno and Julian Martin Eisenschlos.
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](model_doc/tapex)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou.
|
||||
1. **[Trajectory Transformer](model_doc/trajectory_transformers)** (from the University of California at Berkeley) released with the paper [Offline Reinforcement Learning as One Big Sequence Modeling Problem](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.02039) by Michael Janner, Qiyang Li, Sergey Levine
|
||||
1. **[Transformer-XL](model_doc/transfo-xl)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860) by Zihang Dai*, Zhilin Yang*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Quoc V. Le, Ruslan Salakhutdinov.
|
||||
1. **[TrOCR](model_doc/trocr)** (from Microsoft), released together with the paper [TrOCR: Transformer-based Optical Character Recognition with Pre-trained Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.10282) by Minghao Li, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Zhoujun Li, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[UL2](model_doc/ul2)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Unifying Language Learning Paradigms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.05131v1) by Yi Tay, Mostafa Dehghani, Vinh Q. Tran, Xavier Garcia, Dara Bahri, Tal Schuster, Huaixiu Steven Zheng, Neil Houlsby, Donald Metzler
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeech](model_doc/unispeech)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.07597) by Chengyi Wang, Yu Wu, Yao Qian, Kenichi Kumatani, Shujie Liu, Furu Wei, Michael Zeng, Xuedong Huang.
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeechSat](model_doc/unispeech-sat)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UNISPEECH-SAT: UNIVERSAL SPEECH REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH SPEAKER AWARE PRE-TRAINING](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.05752) by Sanyuan Chen, Yu Wu, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Zhuo Chen, Shujie Liu, Jian Wu, Yao Qian, Furu Wei, Jinyu Li, Xiangzhan Yu.
|
||||
1. **[VAN](model_doc/van)** (from Tsinghua University and Nankai University) released with the paper [Visual Attention Network](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.09741) by Meng-Hao Guo, Cheng-Ze Lu, Zheng-Ning Liu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Shi-Min Hu.
|
||||
1. **[VideoMAE](model_doc/videomae)** (from Multimedia Computing Group, Nanjing University) released with the paper [VideoMAE: Masked Autoencoders are Data-Efficient Learners for Self-Supervised Video Pre-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.12602) by Zhan Tong, Yibing Song, Jue Wang, Limin Wang.
|
||||
1. **[ViLT](model_doc/vilt)** (from NAVER AI Lab/Kakao Enterprise/Kakao Brain) released with the paper [ViLT: Vision-and-Language Transformer Without Convolution or Region Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03334) by Wonjae Kim, Bokyung Son, Ildoo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[Vision Transformer (ViT)](model_doc/vit)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929) by Alexey Dosovitskiy, Lucas Beyer, Alexander Kolesnikov, Dirk Weissenborn, Xiaohua Zhai, Thomas Unterthiner, Mostafa Dehghani, Matthias Minderer, Georg Heigold, Sylvain Gelly, Jakob Uszkoreit, Neil Houlsby.
|
||||
1. **[VisualBERT](model_doc/visual_bert)** (from UCLA NLP) released with the paper [VisualBERT: A Simple and Performant Baseline for Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.03557) by Liunian Harold Li, Mark Yatskar, Da Yin, Cho-Jui Hsieh, Kai-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[ViTMAE](model_doc/vit_mae)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.06377) by Kaiming He, Xinlei Chen, Saining Xie, Yanghao Li, Piotr Dollár, Ross Girshick.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2](model_doc/wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [wav2vec 2.0: A Framework for Self-Supervised Learning of Speech Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11477) by Alexei Baevski, Henry Zhou, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2-Conformer](model_doc/wav2vec2-conformer)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FAIRSEQ S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with FAIRSEQ](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Sravya Popuri, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2Phoneme](model_doc/wav2vec2_phoneme)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Simple and Effective Zero-shot Cross-lingual Phoneme Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.11680) by Qiantong Xu, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[WavLM](model_doc/wavlm)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [WavLM: Large-Scale Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Full Stack Speech Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.13900) by Sanyuan Chen, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Yu Wu, Shujie Liu, Zhuo Chen, Jinyu Li, Naoyuki Kanda, Takuya Yoshioka, Xiong Xiao, Jian Wu, Long Zhou, Shuo Ren, Yanmin Qian, Yao Qian, Jian Wu, Michael Zeng, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[XGLM](model_doc/xglm)** (From Facebook AI) released with the paper [Few-shot Learning with Multilingual Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10668) by Xi Victoria Lin, Todor Mihaylov, Mikel Artetxe, Tianlu Wang, Shuohui Chen, Daniel Simig, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Shruti Bhosale, Jingfei Du, Ramakanth Pasunuru, Sam Shleifer, Punit Singh Koura, Vishrav Chaudhary, Brian O'Horo, Jeff Wang, Luke Zettlemoyer, Zornitsa Kozareva, Mona Diab, Veselin Stoyanov, Xian Li.
|
||||
1. **[XLM](model_doc/xlm)** (from Facebook) released together with the paper [Cross-lingual Language Model Pretraining](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.07291) by Guillaume Lample and Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-ProphetNet](model_doc/xlm-prophetnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [ProphetNet: Predicting Future N-gram for Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04063) by Yu Yan, Weizhen Qi, Yeyun Gong, Dayiheng Liu, Nan Duan, Jiusheng Chen, Ruofei Zhang and Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-RoBERTa](model_doc/xlm-roberta)** (from Facebook AI), released together with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-lingual Representation Learning at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.02116) by Alexis Conneau*, Kartikay Khandelwal*, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Guillaume Wenzek, Francisco Guzmán, Edouard Grave, Myle Ott, Luke Zettlemoyer and Veselin Stoyanov.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-RoBERTa-XL](model_doc/xlm-roberta-xl)** (from Facebook AI), released together with the paper [Larger-Scale Transformers for Multilingual Masked Language Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.00572) by Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Myle Ott, Giri Anantharaman, Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-V](model_doc/xlm-v)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [XLM-V: Overcoming the Vocabulary Bottleneck in Multilingual Masked Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.10472) by Davis Liang, Hila Gonen, Yuning Mao, Rui Hou, Naman Goyal, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Luke Zettlemoyer, Madian Khabsa.
|
||||
1. **[XLNet](model_doc/xlnet)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [XLNet: Generalized Autoregressive Pretraining for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.08237) by Zhilin Yang*, Zihang Dai*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[XLS-R](model_doc/xls_r)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [XLS-R: Self-supervised Cross-lingual Speech Representation Learning at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09296) by Arun Babu, Changhan Wang, Andros Tjandra, Kushal Lakhotia, Qiantong Xu, Naman Goyal, Kritika Singh, Patrick von Platen, Yatharth Saraf, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Alexis Conneau, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[XLSR-Wav2Vec2](model_doc/xlsr_wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-Lingual Representation Learning For Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.13979) by Alexis Conneau, Alexei Baevski, Ronan Collobert, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[YOLOS](model_doc/yolos)** (from Huazhong University of Science & Technology) released with the paper [You Only Look at One Sequence: Rethinking Transformer in Vision through Object Detection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00666) by Yuxin Fang, Bencheng Liao, Xinggang Wang, Jiemin Fang, Jiyang Qi, Rui Wu, Jianwei Niu, Wenyu Liu.
|
||||
1. **[YOSO](model_doc/yoso)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [You Only Sample (Almost) Once: Linear Cost Self-Attention Via Bernoulli Sampling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09714) by Zhanpeng Zeng, Yunyang Xiong, Sathya N. Ravi, Shailesh Acharya, Glenn Fung, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Unterstützte Frameworks
|
||||
|
||||
Die folgende Tabelle zeigt die derzeitige Unterstützung in der Bibliothek für jedes dieser Modelle, unabhängig davon, ob sie einen Python
|
||||
Tokenizer haben (als "langsam" bezeichnet), ein "schneller" Tokenizer, der von der 🤗 Tokenizers Bibliothek unterstützt wird, ob sie Unterstützung in Jax (via
|
||||
Flax), PyTorch, und/oder TensorFlow haben.
|
||||
|
||||
<!--This table is updated automatically from the auto modules with _make fix-copies_. Do not update manually!-->
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Tokenizer slow | Tokenizer fast | PyTorch support | TensorFlow support | Flax Support |
|
||||
|:---------------------------:|:--------------:|:--------------:|:---------------:|:------------------:|:------------:|
|
||||
| ALBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BART | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BEiT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Bert Generation | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BigBird | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BigBird-Pegasus | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Blenderbot | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BlenderbotSmall | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BLOOM | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CamemBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CANINE | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CLIP | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| CodeGen | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ConvBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ConvNeXT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CTRL | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CvT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Data2VecAudio | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Data2VecText | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Data2VecVision | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeBERTa-v2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Decision Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeiT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DETR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DistilBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| DPR | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ELECTRA | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Encoder decoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| FairSeq Machine-Translation | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FlauBERT | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FLAVA | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FNet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Funnel Transformer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GLPN | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GPT Neo | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GPT NeoX | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GPT-J | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GroupViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Hubert | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| I-BERT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ImageGPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LayoutLM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LayoutLMv2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LayoutLMv3 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LED | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LeViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Longformer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LongT5 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| LUKE | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LXMERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| M-CTC-T | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| M2M100 | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Marian | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| MaskFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| mBART | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Megatron-BERT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MPNet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MT5 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| MVP | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Nezha | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Nyströmformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| OpenAI GPT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| OpenAI GPT-2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| OPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| OWL-ViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Pegasus | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Perceiver | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| PLBart | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| PoolFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ProphetNet | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| QDQBert | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RAG | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| REALM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Reformer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RegNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RemBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ResNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RetriBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RoBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RoFormer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| SegFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SEW | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SEW-D | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Speech Encoder decoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Speech2Text | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Speech2Text2 | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Splinter | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SqueezeBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Swin Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Swin Transformer V2 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| T5 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| TAPAS | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Trajectory Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Transformer-XL | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TrOCR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| UniSpeech | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| UniSpeechSat | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| VAN | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| VideoMAE | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ViLT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Vision Encoder decoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| VisionTextDualEncoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| VisualBERT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| ViTMAE | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Wav2Vec2 | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Wav2Vec2-Conformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| WavLM | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XGLM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| XLM | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLM-ProphetNet | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLM-RoBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| XLM-RoBERTa-XL | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLNet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| YOLOS | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| YOSO | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- End table-->
|
||||
250
docs/source/de/installation.md
Normal file
250
docs/source/de/installation.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,250 @@
|
||||
<!---
|
||||
Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Installieren Sie 🤗 Transformers für die Deep-Learning-Bibliothek, mit der Sie arbeiten, richten Sie Ihren Cache ein und konfigurieren Sie 🤗 Transformers optional für den Offline-Betrieb.
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers wurde unter Python 3.6+, PyTorch 1.1.0+, TensorFlow 2.0+, und Flax getestet. Folgen Sie den Installationsanweisungen unten für die von Ihnen verwendete Deep-Learning-Bibliothek:
|
||||
|
||||
* [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/) installation instructions.
|
||||
* [TensorFlow 2.0](https://www.tensorflow.org/install/pip) installation instructions.
|
||||
* [Flax](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) installation instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation mit pip
|
||||
|
||||
Sie sollten 🤗 Transformers in einer [virtuellen Umgebung](https://docs.python.org/3/library/venv.html) installieren. Wenn Sie mit virtuellen Python-Umgebungen nicht vertraut sind, werfen Sie einen Blick auf diese [Anleitung](https://packaging.python.org/guides/installing-using-pip-and-virtual-environments/). Eine virtuelle Umgebung macht es einfacher, verschiedene Projekte zu verwalten und Kompatibilitätsprobleme zwischen Abhängigkeiten zu vermeiden.
|
||||
|
||||
Beginnen wir mit der Erstellung einer virtuellen Umgebung in Ihrem Projektverzeichnis:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m venv .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Aktivieren wir die virtuelle Umgebung. Unter Linux und MacOs:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
source .env/bin/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
Aktivieren wir die virtuelle Umgebung unter Windows
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
.env/Scripts/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Jetzt können wir die 🤗 Transformers mit dem folgenden Befehl installieren:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Bei reiner CPU-Unterstützung können wir 🤗 Transformers und eine Deep-Learning-Bibliothek bequem in einer Zeile installieren. Installieren wir zum Beispiel 🤗 Transformers und PyTorch mit:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers[torch]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers und TensorFlow 2.0:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers[tf-cpu]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers und Flax:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers[flax]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Überprüfen wir abschließend, ob 🤗 Transformers ordnungsgemäß installiert wurde, indem wir den folgenden Befehl ausführen. Es wird ein vortrainiertes Modell heruntergeladen:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -c "from transformers import pipeline; print(pipeline('sentiment-analysis')('we love you'))"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dann wird die Kategorie und die Wahrscheinlichkeit ausgegeben:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
[{'label': 'POSITIVE', 'score': 0.9998704791069031}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation aus dem Code
|
||||
|
||||
Installieren wir 🤗 Transformers aus dem Quellcode mit dem folgenden Befehl:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dieser Befehl installiert die aktuelle `main` Version und nicht die neueste `stable` Version. Die `main`-Version ist nützlich, um mit den neuesten Entwicklungen Schritt zu halten. Zum Beispiel, wenn ein Fehler seit der letzten offiziellen Version behoben wurde, aber eine neue Version noch nicht veröffentlicht wurde. Das bedeutet jedoch, dass die "Hauptversion" nicht immer stabil ist. Wir bemühen uns, die Hauptversion einsatzbereit zu halten, und die meisten Probleme werden normalerweise innerhalb weniger Stunden oder eines Tages behoben. Wenn Sie auf ein Problem stoßen, öffnen Sie bitte ein [Issue] (https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues), damit wir es noch schneller beheben können!
|
||||
|
||||
Überprüfen wir, ob 🤗 Transformers richtig installiert wurde, indem Sie den folgenden Befehl ausführen:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -c "from transformers import pipeline; print(pipeline('sentiment-analysis')('I love you'))"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Editierbare Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Sie benötigen eine bearbeitbare Installation, wenn Sie:
|
||||
|
||||
* die "Haupt"-Version des Quellcodes verwenden möchten.
|
||||
* Zu 🤗 Transformers beitragen und Änderungen am Code testen wollen.
|
||||
|
||||
Klonen Sie das Repository und installieren 🤗 Transformers mit den folgenden Befehlen:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
|
||||
cd transformers
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Diese Befehle verknüpfen den Ordner, in den Sie das Repository geklont haben, mit den Pfaden Ihrer Python-Bibliotheken. Python wird nun in dem Ordner suchen, in den Sie geklont haben, zusätzlich zu den normalen Bibliothekspfaden. Wenn zum Beispiel Ihre Python-Pakete normalerweise in `~/anaconda3/envs/main/lib/python3.7/site-packages/` installiert sind, wird Python auch den Ordner durchsuchen, in den Sie geklont haben: `~/transformers/`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Sie müssen den Ordner `transformers` behalten, wenn Sie die Bibliothek weiter verwenden wollen.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Jetzt können Sie Ihren Klon mit dem folgenden Befehl ganz einfach auf die neueste Version von 🤗 Transformers aktualisieren:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ~/transformers/
|
||||
git pull
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Ihre Python-Umgebung wird beim nächsten Ausführen die `main`-Version von 🤗 Transformers finden.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation mit conda
|
||||
|
||||
Installation von dem conda Kanal `huggingface`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Cache Einrichtung
|
||||
|
||||
Vorgefertigte Modelle werden heruntergeladen und lokal zwischengespeichert unter: `~/.cache/huggingface/hub`. Dies ist das Standardverzeichnis, das durch die Shell-Umgebungsvariable "TRANSFORMERS_CACHE" vorgegeben ist. Unter Windows wird das Standardverzeichnis durch `C:\Benutzer\Benutzername\.cache\huggingface\hub` angegeben. Sie können die unten aufgeführten Shell-Umgebungsvariablen - in der Reihenfolge ihrer Priorität - ändern, um ein anderes Cache-Verzeichnis anzugeben:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Shell-Umgebungsvariable (Standard): `HUGGINGFACE_HUB_CACHE` oder `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
2. Shell-Umgebungsvariable: `HF_HOME`.
|
||||
3. Shell-Umgebungsvariable: `XDG_CACHE_HOME` + `/huggingface`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers verwendet die Shell-Umgebungsvariablen `PYTORCH_TRANSFORMERS_CACHE` oder `PYTORCH_PRETRAINED_BERT_CACHE`, wenn Sie von einer früheren Iteration dieser Bibliothek kommen und diese Umgebungsvariablen gesetzt haben, sofern Sie nicht die Shell-Umgebungsvariable `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE` angeben.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Offline Modus
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers ist in der Lage, in einer Firewall- oder Offline-Umgebung zu laufen, indem es nur lokale Dateien verwendet. Setzen Sie die Umgebungsvariable `TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE=1`, um dieses Verhalten zu aktivieren.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Fügen sie [🤗 Datasets](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/) zu Ihrem Offline-Trainingsworkflow hinzufügen, indem Sie die Umgebungsvariable `HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE=1` setzen.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
So würden Sie beispielsweise ein Programm in einem normalen Netzwerk mit einer Firewall für externe Instanzen mit dem folgenden Befehl ausführen:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py --model_name_or_path t5-small --dataset_name wmt16 --dataset_config ro-en ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Führen Sie das gleiche Programm in einer Offline-Instanz mit aus:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE=1 TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE=1 \
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py --model_name_or_path t5-small --dataset_name wmt16 --dataset_config ro-en ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Das Skript sollte nun laufen, ohne sich aufzuhängen oder eine Zeitüberschreitung abzuwarten, da es weiß, dass es nur nach lokalen Dateien suchen soll.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Abrufen von Modellen und Tokenizern zur Offline-Verwendung
|
||||
|
||||
Eine andere Möglichkeit, 🤗 Transformers offline zu verwenden, besteht darin, die Dateien im Voraus herunterzuladen und dann auf ihren lokalen Pfad zu verweisen, wenn Sie sie offline verwenden müssen. Es gibt drei Möglichkeiten, dies zu tun:
|
||||
|
||||
* Laden Sie eine Datei über die Benutzeroberfläche des [Model Hub](https://huggingface.co/models) herunter, indem Sie auf das ↓-Symbol klicken.
|
||||
|
||||
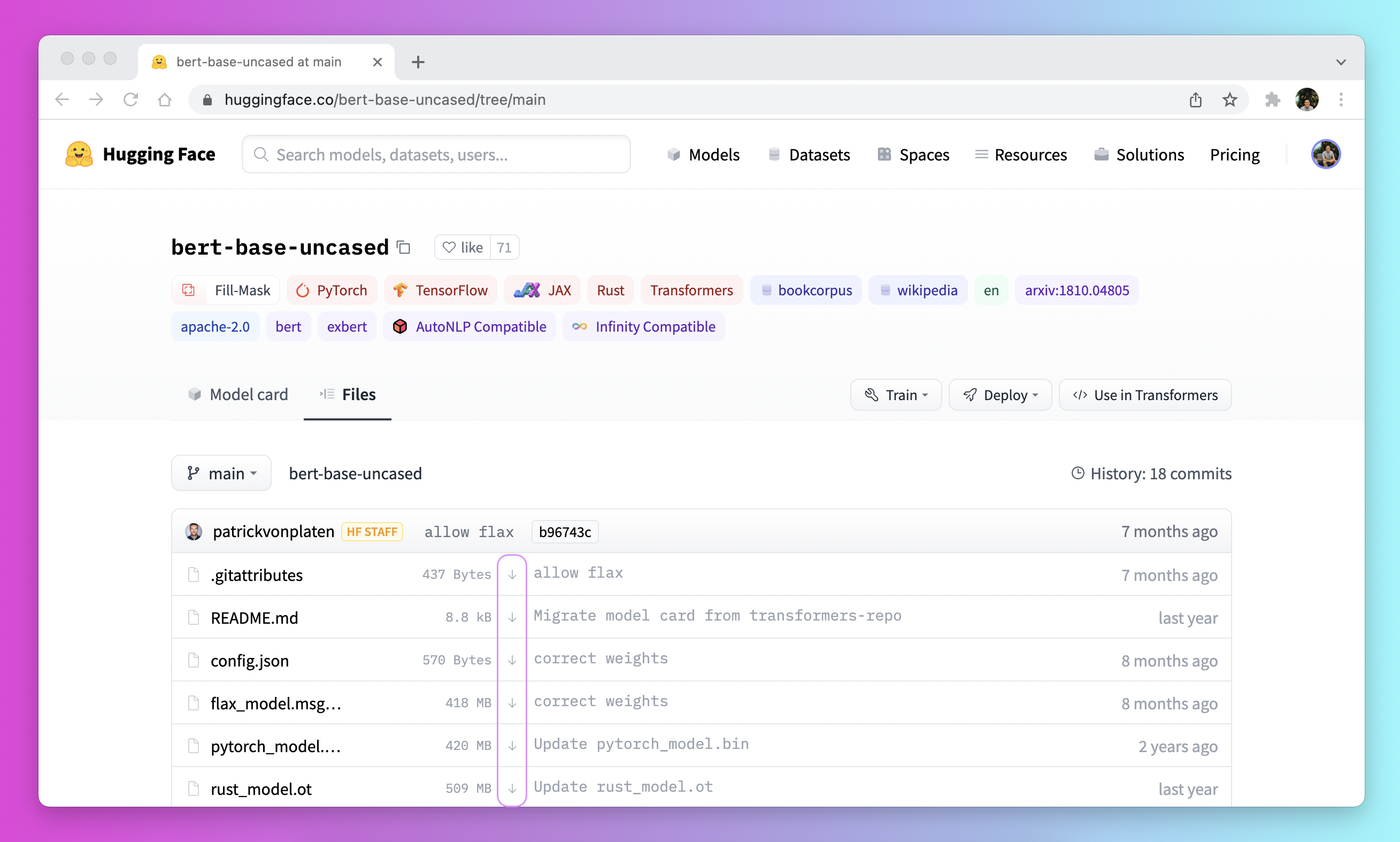
|
||||
|
||||
* Verwenden Sie den [PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained] und [PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained] Workflow:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Laden Sie Ihre Dateien im Voraus mit [`PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] herunter:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0_3B")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0_3B")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Speichern Sie Ihre Dateien in einem bestimmten Verzeichnis mit [`PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.save_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
>>> model.save_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Wenn Sie nun offline sind, laden Sie Ihre Dateien mit [`PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] aus dem bestimmten Verzeichnis:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Programmatisches Herunterladen von Dateien mit der [huggingface_hub](https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface_hub/tree/main/src/huggingface_hub) Bibliothek:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Installieren Sie die "huggingface_hub"-Bibliothek in Ihrer virtuellen Umgebung:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m pip install huggingface_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Verwenden Sie die Funktion [`hf_hub_download`](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/adding-a-library#download-files-from-the-hub), um eine Datei in einen bestimmten Pfad herunterzuladen. Der folgende Befehl lädt zum Beispiel die Datei "config.json" aus dem Modell [T0](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/T0_3B) in den gewünschten Pfad herunter:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
|
||||
|
||||
>>> hf_hub_download(repo_id="bigscience/T0_3B", filename="config.json", cache_dir="./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sobald Ihre Datei heruntergeladen und lokal zwischengespeichert ist, geben Sie den lokalen Pfad an, um sie zu laden und zu verwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0/config.json")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Informationen zum Herunterladen von Dateien, die auf dem Hub gespeichert sind, finden Sie im Abschnitt [Wie man Dateien vom Hub herunterlädt] (https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/how-to-downstream).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
@ -1,246 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!---
|
||||
Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Installieren Sie 🤗 Transformers für die Deep-Learning-Bibliothek, mit der Sie arbeiten, richten Sie Ihren Cache ein und konfigurieren Sie 🤗 Transformers optional für den Offline-Betrieb.
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers wurde unter Python 3.6+, PyTorch 1.1.0+, TensorFlow 2.0+, und Flax getestet. Folgen Sie den Installationsanweisungen unten für die von Ihnen verwendete Deep-Learning-Bibliothek:
|
||||
|
||||
* [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/) installation instructions.
|
||||
* [TensorFlow 2.0](https://www.tensorflow.org/install/pip) installation instructions.
|
||||
* [Flax](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) installation instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation mit pip
|
||||
|
||||
Sie sollten 🤗 Transformers in einer [virtuellen Umgebung](https://docs.python.org/3/library/venv.html) installieren. Wenn Sie mit virtuellen Python-Umgebungen nicht vertraut sind, werfen Sie einen Blick auf diese [Anleitung](https://packaging.python.org/guides/installing-using-pip-and-virtual-environments/). Eine virtuelle Umgebung macht es einfacher, verschiedene Projekte zu verwalten und Kompatibilitätsprobleme zwischen Abhängigkeiten zu vermeiden.
|
||||
|
||||
Beginnen wir mit der Erstellung einer virtuellen Umgebung in Ihrem Projektverzeichnis:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m venv .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Aktivieren wir die virtuelle Umgebung. Unter Linux und MacOs:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
source .env/bin/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
Aktivieren wir die virtuelle Umgebung unter Windows
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
.env/Scripts/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Jetzt können wir die 🤗 Transformers mit dem folgenden Befehl installieren:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Bei reiner CPU-Unterstützung können wir 🤗 Transformers und eine Deep-Learning-Bibliothek bequem in einer Zeile installieren. Installieren wir zum Beispiel 🤗 Transformers und PyTorch mit:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers[torch]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers und TensorFlow 2.0:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers[tf-cpu]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers und Flax:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers[flax]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Überprüfen wir abschließend, ob 🤗 Transformers ordnungsgemäß installiert wurde, indem wir den folgenden Befehl ausführen. Es wird ein vortrainiertes Modell heruntergeladen:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -c "from transformers import pipeline; print(pipeline('sentiment-analysis')('we love you'))"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dann wird die Kategorie und die Wahrscheinlichkeit ausgegeben:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
[{'label': 'POSITIVE', 'score': 0.9998704791069031}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation aus dem Code
|
||||
|
||||
Installieren wir 🤗 Transformers aus dem Quellcode mit dem folgenden Befehl:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dieser Befehl installiert die aktuelle `main` Version und nicht die neueste `stable` Version. Die `main`-Version ist nützlich, um mit den neuesten Entwicklungen Schritt zu halten. Zum Beispiel, wenn ein Fehler seit der letzten offiziellen Version behoben wurde, aber eine neue Version noch nicht veröffentlicht wurde. Das bedeutet jedoch, dass die "Hauptversion" nicht immer stabil ist. Wir bemühen uns, die Hauptversion einsatzbereit zu halten, und die meisten Probleme werden normalerweise innerhalb weniger Stunden oder eines Tages behoben. Wenn Sie auf ein Problem stoßen, öffnen Sie bitte ein [Issue] (https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues), damit wir es noch schneller beheben können!
|
||||
|
||||
Überprüfen wir, ob 🤗 Transformers richtig installiert wurde, indem Sie den folgenden Befehl ausführen:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -c "from transformers import pipeline; print(pipeline('sentiment-analysis')('I love you'))"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Editierbare Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Sie benötigen eine bearbeitbare Installation, wenn Sie:
|
||||
|
||||
* die "Haupt"-Version des Quellcodes verwenden möchten.
|
||||
* Zu 🤗 Transformers beitragen und Änderungen am Code testen wollen.
|
||||
|
||||
Klonen Sie das Repository und installieren 🤗 Transformers mit den folgenden Befehlen:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
|
||||
cd transformers
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Diese Befehle verknüpfen den Ordner, in den Sie das Repository geklont haben, mit den Pfaden Ihrer Python-Bibliotheken. Python wird nun in dem Ordner suchen, in den Sie geklont haben, zusätzlich zu den normalen Bibliothekspfaden. Wenn zum Beispiel Ihre Python-Pakete normalerweise in `~/anaconda3/envs/main/lib/python3.7/site-packages/` installiert sind, wird Python auch den Ordner durchsuchen, in den Sie geklont haben: `~/transformers/`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Sie müssen den Ordner `transformers` behalten, wenn Sie die Bibliothek weiter verwenden wollen.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Jetzt können Sie Ihren Klon mit dem folgenden Befehl ganz einfach auf die neueste Version von 🤗 Transformers aktualisieren:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ~/transformers/
|
||||
git pull
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Ihre Python-Umgebung wird beim nächsten Ausführen die `main`-Version von 🤗 Transformers finden.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation mit conda
|
||||
|
||||
Installation von dem conda Kanal `huggingface`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Cache Einrichtung
|
||||
|
||||
Vorgefertigte Modelle werden heruntergeladen und lokal zwischengespeichert unter: `~/.cache/huggingface/hub`. Dies ist das Standardverzeichnis, das durch die Shell-Umgebungsvariable "TRANSFORMERS_CACHE" vorgegeben ist. Unter Windows wird das Standardverzeichnis durch `C:\Benutzer\Benutzername\.cache\huggingface\hub` angegeben. Sie können die unten aufgeführten Shell-Umgebungsvariablen - in der Reihenfolge ihrer Priorität - ändern, um ein anderes Cache-Verzeichnis anzugeben:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Shell-Umgebungsvariable (Standard): `HUGGINGFACE_HUB_CACHE` oder `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
2. Shell-Umgebungsvariable: `HF_HOME`.
|
||||
3. Shell-Umgebungsvariable: `XDG_CACHE_HOME` + `/huggingface`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers verwendet die Shell-Umgebungsvariablen `PYTORCH_TRANSFORMERS_CACHE` oder `PYTORCH_PRETRAINED_BERT_CACHE`, wenn Sie von einer früheren Iteration dieser Bibliothek kommen und diese Umgebungsvariablen gesetzt haben, sofern Sie nicht die Shell-Umgebungsvariable `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE` angeben.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Offline Modus
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers ist in der Lage, in einer Firewall- oder Offline-Umgebung zu laufen, indem es nur lokale Dateien verwendet. Setzen Sie die Umgebungsvariable `TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE=1`, um dieses Verhalten zu aktivieren.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Fügen sie [🤗 Datasets](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/) zu Ihrem Offline-Trainingsworkflow hinzufügen, indem Sie die Umgebungsvariable `HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE=1` setzen.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
So würden Sie beispielsweise ein Programm in einem normalen Netzwerk mit einer Firewall für externe Instanzen mit dem folgenden Befehl ausführen:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py --model_name_or_path t5-small --dataset_name wmt16 --dataset_config ro-en ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Führen Sie das gleiche Programm in einer Offline-Instanz mit aus:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE=1 TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE=1 \
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py --model_name_or_path t5-small --dataset_name wmt16 --dataset_config ro-en ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Das Skript sollte nun laufen, ohne sich aufzuhängen oder eine Zeitüberschreitung abzuwarten, da es weiß, dass es nur nach lokalen Dateien suchen soll.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Abrufen von Modellen und Tokenizern zur Offline-Verwendung
|
||||
|
||||
Eine andere Möglichkeit, 🤗 Transformers offline zu verwenden, besteht darin, die Dateien im Voraus herunterzuladen und dann auf ihren lokalen Pfad zu verweisen, wenn Sie sie offline verwenden müssen. Es gibt drei Möglichkeiten, dies zu tun:
|
||||
|
||||
* Laden Sie eine Datei über die Benutzeroberfläche des [Model Hub](https://huggingface.co/models) herunter, indem Sie auf das ↓-Symbol klicken.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Verwenden Sie den [PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained] und [PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained] Workflow:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Laden Sie Ihre Dateien im Voraus mit [`PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] herunter:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0_3B")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0_3B")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Speichern Sie Ihre Dateien in einem bestimmten Verzeichnis mit [`PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.save_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
>>> model.save_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Wenn Sie nun offline sind, laden Sie Ihre Dateien mit [`PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] aus dem bestimmten Verzeichnis:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Programmatisches Herunterladen von Dateien mit der [huggingface_hub](https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface_hub/tree/main/src/huggingface_hub) Bibliothek:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Installieren Sie die "huggingface_hub"-Bibliothek in Ihrer virtuellen Umgebung:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m pip install huggingface_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Verwenden Sie die Funktion [`hf_hub_download`](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/adding-a-library#download-files-from-the-hub), um eine Datei in einen bestimmten Pfad herunterzuladen. Der folgende Befehl lädt zum Beispiel die Datei "config.json" aus dem Modell [T0](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/T0_3B) in den gewünschten Pfad herunter:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
|
||||
|
||||
>>> hf_hub_download(repo_id="bigscience/T0_3B", filename="config.json", cache_dir="./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Sobald Ihre Datei heruntergeladen und lokal zwischengespeichert ist, geben Sie den lokalen Pfad an, um sie zu laden und zu verwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0/config.json")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Informationen zum Herunterladen von Dateien, die auf dem Hub gespeichert sind, finden Sie im Abschnitt [Wie man Dateien vom Hub herunterlädt] (https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/how-to-downstream).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
232
docs/source/de/model_sharing.md
Normal file
232
docs/source/de/model_sharing.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,232 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Ein Modell teilen
|
||||
|
||||
Die letzten beiden Tutorials haben gezeigt, wie man ein Modell mit PyTorch, Keras und 🤗 Accelerate für verteilte Setups feinabstimmen kann. Der nächste Schritt besteht darin, Ihr Modell mit der Community zu teilen! Bei Hugging Face glauben wir an den offenen Austausch von Wissen und Ressourcen, um künstliche Intelligenz für alle zu demokratisieren. Wir ermutigen Sie, Ihr Modell mit der Community zu teilen, um anderen zu helfen, Zeit und Ressourcen zu sparen.
|
||||
|
||||
In diesem Tutorial lernen Sie zwei Methoden kennen, wie Sie ein trainiertes oder verfeinertes Modell auf dem [Model Hub](https://huggingface.co/models) teilen können:
|
||||
|
||||
- Programmgesteuertes Übertragen Ihrer Dateien auf den Hub.
|
||||
- Ziehen Sie Ihre Dateien per Drag-and-Drop über die Weboberfläche in den Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/XvSGPZFEjDY" title="YouTube video player"
|
||||
frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope;
|
||||
picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Um ein Modell mit der Öffentlichkeit zu teilen, benötigen Sie ein Konto auf [huggingface.co](https://huggingface.co/join). Sie können auch einer bestehenden Organisation beitreten oder eine neue Organisation gründen.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Repository-Funktionen
|
||||
|
||||
Jedes Repository im Model Hub verhält sich wie ein typisches GitHub-Repository. Unsere Repositorys bieten Versionierung, Commit-Historie und die Möglichkeit, Unterschiede zu visualisieren.
|
||||
|
||||
Die integrierte Versionierung des Model Hub basiert auf Git und [git-lfs](https://git-lfs.github.com/). Mit anderen Worten: Sie können ein Modell als ein Repository behandeln, was eine bessere Zugriffskontrolle und Skalierbarkeit ermöglicht. Die Versionskontrolle ermöglicht *Revisionen*, eine Methode zum Anheften einer bestimmten Version eines Modells mit einem Commit-Hash, Tag oder Branch.
|
||||
|
||||
Folglich können Sie eine bestimmte Modellversion mit dem Parameter "Revision" laden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
... "julien-c/EsperBERTo-small", revision="v2.0.1" # tag name, or branch name, or commit hash
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dateien lassen sich auch in einem Repository leicht bearbeiten, und Sie können die Commit-Historie sowie die Unterschiede einsehen:
|
||||
|
||||
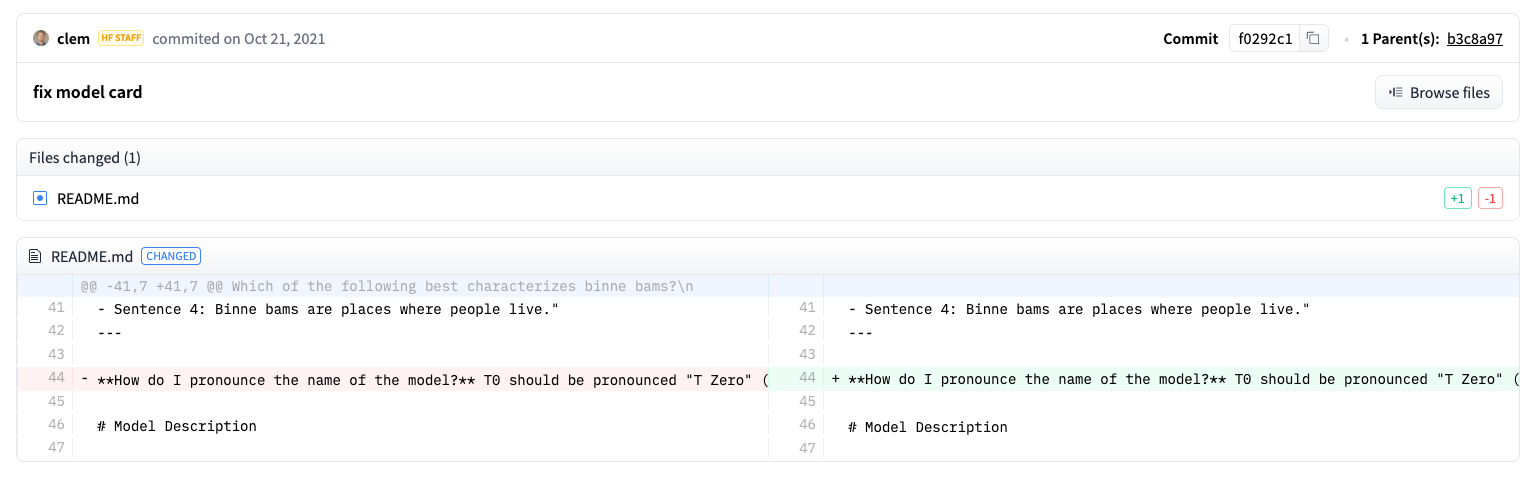
|
||||
|
||||
## Einrichtung
|
||||
|
||||
Bevor Sie ein Modell für den Hub freigeben, benötigen Sie Ihre Hugging Face-Anmeldedaten. Wenn Sie Zugang zu einem Terminal haben, führen Sie den folgenden Befehl in der virtuellen Umgebung aus, in der 🤗 Transformers installiert ist. Dadurch werden Ihre Zugangsdaten in Ihrem Hugging Face-Cache-Ordner (standardmäßig `~/.cache/`) gespeichert:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
huggingface-cli login
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie ein Notebook wie Jupyter oder Colaboratory verwenden, stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie die [`huggingface_hub`](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/adding-a-library) Bibliothek installiert haben. Diese Bibliothek ermöglicht Ihnen die programmatische Interaktion mit dem Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install huggingface_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Verwenden Sie dann `notebook_login`, um sich beim Hub anzumelden, und folgen Sie dem Link [hier](https://huggingface.co/settings/token), um ein Token für die Anmeldung zu generieren:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
|
||||
|
||||
>>> notebook_login()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Ein Modell für alle Frameworks konvertieren
|
||||
|
||||
Um sicherzustellen, dass Ihr Modell von jemandem verwendet werden kann, der mit einem anderen Framework arbeitet, empfehlen wir Ihnen, Ihr Modell sowohl mit PyTorch- als auch mit TensorFlow-Checkpoints zu konvertieren und hochzuladen. Während Benutzer immer noch in der Lage sind, Ihr Modell von einem anderen Framework zu laden, wenn Sie diesen Schritt überspringen, wird es langsamer sein, weil 🤗 Transformers den Checkpoint on-the-fly konvertieren müssen.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Konvertierung eines Checkpoints für ein anderes Framework ist einfach. Stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie PyTorch und TensorFlow installiert haben (siehe [hier](installation) für Installationsanweisungen), und finden Sie dann das spezifische Modell für Ihre Aufgabe in dem anderen Framework.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Geben Sie `from_tf=True` an, um einen Prüfpunkt von TensorFlow nach PyTorch zu konvertieren:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pt_model = DistilBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("path/to/awesome-name-you-picked", from_tf=True)
|
||||
>>> pt_model.save_pretrained("path/to/awesome-name-you-picked")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Geben Sie `from_pt=True` an, um einen Prüfpunkt von PyTorch nach TensorFlow zu konvertieren:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("path/to/awesome-name-you-picked", from_pt=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dann können Sie Ihr neues TensorFlow-Modell mit seinem neuen Checkpoint speichern:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_model.save_pretrained("path/to/awesome-name-you-picked")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
<jax>
|
||||
Wenn ein Modell in Flax verfügbar ist, können Sie auch einen Kontrollpunkt von PyTorch nach Flax konvertieren:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> flax_model = FlaxDistilBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
|
||||
... "path/to/awesome-name-you-picked", from_pt=True
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
</jax>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Ein Modell während des Trainings hochladen
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
<Youtube id="Z1-XMy-GNLQ"/>
|
||||
|
||||
Die Weitergabe eines Modells an den Hub ist so einfach wie das Hinzufügen eines zusätzlichen Parameters oder Rückrufs. Erinnern Sie sich an das [Feinabstimmungs-Tutorial](training), in der Klasse [`TrainingArguments`] geben Sie Hyperparameter und zusätzliche Trainingsoptionen an. Eine dieser Trainingsoptionen beinhaltet die Möglichkeit, ein Modell direkt an den Hub zu pushen. Setzen Sie `push_to_hub=True` in Ihrer [`TrainingArguments`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> training_args = TrainingArguments(output_dir="my-awesome-model", push_to_hub=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Übergeben Sie Ihre Trainingsargumente wie gewohnt an [`Trainer`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> trainer = Trainer(
|
||||
... model=model,
|
||||
... args=training_args,
|
||||
... train_dataset=small_train_dataset,
|
||||
... eval_dataset=small_eval_dataset,
|
||||
... compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Nach der Feinabstimmung Ihres Modells rufen Sie [`~transformers.Trainer.push_to_hub`] auf [`Trainer`] auf, um das trainierte Modell an den Hub zu übertragen. Transformers fügt sogar automatisch Trainings-Hyperparameter, Trainingsergebnisse und Framework-Versionen zu Ihrer Modellkarte hinzu!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> trainer.push_to_hub()
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Geben Sie ein Modell mit [`PushToHubCallback`] an den Hub weiter. In der [`PushToHubCallback`] Funktion, fügen Sie hinzu:
|
||||
|
||||
- Ein Ausgabeverzeichnis für Ihr Modell.
|
||||
- Einen Tokenizer.
|
||||
- Die `hub_model_id`, die Ihr Hub-Benutzername und Modellname ist.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PushToHubCallback
|
||||
|
||||
>>> push_to_hub_callback = PushToHubCallback(
|
||||
... output_dir="./your_model_save_path", tokenizer=tokenizer, hub_model_id="your-username/my-awesome-model"
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Fügen Sie den Callback zu [`fit`](https://keras.io/api/models/model_training_apis/) hinzu, und 🤗 Transformers wird das trainierte Modell an den Hub weiterleiten:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model.fit(tf_train_dataset, validation_data=tf_validation_dataset, epochs=3, callbacks=push_to_hub_callback)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Verwenden Sie die Funktion `push_to_hub`.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können `push_to_hub` auch direkt für Ihr Modell aufrufen, um es in den Hub hochzuladen.
|
||||
|
||||
Geben Sie den Namen Ihres Modells in "push_to_hub" an:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pt_model.push_to_hub("my-awesome-model")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dadurch wird ein Repository unter Ihrem Benutzernamen mit dem Modellnamen `my-awesome-model` erstellt. Benutzer können nun Ihr Modell mit der Funktion `from_pretrained` laden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("your_username/my-awesome-model")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie zu einer Organisation gehören und Ihr Modell stattdessen unter dem Namen der Organisation pushen wollen, fügen Sie diesen einfach zur `repo_id` hinzu:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pt_model.push_to_hub("my-awesome-org/my-awesome-model")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Die Funktion "push_to_hub" kann auch verwendet werden, um andere Dateien zu einem Modell-Repository hinzuzufügen. Zum Beispiel kann man einen Tokenizer zu einem Modell-Repository hinzufügen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.push_to_hub("my-awesome-model")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Oder vielleicht möchten Sie die TensorFlow-Version Ihres fein abgestimmten PyTorch-Modells hinzufügen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_model.push_to_hub("my-awesome-model")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie nun zu Ihrem Hugging Face-Profil navigieren, sollten Sie Ihr neu erstelltes Modell-Repository sehen. Wenn Sie auf die Registerkarte **Dateien** klicken, werden alle Dateien angezeigt, die Sie in das Repository hochgeladen haben.
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Einzelheiten zum Erstellen und Hochladen von Dateien in ein Repository finden Sie in der Hub-Dokumentation [hier](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/how-to-upstream).
|
||||
|
||||
## Hochladen mit der Weboberfläche
|
||||
|
||||
Benutzer, die einen no-code Ansatz bevorzugen, können ein Modell über das Webinterface des Hubs hochladen. Besuchen Sie [huggingface.co/new](https://huggingface.co/new) um ein neues Repository zu erstellen:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Fügen Sie von hier aus einige Informationen über Ihr Modell hinzu:
|
||||
|
||||
- Wählen Sie den **Besitzer** des Repositorys. Dies können Sie selbst oder eine der Organisationen sein, denen Sie angehören.
|
||||
- Wählen Sie einen Namen für Ihr Modell, der auch der Name des Repositorys sein wird.
|
||||
- Wählen Sie, ob Ihr Modell öffentlich oder privat ist.
|
||||
- Geben Sie die Lizenzverwendung für Ihr Modell an.
|
||||
|
||||
Klicken Sie nun auf die Registerkarte **Dateien** und klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche **Datei hinzufügen**, um eine neue Datei in Ihr Repository hochzuladen. Ziehen Sie dann eine Datei per Drag-and-Drop hoch und fügen Sie eine Übergabemeldung hinzu.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Hinzufügen einer Modellkarte
|
||||
|
||||
Um sicherzustellen, dass die Benutzer die Fähigkeiten, Grenzen, möglichen Verzerrungen und ethischen Aspekte Ihres Modells verstehen, fügen Sie bitte eine Modellkarte zu Ihrem Repository hinzu. Die Modellkarte wird in der Datei `README.md` definiert. Sie können eine Modellkarte hinzufügen, indem Sie:
|
||||
|
||||
* Manuelles Erstellen und Hochladen einer "README.md"-Datei.
|
||||
* Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche **Modellkarte bearbeiten** in Ihrem Modell-Repository.
|
||||
|
||||
Werfen Sie einen Blick auf die DistilBert [model card](https://huggingface.co/distilbert-base-uncased) als gutes Beispiel für die Art von Informationen, die eine Modellkarte enthalten sollte. Weitere Details über andere Optionen, die Sie in der Datei "README.md" einstellen können, wie z.B. den Kohlenstoff-Fußabdruck eines Modells oder Beispiele für Widgets, finden Sie in der Dokumentation [hier](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/models-cards).
|
||||
@ -1,228 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Ein Modell teilen
|
||||
|
||||
Die letzten beiden Tutorials haben gezeigt, wie man ein Modell mit PyTorch, Keras und 🤗 Accelerate für verteilte Setups feinabstimmen kann. Der nächste Schritt besteht darin, Ihr Modell mit der Community zu teilen! Bei Hugging Face glauben wir an den offenen Austausch von Wissen und Ressourcen, um künstliche Intelligenz für alle zu demokratisieren. Wir ermutigen Sie, Ihr Modell mit der Community zu teilen, um anderen zu helfen, Zeit und Ressourcen zu sparen.
|
||||
|
||||
In diesem Tutorial lernen Sie zwei Methoden kennen, wie Sie ein trainiertes oder verfeinertes Modell auf dem [Model Hub](https://huggingface.co/models) teilen können:
|
||||
|
||||
- Programmgesteuertes Übertragen Ihrer Dateien auf den Hub.
|
||||
- Ziehen Sie Ihre Dateien per Drag-and-Drop über die Weboberfläche in den Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/XvSGPZFEjDY" title="YouTube video player"
|
||||
frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope;
|
||||
picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Um ein Modell mit der Öffentlichkeit zu teilen, benötigen Sie ein Konto auf [huggingface.co](https://huggingface.co/join). Sie können auch einer bestehenden Organisation beitreten oder eine neue Organisation gründen.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Repository-Funktionen
|
||||
|
||||
Jedes Repository im Model Hub verhält sich wie ein typisches GitHub-Repository. Unsere Repositorys bieten Versionierung, Commit-Historie und die Möglichkeit, Unterschiede zu visualisieren.
|
||||
|
||||
Die integrierte Versionierung des Model Hub basiert auf Git und [git-lfs](https://git-lfs.github.com/). Mit anderen Worten: Sie können ein Modell als ein Repository behandeln, was eine bessere Zugriffskontrolle und Skalierbarkeit ermöglicht. Die Versionskontrolle ermöglicht *Revisionen*, eine Methode zum Anheften einer bestimmten Version eines Modells mit einem Commit-Hash, Tag oder Branch.
|
||||
|
||||
Folglich können Sie eine bestimmte Modellversion mit dem Parameter "Revision" laden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
... "julien-c/EsperBERTo-small", revision="v2.0.1" # tag name, or branch name, or commit hash
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dateien lassen sich auch in einem Repository leicht bearbeiten, und Sie können die Commit-Historie sowie die Unterschiede einsehen:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Einrichtung
|
||||
|
||||
Bevor Sie ein Modell für den Hub freigeben, benötigen Sie Ihre Hugging Face-Anmeldedaten. Wenn Sie Zugang zu einem Terminal haben, führen Sie den folgenden Befehl in der virtuellen Umgebung aus, in der 🤗 Transformers installiert ist. Dadurch werden Ihre Zugangsdaten in Ihrem Hugging Face-Cache-Ordner (standardmäßig `~/.cache/`) gespeichert:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
huggingface-cli login
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie ein Notebook wie Jupyter oder Colaboratory verwenden, stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie die [`huggingface_hub`](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/adding-a-library) Bibliothek installiert haben. Diese Bibliothek ermöglicht Ihnen die programmatische Interaktion mit dem Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install huggingface_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Verwenden Sie dann `notebook_login`, um sich beim Hub anzumelden, und folgen Sie dem Link [hier](https://huggingface.co/settings/token), um ein Token für die Anmeldung zu generieren:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
|
||||
|
||||
>>> notebook_login()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Ein Modell für alle Frameworks konvertieren
|
||||
|
||||
Um sicherzustellen, dass Ihr Modell von jemandem verwendet werden kann, der mit einem anderen Framework arbeitet, empfehlen wir Ihnen, Ihr Modell sowohl mit PyTorch- als auch mit TensorFlow-Checkpoints zu konvertieren und hochzuladen. Während Benutzer immer noch in der Lage sind, Ihr Modell von einem anderen Framework zu laden, wenn Sie diesen Schritt überspringen, wird es langsamer sein, weil 🤗 Transformers den Checkpoint on-the-fly konvertieren müssen.
|
||||
|
||||
Die Konvertierung eines Checkpoints für ein anderes Framework ist einfach. Stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie PyTorch und TensorFlow installiert haben (siehe [hier](installation) für Installationsanweisungen), und finden Sie dann das spezifische Modell für Ihre Aufgabe in dem anderen Framework.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Geben Sie `from_tf=True` an, um einen Prüfpunkt von TensorFlow nach PyTorch zu konvertieren:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pt_model = DistilBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("path/to/awesome-name-you-picked", from_tf=True)
|
||||
>>> pt_model.save_pretrained("path/to/awesome-name-you-picked")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Geben Sie `from_pt=True` an, um einen Prüfpunkt von PyTorch nach TensorFlow zu konvertieren:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("path/to/awesome-name-you-picked", from_pt=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dann können Sie Ihr neues TensorFlow-Modell mit seinem neuen Checkpoint speichern:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_model.save_pretrained("path/to/awesome-name-you-picked")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
<jax>
|
||||
Wenn ein Modell in Flax verfügbar ist, können Sie auch einen Kontrollpunkt von PyTorch nach Flax konvertieren:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> flax_model = FlaxDistilBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
|
||||
... "path/to/awesome-name-you-picked", from_pt=True
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
</jax>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Ein Modell während des Trainings hochladen
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
<Youtube id="Z1-XMy-GNLQ"/>
|
||||
|
||||
Die Weitergabe eines Modells an den Hub ist so einfach wie das Hinzufügen eines zusätzlichen Parameters oder Rückrufs. Erinnern Sie sich an das [Feinabstimmungs-Tutorial](training), in der Klasse [`TrainingArguments`] geben Sie Hyperparameter und zusätzliche Trainingsoptionen an. Eine dieser Trainingsoptionen beinhaltet die Möglichkeit, ein Modell direkt an den Hub zu pushen. Setzen Sie `push_to_hub=True` in Ihrer [`TrainingArguments`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> training_args = TrainingArguments(output_dir="my-awesome-model", push_to_hub=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Übergeben Sie Ihre Trainingsargumente wie gewohnt an [`Trainer`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> trainer = Trainer(
|
||||
... model=model,
|
||||
... args=training_args,
|
||||
... train_dataset=small_train_dataset,
|
||||
... eval_dataset=small_eval_dataset,
|
||||
... compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Nach der Feinabstimmung Ihres Modells rufen Sie [`~transformers.Trainer.push_to_hub`] auf [`Trainer`] auf, um das trainierte Modell an den Hub zu übertragen. Transformers fügt sogar automatisch Trainings-Hyperparameter, Trainingsergebnisse und Framework-Versionen zu Ihrer Modellkarte hinzu!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> trainer.push_to_hub()
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Geben Sie ein Modell mit [`PushToHubCallback`] an den Hub weiter. In der [`PushToHubCallback`] Funktion, fügen Sie hinzu:
|
||||
|
||||
- Ein Ausgabeverzeichnis für Ihr Modell.
|
||||
- Einen Tokenizer.
|
||||
- Die `hub_model_id`, die Ihr Hub-Benutzername und Modellname ist.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PushToHubCallback
|
||||
|
||||
>>> push_to_hub_callback = PushToHubCallback(
|
||||
... output_dir="./your_model_save_path", tokenizer=tokenizer, hub_model_id="your-username/my-awesome-model"
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Fügen Sie den Callback zu [`fit`](https://keras.io/api/models/model_training_apis/) hinzu, und 🤗 Transformers wird das trainierte Modell an den Hub weiterleiten:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model.fit(tf_train_dataset, validation_data=tf_validation_dataset, epochs=3, callbacks=push_to_hub_callback)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Verwenden Sie die Funktion `push_to_hub`.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können `push_to_hub` auch direkt für Ihr Modell aufrufen, um es in den Hub hochzuladen.
|
||||
|
||||
Geben Sie den Namen Ihres Modells in "push_to_hub" an:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pt_model.push_to_hub("my-awesome-model")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dadurch wird ein Repository unter Ihrem Benutzernamen mit dem Modellnamen `my-awesome-model` erstellt. Benutzer können nun Ihr Modell mit der Funktion `from_pretrained` laden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("your_username/my-awesome-model")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie zu einer Organisation gehören und Ihr Modell stattdessen unter dem Namen der Organisation pushen wollen, fügen Sie diesen einfach zur `repo_id` hinzu:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pt_model.push_to_hub("my-awesome-org/my-awesome-model")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Die Funktion "push_to_hub" kann auch verwendet werden, um andere Dateien zu einem Modell-Repository hinzuzufügen. Zum Beispiel kann man einen Tokenizer zu einem Modell-Repository hinzufügen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.push_to_hub("my-awesome-model")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Oder vielleicht möchten Sie die TensorFlow-Version Ihres fein abgestimmten PyTorch-Modells hinzufügen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_model.push_to_hub("my-awesome-model")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie nun zu Ihrem Hugging Face-Profil navigieren, sollten Sie Ihr neu erstelltes Modell-Repository sehen. Wenn Sie auf die Registerkarte **Dateien** klicken, werden alle Dateien angezeigt, die Sie in das Repository hochgeladen haben.
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Einzelheiten zum Erstellen und Hochladen von Dateien in ein Repository finden Sie in der Hub-Dokumentation [hier](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/how-to-upstream).
|
||||
|
||||
## Hochladen mit der Weboberfläche
|
||||
|
||||
Benutzer, die einen no-code Ansatz bevorzugen, können ein Modell über das Webinterface des Hubs hochladen. Besuchen Sie [huggingface.co/new](https://huggingface.co/new) um ein neues Repository zu erstellen:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Fügen Sie von hier aus einige Informationen über Ihr Modell hinzu:
|
||||
|
||||
- Wählen Sie den **Besitzer** des Repositorys. Dies können Sie selbst oder eine der Organisationen sein, denen Sie angehören.
|
||||
- Wählen Sie einen Namen für Ihr Modell, der auch der Name des Repositorys sein wird.
|
||||
- Wählen Sie, ob Ihr Modell öffentlich oder privat ist.
|
||||
- Geben Sie die Lizenzverwendung für Ihr Modell an.
|
||||
|
||||
Klicken Sie nun auf die Registerkarte **Dateien** und klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche **Datei hinzufügen**, um eine neue Datei in Ihr Repository hochzuladen. Ziehen Sie dann eine Datei per Drag-and-Drop hoch und fügen Sie eine Übergabemeldung hinzu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Hinzufügen einer Modellkarte
|
||||
|
||||
Um sicherzustellen, dass die Benutzer die Fähigkeiten, Grenzen, möglichen Verzerrungen und ethischen Aspekte Ihres Modells verstehen, fügen Sie bitte eine Modellkarte zu Ihrem Repository hinzu. Die Modellkarte wird in der Datei `README.md` definiert. Sie können eine Modellkarte hinzufügen, indem Sie:
|
||||
|
||||
* Manuelles Erstellen und Hochladen einer "README.md"-Datei.
|
||||
* Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche **Modellkarte bearbeiten** in Ihrem Modell-Repository.
|
||||
|
||||
Werfen Sie einen Blick auf die DistilBert [model card](https://huggingface.co/distilbert-base-uncased) als gutes Beispiel für die Art von Informationen, die eine Modellkarte enthalten sollte. Weitere Details über andere Optionen, die Sie in der Datei "README.md" einstellen können, wie z.B. den Kohlenstoff-Fußabdruck eines Modells oder Beispiele für Widgets, finden Sie in der Dokumentation [hier](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/models-cards).
|
||||
175
docs/source/de/pipeline_tutorial.md
Normal file
175
docs/source/de/pipeline_tutorial.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,175 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Pipelines für Inferenzen
|
||||
|
||||
Die [`pipeline`] macht es einfach, jedes beliebige Modell aus dem [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models) für die Inferenz auf jede Sprache, Computer Vision, Sprache und multimodale Aufgaben zu verwenden. Selbst wenn Sie keine Erfahrung mit einer bestimmten Modalität haben oder nicht mit dem zugrundeliegenden Code hinter den Modellen vertraut sind, können Sie sie mit der [`pipeline`] für Inferenzen verwenden! In diesem Beispiel lernen Sie, wie:
|
||||
|
||||
* Eine [`pipeline`] für Inferenz zu verwenden.
|
||||
* Einen bestimmten Tokenizer oder ein bestimmtes Modell zu verwenden.
|
||||
* Eine [`pipeline`] für Audio-, Vision- und multimodale Aufgaben zu verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Eine vollständige Liste der unterstützten Aufgaben und verfügbaren Parameter finden Sie in der [`pipeline`]-Dokumentation.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Verwendung von Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
Obwohl jede Aufgabe eine zugehörige [`pipeline`] hat, ist es einfacher, die allgemeine [`pipeline`]-Abstraktion zu verwenden, die alle aufgabenspezifischen Pipelines enthält. Die [`pipeline`] lädt automatisch ein Standardmodell und eine Vorverarbeitungsklasse, die für Ihre Aufgabe inferenzfähig ist.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Beginnen Sie mit der Erstellung einer [`pipeline`] und geben Sie eine Inferenzaufgabe an:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> generator = pipeline(task="text-generation")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Übergeben Sie Ihren Eingabetext an die [`pipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> generator(
|
||||
... "Three Rings for the Elven-kings under the sky, Seven for the Dwarf-lords in their halls of stone"
|
||||
... ) # doctest: +SKIP
|
||||
[{'generated_text': 'Three Rings for the Elven-kings under the sky, Seven for the Dwarf-lords in their halls of stone, Seven for the Iron-priests at the door to the east, and thirteen for the Lord Kings at the end of the mountain'}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie mehr als eine Eingabe haben, übergeben Sie die Eingabe als Liste:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> generator(
|
||||
... [
|
||||
... "Three Rings for the Elven-kings under the sky, Seven for the Dwarf-lords in their halls of stone",
|
||||
... "Nine for Mortal Men, doomed to die, One for the Dark Lord on his dark throne",
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
... ) # doctest: +SKIP
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alle zusätzlichen Parameter für Ihre Aufgabe können auch in die [`pipeline`] aufgenommen werden. Die Aufgabe `Text-Generierung` hat eine [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`]-Methode mit mehreren Parametern zur Steuerung der Ausgabe. Wenn Sie zum Beispiel mehr als eine Ausgabe erzeugen wollen, setzen Sie den Parameter `num_return_sequences`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> generator(
|
||||
... "Three Rings for the Elven-kings under the sky, Seven for the Dwarf-lords in their halls of stone",
|
||||
... num_return_sequences=2,
|
||||
... ) # doctest: +SKIP
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Wählen Sie ein Modell und einen Tokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
Die [`pipeline`] akzeptiert jedes Modell aus dem [Hub] (https://huggingface.co/models). Auf dem Hub gibt es Tags, mit denen Sie nach einem Modell filtern können, das Sie für Ihre Aufgabe verwenden möchten. Sobald Sie ein passendes Modell ausgewählt haben, laden Sie es mit der entsprechenden `AutoModelFor` und [`AutoTokenizer`] Klasse. Laden Sie zum Beispiel die Klasse [`AutoModelForCausalLM`] für eine kausale Sprachmodellierungsaufgabe:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("distilgpt2")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("distilgpt2")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen Sie eine [`pipeline`] für Ihre Aufgabe, und geben Sie das Modell und den Tokenizer an, die Sie geladen haben:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> generator = pipeline(task="text-generation", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Übergeben Sie Ihren Eingabetext an die [`pipeline`] , um einen Text zu erzeugen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> generator(
|
||||
... "Three Rings for the Elven-kings under the sky, Seven for the Dwarf-lords in their halls of stone"
|
||||
... ) # doctest: +SKIP
|
||||
[{'generated_text': 'Three Rings for the Elven-kings under the sky, Seven for the Dwarf-lords in their halls of stone, Seven for the Dragon-lords (for them to rule in a world ruled by their rulers, and all who live within the realm'}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Audio-Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
Die [`pipeline`] unterstützt auch Audioaufgaben wie Audioklassifizierung und automatische Spracherkennung.
|
||||
|
||||
Lassen Sie uns zum Beispiel die Emotion in diesem Audioclip klassifizieren:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
|
||||
>>> torch.manual_seed(42) # doctest: +IGNORE_RESULT
|
||||
>>> ds = load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/librispeech_asr_demo", "clean", split="validation")
|
||||
>>> audio_file = ds[0]["audio"]["path"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finden Sie ein [Audioklassifikation](https://huggingface.co/models?pipeline_tag=audio-classification) Modell auf dem Model Hub für Emotionserkennung und laden Sie es in die [`pipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> audio_classifier = pipeline(
|
||||
... task="audio-classification", model="ehcalabres/wav2vec2-lg-xlsr-en-speech-emotion-recognition"
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Übergeben Sie die Audiodatei an die [`pipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> preds = audio_classifier(audio_file)
|
||||
>>> preds = [{"score": round(pred["score"], 4), "label": pred["label"]} for pred in preds]
|
||||
>>> preds
|
||||
[{'score': 0.1315, 'label': 'calm'}, {'score': 0.1307, 'label': 'neutral'}, {'score': 0.1274, 'label': 'sad'}, {'score': 0.1261, 'label': 'fearful'}, {'score': 0.1242, 'label': 'happy'}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Bildverarbeitungs-Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
Die Verwendung einer [`pipeline`] für Bildverarbeitungsaufgaben ist praktisch identisch.
|
||||
|
||||
Geben Sie Ihre Aufgabe an und übergeben Sie Ihr Bild an den Klassifikator. Das Bild kann ein Link oder ein lokaler Pfad zu dem Bild sein. Zum Beispiel: Welche Katzenart ist unten abgebildet?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> vision_classifier = pipeline(task="image-classification")
|
||||
>>> preds = vision_classifier(
|
||||
... images="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/pipeline-cat-chonk.jpeg"
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> preds = [{"score": round(pred["score"], 4), "label": pred["label"]} for pred in preds]
|
||||
>>> preds
|
||||
[{'score': 0.4335, 'label': 'lynx, catamount'}, {'score': 0.0348, 'label': 'cougar, puma, catamount, mountain lion, painter, panther, Felis concolor'}, {'score': 0.0324, 'label': 'snow leopard, ounce, Panthera uncia'}, {'score': 0.0239, 'label': 'Egyptian cat'}, {'score': 0.0229, 'label': 'tiger cat'}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Multimodale Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
Die [`pipeline`] unterstützt mehr als eine Modalität. Eine Aufgabe zur Beantwortung visueller Fragen (VQA) kombiniert zum Beispiel Text und Bild. Verwenden Sie einen beliebigen Bildlink und eine Frage, die Sie zu dem Bild stellen möchten. Das Bild kann eine URL oder ein lokaler Pfad zu dem Bild sein.
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie zum Beispiel das gleiche Bild wie in der obigen Vision-Pipeline verwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> image = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/pipeline-cat-chonk.jpeg"
|
||||
>>> question = "Where is the cat?"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen Sie eine Pipeline für "vqa" und übergeben Sie ihr das Bild und die Frage:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> vqa = pipeline(task="vqa")
|
||||
>>> preds = vqa(image=image, question=question)
|
||||
>>> preds = [{"score": round(pred["score"], 4), "answer": pred["answer"]} for pred in preds]
|
||||
>>> preds
|
||||
[{'score': 0.9112, 'answer': 'snow'}, {'score': 0.8796, 'answer': 'in snow'}, {'score': 0.6717, 'answer': 'outside'}, {'score': 0.0291, 'answer': 'on ground'}, {'score': 0.027, 'answer': 'ground'}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,171 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Pipelines für Inferenzen
|
||||
|
||||
Die [`pipeline`] macht es einfach, jedes beliebige Modell aus dem [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models) für die Inferenz auf jede Sprache, Computer Vision, Sprache und multimodale Aufgaben zu verwenden. Selbst wenn Sie keine Erfahrung mit einer bestimmten Modalität haben oder nicht mit dem zugrundeliegenden Code hinter den Modellen vertraut sind, können Sie sie mit der [`pipeline`] für Inferenzen verwenden! In diesem Beispiel lernen Sie, wie:
|
||||
|
||||
* Eine [`pipeline`] für Inferenz zu verwenden.
|
||||
* Einen bestimmten Tokenizer oder ein bestimmtes Modell zu verwenden.
|
||||
* Eine [`pipeline`] für Audio-, Vision- und multimodale Aufgaben zu verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Eine vollständige Liste der unterstützten Aufgaben und verfügbaren Parameter finden Sie in der [`pipeline`]-Dokumentation.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Verwendung von Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
Obwohl jede Aufgabe eine zugehörige [`pipeline`] hat, ist es einfacher, die allgemeine [`pipeline`]-Abstraktion zu verwenden, die alle aufgabenspezifischen Pipelines enthält. Die [`pipeline`] lädt automatisch ein Standardmodell und eine Vorverarbeitungsklasse, die für Ihre Aufgabe inferenzfähig ist.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Beginnen Sie mit der Erstellung einer [`pipeline`] und geben Sie eine Inferenzaufgabe an:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> generator = pipeline(task="text-generation")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Übergeben Sie Ihren Eingabetext an die [`pipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> generator(
|
||||
... "Three Rings for the Elven-kings under the sky, Seven for the Dwarf-lords in their halls of stone"
|
||||
... ) # doctest: +SKIP
|
||||
[{'generated_text': 'Three Rings for the Elven-kings under the sky, Seven for the Dwarf-lords in their halls of stone, Seven for the Iron-priests at the door to the east, and thirteen for the Lord Kings at the end of the mountain'}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie mehr als eine Eingabe haben, übergeben Sie die Eingabe als Liste:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> generator(
|
||||
... [
|
||||
... "Three Rings for the Elven-kings under the sky, Seven for the Dwarf-lords in their halls of stone",
|
||||
... "Nine for Mortal Men, doomed to die, One for the Dark Lord on his dark throne",
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
... ) # doctest: +SKIP
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alle zusätzlichen Parameter für Ihre Aufgabe können auch in die [`pipeline`] aufgenommen werden. Die Aufgabe `Text-Generierung` hat eine [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`]-Methode mit mehreren Parametern zur Steuerung der Ausgabe. Wenn Sie zum Beispiel mehr als eine Ausgabe erzeugen wollen, setzen Sie den Parameter `num_return_sequences`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> generator(
|
||||
... "Three Rings for the Elven-kings under the sky, Seven for the Dwarf-lords in their halls of stone",
|
||||
... num_return_sequences=2,
|
||||
... ) # doctest: +SKIP
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Wählen Sie ein Modell und einen Tokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
Die [`pipeline`] akzeptiert jedes Modell aus dem [Hub] (https://huggingface.co/models). Auf dem Hub gibt es Tags, mit denen Sie nach einem Modell filtern können, das Sie für Ihre Aufgabe verwenden möchten. Sobald Sie ein passendes Modell ausgewählt haben, laden Sie es mit der entsprechenden `AutoModelFor` und [`AutoTokenizer`] Klasse. Laden Sie zum Beispiel die Klasse [`AutoModelForCausalLM`] für eine kausale Sprachmodellierungsaufgabe:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("distilgpt2")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("distilgpt2")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen Sie eine [`pipeline`] für Ihre Aufgabe, und geben Sie das Modell und den Tokenizer an, die Sie geladen haben:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> generator = pipeline(task="text-generation", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Übergeben Sie Ihren Eingabetext an die [`pipeline`] , um einen Text zu erzeugen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> generator(
|
||||
... "Three Rings for the Elven-kings under the sky, Seven for the Dwarf-lords in their halls of stone"
|
||||
... ) # doctest: +SKIP
|
||||
[{'generated_text': 'Three Rings for the Elven-kings under the sky, Seven for the Dwarf-lords in their halls of stone, Seven for the Dragon-lords (for them to rule in a world ruled by their rulers, and all who live within the realm'}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Audio-Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
Die [`pipeline`] unterstützt auch Audioaufgaben wie Audioklassifizierung und automatische Spracherkennung.
|
||||
|
||||
Lassen Sie uns zum Beispiel die Emotion in diesem Audioclip klassifizieren:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
|
||||
>>> torch.manual_seed(42) # doctest: +IGNORE_RESULT
|
||||
>>> ds = load_dataset("hf-internal-testing/librispeech_asr_demo", "clean", split="validation")
|
||||
>>> audio_file = ds[0]["audio"]["path"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finden Sie ein [Audioklassifikation](https://huggingface.co/models?pipeline_tag=audio-classification) Modell auf dem Model Hub für Emotionserkennung und laden Sie es in die [`pipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> audio_classifier = pipeline(
|
||||
... task="audio-classification", model="ehcalabres/wav2vec2-lg-xlsr-en-speech-emotion-recognition"
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Übergeben Sie die Audiodatei an die [`pipeline`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> preds = audio_classifier(audio_file)
|
||||
>>> preds = [{"score": round(pred["score"], 4), "label": pred["label"]} for pred in preds]
|
||||
>>> preds
|
||||
[{'score': 0.1315, 'label': 'calm'}, {'score': 0.1307, 'label': 'neutral'}, {'score': 0.1274, 'label': 'sad'}, {'score': 0.1261, 'label': 'fearful'}, {'score': 0.1242, 'label': 'happy'}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Bildverarbeitungs-Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
Die Verwendung einer [`pipeline`] für Bildverarbeitungsaufgaben ist praktisch identisch.
|
||||
|
||||
Geben Sie Ihre Aufgabe an und übergeben Sie Ihr Bild an den Klassifikator. Das Bild kann ein Link oder ein lokaler Pfad zu dem Bild sein. Zum Beispiel: Welche Katzenart ist unten abgebildet?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> vision_classifier = pipeline(task="image-classification")
|
||||
>>> preds = vision_classifier(
|
||||
... images="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/pipeline-cat-chonk.jpeg"
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> preds = [{"score": round(pred["score"], 4), "label": pred["label"]} for pred in preds]
|
||||
>>> preds
|
||||
[{'score': 0.4335, 'label': 'lynx, catamount'}, {'score': 0.0348, 'label': 'cougar, puma, catamount, mountain lion, painter, panther, Felis concolor'}, {'score': 0.0324, 'label': 'snow leopard, ounce, Panthera uncia'}, {'score': 0.0239, 'label': 'Egyptian cat'}, {'score': 0.0229, 'label': 'tiger cat'}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Multimodale Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
Die [`pipeline`] unterstützt mehr als eine Modalität. Eine Aufgabe zur Beantwortung visueller Fragen (VQA) kombiniert zum Beispiel Text und Bild. Verwenden Sie einen beliebigen Bildlink und eine Frage, die Sie zu dem Bild stellen möchten. Das Bild kann eine URL oder ein lokaler Pfad zu dem Bild sein.
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie zum Beispiel das gleiche Bild wie in der obigen Vision-Pipeline verwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> image = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/pipeline-cat-chonk.jpeg"
|
||||
>>> question = "Where is the cat?"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen Sie eine Pipeline für "vqa" und übergeben Sie ihr das Bild und die Frage:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> vqa = pipeline(task="vqa")
|
||||
>>> preds = vqa(image=image, question=question)
|
||||
>>> preds = [{"score": round(pred["score"], 4), "answer": pred["answer"]} for pred in preds]
|
||||
>>> preds
|
||||
[{'score': 0.9112, 'answer': 'snow'}, {'score': 0.8796, 'answer': 'in snow'}, {'score': 0.6717, 'answer': 'outside'}, {'score': 0.0291, 'answer': 'on ground'}, {'score': 0.027, 'answer': 'ground'}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
506
docs/source/de/preprocessing.md
Normal file
506
docs/source/de/preprocessing.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,506 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Vorverarbeiten
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Bevor Sie Ihre Daten in einem Modell verwenden können, müssen die Daten in ein für das Modell akzeptables Format gebracht werden. Ein Modell versteht keine Rohtexte, Bilder oder Audiodaten. Diese Eingaben müssen in Zahlen umgewandelt und zu Tensoren zusammengesetzt werden. In dieser Anleitung werden Sie:
|
||||
|
||||
* Textdaten mit einem Tokenizer vorverarbeiten.
|
||||
* Bild- oder Audiodaten mit einem Feature Extractor vorverarbeiten.
|
||||
* Daten für eine multimodale Aufgabe mit einem Prozessor vorverarbeiten.
|
||||
|
||||
## NLP
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="Yffk5aydLzg"/>
|
||||
|
||||
Das wichtigste Werkzeug zur Verarbeitung von Textdaten ist ein [Tokenizer](main_classes/tokenizer). Ein Tokenizer zerlegt Text zunächst nach einer Reihe von Regeln in *Token*. Die Token werden in Zahlen umgewandelt, die zum Aufbau von Tensoren als Eingabe für ein Modell verwendet werden. Alle zusätzlichen Eingaben, die ein Modell benötigt, werden ebenfalls vom Tokenizer hinzugefügt.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie ein vortrainiertes Modell verwenden möchten, ist es wichtig, den zugehörigen vortrainierten Tokenizer zu verwenden. Dadurch wird sichergestellt, dass der Text auf die gleiche Weise aufgeteilt wird wie das Pretraining-Korpus und die gleichen entsprechenden Token-zu-Index (in der Regel als *vocab* bezeichnet) während des Pretrainings verwendet werden.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie einen vortrainierten Tokenizer mit der Klasse [AutoTokenizer], um schnell loszulegen. Damit wird das *vocab* heruntergeladen, das verwendet wird, wenn ein Modell vortrainiert wird.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tokenize
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie einen vortrainierten Tokenizer mit [`AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dann übergeben Sie Ihren Satz an den Tokenizer:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> encoded_input = tokenizer("Do not meddle in the affairs of wizards, for they are subtle and quick to anger.")
|
||||
>>> print(encoded_input)
|
||||
{'input_ids': [101, 2079, 2025, 19960, 10362, 1999, 1996, 3821, 1997, 16657, 1010, 2005, 2027, 2024, 11259, 1998, 4248, 2000, 4963, 1012, 102],
|
||||
'token_type_ids': [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
'attention_mask': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Der Tokenizer gibt ein Wörterbuch mit drei wichtigen Elementen zurück:
|
||||
|
||||
* [input_ids](glossary#input-ids) sind die Indizes, die den einzelnen Token im Satz entsprechen.
|
||||
* [attention_mask](glossary#attention-mask) gibt an, ob ein Token beachtet werden soll oder nicht.
|
||||
* [token_type_ids](glossary#token-type-ids) gibt an, zu welcher Sequenz ein Token gehört, wenn es mehr als eine Sequenz gibt.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können die `input_ids` dekodieren, um die ursprüngliche Eingabe zurückzugeben:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.decode(encoded_input["input_ids"])
|
||||
'[CLS] Do not meddle in the affairs of wizards, for they are subtle and quick to anger. [SEP]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wie Sie sehen können, hat der Tokenisierer zwei spezielle Token - `CLS` und `SEP` (Klassifikator und Separator) - zum Satz hinzugefügt. Nicht alle Modelle benötigen
|
||||
spezielle Token, aber wenn dies der Fall ist, fügt der Tokenisierer sie automatisch für Sie hinzu.
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie mehrere Sätze verarbeiten wollen, übergeben Sie die Sätze als Liste an den Tokenizer:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> batch_sentences = [
|
||||
... "But what about second breakfast?",
|
||||
... "Don't think he knows about second breakfast, Pip.",
|
||||
... "What about elevensies?",
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
>>> encoded_inputs = tokenizer(batch_sentences)
|
||||
>>> print(encoded_inputs)
|
||||
{'input_ids': [[101, 1252, 1184, 1164, 1248, 6462, 136, 102],
|
||||
[101, 1790, 112, 189, 1341, 1119, 3520, 1164, 1248, 6462, 117, 21902, 1643, 119, 102],
|
||||
[101, 1327, 1164, 5450, 23434, 136, 102]],
|
||||
'token_type_ids': [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
|
||||
'attention_mask': [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Pad
|
||||
|
||||
Dies bringt uns zu einem wichtigen Thema. Wenn Sie einen Haufen von Sätzen verarbeiten, sind diese nicht immer gleich lang. Das ist ein Problem, weil Tensoren, die Eingabe für das Modell, eine einheitliche Form haben müssen. Padding ist eine Strategie, die sicherstellt, dass Tensoren rechteckig sind, indem ein spezielles *Padding-Token* zu Sätzen mit weniger Token hinzugefügt wird.
|
||||
|
||||
Setzen Sie den Parameter "padding" auf "true", um die kürzeren Sequenzen im Stapel so aufzufüllen, dass sie der längsten Sequenz entsprechen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> batch_sentences = [
|
||||
... "But what about second breakfast?",
|
||||
... "Don't think he knows about second breakfast, Pip.",
|
||||
... "What about elevensies?",
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
>>> encoded_input = tokenizer(batch_sentences, padding=True)
|
||||
>>> print(encoded_input)
|
||||
{'input_ids': [[101, 1252, 1184, 1164, 1248, 6462, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[101, 1790, 112, 189, 1341, 1119, 3520, 1164, 1248, 6462, 117, 21902, 1643, 119, 102],
|
||||
[101, 1327, 1164, 5450, 23434, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
|
||||
'token_type_ids': [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
|
||||
'attention_mask': [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Beachten Sie, dass der Tokenizer den ersten und den dritten Satz mit einer "0" aufgefüllt hat, weil sie kürzer sind!
|
||||
|
||||
### Kürzung
|
||||
|
||||
Auf der anderen Seite des Spektrums kann es vorkommen, dass eine Sequenz zu lang für ein Modell ist. In diesem Fall müssen Sie die Sequenz auf eine kürzere Länge kürzen.
|
||||
|
||||
Setzen Sie den Parameter "truncation" auf "true", um eine Sequenz auf die vom Modell akzeptierte Höchstlänge zu kürzen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> batch_sentences = [
|
||||
... "But what about second breakfast?",
|
||||
... "Don't think he knows about second breakfast, Pip.",
|
||||
... "What about elevensies?",
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
>>> encoded_input = tokenizer(batch_sentences, padding=True, truncation=True)
|
||||
>>> print(encoded_input)
|
||||
{'input_ids': [[101, 1252, 1184, 1164, 1248, 6462, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[101, 1790, 112, 189, 1341, 1119, 3520, 1164, 1248, 6462, 117, 21902, 1643, 119, 102],
|
||||
[101, 1327, 1164, 5450, 23434, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
|
||||
'token_type_ids': [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
|
||||
'attention_mask': [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Tensoren erstellen
|
||||
|
||||
Schließlich möchten Sie, dass der Tokenizer die tatsächlichen Tensoren zurückgibt, die dem Modell zugeführt werden.
|
||||
|
||||
Setzen Sie den Parameter `return_tensors` entweder auf `pt` für PyTorch, oder `tf` für TensorFlow:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> batch_sentences = [
|
||||
... "But what about second breakfast?",
|
||||
... "Don't think he knows about second breakfast, Pip.",
|
||||
... "What about elevensies?",
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
>>> encoded_input = tokenizer(batch_sentences, padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> print(encoded_input)
|
||||
{'input_ids': tensor([[101, 1252, 1184, 1164, 1248, 6462, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[101, 1790, 112, 189, 1341, 1119, 3520, 1164, 1248, 6462, 117, 21902, 1643, 119, 102],
|
||||
[101, 1327, 1164, 5450, 23434, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]),
|
||||
'token_type_ids': tensor([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]),
|
||||
'attention_mask': tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> batch_sentences = [
|
||||
... "But what about second breakfast?",
|
||||
... "Don't think he knows about second breakfast, Pip.",
|
||||
... "What about elevensies?",
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
>>> encoded_input = tokenizer(batch_sentences, padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors="tf")
|
||||
>>> print(encoded_input)
|
||||
{'input_ids': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 9), dtype=int32, numpy=
|
||||
array([[101, 1252, 1184, 1164, 1248, 6462, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[101, 1790, 112, 189, 1341, 1119, 3520, 1164, 1248, 6462, 117, 21902, 1643, 119, 102],
|
||||
[101, 1327, 1164, 5450, 23434, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
|
||||
dtype=int32)>,
|
||||
'token_type_ids': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 9), dtype=int32, numpy=
|
||||
array([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]], dtype=int32)>,
|
||||
'attention_mask': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 9), dtype=int32, numpy=
|
||||
array([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]], dtype=int32)>}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Audio
|
||||
|
||||
Audioeingaben werden anders vorverarbeitet als Texteingaben, aber das Endziel bleibt dasselbe: numerische Sequenzen zu erstellen, die das Modell verstehen kann. Ein [feature extractor](main_classes/feature_extractor) dient dem ausdrücklichen Zweck, Merkmale aus Rohbild- oder Audiodaten zu extrahieren und in Tensoren zu konvertieren. Bevor Sie beginnen, installieren Sie 🤗 Datasets, um einen Audio-Datensatz zu laden, mit dem Sie experimentieren können:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install datasets
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie den [MInDS-14](https://huggingface.co/datasets/PolyAI/minds14) Datensatz (weitere Informationen zum Laden eines Datensatzes finden Sie im 🤗 [Datasets tutorial](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/load_hub.html)):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from datasets import load_dataset, Audio
|
||||
|
||||
>>> dataset = load_dataset("PolyAI/minds14", name="en-US", split="train")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Greifen Sie auf das erste Element der `audio`-Spalte zu, um einen Blick auf die Eingabe zu werfen. Durch den Aufruf der Spalte "audio" wird die Audiodatei automatisch geladen und neu gesampelt:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset[0]["audio"]
|
||||
{'array': array([ 0. , 0.00024414, -0.00024414, ..., -0.00024414,
|
||||
0. , 0. ], dtype=float32),
|
||||
'path': '/root/.cache/huggingface/datasets/downloads/extracted/f14948e0e84be638dd7943ac36518a4cf3324e8b7aa331c5ab11541518e9368c/en-US~JOINT_ACCOUNT/602ba55abb1e6d0fbce92065.wav',
|
||||
'sampling_rate': 8000}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dies gibt drei Elemente zurück:
|
||||
|
||||
* "array" ist das Sprachsignal, das als 1D-Array geladen - und möglicherweise neu gesampelt - wurde.
|
||||
* Pfad" zeigt auf den Speicherort der Audiodatei.
|
||||
* `sampling_rate` bezieht sich darauf, wie viele Datenpunkte im Sprachsignal pro Sekunde gemessen werden.
|
||||
|
||||
### Resample
|
||||
|
||||
Für dieses Tutorial werden Sie das Modell [Wav2Vec2](https://huggingface.co/facebook/wav2vec2-base) verwenden. Wie Sie aus der Modellkarte ersehen können, ist das Wav2Vec2-Modell auf 16kHz abgetastetes Sprachaudio vortrainiert. Es ist wichtig, dass die Abtastrate Ihrer Audiodaten mit der Abtastrate des Datensatzes übereinstimmt, der für das Pre-Training des Modells verwendet wurde. Wenn die Abtastrate Ihrer Daten nicht dieselbe ist, müssen Sie Ihre Audiodaten neu abtasten.
|
||||
|
||||
Der Datensatz [MInDS-14](https://huggingface.co/datasets/PolyAI/minds14) hat zum Beispiel eine Abtastrate von 8000 kHz. Um das Wav2Vec2-Modell mit diesem Datensatz verwenden zu können, müssen Sie die Abtastrate auf 16 kHz erhöhen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset = load_dataset("PolyAI/minds14", name="en-US", split="train")
|
||||
>>> dataset[0]["audio"]
|
||||
{'array': array([ 0. , 0.00024414, -0.00024414, ..., -0.00024414,
|
||||
0. , 0. ], dtype=float32),
|
||||
'path': '/root/.cache/huggingface/datasets/downloads/extracted/f14948e0e84be638dd7943ac36518a4cf3324e8b7aa331c5ab11541518e9368c/en-US~JOINT_ACCOUNT/602ba55abb1e6d0fbce92065.wav',
|
||||
'sampling_rate': 8000}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. Verwenden Sie die Methode [~datasets.Dataset.cast_column] von 🤗 Datasets, um die Abtastrate auf 16kHz zu erhöhen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset = dataset.cast_column("audio", Audio(sampling_rate=16_000))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Laden Sie die Audiodatei:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset[0]["audio"]
|
||||
{'array': array([ 2.3443763e-05, 2.1729663e-04, 2.2145823e-04, ...,
|
||||
3.8356509e-05, -7.3497440e-06, -2.1754686e-05], dtype=float32),
|
||||
'path': '/root/.cache/huggingface/datasets/downloads/extracted/f14948e0e84be638dd7943ac36518a4cf3324e8b7aa331c5ab11541518e9368c/en-US~JOINT_ACCOUNT/602ba55abb1e6d0fbce92065.wav',
|
||||
'sampling_rate': 16000}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wie Sie sehen können, ist die Abtastrate jetzt 16kHz!
|
||||
|
||||
### Merkmalsextraktor
|
||||
|
||||
Der nächste Schritt ist das Laden eines Merkmalsextraktors, um die Eingabe zu normalisieren und aufzufüllen. Beim Auffüllen von Textdaten wird für kürzere Sequenzen ein `0` hinzugefügt. Die gleiche Idee gilt für Audiodaten, und der Audio-Feature-Extraktor fügt eine `0` - interpretiert als Stille - zu `array` hinzu.
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie den Merkmalsextraktor mit [`AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> feature_extractor = AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained("facebook/wav2vec2-base")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Übergeben Sie das Audio-"Array" an den Feature-Extraktor. Wir empfehlen auch, das Argument `sampling_rate` im Feature Extractor hinzuzufügen, um eventuell auftretende stille Fehler besser zu beheben.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> audio_input = [dataset[0]["audio"]["array"]]
|
||||
>>> feature_extractor(audio_input, sampling_rate=16000)
|
||||
{'input_values': [array([ 3.8106556e-04, 2.7506407e-03, 2.8015103e-03, ...,
|
||||
5.6335266e-04, 4.6588284e-06, -1.7142107e-04], dtype=float32)]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Auffüllen und Kürzen
|
||||
|
||||
Genau wie beim Tokenizer können Sie variable Sequenzen in einem Stapel durch Auffüllen oder Abschneiden behandeln. Werfen Sie einen Blick auf die Sequenzlänge dieser beiden Audiobeispiele:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset[0]["audio"]["array"].shape
|
||||
(173398,)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> dataset[1]["audio"]["array"].shape
|
||||
(106496,)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wie Sie sehen können, hat das erste Beispiel eine längere Sequenz als das zweite Beispiel. Lassen Sie uns eine Funktion erstellen, die den Datensatz vorverarbeitet. Geben Sie eine maximale Länge der Probe an, und der Feature-Extraktor wird die Sequenzen entweder auffüllen oder abschneiden, damit sie dieser Länge entsprechen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def preprocess_function(examples):
|
||||
... audio_arrays = [x["array"] for x in examples["audio"]]
|
||||
... inputs = feature_extractor(
|
||||
... audio_arrays,
|
||||
... sampling_rate=16000,
|
||||
... padding=True,
|
||||
... max_length=100000,
|
||||
... truncation=True,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
... return inputs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenden Sie die Funktion auf die ersten paar Beispiele im Datensatz an:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> processed_dataset = preprocess_function(dataset[:5])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Schauen Sie sich nun noch einmal die verarbeiteten Beispiel-Längen an:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> processed_dataset["input_values"][0].shape
|
||||
(100000,)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> processed_dataset["input_values"][1].shape
|
||||
(100000,)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Die Länge der ersten beiden Beispiele entspricht nun der von Ihnen angegebenen Maximallänge.
|
||||
|
||||
## Bildverarbeitung
|
||||
|
||||
Ein Merkmalsextraktor wird auch verwendet, um Bilder für Bildverarbeitungsaufgaben zu verarbeiten. Auch hier besteht das Ziel darin, das Rohbild in eine Reihe von Tensoren als Eingabe zu konvertieren.
|
||||
|
||||
Laden wir den [food101](https://huggingface.co/datasets/food101) Datensatz für dieses Tutorial. Verwenden Sie den Parameter 🤗 Datasets `split`, um nur eine kleine Stichprobe aus dem Trainingssplit zu laden, da der Datensatz recht groß ist:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
>>> dataset = load_dataset("food101", split="train[:100]")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Als Nächstes sehen Sie sich das Bild mit dem Merkmal 🤗 Datensätze [Bild] (https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/package_reference/main_classes.html?highlight=image#datasets.Image) an:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset[0]["image"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Merkmalsextraktor
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie den Merkmalsextraktor mit [`AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> feature_extractor = AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained("google/vit-base-patch16-224")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Datenerweiterung
|
||||
|
||||
Bei Bildverarbeitungsaufgaben ist es üblich, den Bildern als Teil der Vorverarbeitung eine Art von Datenerweiterung hinzuzufügen. Sie können Erweiterungen mit jeder beliebigen Bibliothek hinzufügen, aber in diesem Tutorial werden Sie das Modul [`transforms`](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html) von torchvision verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Normalisieren Sie das Bild und verwenden Sie [`Compose`](https://pytorch.org/vision/master/generated/torchvision.transforms.Compose.html), um einige Transformationen - [`RandomResizedCrop`](https://pytorch.org/vision/main/generated/torchvision.transforms.RandomResizedCrop.html) und [`ColorJitter`](https://pytorch.org/vision/main/generated/torchvision.transforms.ColorJitter.html) - miteinander zu verknüpfen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from torchvision.transforms import Compose, Normalize, RandomResizedCrop, ColorJitter, ToTensor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> normalize = Normalize(mean=feature_extractor.image_mean, std=feature_extractor.image_std)
|
||||
>>> _transforms = Compose(
|
||||
... [RandomResizedCrop(feature_extractor.size), ColorJitter(brightness=0.5, hue=0.5), ToTensor(), normalize]
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Das Modell akzeptiert [`pixel_values`](model_doc/visionencoderdecoder#transformers.VisionEncoderDecoderModel.forward.pixel_values) als Eingabe. Dieser Wert wird vom Merkmalsextraktor erzeugt. Erstellen Sie eine Funktion, die `pixel_values` aus den Transformationen erzeugt:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def transforms(examples):
|
||||
... examples["pixel_values"] = [_transforms(image.convert("RGB")) for image in examples["image"]]
|
||||
... return examples
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Dann verwenden Sie 🤗 Datasets [`set_transform`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/process.html#format-transform), um die Transformationen im laufenden Betrieb anzuwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset.set_transform(transforms)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Wenn Sie nun auf das Bild zugreifen, werden Sie feststellen, dass der Feature Extractor die Modelleingabe "pixel_values" hinzugefügt hat:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset[0]["image"]
|
||||
{'image': <PIL.JpegImagePlugin.JpegImageFile image mode=RGB size=384x512 at 0x7F1A7B0630D0>,
|
||||
'label': 6,
|
||||
'pixel_values': tensor([[[ 0.0353, 0.0745, 0.1216, ..., -0.9922, -0.9922, -0.9922],
|
||||
[-0.0196, 0.0667, 0.1294, ..., -0.9765, -0.9843, -0.9922],
|
||||
[ 0.0196, 0.0824, 0.1137, ..., -0.9765, -0.9686, -0.8667],
|
||||
...,
|
||||
[ 0.0275, 0.0745, 0.0510, ..., -0.1137, -0.1216, -0.0824],
|
||||
[ 0.0667, 0.0824, 0.0667, ..., -0.0588, -0.0745, -0.0980],
|
||||
[ 0.0353, 0.0353, 0.0431, ..., -0.0039, -0.0039, -0.0588]],
|
||||
|
||||
[[ 0.2078, 0.2471, 0.2863, ..., -0.9451, -0.9373, -0.9451],
|
||||
[ 0.1608, 0.2471, 0.3098, ..., -0.9373, -0.9451, -0.9373],
|
||||
[ 0.2078, 0.2706, 0.3020, ..., -0.9608, -0.9373, -0.8275],
|
||||
...,
|
||||
[-0.0353, 0.0118, -0.0039, ..., -0.2392, -0.2471, -0.2078],
|
||||
[ 0.0196, 0.0353, 0.0196, ..., -0.1843, -0.2000, -0.2235],
|
||||
[-0.0118, -0.0039, -0.0039, ..., -0.0980, -0.0980, -0.1529]],
|
||||
|
||||
[[ 0.3961, 0.4431, 0.4980, ..., -0.9216, -0.9137, -0.9216],
|
||||
[ 0.3569, 0.4510, 0.5216, ..., -0.9059, -0.9137, -0.9137],
|
||||
[ 0.4118, 0.4745, 0.5216, ..., -0.9137, -0.8902, -0.7804],
|
||||
...,
|
||||
[-0.2314, -0.1922, -0.2078, ..., -0.4196, -0.4275, -0.3882],
|
||||
[-0.1843, -0.1686, -0.2000, ..., -0.3647, -0.3804, -0.4039],
|
||||
[-0.1922, -0.1922, -0.1922, ..., -0.2941, -0.2863, -0.3412]]])}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Hier sehen Sie, wie das Bild nach der Vorverarbeitung aussieht. Wie von den angewandten Transformationen zu erwarten, wurde das Bild willkürlich beschnitten und seine Farbeigenschaften sind anders.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import numpy as np
|
||||
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
|
||||
>>> img = dataset[0]["pixel_values"]
|
||||
>>> plt.imshow(img.permute(1, 2, 0))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Multimodal
|
||||
|
||||
Für multimodale Aufgaben werden Sie eine Kombination aus allem, was Sie bisher gelernt haben, verwenden und Ihre Fähigkeiten auf eine Aufgabe der automatischen Spracherkennung (ASR) anwenden. Dies bedeutet, dass Sie einen:
|
||||
|
||||
* Feature Extractor zur Vorverarbeitung der Audiodaten.
|
||||
* Tokenizer, um den Text zu verarbeiten.
|
||||
|
||||
Kehren wir zum [LJ Speech](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lj_speech) Datensatz zurück:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
>>> lj_speech = load_dataset("lj_speech", split="train")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Da Sie hauptsächlich an den Spalten "Audio" und "Text" interessiert sind, entfernen Sie die anderen Spalten:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> lj_speech = lj_speech.map(remove_columns=["file", "id", "normalized_text"])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Schauen Sie sich nun die Spalten "Audio" und "Text" an:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> lj_speech[0]["audio"]
|
||||
{'array': array([-7.3242188e-04, -7.6293945e-04, -6.4086914e-04, ...,
|
||||
7.3242188e-04, 2.1362305e-04, 6.1035156e-05], dtype=float32),
|
||||
'path': '/root/.cache/huggingface/datasets/downloads/extracted/917ece08c95cf0c4115e45294e3cd0dee724a1165b7fc11798369308a465bd26/LJSpeech-1.1/wavs/LJ001-0001.wav',
|
||||
'sampling_rate': 22050}
|
||||
|
||||
>>> lj_speech[0]["text"]
|
||||
'Printing, in the only sense with which we are at present concerned, differs from most if not from all the arts and crafts represented in the Exhibition'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Erinnern Sie sich an den früheren Abschnitt über die Verarbeitung von Audiodaten: Sie sollten immer die Abtastrate Ihrer Audiodaten [resample](preprocessing#audio), damit sie mit der Abtastrate des Datensatzes übereinstimmt, der für das Vortraining eines Modells verwendet wird:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> lj_speech = lj_speech.cast_column("audio", Audio(sampling_rate=16_000))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Prozessor
|
||||
|
||||
Ein Processor kombiniert einen Feature-Extraktor und einen Tokenizer. Laden Sie einen Processor mit [`AutoProcessor.from_pretrained]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/wav2vec2-base-960h")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. Erstellen Sie eine Funktion, die die Audiodaten zu `input_values` verarbeitet und den Text zu `labels` tokenisiert. Dies sind Ihre Eingaben für das Modell:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def prepare_dataset(example):
|
||||
... audio = example["audio"]
|
||||
|
||||
... example.update(processor(audio=audio["array"], text=example["text"], sampling_rate=16000))
|
||||
|
||||
... return example
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Wenden Sie die Funktion "prepare_dataset" auf ein Beispiel an:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> prepare_dataset(lj_speech[0])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Beachten Sie, dass der Processor `input_values` und `labels` hinzugefügt hat. Auch die Abtastrate wurde korrekt auf 16kHz heruntergerechnet.
|
||||
|
||||
Toll, Sie sollten jetzt in der Lage sein, Daten für jede Modalität vorzuverarbeiten und sogar verschiedene Modalitäten zu kombinieren! Im nächsten Kurs lernen Sie, wie Sie ein Modell mit Ihren neu aufbereiteten Daten feinabstimmen können.
|
||||
@ -1,502 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Vorverarbeiten
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Bevor Sie Ihre Daten in einem Modell verwenden können, müssen die Daten in ein für das Modell akzeptables Format gebracht werden. Ein Modell versteht keine Rohtexte, Bilder oder Audiodaten. Diese Eingaben müssen in Zahlen umgewandelt und zu Tensoren zusammengesetzt werden. In dieser Anleitung werden Sie:
|
||||
|
||||
* Textdaten mit einem Tokenizer vorverarbeiten.
|
||||
* Bild- oder Audiodaten mit einem Feature Extractor vorverarbeiten.
|
||||
* Daten für eine multimodale Aufgabe mit einem Prozessor vorverarbeiten.
|
||||
|
||||
## NLP
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="Yffk5aydLzg"/>
|
||||
|
||||
Das wichtigste Werkzeug zur Verarbeitung von Textdaten ist ein [Tokenizer](main_classes/tokenizer). Ein Tokenizer zerlegt Text zunächst nach einer Reihe von Regeln in *Token*. Die Token werden in Zahlen umgewandelt, die zum Aufbau von Tensoren als Eingabe für ein Modell verwendet werden. Alle zusätzlichen Eingaben, die ein Modell benötigt, werden ebenfalls vom Tokenizer hinzugefügt.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie ein vortrainiertes Modell verwenden möchten, ist es wichtig, den zugehörigen vortrainierten Tokenizer zu verwenden. Dadurch wird sichergestellt, dass der Text auf die gleiche Weise aufgeteilt wird wie das Pretraining-Korpus und die gleichen entsprechenden Token-zu-Index (in der Regel als *vocab* bezeichnet) während des Pretrainings verwendet werden.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie einen vortrainierten Tokenizer mit der Klasse [AutoTokenizer], um schnell loszulegen. Damit wird das *vocab* heruntergeladen, das verwendet wird, wenn ein Modell vortrainiert wird.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tokenize
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie einen vortrainierten Tokenizer mit [`AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dann übergeben Sie Ihren Satz an den Tokenizer:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> encoded_input = tokenizer("Do not meddle in the affairs of wizards, for they are subtle and quick to anger.")
|
||||
>>> print(encoded_input)
|
||||
{'input_ids': [101, 2079, 2025, 19960, 10362, 1999, 1996, 3821, 1997, 16657, 1010, 2005, 2027, 2024, 11259, 1998, 4248, 2000, 4963, 1012, 102],
|
||||
'token_type_ids': [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
'attention_mask': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Der Tokenizer gibt ein Wörterbuch mit drei wichtigen Elementen zurück:
|
||||
|
||||
* [input_ids](glossary#input-ids) sind die Indizes, die den einzelnen Token im Satz entsprechen.
|
||||
* [attention_mask](glossary#attention-mask) gibt an, ob ein Token beachtet werden soll oder nicht.
|
||||
* [token_type_ids](glossary#token-type-ids) gibt an, zu welcher Sequenz ein Token gehört, wenn es mehr als eine Sequenz gibt.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können die `input_ids` dekodieren, um die ursprüngliche Eingabe zurückzugeben:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.decode(encoded_input["input_ids"])
|
||||
'[CLS] Do not meddle in the affairs of wizards, for they are subtle and quick to anger. [SEP]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wie Sie sehen können, hat der Tokenisierer zwei spezielle Token - `CLS` und `SEP` (Klassifikator und Separator) - zum Satz hinzugefügt. Nicht alle Modelle benötigen
|
||||
spezielle Token, aber wenn dies der Fall ist, fügt der Tokenisierer sie automatisch für Sie hinzu.
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie mehrere Sätze verarbeiten wollen, übergeben Sie die Sätze als Liste an den Tokenizer:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> batch_sentences = [
|
||||
... "But what about second breakfast?",
|
||||
... "Don't think he knows about second breakfast, Pip.",
|
||||
... "What about elevensies?",
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
>>> encoded_inputs = tokenizer(batch_sentences)
|
||||
>>> print(encoded_inputs)
|
||||
{'input_ids': [[101, 1252, 1184, 1164, 1248, 6462, 136, 102],
|
||||
[101, 1790, 112, 189, 1341, 1119, 3520, 1164, 1248, 6462, 117, 21902, 1643, 119, 102],
|
||||
[101, 1327, 1164, 5450, 23434, 136, 102]],
|
||||
'token_type_ids': [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
|
||||
'attention_mask': [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Pad
|
||||
|
||||
Dies bringt uns zu einem wichtigen Thema. Wenn Sie einen Haufen von Sätzen verarbeiten, sind diese nicht immer gleich lang. Das ist ein Problem, weil Tensoren, die Eingabe für das Modell, eine einheitliche Form haben müssen. Padding ist eine Strategie, die sicherstellt, dass Tensoren rechteckig sind, indem ein spezielles *Padding-Token* zu Sätzen mit weniger Token hinzugefügt wird.
|
||||
|
||||
Setzen Sie den Parameter "padding" auf "true", um die kürzeren Sequenzen im Stapel so aufzufüllen, dass sie der längsten Sequenz entsprechen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> batch_sentences = [
|
||||
... "But what about second breakfast?",
|
||||
... "Don't think he knows about second breakfast, Pip.",
|
||||
... "What about elevensies?",
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
>>> encoded_input = tokenizer(batch_sentences, padding=True)
|
||||
>>> print(encoded_input)
|
||||
{'input_ids': [[101, 1252, 1184, 1164, 1248, 6462, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[101, 1790, 112, 189, 1341, 1119, 3520, 1164, 1248, 6462, 117, 21902, 1643, 119, 102],
|
||||
[101, 1327, 1164, 5450, 23434, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
|
||||
'token_type_ids': [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
|
||||
'attention_mask': [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Beachten Sie, dass der Tokenizer den ersten und den dritten Satz mit einer "0" aufgefüllt hat, weil sie kürzer sind!
|
||||
|
||||
### Kürzung
|
||||
|
||||
Auf der anderen Seite des Spektrums kann es vorkommen, dass eine Sequenz zu lang für ein Modell ist. In diesem Fall müssen Sie die Sequenz auf eine kürzere Länge kürzen.
|
||||
|
||||
Setzen Sie den Parameter "truncation" auf "true", um eine Sequenz auf die vom Modell akzeptierte Höchstlänge zu kürzen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> batch_sentences = [
|
||||
... "But what about second breakfast?",
|
||||
... "Don't think he knows about second breakfast, Pip.",
|
||||
... "What about elevensies?",
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
>>> encoded_input = tokenizer(batch_sentences, padding=True, truncation=True)
|
||||
>>> print(encoded_input)
|
||||
{'input_ids': [[101, 1252, 1184, 1164, 1248, 6462, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[101, 1790, 112, 189, 1341, 1119, 3520, 1164, 1248, 6462, 117, 21902, 1643, 119, 102],
|
||||
[101, 1327, 1164, 5450, 23434, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
|
||||
'token_type_ids': [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
|
||||
'attention_mask': [[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Tensoren erstellen
|
||||
|
||||
Schließlich möchten Sie, dass der Tokenizer die tatsächlichen Tensoren zurückgibt, die dem Modell zugeführt werden.
|
||||
|
||||
Setzen Sie den Parameter `return_tensors` entweder auf `pt` für PyTorch, oder `tf` für TensorFlow:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> batch_sentences = [
|
||||
... "But what about second breakfast?",
|
||||
... "Don't think he knows about second breakfast, Pip.",
|
||||
... "What about elevensies?",
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
>>> encoded_input = tokenizer(batch_sentences, padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> print(encoded_input)
|
||||
{'input_ids': tensor([[101, 1252, 1184, 1164, 1248, 6462, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[101, 1790, 112, 189, 1341, 1119, 3520, 1164, 1248, 6462, 117, 21902, 1643, 119, 102],
|
||||
[101, 1327, 1164, 5450, 23434, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]),
|
||||
'token_type_ids': tensor([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]),
|
||||
'attention_mask': tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> batch_sentences = [
|
||||
... "But what about second breakfast?",
|
||||
... "Don't think he knows about second breakfast, Pip.",
|
||||
... "What about elevensies?",
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
>>> encoded_input = tokenizer(batch_sentences, padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors="tf")
|
||||
>>> print(encoded_input)
|
||||
{'input_ids': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 9), dtype=int32, numpy=
|
||||
array([[101, 1252, 1184, 1164, 1248, 6462, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[101, 1790, 112, 189, 1341, 1119, 3520, 1164, 1248, 6462, 117, 21902, 1643, 119, 102],
|
||||
[101, 1327, 1164, 5450, 23434, 136, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
|
||||
dtype=int32)>,
|
||||
'token_type_ids': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 9), dtype=int32, numpy=
|
||||
array([[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]], dtype=int32)>,
|
||||
'attention_mask': <tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 9), dtype=int32, numpy=
|
||||
array([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
|
||||
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]], dtype=int32)>}
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Audio
|
||||
|
||||
Audioeingaben werden anders vorverarbeitet als Texteingaben, aber das Endziel bleibt dasselbe: numerische Sequenzen zu erstellen, die das Modell verstehen kann. Ein [feature extractor](main_classes/feature_extractor) dient dem ausdrücklichen Zweck, Merkmale aus Rohbild- oder Audiodaten zu extrahieren und in Tensoren zu konvertieren. Bevor Sie beginnen, installieren Sie 🤗 Datasets, um einen Audio-Datensatz zu laden, mit dem Sie experimentieren können:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install datasets
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie den [MInDS-14](https://huggingface.co/datasets/PolyAI/minds14) Datensatz (weitere Informationen zum Laden eines Datensatzes finden Sie im 🤗 [Datasets tutorial](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/load_hub.html)):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from datasets import load_dataset, Audio
|
||||
|
||||
>>> dataset = load_dataset("PolyAI/minds14", name="en-US", split="train")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Greifen Sie auf das erste Element der `audio`-Spalte zu, um einen Blick auf die Eingabe zu werfen. Durch den Aufruf der Spalte "audio" wird die Audiodatei automatisch geladen und neu gesampelt:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset[0]["audio"]
|
||||
{'array': array([ 0. , 0.00024414, -0.00024414, ..., -0.00024414,
|
||||
0. , 0. ], dtype=float32),
|
||||
'path': '/root/.cache/huggingface/datasets/downloads/extracted/f14948e0e84be638dd7943ac36518a4cf3324e8b7aa331c5ab11541518e9368c/en-US~JOINT_ACCOUNT/602ba55abb1e6d0fbce92065.wav',
|
||||
'sampling_rate': 8000}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Dies gibt drei Elemente zurück:
|
||||
|
||||
* "array" ist das Sprachsignal, das als 1D-Array geladen - und möglicherweise neu gesampelt - wurde.
|
||||
* Pfad" zeigt auf den Speicherort der Audiodatei.
|
||||
* `sampling_rate` bezieht sich darauf, wie viele Datenpunkte im Sprachsignal pro Sekunde gemessen werden.
|
||||
|
||||
### Resample
|
||||
|
||||
Für dieses Tutorial werden Sie das Modell [Wav2Vec2](https://huggingface.co/facebook/wav2vec2-base) verwenden. Wie Sie aus der Modellkarte ersehen können, ist das Wav2Vec2-Modell auf 16kHz abgetastetes Sprachaudio vortrainiert. Es ist wichtig, dass die Abtastrate Ihrer Audiodaten mit der Abtastrate des Datensatzes übereinstimmt, der für das Pre-Training des Modells verwendet wurde. Wenn die Abtastrate Ihrer Daten nicht dieselbe ist, müssen Sie Ihre Audiodaten neu abtasten.
|
||||
|
||||
Der Datensatz [MInDS-14](https://huggingface.co/datasets/PolyAI/minds14) hat zum Beispiel eine Abtastrate von 8000 kHz. Um das Wav2Vec2-Modell mit diesem Datensatz verwenden zu können, müssen Sie die Abtastrate auf 16 kHz erhöhen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset = load_dataset("PolyAI/minds14", name="en-US", split="train")
|
||||
>>> dataset[0]["audio"]
|
||||
{'array': array([ 0. , 0.00024414, -0.00024414, ..., -0.00024414,
|
||||
0. , 0. ], dtype=float32),
|
||||
'path': '/root/.cache/huggingface/datasets/downloads/extracted/f14948e0e84be638dd7943ac36518a4cf3324e8b7aa331c5ab11541518e9368c/en-US~JOINT_ACCOUNT/602ba55abb1e6d0fbce92065.wav',
|
||||
'sampling_rate': 8000}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. Verwenden Sie die Methode [~datasets.Dataset.cast_column] von 🤗 Datasets, um die Abtastrate auf 16kHz zu erhöhen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset = dataset.cast_column("audio", Audio(sampling_rate=16_000))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Laden Sie die Audiodatei:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset[0]["audio"]
|
||||
{'array': array([ 2.3443763e-05, 2.1729663e-04, 2.2145823e-04, ...,
|
||||
3.8356509e-05, -7.3497440e-06, -2.1754686e-05], dtype=float32),
|
||||
'path': '/root/.cache/huggingface/datasets/downloads/extracted/f14948e0e84be638dd7943ac36518a4cf3324e8b7aa331c5ab11541518e9368c/en-US~JOINT_ACCOUNT/602ba55abb1e6d0fbce92065.wav',
|
||||
'sampling_rate': 16000}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wie Sie sehen können, ist die Abtastrate jetzt 16kHz!
|
||||
|
||||
### Merkmalsextraktor
|
||||
|
||||
Der nächste Schritt ist das Laden eines Merkmalsextraktors, um die Eingabe zu normalisieren und aufzufüllen. Beim Auffüllen von Textdaten wird für kürzere Sequenzen ein `0` hinzugefügt. Die gleiche Idee gilt für Audiodaten, und der Audio-Feature-Extraktor fügt eine `0` - interpretiert als Stille - zu `array` hinzu.
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie den Merkmalsextraktor mit [`AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> feature_extractor = AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained("facebook/wav2vec2-base")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Übergeben Sie das Audio-"Array" an den Feature-Extraktor. Wir empfehlen auch, das Argument `sampling_rate` im Feature Extractor hinzuzufügen, um eventuell auftretende stille Fehler besser zu beheben.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> audio_input = [dataset[0]["audio"]["array"]]
|
||||
>>> feature_extractor(audio_input, sampling_rate=16000)
|
||||
{'input_values': [array([ 3.8106556e-04, 2.7506407e-03, 2.8015103e-03, ...,
|
||||
5.6335266e-04, 4.6588284e-06, -1.7142107e-04], dtype=float32)]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Auffüllen und Kürzen
|
||||
|
||||
Genau wie beim Tokenizer können Sie variable Sequenzen in einem Stapel durch Auffüllen oder Abschneiden behandeln. Werfen Sie einen Blick auf die Sequenzlänge dieser beiden Audiobeispiele:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset[0]["audio"]["array"].shape
|
||||
(173398,)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> dataset[1]["audio"]["array"].shape
|
||||
(106496,)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wie Sie sehen können, hat das erste Beispiel eine längere Sequenz als das zweite Beispiel. Lassen Sie uns eine Funktion erstellen, die den Datensatz vorverarbeitet. Geben Sie eine maximale Länge der Probe an, und der Feature-Extraktor wird die Sequenzen entweder auffüllen oder abschneiden, damit sie dieser Länge entsprechen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def preprocess_function(examples):
|
||||
... audio_arrays = [x["array"] for x in examples["audio"]]
|
||||
... inputs = feature_extractor(
|
||||
... audio_arrays,
|
||||
... sampling_rate=16000,
|
||||
... padding=True,
|
||||
... max_length=100000,
|
||||
... truncation=True,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
... return inputs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenden Sie die Funktion auf die ersten paar Beispiele im Datensatz an:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> processed_dataset = preprocess_function(dataset[:5])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Schauen Sie sich nun noch einmal die verarbeiteten Beispiel-Längen an:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> processed_dataset["input_values"][0].shape
|
||||
(100000,)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> processed_dataset["input_values"][1].shape
|
||||
(100000,)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Die Länge der ersten beiden Beispiele entspricht nun der von Ihnen angegebenen Maximallänge.
|
||||
|
||||
## Bildverarbeitung
|
||||
|
||||
Ein Merkmalsextraktor wird auch verwendet, um Bilder für Bildverarbeitungsaufgaben zu verarbeiten. Auch hier besteht das Ziel darin, das Rohbild in eine Reihe von Tensoren als Eingabe zu konvertieren.
|
||||
|
||||
Laden wir den [food101](https://huggingface.co/datasets/food101) Datensatz für dieses Tutorial. Verwenden Sie den Parameter 🤗 Datasets `split`, um nur eine kleine Stichprobe aus dem Trainingssplit zu laden, da der Datensatz recht groß ist:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
>>> dataset = load_dataset("food101", split="train[:100]")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Als Nächstes sehen Sie sich das Bild mit dem Merkmal 🤗 Datensätze [Bild] (https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/package_reference/main_classes.html?highlight=image#datasets.Image) an:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset[0]["image"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Merkmalsextraktor
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie den Merkmalsextraktor mit [`AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> feature_extractor = AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained("google/vit-base-patch16-224")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Datenerweiterung
|
||||
|
||||
Bei Bildverarbeitungsaufgaben ist es üblich, den Bildern als Teil der Vorverarbeitung eine Art von Datenerweiterung hinzuzufügen. Sie können Erweiterungen mit jeder beliebigen Bibliothek hinzufügen, aber in diesem Tutorial werden Sie das Modul [`transforms`](https://pytorch.org/vision/stable/transforms.html) von torchvision verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Normalisieren Sie das Bild und verwenden Sie [`Compose`](https://pytorch.org/vision/master/generated/torchvision.transforms.Compose.html), um einige Transformationen - [`RandomResizedCrop`](https://pytorch.org/vision/main/generated/torchvision.transforms.RandomResizedCrop.html) und [`ColorJitter`](https://pytorch.org/vision/main/generated/torchvision.transforms.ColorJitter.html) - miteinander zu verknüpfen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from torchvision.transforms import Compose, Normalize, RandomResizedCrop, ColorJitter, ToTensor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> normalize = Normalize(mean=feature_extractor.image_mean, std=feature_extractor.image_std)
|
||||
>>> _transforms = Compose(
|
||||
... [RandomResizedCrop(feature_extractor.size), ColorJitter(brightness=0.5, hue=0.5), ToTensor(), normalize]
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Das Modell akzeptiert [`pixel_values`](model_doc/visionencoderdecoder#transformers.VisionEncoderDecoderModel.forward.pixel_values) als Eingabe. Dieser Wert wird vom Merkmalsextraktor erzeugt. Erstellen Sie eine Funktion, die `pixel_values` aus den Transformationen erzeugt:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def transforms(examples):
|
||||
... examples["pixel_values"] = [_transforms(image.convert("RGB")) for image in examples["image"]]
|
||||
... return examples
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Dann verwenden Sie 🤗 Datasets [`set_transform`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/process.html#format-transform), um die Transformationen im laufenden Betrieb anzuwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset.set_transform(transforms)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Wenn Sie nun auf das Bild zugreifen, werden Sie feststellen, dass der Feature Extractor die Modelleingabe "pixel_values" hinzugefügt hat:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset[0]["image"]
|
||||
{'image': <PIL.JpegImagePlugin.JpegImageFile image mode=RGB size=384x512 at 0x7F1A7B0630D0>,
|
||||
'label': 6,
|
||||
'pixel_values': tensor([[[ 0.0353, 0.0745, 0.1216, ..., -0.9922, -0.9922, -0.9922],
|
||||
[-0.0196, 0.0667, 0.1294, ..., -0.9765, -0.9843, -0.9922],
|
||||
[ 0.0196, 0.0824, 0.1137, ..., -0.9765, -0.9686, -0.8667],
|
||||
...,
|
||||
[ 0.0275, 0.0745, 0.0510, ..., -0.1137, -0.1216, -0.0824],
|
||||
[ 0.0667, 0.0824, 0.0667, ..., -0.0588, -0.0745, -0.0980],
|
||||
[ 0.0353, 0.0353, 0.0431, ..., -0.0039, -0.0039, -0.0588]],
|
||||
|
||||
[[ 0.2078, 0.2471, 0.2863, ..., -0.9451, -0.9373, -0.9451],
|
||||
[ 0.1608, 0.2471, 0.3098, ..., -0.9373, -0.9451, -0.9373],
|
||||
[ 0.2078, 0.2706, 0.3020, ..., -0.9608, -0.9373, -0.8275],
|
||||
...,
|
||||
[-0.0353, 0.0118, -0.0039, ..., -0.2392, -0.2471, -0.2078],
|
||||
[ 0.0196, 0.0353, 0.0196, ..., -0.1843, -0.2000, -0.2235],
|
||||
[-0.0118, -0.0039, -0.0039, ..., -0.0980, -0.0980, -0.1529]],
|
||||
|
||||
[[ 0.3961, 0.4431, 0.4980, ..., -0.9216, -0.9137, -0.9216],
|
||||
[ 0.3569, 0.4510, 0.5216, ..., -0.9059, -0.9137, -0.9137],
|
||||
[ 0.4118, 0.4745, 0.5216, ..., -0.9137, -0.8902, -0.7804],
|
||||
...,
|
||||
[-0.2314, -0.1922, -0.2078, ..., -0.4196, -0.4275, -0.3882],
|
||||
[-0.1843, -0.1686, -0.2000, ..., -0.3647, -0.3804, -0.4039],
|
||||
[-0.1922, -0.1922, -0.1922, ..., -0.2941, -0.2863, -0.3412]]])}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Hier sehen Sie, wie das Bild nach der Vorverarbeitung aussieht. Wie von den angewandten Transformationen zu erwarten, wurde das Bild willkürlich beschnitten und seine Farbeigenschaften sind anders.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import numpy as np
|
||||
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
|
||||
|
||||
>>> img = dataset[0]["pixel_values"]
|
||||
>>> plt.imshow(img.permute(1, 2, 0))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Multimodal
|
||||
|
||||
Für multimodale Aufgaben werden Sie eine Kombination aus allem, was Sie bisher gelernt haben, verwenden und Ihre Fähigkeiten auf eine Aufgabe der automatischen Spracherkennung (ASR) anwenden. Dies bedeutet, dass Sie einen:
|
||||
|
||||
* Feature Extractor zur Vorverarbeitung der Audiodaten.
|
||||
* Tokenizer, um den Text zu verarbeiten.
|
||||
|
||||
Kehren wir zum [LJ Speech](https://huggingface.co/datasets/lj_speech) Datensatz zurück:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
>>> lj_speech = load_dataset("lj_speech", split="train")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Da Sie hauptsächlich an den Spalten "Audio" und "Text" interessiert sind, entfernen Sie die anderen Spalten:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> lj_speech = lj_speech.map(remove_columns=["file", "id", "normalized_text"])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Schauen Sie sich nun die Spalten "Audio" und "Text" an:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> lj_speech[0]["audio"]
|
||||
{'array': array([-7.3242188e-04, -7.6293945e-04, -6.4086914e-04, ...,
|
||||
7.3242188e-04, 2.1362305e-04, 6.1035156e-05], dtype=float32),
|
||||
'path': '/root/.cache/huggingface/datasets/downloads/extracted/917ece08c95cf0c4115e45294e3cd0dee724a1165b7fc11798369308a465bd26/LJSpeech-1.1/wavs/LJ001-0001.wav',
|
||||
'sampling_rate': 22050}
|
||||
|
||||
>>> lj_speech[0]["text"]
|
||||
'Printing, in the only sense with which we are at present concerned, differs from most if not from all the arts and crafts represented in the Exhibition'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Erinnern Sie sich an den früheren Abschnitt über die Verarbeitung von Audiodaten: Sie sollten immer die Abtastrate Ihrer Audiodaten [resample](preprocessing#audio), damit sie mit der Abtastrate des Datensatzes übereinstimmt, der für das Vortraining eines Modells verwendet wird:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> lj_speech = lj_speech.cast_column("audio", Audio(sampling_rate=16_000))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Prozessor
|
||||
|
||||
Ein Processor kombiniert einen Feature-Extraktor und einen Tokenizer. Laden Sie einen Processor mit [`AutoProcessor.from_pretrained]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/wav2vec2-base-960h")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. Erstellen Sie eine Funktion, die die Audiodaten zu `input_values` verarbeitet und den Text zu `labels` tokenisiert. Dies sind Ihre Eingaben für das Modell:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def prepare_dataset(example):
|
||||
... audio = example["audio"]
|
||||
|
||||
... example.update(processor(audio=audio["array"], text=example["text"], sampling_rate=16000))
|
||||
|
||||
... return example
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Wenden Sie die Funktion "prepare_dataset" auf ein Beispiel an:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> prepare_dataset(lj_speech[0])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Beachten Sie, dass der Processor `input_values` und `labels` hinzugefügt hat. Auch die Abtastrate wurde korrekt auf 16kHz heruntergerechnet.
|
||||
|
||||
Toll, Sie sollten jetzt in der Lage sein, Daten für jede Modalität vorzuverarbeiten und sogar verschiedene Modalitäten zu kombinieren! Im nächsten Kurs lernen Sie, wie Sie ein Modell mit Ihren neu aufbereiteten Daten feinabstimmen können.
|
||||
432
docs/source/de/quicktour.md
Normal file
432
docs/source/de/quicktour.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,432 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Schnellstart
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Mit 🤗 Transformers können Sie sofort loslegen! Verwenden Sie die [`pipeline`] für schnelle Inferenz und laden Sie schnell ein vortrainiertes Modell und einen Tokenizer mit einer [AutoClass](./model_doc/auto), um Ihre Text-, Bild- oder Audioaufgabe zu lösen.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Alle in der Dokumentation vorgestellten Codebeispiele haben oben links einen Umschalter für PyTorch und TensorFlow. Wenn
|
||||
nicht, wird erwartet, dass der Code für beide Backends ohne Änderungen funktioniert.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[`pipeline`] ist der einfachste Weg, ein vortrainiertes Modell für eine bestimmte Aufgabe zu verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="tiZFewofSLM"/>
|
||||
|
||||
Die [`pipeline`] unterstützt viele gängige Aufgaben:
|
||||
|
||||
**Text**:
|
||||
* Stimmungsanalyse: Klassifizierung der Polarität eines gegebenen Textes.
|
||||
* Textgenerierung (auf Englisch): Generierung von Text aus einer gegebenen Eingabe.
|
||||
* Name-Entity-Recognition (NER): Kennzeichnung jedes Worts mit der Entität, die es repräsentiert (Person, Datum, Ort usw.).
|
||||
* Beantwortung von Fragen: Extrahieren der Antwort aus dem Kontext, wenn ein gewisser Kontext und eine Frage gegeben sind.
|
||||
* Fill-mask: Ausfüllen von Lücken in einem Text mit maskierten Wörtern.
|
||||
* Zusammenfassung: Erstellung einer Zusammenfassung einer langen Text- oder Dokumentensequenz.
|
||||
* Übersetzung: Übersetzen eines Textes in eine andere Sprache.
|
||||
* Merkmalsextraktion: Erstellen einer Tensordarstellung des Textes.
|
||||
|
||||
**Bild**:
|
||||
* Bildklassifizierung: Klassifizierung eines Bildes.
|
||||
* Bildsegmentierung: Klassifizierung jedes Pixels in einem Bild.
|
||||
* Objekterkennung: Erkennen von Objekten innerhalb eines Bildes.
|
||||
|
||||
**Audio**:
|
||||
* Audioklassifizierung: Zuweisung eines Labels zu einem bestimmten Audiosegment.
|
||||
* Automatische Spracherkennung (ASR): Transkription von Audiodaten in Text.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Für mehr Details über die [`pipeline`] und assoziierte Aufgaben, schauen Sie in die Dokumentation [hier](./main_classes/pipelines).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Verwendung der Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
Im folgenden Beispiel werden Sie die [`pipeline`] für die Stimmungsanalyse verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
Installieren Sie die folgenden Abhängigkeiten, falls Sie dies nicht bereits getan haben:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install torch
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install tensorflow
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
Importieren sie die [`pipeline`] und spezifizieren sie die Aufgabe, welche sie lösen möchten:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> classifier = pipeline("sentiment-analysis")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Die Pipeline lädt ein standardmäßiges [vortrainiertes Modell] (https://huggingface.co/distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english) und einen Tokenizer für die Stimmungs-Analyse herunter und speichert sie. Jetzt können Sie den "Klassifikator" auf Ihren Zieltext anwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> classifier("We are very happy to show you the 🤗 Transformers library.")
|
||||
[{'label': 'POSITIVE', 'score': 0.9998}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more than one sentence, pass a list of sentences to the [`pipeline`] which returns a list of dictionaries:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> results = classifier(["We are very happy to show you the 🤗 Transformers library.", "We hope you don't hate it."])
|
||||
>>> for result in results:
|
||||
... print(f"label: {result['label']}, with score: {round(result['score'], 4)}")
|
||||
label: POSITIVE, with score: 0.9998
|
||||
label: NEGATIVE, with score: 0.5309
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Die [`pipeline`] kann auch über einen ganzen Datensatz iterieren. Starten wir mit der Installation der [🤗 Datasets](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/) Bibliothek:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install datasets
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen wir eine [`pipeline`] mit der Aufgabe die wir lösen und dem Modell welches wir nutzen möchten.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> speech_recognizer = pipeline("automatic-speech-recognition", model="facebook/wav2vec2-base-960h")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Als nächstes laden wir den Datensatz (siehe 🤗 Datasets [Quick Start](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/quickstart.html) für mehr Details) welches wir nutzen möchten. Zum Beispiel laden wir den [MInDS-14](https://huggingface.co/datasets/PolyAI/minds14) Datensatz:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from datasets import load_dataset, Audio
|
||||
|
||||
>>> dataset = load_dataset("PolyAI/minds14", name="en-US", split="train") # doctest: +IGNORE_RESULT
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wir müssen sicherstellen, dass die Abtastrate des Datensatzes der Abtastrate entspricht, mit der `facebook/wav2vec2-base-960h` trainiert wurde.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset = dataset.cast_column("audio", Audio(sampling_rate=speech_recognizer.feature_extractor.sampling_rate))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Audiodateien werden automatisch geladen und neu abgetastet, wenn die Spalte "audio" aufgerufen wird.
|
||||
Extrahieren wir die rohen Wellenform-Arrays der ersten 4 Beispiele und übergeben wir sie als Liste an die Pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> result = speech_recognizer(dataset[:4]["audio"])
|
||||
>>> print([d["text"] for d in result])
|
||||
['I WOULD LIKE TO SET UP A JOINT ACCOUNT WITH MY PARTNER HOW DO I PROCEED WITH DOING THAT', "FODING HOW I'D SET UP A JOIN TO HET WITH MY WIFE AND WHERE THE AP MIGHT BE", "I I'D LIKE TOY SET UP A JOINT ACCOUNT WITH MY PARTNER I'M NOT SEEING THE OPTION TO DO IT ON THE AP SO I CALLED IN TO GET SOME HELP CAN I JUST DO IT OVER THE PHONE WITH YOU AND GIVE YOU THE INFORMATION OR SHOULD I DO IT IN THE AP AND I'M MISSING SOMETHING UQUETTE HAD PREFERRED TO JUST DO IT OVER THE PHONE OF POSSIBLE THINGS", 'HOW DO I THURN A JOIN A COUNT']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Bei einem größeren Datensatz mit vielen Eingaben (wie bei Sprache oder Bildverarbeitung) sollten Sie einen Generator anstelle einer Liste übergeben, der alle Eingaben in den Speicher lädt. Weitere Informationen finden Sie in der [Pipeline-Dokumentation](./main_classes/pipelines).
|
||||
|
||||
### Ein anderes Modell und einen anderen Tokenizer in der Pipeline verwenden
|
||||
|
||||
Die [`pipeline`] kann jedes Modell aus dem [Model Hub] (https://huggingface.co/models) verwenden, wodurch es einfach ist, die [`pipeline`] für andere Anwendungsfälle anzupassen. Wenn Sie beispielsweise ein Modell wünschen, das französischen Text verarbeiten kann, verwenden Sie die Tags im Model Hub, um nach einem geeigneten Modell zu filtern. Das oberste gefilterte Ergebnis liefert ein mehrsprachiges [BERT-Modell](https://huggingface.co/nlptown/bert-base-multilingual-uncased-sentiment), das auf die Stimmungsanalyse abgestimmt ist. Großartig, verwenden wir dieses Modell!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model_name = "nlptown/bert-base-multilingual-uncased-sentiment"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Use the [`AutoModelForSequenceClassification`] and [`AutoTokenizer`] to load the pretrained model and it's associated tokenizer (more on an `AutoClass` below):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Use the [`TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification`] and [`AutoTokenizer`] to load the pretrained model and it's associated tokenizer (more on an `TFAutoClass` below):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
Dann können Sie das Modell und den Tokenizer in der [`pipeline`] angeben und den `Klassifikator` auf Ihren Zieltext anwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> classifier = pipeline("sentiment-analysis", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
>>> classifier("Nous sommes très heureux de vous présenter la bibliothèque 🤗 Transformers.")
|
||||
[{'label': '5 stars', 'score': 0.7273}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie kein Modell für Ihren Anwendungsfall finden können, müssen Sie ein vortrainiertes Modell auf Ihren Daten feinabstimmen. Schauen Sie sich unser [Feinabstimmungs-Tutorial](./training) an, um zu erfahren, wie das geht. Und schließlich, nachdem Sie Ihr trainiertes Modell verfeinert haben, sollten Sie es mit der Community im Model Hub teilen (siehe Tutorial [hier](./model_sharing)), um NLP für alle zu demokratisieren! 🤗
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoClass
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="AhChOFRegn4"/>
|
||||
|
||||
Unter der Haube arbeiten die Klassen [`AutoModelForSequenceClassification`] und [`AutoTokenizer`] zusammen, um die [`pipeline`] zu betreiben. Eine [`AutoClass`](./model_doc/auto) ist eine Abkürzung, die automatisch die Architektur eines trainierten Modells aus dessen Namen oder Pfad abruft. Sie müssen nur die passende `AutoClass` für Ihre Aufgabe und den zugehörigen Tokenizer mit [`AutoTokenizer`] auswählen.
|
||||
|
||||
Kehren wir zu unserem Beispiel zurück und sehen wir uns an, wie Sie die `AutoClass` verwenden können, um die Ergebnisse der [`pipeline`] zu replizieren.
|
||||
|
||||
### AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
Ein Tokenizer ist für die Vorverarbeitung von Text in ein für das Modell verständliches Format zuständig. Zunächst zerlegt der Tokenisierer den Text in Wörter, die *Token* genannt werden. Es gibt mehrere Regeln für den Tokenisierungsprozess, z. B. wie und auf welcher Ebene ein Wort aufgespalten wird (weitere Informationen über Tokenisierung [hier](./tokenizer_summary)). Das Wichtigste ist jedoch, dass Sie den Tokenizer mit demselben Modellnamen instanziieren müssen, um sicherzustellen, dass Sie dieselben Tokenisierungsregeln verwenden, mit denen ein Modell zuvor trainiert wurde.
|
||||
Laden sie einen Tokenizer mit [`AutoTokenizer`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model_name = "nlptown/bert-base-multilingual-uncased-sentiment"
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Anschließend wandelt der Tokenizer die Token in Zahlen um, um einen Tensor als Eingabe für das Modell zu konstruieren. Dieser wird als *Vokabular* des Modells bezeichnet.
|
||||
|
||||
Übergeben Sie Ihren Text an den Tokenizer:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> encoding = tokenizer("We are very happy to show you the 🤗 Transformers library.")
|
||||
>>> print(encoding)
|
||||
{'input_ids': [101, 11312, 10320, 12495, 19308, 10114, 11391, 10855, 10103, 100, 58263, 13299, 119, 102],
|
||||
'token_type_ids': [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
'attention_mask': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Der Tokenizer gibt ein Wörterbuch zurück, das Folgendes enthält:
|
||||
|
||||
* [input_ids](./glossary#input-ids): numerische Repräsentationen Ihrer Token.
|
||||
* [atttention_mask](.glossary#attention-mask): gibt an, welche Token beachtet werden sollen.
|
||||
|
||||
Genau wie die [`pipeline`] akzeptiert der Tokenizer eine Liste von Eingaben. Darüber hinaus kann der Tokenizer den Text auch auffüllen und kürzen, um einen Stapel mit einheitlicher Länge zurückzugeben:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pt_batch = tokenizer(
|
||||
... ["We are very happy to show you the 🤗 Transformers library.", "We hope you don't hate it."],
|
||||
... padding=True,
|
||||
... truncation=True,
|
||||
... max_length=512,
|
||||
... return_tensors="pt",
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_batch = tokenizer(
|
||||
... ["We are very happy to show you the 🤗 Transformers library.", "We hope you don't hate it."],
|
||||
... padding=True,
|
||||
... truncation=True,
|
||||
... max_length=512,
|
||||
... return_tensors="tf",
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
Lesen Sie das Tutorial [preprocessing](./preprocessing) für weitere Details zur Tokenisierung.
|
||||
|
||||
### AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
🤗 Transformers bietet eine einfache und einheitliche Möglichkeit, vortrainierte Instanzen zu laden. Das bedeutet, dass Sie ein [`AutoModel`] laden können, wie Sie einen [`AutoTokenizer`] laden würden. Der einzige Unterschied ist die Auswahl des richtigen [`AutoModel`] für die Aufgabe. Da Sie eine Text- oder Sequenzklassifizierung vornehmen, laden Sie [`AutoModelForSequenceClassification`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model_name = "nlptown/bert-base-multilingual-uncased-sentiment"
|
||||
>>> pt_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In der [Aufgabenzusammenfassung](./task_summary) steht, welche [AutoModel]-Klasse für welche Aufgabe zu verwenden ist.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Jetzt können Sie Ihren vorverarbeiteten Stapel von Eingaben direkt an das Modell übergeben. Sie müssen nur das Wörterbuch entpacken, indem Sie `**` hinzufügen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pt_outputs = pt_model(**pt_batch)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Das Modell gibt die endgültigen Aktivierungen in dem Attribut "logits" aus. Wenden Sie die Softmax-Funktion auf die "logits" an, um die Wahrscheinlichkeiten zu erhalten:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from torch import nn
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pt_predictions = nn.functional.softmax(pt_outputs.logits, dim=-1)
|
||||
>>> print(pt_predictions)
|
||||
tensor([[0.0021, 0.0018, 0.0115, 0.2121, 0.7725],
|
||||
[0.2084, 0.1826, 0.1969, 0.1755, 0.2365]], grad_fn=<SoftmaxBackward0>)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
🤗 Transformers bietet eine einfache und einheitliche Methode zum Laden von vortrainierten Instanzen. Das bedeutet, dass Sie ein [`TFAutoModel`] genauso laden können, wie Sie einen [`AutoTokenizer`] laden würden. Der einzige Unterschied ist die Auswahl des richtigen [`TFAutoModel`] für die Aufgabe. Da Sie Text - oder Sequenz - Klassifizierung machen, laden Sie [`TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model_name = "nlptown/bert-base-multilingual-uncased-sentiment"
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In der [Aufgabenzusammenfassung](./task_summary) steht, welche [AutoModel]-Klasse für welche Aufgabe zu verwenden ist.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Jetzt können Sie Ihren vorverarbeiteten Stapel von Eingaben direkt an das Modell übergeben, indem Sie die Wörterbuchschlüssel direkt an die Tensoren übergeben:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_outputs = tf_model(tf_batch)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Das Modell gibt die endgültigen Aktivierungen in dem Attribut "logits" aus. Wenden Sie die Softmax-Funktion auf die "logits" an, um die Wahrscheinlichkeiten zu erhalten:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import tensorflow as tf
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tf_predictions = tf.nn.softmax(tf_outputs.logits, axis=-1)
|
||||
>>> tf_predictions # doctest: +IGNORE_RESULT
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Alle 🤗 Transformers-Modelle (PyTorch oder TensorFlow) geben die Tensoren *vor* der endgültigen Aktivierungsfunktion
|
||||
Funktion (wie Softmax) aus, da die endgültige Aktivierungsfunktion oft mit dem Verlusten verschmolzen ist.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Modelle sind ein standardmäßiges [`torch.nn.Module`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.Module) oder ein [`tf.keras.Model`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/Model), sodass Sie sie in Ihrer üblichen Trainingsschleife verwenden können. Um jedoch die Dinge einfacher zu machen, bietet 🤗 Transformers eine [`Trainer`]-Klasse für PyTorch, die Funktionalität für verteiltes Training, gemischte Präzision und mehr bietet. Für TensorFlow können Sie die Methode `fit` aus [Keras](https://keras.io/) verwenden. Siehe das [training tutorial](./training) für weitere Details.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers-Modellausgaben sind spezielle Datenklassen, so dass ihre Attribute in einer IDE automatisch vervollständigt werden.
|
||||
Die Modellausgänge verhalten sich auch wie ein Tupel oder ein Wörterbuch (z.B. können Sie mit einem Integer, einem Slice oder einem String indexieren), wobei die Attribute, die "None" sind, ignoriert werden.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Modell speichern
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Sobald Ihr Modell feinabgestimmt ist, können Sie es mit seinem Tokenizer speichern, indem Sie [`PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] verwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pt_save_directory = "./pt_save_pretrained"
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.save_pretrained(pt_save_directory) # doctest: +IGNORE_RESULT
|
||||
>>> pt_model.save_pretrained(pt_save_directory)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie bereit sind, das Modell erneut zu verwenden, laden Sie es mit [`PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pt_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("./pt_save_pretrained")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Sobald Ihr Modell feinabgestimmt ist, können Sie es mit seinem Tokenizer unter Verwendung von [`TFPreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] speichern:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_save_directory = "./tf_save_pretrained"
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.save_pretrained(tf_save_directory) # doctest: +IGNORE_RESULT
|
||||
>>> tf_model.save_pretrained(tf_save_directory)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie bereit sind, das Modell wieder zu verwenden, laden Sie es mit [`TFPreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("./tf_save_pretrained")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
Ein besonders cooles 🤗 Transformers-Feature ist die Möglichkeit, ein Modell zu speichern und es entweder als PyTorch- oder TensorFlow-Modell wieder zu laden. Der Parameter "from_pt" oder "from_tf" kann das Modell von einem Framework in das andere konvertieren:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(tf_save_directory)
|
||||
>>> pt_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(tf_save_directory, from_tf=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(pt_save_directory)
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(pt_save_directory, from_pt=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Custom model builds
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können die Konfigurationsklasse des Modells ändern, um zu bestimmen, wie ein Modell aufgebaut ist. Die Konfiguration legt die Attribute eines Modells fest, z. B. die Anzahl der verborgenen Schichten oder der Aufmerksamkeitsköpfe. Wenn Sie ein Modell aus einer benutzerdefinierten Konfigurationsklasse initialisieren, beginnen Sie bei Null. Die Modellattribute werden zufällig initialisiert, und Sie müssen das Modell trainieren, bevor Sie es verwenden können, um aussagekräftige Ergebnisse zu erhalten.
|
||||
|
||||
Beginnen Sie mit dem Import von [`AutoConfig`] und laden Sie dann das trainierte Modell, das Sie ändern möchten. Innerhalb von [`AutoConfig.from_pretrained`] können Sie das Attribut angeben, das Sie ändern möchten, z. B. die Anzahl der Aufmerksamkeitsköpfe:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased", n_heads=12)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Create a model from your custom configuration with [`AutoModel.from_config`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_model = AutoModel.from_config(my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Create a model from your custom configuration with [`TFAutoModel.from_config`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_model = TFAutoModel.from_config(my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Informationen zur Erstellung von benutzerdefinierten Konfigurationen finden Sie in der Anleitung [Erstellen einer benutzerdefinierten Architektur](./create_a_model).
|
||||
|
||||
## Wie geht es weiter?
|
||||
|
||||
Nachdem Sie nun die 🤗 Transformers-Kurztour abgeschlossen haben, schauen Sie sich unsere Anleitungen an und erfahren Sie, wie Sie spezifischere Dinge tun können, wie das Schreiben eines benutzerdefinierten Modells, die Feinabstimmung eines Modells für eine Aufgabe und wie man ein Modell mit einem Skript trainiert. Wenn Sie mehr über die Kernkonzepte von 🤗 Transformers erfahren möchten, nehmen Sie sich eine Tasse Kaffee und werfen Sie einen Blick auf unsere konzeptionellen Leitfäden!
|
||||
@ -1,428 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Schnellstart
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Mit 🤗 Transformers können Sie sofort loslegen! Verwenden Sie die [`pipeline`] für schnelle Inferenz und laden Sie schnell ein vortrainiertes Modell und einen Tokenizer mit einer [AutoClass](./model_doc/auto), um Ihre Text-, Bild- oder Audioaufgabe zu lösen.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Alle in der Dokumentation vorgestellten Codebeispiele haben oben links einen Umschalter für PyTorch und TensorFlow. Wenn
|
||||
nicht, wird erwartet, dass der Code für beide Backends ohne Änderungen funktioniert.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[`pipeline`] ist der einfachste Weg, ein vortrainiertes Modell für eine bestimmte Aufgabe zu verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="tiZFewofSLM"/>
|
||||
|
||||
Die [`pipeline`] unterstützt viele gängige Aufgaben:
|
||||
|
||||
**Text**:
|
||||
* Stimmungsanalyse: Klassifizierung der Polarität eines gegebenen Textes.
|
||||
* Textgenerierung (auf Englisch): Generierung von Text aus einer gegebenen Eingabe.
|
||||
* Name-Entity-Recognition (NER): Kennzeichnung jedes Worts mit der Entität, die es repräsentiert (Person, Datum, Ort usw.).
|
||||
* Beantwortung von Fragen: Extrahieren der Antwort aus dem Kontext, wenn ein gewisser Kontext und eine Frage gegeben sind.
|
||||
* Fill-mask: Ausfüllen von Lücken in einem Text mit maskierten Wörtern.
|
||||
* Zusammenfassung: Erstellung einer Zusammenfassung einer langen Text- oder Dokumentensequenz.
|
||||
* Übersetzung: Übersetzen eines Textes in eine andere Sprache.
|
||||
* Merkmalsextraktion: Erstellen einer Tensordarstellung des Textes.
|
||||
|
||||
**Bild**:
|
||||
* Bildklassifizierung: Klassifizierung eines Bildes.
|
||||
* Bildsegmentierung: Klassifizierung jedes Pixels in einem Bild.
|
||||
* Objekterkennung: Erkennen von Objekten innerhalb eines Bildes.
|
||||
|
||||
**Audio**:
|
||||
* Audioklassifizierung: Zuweisung eines Labels zu einem bestimmten Audiosegment.
|
||||
* Automatische Spracherkennung (ASR): Transkription von Audiodaten in Text.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Für mehr Details über die [`pipeline`] und assoziierte Aufgaben, schauen Sie in die Dokumentation [hier](./main_classes/pipelines).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Verwendung der Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
Im folgenden Beispiel werden Sie die [`pipeline`] für die Stimmungsanalyse verwenden.
|
||||
|
||||
Installieren Sie die folgenden Abhängigkeiten, falls Sie dies nicht bereits getan haben:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install torch
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install tensorflow
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
Importieren sie die [`pipeline`] und spezifizieren sie die Aufgabe, welche sie lösen möchten:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> classifier = pipeline("sentiment-analysis")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Die Pipeline lädt ein standardmäßiges [vortrainiertes Modell] (https://huggingface.co/distilbert-base-uncased-finetuned-sst-2-english) und einen Tokenizer für die Stimmungs-Analyse herunter und speichert sie. Jetzt können Sie den "Klassifikator" auf Ihren Zieltext anwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> classifier("We are very happy to show you the 🤗 Transformers library.")
|
||||
[{'label': 'POSITIVE', 'score': 0.9998}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more than one sentence, pass a list of sentences to the [`pipeline`] which returns a list of dictionaries:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> results = classifier(["We are very happy to show you the 🤗 Transformers library.", "We hope you don't hate it."])
|
||||
>>> for result in results:
|
||||
... print(f"label: {result['label']}, with score: {round(result['score'], 4)}")
|
||||
label: POSITIVE, with score: 0.9998
|
||||
label: NEGATIVE, with score: 0.5309
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Die [`pipeline`] kann auch über einen ganzen Datensatz iterieren. Starten wir mit der Installation der [🤗 Datasets](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/) Bibliothek:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install datasets
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen wir eine [`pipeline`] mit der Aufgabe die wir lösen und dem Modell welches wir nutzen möchten.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
>>> speech_recognizer = pipeline("automatic-speech-recognition", model="facebook/wav2vec2-base-960h")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Als nächstes laden wir den Datensatz (siehe 🤗 Datasets [Quick Start](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/quickstart.html) für mehr Details) welches wir nutzen möchten. Zum Beispiel laden wir den [MInDS-14](https://huggingface.co/datasets/PolyAI/minds14) Datensatz:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from datasets import load_dataset, Audio
|
||||
|
||||
>>> dataset = load_dataset("PolyAI/minds14", name="en-US", split="train") # doctest: +IGNORE_RESULT
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wir müssen sicherstellen, dass die Abtastrate des Datensatzes der Abtastrate entspricht, mit der `facebook/wav2vec2-base-960h` trainiert wurde.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset = dataset.cast_column("audio", Audio(sampling_rate=speech_recognizer.feature_extractor.sampling_rate))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Audiodateien werden automatisch geladen und neu abgetastet, wenn die Spalte "audio" aufgerufen wird.
|
||||
Extrahieren wir die rohen Wellenform-Arrays der ersten 4 Beispiele und übergeben wir sie als Liste an die Pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> result = speech_recognizer(dataset[:4]["audio"])
|
||||
>>> print([d["text"] for d in result])
|
||||
['I WOULD LIKE TO SET UP A JOINT ACCOUNT WITH MY PARTNER HOW DO I PROCEED WITH DOING THAT', "FODING HOW I'D SET UP A JOIN TO HET WITH MY WIFE AND WHERE THE AP MIGHT BE", "I I'D LIKE TOY SET UP A JOINT ACCOUNT WITH MY PARTNER I'M NOT SEEING THE OPTION TO DO IT ON THE AP SO I CALLED IN TO GET SOME HELP CAN I JUST DO IT OVER THE PHONE WITH YOU AND GIVE YOU THE INFORMATION OR SHOULD I DO IT IN THE AP AND I'M MISSING SOMETHING UQUETTE HAD PREFERRED TO JUST DO IT OVER THE PHONE OF POSSIBLE THINGS", 'HOW DO I THURN A JOIN A COUNT']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Bei einem größeren Datensatz mit vielen Eingaben (wie bei Sprache oder Bildverarbeitung) sollten Sie einen Generator anstelle einer Liste übergeben, der alle Eingaben in den Speicher lädt. Weitere Informationen finden Sie in der [Pipeline-Dokumentation](./main_classes/pipelines).
|
||||
|
||||
### Ein anderes Modell und einen anderen Tokenizer in der Pipeline verwenden
|
||||
|
||||
Die [`pipeline`] kann jedes Modell aus dem [Model Hub] (https://huggingface.co/models) verwenden, wodurch es einfach ist, die [`pipeline`] für andere Anwendungsfälle anzupassen. Wenn Sie beispielsweise ein Modell wünschen, das französischen Text verarbeiten kann, verwenden Sie die Tags im Model Hub, um nach einem geeigneten Modell zu filtern. Das oberste gefilterte Ergebnis liefert ein mehrsprachiges [BERT-Modell](https://huggingface.co/nlptown/bert-base-multilingual-uncased-sentiment), das auf die Stimmungsanalyse abgestimmt ist. Großartig, verwenden wir dieses Modell!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model_name = "nlptown/bert-base-multilingual-uncased-sentiment"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Use the [`AutoModelForSequenceClassification`] and [`AutoTokenizer`] to load the pretrained model and it's associated tokenizer (more on an `AutoClass` below):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Use the [`TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification`] and [`AutoTokenizer`] to load the pretrained model and it's associated tokenizer (more on an `TFAutoClass` below):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
Dann können Sie das Modell und den Tokenizer in der [`pipeline`] angeben und den `Klassifikator` auf Ihren Zieltext anwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> classifier = pipeline("sentiment-analysis", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
>>> classifier("Nous sommes très heureux de vous présenter la bibliothèque 🤗 Transformers.")
|
||||
[{'label': '5 stars', 'score': 0.7273}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie kein Modell für Ihren Anwendungsfall finden können, müssen Sie ein vortrainiertes Modell auf Ihren Daten feinabstimmen. Schauen Sie sich unser [Feinabstimmungs-Tutorial](./training) an, um zu erfahren, wie das geht. Und schließlich, nachdem Sie Ihr trainiertes Modell verfeinert haben, sollten Sie es mit der Community im Model Hub teilen (siehe Tutorial [hier](./model_sharing)), um NLP für alle zu demokratisieren! 🤗
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoClass
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="AhChOFRegn4"/>
|
||||
|
||||
Unter der Haube arbeiten die Klassen [`AutoModelForSequenceClassification`] und [`AutoTokenizer`] zusammen, um die [`pipeline`] zu betreiben. Eine [`AutoClass`](./model_doc/auto) ist eine Abkürzung, die automatisch die Architektur eines trainierten Modells aus dessen Namen oder Pfad abruft. Sie müssen nur die passende `AutoClass` für Ihre Aufgabe und den zugehörigen Tokenizer mit [`AutoTokenizer`] auswählen.
|
||||
|
||||
Kehren wir zu unserem Beispiel zurück und sehen wir uns an, wie Sie die `AutoClass` verwenden können, um die Ergebnisse der [`pipeline`] zu replizieren.
|
||||
|
||||
### AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
Ein Tokenizer ist für die Vorverarbeitung von Text in ein für das Modell verständliches Format zuständig. Zunächst zerlegt der Tokenisierer den Text in Wörter, die *Token* genannt werden. Es gibt mehrere Regeln für den Tokenisierungsprozess, z. B. wie und auf welcher Ebene ein Wort aufgespalten wird (weitere Informationen über Tokenisierung [hier](./tokenizer_summary)). Das Wichtigste ist jedoch, dass Sie den Tokenizer mit demselben Modellnamen instanziieren müssen, um sicherzustellen, dass Sie dieselben Tokenisierungsregeln verwenden, mit denen ein Modell zuvor trainiert wurde.
|
||||
Laden sie einen Tokenizer mit [`AutoTokenizer`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model_name = "nlptown/bert-base-multilingual-uncased-sentiment"
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Anschließend wandelt der Tokenizer die Token in Zahlen um, um einen Tensor als Eingabe für das Modell zu konstruieren. Dieser wird als *Vokabular* des Modells bezeichnet.
|
||||
|
||||
Übergeben Sie Ihren Text an den Tokenizer:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> encoding = tokenizer("We are very happy to show you the 🤗 Transformers library.")
|
||||
>>> print(encoding)
|
||||
{'input_ids': [101, 11312, 10320, 12495, 19308, 10114, 11391, 10855, 10103, 100, 58263, 13299, 119, 102],
|
||||
'token_type_ids': [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
'attention_mask': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Der Tokenizer gibt ein Wörterbuch zurück, das Folgendes enthält:
|
||||
|
||||
* [input_ids](./glossary#input-ids): numerische Repräsentationen Ihrer Token.
|
||||
* [atttention_mask](.glossary#attention-mask): gibt an, welche Token beachtet werden sollen.
|
||||
|
||||
Genau wie die [`pipeline`] akzeptiert der Tokenizer eine Liste von Eingaben. Darüber hinaus kann der Tokenizer den Text auch auffüllen und kürzen, um einen Stapel mit einheitlicher Länge zurückzugeben:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pt_batch = tokenizer(
|
||||
... ["We are very happy to show you the 🤗 Transformers library.", "We hope you don't hate it."],
|
||||
... padding=True,
|
||||
... truncation=True,
|
||||
... max_length=512,
|
||||
... return_tensors="pt",
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_batch = tokenizer(
|
||||
... ["We are very happy to show you the 🤗 Transformers library.", "We hope you don't hate it."],
|
||||
... padding=True,
|
||||
... truncation=True,
|
||||
... max_length=512,
|
||||
... return_tensors="tf",
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
Lesen Sie das Tutorial [preprocessing](./preprocessing) für weitere Details zur Tokenisierung.
|
||||
|
||||
### AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
🤗 Transformers bietet eine einfache und einheitliche Möglichkeit, vortrainierte Instanzen zu laden. Das bedeutet, dass Sie ein [`AutoModel`] laden können, wie Sie einen [`AutoTokenizer`] laden würden. Der einzige Unterschied ist die Auswahl des richtigen [`AutoModel`] für die Aufgabe. Da Sie eine Text- oder Sequenzklassifizierung vornehmen, laden Sie [`AutoModelForSequenceClassification`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model_name = "nlptown/bert-base-multilingual-uncased-sentiment"
|
||||
>>> pt_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In der [Aufgabenzusammenfassung](./task_summary) steht, welche [AutoModel]-Klasse für welche Aufgabe zu verwenden ist.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Jetzt können Sie Ihren vorverarbeiteten Stapel von Eingaben direkt an das Modell übergeben. Sie müssen nur das Wörterbuch entpacken, indem Sie `**` hinzufügen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pt_outputs = pt_model(**pt_batch)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Das Modell gibt die endgültigen Aktivierungen in dem Attribut "logits" aus. Wenden Sie die Softmax-Funktion auf die "logits" an, um die Wahrscheinlichkeiten zu erhalten:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from torch import nn
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pt_predictions = nn.functional.softmax(pt_outputs.logits, dim=-1)
|
||||
>>> print(pt_predictions)
|
||||
tensor([[0.0021, 0.0018, 0.0115, 0.2121, 0.7725],
|
||||
[0.2084, 0.1826, 0.1969, 0.1755, 0.2365]], grad_fn=<SoftmaxBackward0>)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
🤗 Transformers bietet eine einfache und einheitliche Methode zum Laden von vortrainierten Instanzen. Das bedeutet, dass Sie ein [`TFAutoModel`] genauso laden können, wie Sie einen [`AutoTokenizer`] laden würden. Der einzige Unterschied ist die Auswahl des richtigen [`TFAutoModel`] für die Aufgabe. Da Sie Text - oder Sequenz - Klassifizierung machen, laden Sie [`TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model_name = "nlptown/bert-base-multilingual-uncased-sentiment"
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In der [Aufgabenzusammenfassung](./task_summary) steht, welche [AutoModel]-Klasse für welche Aufgabe zu verwenden ist.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Jetzt können Sie Ihren vorverarbeiteten Stapel von Eingaben direkt an das Modell übergeben, indem Sie die Wörterbuchschlüssel direkt an die Tensoren übergeben:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_outputs = tf_model(tf_batch)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Das Modell gibt die endgültigen Aktivierungen in dem Attribut "logits" aus. Wenden Sie die Softmax-Funktion auf die "logits" an, um die Wahrscheinlichkeiten zu erhalten:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import tensorflow as tf
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tf_predictions = tf.nn.softmax(tf_outputs.logits, axis=-1)
|
||||
>>> tf_predictions # doctest: +IGNORE_RESULT
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Alle 🤗 Transformers-Modelle (PyTorch oder TensorFlow) geben die Tensoren *vor* der endgültigen Aktivierungsfunktion
|
||||
Funktion (wie Softmax) aus, da die endgültige Aktivierungsfunktion oft mit dem Verlusten verschmolzen ist.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Modelle sind ein standardmäßiges [`torch.nn.Module`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.Module) oder ein [`tf.keras.Model`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/Model), sodass Sie sie in Ihrer üblichen Trainingsschleife verwenden können. Um jedoch die Dinge einfacher zu machen, bietet 🤗 Transformers eine [`Trainer`]-Klasse für PyTorch, die Funktionalität für verteiltes Training, gemischte Präzision und mehr bietet. Für TensorFlow können Sie die Methode `fit` aus [Keras](https://keras.io/) verwenden. Siehe das [training tutorial](./training) für weitere Details.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers-Modellausgaben sind spezielle Datenklassen, so dass ihre Attribute in einer IDE automatisch vervollständigt werden.
|
||||
Die Modellausgänge verhalten sich auch wie ein Tupel oder ein Wörterbuch (z.B. können Sie mit einem Integer, einem Slice oder einem String indexieren), wobei die Attribute, die "None" sind, ignoriert werden.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Modell speichern
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Sobald Ihr Modell feinabgestimmt ist, können Sie es mit seinem Tokenizer speichern, indem Sie [`PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] verwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pt_save_directory = "./pt_save_pretrained"
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.save_pretrained(pt_save_directory) # doctest: +IGNORE_RESULT
|
||||
>>> pt_model.save_pretrained(pt_save_directory)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie bereit sind, das Modell erneut zu verwenden, laden Sie es mit [`PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> pt_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("./pt_save_pretrained")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Sobald Ihr Modell feinabgestimmt ist, können Sie es mit seinem Tokenizer unter Verwendung von [`TFPreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] speichern:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_save_directory = "./tf_save_pretrained"
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.save_pretrained(tf_save_directory) # doctest: +IGNORE_RESULT
|
||||
>>> tf_model.save_pretrained(tf_save_directory)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie bereit sind, das Modell wieder zu verwenden, laden Sie es mit [`TFPreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("./tf_save_pretrained")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
Ein besonders cooles 🤗 Transformers-Feature ist die Möglichkeit, ein Modell zu speichern und es entweder als PyTorch- oder TensorFlow-Modell wieder zu laden. Der Parameter "from_pt" oder "from_tf" kann das Modell von einem Framework in das andere konvertieren:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(tf_save_directory)
|
||||
>>> pt_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(tf_save_directory, from_tf=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(pt_save_directory)
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(pt_save_directory, from_pt=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Custom model builds
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können die Konfigurationsklasse des Modells ändern, um zu bestimmen, wie ein Modell aufgebaut ist. Die Konfiguration legt die Attribute eines Modells fest, z. B. die Anzahl der verborgenen Schichten oder der Aufmerksamkeitsköpfe. Wenn Sie ein Modell aus einer benutzerdefinierten Konfigurationsklasse initialisieren, beginnen Sie bei Null. Die Modellattribute werden zufällig initialisiert, und Sie müssen das Modell trainieren, bevor Sie es verwenden können, um aussagekräftige Ergebnisse zu erhalten.
|
||||
|
||||
Beginnen Sie mit dem Import von [`AutoConfig`] und laden Sie dann das trainierte Modell, das Sie ändern möchten. Innerhalb von [`AutoConfig.from_pretrained`] können Sie das Attribut angeben, das Sie ändern möchten, z. B. die Anzahl der Aufmerksamkeitsköpfe:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased", n_heads=12)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Create a model from your custom configuration with [`AutoModel.from_config`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_model = AutoModel.from_config(my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Create a model from your custom configuration with [`TFAutoModel.from_config`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_model = TFAutoModel.from_config(my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Informationen zur Erstellung von benutzerdefinierten Konfigurationen finden Sie in der Anleitung [Erstellen einer benutzerdefinierten Architektur](./create_a_model).
|
||||
|
||||
## Wie geht es weiter?
|
||||
|
||||
Nachdem Sie nun die 🤗 Transformers-Kurztour abgeschlossen haben, schauen Sie sich unsere Anleitungen an und erfahren Sie, wie Sie spezifischere Dinge tun können, wie das Schreiben eines benutzerdefinierten Modells, die Feinabstimmung eines Modells für eine Aufgabe und wie man ein Modell mit einem Skript trainiert. Wenn Sie mehr über die Kernkonzepte von 🤗 Transformers erfahren möchten, nehmen Sie sich eine Tasse Kaffee und werfen Sie einen Blick auf unsere konzeptionellen Leitfäden!
|
||||
433
docs/source/de/training.md
Normal file
433
docs/source/de/training.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,433 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Optimierung eines vortrainierten Modells
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Die Verwendung eines vorab trainierten Modells hat erhebliche Vorteile. Es reduziert die Rechenkosten und den CO2-Fußabdruck und ermöglicht Ihnen die Verwendung von Modellen, die dem neuesten Stand der Technik entsprechen, ohne dass Sie ein Modell von Grund auf neu trainieren müssen. Transformers bietet Zugang zu Tausenden von vortrainierten Modellen für eine Vielzahl von Aufgaben. Wenn Sie ein vorab trainiertes Modell verwenden, trainieren Sie es auf einem für Ihre Aufgabe spezifischen Datensatz. Dies wird als Feinabstimmung bezeichnet und ist eine unglaublich leistungsfähige Trainingstechnik. In diesem Tutorial werden Sie ein vortrainiertes Modell mit einem Deep-Learning-Framework Ihrer Wahl feinabstimmen:
|
||||
|
||||
* Feinabstimmung eines vorab trainierten Modells mit 🤗 Transformers [`Trainer`].
|
||||
* Feinabstimmung eines vorab trainierten Modells in TensorFlow mit Keras.
|
||||
* Feinabstimmung eines vorab trainierten Modells in nativem PyTorch.
|
||||
|
||||
<a id='data-processing'></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Vorbereitung eines Datensatzes
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="_BZearw7f0w"/>
|
||||
|
||||
Bevor Sie die Feinabstimmung eines vortrainierten Modells vornehmen können, müssen Sie einen Datensatz herunterladen und für das Training vorbereiten. Im vorangegangenen Leitfaden haben Sie gelernt, wie man Daten für das Training aufbereitet, und jetzt haben Sie die Gelegenheit, diese Fähigkeiten zu testen!
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie zunächst den Datensatz [Yelp Reviews](https://huggingface.co/datasets/yelp_review_full):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
>>> dataset = load_dataset("yelp_review_full")
|
||||
>>> dataset["train"][100]
|
||||
{'label': 0,
|
||||
'text': 'My expectations for McDonalds are t rarely high. But for one to still fail so spectacularly...that takes something special!\\nThe cashier took my friends\'s order, then promptly ignored me. I had to force myself in front of a cashier who opened his register to wait on the person BEHIND me. I waited over five minutes for a gigantic order that included precisely one kid\'s meal. After watching two people who ordered after me be handed their food, I asked where mine was. The manager started yelling at the cashiers for \\"serving off their orders\\" when they didn\'t have their food. But neither cashier was anywhere near those controls, and the manager was the one serving food to customers and clearing the boards.\\nThe manager was rude when giving me my order. She didn\'t make sure that I had everything ON MY RECEIPT, and never even had the decency to apologize that I felt I was getting poor service.\\nI\'ve eaten at various McDonalds restaurants for over 30 years. I\'ve worked at more than one location. I expect bad days, bad moods, and the occasional mistake. But I have yet to have a decent experience at this store. It will remain a place I avoid unless someone in my party needs to avoid illness from low blood sugar. Perhaps I should go back to the racially biased service of Steak n Shake instead!'}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wie Sie nun wissen, benötigen Sie einen Tokenizer, um den Text zu verarbeiten und eine Auffüll- und Abschneidungsstrategie einzubauen, um mit variablen Sequenzlängen umzugehen. Um Ihren Datensatz in einem Schritt zu verarbeiten, verwenden Sie die 🤗 Methode Datasets [`map`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/process.html#map), um eine Vorverarbeitungsfunktion auf den gesamten Datensatz anzuwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def tokenize_function(examples):
|
||||
... return tokenizer(examples["text"], padding="max_length", truncation=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenized_datasets = dataset.map(tokenize_function, batched=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie möchten, können Sie eine kleinere Teilmenge des gesamten Datensatzes für die Feinabstimmung erstellen, um den Zeitaufwand zu verringern:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> small_train_dataset = tokenized_datasets["train"].shuffle(seed=42).select(range(1000))
|
||||
>>> small_eval_dataset = tokenized_datasets["test"].shuffle(seed=42).select(range(1000))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<a id='trainer'></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Training
|
||||
|
||||
An dieser Stelle sollten Sie dem Abschnitt folgen, der dem Rahmen entspricht, den Sie verwenden möchten. Sie können über die Links
|
||||
in der rechten Seitenleiste können Sie zu dem gewünschten Abschnitt springen - und wenn Sie den gesamten Inhalt eines bestimmten Frameworks ausblenden möchten,
|
||||
klicken Sie einfach auf die Schaltfläche oben rechts im Block des jeweiligen Frameworks!
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
<Youtube id="nvBXf7s7vTI"/>
|
||||
|
||||
## Trainieren mit PyTorch Trainer
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers bietet eine [`Trainer`]-Klasse, die für das Training von 🤗 Transformers-Modellen optimiert ist und es einfacher macht, mit dem Training zu beginnen, ohne manuell eine eigene Trainingsschleife zu schreiben. Die [`Trainer`]-API unterstützt eine breite Palette von Trainingsoptionen und Funktionen wie Logging, Gradientenakkumulation und gemischte Präzision.
|
||||
|
||||
Beginnen Sie mit dem Laden Ihres Modells und geben Sie die Anzahl der erwarteten Labels an. Aus dem Yelp Review [dataset card](https://huggingface.co/datasets/yelp_review_full#data-fields) wissen Sie, dass es fünf Labels gibt:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased", num_labels=5)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Es wird eine Warnung angezeigt, dass einige der trainierten Parameter nicht verwendet werden und einige Parameter zufällig
|
||||
initialisiert werden. Machen Sie sich keine Sorgen, das ist völlig normal! Der vorher trainierte Kopf des BERT-Modells wird verworfen und durch einen zufällig initialisierten Klassifikationskopf ersetzt. Sie werden diesen neuen Modellkopf in Ihrer Sequenzklassifizierungsaufgabe feinabstimmen, indem Sie das Wissen des vortrainierten Modells auf ihn übertragen.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Hyperparameter für das Training
|
||||
|
||||
Als Nächstes erstellen Sie eine Klasse [`TrainingArguments`], die alle Hyperparameter enthält, die Sie einstellen können, sowie Flags zur Aktivierung verschiedener Trainingsoptionen. Für dieses Lernprogramm können Sie mit den Standard- [Hyperparametern](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/trainer#transformers.TrainingArguments) beginnen, aber Sie können mit diesen experimentieren, um Ihre optimalen Einstellungen zu finden.
|
||||
|
||||
Geben Sie an, wo die Kontrollpunkte Ihres Trainings gespeichert werden sollen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TrainingArguments
|
||||
|
||||
>>> training_args = TrainingArguments(output_dir="test_trainer")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Auswerten
|
||||
|
||||
Der [`Trainer`] wertet die Leistung des Modells während des Trainings nicht automatisch aus. Sie müssen [`Trainer`] eine Funktion übergeben, um Metriken zu berechnen und zu berichten. Die [🤗 Evaluate](https://huggingface.co/docs/evaluate/index) Bibliothek bietet eine einfache [`accuracy`](https://huggingface.co/spaces/evaluate-metric/accuracy) Funktion, die Sie mit der [`evaluate.load`] Funktion laden können (siehe diese [quicktour](https://huggingface.co/docs/evaluate/a_quick_tour) für weitere Informationen):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import numpy as np
|
||||
>>> import evaluate
|
||||
|
||||
>>> metric = evaluate.load("accuracy")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Rufen Sie [`~evaluate.compute`] auf `metric` auf, um die Genauigkeit Ihrer Vorhersagen zu berechnen. Bevor Sie Ihre Vorhersagen an `compute` übergeben, müssen Sie die Vorhersagen in Logits umwandeln (denken Sie daran, dass alle 🤗 Transformers-Modelle Logits zurückgeben):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def compute_metrics(eval_pred):
|
||||
... logits, labels = eval_pred
|
||||
... predictions = np.argmax(logits, axis=-1)
|
||||
... return metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=labels)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie Ihre Bewertungsmetriken während der Feinabstimmung überwachen möchten, geben Sie den Parameter `evaluation_strategy` in Ihren Trainingsargumenten an, um die Bewertungsmetrik am Ende jeder Epoche zu ermitteln:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TrainingArguments, Trainer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> training_args = TrainingArguments(output_dir="test_trainer", evaluation_strategy="epoch")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Trainer
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen Sie ein [`Trainer`]-Objekt mit Ihrem Modell, Trainingsargumenten, Trainings- und Testdatensätzen und einer Evaluierungsfunktion:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> trainer = Trainer(
|
||||
... model=model,
|
||||
... args=training_args,
|
||||
... train_dataset=small_train_dataset,
|
||||
... eval_dataset=small_eval_dataset,
|
||||
... compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Anschließend können Sie Ihr Modell durch den Aufruf von [`~transformers.Trainer.train`] optimieren:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
<a id='keras'></a>
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="rnTGBy2ax1c"/>
|
||||
|
||||
## Trainieren Sie ein TensorFlow-Modell mit Keras
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können auch 🤗 Transformers Modelle in TensorFlow mit der Keras API trainieren!
|
||||
|
||||
### Laden von Daten für Keras
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie ein 🤗 Transformers Modell mit der Keras API trainieren wollen, müssen Sie Ihren Datensatz in ein Format konvertieren, das
|
||||
Keras versteht. Wenn Ihr Datensatz klein ist, können Sie das Ganze einfach in NumPy-Arrays konvertieren und an Keras übergeben.
|
||||
Probieren wir das zuerst aus, bevor wir etwas Komplizierteres tun.
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie zunächst ein Dataset. Wir werden den CoLA-Datensatz aus dem [GLUE-Benchmark](https://huggingface.co/datasets/glue) verwenden,
|
||||
da es sich um eine einfache Aufgabe zur Klassifizierung von binärem Text handelt, und nehmen vorerst nur den Trainingssplit.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("glue", "cola")
|
||||
dataset = dataset["train"] # Just take the training split for now
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Als nächstes laden Sie einen Tokenizer und tokenisieren die Daten als NumPy-Arrays. Beachten Sie, dass die Beschriftungen bereits eine Liste von 0 und 1en sind,
|
||||
Wir können sie also ohne Tokenisierung direkt in ein NumPy-Array konvertieren!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
tokenized_data = tokenizer(dataset["text"], return_tensors="np", padding=True)
|
||||
# Tokenizer returns a BatchEncoding, but we convert that to a dict for Keras
|
||||
tokenized_data = dict(tokenized_data)
|
||||
|
||||
labels = np.array(dataset["label"]) # Label is already an array of 0 and 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Schließlich laden, [`compile`](https://keras.io/api/models/model_training_apis/#compile-method) und [`fit`](https://keras.io/api/models/model_training_apis/#fit-method) Sie das Modell:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
|
||||
|
||||
# Load and compile our model
|
||||
model = TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
# Lower learning rates are often better for fine-tuning transformers
|
||||
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(3e-5))
|
||||
|
||||
model.fit(tokenized_data, labels)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Sie müssen Ihren Modellen kein Verlustargument übergeben, wenn Sie sie `compile()`! Hugging-Face-Modelle wählen automatisch
|
||||
einen Loss, der für ihre Aufgabe und Modellarchitektur geeignet ist, wenn dieses Argument leer gelassen wird. Sie können jederzeit außer Kraft setzen, indem Sie selbst einen Loss angeben, wenn Sie das möchten!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Dieser Ansatz eignet sich hervorragend für kleinere Datensätze, aber bei größeren Datensätzen kann er zu einem Problem werden. Warum?
|
||||
Weil das tokenisierte Array und die Beschriftungen vollständig in den Speicher geladen werden müssten, und weil NumPy nicht mit
|
||||
"gezackte" Arrays nicht verarbeiten kann, so dass jedes tokenisierte Sample auf die Länge des längsten Samples im gesamten Datensatz aufgefüllt werden müsste.
|
||||
Datensatzes aufgefüllt werden. Dadurch wird das Array noch größer, und all die aufgefüllten Token verlangsamen auch das Training!
|
||||
|
||||
### Laden von Daten als tf.data.Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie eine Verlangsamung des Trainings vermeiden wollen, können Sie Ihre Daten stattdessen als `tf.data.Dataset` laden. Sie können zwar Ihre eigene
|
||||
tf.data"-Pipeline schreiben können, wenn Sie wollen, haben wir zwei bequeme Methoden, um dies zu tun:
|
||||
|
||||
- [`~TFPreTrainedModel.prepare_tf_dataset`]: Dies ist die Methode, die wir in den meisten Fällen empfehlen. Da es sich um eine Methode
|
||||
Ihres Modells ist, kann sie das Modell inspizieren, um automatisch herauszufinden, welche Spalten als Modelleingaben verwendet werden können, und
|
||||
verwirft die anderen, um einen einfacheren, leistungsfähigeren Datensatz zu erstellen.
|
||||
- [~datasets.Dataset.to_tf_dataset`]: Diese Methode ist eher auf niedriger Ebene angesiedelt und ist nützlich, wenn Sie genau kontrollieren wollen, wie
|
||||
Dataset erstellt wird, indem man genau angibt, welche `columns` und `label_cols` einbezogen werden sollen.
|
||||
|
||||
Bevor Sie [~TFPreTrainedModel.prepare_tf_dataset`] verwenden können, müssen Sie die Tokenizer-Ausgaben als Spalten zu Ihrem Datensatz hinzufügen, wie in
|
||||
dem folgenden Codebeispiel:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
def tokenize_dataset(data):
|
||||
# Keys of the returned dictionary will be added to the dataset as columns
|
||||
return tokenizer(data["text"])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = dataset.map(tokenize_dataset)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Denken Sie daran, dass Hugging Face-Datensätze standardmäßig auf der Festplatte gespeichert werden, so dass dies nicht zu einem erhöhten Arbeitsspeicherbedarf führen wird! Sobald die
|
||||
Spalten hinzugefügt wurden, können Sie Batches aus dem Datensatz streamen und zu jedem Batch Auffüllungen hinzufügen, was die Anzahl der Auffüllungs-Token im Vergleich zum Auffüllen des gesamten Datensatzes reduziert.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_dataset = model.prepare_tf_dataset(dataset, batch_size=16, shuffle=True, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Beachten Sie, dass Sie im obigen Codebeispiel den Tokenizer an `prepare_tf_dataset` übergeben müssen, damit die Stapel beim Laden korrekt aufgefüllt werden können.
|
||||
Wenn alle Stichproben in Ihrem Datensatz die gleiche Länge haben und kein Auffüllen erforderlich ist, können Sie dieses Argument weglassen.
|
||||
Wenn Sie etwas Komplexeres als nur das Auffüllen von Stichproben benötigen (z. B. das Korrumpieren von Token für die maskierte Sprachmodellierung), können Sie das Argument
|
||||
Modellierung), können Sie stattdessen das Argument `collate_fn` verwenden, um eine Funktion zu übergeben, die aufgerufen wird, um die
|
||||
Liste von Stichproben in einen Stapel umwandelt und alle gewünschten Vorverarbeitungen vornimmt. Siehe unsere
|
||||
[examples](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples) oder
|
||||
[notebooks](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/notebooks), um diesen Ansatz in Aktion zu sehen.
|
||||
|
||||
Sobald Sie einen `tf.data.Dataset` erstellt haben, können Sie das Modell wie zuvor kompilieren und anpassen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(3e-5))
|
||||
|
||||
model.fit(tf_dataset)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
<a id='pytorch_native'></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Trainieren in nativem PyTorch
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
<Youtube id="Dh9CL8fyG80"/>
|
||||
|
||||
[`Trainer`] kümmert sich um die Trainingsschleife und ermöglicht die Feinabstimmung eines Modells in einer einzigen Codezeile. Für Benutzer, die es vorziehen, ihre eigene Trainingsschleife zu schreiben, können Sie auch eine Feinabstimmung eines 🤗 Transformers-Modells in nativem PyTorch vornehmen.
|
||||
|
||||
An diesem Punkt müssen Sie möglicherweise Ihr Notebook neu starten oder den folgenden Code ausführen, um etwas Speicher freizugeben:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
del model
|
||||
del pytorch_model
|
||||
del trainer
|
||||
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Als Nächstes müssen Sie den Datensatz `tokenized_dataset` manuell nachbearbeiten, um ihn für das Training vorzubereiten.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Entfernen Sie die Spalte "Text", da das Modell keinen Rohtext als Eingabe akzeptiert:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenized_datasets = tokenized_datasets.remove_columns(["text"])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Benennen Sie die Spalte "Label" in "Labels" um, da das Modell erwartet, dass das Argument "Labels" genannt wird:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenized_datasets = tokenized_datasets.rename_column("label", "labels")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Stellen Sie das Format des Datensatzes so ein, dass PyTorch-Tensoren anstelle von Listen zurückgegeben werden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenized_datasets.set_format("torch")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen Sie dann eine kleinere Teilmenge des Datensatzes, wie zuvor gezeigt, um die Feinabstimmung zu beschleunigen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> small_train_dataset = tokenized_datasets["train"].shuffle(seed=42).select(range(1000))
|
||||
>>> small_eval_dataset = tokenized_datasets["test"].shuffle(seed=42).select(range(1000))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### DataLoader
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen Sie einen `DataLoader` für Ihre Trainings- und Testdatensätze, damit Sie über die Datenstapel iterieren können:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
|
||||
|
||||
>>> train_dataloader = DataLoader(small_train_dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=8)
|
||||
>>> eval_dataloader = DataLoader(small_eval_dataset, batch_size=8)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie Ihr Modell mit der Anzahl der erwarteten Kennzeichnungen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased", num_labels=5)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Optimierer und Lernratensteuerung
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen Sie einen Optimierer und einen Scheduler für die Lernrate, um das Modell fein abzustimmen. Wir verwenden den Optimierer [`AdamW`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.optim.AdamW.html) aus PyTorch:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from torch.optim import AdamW
|
||||
|
||||
>>> optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=5e-5)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen Sie den Standard-Lernratenplaner aus [`Trainer`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import get_scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
>>> num_epochs = 3
|
||||
>>> num_training_steps = num_epochs * len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
>>> lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
|
||||
... name="linear", optimizer=optimizer, num_warmup_steps=0, num_training_steps=num_training_steps
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Geben Sie schließlich `device` an, um einen Grafikprozessor zu verwenden, wenn Sie Zugang zu einem solchen haben. Andernfalls kann das Training auf einer CPU mehrere Stunden statt ein paar Minuten dauern.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
|
||||
>>> device = torch.device("cuda") if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.device("cpu")
|
||||
>>> model.to(device)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Holen Sie sich mit einem gehosteten Notebook wie [Colaboratory](https://colab.research.google.com/) oder [SageMaker StudioLab](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/) kostenlosen Zugang zu einem Cloud-GPU, wenn Sie noch keinen haben.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Großartig, Sie sind bereit für das Training! 🥳
|
||||
|
||||
### Trainingsschleife
|
||||
|
||||
Um Ihren Trainingsfortschritt zu verfolgen, verwenden Sie die [tqdm](https://tqdm.github.io/) Bibliothek, um einen Fortschrittsbalken über die Anzahl der Trainingsschritte hinzuzufügen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from tqdm.auto import tqdm
|
||||
|
||||
>>> progress_bar = tqdm(range(num_training_steps))
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model.train()
|
||||
>>> for epoch in range(num_epochs):
|
||||
... for batch in train_dataloader:
|
||||
... batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
|
||||
... outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
... loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
... loss.backward()
|
||||
|
||||
... optimizer.step()
|
||||
... lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
... optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
... progress_bar.update(1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Auswertung
|
||||
|
||||
Genauso wie Sie eine Bewertungsfunktion zu [`Trainer`] hinzugefügt haben, müssen Sie dasselbe tun, wenn Sie Ihre eigene Trainingsschleife schreiben. Aber anstatt die Metrik am Ende jeder Epoche zu berechnen und zu melden, werden Sie dieses Mal alle Stapel mit [`~evaluate.add_batch`] akkumulieren und die Metrik ganz am Ende berechnen.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import evaluate
|
||||
|
||||
>>> metric = evaluate.load("accuracy")
|
||||
>>> model.eval()
|
||||
>>> for batch in eval_dataloader:
|
||||
... batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
|
||||
... with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
... outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
|
||||
... logits = outputs.logits
|
||||
... predictions = torch.argmax(logits, dim=-1)
|
||||
... metric.add_batch(predictions=predictions, references=batch["labels"])
|
||||
|
||||
>>> metric.compute()
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
<a id='additional-resources'></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Zusätzliche Ressourcen
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Beispiele für die Feinabstimmung finden Sie unter:
|
||||
|
||||
- [🤗 Transformers Examples](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples) enthält Skripte
|
||||
um gängige NLP-Aufgaben in PyTorch und TensorFlow zu trainieren.
|
||||
|
||||
- [🤗 Transformers Notebooks](notebooks) enthält verschiedene Notebooks zur Feinabstimmung eines Modells für bestimmte Aufgaben in PyTorch und TensorFlow.
|
||||
@ -1,429 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Optimierung eines vortrainierten Modells
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Die Verwendung eines vorab trainierten Modells hat erhebliche Vorteile. Es reduziert die Rechenkosten und den CO2-Fußabdruck und ermöglicht Ihnen die Verwendung von Modellen, die dem neuesten Stand der Technik entsprechen, ohne dass Sie ein Modell von Grund auf neu trainieren müssen. Transformers bietet Zugang zu Tausenden von vortrainierten Modellen für eine Vielzahl von Aufgaben. Wenn Sie ein vorab trainiertes Modell verwenden, trainieren Sie es auf einem für Ihre Aufgabe spezifischen Datensatz. Dies wird als Feinabstimmung bezeichnet und ist eine unglaublich leistungsfähige Trainingstechnik. In diesem Tutorial werden Sie ein vortrainiertes Modell mit einem Deep-Learning-Framework Ihrer Wahl feinabstimmen:
|
||||
|
||||
* Feinabstimmung eines vorab trainierten Modells mit 🤗 Transformers [`Trainer`].
|
||||
* Feinabstimmung eines vorab trainierten Modells in TensorFlow mit Keras.
|
||||
* Feinabstimmung eines vorab trainierten Modells in nativem PyTorch.
|
||||
|
||||
<a id='data-processing'></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Vorbereitung eines Datensatzes
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="_BZearw7f0w"/>
|
||||
|
||||
Bevor Sie die Feinabstimmung eines vortrainierten Modells vornehmen können, müssen Sie einen Datensatz herunterladen und für das Training vorbereiten. Im vorangegangenen Leitfaden haben Sie gelernt, wie man Daten für das Training aufbereitet, und jetzt haben Sie die Gelegenheit, diese Fähigkeiten zu testen!
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie zunächst den Datensatz [Yelp Reviews](https://huggingface.co/datasets/yelp_review_full):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
>>> dataset = load_dataset("yelp_review_full")
|
||||
>>> dataset["train"][100]
|
||||
{'label': 0,
|
||||
'text': 'My expectations for McDonalds are t rarely high. But for one to still fail so spectacularly...that takes something special!\\nThe cashier took my friends\'s order, then promptly ignored me. I had to force myself in front of a cashier who opened his register to wait on the person BEHIND me. I waited over five minutes for a gigantic order that included precisely one kid\'s meal. After watching two people who ordered after me be handed their food, I asked where mine was. The manager started yelling at the cashiers for \\"serving off their orders\\" when they didn\'t have their food. But neither cashier was anywhere near those controls, and the manager was the one serving food to customers and clearing the boards.\\nThe manager was rude when giving me my order. She didn\'t make sure that I had everything ON MY RECEIPT, and never even had the decency to apologize that I felt I was getting poor service.\\nI\'ve eaten at various McDonalds restaurants for over 30 years. I\'ve worked at more than one location. I expect bad days, bad moods, and the occasional mistake. But I have yet to have a decent experience at this store. It will remain a place I avoid unless someone in my party needs to avoid illness from low blood sugar. Perhaps I should go back to the racially biased service of Steak n Shake instead!'}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wie Sie nun wissen, benötigen Sie einen Tokenizer, um den Text zu verarbeiten und eine Auffüll- und Abschneidungsstrategie einzubauen, um mit variablen Sequenzlängen umzugehen. Um Ihren Datensatz in einem Schritt zu verarbeiten, verwenden Sie die 🤗 Methode Datasets [`map`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/process.html#map), um eine Vorverarbeitungsfunktion auf den gesamten Datensatz anzuwenden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def tokenize_function(examples):
|
||||
... return tokenizer(examples["text"], padding="max_length", truncation=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenized_datasets = dataset.map(tokenize_function, batched=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie möchten, können Sie eine kleinere Teilmenge des gesamten Datensatzes für die Feinabstimmung erstellen, um den Zeitaufwand zu verringern:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> small_train_dataset = tokenized_datasets["train"].shuffle(seed=42).select(range(1000))
|
||||
>>> small_eval_dataset = tokenized_datasets["test"].shuffle(seed=42).select(range(1000))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<a id='trainer'></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Training
|
||||
|
||||
An dieser Stelle sollten Sie dem Abschnitt folgen, der dem Rahmen entspricht, den Sie verwenden möchten. Sie können über die Links
|
||||
in der rechten Seitenleiste können Sie zu dem gewünschten Abschnitt springen - und wenn Sie den gesamten Inhalt eines bestimmten Frameworks ausblenden möchten,
|
||||
klicken Sie einfach auf die Schaltfläche oben rechts im Block des jeweiligen Frameworks!
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
<Youtube id="nvBXf7s7vTI"/>
|
||||
|
||||
## Trainieren mit PyTorch Trainer
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers bietet eine [`Trainer`]-Klasse, die für das Training von 🤗 Transformers-Modellen optimiert ist und es einfacher macht, mit dem Training zu beginnen, ohne manuell eine eigene Trainingsschleife zu schreiben. Die [`Trainer`]-API unterstützt eine breite Palette von Trainingsoptionen und Funktionen wie Logging, Gradientenakkumulation und gemischte Präzision.
|
||||
|
||||
Beginnen Sie mit dem Laden Ihres Modells und geben Sie die Anzahl der erwarteten Labels an. Aus dem Yelp Review [dataset card](https://huggingface.co/datasets/yelp_review_full#data-fields) wissen Sie, dass es fünf Labels gibt:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased", num_labels=5)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Es wird eine Warnung angezeigt, dass einige der trainierten Parameter nicht verwendet werden und einige Parameter zufällig
|
||||
initialisiert werden. Machen Sie sich keine Sorgen, das ist völlig normal! Der vorher trainierte Kopf des BERT-Modells wird verworfen und durch einen zufällig initialisierten Klassifikationskopf ersetzt. Sie werden diesen neuen Modellkopf in Ihrer Sequenzklassifizierungsaufgabe feinabstimmen, indem Sie das Wissen des vortrainierten Modells auf ihn übertragen.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Hyperparameter für das Training
|
||||
|
||||
Als Nächstes erstellen Sie eine Klasse [`TrainingArguments`], die alle Hyperparameter enthält, die Sie einstellen können, sowie Flags zur Aktivierung verschiedener Trainingsoptionen. Für dieses Lernprogramm können Sie mit den Standard- [Hyperparametern](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/trainer#transformers.TrainingArguments) beginnen, aber Sie können mit diesen experimentieren, um Ihre optimalen Einstellungen zu finden.
|
||||
|
||||
Geben Sie an, wo die Kontrollpunkte Ihres Trainings gespeichert werden sollen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TrainingArguments
|
||||
|
||||
>>> training_args = TrainingArguments(output_dir="test_trainer")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Auswerten
|
||||
|
||||
Der [`Trainer`] wertet die Leistung des Modells während des Trainings nicht automatisch aus. Sie müssen [`Trainer`] eine Funktion übergeben, um Metriken zu berechnen und zu berichten. Die [🤗 Evaluate](https://huggingface.co/docs/evaluate/index) Bibliothek bietet eine einfache [`accuracy`](https://huggingface.co/spaces/evaluate-metric/accuracy) Funktion, die Sie mit der [`evaluate.load`] Funktion laden können (siehe diese [quicktour](https://huggingface.co/docs/evaluate/a_quick_tour) für weitere Informationen):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import numpy as np
|
||||
>>> import evaluate
|
||||
|
||||
>>> metric = evaluate.load("accuracy")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Rufen Sie [`~evaluate.compute`] auf `metric` auf, um die Genauigkeit Ihrer Vorhersagen zu berechnen. Bevor Sie Ihre Vorhersagen an `compute` übergeben, müssen Sie die Vorhersagen in Logits umwandeln (denken Sie daran, dass alle 🤗 Transformers-Modelle Logits zurückgeben):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def compute_metrics(eval_pred):
|
||||
... logits, labels = eval_pred
|
||||
... predictions = np.argmax(logits, axis=-1)
|
||||
... return metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=labels)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie Ihre Bewertungsmetriken während der Feinabstimmung überwachen möchten, geben Sie den Parameter `evaluation_strategy` in Ihren Trainingsargumenten an, um die Bewertungsmetrik am Ende jeder Epoche zu ermitteln:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TrainingArguments, Trainer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> training_args = TrainingArguments(output_dir="test_trainer", evaluation_strategy="epoch")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Trainer
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen Sie ein [`Trainer`]-Objekt mit Ihrem Modell, Trainingsargumenten, Trainings- und Testdatensätzen und einer Evaluierungsfunktion:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> trainer = Trainer(
|
||||
... model=model,
|
||||
... args=training_args,
|
||||
... train_dataset=small_train_dataset,
|
||||
... eval_dataset=small_eval_dataset,
|
||||
... compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Anschließend können Sie Ihr Modell durch den Aufruf von [`~transformers.Trainer.train`] optimieren:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
<a id='keras'></a>
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="rnTGBy2ax1c"/>
|
||||
|
||||
## Trainieren Sie ein TensorFlow-Modell mit Keras
|
||||
|
||||
Sie können auch 🤗 Transformers Modelle in TensorFlow mit der Keras API trainieren!
|
||||
|
||||
### Laden von Daten für Keras
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie ein 🤗 Transformers Modell mit der Keras API trainieren wollen, müssen Sie Ihren Datensatz in ein Format konvertieren, das
|
||||
Keras versteht. Wenn Ihr Datensatz klein ist, können Sie das Ganze einfach in NumPy-Arrays konvertieren und an Keras übergeben.
|
||||
Probieren wir das zuerst aus, bevor wir etwas Komplizierteres tun.
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie zunächst ein Dataset. Wir werden den CoLA-Datensatz aus dem [GLUE-Benchmark](https://huggingface.co/datasets/glue) verwenden,
|
||||
da es sich um eine einfache Aufgabe zur Klassifizierung von binärem Text handelt, und nehmen vorerst nur den Trainingssplit.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("glue", "cola")
|
||||
dataset = dataset["train"] # Just take the training split for now
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Als nächstes laden Sie einen Tokenizer und tokenisieren die Daten als NumPy-Arrays. Beachten Sie, dass die Beschriftungen bereits eine Liste von 0 und 1en sind,
|
||||
Wir können sie also ohne Tokenisierung direkt in ein NumPy-Array konvertieren!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
tokenized_data = tokenizer(dataset["text"], return_tensors="np", padding=True)
|
||||
# Tokenizer returns a BatchEncoding, but we convert that to a dict for Keras
|
||||
tokenized_data = dict(tokenized_data)
|
||||
|
||||
labels = np.array(dataset["label"]) # Label is already an array of 0 and 1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Schließlich laden, [`compile`](https://keras.io/api/models/model_training_apis/#compile-method) und [`fit`](https://keras.io/api/models/model_training_apis/#fit-method) Sie das Modell:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
from tensorflow.keras.optimizers import Adam
|
||||
|
||||
# Load and compile our model
|
||||
model = TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
# Lower learning rates are often better for fine-tuning transformers
|
||||
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(3e-5))
|
||||
|
||||
model.fit(tokenized_data, labels)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Sie müssen Ihren Modellen kein Verlustargument übergeben, wenn Sie sie `compile()`! Hugging-Face-Modelle wählen automatisch
|
||||
einen Loss, der für ihre Aufgabe und Modellarchitektur geeignet ist, wenn dieses Argument leer gelassen wird. Sie können jederzeit außer Kraft setzen, indem Sie selbst einen Loss angeben, wenn Sie das möchten!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Dieser Ansatz eignet sich hervorragend für kleinere Datensätze, aber bei größeren Datensätzen kann er zu einem Problem werden. Warum?
|
||||
Weil das tokenisierte Array und die Beschriftungen vollständig in den Speicher geladen werden müssten, und weil NumPy nicht mit
|
||||
"gezackte" Arrays nicht verarbeiten kann, so dass jedes tokenisierte Sample auf die Länge des längsten Samples im gesamten Datensatz aufgefüllt werden müsste.
|
||||
Datensatzes aufgefüllt werden. Dadurch wird das Array noch größer, und all die aufgefüllten Token verlangsamen auch das Training!
|
||||
|
||||
### Laden von Daten als tf.data.Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
Wenn Sie eine Verlangsamung des Trainings vermeiden wollen, können Sie Ihre Daten stattdessen als `tf.data.Dataset` laden. Sie können zwar Ihre eigene
|
||||
tf.data"-Pipeline schreiben können, wenn Sie wollen, haben wir zwei bequeme Methoden, um dies zu tun:
|
||||
|
||||
- [`~TFPreTrainedModel.prepare_tf_dataset`]: Dies ist die Methode, die wir in den meisten Fällen empfehlen. Da es sich um eine Methode
|
||||
Ihres Modells ist, kann sie das Modell inspizieren, um automatisch herauszufinden, welche Spalten als Modelleingaben verwendet werden können, und
|
||||
verwirft die anderen, um einen einfacheren, leistungsfähigeren Datensatz zu erstellen.
|
||||
- [~datasets.Dataset.to_tf_dataset`]: Diese Methode ist eher auf niedriger Ebene angesiedelt und ist nützlich, wenn Sie genau kontrollieren wollen, wie
|
||||
Dataset erstellt wird, indem man genau angibt, welche `columns` und `label_cols` einbezogen werden sollen.
|
||||
|
||||
Bevor Sie [~TFPreTrainedModel.prepare_tf_dataset`] verwenden können, müssen Sie die Tokenizer-Ausgaben als Spalten zu Ihrem Datensatz hinzufügen, wie in
|
||||
dem folgenden Codebeispiel:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
def tokenize_dataset(data):
|
||||
# Keys of the returned dictionary will be added to the dataset as columns
|
||||
return tokenizer(data["text"])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = dataset.map(tokenize_dataset)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Denken Sie daran, dass Hugging Face-Datensätze standardmäßig auf der Festplatte gespeichert werden, so dass dies nicht zu einem erhöhten Arbeitsspeicherbedarf führen wird! Sobald die
|
||||
Spalten hinzugefügt wurden, können Sie Batches aus dem Datensatz streamen und zu jedem Batch Auffüllungen hinzufügen, was die Anzahl der Auffüllungs-Token im Vergleich zum Auffüllen des gesamten Datensatzes reduziert.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_dataset = model.prepare_tf_dataset(dataset, batch_size=16, shuffle=True, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Beachten Sie, dass Sie im obigen Codebeispiel den Tokenizer an `prepare_tf_dataset` übergeben müssen, damit die Stapel beim Laden korrekt aufgefüllt werden können.
|
||||
Wenn alle Stichproben in Ihrem Datensatz die gleiche Länge haben und kein Auffüllen erforderlich ist, können Sie dieses Argument weglassen.
|
||||
Wenn Sie etwas Komplexeres als nur das Auffüllen von Stichproben benötigen (z. B. das Korrumpieren von Token für die maskierte Sprachmodellierung), können Sie das Argument
|
||||
Modellierung), können Sie stattdessen das Argument `collate_fn` verwenden, um eine Funktion zu übergeben, die aufgerufen wird, um die
|
||||
Liste von Stichproben in einen Stapel umwandelt und alle gewünschten Vorverarbeitungen vornimmt. Siehe unsere
|
||||
[examples](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples) oder
|
||||
[notebooks](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/notebooks), um diesen Ansatz in Aktion zu sehen.
|
||||
|
||||
Sobald Sie einen `tf.data.Dataset` erstellt haben, können Sie das Modell wie zuvor kompilieren und anpassen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(3e-5))
|
||||
|
||||
model.fit(tf_dataset)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
<a id='pytorch_native'></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Trainieren in nativem PyTorch
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
<Youtube id="Dh9CL8fyG80"/>
|
||||
|
||||
[`Trainer`] kümmert sich um die Trainingsschleife und ermöglicht die Feinabstimmung eines Modells in einer einzigen Codezeile. Für Benutzer, die es vorziehen, ihre eigene Trainingsschleife zu schreiben, können Sie auch eine Feinabstimmung eines 🤗 Transformers-Modells in nativem PyTorch vornehmen.
|
||||
|
||||
An diesem Punkt müssen Sie möglicherweise Ihr Notebook neu starten oder den folgenden Code ausführen, um etwas Speicher freizugeben:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
del model
|
||||
del pytorch_model
|
||||
del trainer
|
||||
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Als Nächstes müssen Sie den Datensatz `tokenized_dataset` manuell nachbearbeiten, um ihn für das Training vorzubereiten.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Entfernen Sie die Spalte "Text", da das Modell keinen Rohtext als Eingabe akzeptiert:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenized_datasets = tokenized_datasets.remove_columns(["text"])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Benennen Sie die Spalte "Label" in "Labels" um, da das Modell erwartet, dass das Argument "Labels" genannt wird:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenized_datasets = tokenized_datasets.rename_column("label", "labels")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Stellen Sie das Format des Datensatzes so ein, dass PyTorch-Tensoren anstelle von Listen zurückgegeben werden:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenized_datasets.set_format("torch")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen Sie dann eine kleinere Teilmenge des Datensatzes, wie zuvor gezeigt, um die Feinabstimmung zu beschleunigen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> small_train_dataset = tokenized_datasets["train"].shuffle(seed=42).select(range(1000))
|
||||
>>> small_eval_dataset = tokenized_datasets["test"].shuffle(seed=42).select(range(1000))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### DataLoader
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen Sie einen `DataLoader` für Ihre Trainings- und Testdatensätze, damit Sie über die Datenstapel iterieren können:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
|
||||
|
||||
>>> train_dataloader = DataLoader(small_train_dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=8)
|
||||
>>> eval_dataloader = DataLoader(small_eval_dataset, batch_size=8)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Laden Sie Ihr Modell mit der Anzahl der erwarteten Kennzeichnungen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased", num_labels=5)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Optimierer und Lernratensteuerung
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen Sie einen Optimierer und einen Scheduler für die Lernrate, um das Modell fein abzustimmen. Wir verwenden den Optimierer [`AdamW`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.optim.AdamW.html) aus PyTorch:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from torch.optim import AdamW
|
||||
|
||||
>>> optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=5e-5)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Erstellen Sie den Standard-Lernratenplaner aus [`Trainer`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import get_scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
>>> num_epochs = 3
|
||||
>>> num_training_steps = num_epochs * len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
>>> lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
|
||||
... name="linear", optimizer=optimizer, num_warmup_steps=0, num_training_steps=num_training_steps
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Geben Sie schließlich `device` an, um einen Grafikprozessor zu verwenden, wenn Sie Zugang zu einem solchen haben. Andernfalls kann das Training auf einer CPU mehrere Stunden statt ein paar Minuten dauern.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
|
||||
>>> device = torch.device("cuda") if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.device("cpu")
|
||||
>>> model.to(device)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Holen Sie sich mit einem gehosteten Notebook wie [Colaboratory](https://colab.research.google.com/) oder [SageMaker StudioLab](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/) kostenlosen Zugang zu einem Cloud-GPU, wenn Sie noch keinen haben.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Großartig, Sie sind bereit für das Training! 🥳
|
||||
|
||||
### Trainingsschleife
|
||||
|
||||
Um Ihren Trainingsfortschritt zu verfolgen, verwenden Sie die [tqdm](https://tqdm.github.io/) Bibliothek, um einen Fortschrittsbalken über die Anzahl der Trainingsschritte hinzuzufügen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from tqdm.auto import tqdm
|
||||
|
||||
>>> progress_bar = tqdm(range(num_training_steps))
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model.train()
|
||||
>>> for epoch in range(num_epochs):
|
||||
... for batch in train_dataloader:
|
||||
... batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
|
||||
... outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
... loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
... loss.backward()
|
||||
|
||||
... optimizer.step()
|
||||
... lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
... optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
... progress_bar.update(1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Auswertung
|
||||
|
||||
Genauso wie Sie eine Bewertungsfunktion zu [`Trainer`] hinzugefügt haben, müssen Sie dasselbe tun, wenn Sie Ihre eigene Trainingsschleife schreiben. Aber anstatt die Metrik am Ende jeder Epoche zu berechnen und zu melden, werden Sie dieses Mal alle Stapel mit [`~evaluate.add_batch`] akkumulieren und die Metrik ganz am Ende berechnen.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import evaluate
|
||||
|
||||
>>> metric = evaluate.load("accuracy")
|
||||
>>> model.eval()
|
||||
>>> for batch in eval_dataloader:
|
||||
... batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
|
||||
... with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
... outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
|
||||
... logits = outputs.logits
|
||||
... predictions = torch.argmax(logits, dim=-1)
|
||||
... metric.add_batch(predictions=predictions, references=batch["labels"])
|
||||
|
||||
>>> metric.compute()
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
<a id='additional-resources'></a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Zusätzliche Ressourcen
|
||||
|
||||
Weitere Beispiele für die Feinabstimmung finden Sie unter:
|
||||
|
||||
- [🤗 Transformers Examples](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples) enthält Skripte
|
||||
um gängige NLP-Aufgaben in PyTorch und TensorFlow zu trainieren.
|
||||
|
||||
- [🤗 Transformers Notebooks](notebooks) enthält verschiedene Notebooks zur Feinabstimmung eines Modells für bestimmte Aufgaben in PyTorch und TensorFlow.
|
||||
136
docs/source/en/accelerate.md
Normal file
136
docs/source/en/accelerate.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Distributed training with 🤗 Accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
As models get bigger, parallelism has emerged as a strategy for training larger models on limited hardware and accelerating training speed by several orders of magnitude. At Hugging Face, we created the [🤗 Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate) library to help users easily train a 🤗 Transformers model on any type of distributed setup, whether it is multiple GPU's on one machine or multiple GPU's across several machines. In this tutorial, learn how to customize your native PyTorch training loop to enable training in a distributed environment.
|
||||
|
||||
## Setup
|
||||
|
||||
Get started by installing 🤗 Accelerate:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install accelerate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then import and create an [`~accelerate.Accelerator`] object. The [`~accelerate.Accelerator`] will automatically detect your type of distributed setup and initialize all the necessary components for training. You don't need to explicitly place your model on a device.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
|
||||
>>> accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Prepare to accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
The next step is to pass all the relevant training objects to the [`~accelerate.Accelerator.prepare`] method. This includes your training and evaluation DataLoaders, a model and an optimizer:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
... train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Backward
|
||||
|
||||
The last addition is to replace the typical `loss.backward()` in your training loop with 🤗 Accelerate's [`~accelerate.Accelerator.backward`]method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> for epoch in range(num_epochs):
|
||||
... for batch in train_dataloader:
|
||||
... outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
... loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
... accelerator.backward(loss)
|
||||
|
||||
... optimizer.step()
|
||||
... lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
... optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
... progress_bar.update(1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see in the following code, you only need to add four additional lines of code to your training loop to enable distributed training!
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
+ from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from transformers import AdamW, AutoModelForSequenceClassification, get_scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
+ accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(checkpoint, num_labels=2)
|
||||
optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=3e-5)
|
||||
|
||||
- device = torch.device("cuda") if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.device("cpu")
|
||||
- model.to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
+ train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
+ train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer
|
||||
+ )
|
||||
|
||||
num_epochs = 3
|
||||
num_training_steps = num_epochs * len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
|
||||
"linear",
|
||||
optimizer=optimizer,
|
||||
num_warmup_steps=0,
|
||||
num_training_steps=num_training_steps
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
progress_bar = tqdm(range(num_training_steps))
|
||||
|
||||
model.train()
|
||||
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
|
||||
for batch in train_dataloader:
|
||||
- batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
|
||||
outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
- loss.backward()
|
||||
+ accelerator.backward(loss)
|
||||
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
progress_bar.update(1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Train
|
||||
|
||||
Once you've added the relevant lines of code, launch your training in a script or a notebook like Colaboratory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Train with a script
|
||||
|
||||
If you are running your training from a script, run the following command to create and save a configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then launch your training with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch train.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Train with a notebook
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Accelerate can also run in a notebook if you're planning on using Colaboratory's TPUs. Wrap all the code responsible for training in a function, and pass it to [`~accelerate.notebook_launcher`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from accelerate import notebook_launcher
|
||||
|
||||
>>> notebook_launcher(training_function)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more information about 🤗 Accelerate and it's rich features, refer to the [documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate).
|
||||
@ -1,132 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Distributed training with 🤗 Accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
As models get bigger, parallelism has emerged as a strategy for training larger models on limited hardware and accelerating training speed by several orders of magnitude. At Hugging Face, we created the [🤗 Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate) library to help users easily train a 🤗 Transformers model on any type of distributed setup, whether it is multiple GPU's on one machine or multiple GPU's across several machines. In this tutorial, learn how to customize your native PyTorch training loop to enable training in a distributed environment.
|
||||
|
||||
## Setup
|
||||
|
||||
Get started by installing 🤗 Accelerate:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install accelerate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then import and create an [`~accelerate.Accelerator`] object. The [`~accelerate.Accelerator`] will automatically detect your type of distributed setup and initialize all the necessary components for training. You don't need to explicitly place your model on a device.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
|
||||
>>> accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Prepare to accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
The next step is to pass all the relevant training objects to the [`~accelerate.Accelerator.prepare`] method. This includes your training and evaluation DataLoaders, a model and an optimizer:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
... train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Backward
|
||||
|
||||
The last addition is to replace the typical `loss.backward()` in your training loop with 🤗 Accelerate's [`~accelerate.Accelerator.backward`]method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> for epoch in range(num_epochs):
|
||||
... for batch in train_dataloader:
|
||||
... outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
... loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
... accelerator.backward(loss)
|
||||
|
||||
... optimizer.step()
|
||||
... lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
... optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
... progress_bar.update(1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see in the following code, you only need to add four additional lines of code to your training loop to enable distributed training!
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
+ from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from transformers import AdamW, AutoModelForSequenceClassification, get_scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
+ accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(checkpoint, num_labels=2)
|
||||
optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=3e-5)
|
||||
|
||||
- device = torch.device("cuda") if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.device("cpu")
|
||||
- model.to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
+ train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
+ train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, model, optimizer
|
||||
+ )
|
||||
|
||||
num_epochs = 3
|
||||
num_training_steps = num_epochs * len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
|
||||
"linear",
|
||||
optimizer=optimizer,
|
||||
num_warmup_steps=0,
|
||||
num_training_steps=num_training_steps
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
progress_bar = tqdm(range(num_training_steps))
|
||||
|
||||
model.train()
|
||||
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
|
||||
for batch in train_dataloader:
|
||||
- batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
|
||||
outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
- loss.backward()
|
||||
+ accelerator.backward(loss)
|
||||
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
progress_bar.update(1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Train
|
||||
|
||||
Once you've added the relevant lines of code, launch your training in a script or a notebook like Colaboratory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Train with a script
|
||||
|
||||
If you are running your training from a script, run the following command to create and save a configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then launch your training with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch train.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Train with a notebook
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Accelerate can also run in a notebook if you're planning on using Colaboratory's TPUs. Wrap all the code responsible for training in a function, and pass it to [`~accelerate.notebook_launcher`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from accelerate import notebook_launcher
|
||||
|
||||
>>> notebook_launcher(training_function)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more information about 🤗 Accelerate and it's rich features, refer to the [documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate).
|
||||
895
docs/source/en/add_new_model.md
Normal file
895
docs/source/en/add_new_model.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,895 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# How to add a model to 🤗 Transformers?
|
||||
|
||||
The 🤗 Transformers library is often able to offer new models thanks to community contributors. But this can be a challenging project and requires an in-depth knowledge of the 🤗 Transformers library and the model to implement. At Hugging Face, we're trying to empower more of the community to actively add models and we've put together this guide to walk you through the process of adding a PyTorch model (make sure you have [PyTorch installed](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/)).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If you're interested in implementing a TensorFlow model, take a look at the [How to convert a 🤗 Transformers model to TensorFlow](add_tensorflow_model) guide!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Along the way, you'll:
|
||||
|
||||
- get insights into open-source best practices
|
||||
- understand the design principles behind one of the most popular deep learning libraries
|
||||
- learn how to efficiently test large models
|
||||
- learn how to integrate Python utilities like `black`, `ruff`, and `make fix-copies` to ensure clean and readable code
|
||||
|
||||
A Hugging Face team member will be available to help you along the way so you'll never be alone. 🤗 ❤️
|
||||
|
||||
To get started, open a [New model addition](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=New+model&template=new-model-addition.yml) issue for the model you want to see in 🤗 Transformers. If you're not especially picky about contributing a specific model, you can filter by the [New model label](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/labels/New%20model) to see if there are any unclaimed model requests and work on it.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you've opened a new model request, the first step is to get familiar with 🤗 Transformers if you aren't already!
|
||||
|
||||
## General overview of 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
First, you should get a general overview of 🤗 Transformers. 🤗 Transformers is a very opinionated library, so there is a
|
||||
chance that you don't agree with some of the library's philosophies or design choices. From our experience, however, we
|
||||
found that the fundamental design choices and philosophies of the library are crucial to efficiently scale 🤗
|
||||
Transformers while keeping maintenance costs at a reasonable level.
|
||||
|
||||
A good first starting point to better understand the library is to read the [documentation of our philosophy](philosophy). As a result of our way of working, there are some choices that we try to apply to all models:
|
||||
|
||||
- Composition is generally favored over-abstraction
|
||||
- Duplicating code is not always bad if it strongly improves the readability or accessibility of a model
|
||||
- Model files are as self-contained as possible so that when you read the code of a specific model, you ideally only
|
||||
have to look into the respective `modeling_....py` file.
|
||||
|
||||
In our opinion, the library's code is not just a means to provide a product, *e.g.* the ability to use BERT for
|
||||
inference, but also as the very product that we want to improve. Hence, when adding a model, the user is not only the
|
||||
person that will use your model, but also everybody that will read, try to understand, and possibly tweak your code.
|
||||
|
||||
With this in mind, let's go a bit deeper into the general library design.
|
||||
|
||||
### Overview of models
|
||||
|
||||
To successfully add a model, it is important to understand the interaction between your model and its config,
|
||||
[`PreTrainedModel`], and [`PretrainedConfig`]. For exemplary purposes, we will
|
||||
call the model to be added to 🤗 Transformers `BrandNewBert`.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take a look:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers_overview.png"/>
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, we do make use of inheritance in 🤗 Transformers, but we keep the level of abstraction to an absolute
|
||||
minimum. There are never more than two levels of abstraction for any model in the library. `BrandNewBertModel`
|
||||
inherits from `BrandNewBertPreTrainedModel` which in turn inherits from [`PreTrainedModel`] and
|
||||
that's it. As a general rule, we want to make sure that a new model only depends on
|
||||
[`PreTrainedModel`]. The important functionalities that are automatically provided to every new
|
||||
model are [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] and
|
||||
[`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`], which are used for serialization and deserialization. All of the
|
||||
other important functionalities, such as `BrandNewBertModel.forward` should be completely defined in the new
|
||||
`modeling_brand_new_bert.py` script. Next, we want to make sure that a model with a specific head layer, such as
|
||||
`BrandNewBertForMaskedLM` does not inherit from `BrandNewBertModel`, but rather uses `BrandNewBertModel`
|
||||
as a component that can be called in its forward pass to keep the level of abstraction low. Every new model requires a
|
||||
configuration class, called `BrandNewBertConfig`. This configuration is always stored as an attribute in
|
||||
[`PreTrainedModel`], and thus can be accessed via the `config` attribute for all classes
|
||||
inheriting from `BrandNewBertPreTrainedModel`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = BrandNewBertModel.from_pretrained("brandy/brand_new_bert")
|
||||
model.config # model has access to its config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to the model, the configuration inherits basic serialization and deserialization functionalities from
|
||||
[`PretrainedConfig`]. Note that the configuration and the model are always serialized into two
|
||||
different formats - the model to a *pytorch_model.bin* file and the configuration to a *config.json* file. Calling
|
||||
[`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] will automatically call
|
||||
[`~PretrainedConfig.save_pretrained`], so that both model and configuration are saved.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Code style
|
||||
|
||||
When coding your new model, keep in mind that Transformers is an opinionated library and we have a few quirks of our
|
||||
own regarding how code should be written :-)
|
||||
|
||||
1. The forward pass of your model should be fully written in the modeling file while being fully independent of other
|
||||
models in the library. If you want to reuse a block from another model, copy the code and paste it with a
|
||||
`# Copied from` comment on top (see [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/v4.17.0/src/transformers/models/roberta/modeling_roberta.py#L160)
|
||||
for a good example).
|
||||
2. The code should be fully understandable, even by a non-native English speaker. This means you should pick
|
||||
descriptive variable names and avoid abbreviations. As an example, `activation` is preferred to `act`.
|
||||
One-letter variable names are strongly discouraged unless it's an index in a for loop.
|
||||
3. More generally we prefer longer explicit code to short magical one.
|
||||
4. Avoid subclassing `nn.Sequential` in PyTorch but subclass `nn.Module` and write the forward pass, so that anyone
|
||||
using your code can quickly debug it by adding print statements or breaking points.
|
||||
5. Your function signature should be type-annotated. For the rest, good variable names are way more readable and
|
||||
understandable than type annotations.
|
||||
|
||||
### Overview of tokenizers
|
||||
|
||||
Not quite ready yet :-( This section will be added soon!
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-by-step recipe to add a model to 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
Everyone has different preferences of how to port a model so it can be very helpful for you to take a look at summaries
|
||||
of how other contributors ported models to Hugging Face. Here is a list of community blog posts on how to port a model:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Porting GPT2 Model](https://medium.com/huggingface/from-tensorflow-to-pytorch-265f40ef2a28) by [Thomas](https://huggingface.co/thomwolf)
|
||||
2. [Porting WMT19 MT Model](https://huggingface.co/blog/porting-fsmt) by [Stas](https://huggingface.co/stas)
|
||||
|
||||
From experience, we can tell you that the most important things to keep in mind when adding a model are:
|
||||
|
||||
- Don't reinvent the wheel! Most parts of the code you will add for the new 🤗 Transformers model already exist
|
||||
somewhere in 🤗 Transformers. Take some time to find similar, already existing models and tokenizers you can copy
|
||||
from. [grep](https://www.gnu.org/software/grep/) and [rg](https://github.com/BurntSushi/ripgrep) are your
|
||||
friends. Note that it might very well happen that your model's tokenizer is based on one model implementation, and
|
||||
your model's modeling code on another one. *E.g.* FSMT's modeling code is based on BART, while FSMT's tokenizer code
|
||||
is based on XLM.
|
||||
- It's more of an engineering challenge than a scientific challenge. You should spend more time on creating an
|
||||
efficient debugging environment than trying to understand all theoretical aspects of the model in the paper.
|
||||
- Ask for help, when you're stuck! Models are the core component of 🤗 Transformers so that we at Hugging Face are more
|
||||
than happy to help you at every step to add your model. Don't hesitate to ask if you notice you are not making
|
||||
progress.
|
||||
|
||||
In the following, we try to give you a general recipe that we found most useful when porting a model to 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
The following list is a summary of everything that has to be done to add a model and can be used by you as a To-Do
|
||||
List:
|
||||
|
||||
☐ (Optional) Understood the model's theoretical aspects<br>
|
||||
☐ Prepared 🤗 Transformers dev environment<br>
|
||||
☐ Set up debugging environment of the original repository<br>
|
||||
☐ Created script that successfully runs the `forward()` pass using the original repository and checkpoint<br>
|
||||
☐ Successfully added the model skeleton to 🤗 Transformers<br>
|
||||
☐ Successfully converted original checkpoint to 🤗 Transformers checkpoint<br>
|
||||
☐ Successfully ran `forward()` pass in 🤗 Transformers that gives identical output to original checkpoint<br>
|
||||
☐ Finished model tests in 🤗 Transformers<br>
|
||||
☐ Successfully added tokenizer in 🤗 Transformers<br>
|
||||
☐ Run end-to-end integration tests<br>
|
||||
☐ Finished docs<br>
|
||||
☐ Uploaded model weights to the Hub<br>
|
||||
☐ Submitted the pull request<br>
|
||||
☐ (Optional) Added a demo notebook
|
||||
|
||||
To begin with, we usually recommend to start by getting a good theoretical understanding of `BrandNewBert`. However,
|
||||
if you prefer to understand the theoretical aspects of the model *on-the-job*, then it is totally fine to directly dive
|
||||
into the `BrandNewBert`'s code-base. This option might suit you better, if your engineering skills are better than
|
||||
your theoretical skill, if you have trouble understanding `BrandNewBert`'s paper, or if you just enjoy programming
|
||||
much more than reading scientific papers.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. (Optional) Theoretical aspects of BrandNewBert
|
||||
|
||||
You should take some time to read *BrandNewBert's* paper, if such descriptive work exists. There might be large
|
||||
sections of the paper that are difficult to understand. If this is the case, this is fine - don't worry! The goal is
|
||||
not to get a deep theoretical understanding of the paper, but to extract the necessary information required to
|
||||
effectively re-implement the model in 🤗 Transformers. That being said, you don't have to spend too much time on the
|
||||
theoretical aspects, but rather focus on the practical ones, namely:
|
||||
|
||||
- What type of model is *brand_new_bert*? BERT-like encoder-only model? GPT2-like decoder-only model? BART-like
|
||||
encoder-decoder model? Look at the [model_summary](model_summary) if you're not familiar with the differences between those.
|
||||
- What are the applications of *brand_new_bert*? Text classification? Text generation? Seq2Seq tasks, *e.g.,*
|
||||
summarization?
|
||||
- What is the novel feature of the model making it different from BERT/GPT-2/BART?
|
||||
- Which of the already existing [🤗 Transformers models](https://huggingface.co/transformers/#contents) is most
|
||||
similar to *brand_new_bert*?
|
||||
- What type of tokenizer is used? A sentencepiece tokenizer? Word piece tokenizer? Is it the same tokenizer as used
|
||||
for BERT or BART?
|
||||
|
||||
After you feel like you have gotten a good overview of the architecture of the model, you might want to write to the
|
||||
Hugging Face team with any questions you might have. This might include questions regarding the model's architecture,
|
||||
its attention layer, etc. We will be more than happy to help you.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Next prepare your environment
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fork the [repository](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers) by clicking on the ‘Fork' button on the
|
||||
repository's page. This creates a copy of the code under your GitHub user account.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Clone your `transformers` fork to your local disk, and add the base repository as a remote:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/[your Github handle]/transformers.git
|
||||
cd transformers
|
||||
git remote add upstream https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Set up a development environment, for instance by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m venv .env
|
||||
source .env/bin/activate
|
||||
pip install -e ".[dev]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on your OS, and since the number of optional dependencies of Transformers is growing, you might get a
|
||||
failure with this command. If that's the case make sure to install the Deep Learning framework you are working with
|
||||
(PyTorch, TensorFlow and/or Flax) then do:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -e ".[quality]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which should be enough for most use cases. You can then return to the parent directory
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ..
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. We recommend adding the PyTorch version of *brand_new_bert* to Transformers. To install PyTorch, please follow the
|
||||
instructions on https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** You don't need to have CUDA installed. Making the new model work on CPU is sufficient.
|
||||
|
||||
5. To port *brand_new_bert*, you will also need access to its original repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/org_that_created_brand_new_bert_org/brand_new_bert.git
|
||||
cd brand_new_bert
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you have set up a development environment to port *brand_new_bert* to 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.-4. Run a pretrained checkpoint using the original repository
|
||||
|
||||
At first, you will work on the original *brand_new_bert* repository. Often, the original implementation is very
|
||||
“researchy”. Meaning that documentation might be lacking and the code can be difficult to understand. But this should
|
||||
be exactly your motivation to reimplement *brand_new_bert*. At Hugging Face, one of our main goals is to *make people
|
||||
stand on the shoulders of giants* which translates here very well into taking a working model and rewriting it to make
|
||||
it as **accessible, user-friendly, and beautiful** as possible. This is the number-one motivation to re-implement
|
||||
models into 🤗 Transformers - trying to make complex new NLP technology accessible to **everybody**.
|
||||
|
||||
You should start thereby by diving into the original repository.
|
||||
|
||||
Successfully running the official pretrained model in the original repository is often **the most difficult** step.
|
||||
From our experience, it is very important to spend some time getting familiar with the original code-base. You need to
|
||||
figure out the following:
|
||||
|
||||
- Where to find the pretrained weights?
|
||||
- How to load the pretrained weights into the corresponding model?
|
||||
- How to run the tokenizer independently from the model?
|
||||
- Trace one forward pass so that you know which classes and functions are required for a simple forward pass. Usually,
|
||||
you only have to reimplement those functions.
|
||||
- Be able to locate the important components of the model: Where is the model's class? Are there model sub-classes,
|
||||
*e.g.* EncoderModel, DecoderModel? Where is the self-attention layer? Are there multiple different attention layers,
|
||||
*e.g.* *self-attention*, *cross-attention*...?
|
||||
- How can you debug the model in the original environment of the repo? Do you have to add *print* statements, can you
|
||||
work with an interactive debugger like *ipdb*, or should you use an efficient IDE to debug the model, like PyCharm?
|
||||
|
||||
It is very important that before you start the porting process, that you can **efficiently** debug code in the original
|
||||
repository! Also, remember that you are working with an open-source library, so do not hesitate to open an issue, or
|
||||
even a pull request in the original repository. The maintainers of this repository are most likely very happy about
|
||||
someone looking into their code!
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, it is really up to you which debugging environment and strategy you prefer to use to debug the original
|
||||
model. We strongly advise against setting up a costly GPU environment, but simply work on a CPU both when starting to
|
||||
dive into the original repository and also when starting to write the 🤗 Transformers implementation of the model. Only
|
||||
at the very end, when the model has already been successfully ported to 🤗 Transformers, one should verify that the
|
||||
model also works as expected on GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
In general, there are two possible debugging environments for running the original model
|
||||
|
||||
- [Jupyter notebooks](https://jupyter.org/) / [google colab](https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/intro.ipynb)
|
||||
- Local python scripts.
|
||||
|
||||
Jupyter notebooks have the advantage that they allow for cell-by-cell execution which can be helpful to better split
|
||||
logical components from one another and to have faster debugging cycles as intermediate results can be stored. Also,
|
||||
notebooks are often easier to share with other contributors, which might be very helpful if you want to ask the Hugging
|
||||
Face team for help. If you are familiar with Jupyter notebooks, we strongly recommend you to work with them.
|
||||
|
||||
The obvious disadvantage of Jupyter notebooks is that if you are not used to working with them you will have to spend
|
||||
some time adjusting to the new programming environment and that you might not be able to use your known debugging tools
|
||||
anymore, like `ipdb`.
|
||||
|
||||
For each code-base, a good first step is always to load a **small** pretrained checkpoint and to be able to reproduce a
|
||||
single forward pass using a dummy integer vector of input IDs as an input. Such a script could look like this (in
|
||||
pseudocode):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = BrandNewBertModel.load_pretrained_checkpoint("/path/to/checkpoint/")
|
||||
input_ids = [0, 4, 5, 2, 3, 7, 9] # vector of input ids
|
||||
original_output = model.predict(input_ids)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, regarding the debugging strategy, there are generally a few from which to choose from:
|
||||
|
||||
- Decompose the original model into many small testable components and run a forward pass on each of those for
|
||||
verification
|
||||
- Decompose the original model only into the original *tokenizer* and the original *model*, run a forward pass on
|
||||
those, and use intermediate print statements or breakpoints for verification
|
||||
|
||||
Again, it is up to you which strategy to choose. Often, one or the other is advantageous depending on the original code
|
||||
base.
|
||||
|
||||
If the original code-base allows you to decompose the model into smaller sub-components, *e.g.* if the original
|
||||
code-base can easily be run in eager mode, it is usually worth the effort to do so. There are some important advantages
|
||||
to taking the more difficult road in the beginning:
|
||||
|
||||
- at a later stage when comparing the original model to the Hugging Face implementation, you can verify automatically
|
||||
for each component individually that the corresponding component of the 🤗 Transformers implementation matches instead
|
||||
of relying on visual comparison via print statements
|
||||
- it can give you some rope to decompose the big problem of porting a model into smaller problems of just porting
|
||||
individual components and thus structure your work better
|
||||
- separating the model into logical meaningful components will help you to get a better overview of the model's design
|
||||
and thus to better understand the model
|
||||
- at a later stage those component-by-component tests help you to ensure that no regression occurs as you continue
|
||||
changing your code
|
||||
|
||||
[Lysandre's](https://gist.github.com/LysandreJik/db4c948f6b4483960de5cbac598ad4ed) integration checks for ELECTRA
|
||||
gives a nice example of how this can be done.
|
||||
|
||||
However, if the original code-base is very complex or only allows intermediate components to be run in a compiled mode,
|
||||
it might be too time-consuming or even impossible to separate the model into smaller testable sub-components. A good
|
||||
example is [T5's MeshTensorFlow](https://github.com/tensorflow/mesh/tree/master/mesh_tensorflow) library which is
|
||||
very complex and does not offer a simple way to decompose the model into its sub-components. For such libraries, one
|
||||
often relies on verifying print statements.
|
||||
|
||||
No matter which strategy you choose, the recommended procedure is often the same in that you should start to debug the
|
||||
starting layers first and the ending layers last.
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended that you retrieve the output, either by print statements or sub-component functions, of the following
|
||||
layers in the following order:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Retrieve the input IDs passed to the model
|
||||
2. Retrieve the word embeddings
|
||||
3. Retrieve the input of the first Transformer layer
|
||||
4. Retrieve the output of the first Transformer layer
|
||||
5. Retrieve the output of the following n - 1 Transformer layers
|
||||
6. Retrieve the output of the whole BrandNewBert Model
|
||||
|
||||
Input IDs should thereby consists of an array of integers, *e.g.* `input_ids = [0, 4, 4, 3, 2, 4, 1, 7, 19]`
|
||||
|
||||
The outputs of the following layers often consist of multi-dimensional float arrays and can look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[[
|
||||
[-0.1465, -0.6501, 0.1993, ..., 0.1451, 0.3430, 0.6024],
|
||||
[-0.4417, -0.5920, 0.3450, ..., -0.3062, 0.6182, 0.7132],
|
||||
[-0.5009, -0.7122, 0.4548, ..., -0.3662, 0.6091, 0.7648],
|
||||
...,
|
||||
[-0.5613, -0.6332, 0.4324, ..., -0.3792, 0.7372, 0.9288],
|
||||
[-0.5416, -0.6345, 0.4180, ..., -0.3564, 0.6992, 0.9191],
|
||||
[-0.5334, -0.6403, 0.4271, ..., -0.3339, 0.6533, 0.8694]]],
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We expect that every model added to 🤗 Transformers passes a couple of integration tests, meaning that the original
|
||||
model and the reimplemented version in 🤗 Transformers have to give the exact same output up to a precision of 0.001!
|
||||
Since it is normal that the exact same model written in different libraries can give a slightly different output
|
||||
depending on the library framework, we accept an error tolerance of 1e-3 (0.001). It is not enough if the model gives
|
||||
nearly the same output, they have to be the almost identical. Therefore, you will certainly compare the intermediate
|
||||
outputs of the 🤗 Transformers version multiple times against the intermediate outputs of the original implementation of
|
||||
*brand_new_bert* in which case an **efficient** debugging environment of the original repository is absolutely
|
||||
important. Here is some advice is to make your debugging environment as efficient as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
- Find the best way of debugging intermediate results. Is the original repository written in PyTorch? Then you should
|
||||
probably take the time to write a longer script that decomposes the original model into smaller sub-components to
|
||||
retrieve intermediate values. Is the original repository written in Tensorflow 1? Then you might have to rely on
|
||||
TensorFlow print operations like [tf.print](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/print) to output
|
||||
intermediate values. Is the original repository written in Jax? Then make sure that the model is **not jitted** when
|
||||
running the forward pass, *e.g.* check-out [this link](https://github.com/google/jax/issues/196).
|
||||
- Use the smallest pretrained checkpoint you can find. The smaller the checkpoint, the faster your debug cycle
|
||||
becomes. It is not efficient if your pretrained model is so big that your forward pass takes more than 10 seconds.
|
||||
In case only very large checkpoints are available, it might make more sense to create a dummy model in the new
|
||||
environment with randomly initialized weights and save those weights for comparison with the 🤗 Transformers version
|
||||
of your model
|
||||
- Make sure you are using the easiest way of calling a forward pass in the original repository. Ideally, you want to
|
||||
find the function in the original repository that **only** calls a single forward pass, *i.e.* that is often called
|
||||
`predict`, `evaluate`, `forward` or `__call__`. You don't want to debug a function that calls `forward`
|
||||
multiple times, *e.g.* to generate text, like `autoregressive_sample`, `generate`.
|
||||
- Try to separate the tokenization from the model's *forward* pass. If the original repository shows examples where
|
||||
you have to input a string, then try to find out where in the forward call the string input is changed to input ids
|
||||
and start from this point. This might mean that you have to possibly write a small script yourself or change the
|
||||
original code so that you can directly input the ids instead of an input string.
|
||||
- Make sure that the model in your debugging setup is **not** in training mode, which often causes the model to yield
|
||||
random outputs due to multiple dropout layers in the model. Make sure that the forward pass in your debugging
|
||||
environment is **deterministic** so that the dropout layers are not used. Or use *transformers.utils.set_seed*
|
||||
if the old and new implementations are in the same framework.
|
||||
|
||||
The following section gives you more specific details/tips on how you can do this for *brand_new_bert*.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.-14. Port BrandNewBert to 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
Next, you can finally start adding new code to 🤗 Transformers. Go into the clone of your 🤗 Transformers' fork:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the special case that you are adding a model whose architecture exactly matches the model architecture of an
|
||||
existing model you only have to add a conversion script as described in [this section](#write-a-conversion-script).
|
||||
In this case, you can just re-use the whole model architecture of the already existing model.
|
||||
|
||||
Otherwise, let's start generating a new model. You have two choices here:
|
||||
|
||||
- `transformers-cli add-new-model-like` to add a new model like an existing one
|
||||
- `transformers-cli add-new-model` to add a new model from our template (will look like BERT or Bart depending on the type of model you select)
|
||||
|
||||
In both cases, you will be prompted with a questionnaire to fill the basic information of your model. The second command requires to install `cookiecutter`, you can find more information on it [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/templates/adding_a_new_model).
|
||||
|
||||
**Open a Pull Request on the main huggingface/transformers repo**
|
||||
|
||||
Before starting to adapt the automatically generated code, now is the time to open a “Work in progress (WIP)” pull
|
||||
request, *e.g.* “[WIP] Add *brand_new_bert*”, in 🤗 Transformers so that you and the Hugging Face team can work
|
||||
side-by-side on integrating the model into 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
You should do the following:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create a branch with a descriptive name from your main branch
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git checkout -b add_brand_new_bert
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Commit the automatically generated code:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git add .
|
||||
git commit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Fetch and rebase to current main
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git fetch upstream
|
||||
git rebase upstream/main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Push the changes to your account using:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git push -u origin a-descriptive-name-for-my-changes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Once you are satisfied, go to the webpage of your fork on GitHub. Click on “Pull request”. Make sure to add the
|
||||
GitHub handle of some members of the Hugging Face team as reviewers, so that the Hugging Face team gets notified for
|
||||
future changes.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Change the PR into a draft by clicking on “Convert to draft” on the right of the GitHub pull request web page.
|
||||
|
||||
In the following, whenever you have done some progress, don't forget to commit your work and push it to your account so
|
||||
that it shows in the pull request. Additionally, you should make sure to update your work with the current main from
|
||||
time to time by doing:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git fetch upstream
|
||||
git merge upstream/main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In general, all questions you might have regarding the model or your implementation should be asked in your PR and
|
||||
discussed/solved in the PR. This way, the Hugging Face team will always be notified when you are committing new code or
|
||||
if you have a question. It is often very helpful to point the Hugging Face team to your added code so that the Hugging
|
||||
Face team can efficiently understand your problem or question.
|
||||
|
||||
To do so, you can go to the “Files changed” tab where you see all of your changes, go to a line regarding which you
|
||||
want to ask a question, and click on the “+” symbol to add a comment. Whenever a question or problem has been solved,
|
||||
you can click on the “Resolve” button of the created comment.
|
||||
|
||||
In the same way, the Hugging Face team will open comments when reviewing your code. We recommend asking most questions
|
||||
on GitHub on your PR. For some very general questions that are not very useful for the public, feel free to ping the
|
||||
Hugging Face team by Slack or email.
|
||||
|
||||
**5. Adapt the generated models code for brand_new_bert**
|
||||
|
||||
At first, we will focus only on the model itself and not care about the tokenizer. All the relevant code should be
|
||||
found in the generated files `src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/modeling_brand_new_bert.py` and
|
||||
`src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/configuration_brand_new_bert.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can finally start coding :). The generated code in
|
||||
`src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/modeling_brand_new_bert.py` will either have the same architecture as BERT if
|
||||
it's an encoder-only model or BART if it's an encoder-decoder model. At this point, you should remind yourself what
|
||||
you've learned in the beginning about the theoretical aspects of the model: *How is the model different from BERT or
|
||||
BART?*". Implement those changes which often means to change the *self-attention* layer, the order of the normalization
|
||||
layer, etc… Again, it is often useful to look at the similar architecture of already existing models in Transformers to
|
||||
get a better feeling of how your model should be implemented.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note** that at this point, you don't have to be very sure that your code is fully correct or clean. Rather, it is
|
||||
advised to add a first *unclean*, copy-pasted version of the original code to
|
||||
`src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/modeling_brand_new_bert.py` until you feel like all the necessary code is
|
||||
added. From our experience, it is much more efficient to quickly add a first version of the required code and
|
||||
improve/correct the code iteratively with the conversion script as described in the next section. The only thing that
|
||||
has to work at this point is that you can instantiate the 🤗 Transformers implementation of *brand_new_bert*, *i.e.* the
|
||||
following command should work:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import BrandNewBertModel, BrandNewBertConfig
|
||||
|
||||
model = BrandNewBertModel(BrandNewBertConfig())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will create a model according to the default parameters as defined in `BrandNewBertConfig()` with
|
||||
random weights, thus making sure that the `init()` methods of all components works.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that all random initialization should happen in the `_init_weights` method of your `BrandnewBertPreTrainedModel`
|
||||
class. It should initialize all leaf modules depending on the variables of the config. Here is an example with the
|
||||
BERT `_init_weights` method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
def _init_weights(self, module):
|
||||
"""Initialize the weights"""
|
||||
if isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
|
||||
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
|
||||
if module.bias is not None:
|
||||
module.bias.data.zero_()
|
||||
elif isinstance(module, nn.Embedding):
|
||||
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
|
||||
if module.padding_idx is not None:
|
||||
module.weight.data[module.padding_idx].zero_()
|
||||
elif isinstance(module, nn.LayerNorm):
|
||||
module.bias.data.zero_()
|
||||
module.weight.data.fill_(1.0)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can have some more custom schemes if you need a special initialization for some modules. For instance, in
|
||||
`Wav2Vec2ForPreTraining`, the last two linear layers need to have the initialization of the regular PyTorch `nn.Linear`
|
||||
but all the other ones should use an initialization as above. This is coded like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
def _init_weights(self, module):
|
||||
"""Initialize the weights"""
|
||||
if isinstnace(module, Wav2Vec2ForPreTraining):
|
||||
module.project_hid.reset_parameters()
|
||||
module.project_q.reset_parameters()
|
||||
module.project_hid._is_hf_initialized = True
|
||||
module.project_q._is_hf_initialized = True
|
||||
elif isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
|
||||
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
|
||||
if module.bias is not None:
|
||||
module.bias.data.zero_()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `_is_hf_initialized` flag is internally used to make sure we only initialize a submodule once. By setting it to
|
||||
`True` for `module.project_q` and `module.project_hid`, we make sure the custom initialization we did is not overridden later on,
|
||||
the `_init_weights` function won't be applied to them.
|
||||
|
||||
**6. Write a conversion script**
|
||||
|
||||
Next, you should write a conversion script that lets you convert the checkpoint you used to debug *brand_new_bert* in
|
||||
the original repository to a checkpoint compatible with your just created 🤗 Transformers implementation of
|
||||
*brand_new_bert*. It is not advised to write the conversion script from scratch, but rather to look through already
|
||||
existing conversion scripts in 🤗 Transformers for one that has been used to convert a similar model that was written in
|
||||
the same framework as *brand_new_bert*. Usually, it is enough to copy an already existing conversion script and
|
||||
slightly adapt it for your use case. Don't hesitate to ask the Hugging Face team to point you to a similar already
|
||||
existing conversion script for your model.
|
||||
|
||||
- If you are porting a model from TensorFlow to PyTorch, a good starting point might be BERT's conversion script [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/7acfa95afb8194f8f9c1f4d2c6028224dbed35a2/src/transformers/models/bert/modeling_bert.py#L91)
|
||||
- If you are porting a model from PyTorch to PyTorch, a good starting point might be BART's conversion script [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/models/bart/convert_bart_original_pytorch_checkpoint_to_pytorch.py)
|
||||
|
||||
In the following, we'll quickly explain how PyTorch models store layer weights and define layer names. In PyTorch, the
|
||||
name of a layer is defined by the name of the class attribute you give the layer. Let's define a dummy model in
|
||||
PyTorch, called `SimpleModel` as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class SimpleModel(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.dense = nn.Linear(10, 10)
|
||||
self.intermediate = nn.Linear(10, 10)
|
||||
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(10)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can create an instance of this model definition which will fill all weights: `dense`, `intermediate`,
|
||||
`layer_norm` with random weights. We can print the model to see its architecture
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = SimpleModel()
|
||||
|
||||
print(model)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will print out the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
SimpleModel(
|
||||
(dense): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=10, bias=True)
|
||||
(intermediate): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=10, bias=True)
|
||||
(layer_norm): LayerNorm((10,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can see that the layer names are defined by the name of the class attribute in PyTorch. You can print out the weight
|
||||
values of a specific layer:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
print(model.dense.weight.data)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
to see that the weights were randomly initialized
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
tensor([[-0.0818, 0.2207, -0.0749, -0.0030, 0.0045, -0.1569, -0.1598, 0.0212,
|
||||
-0.2077, 0.2157],
|
||||
[ 0.1044, 0.0201, 0.0990, 0.2482, 0.3116, 0.2509, 0.2866, -0.2190,
|
||||
0.2166, -0.0212],
|
||||
[-0.2000, 0.1107, -0.1999, -0.3119, 0.1559, 0.0993, 0.1776, -0.1950,
|
||||
-0.1023, -0.0447],
|
||||
[-0.0888, -0.1092, 0.2281, 0.0336, 0.1817, -0.0115, 0.2096, 0.1415,
|
||||
-0.1876, -0.2467],
|
||||
[ 0.2208, -0.2352, -0.1426, -0.2636, -0.2889, -0.2061, -0.2849, -0.0465,
|
||||
0.2577, 0.0402],
|
||||
[ 0.1502, 0.2465, 0.2566, 0.0693, 0.2352, -0.0530, 0.1859, -0.0604,
|
||||
0.2132, 0.1680],
|
||||
[ 0.1733, -0.2407, -0.1721, 0.1484, 0.0358, -0.0633, -0.0721, -0.0090,
|
||||
0.2707, -0.2509],
|
||||
[-0.1173, 0.1561, 0.2945, 0.0595, -0.1996, 0.2988, -0.0802, 0.0407,
|
||||
0.1829, -0.1568],
|
||||
[-0.1164, -0.2228, -0.0403, 0.0428, 0.1339, 0.0047, 0.1967, 0.2923,
|
||||
0.0333, -0.0536],
|
||||
[-0.1492, -0.1616, 0.1057, 0.1950, -0.2807, -0.2710, -0.1586, 0.0739,
|
||||
0.2220, 0.2358]]).
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the conversion script, you should fill those randomly initialized weights with the exact weights of the
|
||||
corresponding layer in the checkpoint. *E.g.*
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# retrieve matching layer weights, e.g. by
|
||||
# recursive algorithm
|
||||
layer_name = "dense"
|
||||
pretrained_weight = array_of_dense_layer
|
||||
|
||||
model_pointer = getattr(model, "dense")
|
||||
|
||||
model_pointer.weight.data = torch.from_numpy(pretrained_weight)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
While doing so, you must verify that each randomly initialized weight of your PyTorch model and its corresponding
|
||||
pretrained checkpoint weight exactly match in both **shape and name**. To do so, it is **necessary** to add assert
|
||||
statements for the shape and print out the names of the checkpoints weights. E.g. you should add statements like:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
model_pointer.weight.shape == pretrained_weight.shape
|
||||
), f"Pointer shape of random weight {model_pointer.shape} and array shape of checkpoint weight {pretrained_weight.shape} mismatched"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Besides, you should also print out the names of both weights to make sure they match, *e.g.*
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
logger.info(f"Initialize PyTorch weight {layer_name} from {pretrained_weight.name}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If either the shape or the name doesn't match, you probably assigned the wrong checkpoint weight to a randomly
|
||||
initialized layer of the 🤗 Transformers implementation.
|
||||
|
||||
An incorrect shape is most likely due to an incorrect setting of the config parameters in `BrandNewBertConfig()` that
|
||||
do not exactly match those that were used for the checkpoint you want to convert. However, it could also be that
|
||||
PyTorch's implementation of a layer requires the weight to be transposed beforehand.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, you should also check that **all** required weights are initialized and print out all checkpoint weights that
|
||||
were not used for initialization to make sure the model is correctly converted. It is completely normal, that the
|
||||
conversion trials fail with either a wrong shape statement or wrong name assignment. This is most likely because either
|
||||
you used incorrect parameters in `BrandNewBertConfig()`, have a wrong architecture in the 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
implementation, you have a bug in the `init()` functions of one of the components of the 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
implementation or you need to transpose one of the checkpoint weights.
|
||||
|
||||
This step should be iterated with the previous step until all weights of the checkpoint are correctly loaded in the
|
||||
Transformers model. Having correctly loaded the checkpoint into the 🤗 Transformers implementation, you can then save
|
||||
the model under a folder of your choice `/path/to/converted/checkpoint/folder` that should then contain both a
|
||||
`pytorch_model.bin` file and a `config.json` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model.save_pretrained("/path/to/converted/checkpoint/folder")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**7. Implement the forward pass**
|
||||
|
||||
Having managed to correctly load the pretrained weights into the 🤗 Transformers implementation, you should now make
|
||||
sure that the forward pass is correctly implemented. In [Get familiar with the original repository](#34-run-a-pretrained-checkpoint-using-the-original-repository), you have already created a script that runs a forward
|
||||
pass of the model using the original repository. Now you should write an analogous script using the 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
implementation instead of the original one. It should look as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = BrandNewBertModel.from_pretrained("/path/to/converted/checkpoint/folder")
|
||||
input_ids = [0, 4, 4, 3, 2, 4, 1, 7, 19]
|
||||
output = model(input_ids).last_hidden_states
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is very likely that the 🤗 Transformers implementation and the original model implementation don't give the exact
|
||||
same output the very first time or that the forward pass throws an error. Don't be disappointed - it's expected! First,
|
||||
you should make sure that the forward pass doesn't throw any errors. It often happens that the wrong dimensions are
|
||||
used leading to a *Dimensionality mismatch* error or that the wrong data type object is used, *e.g.* `torch.long`
|
||||
instead of `torch.float32`. Don't hesitate to ask the Hugging Face team for help, if you don't manage to solve
|
||||
certain errors.
|
||||
|
||||
The final part to make sure the 🤗 Transformers implementation works correctly is to ensure that the outputs are
|
||||
equivalent to a precision of `1e-3`. First, you should ensure that the output shapes are identical, *i.e.*
|
||||
`outputs.shape` should yield the same value for the script of the 🤗 Transformers implementation and the original
|
||||
implementation. Next, you should make sure that the output values are identical as well. This one of the most difficult
|
||||
parts of adding a new model. Common mistakes why the outputs are not identical are:
|
||||
|
||||
- Some layers were not added, *i.e.* an *activation* layer was not added, or the residual connection was forgotten
|
||||
- The word embedding matrix was not tied
|
||||
- The wrong positional embeddings are used because the original implementation uses on offset
|
||||
- Dropout is applied during the forward pass. To fix this make sure *model.training is False* and that no dropout
|
||||
layer is falsely activated during the forward pass, *i.e.* pass *self.training* to [PyTorch's functional dropout](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.functional.html?highlight=dropout#torch.nn.functional.dropout)
|
||||
|
||||
The best way to fix the problem is usually to look at the forward pass of the original implementation and the 🤗
|
||||
Transformers implementation side-by-side and check if there are any differences. Ideally, you should debug/print out
|
||||
intermediate outputs of both implementations of the forward pass to find the exact position in the network where the 🤗
|
||||
Transformers implementation shows a different output than the original implementation. First, make sure that the
|
||||
hard-coded `input_ids` in both scripts are identical. Next, verify that the outputs of the first transformation of
|
||||
the `input_ids` (usually the word embeddings) are identical. And then work your way up to the very last layer of the
|
||||
network. At some point, you will notice a difference between the two implementations, which should point you to the bug
|
||||
in the 🤗 Transformers implementation. From our experience, a simple and efficient way is to add many print statements
|
||||
in both the original implementation and 🤗 Transformers implementation, at the same positions in the network
|
||||
respectively, and to successively remove print statements showing the same values for intermediate presentations.
|
||||
|
||||
When you're confident that both implementations yield the same output, verifying the outputs with
|
||||
`torch.allclose(original_output, output, atol=1e-3)`, you're done with the most difficult part! Congratulations - the
|
||||
work left to be done should be a cakewalk 😊.
|
||||
|
||||
**8. Adding all necessary model tests**
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, you have successfully added a new model. However, it is very much possible that the model does not yet
|
||||
fully comply with the required design. To make sure, the implementation is fully compatible with 🤗 Transformers, all
|
||||
common tests should pass. The Cookiecutter should have automatically added a test file for your model, probably under
|
||||
the same `tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_brand_new_bert.py`. Run this test file to verify that all common
|
||||
tests pass:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pytest tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_brand_new_bert.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Having fixed all common tests, it is now crucial to ensure that all the nice work you have done is well tested, so that
|
||||
|
||||
- a) The community can easily understand your work by looking at specific tests of *brand_new_bert*
|
||||
- b) Future changes to your model will not break any important feature of the model.
|
||||
|
||||
At first, integration tests should be added. Those integration tests essentially do the same as the debugging scripts
|
||||
you used earlier to implement the model to 🤗 Transformers. A template of those model tests is already added by the
|
||||
Cookiecutter, called `BrandNewBertModelIntegrationTests` and only has to be filled out by you. To ensure that those
|
||||
tests are passing, run
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
RUN_SLOW=1 pytest -sv tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_brand_new_bert.py::BrandNewBertModelIntegrationTests
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In case you are using Windows, you should replace `RUN_SLOW=1` with `SET RUN_SLOW=1`
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Second, all features that are special to *brand_new_bert* should be tested additionally in a separate test under
|
||||
`BrandNewBertModelTester`/``BrandNewBertModelTest`. This part is often forgotten but is extremely useful in two
|
||||
ways:
|
||||
|
||||
- It helps to transfer the knowledge you have acquired during the model addition to the community by showing how the
|
||||
special features of *brand_new_bert* should work.
|
||||
- Future contributors can quickly test changes to the model by running those special tests.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**9. Implement the tokenizer**
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we should add the tokenizer of *brand_new_bert*. Usually, the tokenizer is equivalent or very similar to an
|
||||
already existing tokenizer of 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
It is very important to find/extract the original tokenizer file and to manage to load this file into the 🤗
|
||||
Transformers' implementation of the tokenizer.
|
||||
|
||||
To ensure that the tokenizer works correctly, it is recommended to first create a script in the original repository
|
||||
that inputs a string and returns the `input_ids``. It could look similar to this (in pseudo-code):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
input_str = "This is a long example input string containing special characters .$?-, numbers 2872 234 12 and words."
|
||||
model = BrandNewBertModel.load_pretrained_checkpoint("/path/to/checkpoint/")
|
||||
input_ids = model.tokenize(input_str)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You might have to take a deeper look again into the original repository to find the correct tokenizer function or you
|
||||
might even have to do changes to your clone of the original repository to only output the `input_ids`. Having written
|
||||
a functional tokenization script that uses the original repository, an analogous script for 🤗 Transformers should be
|
||||
created. It should look similar to this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import BrandNewBertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
input_str = "This is a long example input string containing special characters .$?-, numbers 2872 234 12 and words."
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = BrandNewBertTokenizer.from_pretrained("/path/to/tokenizer/folder/")
|
||||
|
||||
input_ids = tokenizer(input_str).input_ids
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When both `input_ids` yield the same values, as a final step a tokenizer test file should also be added.
|
||||
|
||||
Analogous to the modeling test files of *brand_new_bert*, the tokenization test files of *brand_new_bert* should
|
||||
contain a couple of hard-coded integration tests.
|
||||
|
||||
**10. Run End-to-end integration tests**
|
||||
|
||||
Having added the tokenizer, you should also add a couple of end-to-end integration tests using both the model and the
|
||||
tokenizer to `tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_brand_new_bert.py` in 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
Such a test should show on a meaningful
|
||||
text-to-text sample that the 🤗 Transformers implementation works as expected. A meaningful text-to-text sample can
|
||||
include *e.g.* a source-to-target-translation pair, an article-to-summary pair, a question-to-answer pair, etc… If none
|
||||
of the ported checkpoints has been fine-tuned on a downstream task it is enough to simply rely on the model tests. In a
|
||||
final step to ensure that the model is fully functional, it is advised that you also run all tests on GPU. It can
|
||||
happen that you forgot to add some `.to(self.device)` statements to internal tensors of the model, which in such a
|
||||
test would show in an error. In case you have no access to a GPU, the Hugging Face team can take care of running those
|
||||
tests for you.
|
||||
|
||||
**11. Add Docstring**
|
||||
|
||||
Now, all the necessary functionality for *brand_new_bert* is added - you're almost done! The only thing left to add is
|
||||
a nice docstring and a doc page. The Cookiecutter should have added a template file called
|
||||
`docs/source/model_doc/brand_new_bert.md` that you should fill out. Users of your model will usually first look at
|
||||
this page before using your model. Hence, the documentation must be understandable and concise. It is very useful for
|
||||
the community to add some *Tips* to show how the model should be used. Don't hesitate to ping the Hugging Face team
|
||||
regarding the docstrings.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, make sure that the docstring added to `src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/modeling_brand_new_bert.py` is
|
||||
correct and included all necessary inputs and outputs. We have a detailed guide about writing documentation and our docstring format [here](writing-documentation). It is always to good to remind oneself that documentation should
|
||||
be treated at least as carefully as the code in 🤗 Transformers since the documentation is usually the first contact
|
||||
point of the community with the model.
|
||||
|
||||
**Code refactor**
|
||||
|
||||
Great, now you have added all the necessary code for *brand_new_bert*. At this point, you should correct some potential
|
||||
incorrect code style by running:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
make style
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and verify that your coding style passes the quality check:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
make quality
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are a couple of other very strict design tests in 🤗 Transformers that might still be failing, which shows up in
|
||||
the tests of your pull request. This is often because of some missing information in the docstring or some incorrect
|
||||
naming. The Hugging Face team will surely help you if you're stuck here.
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, it is always a good idea to refactor one's code after having ensured that the code works correctly. With all
|
||||
tests passing, now it's a good time to go over the added code again and do some refactoring.
|
||||
|
||||
You have now finished the coding part, congratulation! 🎉 You are Awesome! 😎
|
||||
|
||||
**12. Upload the models to the model hub**
|
||||
|
||||
In this final part, you should convert and upload all checkpoints to the model hub and add a model card for each
|
||||
uploaded model checkpoint. You can get familiar with the hub functionalities by reading our [Model sharing and uploading Page](model_sharing). You should work alongside the Hugging Face team here to decide on a fitting name for each
|
||||
checkpoint and to get the required access rights to be able to upload the model under the author's organization of
|
||||
*brand_new_bert*. The `push_to_hub` method, present in all models in `transformers`, is a quick and efficient way to push your checkpoint to the hub. A little snippet is pasted below:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
brand_new_bert.push_to_hub("brand_new_bert")
|
||||
# Uncomment the following line to push to an organization.
|
||||
# brand_new_bert.push_to_hub("<organization>/brand_new_bert")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is worth spending some time to create fitting model cards for each checkpoint. The model cards should highlight the
|
||||
specific characteristics of this particular checkpoint, *e.g.* On which dataset was the checkpoint
|
||||
pretrained/fine-tuned on? On what down-stream task should the model be used? And also include some code on how to
|
||||
correctly use the model.
|
||||
|
||||
**13. (Optional) Add notebook**
|
||||
|
||||
It is very helpful to add a notebook that showcases in-detail how *brand_new_bert* can be used for inference and/or
|
||||
fine-tuned on a downstream task. This is not mandatory to merge your PR, but very useful for the community.
|
||||
|
||||
**14. Submit your finished PR**
|
||||
|
||||
You're done programming now and can move to the last step, which is getting your PR merged into main. Usually, the
|
||||
Hugging Face team should have helped you already at this point, but it is worth taking some time to give your finished
|
||||
PR a nice description and eventually add comments to your code, if you want to point out certain design choices to your
|
||||
reviewer.
|
||||
|
||||
### Share your work!!
|
||||
|
||||
Now, it's time to get some credit from the community for your work! Having completed a model addition is a major
|
||||
contribution to Transformers and the whole NLP community. Your code and the ported pre-trained models will certainly be
|
||||
used by hundreds and possibly even thousands of developers and researchers. You should be proud of your work and share
|
||||
your achievement with the community.
|
||||
|
||||
**You have made another model that is super easy to access for everyone in the community! 🤯**
|
||||
@ -1,891 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# How to add a model to 🤗 Transformers?
|
||||
|
||||
The 🤗 Transformers library is often able to offer new models thanks to community contributors. But this can be a challenging project and requires an in-depth knowledge of the 🤗 Transformers library and the model to implement. At Hugging Face, we're trying to empower more of the community to actively add models and we've put together this guide to walk you through the process of adding a PyTorch model (make sure you have [PyTorch installed](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/)).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If you're interested in implementing a TensorFlow model, take a look at the [How to convert a 🤗 Transformers model to TensorFlow](add_tensorflow_model) guide!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Along the way, you'll:
|
||||
|
||||
- get insights into open-source best practices
|
||||
- understand the design principles behind one of the most popular deep learning libraries
|
||||
- learn how to efficiently test large models
|
||||
- learn how to integrate Python utilities like `black`, `ruff`, and `make fix-copies` to ensure clean and readable code
|
||||
|
||||
A Hugging Face team member will be available to help you along the way so you'll never be alone. 🤗 ❤️
|
||||
|
||||
To get started, open a [New model addition](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=New+model&template=new-model-addition.yml) issue for the model you want to see in 🤗 Transformers. If you're not especially picky about contributing a specific model, you can filter by the [New model label](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/labels/New%20model) to see if there are any unclaimed model requests and work on it.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you've opened a new model request, the first step is to get familiar with 🤗 Transformers if you aren't already!
|
||||
|
||||
## General overview of 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
First, you should get a general overview of 🤗 Transformers. 🤗 Transformers is a very opinionated library, so there is a
|
||||
chance that you don't agree with some of the library's philosophies or design choices. From our experience, however, we
|
||||
found that the fundamental design choices and philosophies of the library are crucial to efficiently scale 🤗
|
||||
Transformers while keeping maintenance costs at a reasonable level.
|
||||
|
||||
A good first starting point to better understand the library is to read the [documentation of our philosophy](philosophy). As a result of our way of working, there are some choices that we try to apply to all models:
|
||||
|
||||
- Composition is generally favored over-abstraction
|
||||
- Duplicating code is not always bad if it strongly improves the readability or accessibility of a model
|
||||
- Model files are as self-contained as possible so that when you read the code of a specific model, you ideally only
|
||||
have to look into the respective `modeling_....py` file.
|
||||
|
||||
In our opinion, the library's code is not just a means to provide a product, *e.g.* the ability to use BERT for
|
||||
inference, but also as the very product that we want to improve. Hence, when adding a model, the user is not only the
|
||||
person that will use your model, but also everybody that will read, try to understand, and possibly tweak your code.
|
||||
|
||||
With this in mind, let's go a bit deeper into the general library design.
|
||||
|
||||
### Overview of models
|
||||
|
||||
To successfully add a model, it is important to understand the interaction between your model and its config,
|
||||
[`PreTrainedModel`], and [`PretrainedConfig`]. For exemplary purposes, we will
|
||||
call the model to be added to 🤗 Transformers `BrandNewBert`.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take a look:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers_overview.png"/>
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, we do make use of inheritance in 🤗 Transformers, but we keep the level of abstraction to an absolute
|
||||
minimum. There are never more than two levels of abstraction for any model in the library. `BrandNewBertModel`
|
||||
inherits from `BrandNewBertPreTrainedModel` which in turn inherits from [`PreTrainedModel`] and
|
||||
that's it. As a general rule, we want to make sure that a new model only depends on
|
||||
[`PreTrainedModel`]. The important functionalities that are automatically provided to every new
|
||||
model are [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] and
|
||||
[`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`], which are used for serialization and deserialization. All of the
|
||||
other important functionalities, such as `BrandNewBertModel.forward` should be completely defined in the new
|
||||
`modeling_brand_new_bert.py` script. Next, we want to make sure that a model with a specific head layer, such as
|
||||
`BrandNewBertForMaskedLM` does not inherit from `BrandNewBertModel`, but rather uses `BrandNewBertModel`
|
||||
as a component that can be called in its forward pass to keep the level of abstraction low. Every new model requires a
|
||||
configuration class, called `BrandNewBertConfig`. This configuration is always stored as an attribute in
|
||||
[`PreTrainedModel`], and thus can be accessed via the `config` attribute for all classes
|
||||
inheriting from `BrandNewBertPreTrainedModel`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = BrandNewBertModel.from_pretrained("brandy/brand_new_bert")
|
||||
model.config # model has access to its config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to the model, the configuration inherits basic serialization and deserialization functionalities from
|
||||
[`PretrainedConfig`]. Note that the configuration and the model are always serialized into two
|
||||
different formats - the model to a *pytorch_model.bin* file and the configuration to a *config.json* file. Calling
|
||||
[`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] will automatically call
|
||||
[`~PretrainedConfig.save_pretrained`], so that both model and configuration are saved.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Code style
|
||||
|
||||
When coding your new model, keep in mind that Transformers is an opinionated library and we have a few quirks of our
|
||||
own regarding how code should be written :-)
|
||||
|
||||
1. The forward pass of your model should be fully written in the modeling file while being fully independent of other
|
||||
models in the library. If you want to reuse a block from another model, copy the code and paste it with a
|
||||
`# Copied from` comment on top (see [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/v4.17.0/src/transformers/models/roberta/modeling_roberta.py#L160)
|
||||
for a good example).
|
||||
2. The code should be fully understandable, even by a non-native English speaker. This means you should pick
|
||||
descriptive variable names and avoid abbreviations. As an example, `activation` is preferred to `act`.
|
||||
One-letter variable names are strongly discouraged unless it's an index in a for loop.
|
||||
3. More generally we prefer longer explicit code to short magical one.
|
||||
4. Avoid subclassing `nn.Sequential` in PyTorch but subclass `nn.Module` and write the forward pass, so that anyone
|
||||
using your code can quickly debug it by adding print statements or breaking points.
|
||||
5. Your function signature should be type-annotated. For the rest, good variable names are way more readable and
|
||||
understandable than type annotations.
|
||||
|
||||
### Overview of tokenizers
|
||||
|
||||
Not quite ready yet :-( This section will be added soon!
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-by-step recipe to add a model to 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
Everyone has different preferences of how to port a model so it can be very helpful for you to take a look at summaries
|
||||
of how other contributors ported models to Hugging Face. Here is a list of community blog posts on how to port a model:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Porting GPT2 Model](https://medium.com/huggingface/from-tensorflow-to-pytorch-265f40ef2a28) by [Thomas](https://huggingface.co/thomwolf)
|
||||
2. [Porting WMT19 MT Model](https://huggingface.co/blog/porting-fsmt) by [Stas](https://huggingface.co/stas)
|
||||
|
||||
From experience, we can tell you that the most important things to keep in mind when adding a model are:
|
||||
|
||||
- Don't reinvent the wheel! Most parts of the code you will add for the new 🤗 Transformers model already exist
|
||||
somewhere in 🤗 Transformers. Take some time to find similar, already existing models and tokenizers you can copy
|
||||
from. [grep](https://www.gnu.org/software/grep/) and [rg](https://github.com/BurntSushi/ripgrep) are your
|
||||
friends. Note that it might very well happen that your model's tokenizer is based on one model implementation, and
|
||||
your model's modeling code on another one. *E.g.* FSMT's modeling code is based on BART, while FSMT's tokenizer code
|
||||
is based on XLM.
|
||||
- It's more of an engineering challenge than a scientific challenge. You should spend more time on creating an
|
||||
efficient debugging environment than trying to understand all theoretical aspects of the model in the paper.
|
||||
- Ask for help, when you're stuck! Models are the core component of 🤗 Transformers so that we at Hugging Face are more
|
||||
than happy to help you at every step to add your model. Don't hesitate to ask if you notice you are not making
|
||||
progress.
|
||||
|
||||
In the following, we try to give you a general recipe that we found most useful when porting a model to 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
The following list is a summary of everything that has to be done to add a model and can be used by you as a To-Do
|
||||
List:
|
||||
|
||||
☐ (Optional) Understood the model's theoretical aspects<br>
|
||||
☐ Prepared 🤗 Transformers dev environment<br>
|
||||
☐ Set up debugging environment of the original repository<br>
|
||||
☐ Created script that successfully runs the `forward()` pass using the original repository and checkpoint<br>
|
||||
☐ Successfully added the model skeleton to 🤗 Transformers<br>
|
||||
☐ Successfully converted original checkpoint to 🤗 Transformers checkpoint<br>
|
||||
☐ Successfully ran `forward()` pass in 🤗 Transformers that gives identical output to original checkpoint<br>
|
||||
☐ Finished model tests in 🤗 Transformers<br>
|
||||
☐ Successfully added tokenizer in 🤗 Transformers<br>
|
||||
☐ Run end-to-end integration tests<br>
|
||||
☐ Finished docs<br>
|
||||
☐ Uploaded model weights to the Hub<br>
|
||||
☐ Submitted the pull request<br>
|
||||
☐ (Optional) Added a demo notebook
|
||||
|
||||
To begin with, we usually recommend to start by getting a good theoretical understanding of `BrandNewBert`. However,
|
||||
if you prefer to understand the theoretical aspects of the model *on-the-job*, then it is totally fine to directly dive
|
||||
into the `BrandNewBert`'s code-base. This option might suit you better, if your engineering skills are better than
|
||||
your theoretical skill, if you have trouble understanding `BrandNewBert`'s paper, or if you just enjoy programming
|
||||
much more than reading scientific papers.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. (Optional) Theoretical aspects of BrandNewBert
|
||||
|
||||
You should take some time to read *BrandNewBert's* paper, if such descriptive work exists. There might be large
|
||||
sections of the paper that are difficult to understand. If this is the case, this is fine - don't worry! The goal is
|
||||
not to get a deep theoretical understanding of the paper, but to extract the necessary information required to
|
||||
effectively re-implement the model in 🤗 Transformers. That being said, you don't have to spend too much time on the
|
||||
theoretical aspects, but rather focus on the practical ones, namely:
|
||||
|
||||
- What type of model is *brand_new_bert*? BERT-like encoder-only model? GPT2-like decoder-only model? BART-like
|
||||
encoder-decoder model? Look at the [model_summary](model_summary) if you're not familiar with the differences between those.
|
||||
- What are the applications of *brand_new_bert*? Text classification? Text generation? Seq2Seq tasks, *e.g.,*
|
||||
summarization?
|
||||
- What is the novel feature of the model making it different from BERT/GPT-2/BART?
|
||||
- Which of the already existing [🤗 Transformers models](https://huggingface.co/transformers/#contents) is most
|
||||
similar to *brand_new_bert*?
|
||||
- What type of tokenizer is used? A sentencepiece tokenizer? Word piece tokenizer? Is it the same tokenizer as used
|
||||
for BERT or BART?
|
||||
|
||||
After you feel like you have gotten a good overview of the architecture of the model, you might want to write to the
|
||||
Hugging Face team with any questions you might have. This might include questions regarding the model's architecture,
|
||||
its attention layer, etc. We will be more than happy to help you.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Next prepare your environment
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fork the [repository](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers) by clicking on the ‘Fork' button on the
|
||||
repository's page. This creates a copy of the code under your GitHub user account.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Clone your `transformers` fork to your local disk, and add the base repository as a remote:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/[your Github handle]/transformers.git
|
||||
cd transformers
|
||||
git remote add upstream https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Set up a development environment, for instance by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m venv .env
|
||||
source .env/bin/activate
|
||||
pip install -e ".[dev]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on your OS, and since the number of optional dependencies of Transformers is growing, you might get a
|
||||
failure with this command. If that's the case make sure to install the Deep Learning framework you are working with
|
||||
(PyTorch, TensorFlow and/or Flax) then do:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -e ".[quality]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which should be enough for most use cases. You can then return to the parent directory
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ..
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. We recommend adding the PyTorch version of *brand_new_bert* to Transformers. To install PyTorch, please follow the
|
||||
instructions on https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** You don't need to have CUDA installed. Making the new model work on CPU is sufficient.
|
||||
|
||||
5. To port *brand_new_bert*, you will also need access to its original repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/org_that_created_brand_new_bert_org/brand_new_bert.git
|
||||
cd brand_new_bert
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you have set up a development environment to port *brand_new_bert* to 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.-4. Run a pretrained checkpoint using the original repository
|
||||
|
||||
At first, you will work on the original *brand_new_bert* repository. Often, the original implementation is very
|
||||
“researchy”. Meaning that documentation might be lacking and the code can be difficult to understand. But this should
|
||||
be exactly your motivation to reimplement *brand_new_bert*. At Hugging Face, one of our main goals is to *make people
|
||||
stand on the shoulders of giants* which translates here very well into taking a working model and rewriting it to make
|
||||
it as **accessible, user-friendly, and beautiful** as possible. This is the number-one motivation to re-implement
|
||||
models into 🤗 Transformers - trying to make complex new NLP technology accessible to **everybody**.
|
||||
|
||||
You should start thereby by diving into the original repository.
|
||||
|
||||
Successfully running the official pretrained model in the original repository is often **the most difficult** step.
|
||||
From our experience, it is very important to spend some time getting familiar with the original code-base. You need to
|
||||
figure out the following:
|
||||
|
||||
- Where to find the pretrained weights?
|
||||
- How to load the pretrained weights into the corresponding model?
|
||||
- How to run the tokenizer independently from the model?
|
||||
- Trace one forward pass so that you know which classes and functions are required for a simple forward pass. Usually,
|
||||
you only have to reimplement those functions.
|
||||
- Be able to locate the important components of the model: Where is the model's class? Are there model sub-classes,
|
||||
*e.g.* EncoderModel, DecoderModel? Where is the self-attention layer? Are there multiple different attention layers,
|
||||
*e.g.* *self-attention*, *cross-attention*...?
|
||||
- How can you debug the model in the original environment of the repo? Do you have to add *print* statements, can you
|
||||
work with an interactive debugger like *ipdb*, or should you use an efficient IDE to debug the model, like PyCharm?
|
||||
|
||||
It is very important that before you start the porting process, that you can **efficiently** debug code in the original
|
||||
repository! Also, remember that you are working with an open-source library, so do not hesitate to open an issue, or
|
||||
even a pull request in the original repository. The maintainers of this repository are most likely very happy about
|
||||
someone looking into their code!
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, it is really up to you which debugging environment and strategy you prefer to use to debug the original
|
||||
model. We strongly advise against setting up a costly GPU environment, but simply work on a CPU both when starting to
|
||||
dive into the original repository and also when starting to write the 🤗 Transformers implementation of the model. Only
|
||||
at the very end, when the model has already been successfully ported to 🤗 Transformers, one should verify that the
|
||||
model also works as expected on GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
In general, there are two possible debugging environments for running the original model
|
||||
|
||||
- [Jupyter notebooks](https://jupyter.org/) / [google colab](https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/intro.ipynb)
|
||||
- Local python scripts.
|
||||
|
||||
Jupyter notebooks have the advantage that they allow for cell-by-cell execution which can be helpful to better split
|
||||
logical components from one another and to have faster debugging cycles as intermediate results can be stored. Also,
|
||||
notebooks are often easier to share with other contributors, which might be very helpful if you want to ask the Hugging
|
||||
Face team for help. If you are familiar with Jupyter notebooks, we strongly recommend you to work with them.
|
||||
|
||||
The obvious disadvantage of Jupyter notebooks is that if you are not used to working with them you will have to spend
|
||||
some time adjusting to the new programming environment and that you might not be able to use your known debugging tools
|
||||
anymore, like `ipdb`.
|
||||
|
||||
For each code-base, a good first step is always to load a **small** pretrained checkpoint and to be able to reproduce a
|
||||
single forward pass using a dummy integer vector of input IDs as an input. Such a script could look like this (in
|
||||
pseudocode):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = BrandNewBertModel.load_pretrained_checkpoint("/path/to/checkpoint/")
|
||||
input_ids = [0, 4, 5, 2, 3, 7, 9] # vector of input ids
|
||||
original_output = model.predict(input_ids)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, regarding the debugging strategy, there are generally a few from which to choose from:
|
||||
|
||||
- Decompose the original model into many small testable components and run a forward pass on each of those for
|
||||
verification
|
||||
- Decompose the original model only into the original *tokenizer* and the original *model*, run a forward pass on
|
||||
those, and use intermediate print statements or breakpoints for verification
|
||||
|
||||
Again, it is up to you which strategy to choose. Often, one or the other is advantageous depending on the original code
|
||||
base.
|
||||
|
||||
If the original code-base allows you to decompose the model into smaller sub-components, *e.g.* if the original
|
||||
code-base can easily be run in eager mode, it is usually worth the effort to do so. There are some important advantages
|
||||
to taking the more difficult road in the beginning:
|
||||
|
||||
- at a later stage when comparing the original model to the Hugging Face implementation, you can verify automatically
|
||||
for each component individually that the corresponding component of the 🤗 Transformers implementation matches instead
|
||||
of relying on visual comparison via print statements
|
||||
- it can give you some rope to decompose the big problem of porting a model into smaller problems of just porting
|
||||
individual components and thus structure your work better
|
||||
- separating the model into logical meaningful components will help you to get a better overview of the model's design
|
||||
and thus to better understand the model
|
||||
- at a later stage those component-by-component tests help you to ensure that no regression occurs as you continue
|
||||
changing your code
|
||||
|
||||
[Lysandre's](https://gist.github.com/LysandreJik/db4c948f6b4483960de5cbac598ad4ed) integration checks for ELECTRA
|
||||
gives a nice example of how this can be done.
|
||||
|
||||
However, if the original code-base is very complex or only allows intermediate components to be run in a compiled mode,
|
||||
it might be too time-consuming or even impossible to separate the model into smaller testable sub-components. A good
|
||||
example is [T5's MeshTensorFlow](https://github.com/tensorflow/mesh/tree/master/mesh_tensorflow) library which is
|
||||
very complex and does not offer a simple way to decompose the model into its sub-components. For such libraries, one
|
||||
often relies on verifying print statements.
|
||||
|
||||
No matter which strategy you choose, the recommended procedure is often the same in that you should start to debug the
|
||||
starting layers first and the ending layers last.
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended that you retrieve the output, either by print statements or sub-component functions, of the following
|
||||
layers in the following order:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Retrieve the input IDs passed to the model
|
||||
2. Retrieve the word embeddings
|
||||
3. Retrieve the input of the first Transformer layer
|
||||
4. Retrieve the output of the first Transformer layer
|
||||
5. Retrieve the output of the following n - 1 Transformer layers
|
||||
6. Retrieve the output of the whole BrandNewBert Model
|
||||
|
||||
Input IDs should thereby consists of an array of integers, *e.g.* `input_ids = [0, 4, 4, 3, 2, 4, 1, 7, 19]`
|
||||
|
||||
The outputs of the following layers often consist of multi-dimensional float arrays and can look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[[
|
||||
[-0.1465, -0.6501, 0.1993, ..., 0.1451, 0.3430, 0.6024],
|
||||
[-0.4417, -0.5920, 0.3450, ..., -0.3062, 0.6182, 0.7132],
|
||||
[-0.5009, -0.7122, 0.4548, ..., -0.3662, 0.6091, 0.7648],
|
||||
...,
|
||||
[-0.5613, -0.6332, 0.4324, ..., -0.3792, 0.7372, 0.9288],
|
||||
[-0.5416, -0.6345, 0.4180, ..., -0.3564, 0.6992, 0.9191],
|
||||
[-0.5334, -0.6403, 0.4271, ..., -0.3339, 0.6533, 0.8694]]],
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We expect that every model added to 🤗 Transformers passes a couple of integration tests, meaning that the original
|
||||
model and the reimplemented version in 🤗 Transformers have to give the exact same output up to a precision of 0.001!
|
||||
Since it is normal that the exact same model written in different libraries can give a slightly different output
|
||||
depending on the library framework, we accept an error tolerance of 1e-3 (0.001). It is not enough if the model gives
|
||||
nearly the same output, they have to be the almost identical. Therefore, you will certainly compare the intermediate
|
||||
outputs of the 🤗 Transformers version multiple times against the intermediate outputs of the original implementation of
|
||||
*brand_new_bert* in which case an **efficient** debugging environment of the original repository is absolutely
|
||||
important. Here is some advice is to make your debugging environment as efficient as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
- Find the best way of debugging intermediate results. Is the original repository written in PyTorch? Then you should
|
||||
probably take the time to write a longer script that decomposes the original model into smaller sub-components to
|
||||
retrieve intermediate values. Is the original repository written in Tensorflow 1? Then you might have to rely on
|
||||
TensorFlow print operations like [tf.print](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/print) to output
|
||||
intermediate values. Is the original repository written in Jax? Then make sure that the model is **not jitted** when
|
||||
running the forward pass, *e.g.* check-out [this link](https://github.com/google/jax/issues/196).
|
||||
- Use the smallest pretrained checkpoint you can find. The smaller the checkpoint, the faster your debug cycle
|
||||
becomes. It is not efficient if your pretrained model is so big that your forward pass takes more than 10 seconds.
|
||||
In case only very large checkpoints are available, it might make more sense to create a dummy model in the new
|
||||
environment with randomly initialized weights and save those weights for comparison with the 🤗 Transformers version
|
||||
of your model
|
||||
- Make sure you are using the easiest way of calling a forward pass in the original repository. Ideally, you want to
|
||||
find the function in the original repository that **only** calls a single forward pass, *i.e.* that is often called
|
||||
`predict`, `evaluate`, `forward` or `__call__`. You don't want to debug a function that calls `forward`
|
||||
multiple times, *e.g.* to generate text, like `autoregressive_sample`, `generate`.
|
||||
- Try to separate the tokenization from the model's *forward* pass. If the original repository shows examples where
|
||||
you have to input a string, then try to find out where in the forward call the string input is changed to input ids
|
||||
and start from this point. This might mean that you have to possibly write a small script yourself or change the
|
||||
original code so that you can directly input the ids instead of an input string.
|
||||
- Make sure that the model in your debugging setup is **not** in training mode, which often causes the model to yield
|
||||
random outputs due to multiple dropout layers in the model. Make sure that the forward pass in your debugging
|
||||
environment is **deterministic** so that the dropout layers are not used. Or use *transformers.utils.set_seed*
|
||||
if the old and new implementations are in the same framework.
|
||||
|
||||
The following section gives you more specific details/tips on how you can do this for *brand_new_bert*.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5.-14. Port BrandNewBert to 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
Next, you can finally start adding new code to 🤗 Transformers. Go into the clone of your 🤗 Transformers' fork:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the special case that you are adding a model whose architecture exactly matches the model architecture of an
|
||||
existing model you only have to add a conversion script as described in [this section](#write-a-conversion-script).
|
||||
In this case, you can just re-use the whole model architecture of the already existing model.
|
||||
|
||||
Otherwise, let's start generating a new model. You have two choices here:
|
||||
|
||||
- `transformers-cli add-new-model-like` to add a new model like an existing one
|
||||
- `transformers-cli add-new-model` to add a new model from our template (will look like BERT or Bart depending on the type of model you select)
|
||||
|
||||
In both cases, you will be prompted with a questionnaire to fill the basic information of your model. The second command requires to install `cookiecutter`, you can find more information on it [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/templates/adding_a_new_model).
|
||||
|
||||
**Open a Pull Request on the main huggingface/transformers repo**
|
||||
|
||||
Before starting to adapt the automatically generated code, now is the time to open a “Work in progress (WIP)” pull
|
||||
request, *e.g.* “[WIP] Add *brand_new_bert*”, in 🤗 Transformers so that you and the Hugging Face team can work
|
||||
side-by-side on integrating the model into 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
You should do the following:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create a branch with a descriptive name from your main branch
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git checkout -b add_brand_new_bert
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Commit the automatically generated code:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git add .
|
||||
git commit
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Fetch and rebase to current main
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git fetch upstream
|
||||
git rebase upstream/main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
4. Push the changes to your account using:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git push -u origin a-descriptive-name-for-my-changes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Once you are satisfied, go to the webpage of your fork on GitHub. Click on “Pull request”. Make sure to add the
|
||||
GitHub handle of some members of the Hugging Face team as reviewers, so that the Hugging Face team gets notified for
|
||||
future changes.
|
||||
|
||||
6. Change the PR into a draft by clicking on “Convert to draft” on the right of the GitHub pull request web page.
|
||||
|
||||
In the following, whenever you have done some progress, don't forget to commit your work and push it to your account so
|
||||
that it shows in the pull request. Additionally, you should make sure to update your work with the current main from
|
||||
time to time by doing:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git fetch upstream
|
||||
git merge upstream/main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In general, all questions you might have regarding the model or your implementation should be asked in your PR and
|
||||
discussed/solved in the PR. This way, the Hugging Face team will always be notified when you are committing new code or
|
||||
if you have a question. It is often very helpful to point the Hugging Face team to your added code so that the Hugging
|
||||
Face team can efficiently understand your problem or question.
|
||||
|
||||
To do so, you can go to the “Files changed” tab where you see all of your changes, go to a line regarding which you
|
||||
want to ask a question, and click on the “+” symbol to add a comment. Whenever a question or problem has been solved,
|
||||
you can click on the “Resolve” button of the created comment.
|
||||
|
||||
In the same way, the Hugging Face team will open comments when reviewing your code. We recommend asking most questions
|
||||
on GitHub on your PR. For some very general questions that are not very useful for the public, feel free to ping the
|
||||
Hugging Face team by Slack or email.
|
||||
|
||||
**5. Adapt the generated models code for brand_new_bert**
|
||||
|
||||
At first, we will focus only on the model itself and not care about the tokenizer. All the relevant code should be
|
||||
found in the generated files `src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/modeling_brand_new_bert.py` and
|
||||
`src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/configuration_brand_new_bert.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can finally start coding :). The generated code in
|
||||
`src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/modeling_brand_new_bert.py` will either have the same architecture as BERT if
|
||||
it's an encoder-only model or BART if it's an encoder-decoder model. At this point, you should remind yourself what
|
||||
you've learned in the beginning about the theoretical aspects of the model: *How is the model different from BERT or
|
||||
BART?*". Implement those changes which often means to change the *self-attention* layer, the order of the normalization
|
||||
layer, etc… Again, it is often useful to look at the similar architecture of already existing models in Transformers to
|
||||
get a better feeling of how your model should be implemented.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note** that at this point, you don't have to be very sure that your code is fully correct or clean. Rather, it is
|
||||
advised to add a first *unclean*, copy-pasted version of the original code to
|
||||
`src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/modeling_brand_new_bert.py` until you feel like all the necessary code is
|
||||
added. From our experience, it is much more efficient to quickly add a first version of the required code and
|
||||
improve/correct the code iteratively with the conversion script as described in the next section. The only thing that
|
||||
has to work at this point is that you can instantiate the 🤗 Transformers implementation of *brand_new_bert*, *i.e.* the
|
||||
following command should work:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import BrandNewBertModel, BrandNewBertConfig
|
||||
|
||||
model = BrandNewBertModel(BrandNewBertConfig())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will create a model according to the default parameters as defined in `BrandNewBertConfig()` with
|
||||
random weights, thus making sure that the `init()` methods of all components works.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that all random initialization should happen in the `_init_weights` method of your `BrandnewBertPreTrainedModel`
|
||||
class. It should initialize all leaf modules depending on the variables of the config. Here is an example with the
|
||||
BERT `_init_weights` method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
def _init_weights(self, module):
|
||||
"""Initialize the weights"""
|
||||
if isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
|
||||
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
|
||||
if module.bias is not None:
|
||||
module.bias.data.zero_()
|
||||
elif isinstance(module, nn.Embedding):
|
||||
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
|
||||
if module.padding_idx is not None:
|
||||
module.weight.data[module.padding_idx].zero_()
|
||||
elif isinstance(module, nn.LayerNorm):
|
||||
module.bias.data.zero_()
|
||||
module.weight.data.fill_(1.0)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can have some more custom schemes if you need a special initialization for some modules. For instance, in
|
||||
`Wav2Vec2ForPreTraining`, the last two linear layers need to have the initialization of the regular PyTorch `nn.Linear`
|
||||
but all the other ones should use an initialization as above. This is coded like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
def _init_weights(self, module):
|
||||
"""Initialize the weights"""
|
||||
if isinstnace(module, Wav2Vec2ForPreTraining):
|
||||
module.project_hid.reset_parameters()
|
||||
module.project_q.reset_parameters()
|
||||
module.project_hid._is_hf_initialized = True
|
||||
module.project_q._is_hf_initialized = True
|
||||
elif isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
|
||||
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=self.config.initializer_range)
|
||||
if module.bias is not None:
|
||||
module.bias.data.zero_()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `_is_hf_initialized` flag is internally used to make sure we only initialize a submodule once. By setting it to
|
||||
`True` for `module.project_q` and `module.project_hid`, we make sure the custom initialization we did is not overridden later on,
|
||||
the `_init_weights` function won't be applied to them.
|
||||
|
||||
**6. Write a conversion script**
|
||||
|
||||
Next, you should write a conversion script that lets you convert the checkpoint you used to debug *brand_new_bert* in
|
||||
the original repository to a checkpoint compatible with your just created 🤗 Transformers implementation of
|
||||
*brand_new_bert*. It is not advised to write the conversion script from scratch, but rather to look through already
|
||||
existing conversion scripts in 🤗 Transformers for one that has been used to convert a similar model that was written in
|
||||
the same framework as *brand_new_bert*. Usually, it is enough to copy an already existing conversion script and
|
||||
slightly adapt it for your use case. Don't hesitate to ask the Hugging Face team to point you to a similar already
|
||||
existing conversion script for your model.
|
||||
|
||||
- If you are porting a model from TensorFlow to PyTorch, a good starting point might be BERT's conversion script [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/7acfa95afb8194f8f9c1f4d2c6028224dbed35a2/src/transformers/models/bert/modeling_bert.py#L91)
|
||||
- If you are porting a model from PyTorch to PyTorch, a good starting point might be BART's conversion script [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/models/bart/convert_bart_original_pytorch_checkpoint_to_pytorch.py)
|
||||
|
||||
In the following, we'll quickly explain how PyTorch models store layer weights and define layer names. In PyTorch, the
|
||||
name of a layer is defined by the name of the class attribute you give the layer. Let's define a dummy model in
|
||||
PyTorch, called `SimpleModel` as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class SimpleModel(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.dense = nn.Linear(10, 10)
|
||||
self.intermediate = nn.Linear(10, 10)
|
||||
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(10)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can create an instance of this model definition which will fill all weights: `dense`, `intermediate`,
|
||||
`layer_norm` with random weights. We can print the model to see its architecture
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = SimpleModel()
|
||||
|
||||
print(model)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will print out the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
SimpleModel(
|
||||
(dense): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=10, bias=True)
|
||||
(intermediate): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=10, bias=True)
|
||||
(layer_norm): LayerNorm((10,), eps=1e-05, elementwise_affine=True)
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can see that the layer names are defined by the name of the class attribute in PyTorch. You can print out the weight
|
||||
values of a specific layer:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
print(model.dense.weight.data)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
to see that the weights were randomly initialized
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
tensor([[-0.0818, 0.2207, -0.0749, -0.0030, 0.0045, -0.1569, -0.1598, 0.0212,
|
||||
-0.2077, 0.2157],
|
||||
[ 0.1044, 0.0201, 0.0990, 0.2482, 0.3116, 0.2509, 0.2866, -0.2190,
|
||||
0.2166, -0.0212],
|
||||
[-0.2000, 0.1107, -0.1999, -0.3119, 0.1559, 0.0993, 0.1776, -0.1950,
|
||||
-0.1023, -0.0447],
|
||||
[-0.0888, -0.1092, 0.2281, 0.0336, 0.1817, -0.0115, 0.2096, 0.1415,
|
||||
-0.1876, -0.2467],
|
||||
[ 0.2208, -0.2352, -0.1426, -0.2636, -0.2889, -0.2061, -0.2849, -0.0465,
|
||||
0.2577, 0.0402],
|
||||
[ 0.1502, 0.2465, 0.2566, 0.0693, 0.2352, -0.0530, 0.1859, -0.0604,
|
||||
0.2132, 0.1680],
|
||||
[ 0.1733, -0.2407, -0.1721, 0.1484, 0.0358, -0.0633, -0.0721, -0.0090,
|
||||
0.2707, -0.2509],
|
||||
[-0.1173, 0.1561, 0.2945, 0.0595, -0.1996, 0.2988, -0.0802, 0.0407,
|
||||
0.1829, -0.1568],
|
||||
[-0.1164, -0.2228, -0.0403, 0.0428, 0.1339, 0.0047, 0.1967, 0.2923,
|
||||
0.0333, -0.0536],
|
||||
[-0.1492, -0.1616, 0.1057, 0.1950, -0.2807, -0.2710, -0.1586, 0.0739,
|
||||
0.2220, 0.2358]]).
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In the conversion script, you should fill those randomly initialized weights with the exact weights of the
|
||||
corresponding layer in the checkpoint. *E.g.*
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# retrieve matching layer weights, e.g. by
|
||||
# recursive algorithm
|
||||
layer_name = "dense"
|
||||
pretrained_weight = array_of_dense_layer
|
||||
|
||||
model_pointer = getattr(model, "dense")
|
||||
|
||||
model_pointer.weight.data = torch.from_numpy(pretrained_weight)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
While doing so, you must verify that each randomly initialized weight of your PyTorch model and its corresponding
|
||||
pretrained checkpoint weight exactly match in both **shape and name**. To do so, it is **necessary** to add assert
|
||||
statements for the shape and print out the names of the checkpoints weights. E.g. you should add statements like:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
model_pointer.weight.shape == pretrained_weight.shape
|
||||
), f"Pointer shape of random weight {model_pointer.shape} and array shape of checkpoint weight {pretrained_weight.shape} mismatched"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Besides, you should also print out the names of both weights to make sure they match, *e.g.*
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
logger.info(f"Initialize PyTorch weight {layer_name} from {pretrained_weight.name}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If either the shape or the name doesn't match, you probably assigned the wrong checkpoint weight to a randomly
|
||||
initialized layer of the 🤗 Transformers implementation.
|
||||
|
||||
An incorrect shape is most likely due to an incorrect setting of the config parameters in `BrandNewBertConfig()` that
|
||||
do not exactly match those that were used for the checkpoint you want to convert. However, it could also be that
|
||||
PyTorch's implementation of a layer requires the weight to be transposed beforehand.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, you should also check that **all** required weights are initialized and print out all checkpoint weights that
|
||||
were not used for initialization to make sure the model is correctly converted. It is completely normal, that the
|
||||
conversion trials fail with either a wrong shape statement or wrong name assignment. This is most likely because either
|
||||
you used incorrect parameters in `BrandNewBertConfig()`, have a wrong architecture in the 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
implementation, you have a bug in the `init()` functions of one of the components of the 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
implementation or you need to transpose one of the checkpoint weights.
|
||||
|
||||
This step should be iterated with the previous step until all weights of the checkpoint are correctly loaded in the
|
||||
Transformers model. Having correctly loaded the checkpoint into the 🤗 Transformers implementation, you can then save
|
||||
the model under a folder of your choice `/path/to/converted/checkpoint/folder` that should then contain both a
|
||||
`pytorch_model.bin` file and a `config.json` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model.save_pretrained("/path/to/converted/checkpoint/folder")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**7. Implement the forward pass**
|
||||
|
||||
Having managed to correctly load the pretrained weights into the 🤗 Transformers implementation, you should now make
|
||||
sure that the forward pass is correctly implemented. In [Get familiar with the original repository](#34-run-a-pretrained-checkpoint-using-the-original-repository), you have already created a script that runs a forward
|
||||
pass of the model using the original repository. Now you should write an analogous script using the 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
implementation instead of the original one. It should look as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = BrandNewBertModel.from_pretrained("/path/to/converted/checkpoint/folder")
|
||||
input_ids = [0, 4, 4, 3, 2, 4, 1, 7, 19]
|
||||
output = model(input_ids).last_hidden_states
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is very likely that the 🤗 Transformers implementation and the original model implementation don't give the exact
|
||||
same output the very first time or that the forward pass throws an error. Don't be disappointed - it's expected! First,
|
||||
you should make sure that the forward pass doesn't throw any errors. It often happens that the wrong dimensions are
|
||||
used leading to a *Dimensionality mismatch* error or that the wrong data type object is used, *e.g.* `torch.long`
|
||||
instead of `torch.float32`. Don't hesitate to ask the Hugging Face team for help, if you don't manage to solve
|
||||
certain errors.
|
||||
|
||||
The final part to make sure the 🤗 Transformers implementation works correctly is to ensure that the outputs are
|
||||
equivalent to a precision of `1e-3`. First, you should ensure that the output shapes are identical, *i.e.*
|
||||
`outputs.shape` should yield the same value for the script of the 🤗 Transformers implementation and the original
|
||||
implementation. Next, you should make sure that the output values are identical as well. This one of the most difficult
|
||||
parts of adding a new model. Common mistakes why the outputs are not identical are:
|
||||
|
||||
- Some layers were not added, *i.e.* an *activation* layer was not added, or the residual connection was forgotten
|
||||
- The word embedding matrix was not tied
|
||||
- The wrong positional embeddings are used because the original implementation uses on offset
|
||||
- Dropout is applied during the forward pass. To fix this make sure *model.training is False* and that no dropout
|
||||
layer is falsely activated during the forward pass, *i.e.* pass *self.training* to [PyTorch's functional dropout](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.functional.html?highlight=dropout#torch.nn.functional.dropout)
|
||||
|
||||
The best way to fix the problem is usually to look at the forward pass of the original implementation and the 🤗
|
||||
Transformers implementation side-by-side and check if there are any differences. Ideally, you should debug/print out
|
||||
intermediate outputs of both implementations of the forward pass to find the exact position in the network where the 🤗
|
||||
Transformers implementation shows a different output than the original implementation. First, make sure that the
|
||||
hard-coded `input_ids` in both scripts are identical. Next, verify that the outputs of the first transformation of
|
||||
the `input_ids` (usually the word embeddings) are identical. And then work your way up to the very last layer of the
|
||||
network. At some point, you will notice a difference between the two implementations, which should point you to the bug
|
||||
in the 🤗 Transformers implementation. From our experience, a simple and efficient way is to add many print statements
|
||||
in both the original implementation and 🤗 Transformers implementation, at the same positions in the network
|
||||
respectively, and to successively remove print statements showing the same values for intermediate presentations.
|
||||
|
||||
When you're confident that both implementations yield the same output, verifying the outputs with
|
||||
`torch.allclose(original_output, output, atol=1e-3)`, you're done with the most difficult part! Congratulations - the
|
||||
work left to be done should be a cakewalk 😊.
|
||||
|
||||
**8. Adding all necessary model tests**
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, you have successfully added a new model. However, it is very much possible that the model does not yet
|
||||
fully comply with the required design. To make sure, the implementation is fully compatible with 🤗 Transformers, all
|
||||
common tests should pass. The Cookiecutter should have automatically added a test file for your model, probably under
|
||||
the same `tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_brand_new_bert.py`. Run this test file to verify that all common
|
||||
tests pass:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pytest tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_brand_new_bert.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Having fixed all common tests, it is now crucial to ensure that all the nice work you have done is well tested, so that
|
||||
|
||||
- a) The community can easily understand your work by looking at specific tests of *brand_new_bert*
|
||||
- b) Future changes to your model will not break any important feature of the model.
|
||||
|
||||
At first, integration tests should be added. Those integration tests essentially do the same as the debugging scripts
|
||||
you used earlier to implement the model to 🤗 Transformers. A template of those model tests is already added by the
|
||||
Cookiecutter, called `BrandNewBertModelIntegrationTests` and only has to be filled out by you. To ensure that those
|
||||
tests are passing, run
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
RUN_SLOW=1 pytest -sv tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_brand_new_bert.py::BrandNewBertModelIntegrationTests
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In case you are using Windows, you should replace `RUN_SLOW=1` with `SET RUN_SLOW=1`
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Second, all features that are special to *brand_new_bert* should be tested additionally in a separate test under
|
||||
`BrandNewBertModelTester`/``BrandNewBertModelTest`. This part is often forgotten but is extremely useful in two
|
||||
ways:
|
||||
|
||||
- It helps to transfer the knowledge you have acquired during the model addition to the community by showing how the
|
||||
special features of *brand_new_bert* should work.
|
||||
- Future contributors can quickly test changes to the model by running those special tests.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**9. Implement the tokenizer**
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we should add the tokenizer of *brand_new_bert*. Usually, the tokenizer is equivalent or very similar to an
|
||||
already existing tokenizer of 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
It is very important to find/extract the original tokenizer file and to manage to load this file into the 🤗
|
||||
Transformers' implementation of the tokenizer.
|
||||
|
||||
To ensure that the tokenizer works correctly, it is recommended to first create a script in the original repository
|
||||
that inputs a string and returns the `input_ids``. It could look similar to this (in pseudo-code):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
input_str = "This is a long example input string containing special characters .$?-, numbers 2872 234 12 and words."
|
||||
model = BrandNewBertModel.load_pretrained_checkpoint("/path/to/checkpoint/")
|
||||
input_ids = model.tokenize(input_str)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You might have to take a deeper look again into the original repository to find the correct tokenizer function or you
|
||||
might even have to do changes to your clone of the original repository to only output the `input_ids`. Having written
|
||||
a functional tokenization script that uses the original repository, an analogous script for 🤗 Transformers should be
|
||||
created. It should look similar to this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import BrandNewBertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
input_str = "This is a long example input string containing special characters .$?-, numbers 2872 234 12 and words."
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = BrandNewBertTokenizer.from_pretrained("/path/to/tokenizer/folder/")
|
||||
|
||||
input_ids = tokenizer(input_str).input_ids
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When both `input_ids` yield the same values, as a final step a tokenizer test file should also be added.
|
||||
|
||||
Analogous to the modeling test files of *brand_new_bert*, the tokenization test files of *brand_new_bert* should
|
||||
contain a couple of hard-coded integration tests.
|
||||
|
||||
**10. Run End-to-end integration tests**
|
||||
|
||||
Having added the tokenizer, you should also add a couple of end-to-end integration tests using both the model and the
|
||||
tokenizer to `tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_brand_new_bert.py` in 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
Such a test should show on a meaningful
|
||||
text-to-text sample that the 🤗 Transformers implementation works as expected. A meaningful text-to-text sample can
|
||||
include *e.g.* a source-to-target-translation pair, an article-to-summary pair, a question-to-answer pair, etc… If none
|
||||
of the ported checkpoints has been fine-tuned on a downstream task it is enough to simply rely on the model tests. In a
|
||||
final step to ensure that the model is fully functional, it is advised that you also run all tests on GPU. It can
|
||||
happen that you forgot to add some `.to(self.device)` statements to internal tensors of the model, which in such a
|
||||
test would show in an error. In case you have no access to a GPU, the Hugging Face team can take care of running those
|
||||
tests for you.
|
||||
|
||||
**11. Add Docstring**
|
||||
|
||||
Now, all the necessary functionality for *brand_new_bert* is added - you're almost done! The only thing left to add is
|
||||
a nice docstring and a doc page. The Cookiecutter should have added a template file called
|
||||
`docs/source/model_doc/brand_new_bert.mdx` that you should fill out. Users of your model will usually first look at
|
||||
this page before using your model. Hence, the documentation must be understandable and concise. It is very useful for
|
||||
the community to add some *Tips* to show how the model should be used. Don't hesitate to ping the Hugging Face team
|
||||
regarding the docstrings.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, make sure that the docstring added to `src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/modeling_brand_new_bert.py` is
|
||||
correct and included all necessary inputs and outputs. We have a detailed guide about writing documentation and our docstring format [here](writing-documentation). It is always to good to remind oneself that documentation should
|
||||
be treated at least as carefully as the code in 🤗 Transformers since the documentation is usually the first contact
|
||||
point of the community with the model.
|
||||
|
||||
**Code refactor**
|
||||
|
||||
Great, now you have added all the necessary code for *brand_new_bert*. At this point, you should correct some potential
|
||||
incorrect code style by running:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
make style
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and verify that your coding style passes the quality check:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
make quality
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are a couple of other very strict design tests in 🤗 Transformers that might still be failing, which shows up in
|
||||
the tests of your pull request. This is often because of some missing information in the docstring or some incorrect
|
||||
naming. The Hugging Face team will surely help you if you're stuck here.
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, it is always a good idea to refactor one's code after having ensured that the code works correctly. With all
|
||||
tests passing, now it's a good time to go over the added code again and do some refactoring.
|
||||
|
||||
You have now finished the coding part, congratulation! 🎉 You are Awesome! 😎
|
||||
|
||||
**12. Upload the models to the model hub**
|
||||
|
||||
In this final part, you should convert and upload all checkpoints to the model hub and add a model card for each
|
||||
uploaded model checkpoint. You can get familiar with the hub functionalities by reading our [Model sharing and uploading Page](model_sharing). You should work alongside the Hugging Face team here to decide on a fitting name for each
|
||||
checkpoint and to get the required access rights to be able to upload the model under the author's organization of
|
||||
*brand_new_bert*. The `push_to_hub` method, present in all models in `transformers`, is a quick and efficient way to push your checkpoint to the hub. A little snippet is pasted below:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
brand_new_bert.push_to_hub("brand_new_bert")
|
||||
# Uncomment the following line to push to an organization.
|
||||
# brand_new_bert.push_to_hub("<organization>/brand_new_bert")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is worth spending some time to create fitting model cards for each checkpoint. The model cards should highlight the
|
||||
specific characteristics of this particular checkpoint, *e.g.* On which dataset was the checkpoint
|
||||
pretrained/fine-tuned on? On what down-stream task should the model be used? And also include some code on how to
|
||||
correctly use the model.
|
||||
|
||||
**13. (Optional) Add notebook**
|
||||
|
||||
It is very helpful to add a notebook that showcases in-detail how *brand_new_bert* can be used for inference and/or
|
||||
fine-tuned on a downstream task. This is not mandatory to merge your PR, but very useful for the community.
|
||||
|
||||
**14. Submit your finished PR**
|
||||
|
||||
You're done programming now and can move to the last step, which is getting your PR merged into main. Usually, the
|
||||
Hugging Face team should have helped you already at this point, but it is worth taking some time to give your finished
|
||||
PR a nice description and eventually add comments to your code, if you want to point out certain design choices to your
|
||||
reviewer.
|
||||
|
||||
### Share your work!!
|
||||
|
||||
Now, it's time to get some credit from the community for your work! Having completed a model addition is a major
|
||||
contribution to Transformers and the whole NLP community. Your code and the ported pre-trained models will certainly be
|
||||
used by hundreds and possibly even thousands of developers and researchers. You should be proud of your work and share
|
||||
your achievement with the community.
|
||||
|
||||
**You have made another model that is super easy to access for everyone in the community! 🤯**
|
||||
258
docs/source/en/add_new_pipeline.md
Normal file
258
docs/source/en/add_new_pipeline.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,258 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# How to create a custom pipeline?
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, we will see how to create a custom pipeline and share it on the [Hub](hf.co/models) or add it to the
|
||||
🤗 Transformers library.
|
||||
|
||||
First and foremost, you need to decide the raw entries the pipeline will be able to take. It can be strings, raw bytes,
|
||||
dictionaries or whatever seems to be the most likely desired input. Try to keep these inputs as pure Python as possible
|
||||
as it makes compatibility easier (even through other languages via JSON). Those will be the `inputs` of the
|
||||
pipeline (`preprocess`).
|
||||
|
||||
Then define the `outputs`. Same policy as the `inputs`. The simpler, the better. Those will be the outputs of
|
||||
`postprocess` method.
|
||||
|
||||
Start by inheriting the base class `Pipeline` with the 4 methods needed to implement `preprocess`,
|
||||
`_forward`, `postprocess`, and `_sanitize_parameters`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class MyPipeline(Pipeline):
|
||||
def _sanitize_parameters(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
preprocess_kwargs = {}
|
||||
if "maybe_arg" in kwargs:
|
||||
preprocess_kwargs["maybe_arg"] = kwargs["maybe_arg"]
|
||||
return preprocess_kwargs, {}, {}
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess(self, inputs, maybe_arg=2):
|
||||
model_input = Tensor(inputs["input_ids"])
|
||||
return {"model_input": model_input}
|
||||
|
||||
def _forward(self, model_inputs):
|
||||
# model_inputs == {"model_input": model_input}
|
||||
outputs = self.model(**model_inputs)
|
||||
# Maybe {"logits": Tensor(...)}
|
||||
return outputs
|
||||
|
||||
def postprocess(self, model_outputs):
|
||||
best_class = model_outputs["logits"].softmax(-1)
|
||||
return best_class
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The structure of this breakdown is to support relatively seamless support for CPU/GPU, while supporting doing
|
||||
pre/postprocessing on the CPU on different threads
|
||||
|
||||
`preprocess` will take the originally defined inputs, and turn them into something feedable to the model. It might
|
||||
contain more information and is usually a `Dict`.
|
||||
|
||||
`_forward` is the implementation detail and is not meant to be called directly. `forward` is the preferred
|
||||
called method as it contains safeguards to make sure everything is working on the expected device. If anything is
|
||||
linked to a real model it belongs in the `_forward` method, anything else is in the preprocess/postprocess.
|
||||
|
||||
`postprocess` methods will take the output of `_forward` and turn it into the final output that was decided
|
||||
earlier.
|
||||
|
||||
`_sanitize_parameters` exists to allow users to pass any parameters whenever they wish, be it at initialization
|
||||
time `pipeline(...., maybe_arg=4)` or at call time `pipe = pipeline(...); output = pipe(...., maybe_arg=4)`.
|
||||
|
||||
The returns of `_sanitize_parameters` are the 3 dicts of kwargs that will be passed directly to `preprocess`,
|
||||
`_forward`, and `postprocess`. Don't fill anything if the caller didn't call with any extra parameter. That
|
||||
allows to keep the default arguments in the function definition which is always more "natural".
|
||||
|
||||
A classic example would be a `top_k` argument in the post processing in classification tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> pipe = pipeline("my-new-task")
|
||||
>>> pipe("This is a test")
|
||||
[{"label": "1-star", "score": 0.8}, {"label": "2-star", "score": 0.1}, {"label": "3-star", "score": 0.05}
|
||||
{"label": "4-star", "score": 0.025}, {"label": "5-star", "score": 0.025}]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pipe("This is a test", top_k=2)
|
||||
[{"label": "1-star", "score": 0.8}, {"label": "2-star", "score": 0.1}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In order to achieve that, we'll update our `postprocess` method with a default parameter to `5`. and edit
|
||||
`_sanitize_parameters` to allow this new parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def postprocess(self, model_outputs, top_k=5):
|
||||
best_class = model_outputs["logits"].softmax(-1)
|
||||
# Add logic to handle top_k
|
||||
return best_class
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _sanitize_parameters(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
preprocess_kwargs = {}
|
||||
if "maybe_arg" in kwargs:
|
||||
preprocess_kwargs["maybe_arg"] = kwargs["maybe_arg"]
|
||||
|
||||
postprocess_kwargs = {}
|
||||
if "top_k" in kwargs:
|
||||
postprocess_kwargs["top_k"] = kwargs["top_k"]
|
||||
return preprocess_kwargs, {}, postprocess_kwargs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Try to keep the inputs/outputs very simple and ideally JSON-serializable as it makes the pipeline usage very easy
|
||||
without requiring users to understand new kind of objects. It's also relatively common to support many different types
|
||||
of arguments for ease of use (audio files, can be filenames, URLs or pure bytes)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Adding it to the list of supported tasks
|
||||
|
||||
To register your `new-task` to the list of supported tasks, you have to add it to the `PIPELINE_REGISTRY`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers.pipelines import PIPELINE_REGISTRY
|
||||
|
||||
PIPELINE_REGISTRY.register_pipeline(
|
||||
"new-task",
|
||||
pipeline_class=MyPipeline,
|
||||
pt_model=AutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can specify a default model if you want, in which case it should come with a specific revision (which can be the name of a branch or a commit hash, here we took `"abcdef"`) as well as the type:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
PIPELINE_REGISTRY.register_pipeline(
|
||||
"new-task",
|
||||
pipeline_class=MyPipeline,
|
||||
pt_model=AutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
default={"pt": ("user/awesome_model", "abcdef")},
|
||||
type="text", # current support type: text, audio, image, multimodal
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Share your pipeline on the Hub
|
||||
|
||||
To share your custom pipeline on the Hub, you just have to save the custom code of your `Pipeline` subclass in a
|
||||
python file. For instance, let's say we want to use a custom pipeline for sentence pair classification like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers import Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def softmax(outputs):
|
||||
maxes = np.max(outputs, axis=-1, keepdims=True)
|
||||
shifted_exp = np.exp(outputs - maxes)
|
||||
return shifted_exp / shifted_exp.sum(axis=-1, keepdims=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PairClassificationPipeline(Pipeline):
|
||||
def _sanitize_parameters(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
preprocess_kwargs = {}
|
||||
if "second_text" in kwargs:
|
||||
preprocess_kwargs["second_text"] = kwargs["second_text"]
|
||||
return preprocess_kwargs, {}, {}
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess(self, text, second_text=None):
|
||||
return self.tokenizer(text, text_pair=second_text, return_tensors=self.framework)
|
||||
|
||||
def _forward(self, model_inputs):
|
||||
return self.model(**model_inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
def postprocess(self, model_outputs):
|
||||
logits = model_outputs.logits[0].numpy()
|
||||
probabilities = softmax(logits)
|
||||
|
||||
best_class = np.argmax(probabilities)
|
||||
label = self.model.config.id2label[best_class]
|
||||
score = probabilities[best_class].item()
|
||||
logits = logits.tolist()
|
||||
return {"label": label, "score": score, "logits": logits}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The implementation is framework agnostic, and will work for PyTorch and TensorFlow models. If we have saved this in
|
||||
a file named `pair_classification.py`, we can then import it and register it like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from pair_classification import PairClassificationPipeline
|
||||
from transformers.pipelines import PIPELINE_REGISTRY
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification, TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
PIPELINE_REGISTRY.register_pipeline(
|
||||
"pair-classification",
|
||||
pipeline_class=PairClassificationPipeline,
|
||||
pt_model=AutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
tf_model=TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once this is done, we can use it with a pretrained model. For instance `sgugger/finetuned-bert-mrpc` has been
|
||||
fine-tuned on the MRPC dataset, which classifies pairs of sentences as paraphrases or not.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
classifier = pipeline("pair-classification", model="sgugger/finetuned-bert-mrpc")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then we can share it on the Hub by using the `save_pretrained` method in a `Repository`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import Repository
|
||||
|
||||
repo = Repository("test-dynamic-pipeline", clone_from="{your_username}/test-dynamic-pipeline")
|
||||
classifier.save_pretrained("test-dynamic-pipeline")
|
||||
repo.push_to_hub()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will copy the file where you defined `PairClassificationPipeline` inside the folder `"test-dynamic-pipeline"`,
|
||||
along with saving the model and tokenizer of the pipeline, before pushing everything in the repository
|
||||
`{your_username}/test-dynamic-pipeline`. After that anyone can use it as long as they provide the option
|
||||
`trust_remote_code=True`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
classifier = pipeline(model="{your_username}/test-dynamic-pipeline", trust_remote_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Add the pipeline to 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to contribute your pipeline to 🤗 Transformers, you will need to add a new module in the `pipelines` submodule
|
||||
with the code of your pipeline, then add it in the list of tasks defined in `pipelines/__init__.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you will need to add tests. Create a new file `tests/test_pipelines_MY_PIPELINE.py` with example with the other tests.
|
||||
|
||||
The `run_pipeline_test` function will be very generic and run on small random models on every possible
|
||||
architecture as defined by `model_mapping` and `tf_model_mapping`.
|
||||
|
||||
This is very important to test future compatibility, meaning if someone adds a new model for
|
||||
`XXXForQuestionAnswering` then the pipeline test will attempt to run on it. Because the models are random it's
|
||||
impossible to check for actual values, that's why there is a helper `ANY` that will simply attempt to match the
|
||||
output of the pipeline TYPE.
|
||||
|
||||
You also *need* to implement 2 (ideally 4) tests.
|
||||
|
||||
- `test_small_model_pt` : Define 1 small model for this pipeline (doesn't matter if the results don't make sense)
|
||||
and test the pipeline outputs. The results should be the same as `test_small_model_tf`.
|
||||
- `test_small_model_tf` : Define 1 small model for this pipeline (doesn't matter if the results don't make sense)
|
||||
and test the pipeline outputs. The results should be the same as `test_small_model_pt`.
|
||||
- `test_large_model_pt` (`optional`): Tests the pipeline on a real pipeline where the results are supposed to
|
||||
make sense. These tests are slow and should be marked as such. Here the goal is to showcase the pipeline and to make
|
||||
sure there is no drift in future releases.
|
||||
- `test_large_model_tf` (`optional`): Tests the pipeline on a real pipeline where the results are supposed to
|
||||
make sense. These tests are slow and should be marked as such. Here the goal is to showcase the pipeline and to make
|
||||
sure there is no drift in future releases.
|
||||
@ -1,254 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# How to create a custom pipeline?
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, we will see how to create a custom pipeline and share it on the [Hub](hf.co/models) or add it to the
|
||||
🤗 Transformers library.
|
||||
|
||||
First and foremost, you need to decide the raw entries the pipeline will be able to take. It can be strings, raw bytes,
|
||||
dictionaries or whatever seems to be the most likely desired input. Try to keep these inputs as pure Python as possible
|
||||
as it makes compatibility easier (even through other languages via JSON). Those will be the `inputs` of the
|
||||
pipeline (`preprocess`).
|
||||
|
||||
Then define the `outputs`. Same policy as the `inputs`. The simpler, the better. Those will be the outputs of
|
||||
`postprocess` method.
|
||||
|
||||
Start by inheriting the base class `Pipeline` with the 4 methods needed to implement `preprocess`,
|
||||
`_forward`, `postprocess`, and `_sanitize_parameters`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class MyPipeline(Pipeline):
|
||||
def _sanitize_parameters(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
preprocess_kwargs = {}
|
||||
if "maybe_arg" in kwargs:
|
||||
preprocess_kwargs["maybe_arg"] = kwargs["maybe_arg"]
|
||||
return preprocess_kwargs, {}, {}
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess(self, inputs, maybe_arg=2):
|
||||
model_input = Tensor(inputs["input_ids"])
|
||||
return {"model_input": model_input}
|
||||
|
||||
def _forward(self, model_inputs):
|
||||
# model_inputs == {"model_input": model_input}
|
||||
outputs = self.model(**model_inputs)
|
||||
# Maybe {"logits": Tensor(...)}
|
||||
return outputs
|
||||
|
||||
def postprocess(self, model_outputs):
|
||||
best_class = model_outputs["logits"].softmax(-1)
|
||||
return best_class
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The structure of this breakdown is to support relatively seamless support for CPU/GPU, while supporting doing
|
||||
pre/postprocessing on the CPU on different threads
|
||||
|
||||
`preprocess` will take the originally defined inputs, and turn them into something feedable to the model. It might
|
||||
contain more information and is usually a `Dict`.
|
||||
|
||||
`_forward` is the implementation detail and is not meant to be called directly. `forward` is the preferred
|
||||
called method as it contains safeguards to make sure everything is working on the expected device. If anything is
|
||||
linked to a real model it belongs in the `_forward` method, anything else is in the preprocess/postprocess.
|
||||
|
||||
`postprocess` methods will take the output of `_forward` and turn it into the final output that was decided
|
||||
earlier.
|
||||
|
||||
`_sanitize_parameters` exists to allow users to pass any parameters whenever they wish, be it at initialization
|
||||
time `pipeline(...., maybe_arg=4)` or at call time `pipe = pipeline(...); output = pipe(...., maybe_arg=4)`.
|
||||
|
||||
The returns of `_sanitize_parameters` are the 3 dicts of kwargs that will be passed directly to `preprocess`,
|
||||
`_forward`, and `postprocess`. Don't fill anything if the caller didn't call with any extra parameter. That
|
||||
allows to keep the default arguments in the function definition which is always more "natural".
|
||||
|
||||
A classic example would be a `top_k` argument in the post processing in classification tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> pipe = pipeline("my-new-task")
|
||||
>>> pipe("This is a test")
|
||||
[{"label": "1-star", "score": 0.8}, {"label": "2-star", "score": 0.1}, {"label": "3-star", "score": 0.05}
|
||||
{"label": "4-star", "score": 0.025}, {"label": "5-star", "score": 0.025}]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pipe("This is a test", top_k=2)
|
||||
[{"label": "1-star", "score": 0.8}, {"label": "2-star", "score": 0.1}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In order to achieve that, we'll update our `postprocess` method with a default parameter to `5`. and edit
|
||||
`_sanitize_parameters` to allow this new parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def postprocess(self, model_outputs, top_k=5):
|
||||
best_class = model_outputs["logits"].softmax(-1)
|
||||
# Add logic to handle top_k
|
||||
return best_class
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _sanitize_parameters(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
preprocess_kwargs = {}
|
||||
if "maybe_arg" in kwargs:
|
||||
preprocess_kwargs["maybe_arg"] = kwargs["maybe_arg"]
|
||||
|
||||
postprocess_kwargs = {}
|
||||
if "top_k" in kwargs:
|
||||
postprocess_kwargs["top_k"] = kwargs["top_k"]
|
||||
return preprocess_kwargs, {}, postprocess_kwargs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Try to keep the inputs/outputs very simple and ideally JSON-serializable as it makes the pipeline usage very easy
|
||||
without requiring users to understand new kind of objects. It's also relatively common to support many different types
|
||||
of arguments for ease of use (audio files, can be filenames, URLs or pure bytes)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Adding it to the list of supported tasks
|
||||
|
||||
To register your `new-task` to the list of supported tasks, you have to add it to the `PIPELINE_REGISTRY`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers.pipelines import PIPELINE_REGISTRY
|
||||
|
||||
PIPELINE_REGISTRY.register_pipeline(
|
||||
"new-task",
|
||||
pipeline_class=MyPipeline,
|
||||
pt_model=AutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can specify a default model if you want, in which case it should come with a specific revision (which can be the name of a branch or a commit hash, here we took `"abcdef"`) as well as the type:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
PIPELINE_REGISTRY.register_pipeline(
|
||||
"new-task",
|
||||
pipeline_class=MyPipeline,
|
||||
pt_model=AutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
default={"pt": ("user/awesome_model", "abcdef")},
|
||||
type="text", # current support type: text, audio, image, multimodal
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Share your pipeline on the Hub
|
||||
|
||||
To share your custom pipeline on the Hub, you just have to save the custom code of your `Pipeline` subclass in a
|
||||
python file. For instance, let's say we want to use a custom pipeline for sentence pair classification like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers import Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def softmax(outputs):
|
||||
maxes = np.max(outputs, axis=-1, keepdims=True)
|
||||
shifted_exp = np.exp(outputs - maxes)
|
||||
return shifted_exp / shifted_exp.sum(axis=-1, keepdims=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PairClassificationPipeline(Pipeline):
|
||||
def _sanitize_parameters(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
preprocess_kwargs = {}
|
||||
if "second_text" in kwargs:
|
||||
preprocess_kwargs["second_text"] = kwargs["second_text"]
|
||||
return preprocess_kwargs, {}, {}
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess(self, text, second_text=None):
|
||||
return self.tokenizer(text, text_pair=second_text, return_tensors=self.framework)
|
||||
|
||||
def _forward(self, model_inputs):
|
||||
return self.model(**model_inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
def postprocess(self, model_outputs):
|
||||
logits = model_outputs.logits[0].numpy()
|
||||
probabilities = softmax(logits)
|
||||
|
||||
best_class = np.argmax(probabilities)
|
||||
label = self.model.config.id2label[best_class]
|
||||
score = probabilities[best_class].item()
|
||||
logits = logits.tolist()
|
||||
return {"label": label, "score": score, "logits": logits}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The implementation is framework agnostic, and will work for PyTorch and TensorFlow models. If we have saved this in
|
||||
a file named `pair_classification.py`, we can then import it and register it like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from pair_classification import PairClassificationPipeline
|
||||
from transformers.pipelines import PIPELINE_REGISTRY
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification, TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
PIPELINE_REGISTRY.register_pipeline(
|
||||
"pair-classification",
|
||||
pipeline_class=PairClassificationPipeline,
|
||||
pt_model=AutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
tf_model=TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once this is done, we can use it with a pretrained model. For instance `sgugger/finetuned-bert-mrpc` has been
|
||||
fine-tuned on the MRPC dataset, which classifies pairs of sentences as paraphrases or not.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
classifier = pipeline("pair-classification", model="sgugger/finetuned-bert-mrpc")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then we can share it on the Hub by using the `save_pretrained` method in a `Repository`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import Repository
|
||||
|
||||
repo = Repository("test-dynamic-pipeline", clone_from="{your_username}/test-dynamic-pipeline")
|
||||
classifier.save_pretrained("test-dynamic-pipeline")
|
||||
repo.push_to_hub()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will copy the file where you defined `PairClassificationPipeline` inside the folder `"test-dynamic-pipeline"`,
|
||||
along with saving the model and tokenizer of the pipeline, before pushing everything in the repository
|
||||
`{your_username}/test-dynamic-pipeline`. After that anyone can use it as long as they provide the option
|
||||
`trust_remote_code=True`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
classifier = pipeline(model="{your_username}/test-dynamic-pipeline", trust_remote_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Add the pipeline to 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to contribute your pipeline to 🤗 Transformers, you will need to add a new module in the `pipelines` submodule
|
||||
with the code of your pipeline, then add it in the list of tasks defined in `pipelines/__init__.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you will need to add tests. Create a new file `tests/test_pipelines_MY_PIPELINE.py` with example with the other tests.
|
||||
|
||||
The `run_pipeline_test` function will be very generic and run on small random models on every possible
|
||||
architecture as defined by `model_mapping` and `tf_model_mapping`.
|
||||
|
||||
This is very important to test future compatibility, meaning if someone adds a new model for
|
||||
`XXXForQuestionAnswering` then the pipeline test will attempt to run on it. Because the models are random it's
|
||||
impossible to check for actual values, that's why there is a helper `ANY` that will simply attempt to match the
|
||||
output of the pipeline TYPE.
|
||||
|
||||
You also *need* to implement 2 (ideally 4) tests.
|
||||
|
||||
- `test_small_model_pt` : Define 1 small model for this pipeline (doesn't matter if the results don't make sense)
|
||||
and test the pipeline outputs. The results should be the same as `test_small_model_tf`.
|
||||
- `test_small_model_tf` : Define 1 small model for this pipeline (doesn't matter if the results don't make sense)
|
||||
and test the pipeline outputs. The results should be the same as `test_small_model_pt`.
|
||||
- `test_large_model_pt` (`optional`): Tests the pipeline on a real pipeline where the results are supposed to
|
||||
make sense. These tests are slow and should be marked as such. Here the goal is to showcase the pipeline and to make
|
||||
sure there is no drift in future releases.
|
||||
- `test_large_model_tf` (`optional`): Tests the pipeline on a real pipeline where the results are supposed to
|
||||
make sense. These tests are slow and should be marked as such. Here the goal is to showcase the pipeline and to make
|
||||
sure there is no drift in future releases.
|
||||
357
docs/source/en/add_tensorflow_model.md
Normal file
357
docs/source/en/add_tensorflow_model.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,357 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# How to convert a 🤗 Transformers model to TensorFlow?
|
||||
|
||||
Having multiple frameworks available to use with 🤗 Transformers gives you flexibility to play their strengths when
|
||||
designing your application, but it implies that compatibility must be added on a per-model basis. The good news is that
|
||||
adding TensorFlow compatibility to an existing model is simpler than [adding a new model from scratch](add_new_model)!
|
||||
Whether you wish to have a deeper understanding of large TensorFlow models, make a major open-source contribution, or
|
||||
enable TensorFlow for your model of choice, this guide is for you.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide empowers you, a member of our community, to contribute TensorFlow model weights and/or
|
||||
architectures to be used in 🤗 Transformers, with minimal supervision from the Hugging Face team. Writing a new model
|
||||
is no small feat, but hopefully this guide will make it less of a rollercoaster 🎢 and more of a walk in the park 🚶.
|
||||
Harnessing our collective experiences is absolutely critical to make this process increasingly easier, and thus we
|
||||
highly encourage that you suggest improvements to this guide!
|
||||
|
||||
Before you dive deeper, it is recommended that you check the following resources if you're new to 🤗 Transformers:
|
||||
- [General overview of 🤗 Transformers](add_new_model#general-overview-of-transformers)
|
||||
- [Hugging Face's TensorFlow Philosophy](https://huggingface.co/blog/tensorflow-philosophy)
|
||||
|
||||
In the remainder of this guide, you will learn what's needed to add a new TensorFlow model architecture, the
|
||||
procedure to convert PyTorch into TensorFlow model weights, and how to efficiently debug mismatches across ML
|
||||
frameworks. Let's get started!
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Are you unsure whether the model you wish to use already has a corresponding TensorFlow architecture?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Check the `model_type` field of the `config.json` of your model of choice
|
||||
([example](https://huggingface.co/bert-base-uncased/blob/main/config.json#L14)). If the corresponding model folder in
|
||||
🤗 Transformers has a file whose name starts with "modeling_tf", it means that it has a corresponding TensorFlow
|
||||
architecture ([example](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/src/transformers/models/bert)).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-by-step guide to add TensorFlow model architecture code
|
||||
|
||||
There are many ways to design a large model architecture, and multiple ways of implementing said design. However,
|
||||
you might recall from our [general overview of 🤗 Transformers](add_new_model#general-overview-of-transformers)
|
||||
that we are an opinionated bunch - the ease of use of 🤗 Transformers relies on consistent design choices. From
|
||||
experience, we can tell you a few important things about adding TensorFlow models:
|
||||
|
||||
- Don't reinvent the wheel! More often that not, there are at least two reference implementations you should check: the
|
||||
PyTorch equivalent of the model you are implementing and other TensorFlow models for the same class of problems.
|
||||
- Great model implementations survive the test of time. This doesn't happen because the code is pretty, but rather
|
||||
because the code is clear, easy to debug and build upon. If you make the life of the maintainers easy with your
|
||||
TensorFlow implementation, by replicating the same patterns as in other TensorFlow models and minimizing the mismatch
|
||||
to the PyTorch implementation, you ensure your contribution will be long lived.
|
||||
- Ask for help when you're stuck! The 🤗 Transformers team is here to help, and we've probably found solutions to the same
|
||||
problems you're facing.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an overview of the steps needed to add a TensorFlow model architecture:
|
||||
1. Select the model you wish to convert
|
||||
2. Prepare transformers dev environment
|
||||
3. (Optional) Understand theoretical aspects and the existing implementation
|
||||
4. Implement the model architecture
|
||||
5. Implement model tests
|
||||
6. Submit the pull request
|
||||
7. (Optional) Build demos and share with the world
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.-3. Prepare your model contribution
|
||||
|
||||
**1. Select the model you wish to convert**
|
||||
|
||||
Let's start off with the basics: the first thing you need to know is the architecture you want to convert. If you
|
||||
don't have your eyes set on a specific architecture, asking the 🤗 Transformers team for suggestions is a great way to
|
||||
maximize your impact - we will guide you towards the most prominent architectures that are missing on the TensorFlow
|
||||
side. If the specific model you want to use with TensorFlow already has a TensorFlow architecture implementation in
|
||||
🤗 Transformers but is lacking weights, feel free to jump straight into the
|
||||
[weight conversion section](#adding-tensorflow-weights-to-hub)
|
||||
of this page.
|
||||
|
||||
For simplicity, the remainder of this guide assumes you've decided to contribute with the TensorFlow version of
|
||||
*BrandNewBert* (the same example as in the [guide](add_new_model) to add a new model from scratch).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Before starting the work on a TensorFlow model architecture, double-check that there is no ongoing effort to do so.
|
||||
You can search for `BrandNewBert` on the
|
||||
[pull request GitHub page](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pulls?q=is%3Apr) to confirm that there is no
|
||||
TensorFlow-related pull request.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**2. Prepare transformers dev environment**
|
||||
|
||||
Having selected the model architecture, open an draft PR to signal your intention to work on it. Follow the
|
||||
instructions below to set up your environment and open a draft PR.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fork the [repository](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers) by clicking on the 'Fork' button on the
|
||||
repository's page. This creates a copy of the code under your GitHub user account.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Clone your `transformers` fork to your local disk, and add the base repository as a remote:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/[your Github handle]/transformers.git
|
||||
cd transformers
|
||||
git remote add upstream https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Set up a development environment, for instance by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m venv .env
|
||||
source .env/bin/activate
|
||||
pip install -e ".[dev]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on your OS, and since the number of optional dependencies of Transformers is growing, you might get a
|
||||
failure with this command. If that's the case make sure to install TensorFlow then do:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -e ".[quality]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** You don't need to have CUDA installed. Making the new model work on CPU is sufficient.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Create a branch with a descriptive name from your main branch
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git checkout -b add_tf_brand_new_bert
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Fetch and rebase to current main
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git fetch upstream
|
||||
git rebase upstream/main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
6. Add an empty `.py` file in `transformers/src/models/brandnewbert/` named `modeling_tf_brandnewbert.py`. This will
|
||||
be your TensorFlow model file.
|
||||
|
||||
7. Push the changes to your account using:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git add .
|
||||
git commit -m "initial commit"
|
||||
git push -u origin add_tf_brand_new_bert
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
8. Once you are satisfied, go to the webpage of your fork on GitHub. Click on “Pull request”. Make sure to add the
|
||||
GitHub handle of some members of the Hugging Face team as reviewers, so that the Hugging Face team gets notified for
|
||||
future changes.
|
||||
|
||||
9. Change the PR into a draft by clicking on “Convert to draft” on the right of the GitHub pull request web page.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Now you have set up a development environment to port *BrandNewBert* to TensorFlow in 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**3. (Optional) Understand theoretical aspects and the existing implementation**
|
||||
|
||||
You should take some time to read *BrandNewBert's* paper, if such descriptive work exists. There might be large
|
||||
sections of the paper that are difficult to understand. If this is the case, this is fine - don't worry! The goal is
|
||||
not to get a deep theoretical understanding of the paper, but to extract the necessary information required to
|
||||
effectively re-implement the model in 🤗 Transformers using TensorFlow. That being said, you don't have to spend too
|
||||
much time on the theoretical aspects, but rather focus on the practical ones, namely the existing model documentation
|
||||
page (e.g. [model docs for BERT](model_doc/bert)).
|
||||
|
||||
After you've grasped the basics of the models you are about to implement, it's important to understand the existing
|
||||
implementation. This is a great chance to confirm that a working implementation matches your expectations for the
|
||||
model, as well as to foresee technical challenges on the TensorFlow side.
|
||||
|
||||
It's perfectly natural that you feel overwhelmed with the amount of information that you've just absorbed. It is
|
||||
definitely not a requirement that you understand all facets of the model at this stage. Nevertheless, we highly
|
||||
encourage you to clear any pressing questions in our [forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Model implementation
|
||||
|
||||
Now it's time to finally start coding. Our suggested starting point is the PyTorch file itself: copy the contents of
|
||||
`modeling_brand_new_bert.py` inside `src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/` into
|
||||
`modeling_tf_brand_new_bert.py`. The goal of this section is to modify the file and update the import structure of
|
||||
🤗 Transformers such that you can import `TFBrandNewBert` and
|
||||
`TFBrandNewBert.from_pretrained(model_repo, from_pt=True)` successfully loads a working TensorFlow *BrandNewBert* model.
|
||||
|
||||
Sadly, there is no prescription to convert a PyTorch model into TensorFlow. You can, however, follow our selection of
|
||||
tips to make the process as smooth as possible:
|
||||
- Prepend `TF` to the name of all classes (e.g. `BrandNewBert` becomes `TFBrandNewBert`).
|
||||
- Most PyTorch operations have a direct TensorFlow replacement. For example, `torch.nn.Linear` corresponds to
|
||||
`tf.keras.layers.Dense`, `torch.nn.Dropout` corresponds to `tf.keras.layers.Dropout`, etc. If you're not sure
|
||||
about a specific operation, you can use the [TensorFlow documentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf)
|
||||
or the [PyTorch documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/).
|
||||
- Look for patterns in the 🤗 Transformers codebase. If you come across a certain operation that doesn't have a direct
|
||||
replacement, the odds are that someone else already had the same problem.
|
||||
- By default, keep the same variable names and structure as in PyTorch. This will make it easier to debug, track
|
||||
issues, and add fixes down the line.
|
||||
- Some layers have different default values in each framework. A notable example is the batch normalization layer's
|
||||
epsilon (`1e-5` in [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.BatchNorm2d.html#torch.nn.BatchNorm2d)
|
||||
and `1e-3` in [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/BatchNormalization)).
|
||||
Double-check the documentation!
|
||||
- PyTorch's `nn.Parameter` variables typically need to be initialized within TF Layer's `build()`. See the following
|
||||
example: [PyTorch](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/655f72a6896c0533b1bdee519ed65a059c2425ac/src/transformers/models/vit_mae/modeling_vit_mae.py#L212) /
|
||||
[TensorFlow](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/655f72a6896c0533b1bdee519ed65a059c2425ac/src/transformers/models/vit_mae/modeling_tf_vit_mae.py#L220)
|
||||
- If the PyTorch model has a `#copied from ...` on top of a function, the odds are that your TensorFlow model can also
|
||||
borrow that function from the architecture it was copied from, assuming it has a TensorFlow architecture.
|
||||
- Assigning the `name` attribute correctly in TensorFlow functions is critical to do the `from_pt=True` weight
|
||||
cross-loading. `name` is almost always the name of the corresponding variable in the PyTorch code. If `name` is not
|
||||
properly set, you will see it in the error message when loading the model weights.
|
||||
- The logic of the base model class, `BrandNewBertModel`, will actually reside in `TFBrandNewBertMainLayer`, a Keras
|
||||
layer subclass ([example](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/4fd32a1f499e45f009c2c0dea4d81c321cba7e02/src/transformers/models/bert/modeling_tf_bert.py#L719)).
|
||||
`TFBrandNewBertModel` will simply be a wrapper around this layer.
|
||||
- Keras models need to be built in order to load pretrained weights. For that reason, `TFBrandNewBertPreTrainedModel`
|
||||
will need to hold an example of inputs to the model, the `dummy_inputs`
|
||||
([example](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/4fd32a1f499e45f009c2c0dea4d81c321cba7e02/src/transformers/models/bert/modeling_tf_bert.py#L916)).
|
||||
- If you get stuck, ask for help - we're here to help you! 🤗
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the model file itself, you will also need to add the pointers to the model classes and related
|
||||
documentation pages. You can complete this part entirely following the patterns in other PRs
|
||||
([example](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/18020/files)). Here's a list of the needed manual
|
||||
changes:
|
||||
- Include all public classes of *BrandNewBert* in `src/transformers/__init__.py`
|
||||
- Add *BrandNewBert* classes to the corresponding Auto classes in `src/transformers/models/auto/modeling_tf_auto.py`
|
||||
- Include the modeling file in the documentation test file list in `utils/documentation_tests.txt`
|
||||
- Add the lazy loading classes related to *BrandNewBert* in `src/transformers/utils/dummy_tf_objects.py`
|
||||
- Update the import structures for the public classes in `src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/__init__.py`
|
||||
- Add the documentation pointers to the public methods of *BrandNewBert* in `docs/source/en/model_doc/brand_new_bert.md`
|
||||
- Add yourself to the list of contributors to *BrandNewBert* in `docs/source/en/model_doc/brand_new_bert.md`
|
||||
- Finally, add a green tick ✅ to the TensorFlow column of *BrandNewBert* in `docs/source/en/index.md`
|
||||
|
||||
When you're happy with your implementation, run the following checklist to confirm that your model architecture is
|
||||
ready:
|
||||
1. All layers that behave differently at train time (e.g. Dropout) are called with a `training` argument, which is
|
||||
propagated all the way from the top-level classes
|
||||
2. You have used `#copied from ...` whenever possible
|
||||
3. `TFBrandNewBertMainLayer` and all classes that use it have their `call` function decorated with `@unpack_inputs`
|
||||
4. `TFBrandNewBertMainLayer` is decorated with `@keras_serializable`
|
||||
5. A TensorFlow model can be loaded from PyTorch weights using `TFBrandNewBert.from_pretrained(model_repo, from_pt=True)`
|
||||
6. You can call the TensorFlow model using the expected input format
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Add model tests
|
||||
|
||||
Hurray, you've implemented a TensorFlow model! Now it's time to add tests to make sure that your model behaves as
|
||||
expected. As in the previous section, we suggest you start by copying the `test_modeling_brand_new_bert.py` file in
|
||||
`tests/models/brand_new_bert/` into `test_modeling_tf_brand_new_bert.py`, and continue by making the necessary
|
||||
TensorFlow replacements. For now, in all `.from_pretrained()` calls, you should use the `from_pt=True` flag to load
|
||||
the existing PyTorch weights.
|
||||
|
||||
After you're done, it's time for the moment of truth: run the tests! 😬
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
NVIDIA_TF32_OVERRIDE=0 RUN_SLOW=1 RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS=1 \
|
||||
py.test -vv tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_tf_brand_new_bert.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The most likely outcome is that you'll see a bunch of errors. Don't worry, this is expected! Debugging ML models is
|
||||
notoriously hard, and the key ingredient to success is patience (and `breakpoint()`). In our experience, the hardest
|
||||
problems arise from subtle mismatches between ML frameworks, for which we have a few pointers at the end of this guide.
|
||||
In other cases, a general test might not be directly applicable to your model, in which case we suggest an override
|
||||
at the model test class level. Regardless of the issue, don't hesitate to ask for help in your draft pull request if
|
||||
you're stuck.
|
||||
|
||||
When all tests pass, congratulations, your model is nearly ready to be added to the 🤗 Transformers library! 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.-7. Ensure everyone can use your model
|
||||
|
||||
**6. Submit the pull request**
|
||||
|
||||
Once you're done with the implementation and the tests, it's time to submit a pull request. Before pushing your code,
|
||||
run our code formatting utility, `make fixup` 🪄. This will automatically fix any formatting issues, which would cause
|
||||
our automatic checks to fail.
|
||||
|
||||
It's now time to convert your draft pull request into a real pull request. To do so, click on the "Ready for
|
||||
review" button and add Joao (`@gante`) and Matt (`@Rocketknight1`) as reviewers. A model pull request will need
|
||||
at least 3 reviewers, but they will take care of finding appropriate additional reviewers for your model.
|
||||
|
||||
After all reviewers are happy with the state of your PR, the final action point is to remove the `from_pt=True` flag in
|
||||
`.from_pretrained()` calls. Since there are no TensorFlow weights, you will have to add them! Check the section
|
||||
below for instructions on how to do it.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, when the TensorFlow weights get merged, you have at least 3 reviewer approvals, and all CI checks are
|
||||
green, double-check the tests locally one last time
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
NVIDIA_TF32_OVERRIDE=0 RUN_SLOW=1 RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS=1 \
|
||||
py.test -vv tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_tf_brand_new_bert.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and we will merge your PR! Congratulations on the milestone 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
**7. (Optional) Build demos and share with the world**
|
||||
|
||||
One of the hardest parts about open-source is discovery. How can the other users learn about the existence of your
|
||||
fabulous TensorFlow contribution? With proper communication, of course! 📣
|
||||
|
||||
There are two main ways to share your model with the community:
|
||||
- Build demos. These include Gradio demos, notebooks, and other fun ways to show off your model. We highly
|
||||
encourage you to add a notebook to our [community-driven demos](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/community).
|
||||
- Share stories on social media like Twitter and LinkedIn. You should be proud of your work and share
|
||||
your achievement with the community - your model can now be used by thousands of engineers and researchers around
|
||||
the world 🌍! We will be happy to retweet your posts and help you share your work with the community.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Adding TensorFlow weights to 🤗 Hub
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming that the TensorFlow model architecture is available in 🤗 Transformers, converting PyTorch weights into
|
||||
TensorFlow weights is a breeze!
|
||||
|
||||
Here's how to do it:
|
||||
1. Make sure you are logged into your Hugging Face account in your terminal. You can log in using the command
|
||||
`huggingface-cli login` (you can find your access tokens [here](https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens))
|
||||
2. Run `transformers-cli pt-to-tf --model-name foo/bar`, where `foo/bar` is the name of the model repository
|
||||
containing the PyTorch weights you want to convert
|
||||
3. Tag `@joaogante` and `@Rocketknight1` in the 🤗 Hub PR the command above has just created
|
||||
|
||||
That's it! 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Debugging mismatches across ML frameworks 🐛
|
||||
|
||||
At some point, when adding a new architecture or when creating TensorFlow weights for an existing architecture, you
|
||||
might come across errors compaining about mismatches between PyTorch and TensorFlow. You might even decide to open the
|
||||
model architecture code for the two frameworks, and find that they look identical. What's going on? 🤔
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, let's talk about why understanding these mismatches matters. Many community members will use 🤗
|
||||
Transformers models out of the box, and trust that our models behave as expected. When there is a large mismatch
|
||||
between the two frameworks, it implies that the model is not following the reference implementation for at least one
|
||||
of the frameworks. This might lead to silent failures, in which the model runs but has poor performance. This is
|
||||
arguably worse than a model that fails to run at all! To that end, we aim at having a framework mismatch smaller than
|
||||
`1e-5` at all stages of the model.
|
||||
|
||||
As in other numerical problems, the devil is in the details. And as in any detail-oriented craft, the secret
|
||||
ingredient here is patience. Here is our suggested workflow for when you come across this type of issues:
|
||||
1. Locate the source of mismatches. The model you're converting probably has near identical inner variables up to a
|
||||
certain point. Place `breakpoint()` statements in the two frameworks' architectures, and compare the values of the
|
||||
numerical variables in a top-down fashion until you find the source of the problems.
|
||||
2. Now that you've pinpointed the source of the issue, get in touch with the 🤗 Transformers team. It is possible
|
||||
that we've seen a similar problem before and can promptly provide a solution. As a fallback, scan popular pages
|
||||
like StackOverflow and GitHub issues.
|
||||
3. If there is no solution in sight, it means you'll have to go deeper. The good news is that you've located the
|
||||
issue, so you can focus on the problematic instruction, abstracting away the rest of the model! The bad news is
|
||||
that you'll have to venture into the source implementation of said instruction. In some cases, you might find an
|
||||
issue with a reference implementation - don't abstain from opening an issue in the upstream repository.
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases, in dicussion with the 🤗 Transformers team, we might find that the fixing the mismatch is infeasible.
|
||||
When the mismatch is very small in the output layers of the model (but potentially large in the hidden states), we
|
||||
might decide to ignore it in favor of distributing the model. The `pt-to-tf` CLI mentioned above has a `--max-error`
|
||||
flag to override the error message at weight conversion time.
|
||||
@ -1,353 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# How to convert a 🤗 Transformers model to TensorFlow?
|
||||
|
||||
Having multiple frameworks available to use with 🤗 Transformers gives you flexibility to play their strengths when
|
||||
designing your application, but it implies that compatibility must be added on a per-model basis. The good news is that
|
||||
adding TensorFlow compatibility to an existing model is simpler than [adding a new model from scratch](add_new_model)!
|
||||
Whether you wish to have a deeper understanding of large TensorFlow models, make a major open-source contribution, or
|
||||
enable TensorFlow for your model of choice, this guide is for you.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide empowers you, a member of our community, to contribute TensorFlow model weights and/or
|
||||
architectures to be used in 🤗 Transformers, with minimal supervision from the Hugging Face team. Writing a new model
|
||||
is no small feat, but hopefully this guide will make it less of a rollercoaster 🎢 and more of a walk in the park 🚶.
|
||||
Harnessing our collective experiences is absolutely critical to make this process increasingly easier, and thus we
|
||||
highly encourage that you suggest improvements to this guide!
|
||||
|
||||
Before you dive deeper, it is recommended that you check the following resources if you're new to 🤗 Transformers:
|
||||
- [General overview of 🤗 Transformers](add_new_model#general-overview-of-transformers)
|
||||
- [Hugging Face's TensorFlow Philosophy](https://huggingface.co/blog/tensorflow-philosophy)
|
||||
|
||||
In the remainder of this guide, you will learn what's needed to add a new TensorFlow model architecture, the
|
||||
procedure to convert PyTorch into TensorFlow model weights, and how to efficiently debug mismatches across ML
|
||||
frameworks. Let's get started!
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Are you unsure whether the model you wish to use already has a corresponding TensorFlow architecture?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Check the `model_type` field of the `config.json` of your model of choice
|
||||
([example](https://huggingface.co/bert-base-uncased/blob/main/config.json#L14)). If the corresponding model folder in
|
||||
🤗 Transformers has a file whose name starts with "modeling_tf", it means that it has a corresponding TensorFlow
|
||||
architecture ([example](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/src/transformers/models/bert)).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Step-by-step guide to add TensorFlow model architecture code
|
||||
|
||||
There are many ways to design a large model architecture, and multiple ways of implementing said design. However,
|
||||
you might recall from our [general overview of 🤗 Transformers](add_new_model#general-overview-of-transformers)
|
||||
that we are an opinionated bunch - the ease of use of 🤗 Transformers relies on consistent design choices. From
|
||||
experience, we can tell you a few important things about adding TensorFlow models:
|
||||
|
||||
- Don't reinvent the wheel! More often that not, there are at least two reference implementations you should check: the
|
||||
PyTorch equivalent of the model you are implementing and other TensorFlow models for the same class of problems.
|
||||
- Great model implementations survive the test of time. This doesn't happen because the code is pretty, but rather
|
||||
because the code is clear, easy to debug and build upon. If you make the life of the maintainers easy with your
|
||||
TensorFlow implementation, by replicating the same patterns as in other TensorFlow models and minimizing the mismatch
|
||||
to the PyTorch implementation, you ensure your contribution will be long lived.
|
||||
- Ask for help when you're stuck! The 🤗 Transformers team is here to help, and we've probably found solutions to the same
|
||||
problems you're facing.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an overview of the steps needed to add a TensorFlow model architecture:
|
||||
1. Select the model you wish to convert
|
||||
2. Prepare transformers dev environment
|
||||
3. (Optional) Understand theoretical aspects and the existing implementation
|
||||
4. Implement the model architecture
|
||||
5. Implement model tests
|
||||
6. Submit the pull request
|
||||
7. (Optional) Build demos and share with the world
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.-3. Prepare your model contribution
|
||||
|
||||
**1. Select the model you wish to convert**
|
||||
|
||||
Let's start off with the basics: the first thing you need to know is the architecture you want to convert. If you
|
||||
don't have your eyes set on a specific architecture, asking the 🤗 Transformers team for suggestions is a great way to
|
||||
maximize your impact - we will guide you towards the most prominent architectures that are missing on the TensorFlow
|
||||
side. If the specific model you want to use with TensorFlow already has a TensorFlow architecture implementation in
|
||||
🤗 Transformers but is lacking weights, feel free to jump straight into the
|
||||
[weight conversion section](#adding-tensorflow-weights-to-hub)
|
||||
of this page.
|
||||
|
||||
For simplicity, the remainder of this guide assumes you've decided to contribute with the TensorFlow version of
|
||||
*BrandNewBert* (the same example as in the [guide](add_new_model) to add a new model from scratch).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Before starting the work on a TensorFlow model architecture, double-check that there is no ongoing effort to do so.
|
||||
You can search for `BrandNewBert` on the
|
||||
[pull request GitHub page](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pulls?q=is%3Apr) to confirm that there is no
|
||||
TensorFlow-related pull request.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**2. Prepare transformers dev environment**
|
||||
|
||||
Having selected the model architecture, open an draft PR to signal your intention to work on it. Follow the
|
||||
instructions below to set up your environment and open a draft PR.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fork the [repository](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers) by clicking on the 'Fork' button on the
|
||||
repository's page. This creates a copy of the code under your GitHub user account.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Clone your `transformers` fork to your local disk, and add the base repository as a remote:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/[your Github handle]/transformers.git
|
||||
cd transformers
|
||||
git remote add upstream https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Set up a development environment, for instance by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m venv .env
|
||||
source .env/bin/activate
|
||||
pip install -e ".[dev]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on your OS, and since the number of optional dependencies of Transformers is growing, you might get a
|
||||
failure with this command. If that's the case make sure to install TensorFlow then do:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -e ".[quality]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** You don't need to have CUDA installed. Making the new model work on CPU is sufficient.
|
||||
|
||||
4. Create a branch with a descriptive name from your main branch
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git checkout -b add_tf_brand_new_bert
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
5. Fetch and rebase to current main
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git fetch upstream
|
||||
git rebase upstream/main
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
6. Add an empty `.py` file in `transformers/src/models/brandnewbert/` named `modeling_tf_brandnewbert.py`. This will
|
||||
be your TensorFlow model file.
|
||||
|
||||
7. Push the changes to your account using:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git add .
|
||||
git commit -m "initial commit"
|
||||
git push -u origin add_tf_brand_new_bert
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
8. Once you are satisfied, go to the webpage of your fork on GitHub. Click on “Pull request”. Make sure to add the
|
||||
GitHub handle of some members of the Hugging Face team as reviewers, so that the Hugging Face team gets notified for
|
||||
future changes.
|
||||
|
||||
9. Change the PR into a draft by clicking on “Convert to draft” on the right of the GitHub pull request web page.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Now you have set up a development environment to port *BrandNewBert* to TensorFlow in 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**3. (Optional) Understand theoretical aspects and the existing implementation**
|
||||
|
||||
You should take some time to read *BrandNewBert's* paper, if such descriptive work exists. There might be large
|
||||
sections of the paper that are difficult to understand. If this is the case, this is fine - don't worry! The goal is
|
||||
not to get a deep theoretical understanding of the paper, but to extract the necessary information required to
|
||||
effectively re-implement the model in 🤗 Transformers using TensorFlow. That being said, you don't have to spend too
|
||||
much time on the theoretical aspects, but rather focus on the practical ones, namely the existing model documentation
|
||||
page (e.g. [model docs for BERT](model_doc/bert)).
|
||||
|
||||
After you've grasped the basics of the models you are about to implement, it's important to understand the existing
|
||||
implementation. This is a great chance to confirm that a working implementation matches your expectations for the
|
||||
model, as well as to foresee technical challenges on the TensorFlow side.
|
||||
|
||||
It's perfectly natural that you feel overwhelmed with the amount of information that you've just absorbed. It is
|
||||
definitely not a requirement that you understand all facets of the model at this stage. Nevertheless, we highly
|
||||
encourage you to clear any pressing questions in our [forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Model implementation
|
||||
|
||||
Now it's time to finally start coding. Our suggested starting point is the PyTorch file itself: copy the contents of
|
||||
`modeling_brand_new_bert.py` inside `src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/` into
|
||||
`modeling_tf_brand_new_bert.py`. The goal of this section is to modify the file and update the import structure of
|
||||
🤗 Transformers such that you can import `TFBrandNewBert` and
|
||||
`TFBrandNewBert.from_pretrained(model_repo, from_pt=True)` successfully loads a working TensorFlow *BrandNewBert* model.
|
||||
|
||||
Sadly, there is no prescription to convert a PyTorch model into TensorFlow. You can, however, follow our selection of
|
||||
tips to make the process as smooth as possible:
|
||||
- Prepend `TF` to the name of all classes (e.g. `BrandNewBert` becomes `TFBrandNewBert`).
|
||||
- Most PyTorch operations have a direct TensorFlow replacement. For example, `torch.nn.Linear` corresponds to
|
||||
`tf.keras.layers.Dense`, `torch.nn.Dropout` corresponds to `tf.keras.layers.Dropout`, etc. If you're not sure
|
||||
about a specific operation, you can use the [TensorFlow documentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf)
|
||||
or the [PyTorch documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/).
|
||||
- Look for patterns in the 🤗 Transformers codebase. If you come across a certain operation that doesn't have a direct
|
||||
replacement, the odds are that someone else already had the same problem.
|
||||
- By default, keep the same variable names and structure as in PyTorch. This will make it easier to debug, track
|
||||
issues, and add fixes down the line.
|
||||
- Some layers have different default values in each framework. A notable example is the batch normalization layer's
|
||||
epsilon (`1e-5` in [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.BatchNorm2d.html#torch.nn.BatchNorm2d)
|
||||
and `1e-3` in [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/BatchNormalization)).
|
||||
Double-check the documentation!
|
||||
- PyTorch's `nn.Parameter` variables typically need to be initialized within TF Layer's `build()`. See the following
|
||||
example: [PyTorch](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/655f72a6896c0533b1bdee519ed65a059c2425ac/src/transformers/models/vit_mae/modeling_vit_mae.py#L212) /
|
||||
[TensorFlow](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/655f72a6896c0533b1bdee519ed65a059c2425ac/src/transformers/models/vit_mae/modeling_tf_vit_mae.py#L220)
|
||||
- If the PyTorch model has a `#copied from ...` on top of a function, the odds are that your TensorFlow model can also
|
||||
borrow that function from the architecture it was copied from, assuming it has a TensorFlow architecture.
|
||||
- Assigning the `name` attribute correctly in TensorFlow functions is critical to do the `from_pt=True` weight
|
||||
cross-loading. `name` is almost always the name of the corresponding variable in the PyTorch code. If `name` is not
|
||||
properly set, you will see it in the error message when loading the model weights.
|
||||
- The logic of the base model class, `BrandNewBertModel`, will actually reside in `TFBrandNewBertMainLayer`, a Keras
|
||||
layer subclass ([example](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/4fd32a1f499e45f009c2c0dea4d81c321cba7e02/src/transformers/models/bert/modeling_tf_bert.py#L719)).
|
||||
`TFBrandNewBertModel` will simply be a wrapper around this layer.
|
||||
- Keras models need to be built in order to load pretrained weights. For that reason, `TFBrandNewBertPreTrainedModel`
|
||||
will need to hold an example of inputs to the model, the `dummy_inputs`
|
||||
([example](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/4fd32a1f499e45f009c2c0dea4d81c321cba7e02/src/transformers/models/bert/modeling_tf_bert.py#L916)).
|
||||
- If you get stuck, ask for help - we're here to help you! 🤗
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the model file itself, you will also need to add the pointers to the model classes and related
|
||||
documentation pages. You can complete this part entirely following the patterns in other PRs
|
||||
([example](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/18020/files)). Here's a list of the needed manual
|
||||
changes:
|
||||
- Include all public classes of *BrandNewBert* in `src/transformers/__init__.py`
|
||||
- Add *BrandNewBert* classes to the corresponding Auto classes in `src/transformers/models/auto/modeling_tf_auto.py`
|
||||
- Include the modeling file in the documentation test file list in `utils/documentation_tests.txt`
|
||||
- Add the lazy loading classes related to *BrandNewBert* in `src/transformers/utils/dummy_tf_objects.py`
|
||||
- Update the import structures for the public classes in `src/transformers/models/brand_new_bert/__init__.py`
|
||||
- Add the documentation pointers to the public methods of *BrandNewBert* in `docs/source/en/model_doc/brand_new_bert.mdx`
|
||||
- Add yourself to the list of contributors to *BrandNewBert* in `docs/source/en/model_doc/brand_new_bert.mdx`
|
||||
- Finally, add a green tick ✅ to the TensorFlow column of *BrandNewBert* in `docs/source/en/index.mdx`
|
||||
|
||||
When you're happy with your implementation, run the following checklist to confirm that your model architecture is
|
||||
ready:
|
||||
1. All layers that behave differently at train time (e.g. Dropout) are called with a `training` argument, which is
|
||||
propagated all the way from the top-level classes
|
||||
2. You have used `#copied from ...` whenever possible
|
||||
3. `TFBrandNewBertMainLayer` and all classes that use it have their `call` function decorated with `@unpack_inputs`
|
||||
4. `TFBrandNewBertMainLayer` is decorated with `@keras_serializable`
|
||||
5. A TensorFlow model can be loaded from PyTorch weights using `TFBrandNewBert.from_pretrained(model_repo, from_pt=True)`
|
||||
6. You can call the TensorFlow model using the expected input format
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Add model tests
|
||||
|
||||
Hurray, you've implemented a TensorFlow model! Now it's time to add tests to make sure that your model behaves as
|
||||
expected. As in the previous section, we suggest you start by copying the `test_modeling_brand_new_bert.py` file in
|
||||
`tests/models/brand_new_bert/` into `test_modeling_tf_brand_new_bert.py`, and continue by making the necessary
|
||||
TensorFlow replacements. For now, in all `.from_pretrained()` calls, you should use the `from_pt=True` flag to load
|
||||
the existing PyTorch weights.
|
||||
|
||||
After you're done, it's time for the moment of truth: run the tests! 😬
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
NVIDIA_TF32_OVERRIDE=0 RUN_SLOW=1 RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS=1 \
|
||||
py.test -vv tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_tf_brand_new_bert.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The most likely outcome is that you'll see a bunch of errors. Don't worry, this is expected! Debugging ML models is
|
||||
notoriously hard, and the key ingredient to success is patience (and `breakpoint()`). In our experience, the hardest
|
||||
problems arise from subtle mismatches between ML frameworks, for which we have a few pointers at the end of this guide.
|
||||
In other cases, a general test might not be directly applicable to your model, in which case we suggest an override
|
||||
at the model test class level. Regardless of the issue, don't hesitate to ask for help in your draft pull request if
|
||||
you're stuck.
|
||||
|
||||
When all tests pass, congratulations, your model is nearly ready to be added to the 🤗 Transformers library! 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
### 6.-7. Ensure everyone can use your model
|
||||
|
||||
**6. Submit the pull request**
|
||||
|
||||
Once you're done with the implementation and the tests, it's time to submit a pull request. Before pushing your code,
|
||||
run our code formatting utility, `make fixup` 🪄. This will automatically fix any formatting issues, which would cause
|
||||
our automatic checks to fail.
|
||||
|
||||
It's now time to convert your draft pull request into a real pull request. To do so, click on the "Ready for
|
||||
review" button and add Joao (`@gante`) and Matt (`@Rocketknight1`) as reviewers. A model pull request will need
|
||||
at least 3 reviewers, but they will take care of finding appropriate additional reviewers for your model.
|
||||
|
||||
After all reviewers are happy with the state of your PR, the final action point is to remove the `from_pt=True` flag in
|
||||
`.from_pretrained()` calls. Since there are no TensorFlow weights, you will have to add them! Check the section
|
||||
below for instructions on how to do it.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, when the TensorFlow weights get merged, you have at least 3 reviewer approvals, and all CI checks are
|
||||
green, double-check the tests locally one last time
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
NVIDIA_TF32_OVERRIDE=0 RUN_SLOW=1 RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS=1 \
|
||||
py.test -vv tests/models/brand_new_bert/test_modeling_tf_brand_new_bert.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and we will merge your PR! Congratulations on the milestone 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
**7. (Optional) Build demos and share with the world**
|
||||
|
||||
One of the hardest parts about open-source is discovery. How can the other users learn about the existence of your
|
||||
fabulous TensorFlow contribution? With proper communication, of course! 📣
|
||||
|
||||
There are two main ways to share your model with the community:
|
||||
- Build demos. These include Gradio demos, notebooks, and other fun ways to show off your model. We highly
|
||||
encourage you to add a notebook to our [community-driven demos](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/community).
|
||||
- Share stories on social media like Twitter and LinkedIn. You should be proud of your work and share
|
||||
your achievement with the community - your model can now be used by thousands of engineers and researchers around
|
||||
the world 🌍! We will be happy to retweet your posts and help you share your work with the community.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Adding TensorFlow weights to 🤗 Hub
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming that the TensorFlow model architecture is available in 🤗 Transformers, converting PyTorch weights into
|
||||
TensorFlow weights is a breeze!
|
||||
|
||||
Here's how to do it:
|
||||
1. Make sure you are logged into your Hugging Face account in your terminal. You can log in using the command
|
||||
`huggingface-cli login` (you can find your access tokens [here](https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens))
|
||||
2. Run `transformers-cli pt-to-tf --model-name foo/bar`, where `foo/bar` is the name of the model repository
|
||||
containing the PyTorch weights you want to convert
|
||||
3. Tag `@joaogante` and `@Rocketknight1` in the 🤗 Hub PR the command above has just created
|
||||
|
||||
That's it! 🎉
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Debugging mismatches across ML frameworks 🐛
|
||||
|
||||
At some point, when adding a new architecture or when creating TensorFlow weights for an existing architecture, you
|
||||
might come across errors compaining about mismatches between PyTorch and TensorFlow. You might even decide to open the
|
||||
model architecture code for the two frameworks, and find that they look identical. What's going on? 🤔
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, let's talk about why understanding these mismatches matters. Many community members will use 🤗
|
||||
Transformers models out of the box, and trust that our models behave as expected. When there is a large mismatch
|
||||
between the two frameworks, it implies that the model is not following the reference implementation for at least one
|
||||
of the frameworks. This might lead to silent failures, in which the model runs but has poor performance. This is
|
||||
arguably worse than a model that fails to run at all! To that end, we aim at having a framework mismatch smaller than
|
||||
`1e-5` at all stages of the model.
|
||||
|
||||
As in other numerical problems, the devil is in the details. And as in any detail-oriented craft, the secret
|
||||
ingredient here is patience. Here is our suggested workflow for when you come across this type of issues:
|
||||
1. Locate the source of mismatches. The model you're converting probably has near identical inner variables up to a
|
||||
certain point. Place `breakpoint()` statements in the two frameworks' architectures, and compare the values of the
|
||||
numerical variables in a top-down fashion until you find the source of the problems.
|
||||
2. Now that you've pinpointed the source of the issue, get in touch with the 🤗 Transformers team. It is possible
|
||||
that we've seen a similar problem before and can promptly provide a solution. As a fallback, scan popular pages
|
||||
like StackOverflow and GitHub issues.
|
||||
3. If there is no solution in sight, it means you'll have to go deeper. The good news is that you've located the
|
||||
issue, so you can focus on the problematic instruction, abstracting away the rest of the model! The bad news is
|
||||
that you'll have to venture into the source implementation of said instruction. In some cases, you might find an
|
||||
issue with a reference implementation - don't abstain from opening an issue in the upstream repository.
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases, in dicussion with the 🤗 Transformers team, we might find that the fixing the mismatch is infeasible.
|
||||
When the mismatch is very small in the output layers of the model (but potentially large in the hidden states), we
|
||||
might decide to ignore it in favor of distributing the model. The `pt-to-tf` CLI mentioned above has a `--max-error`
|
||||
flag to override the error message at weight conversion time.
|
||||
61
docs/source/en/attention.md
Normal file
61
docs/source/en/attention.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Attention mechanisms
|
||||
|
||||
Most transformer models use full attention in the sense that the attention matrix is square. It can be a big
|
||||
computational bottleneck when you have long texts. Longformer and reformer are models that try to be more efficient and
|
||||
use a sparse version of the attention matrix to speed up training.
|
||||
|
||||
## LSH attention
|
||||
|
||||
[Reformer](#reformer) uses LSH attention. In the softmax(QK^t), only the biggest elements (in the softmax
|
||||
dimension) of the matrix QK^t are going to give useful contributions. So for each query q in Q, we can consider only
|
||||
the keys k in K that are close to q. A hash function is used to determine if q and k are close. The attention mask is
|
||||
modified to mask the current token (except at the first position), because it will give a query and a key equal (so
|
||||
very similar to each other). Since the hash can be a bit random, several hash functions are used in practice
|
||||
(determined by a n_rounds parameter) and then are averaged together.
|
||||
|
||||
## Local attention
|
||||
|
||||
[Longformer](#longformer) uses local attention: often, the local context (e.g., what are the two tokens to the
|
||||
left and right?) is enough to take action for a given token. Also, by stacking attention layers that have a small
|
||||
window, the last layer will have a receptive field of more than just the tokens in the window, allowing them to build a
|
||||
representation of the whole sentence.
|
||||
|
||||
Some preselected input tokens are also given global attention: for those few tokens, the attention matrix can access
|
||||
all tokens and this process is symmetric: all other tokens have access to those specific tokens (on top of the ones in
|
||||
their local window). This is shown in Figure 2d of the paper, see below for a sample attention mask:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img scale="50 %" align="center" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/local_attention_mask.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Using those attention matrices with less parameters then allows the model to have inputs having a bigger sequence
|
||||
length.
|
||||
|
||||
## Other tricks
|
||||
|
||||
### Axial positional encodings
|
||||
|
||||
[Reformer](#reformer) uses axial positional encodings: in traditional transformer models, the positional encoding
|
||||
E is a matrix of size \\(l\\) by \\(d\\), \\(l\\) being the sequence length and \\(d\\) the dimension of the
|
||||
hidden state. If you have very long texts, this matrix can be huge and take way too much space on the GPU. To alleviate
|
||||
that, axial positional encodings consist of factorizing that big matrix E in two smaller matrices E1 and E2, with
|
||||
dimensions \\(l_{1} \times d_{1}\\) and \\(l_{2} \times d_{2}\\), such that \\(l_{1} \times l_{2} = l\\) and
|
||||
\\(d_{1} + d_{2} = d\\) (with the product for the lengths, this ends up being way smaller). The embedding for time
|
||||
step \\(j\\) in E is obtained by concatenating the embeddings for timestep \\(j \% l1\\) in E1 and \\(j // l1\\)
|
||||
in E2.
|
||||
@ -1,57 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Attention mechanisms
|
||||
|
||||
Most transformer models use full attention in the sense that the attention matrix is square. It can be a big
|
||||
computational bottleneck when you have long texts. Longformer and reformer are models that try to be more efficient and
|
||||
use a sparse version of the attention matrix to speed up training.
|
||||
|
||||
## LSH attention
|
||||
|
||||
[Reformer](#reformer) uses LSH attention. In the softmax(QK^t), only the biggest elements (in the softmax
|
||||
dimension) of the matrix QK^t are going to give useful contributions. So for each query q in Q, we can consider only
|
||||
the keys k in K that are close to q. A hash function is used to determine if q and k are close. The attention mask is
|
||||
modified to mask the current token (except at the first position), because it will give a query and a key equal (so
|
||||
very similar to each other). Since the hash can be a bit random, several hash functions are used in practice
|
||||
(determined by a n_rounds parameter) and then are averaged together.
|
||||
|
||||
## Local attention
|
||||
|
||||
[Longformer](#longformer) uses local attention: often, the local context (e.g., what are the two tokens to the
|
||||
left and right?) is enough to take action for a given token. Also, by stacking attention layers that have a small
|
||||
window, the last layer will have a receptive field of more than just the tokens in the window, allowing them to build a
|
||||
representation of the whole sentence.
|
||||
|
||||
Some preselected input tokens are also given global attention: for those few tokens, the attention matrix can access
|
||||
all tokens and this process is symmetric: all other tokens have access to those specific tokens (on top of the ones in
|
||||
their local window). This is shown in Figure 2d of the paper, see below for a sample attention mask:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img scale="50 %" align="center" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/local_attention_mask.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Using those attention matrices with less parameters then allows the model to have inputs having a bigger sequence
|
||||
length.
|
||||
|
||||
## Other tricks
|
||||
|
||||
### Axial positional encodings
|
||||
|
||||
[Reformer](#reformer) uses axial positional encodings: in traditional transformer models, the positional encoding
|
||||
E is a matrix of size \\(l\\) by \\(d\\), \\(l\\) being the sequence length and \\(d\\) the dimension of the
|
||||
hidden state. If you have very long texts, this matrix can be huge and take way too much space on the GPU. To alleviate
|
||||
that, axial positional encodings consist of factorizing that big matrix E in two smaller matrices E1 and E2, with
|
||||
dimensions \\(l_{1} \times d_{1}\\) and \\(l_{2} \times d_{2}\\), such that \\(l_{1} \times l_{2} = l\\) and
|
||||
\\(d_{1} + d_{2} = d\\) (with the product for the lengths, this ends up being way smaller). The embedding for time
|
||||
step \\(j\\) in E is obtained by concatenating the embeddings for timestep \\(j \% l1\\) in E1 and \\(j // l1\\)
|
||||
in E2.
|
||||
143
docs/source/en/autoclass_tutorial.md
Normal file
143
docs/source/en/autoclass_tutorial.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,143 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Load pretrained instances with an AutoClass
|
||||
|
||||
With so many different Transformer architectures, it can be challenging to create one for your checkpoint. As a part of 🤗 Transformers core philosophy to make the library easy, simple and flexible to use, an `AutoClass` automatically infer and load the correct architecture from a given checkpoint. The `from_pretrained()` method lets you quickly load a pretrained model for any architecture so you don't have to devote time and resources to train a model from scratch. Producing this type of checkpoint-agnostic code means if your code works for one checkpoint, it will work with another checkpoint - as long as it was trained for a similar task - even if the architecture is different.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Remember, architecture refers to the skeleton of the model and checkpoints are the weights for a given architecture. For example, [BERT](https://huggingface.co/bert-base-uncased) is an architecture, while `bert-base-uncased` is a checkpoint. Model is a general term that can mean either architecture or checkpoint.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, learn to:
|
||||
|
||||
* Load a pretrained tokenizer.
|
||||
* Load a pretrained image processor
|
||||
* Load a pretrained feature extractor.
|
||||
* Load a pretrained processor.
|
||||
* Load a pretrained model.
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
Nearly every NLP task begins with a tokenizer. A tokenizer converts your input into a format that can be processed by the model.
|
||||
|
||||
Load a tokenizer with [`AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then tokenize your input as shown below:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> sequence = "In a hole in the ground there lived a hobbit."
|
||||
>>> print(tokenizer(sequence))
|
||||
{'input_ids': [101, 1999, 1037, 4920, 1999, 1996, 2598, 2045, 2973, 1037, 7570, 10322, 4183, 1012, 102],
|
||||
'token_type_ids': [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
'attention_mask': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
For vision tasks, an image processor processes the image into the correct input format.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("google/vit-base-patch16-224")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
For audio tasks, a feature extractor processes the audio signal the correct input format.
|
||||
|
||||
Load a feature extractor with [`AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> feature_extractor = AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained(
|
||||
... "ehcalabres/wav2vec2-lg-xlsr-en-speech-emotion-recognition"
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
Multimodal tasks require a processor that combines two types of preprocessing tools. For example, the [LayoutLMV2](model_doc/layoutlmv2) model requires an image processor to handle images and a tokenizer to handle text; a processor combines both of them.
|
||||
|
||||
Load a processor with [`AutoProcessor.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/layoutlmv2-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Finally, the `AutoModelFor` classes let you load a pretrained model for a given task (see [here](model_doc/auto) for a complete list of available tasks). For example, load a model for sequence classification with [`AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Easily reuse the same checkpoint to load an architecture for a different task:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForTokenClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
For PyTorch models, the `from_pretrained()` method uses `torch.load()` which internally uses `pickle` and is known to be insecure. In general, never load a model that could have come from an untrusted source, or that could have been tampered with. This security risk is partially mitigated for public models hosted on the Hugging Face Hub, which are [scanned for malware](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security-malware) at each commit. See the [Hub documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security) for best practices like [signed commit verification](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security-gpg#signing-commits-with-gpg) with GPG.
|
||||
|
||||
TensorFlow and Flax checkpoints are not affected, and can be loaded within PyTorch architectures using the `from_tf` and `from_flax` kwargs for the `from_pretrained` method to circumvent this issue.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Generally, we recommend using the `AutoTokenizer` class and the `AutoModelFor` class to load pretrained instances of models. This will ensure you load the correct architecture every time. In the next [tutorial](preprocessing), learn how to use your newly loaded tokenizer, image processor, feature extractor and processor to preprocess a dataset for fine-tuning.
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Finally, the `TFAutoModelFor` classes let you load a pretrained model for a given task (see [here](model_doc/auto) for a complete list of available tasks). For example, load a model for sequence classification with [`TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Easily reuse the same checkpoint to load an architecture for a different task:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = TFAutoModelForTokenClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Generally, we recommend using the `AutoTokenizer` class and the `TFAutoModelFor` class to load pretrained instances of models. This will ensure you load the correct architecture every time. In the next [tutorial](preprocessing), learn how to use your newly loaded tokenizer, image processor, feature extractor and processor to preprocess a dataset for fine-tuning.
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
@ -1,139 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Load pretrained instances with an AutoClass
|
||||
|
||||
With so many different Transformer architectures, it can be challenging to create one for your checkpoint. As a part of 🤗 Transformers core philosophy to make the library easy, simple and flexible to use, an `AutoClass` automatically infer and load the correct architecture from a given checkpoint. The `from_pretrained()` method lets you quickly load a pretrained model for any architecture so you don't have to devote time and resources to train a model from scratch. Producing this type of checkpoint-agnostic code means if your code works for one checkpoint, it will work with another checkpoint - as long as it was trained for a similar task - even if the architecture is different.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Remember, architecture refers to the skeleton of the model and checkpoints are the weights for a given architecture. For example, [BERT](https://huggingface.co/bert-base-uncased) is an architecture, while `bert-base-uncased` is a checkpoint. Model is a general term that can mean either architecture or checkpoint.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, learn to:
|
||||
|
||||
* Load a pretrained tokenizer.
|
||||
* Load a pretrained image processor
|
||||
* Load a pretrained feature extractor.
|
||||
* Load a pretrained processor.
|
||||
* Load a pretrained model.
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
Nearly every NLP task begins with a tokenizer. A tokenizer converts your input into a format that can be processed by the model.
|
||||
|
||||
Load a tokenizer with [`AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then tokenize your input as shown below:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> sequence = "In a hole in the ground there lived a hobbit."
|
||||
>>> print(tokenizer(sequence))
|
||||
{'input_ids': [101, 1999, 1037, 4920, 1999, 1996, 2598, 2045, 2973, 1037, 7570, 10322, 4183, 1012, 102],
|
||||
'token_type_ids': [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
'attention_mask': [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
For vision tasks, an image processor processes the image into the correct input format.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("google/vit-base-patch16-224")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
For audio tasks, a feature extractor processes the audio signal the correct input format.
|
||||
|
||||
Load a feature extractor with [`AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> feature_extractor = AutoFeatureExtractor.from_pretrained(
|
||||
... "ehcalabres/wav2vec2-lg-xlsr-en-speech-emotion-recognition"
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
Multimodal tasks require a processor that combines two types of preprocessing tools. For example, the [LayoutLMV2](model_doc/layoutlmv2) model requires an image processor to handle images and a tokenizer to handle text; a processor combines both of them.
|
||||
|
||||
Load a processor with [`AutoProcessor.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("microsoft/layoutlmv2-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Finally, the `AutoModelFor` classes let you load a pretrained model for a given task (see [here](model_doc/auto) for a complete list of available tasks). For example, load a model for sequence classification with [`AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Easily reuse the same checkpoint to load an architecture for a different task:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForTokenClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
For PyTorch models, the `from_pretrained()` method uses `torch.load()` which internally uses `pickle` and is known to be insecure. In general, never load a model that could have come from an untrusted source, or that could have been tampered with. This security risk is partially mitigated for public models hosted on the Hugging Face Hub, which are [scanned for malware](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security-malware) at each commit. See the [Hub documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security) for best practices like [signed commit verification](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security-gpg#signing-commits-with-gpg) with GPG.
|
||||
|
||||
TensorFlow and Flax checkpoints are not affected, and can be loaded within PyTorch architectures using the `from_tf` and `from_flax` kwargs for the `from_pretrained` method to circumvent this issue.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Generally, we recommend using the `AutoTokenizer` class and the `AutoModelFor` class to load pretrained instances of models. This will ensure you load the correct architecture every time. In the next [tutorial](preprocessing), learn how to use your newly loaded tokenizer, image processor, feature extractor and processor to preprocess a dataset for fine-tuning.
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Finally, the `TFAutoModelFor` classes let you load a pretrained model for a given task (see [here](model_doc/auto) for a complete list of available tasks). For example, load a model for sequence classification with [`TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Easily reuse the same checkpoint to load an architecture for a different task:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModelForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = TFAutoModelForTokenClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Generally, we recommend using the `AutoTokenizer` class and the `TFAutoModelFor` class to load pretrained instances of models. This will ensure you load the correct architecture every time. In the next [tutorial](preprocessing), learn how to use your newly loaded tokenizer, image processor, feature extractor and processor to preprocess a dataset for fine-tuning.
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
387
docs/source/en/benchmarks.md
Normal file
387
docs/source/en/benchmarks.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,387 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Benchmarks
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Hugging Face's Benchmarking tools are deprecated and it is advised to use external Benchmarking libraries to measure the speed
|
||||
and memory complexity of Transformer models.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take a look at how 🤗 Transformers models can be benchmarked, best practices, and already available benchmarks.
|
||||
|
||||
A notebook explaining in more detail how to benchmark 🤗 Transformers models can be found [here](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/tree/main/examples/benchmark.ipynb).
|
||||
|
||||
## How to benchmark 🤗 Transformers models
|
||||
|
||||
The classes [`PyTorchBenchmark`] and [`TensorFlowBenchmark`] allow to flexibly benchmark 🤗 Transformers models. The benchmark classes allow us to measure the _peak memory usage_ and _required time_ for both _inference_ and _training_.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Hereby, _inference_ is defined by a single forward pass, and _training_ is defined by a single forward pass and
|
||||
backward pass.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The benchmark classes [`PyTorchBenchmark`] and [`TensorFlowBenchmark`] expect an object of type [`PyTorchBenchmarkArguments`] and
|
||||
[`TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments`], respectively, for instantiation. [`PyTorchBenchmarkArguments`] and [`TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments`] are data classes and contain all relevant configurations for their corresponding benchmark class. In the following example, it is shown how a BERT model of type _bert-base-cased_ can be benchmarked.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PyTorchBenchmark, PyTorchBenchmarkArguments
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = PyTorchBenchmarkArguments(models=["bert-base-uncased"], batch_sizes=[8], sequence_lengths=[8, 32, 128, 512])
|
||||
>>> benchmark = PyTorchBenchmark(args)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TensorFlowBenchmark, TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments(
|
||||
... models=["bert-base-uncased"], batch_sizes=[8], sequence_lengths=[8, 32, 128, 512]
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> benchmark = TensorFlowBenchmark(args)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
Here, three arguments are given to the benchmark argument data classes, namely `models`, `batch_sizes`, and
|
||||
`sequence_lengths`. The argument `models` is required and expects a `list` of model identifiers from the
|
||||
[model hub](https://huggingface.co/models) The `list` arguments `batch_sizes` and `sequence_lengths` define
|
||||
the size of the `input_ids` on which the model is benchmarked. There are many more parameters that can be configured
|
||||
via the benchmark argument data classes. For more detail on these one can either directly consult the files
|
||||
`src/transformers/benchmark/benchmark_args_utils.py`, `src/transformers/benchmark/benchmark_args.py` (for PyTorch)
|
||||
and `src/transformers/benchmark/benchmark_args_tf.py` (for Tensorflow). Alternatively, running the following shell
|
||||
commands from root will print out a descriptive list of all configurable parameters for PyTorch and Tensorflow
|
||||
respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/benchmarking/run_benchmark.py --help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
An instantiated benchmark object can then simply be run by calling `benchmark.run()`.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> results = benchmark.run()
|
||||
>>> print(results)
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - SPEED - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Time in s
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 8 0.006
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 32 0.006
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 128 0.018
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 512 0.088
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - MEMORY - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Memory in MB
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 8 1227
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 32 1281
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 128 1307
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 512 1539
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 2.11.0
|
||||
- framework: PyTorch
|
||||
- use_torchscript: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 1.4.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 08:58:43.371351
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python examples/tensorflow/benchmarking/run_benchmark_tf.py --help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
An instantiated benchmark object can then simply be run by calling `benchmark.run()`.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> results = benchmark.run()
|
||||
>>> print(results)
|
||||
>>> results = benchmark.run()
|
||||
>>> print(results)
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - SPEED - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Time in s
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 8 0.005
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 32 0.008
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 128 0.022
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 512 0.105
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - MEMORY - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Memory in MB
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 8 1330
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 32 1330
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 128 1330
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 512 1770
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 2.11.0
|
||||
- framework: Tensorflow
|
||||
- use_xla: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 2.2.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 09:26:35.617317
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the _time_ and the _required memory_ for _inference_ are benchmarked. In the example output above the first
|
||||
two sections show the result corresponding to _inference time_ and _inference memory_. In addition, all relevant
|
||||
information about the computing environment, _e.g._ the GPU type, the system, the library versions, etc... are printed
|
||||
out in the third section under _ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION_. This information can optionally be saved in a _.csv_ file
|
||||
when adding the argument `save_to_csv=True` to [`PyTorchBenchmarkArguments`] and
|
||||
[`TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments`] respectively. In this case, every section is saved in a separate
|
||||
_.csv_ file. The path to each _.csv_ file can optionally be defined via the argument data classes.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead of benchmarking pre-trained models via their model identifier, _e.g._ `bert-base-uncased`, the user can
|
||||
alternatively benchmark an arbitrary configuration of any available model class. In this case, a `list` of
|
||||
configurations must be inserted with the benchmark args as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PyTorchBenchmark, PyTorchBenchmarkArguments, BertConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = PyTorchBenchmarkArguments(
|
||||
... models=["bert-base", "bert-384-hid", "bert-6-lay"], batch_sizes=[8], sequence_lengths=[8, 32, 128, 512]
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> config_base = BertConfig()
|
||||
>>> config_384_hid = BertConfig(hidden_size=384)
|
||||
>>> config_6_lay = BertConfig(num_hidden_layers=6)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> benchmark = PyTorchBenchmark(args, configs=[config_base, config_384_hid, config_6_lay])
|
||||
>>> benchmark.run()
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - SPEED - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Time in s
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 0.006
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 0.006
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 0.018
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 0.088
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 8 0.006
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 32 0.006
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 128 0.011
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 512 0.054
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 8 0.003
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 32 0.004
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 128 0.009
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 512 0.044
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - MEMORY - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Memory in MB
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base 8 8 1277
|
||||
bert-base 8 32 1281
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 1307
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 1539
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 8 1005
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 32 1027
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 128 1035
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 512 1255
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 8 1097
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 32 1101
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 128 1127
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 512 1359
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 2.11.0
|
||||
- framework: PyTorch
|
||||
- use_torchscript: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 1.4.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 09:35:25.143267
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TensorFlowBenchmark, TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments, BertConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments(
|
||||
... models=["bert-base", "bert-384-hid", "bert-6-lay"], batch_sizes=[8], sequence_lengths=[8, 32, 128, 512]
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> config_base = BertConfig()
|
||||
>>> config_384_hid = BertConfig(hidden_size=384)
|
||||
>>> config_6_lay = BertConfig(num_hidden_layers=6)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> benchmark = TensorFlowBenchmark(args, configs=[config_base, config_384_hid, config_6_lay])
|
||||
>>> benchmark.run()
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - SPEED - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Time in s
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base 8 8 0.005
|
||||
bert-base 8 32 0.008
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 0.022
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 0.106
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 8 0.005
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 32 0.007
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 128 0.018
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 512 0.064
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 8 0.002
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 32 0.003
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 128 0.0011
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 512 0.074
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - MEMORY - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Memory in MB
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base 8 8 1330
|
||||
bert-base 8 32 1330
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 1330
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 1770
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 8 1330
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 32 1330
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 128 1330
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 512 1540
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 8 1330
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 32 1330
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 128 1330
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 512 1540
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 2.11.0
|
||||
- framework: Tensorflow
|
||||
- use_xla: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 2.2.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 09:38:15.487125
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
Again, _inference time_ and _required memory_ for _inference_ are measured, but this time for customized configurations
|
||||
of the `BertModel` class. This feature can especially be helpful when deciding for which configuration the model
|
||||
should be trained.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Benchmark best practices
|
||||
|
||||
This section lists a couple of best practices one should be aware of when benchmarking a model.
|
||||
|
||||
- Currently, only single device benchmarking is supported. When benchmarking on GPU, it is recommended that the user
|
||||
specifies on which device the code should be run by setting the `CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES` environment variable in the
|
||||
shell, _e.g._ `export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0` before running the code.
|
||||
- The option `no_multi_processing` should only be set to `True` for testing and debugging. To ensure accurate
|
||||
memory measurement it is recommended to run each memory benchmark in a separate process by making sure
|
||||
`no_multi_processing` is set to `True`.
|
||||
- One should always state the environment information when sharing the results of a model benchmark. Results can vary
|
||||
heavily between different GPU devices, library versions, etc., so that benchmark results on their own are not very
|
||||
useful for the community.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Sharing your benchmark
|
||||
|
||||
Previously all available core models (10 at the time) have been benchmarked for _inference time_, across many different
|
||||
settings: using PyTorch, with and without TorchScript, using TensorFlow, with and without XLA. All of those tests were
|
||||
done across CPUs (except for TensorFlow XLA) and GPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
The approach is detailed in the [following blogpost](https://medium.com/huggingface/benchmarking-transformers-pytorch-and-tensorflow-e2917fb891c2) and the results are
|
||||
available [here](https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1sryqufw2D0XlUH4sq3e9Wnxu5EAQkaohzrJbd5HdQ_w/edit?usp=sharing).
|
||||
|
||||
With the new _benchmark_ tools, it is easier than ever to share your benchmark results with the community
|
||||
|
||||
- [PyTorch Benchmarking Results](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/benchmarking/README.md).
|
||||
- [TensorFlow Benchmarking Results](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/tensorflow/benchmarking/README.md).
|
||||
@ -1,383 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Benchmarks
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Hugging Face's Benchmarking tools are deprecated and it is advised to use external Benchmarking libraries to measure the speed
|
||||
and memory complexity of Transformer models.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take a look at how 🤗 Transformers models can be benchmarked, best practices, and already available benchmarks.
|
||||
|
||||
A notebook explaining in more detail how to benchmark 🤗 Transformers models can be found [here](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/tree/main/examples/benchmark.ipynb).
|
||||
|
||||
## How to benchmark 🤗 Transformers models
|
||||
|
||||
The classes [`PyTorchBenchmark`] and [`TensorFlowBenchmark`] allow to flexibly benchmark 🤗 Transformers models. The benchmark classes allow us to measure the _peak memory usage_ and _required time_ for both _inference_ and _training_.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Hereby, _inference_ is defined by a single forward pass, and _training_ is defined by a single forward pass and
|
||||
backward pass.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The benchmark classes [`PyTorchBenchmark`] and [`TensorFlowBenchmark`] expect an object of type [`PyTorchBenchmarkArguments`] and
|
||||
[`TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments`], respectively, for instantiation. [`PyTorchBenchmarkArguments`] and [`TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments`] are data classes and contain all relevant configurations for their corresponding benchmark class. In the following example, it is shown how a BERT model of type _bert-base-cased_ can be benchmarked.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PyTorchBenchmark, PyTorchBenchmarkArguments
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = PyTorchBenchmarkArguments(models=["bert-base-uncased"], batch_sizes=[8], sequence_lengths=[8, 32, 128, 512])
|
||||
>>> benchmark = PyTorchBenchmark(args)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TensorFlowBenchmark, TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments(
|
||||
... models=["bert-base-uncased"], batch_sizes=[8], sequence_lengths=[8, 32, 128, 512]
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> benchmark = TensorFlowBenchmark(args)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
Here, three arguments are given to the benchmark argument data classes, namely `models`, `batch_sizes`, and
|
||||
`sequence_lengths`. The argument `models` is required and expects a `list` of model identifiers from the
|
||||
[model hub](https://huggingface.co/models) The `list` arguments `batch_sizes` and `sequence_lengths` define
|
||||
the size of the `input_ids` on which the model is benchmarked. There are many more parameters that can be configured
|
||||
via the benchmark argument data classes. For more detail on these one can either directly consult the files
|
||||
`src/transformers/benchmark/benchmark_args_utils.py`, `src/transformers/benchmark/benchmark_args.py` (for PyTorch)
|
||||
and `src/transformers/benchmark/benchmark_args_tf.py` (for Tensorflow). Alternatively, running the following shell
|
||||
commands from root will print out a descriptive list of all configurable parameters for PyTorch and Tensorflow
|
||||
respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/benchmarking/run_benchmark.py --help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
An instantiated benchmark object can then simply be run by calling `benchmark.run()`.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> results = benchmark.run()
|
||||
>>> print(results)
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - SPEED - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Time in s
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 8 0.006
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 32 0.006
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 128 0.018
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 512 0.088
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - MEMORY - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Memory in MB
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 8 1227
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 32 1281
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 128 1307
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 512 1539
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 2.11.0
|
||||
- framework: PyTorch
|
||||
- use_torchscript: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 1.4.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 08:58:43.371351
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python examples/tensorflow/benchmarking/run_benchmark_tf.py --help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
An instantiated benchmark object can then simply be run by calling `benchmark.run()`.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> results = benchmark.run()
|
||||
>>> print(results)
|
||||
>>> results = benchmark.run()
|
||||
>>> print(results)
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - SPEED - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Time in s
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 8 0.005
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 32 0.008
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 128 0.022
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 512 0.105
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - MEMORY - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Memory in MB
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 8 1330
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 32 1330
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 128 1330
|
||||
bert-base-uncased 8 512 1770
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 2.11.0
|
||||
- framework: Tensorflow
|
||||
- use_xla: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 2.2.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 09:26:35.617317
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the _time_ and the _required memory_ for _inference_ are benchmarked. In the example output above the first
|
||||
two sections show the result corresponding to _inference time_ and _inference memory_. In addition, all relevant
|
||||
information about the computing environment, _e.g._ the GPU type, the system, the library versions, etc... are printed
|
||||
out in the third section under _ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION_. This information can optionally be saved in a _.csv_ file
|
||||
when adding the argument `save_to_csv=True` to [`PyTorchBenchmarkArguments`] and
|
||||
[`TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments`] respectively. In this case, every section is saved in a separate
|
||||
_.csv_ file. The path to each _.csv_ file can optionally be defined via the argument data classes.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead of benchmarking pre-trained models via their model identifier, _e.g._ `bert-base-uncased`, the user can
|
||||
alternatively benchmark an arbitrary configuration of any available model class. In this case, a `list` of
|
||||
configurations must be inserted with the benchmark args as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PyTorchBenchmark, PyTorchBenchmarkArguments, BertConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = PyTorchBenchmarkArguments(
|
||||
... models=["bert-base", "bert-384-hid", "bert-6-lay"], batch_sizes=[8], sequence_lengths=[8, 32, 128, 512]
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> config_base = BertConfig()
|
||||
>>> config_384_hid = BertConfig(hidden_size=384)
|
||||
>>> config_6_lay = BertConfig(num_hidden_layers=6)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> benchmark = PyTorchBenchmark(args, configs=[config_base, config_384_hid, config_6_lay])
|
||||
>>> benchmark.run()
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - SPEED - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Time in s
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 0.006
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 0.006
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 0.018
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 0.088
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 8 0.006
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 32 0.006
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 128 0.011
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 512 0.054
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 8 0.003
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 32 0.004
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 128 0.009
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 512 0.044
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - MEMORY - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Memory in MB
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base 8 8 1277
|
||||
bert-base 8 32 1281
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 1307
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 1539
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 8 1005
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 32 1027
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 128 1035
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 512 1255
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 8 1097
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 32 1101
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 128 1127
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 512 1359
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 2.11.0
|
||||
- framework: PyTorch
|
||||
- use_torchscript: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 1.4.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 09:35:25.143267
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TensorFlowBenchmark, TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments, BertConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments(
|
||||
... models=["bert-base", "bert-384-hid", "bert-6-lay"], batch_sizes=[8], sequence_lengths=[8, 32, 128, 512]
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> config_base = BertConfig()
|
||||
>>> config_384_hid = BertConfig(hidden_size=384)
|
||||
>>> config_6_lay = BertConfig(num_hidden_layers=6)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> benchmark = TensorFlowBenchmark(args, configs=[config_base, config_384_hid, config_6_lay])
|
||||
>>> benchmark.run()
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - SPEED - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Time in s
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base 8 8 0.005
|
||||
bert-base 8 32 0.008
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 0.022
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 0.106
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 8 0.005
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 32 0.007
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 128 0.018
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 512 0.064
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 8 0.002
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 32 0.003
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 128 0.0011
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 512 0.074
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - MEMORY - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Memory in MB
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base 8 8 1330
|
||||
bert-base 8 32 1330
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 1330
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 1770
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 8 1330
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 32 1330
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 128 1330
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 512 1540
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 8 1330
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 32 1330
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 128 1330
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 512 1540
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 2.11.0
|
||||
- framework: Tensorflow
|
||||
- use_xla: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 2.2.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 09:38:15.487125
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
Again, _inference time_ and _required memory_ for _inference_ are measured, but this time for customized configurations
|
||||
of the `BertModel` class. This feature can especially be helpful when deciding for which configuration the model
|
||||
should be trained.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Benchmark best practices
|
||||
|
||||
This section lists a couple of best practices one should be aware of when benchmarking a model.
|
||||
|
||||
- Currently, only single device benchmarking is supported. When benchmarking on GPU, it is recommended that the user
|
||||
specifies on which device the code should be run by setting the `CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES` environment variable in the
|
||||
shell, _e.g._ `export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0` before running the code.
|
||||
- The option `no_multi_processing` should only be set to `True` for testing and debugging. To ensure accurate
|
||||
memory measurement it is recommended to run each memory benchmark in a separate process by making sure
|
||||
`no_multi_processing` is set to `True`.
|
||||
- One should always state the environment information when sharing the results of a model benchmark. Results can vary
|
||||
heavily between different GPU devices, library versions, etc., so that benchmark results on their own are not very
|
||||
useful for the community.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Sharing your benchmark
|
||||
|
||||
Previously all available core models (10 at the time) have been benchmarked for _inference time_, across many different
|
||||
settings: using PyTorch, with and without TorchScript, using TensorFlow, with and without XLA. All of those tests were
|
||||
done across CPUs (except for TensorFlow XLA) and GPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
The approach is detailed in the [following blogpost](https://medium.com/huggingface/benchmarking-transformers-pytorch-and-tensorflow-e2917fb891c2) and the results are
|
||||
available [here](https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1sryqufw2D0XlUH4sq3e9Wnxu5EAQkaohzrJbd5HdQ_w/edit?usp=sharing).
|
||||
|
||||
With the new _benchmark_ tools, it is easier than ever to share your benchmark results with the community
|
||||
|
||||
- [PyTorch Benchmarking Results](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/benchmarking/README.md).
|
||||
- [TensorFlow Benchmarking Results](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/tensorflow/benchmarking/README.md).
|
||||
41
docs/source/en/bertology.md
Normal file
41
docs/source/en/bertology.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# BERTology
|
||||
|
||||
There is a growing field of study concerned with investigating the inner working of large-scale transformers like BERT
|
||||
(that some call "BERTology"). Some good examples of this field are:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- BERT Rediscovers the Classical NLP Pipeline by Ian Tenney, Dipanjan Das, Ellie Pavlick:
|
||||
https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.05950
|
||||
- Are Sixteen Heads Really Better than One? by Paul Michel, Omer Levy, Graham Neubig: https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.10650
|
||||
- What Does BERT Look At? An Analysis of BERT's Attention by Kevin Clark, Urvashi Khandelwal, Omer Levy, Christopher D.
|
||||
Manning: https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.04341
|
||||
- CAT-probing: A Metric-based Approach to Interpret How Pre-trained Models for Programming Language Attend Code Structure: https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.04633
|
||||
|
||||
In order to help this new field develop, we have included a few additional features in the BERT/GPT/GPT-2 models to
|
||||
help people access the inner representations, mainly adapted from the great work of Paul Michel
|
||||
(https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.10650):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- accessing all the hidden-states of BERT/GPT/GPT-2,
|
||||
- accessing all the attention weights for each head of BERT/GPT/GPT-2,
|
||||
- retrieving heads output values and gradients to be able to compute head importance score and prune head as explained
|
||||
in https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.10650.
|
||||
|
||||
To help you understand and use these features, we have added a specific example script: [bertology.py](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/bertology/run_bertology.py) while extract information and prune a model pre-trained on
|
||||
GLUE.
|
||||
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# BERTology
|
||||
|
||||
There is a growing field of study concerned with investigating the inner working of large-scale transformers like BERT
|
||||
(that some call "BERTology"). Some good examples of this field are:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- BERT Rediscovers the Classical NLP Pipeline by Ian Tenney, Dipanjan Das, Ellie Pavlick:
|
||||
https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.05950
|
||||
- Are Sixteen Heads Really Better than One? by Paul Michel, Omer Levy, Graham Neubig: https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.10650
|
||||
- What Does BERT Look At? An Analysis of BERT's Attention by Kevin Clark, Urvashi Khandelwal, Omer Levy, Christopher D.
|
||||
Manning: https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.04341
|
||||
- CAT-probing: A Metric-based Approach to Interpret How Pre-trained Models for Programming Language Attend Code Structure: https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.04633
|
||||
|
||||
In order to help this new field develop, we have included a few additional features in the BERT/GPT/GPT-2 models to
|
||||
help people access the inner representations, mainly adapted from the great work of Paul Michel
|
||||
(https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.10650):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- accessing all the hidden-states of BERT/GPT/GPT-2,
|
||||
- accessing all the attention weights for each head of BERT/GPT/GPT-2,
|
||||
- retrieving heads output values and gradients to be able to compute head importance score and prune head as explained
|
||||
in https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.10650.
|
||||
|
||||
To help you understand and use these features, we have added a specific example script: [bertology.py](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/bertology/run_bertology.py) while extract information and prune a model pre-trained on
|
||||
GLUE.
|
||||
123
docs/source/en/big_models.md
Normal file
123
docs/source/en/big_models.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Instantiating a big model
|
||||
|
||||
When you want to use a very big pretrained model, one challenge is to minimize the use of the RAM. The usual workflow
|
||||
from PyTorch is:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create your model with random weights.
|
||||
2. Load your pretrained weights.
|
||||
3. Put those pretrained weights in your random model.
|
||||
|
||||
Step 1 and 2 both require a full version of the model in memory, which is not a problem in most cases, but if your model starts weighing several GigaBytes, those two copies can make you got our of RAM. Even worse, if you are using `torch.distributed` to launch a distributed training, each process will load the pretrained model and store these two copies in RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the randomly created model is initialized with "empty" tensors, which take the space in memory without filling it (thus the random values are whatever was in this chunk of memory at a given time). The random initialization following the appropriate distribution for the kind of model/parameters instatiated (like a normal distribution for instance) is only performed after step 3 on the non-initialized weights, to be as fast as possible!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, we explore the solutions Transformers offer to deal with this issue. Note that this is an area of active development, so the APIs explained here may change slightly in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
## Sharded checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
Since version 4.18.0, model checkpoints that end up taking more than 10GB of space are automatically sharded in smaller pieces. In terms of having one single checkpoint when you do `model.save_pretrained(save_dir)`, you will end up with several partial checkpoints (each of which being of size < 10GB) and an index that maps parameter names to the files they are stored in.
|
||||
|
||||
You can control the maximum size before sharding with the `max_shard_size` parameter, so for the sake of an example, we'll use a normal-size models with a small shard size: let's take a traditional BERT model.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you save it using [`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`], you will get a new folder with two files: the config of the model and its weights:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import os
|
||||
>>> import tempfile
|
||||
|
||||
>>> with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
|
||||
... model.save_pretrained(tmp_dir)
|
||||
... print(sorted(os.listdir(tmp_dir)))
|
||||
['config.json', 'pytorch_model.bin']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's use a maximum shard size of 200MB:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
|
||||
... model.save_pretrained(tmp_dir, max_shard_size="200MB")
|
||||
... print(sorted(os.listdir(tmp_dir)))
|
||||
['config.json', 'pytorch_model-00001-of-00003.bin', 'pytorch_model-00002-of-00003.bin', 'pytorch_model-00003-of-00003.bin', 'pytorch_model.bin.index.json']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
On top of the configuration of the model, we see three different weights files, and an `index.json` file which is our index. A checkpoint like this can be fully reloaded using the [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
|
||||
... model.save_pretrained(tmp_dir, max_shard_size="200MB")
|
||||
... new_model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(tmp_dir)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The main advantage of doing this for big models is that during step 2 of the workflow shown above, each shard of the checkpoint is loaded after the previous one, capping the memory usage in RAM to the model size plus the size of the biggest shard.
|
||||
|
||||
Behind the scenes, the index file is used to determine which keys are in the checkpoint, and where the corresponding weights are stored. We can load that index like any json and get a dictionary:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import json
|
||||
|
||||
>>> with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
|
||||
... model.save_pretrained(tmp_dir, max_shard_size="200MB")
|
||||
... with open(os.path.join(tmp_dir, "pytorch_model.bin.index.json"), "r") as f:
|
||||
... index = json.load(f)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> print(index.keys())
|
||||
dict_keys(['metadata', 'weight_map'])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The metadata just consists of the total size of the model for now. We plan to add other information in the future:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> index["metadata"]
|
||||
{'total_size': 433245184}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The weights map is the main part of this index, which maps each parameter name (as usually found in a PyTorch model `state_dict`) to the file it's stored in:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> index["weight_map"]
|
||||
{'embeddings.LayerNorm.bias': 'pytorch_model-00001-of-00003.bin',
|
||||
'embeddings.LayerNorm.weight': 'pytorch_model-00001-of-00003.bin',
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to directly load such a sharded checkpoint inside a model without using [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] (like you would do `model.load_state_dict()` for a full checkpoint) you should use [`~modeling_utils.load_sharded_checkpoint`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers.modeling_utils import load_sharded_checkpoint
|
||||
|
||||
>>> with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
|
||||
... model.save_pretrained(tmp_dir, max_shard_size="200MB")
|
||||
... load_sharded_checkpoint(model, tmp_dir)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Low memory loading
|
||||
|
||||
Sharded checkpoints reduce the memory usage during step 2 of the workflow mentioned above, but in order to use that model in a low memory setting, we recommend leveraging our tools based on the Accelerate library.
|
||||
|
||||
Please read the following guide for more information: [Large model loading using Accelerate](./main_classes/model#large-model-loading)
|
||||
@ -1,119 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Instantiating a big model
|
||||
|
||||
When you want to use a very big pretrained model, one challenge is to minimize the use of the RAM. The usual workflow
|
||||
from PyTorch is:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Create your model with random weights.
|
||||
2. Load your pretrained weights.
|
||||
3. Put those pretrained weights in your random model.
|
||||
|
||||
Step 1 and 2 both require a full version of the model in memory, which is not a problem in most cases, but if your model starts weighing several GigaBytes, those two copies can make you got our of RAM. Even worse, if you are using `torch.distributed` to launch a distributed training, each process will load the pretrained model and store these two copies in RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the randomly created model is initialized with "empty" tensors, which take the space in memory without filling it (thus the random values are whatever was in this chunk of memory at a given time). The random initialization following the appropriate distribution for the kind of model/parameters instatiated (like a normal distribution for instance) is only performed after step 3 on the non-initialized weights, to be as fast as possible!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, we explore the solutions Transformers offer to deal with this issue. Note that this is an area of active development, so the APIs explained here may change slightly in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
## Sharded checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
Since version 4.18.0, model checkpoints that end up taking more than 10GB of space are automatically sharded in smaller pieces. In terms of having one single checkpoint when you do `model.save_pretrained(save_dir)`, you will end up with several partial checkpoints (each of which being of size < 10GB) and an index that maps parameter names to the files they are stored in.
|
||||
|
||||
You can control the maximum size before sharding with the `max_shard_size` parameter, so for the sake of an example, we'll use a normal-size models with a small shard size: let's take a traditional BERT model.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you save it using [`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`], you will get a new folder with two files: the config of the model and its weights:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import os
|
||||
>>> import tempfile
|
||||
|
||||
>>> with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
|
||||
... model.save_pretrained(tmp_dir)
|
||||
... print(sorted(os.listdir(tmp_dir)))
|
||||
['config.json', 'pytorch_model.bin']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's use a maximum shard size of 200MB:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
|
||||
... model.save_pretrained(tmp_dir, max_shard_size="200MB")
|
||||
... print(sorted(os.listdir(tmp_dir)))
|
||||
['config.json', 'pytorch_model-00001-of-00003.bin', 'pytorch_model-00002-of-00003.bin', 'pytorch_model-00003-of-00003.bin', 'pytorch_model.bin.index.json']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
On top of the configuration of the model, we see three different weights files, and an `index.json` file which is our index. A checkpoint like this can be fully reloaded using the [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
|
||||
... model.save_pretrained(tmp_dir, max_shard_size="200MB")
|
||||
... new_model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(tmp_dir)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The main advantage of doing this for big models is that during step 2 of the workflow shown above, each shard of the checkpoint is loaded after the previous one, capping the memory usage in RAM to the model size plus the size of the biggest shard.
|
||||
|
||||
Behind the scenes, the index file is used to determine which keys are in the checkpoint, and where the corresponding weights are stored. We can load that index like any json and get a dictionary:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import json
|
||||
|
||||
>>> with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
|
||||
... model.save_pretrained(tmp_dir, max_shard_size="200MB")
|
||||
... with open(os.path.join(tmp_dir, "pytorch_model.bin.index.json"), "r") as f:
|
||||
... index = json.load(f)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> print(index.keys())
|
||||
dict_keys(['metadata', 'weight_map'])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The metadata just consists of the total size of the model for now. We plan to add other information in the future:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> index["metadata"]
|
||||
{'total_size': 433245184}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The weights map is the main part of this index, which maps each parameter name (as usually found in a PyTorch model `state_dict`) to the file it's stored in:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> index["weight_map"]
|
||||
{'embeddings.LayerNorm.bias': 'pytorch_model-00001-of-00003.bin',
|
||||
'embeddings.LayerNorm.weight': 'pytorch_model-00001-of-00003.bin',
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to directly load such a sharded checkpoint inside a model without using [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] (like you would do `model.load_state_dict()` for a full checkpoint) you should use [`~modeling_utils.load_sharded_checkpoint`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers.modeling_utils import load_sharded_checkpoint
|
||||
|
||||
>>> with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
|
||||
... model.save_pretrained(tmp_dir, max_shard_size="200MB")
|
||||
... load_sharded_checkpoint(model, tmp_dir)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Low memory loading
|
||||
|
||||
Sharded checkpoints reduce the memory usage during step 2 of the workflow mentioned above, but in order to use that model in a low memory setting, we recommend leveraging our tools based on the Accelerate library.
|
||||
|
||||
Please read the following guide for more information: [Large model loading using Accelerate](./main_classes/model#large-model-loading)
|
||||
69
docs/source/en/community.md
Normal file
69
docs/source/en/community.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
<!--⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Community
|
||||
|
||||
This page regroups resources around 🤗 Transformers developed by the community.
|
||||
|
||||
## Community resources:
|
||||
|
||||
| Resource | Description | Author |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [Hugging Face Transformers Glossary Flashcards](https://www.darigovresearch.com/huggingface-transformers-glossary-flashcards) | A set of flashcards based on the [Transformers Docs Glossary](glossary) that has been put into a form which can be easily learnt/revised using [Anki ](https://apps.ankiweb.net/) an open source, cross platform app specifically designed for long term knowledge retention. See this [Introductory video on how to use the flashcards](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Dji_h7PILrw). | [Darigov Research](https://www.darigovresearch.com/) |
|
||||
|
||||
## Community notebooks:
|
||||
|
||||
| Notebook | Description | Author | |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [Fine-tune a pre-trained Transformer to generate lyrics](https://github.com/AlekseyKorshuk/huggingartists) | How to generate lyrics in the style of your favorite artist by fine-tuning a GPT-2 model | [Aleksey Korshuk](https://github.com/AlekseyKorshuk) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/AlekseyKorshuk/huggingartists/blob/master/huggingartists-demo.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Train T5 in Tensorflow 2 ](https://github.com/snapthat/TF-T5-text-to-text) | How to train T5 for any task using Tensorflow 2. This notebook demonstrates a Question & Answer task implemented in Tensorflow 2 using SQUAD | [Muhammad Harris](https://github.com/HarrisDePerceptron) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/snapthat/TF-T5-text-to-text/blob/master/snapthatT5/notebooks/TF-T5-Datasets%20Training.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Train T5 on TPU](https://github.com/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/T5_on_TPU.ipynb) | How to train T5 on SQUAD with Transformers and Nlp | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/T5_on_TPU.ipynb#scrollTo=QLGiFCDqvuil) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune T5 for Classification and Multiple Choice](https://github.com/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/t5_fine_tuning.ipynb) | How to fine-tune T5 for classification and multiple choice tasks using a text-to-text format with PyTorch Lightning | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/t5_fine_tuning.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DialoGPT on New Datasets and Languages](https://github.com/ncoop57/i-am-a-nerd/blob/master/_notebooks/2020-05-12-chatbot-part-1.ipynb) | How to fine-tune the DialoGPT model on a new dataset for open-dialog conversational chatbots | [Nathan Cooper](https://github.com/ncoop57) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ncoop57/i-am-a-nerd/blob/master/_notebooks/2020-05-12-chatbot-part-1.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Long Sequence Modeling with Reformer](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/PyTorch_Reformer.ipynb) | How to train on sequences as long as 500,000 tokens with Reformer | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/PyTorch_Reformer.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune BART for Summarization](https://github.com/ohmeow/ohmeow_website/blob/master/posts/2021-05-25-mbart-sequence-classification-with-blurr.ipynb) | How to fine-tune BART for summarization with fastai using blurr | [Wayde Gilliam](https://ohmeow.com/) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ohmeow/ohmeow_website/blob/master/posts/2021-05-25-mbart-sequence-classification-with-blurr.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune a pre-trained Transformer on anyone's tweets](https://colab.research.google.com/github/borisdayma/huggingtweets/blob/master/huggingtweets-demo.ipynb) | How to generate tweets in the style of your favorite Twitter account by fine-tuning a GPT-2 model | [Boris Dayma](https://github.com/borisdayma) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/borisdayma/huggingtweets/blob/master/huggingtweets-demo.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Optimize 🤗 Hugging Face models with Weights & Biases](https://colab.research.google.com/github/wandb/examples/blob/master/colabs/huggingface/Optimize_Hugging_Face_models_with_Weights_%26_Biases.ipynb) | A complete tutorial showcasing W&B integration with Hugging Face | [Boris Dayma](https://github.com/borisdayma) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/wandb/examples/blob/master/colabs/huggingface/Optimize_Hugging_Face_models_with_Weights_%26_Biases.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Pretrain Longformer](https://github.com/allenai/longformer/blob/master/scripts/convert_model_to_long.ipynb) | How to build a "long" version of existing pretrained models | [Iz Beltagy](https://beltagy.net) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/allenai/longformer/blob/master/scripts/convert_model_to_long.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune Longformer for QA](https://github.com/patil-suraj/Notebooks/blob/master/longformer_qa_training.ipynb) | How to fine-tune longformer model for QA task | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patil-suraj/Notebooks/blob/master/longformer_qa_training.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate Model with 🤗nlp](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/How_to_evaluate_Longformer_on_TriviaQA_using_NLP.ipynb) | How to evaluate longformer on TriviaQA with `nlp` | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1m7eTGlPmLRgoPkkA7rkhQdZ9ydpmsdLE?usp=sharing) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune T5 for Sentiment Span Extraction](https://github.com/enzoampil/t5-intro/blob/master/t5_qa_training_pytorch_span_extraction.ipynb) | How to fine-tune T5 for sentiment span extraction using a text-to-text format with PyTorch Lightning | [Lorenzo Ampil](https://github.com/enzoampil) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/enzoampil/t5-intro/blob/master/t5_qa_training_pytorch_span_extraction.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DistilBert for Multiclass Classification](https://github.com/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multiclass_classification.ipynb) | How to fine-tune DistilBert for multiclass classification with PyTorch | [Abhishek Kumar Mishra](https://github.com/abhimishra91) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multiclass_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune BERT for Multi-label Classification](https://github.com/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multi_label_classification.ipynb)|How to fine-tune BERT for multi-label classification using PyTorch|[Abhishek Kumar Mishra](https://github.com/abhimishra91) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multi_label_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune T5 for Summarization](https://github.com/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_summarization_wandb.ipynb)|How to fine-tune T5 for summarization in PyTorch and track experiments with WandB|[Abhishek Kumar Mishra](https://github.com/abhimishra91) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_summarization_wandb.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Speed up Fine-Tuning in Transformers with Dynamic Padding / Bucketing](https://github.com/ELS-RD/transformers-notebook/blob/master/Divide_Hugging_Face_Transformers_training_time_by_2_or_more.ipynb)|How to speed up fine-tuning by a factor of 2 using dynamic padding / bucketing|[Michael Benesty](https://github.com/pommedeterresautee) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1CBfRU1zbfu7-ijiOqAAQUA-RJaxfcJoO?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Pretrain Reformer for Masked Language Modeling](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Reformer_For_Masked_LM.ipynb)| How to train a Reformer model with bi-directional self-attention layers | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1tzzh0i8PgDQGV3SMFUGxM7_gGae3K-uW?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Expand and Fine Tune Sci-BERT](https://github.com/lordtt13/word-embeddings/blob/master/COVID-19%20Research%20Data/COVID-SciBERT.ipynb)| How to increase vocabulary of a pretrained SciBERT model from AllenAI on the CORD dataset and pipeline it. | [Tanmay Thakur](https://github.com/lordtt13) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1rqAR40goxbAfez1xvF3hBJphSCsvXmh8)|
|
||||
|[Fine Tune BlenderBotSmall for Summarization using the Trainer API](https://github.com/lordtt13/transformers-experiments/blob/master/Custom%20Tasks/fine-tune-blenderbot_small-for-summarization.ipynb)| How to fine tune BlenderBotSmall for summarization on a custom dataset, using the Trainer API. | [Tanmay Thakur](https://github.com/lordtt13) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/19Wmupuls7mykSGyRN_Qo6lPQhgp56ymq?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune Electra and interpret with Integrated Gradients](https://github.com/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/electra_fine_tune_interpret_captum_ig.ipynb) | How to fine-tune Electra for sentiment analysis and interpret predictions with Captum Integrated Gradients | [Eliza Szczechla](https://elsanns.github.io) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/electra_fine_tune_interpret_captum_ig.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[fine-tune a non-English GPT-2 Model with Trainer class](https://github.com/philschmid/fine-tune-GPT-2/blob/master/Fine_tune_a_non_English_GPT_2_Model_with_Huggingface.ipynb) | How to fine-tune a non-English GPT-2 Model with Trainer class | [Philipp Schmid](https://www.philschmid.de) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/philschmid/fine-tune-GPT-2/blob/master/Fine_tune_a_non_English_GPT_2_Model_with_Huggingface.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune a DistilBERT Model for Multi Label Classification task](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08/Transformers_scripts/blob/master/Transformers_multilabel_distilbert.ipynb) | How to fine-tune a DistilBERT Model for Multi Label Classification task | [Dhaval Taunk](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/DhavalTaunk08/Transformers_scripts/blob/master/Transformers_multilabel_distilbert.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune ALBERT for sentence-pair classification](https://github.com/NadirEM/nlp-notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_ALBERT_sentence_pair_classification.ipynb) | How to fine-tune an ALBERT model or another BERT-based model for the sentence-pair classification task | [Nadir El Manouzi](https://github.com/NadirEM) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NadirEM/nlp-notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_ALBERT_sentence_pair_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune Roberta for sentiment analysis](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08/NLP_scripts/blob/master/sentiment_analysis_using_roberta.ipynb) | How to fine-tune a Roberta model for sentiment analysis | [Dhaval Taunk](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/DhavalTaunk08/NLP_scripts/blob/master/sentiment_analysis_using_roberta.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluating Question Generation Models](https://github.com/flexudy-pipe/qugeev) | How accurate are the answers to questions generated by your seq2seq transformer model? | [Pascal Zoleko](https://github.com/zolekode) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1bpsSqCQU-iw_5nNoRm_crPq6FRuJthq_?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Classify text with DistilBERT and Tensorflow](https://github.com/peterbayerle/huggingface_notebook/blob/main/distilbert_tf.ipynb) | How to fine-tune DistilBERT for text classification in TensorFlow | [Peter Bayerle](https://github.com/peterbayerle) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/peterbayerle/huggingface_notebook/blob/main/distilbert_tf.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Leverage BERT for Encoder-Decoder Summarization on CNN/Dailymail](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/BERT2BERT_for_CNN_Dailymail.ipynb) | How to warm-start a *EncoderDecoderModel* with a *bert-base-uncased* checkpoint for summarization on CNN/Dailymail | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/BERT2BERT_for_CNN_Dailymail.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Leverage RoBERTa for Encoder-Decoder Summarization on BBC XSum](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/RoBERTaShared_for_BBC_XSum.ipynb) | How to warm-start a shared *EncoderDecoderModel* with a *roberta-base* checkpoint for summarization on BBC/XSum | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/RoBERTaShared_for_BBC_XSum.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune TAPAS on Sequential Question Answering (SQA)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Fine_tuning_TapasForQuestionAnswering_on_SQA.ipynb) | How to fine-tune *TapasForQuestionAnswering* with a *tapas-base* checkpoint on the Sequential Question Answering (SQA) dataset | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Fine_tuning_TapasForQuestionAnswering_on_SQA.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluate TAPAS on Table Fact Checking (TabFact)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Evaluating_TAPAS_on_the_Tabfact_test_set.ipynb) | How to evaluate a fine-tuned *TapasForSequenceClassification* with a *tapas-base-finetuned-tabfact* checkpoint using a combination of the 🤗 datasets and 🤗 transformers libraries | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Evaluating_TAPAS_on_the_Tabfact_test_set.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tuning mBART for translation](https://colab.research.google.com/github/vasudevgupta7/huggingface-tutorials/blob/main/translation_training.ipynb) | How to fine-tune mBART using Seq2SeqTrainer for Hindi to English translation | [Vasudev Gupta](https://github.com/vasudevgupta7) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/vasudevgupta7/huggingface-tutorials/blob/main/translation_training.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune LayoutLM on FUNSD (a form understanding dataset)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForTokenClassification_on_FUNSD.ipynb) | How to fine-tune *LayoutLMForTokenClassification* on the FUNSD dataset for information extraction from scanned documents | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForTokenClassification_on_FUNSD.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-Tune DistilGPT2 and Generate Text](https://colab.research.google.com/github/tripathiaakash/DistilGPT2-Tutorial/blob/main/distilgpt2_fine_tuning.ipynb) | How to fine-tune DistilGPT2 and generate text | [Aakash Tripathi](https://github.com/tripathiaakash) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/tripathiaakash/DistilGPT2-Tutorial/blob/main/distilgpt2_fine_tuning.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-Tune LED on up to 8K tokens](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_Longformer_Encoder_Decoder_(LED)_for_Summarization_on_pubmed.ipynb) | How to fine-tune LED on pubmed for long-range summarization | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_Longformer_Encoder_Decoder_(LED)_for_Summarization_on_pubmed.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluate LED on Arxiv](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/LED_on_Arxiv.ipynb) | How to effectively evaluate LED on long-range summarization | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/LED_on_Arxiv.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune LayoutLM on RVL-CDIP (a document image classification dataset)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForSequenceClassification_on_RVL_CDIP.ipynb) | How to fine-tune *LayoutLMForSequenceClassification* on the RVL-CDIP dataset for scanned document classification | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForSequenceClassification_on_RVL_CDIP.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Wav2Vec2 CTC decoding with GPT2 adjustment](https://github.com/voidful/huggingface_notebook/blob/main/xlsr_gpt.ipynb) | How to decode CTC sequence with language model adjustment | [Eric Lam](https://github.com/voidful) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1e_z5jQHYbO2YKEaUgzb1ww1WwiAyydAj?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune BART for summarization in two languages with Trainer class](https://github.com/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/fine_tune_bart_summarization_two_langs.ipynb) | How to fine-tune BART for summarization in two languages with Trainer class | [Eliza Szczechla](https://github.com/elsanns) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/fine_tune_bart_summarization_two_langs.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluate Big Bird on Trivia QA](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Evaluating_Big_Bird_on_TriviaQA.ipynb) | How to evaluate BigBird on long document question answering on Trivia QA | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Evaluating_Big_Bird_on_TriviaQA.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [Create video captions using Wav2Vec2](https://github.com/Muennighoff/ytclipcc/blob/main/wav2vec_youtube_captions.ipynb) | How to create YouTube captions from any video by transcribing the audio with Wav2Vec | [Niklas Muennighoff](https://github.com/Muennighoff) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/Muennighoff/ytclipcc/blob/main/wav2vec_youtube_captions.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune the Vision Transformer on CIFAR-10 using PyTorch Lightning](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_PyTorch_Lightning.ipynb) | How to fine-tune the Vision Transformer (ViT) on CIFAR-10 using HuggingFace Transformers, Datasets and PyTorch Lightning | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_PyTorch_Lightning.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune the Vision Transformer on CIFAR-10 using the 🤗 Trainer](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_the_%F0%9F%A4%97_Trainer.ipynb) | How to fine-tune the Vision Transformer (ViT) on CIFAR-10 using HuggingFace Transformers, Datasets and the 🤗 Trainer | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_the_%F0%9F%A4%97_Trainer.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate LUKE on Open Entity, an entity typing dataset](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_open_entity.ipynb) | How to evaluate *LukeForEntityClassification* on the Open Entity dataset | [Ikuya Yamada](https://github.com/ikuyamada) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_open_entity.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate LUKE on TACRED, a relation extraction dataset](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_tacred.ipynb) | How to evaluate *LukeForEntityPairClassification* on the TACRED dataset | [Ikuya Yamada](https://github.com/ikuyamada) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_tacred.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate LUKE on CoNLL-2003, an important NER benchmark](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_conll_2003.ipynb) | How to evaluate *LukeForEntitySpanClassification* on the CoNLL-2003 dataset | [Ikuya Yamada](https://github.com/ikuyamada) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_conll_2003.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate BigBird-Pegasus on PubMed dataset](https://github.com/vasudevgupta7/bigbird/blob/main/notebooks/bigbird_pegasus_evaluation.ipynb) | How to evaluate *BigBirdPegasusForConditionalGeneration* on PubMed dataset | [Vasudev Gupta](https://github.com/vasudevgupta7) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/vasudevgupta7/bigbird/blob/main/notebooks/bigbird_pegasus_evaluation.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Speech Emotion Classification with Wav2Vec2](https://github/m3hrdadfi/soxan/blob/main/notebooks/Emotion_recognition_in_Greek_speech_using_Wav2Vec2.ipynb) | How to leverage a pretrained Wav2Vec2 model for Emotion Classification on the MEGA dataset | [Mehrdad Farahani](https://github.com/m3hrdadfi) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/m3hrdadfi/soxan/blob/main/notebooks/Emotion_recognition_in_Greek_speech_using_Wav2Vec2.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Detect objects in an image with DETR](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/DETR_minimal_example_(with_DetrFeatureExtractor).ipynb) | How to use a trained *DetrForObjectDetection* model to detect objects in an image and visualize attention | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/NielsRogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/DETR_minimal_example_(with_DetrFeatureExtractor).ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DETR on a custom object detection dataset](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/Fine_tuning_DetrForObjectDetection_on_custom_dataset_(balloon).ipynb) | How to fine-tune *DetrForObjectDetection* on a custom object detection dataset | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/NielsRogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/Fine_tuning_DetrForObjectDetection_on_custom_dataset_(balloon).ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Finetune T5 for Named Entity Recognition](https://github.com/ToluClassics/Notebooks/blob/main/T5_Ner_Finetuning.ipynb) | How to fine-tune *T5* on a Named Entity Recognition Task | [Ogundepo Odunayo](https://github.com/ToluClassics) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1obr78FY_cBmWY5ODViCmzdY6O1KB65Vc?usp=sharing) |
|
||||
@ -1,65 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Community
|
||||
|
||||
This page regroups resources around 🤗 Transformers developed by the community.
|
||||
|
||||
## Community resources:
|
||||
|
||||
| Resource | Description | Author |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [Hugging Face Transformers Glossary Flashcards](https://www.darigovresearch.com/huggingface-transformers-glossary-flashcards) | A set of flashcards based on the [Transformers Docs Glossary](glossary) that has been put into a form which can be easily learnt/revised using [Anki ](https://apps.ankiweb.net/) an open source, cross platform app specifically designed for long term knowledge retention. See this [Introductory video on how to use the flashcards](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Dji_h7PILrw). | [Darigov Research](https://www.darigovresearch.com/) |
|
||||
|
||||
## Community notebooks:
|
||||
|
||||
| Notebook | Description | Author | |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [Fine-tune a pre-trained Transformer to generate lyrics](https://github.com/AlekseyKorshuk/huggingartists) | How to generate lyrics in the style of your favorite artist by fine-tuning a GPT-2 model | [Aleksey Korshuk](https://github.com/AlekseyKorshuk) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/AlekseyKorshuk/huggingartists/blob/master/huggingartists-demo.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Train T5 in Tensorflow 2 ](https://github.com/snapthat/TF-T5-text-to-text) | How to train T5 for any task using Tensorflow 2. This notebook demonstrates a Question & Answer task implemented in Tensorflow 2 using SQUAD | [Muhammad Harris](https://github.com/HarrisDePerceptron) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/snapthat/TF-T5-text-to-text/blob/master/snapthatT5/notebooks/TF-T5-Datasets%20Training.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Train T5 on TPU](https://github.com/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/T5_on_TPU.ipynb) | How to train T5 on SQUAD with Transformers and Nlp | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/T5_on_TPU.ipynb#scrollTo=QLGiFCDqvuil) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune T5 for Classification and Multiple Choice](https://github.com/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/t5_fine_tuning.ipynb) | How to fine-tune T5 for classification and multiple choice tasks using a text-to-text format with PyTorch Lightning | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/t5_fine_tuning.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DialoGPT on New Datasets and Languages](https://github.com/ncoop57/i-am-a-nerd/blob/master/_notebooks/2020-05-12-chatbot-part-1.ipynb) | How to fine-tune the DialoGPT model on a new dataset for open-dialog conversational chatbots | [Nathan Cooper](https://github.com/ncoop57) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ncoop57/i-am-a-nerd/blob/master/_notebooks/2020-05-12-chatbot-part-1.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Long Sequence Modeling with Reformer](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/PyTorch_Reformer.ipynb) | How to train on sequences as long as 500,000 tokens with Reformer | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/PyTorch_Reformer.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune BART for Summarization](https://github.com/ohmeow/ohmeow_website/blob/master/posts/2021-05-25-mbart-sequence-classification-with-blurr.ipynb) | How to fine-tune BART for summarization with fastai using blurr | [Wayde Gilliam](https://ohmeow.com/) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ohmeow/ohmeow_website/blob/master/posts/2021-05-25-mbart-sequence-classification-with-blurr.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune a pre-trained Transformer on anyone's tweets](https://colab.research.google.com/github/borisdayma/huggingtweets/blob/master/huggingtweets-demo.ipynb) | How to generate tweets in the style of your favorite Twitter account by fine-tuning a GPT-2 model | [Boris Dayma](https://github.com/borisdayma) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/borisdayma/huggingtweets/blob/master/huggingtweets-demo.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Optimize 🤗 Hugging Face models with Weights & Biases](https://colab.research.google.com/github/wandb/examples/blob/master/colabs/huggingface/Optimize_Hugging_Face_models_with_Weights_%26_Biases.ipynb) | A complete tutorial showcasing W&B integration with Hugging Face | [Boris Dayma](https://github.com/borisdayma) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/wandb/examples/blob/master/colabs/huggingface/Optimize_Hugging_Face_models_with_Weights_%26_Biases.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Pretrain Longformer](https://github.com/allenai/longformer/blob/master/scripts/convert_model_to_long.ipynb) | How to build a "long" version of existing pretrained models | [Iz Beltagy](https://beltagy.net) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/allenai/longformer/blob/master/scripts/convert_model_to_long.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune Longformer for QA](https://github.com/patil-suraj/Notebooks/blob/master/longformer_qa_training.ipynb) | How to fine-tune longformer model for QA task | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patil-suraj/Notebooks/blob/master/longformer_qa_training.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate Model with 🤗nlp](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/How_to_evaluate_Longformer_on_TriviaQA_using_NLP.ipynb) | How to evaluate longformer on TriviaQA with `nlp` | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1m7eTGlPmLRgoPkkA7rkhQdZ9ydpmsdLE?usp=sharing) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune T5 for Sentiment Span Extraction](https://github.com/enzoampil/t5-intro/blob/master/t5_qa_training_pytorch_span_extraction.ipynb) | How to fine-tune T5 for sentiment span extraction using a text-to-text format with PyTorch Lightning | [Lorenzo Ampil](https://github.com/enzoampil) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/enzoampil/t5-intro/blob/master/t5_qa_training_pytorch_span_extraction.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DistilBert for Multiclass Classification](https://github.com/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multiclass_classification.ipynb) | How to fine-tune DistilBert for multiclass classification with PyTorch | [Abhishek Kumar Mishra](https://github.com/abhimishra91) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multiclass_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune BERT for Multi-label Classification](https://github.com/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multi_label_classification.ipynb)|How to fine-tune BERT for multi-label classification using PyTorch|[Abhishek Kumar Mishra](https://github.com/abhimishra91) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multi_label_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune T5 for Summarization](https://github.com/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_summarization_wandb.ipynb)|How to fine-tune T5 for summarization in PyTorch and track experiments with WandB|[Abhishek Kumar Mishra](https://github.com/abhimishra91) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_summarization_wandb.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Speed up Fine-Tuning in Transformers with Dynamic Padding / Bucketing](https://github.com/ELS-RD/transformers-notebook/blob/master/Divide_Hugging_Face_Transformers_training_time_by_2_or_more.ipynb)|How to speed up fine-tuning by a factor of 2 using dynamic padding / bucketing|[Michael Benesty](https://github.com/pommedeterresautee) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1CBfRU1zbfu7-ijiOqAAQUA-RJaxfcJoO?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Pretrain Reformer for Masked Language Modeling](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Reformer_For_Masked_LM.ipynb)| How to train a Reformer model with bi-directional self-attention layers | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1tzzh0i8PgDQGV3SMFUGxM7_gGae3K-uW?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Expand and Fine Tune Sci-BERT](https://github.com/lordtt13/word-embeddings/blob/master/COVID-19%20Research%20Data/COVID-SciBERT.ipynb)| How to increase vocabulary of a pretrained SciBERT model from AllenAI on the CORD dataset and pipeline it. | [Tanmay Thakur](https://github.com/lordtt13) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1rqAR40goxbAfez1xvF3hBJphSCsvXmh8)|
|
||||
|[Fine Tune BlenderBotSmall for Summarization using the Trainer API](https://github.com/lordtt13/transformers-experiments/blob/master/Custom%20Tasks/fine-tune-blenderbot_small-for-summarization.ipynb)| How to fine tune BlenderBotSmall for summarization on a custom dataset, using the Trainer API. | [Tanmay Thakur](https://github.com/lordtt13) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/19Wmupuls7mykSGyRN_Qo6lPQhgp56ymq?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune Electra and interpret with Integrated Gradients](https://github.com/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/electra_fine_tune_interpret_captum_ig.ipynb) | How to fine-tune Electra for sentiment analysis and interpret predictions with Captum Integrated Gradients | [Eliza Szczechla](https://elsanns.github.io) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/electra_fine_tune_interpret_captum_ig.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[fine-tune a non-English GPT-2 Model with Trainer class](https://github.com/philschmid/fine-tune-GPT-2/blob/master/Fine_tune_a_non_English_GPT_2_Model_with_Huggingface.ipynb) | How to fine-tune a non-English GPT-2 Model with Trainer class | [Philipp Schmid](https://www.philschmid.de) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/philschmid/fine-tune-GPT-2/blob/master/Fine_tune_a_non_English_GPT_2_Model_with_Huggingface.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune a DistilBERT Model for Multi Label Classification task](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08/Transformers_scripts/blob/master/Transformers_multilabel_distilbert.ipynb) | How to fine-tune a DistilBERT Model for Multi Label Classification task | [Dhaval Taunk](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/DhavalTaunk08/Transformers_scripts/blob/master/Transformers_multilabel_distilbert.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune ALBERT for sentence-pair classification](https://github.com/NadirEM/nlp-notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_ALBERT_sentence_pair_classification.ipynb) | How to fine-tune an ALBERT model or another BERT-based model for the sentence-pair classification task | [Nadir El Manouzi](https://github.com/NadirEM) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NadirEM/nlp-notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_ALBERT_sentence_pair_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune Roberta for sentiment analysis](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08/NLP_scripts/blob/master/sentiment_analysis_using_roberta.ipynb) | How to fine-tune a Roberta model for sentiment analysis | [Dhaval Taunk](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/DhavalTaunk08/NLP_scripts/blob/master/sentiment_analysis_using_roberta.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluating Question Generation Models](https://github.com/flexudy-pipe/qugeev) | How accurate are the answers to questions generated by your seq2seq transformer model? | [Pascal Zoleko](https://github.com/zolekode) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1bpsSqCQU-iw_5nNoRm_crPq6FRuJthq_?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Classify text with DistilBERT and Tensorflow](https://github.com/peterbayerle/huggingface_notebook/blob/main/distilbert_tf.ipynb) | How to fine-tune DistilBERT for text classification in TensorFlow | [Peter Bayerle](https://github.com/peterbayerle) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/peterbayerle/huggingface_notebook/blob/main/distilbert_tf.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Leverage BERT for Encoder-Decoder Summarization on CNN/Dailymail](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/BERT2BERT_for_CNN_Dailymail.ipynb) | How to warm-start a *EncoderDecoderModel* with a *bert-base-uncased* checkpoint for summarization on CNN/Dailymail | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/BERT2BERT_for_CNN_Dailymail.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Leverage RoBERTa for Encoder-Decoder Summarization on BBC XSum](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/RoBERTaShared_for_BBC_XSum.ipynb) | How to warm-start a shared *EncoderDecoderModel* with a *roberta-base* checkpoint for summarization on BBC/XSum | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/RoBERTaShared_for_BBC_XSum.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune TAPAS on Sequential Question Answering (SQA)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Fine_tuning_TapasForQuestionAnswering_on_SQA.ipynb) | How to fine-tune *TapasForQuestionAnswering* with a *tapas-base* checkpoint on the Sequential Question Answering (SQA) dataset | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Fine_tuning_TapasForQuestionAnswering_on_SQA.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluate TAPAS on Table Fact Checking (TabFact)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Evaluating_TAPAS_on_the_Tabfact_test_set.ipynb) | How to evaluate a fine-tuned *TapasForSequenceClassification* with a *tapas-base-finetuned-tabfact* checkpoint using a combination of the 🤗 datasets and 🤗 transformers libraries | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Evaluating_TAPAS_on_the_Tabfact_test_set.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tuning mBART for translation](https://colab.research.google.com/github/vasudevgupta7/huggingface-tutorials/blob/main/translation_training.ipynb) | How to fine-tune mBART using Seq2SeqTrainer for Hindi to English translation | [Vasudev Gupta](https://github.com/vasudevgupta7) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/vasudevgupta7/huggingface-tutorials/blob/main/translation_training.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune LayoutLM on FUNSD (a form understanding dataset)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForTokenClassification_on_FUNSD.ipynb) | How to fine-tune *LayoutLMForTokenClassification* on the FUNSD dataset for information extraction from scanned documents | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForTokenClassification_on_FUNSD.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-Tune DistilGPT2 and Generate Text](https://colab.research.google.com/github/tripathiaakash/DistilGPT2-Tutorial/blob/main/distilgpt2_fine_tuning.ipynb) | How to fine-tune DistilGPT2 and generate text | [Aakash Tripathi](https://github.com/tripathiaakash) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/tripathiaakash/DistilGPT2-Tutorial/blob/main/distilgpt2_fine_tuning.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-Tune LED on up to 8K tokens](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_Longformer_Encoder_Decoder_(LED)_for_Summarization_on_pubmed.ipynb) | How to fine-tune LED on pubmed for long-range summarization | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_Longformer_Encoder_Decoder_(LED)_for_Summarization_on_pubmed.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluate LED on Arxiv](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/LED_on_Arxiv.ipynb) | How to effectively evaluate LED on long-range summarization | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/LED_on_Arxiv.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune LayoutLM on RVL-CDIP (a document image classification dataset)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForSequenceClassification_on_RVL_CDIP.ipynb) | How to fine-tune *LayoutLMForSequenceClassification* on the RVL-CDIP dataset for scanned document classification | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForSequenceClassification_on_RVL_CDIP.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Wav2Vec2 CTC decoding with GPT2 adjustment](https://github.com/voidful/huggingface_notebook/blob/main/xlsr_gpt.ipynb) | How to decode CTC sequence with language model adjustment | [Eric Lam](https://github.com/voidful) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1e_z5jQHYbO2YKEaUgzb1ww1WwiAyydAj?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune BART for summarization in two languages with Trainer class](https://github.com/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/fine_tune_bart_summarization_two_langs.ipynb) | How to fine-tune BART for summarization in two languages with Trainer class | [Eliza Szczechla](https://github.com/elsanns) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/fine_tune_bart_summarization_two_langs.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluate Big Bird on Trivia QA](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Evaluating_Big_Bird_on_TriviaQA.ipynb) | How to evaluate BigBird on long document question answering on Trivia QA | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Evaluating_Big_Bird_on_TriviaQA.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [Create video captions using Wav2Vec2](https://github.com/Muennighoff/ytclipcc/blob/main/wav2vec_youtube_captions.ipynb) | How to create YouTube captions from any video by transcribing the audio with Wav2Vec | [Niklas Muennighoff](https://github.com/Muennighoff) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/Muennighoff/ytclipcc/blob/main/wav2vec_youtube_captions.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune the Vision Transformer on CIFAR-10 using PyTorch Lightning](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_PyTorch_Lightning.ipynb) | How to fine-tune the Vision Transformer (ViT) on CIFAR-10 using HuggingFace Transformers, Datasets and PyTorch Lightning | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_PyTorch_Lightning.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune the Vision Transformer on CIFAR-10 using the 🤗 Trainer](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_the_%F0%9F%A4%97_Trainer.ipynb) | How to fine-tune the Vision Transformer (ViT) on CIFAR-10 using HuggingFace Transformers, Datasets and the 🤗 Trainer | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_the_%F0%9F%A4%97_Trainer.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate LUKE on Open Entity, an entity typing dataset](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_open_entity.ipynb) | How to evaluate *LukeForEntityClassification* on the Open Entity dataset | [Ikuya Yamada](https://github.com/ikuyamada) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_open_entity.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate LUKE on TACRED, a relation extraction dataset](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_tacred.ipynb) | How to evaluate *LukeForEntityPairClassification* on the TACRED dataset | [Ikuya Yamada](https://github.com/ikuyamada) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_tacred.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate LUKE on CoNLL-2003, an important NER benchmark](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_conll_2003.ipynb) | How to evaluate *LukeForEntitySpanClassification* on the CoNLL-2003 dataset | [Ikuya Yamada](https://github.com/ikuyamada) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_conll_2003.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate BigBird-Pegasus on PubMed dataset](https://github.com/vasudevgupta7/bigbird/blob/main/notebooks/bigbird_pegasus_evaluation.ipynb) | How to evaluate *BigBirdPegasusForConditionalGeneration* on PubMed dataset | [Vasudev Gupta](https://github.com/vasudevgupta7) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/vasudevgupta7/bigbird/blob/main/notebooks/bigbird_pegasus_evaluation.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Speech Emotion Classification with Wav2Vec2](https://github/m3hrdadfi/soxan/blob/main/notebooks/Emotion_recognition_in_Greek_speech_using_Wav2Vec2.ipynb) | How to leverage a pretrained Wav2Vec2 model for Emotion Classification on the MEGA dataset | [Mehrdad Farahani](https://github.com/m3hrdadfi) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/m3hrdadfi/soxan/blob/main/notebooks/Emotion_recognition_in_Greek_speech_using_Wav2Vec2.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Detect objects in an image with DETR](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/DETR_minimal_example_(with_DetrFeatureExtractor).ipynb) | How to use a trained *DetrForObjectDetection* model to detect objects in an image and visualize attention | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/NielsRogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/DETR_minimal_example_(with_DetrFeatureExtractor).ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DETR on a custom object detection dataset](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/Fine_tuning_DetrForObjectDetection_on_custom_dataset_(balloon).ipynb) | How to fine-tune *DetrForObjectDetection* on a custom object detection dataset | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/NielsRogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/Fine_tuning_DetrForObjectDetection_on_custom_dataset_(balloon).ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Finetune T5 for Named Entity Recognition](https://github.com/ToluClassics/Notebooks/blob/main/T5_Ner_Finetuning.ipynb) | How to fine-tune *T5* on a Named Entity Recognition Task | [Ogundepo Odunayo](https://github.com/ToluClassics) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1obr78FY_cBmWY5ODViCmzdY6O1KB65Vc?usp=sharing) |
|
||||
389
docs/source/en/create_a_model.md
Normal file
389
docs/source/en/create_a_model.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,389 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a custom architecture
|
||||
|
||||
An [`AutoClass`](model_doc/auto) automatically infers the model architecture and downloads pretrained configuration and weights. Generally, we recommend using an `AutoClass` to produce checkpoint-agnostic code. But users who want more control over specific model parameters can create a custom 🤗 Transformers model from just a few base classes. This could be particularly useful for anyone who is interested in studying, training or experimenting with a 🤗 Transformers model. In this guide, dive deeper into creating a custom model without an `AutoClass`. Learn how to:
|
||||
|
||||
- Load and customize a model configuration.
|
||||
- Create a model architecture.
|
||||
- Create a slow and fast tokenizer for text.
|
||||
- Create an image processor for vision tasks.
|
||||
- Create a feature extractor for audio tasks.
|
||||
- Create a processor for multimodal tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
A [configuration](main_classes/configuration) refers to a model's specific attributes. Each model configuration has different attributes; for instance, all NLP models have the `hidden_size`, `num_attention_heads`, `num_hidden_layers` and `vocab_size` attributes in common. These attributes specify the number of attention heads or hidden layers to construct a model with.
|
||||
|
||||
Get a closer look at [DistilBERT](model_doc/distilbert) by accessing [`DistilBertConfig`] to inspect it's attributes:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> config = DistilBertConfig()
|
||||
>>> print(config)
|
||||
DistilBertConfig {
|
||||
"activation": "gelu",
|
||||
"attention_dropout": 0.1,
|
||||
"dim": 768,
|
||||
"dropout": 0.1,
|
||||
"hidden_dim": 3072,
|
||||
"initializer_range": 0.02,
|
||||
"max_position_embeddings": 512,
|
||||
"model_type": "distilbert",
|
||||
"n_heads": 12,
|
||||
"n_layers": 6,
|
||||
"pad_token_id": 0,
|
||||
"qa_dropout": 0.1,
|
||||
"seq_classif_dropout": 0.2,
|
||||
"sinusoidal_pos_embds": false,
|
||||
"transformers_version": "4.16.2",
|
||||
"vocab_size": 30522
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[`DistilBertConfig`] displays all the default attributes used to build a base [`DistilBertModel`]. All attributes are customizable, creating space for experimentation. For example, you can customize a default model to:
|
||||
|
||||
- Try a different activation function with the `activation` parameter.
|
||||
- Use a higher dropout ratio for the attention probabilities with the `attention_dropout` parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> my_config = DistilBertConfig(activation="relu", attention_dropout=0.4)
|
||||
>>> print(my_config)
|
||||
DistilBertConfig {
|
||||
"activation": "relu",
|
||||
"attention_dropout": 0.4,
|
||||
"dim": 768,
|
||||
"dropout": 0.1,
|
||||
"hidden_dim": 3072,
|
||||
"initializer_range": 0.02,
|
||||
"max_position_embeddings": 512,
|
||||
"model_type": "distilbert",
|
||||
"n_heads": 12,
|
||||
"n_layers": 6,
|
||||
"pad_token_id": 0,
|
||||
"qa_dropout": 0.1,
|
||||
"seq_classif_dropout": 0.2,
|
||||
"sinusoidal_pos_embds": false,
|
||||
"transformers_version": "4.16.2",
|
||||
"vocab_size": 30522
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Pretrained model attributes can be modified in the [`~PretrainedConfig.from_pretrained`] function:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> my_config = DistilBertConfig.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased", activation="relu", attention_dropout=0.4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once you are satisfied with your model configuration, you can save it with [`~PretrainedConfig.save_pretrained`]. Your configuration file is stored as a JSON file in the specified save directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> my_config.save_pretrained(save_directory="./your_model_save_path")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To reuse the configuration file, load it with [`~PretrainedConfig.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> my_config = DistilBertConfig.from_pretrained("./your_model_save_path/config.json")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
You can also save your configuration file as a dictionary or even just the difference between your custom configuration attributes and the default configuration attributes! See the [configuration](main_classes/configuration) documentation for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Model
|
||||
|
||||
The next step is to create a [model](main_classes/models). The model - also loosely referred to as the architecture - defines what each layer is doing and what operations are happening. Attributes like `num_hidden_layers` from the configuration are used to define the architecture. Every model shares the base class [`PreTrainedModel`] and a few common methods like resizing input embeddings and pruning self-attention heads. In addition, all models are also either a [`torch.nn.Module`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Module.html), [`tf.keras.Model`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/Model) or [`flax.linen.Module`](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/flax.linen.html#module) subclass. This means models are compatible with each of their respective framework's usage.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Load your custom configuration attributes into the model:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_config = DistilBertConfig.from_pretrained("./your_model_save_path/config.json")
|
||||
>>> model = DistilBertModel(my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This creates a model with random values instead of pretrained weights. You won't be able to use this model for anything useful yet until you train it. Training is a costly and time-consuming process. It is generally better to use a pretrained model to obtain better results faster, while using only a fraction of the resources required for training.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a pretrained model with [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model = DistilBertModel.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When you load pretrained weights, the default model configuration is automatically loaded if the model is provided by 🤗 Transformers. However, you can still replace - some or all of - the default model configuration attributes with your own if you'd like:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model = DistilBertModel.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased", config=my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Load your custom configuration attributes into the model:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFDistilBertModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_config = DistilBertConfig.from_pretrained("./your_model_save_path/my_config.json")
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertModel(my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This creates a model with random values instead of pretrained weights. You won't be able to use this model for anything useful yet until you train it. Training is a costly and time-consuming process. It is generally better to use a pretrained model to obtain better results faster, while using only a fraction of the resources required for training.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a pretrained model with [`~TFPreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertModel.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When you load pretrained weights, the default model configuration is automatically loaded if the model is provided by 🤗 Transformers. However, you can still replace - some or all of - the default model configuration attributes with your own if you'd like:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertModel.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased", config=my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
### Model heads
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, you have a base DistilBERT model which outputs the *hidden states*. The hidden states are passed as inputs to a model head to produce the final output. 🤗 Transformers provides a different model head for each task as long as a model supports the task (i.e., you can't use DistilBERT for a sequence-to-sequence task like translation).
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
For example, [`DistilBertForSequenceClassification`] is a base DistilBERT model with a sequence classification head. The sequence classification head is a linear layer on top of the pooled outputs.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = DistilBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Easily reuse this checkpoint for another task by switching to a different model head. For a question answering task, you would use the [`DistilBertForQuestionAnswering`] model head. The question answering head is similar to the sequence classification head except it is a linear layer on top of the hidden states output.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = DistilBertForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
For example, [`TFDistilBertForSequenceClassification`] is a base DistilBERT model with a sequence classification head. The sequence classification head is a linear layer on top of the pooled outputs.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFDistilBertForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Easily reuse this checkpoint for another task by switching to a different model head. For a question answering task, you would use the [`TFDistilBertForQuestionAnswering`] model head. The question answering head is similar to the sequence classification head except it is a linear layer on top of the hidden states output.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFDistilBertForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Tokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
The last base class you need before using a model for textual data is a [tokenizer](main_classes/tokenizer) to convert raw text to tensors. There are two types of tokenizers you can use with 🤗 Transformers:
|
||||
|
||||
- [`PreTrainedTokenizer`]: a Python implementation of a tokenizer.
|
||||
- [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`]: a tokenizer from our Rust-based [🤗 Tokenizer](https://huggingface.co/docs/tokenizers/python/latest/) library. This tokenizer type is significantly faster - especially during batch tokenization - due to it's Rust implementation. The fast tokenizer also offers additional methods like *offset mapping* which maps tokens to their original words or characters.
|
||||
|
||||
Both tokenizers support common methods such as encoding and decoding, adding new tokens, and managing special tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Not every model supports a fast tokenizer. Take a look at this [table](index#supported-frameworks) to check if a model has fast tokenizer support.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If you trained your own tokenizer, you can create one from your *vocabulary* file:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizer(vocab_file="my_vocab_file.txt", do_lower_case=False, padding_side="left")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is important to remember the vocabulary from a custom tokenizer will be different from the vocabulary generated by a pretrained model's tokenizer. You need to use a pretrained model's vocabulary if you are using a pretrained model, otherwise the inputs won't make sense. Create a tokenizer with a pretrained model's vocabulary with the [`DistilBertTokenizer`] class:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> slow_tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizer.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a fast tokenizer with the [`DistilBertTokenizerFast`] class:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
>>> fast_tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
By default, [`AutoTokenizer`] will try to load a fast tokenizer. You can disable this behavior by setting `use_fast=False` in `from_pretrained`.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Image Processor
|
||||
|
||||
An image processor processes vision inputs. It inherits from the base [`~image_processing_utils.ImageProcessingMixin`] class.
|
||||
|
||||
To use, create an image processor associated with the model you're using. For example, create a default [`ViTImageProcessor`] if you are using [ViT](model_doc/vit) for image classification:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import ViTImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> vit_extractor = ViTImageProcessor()
|
||||
>>> print(vit_extractor)
|
||||
ViTImageProcessor {
|
||||
"do_normalize": true,
|
||||
"do_resize": true,
|
||||
"feature_extractor_type": "ViTImageProcessor",
|
||||
"image_mean": [
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5
|
||||
],
|
||||
"image_std": [
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5
|
||||
],
|
||||
"resample": 2,
|
||||
"size": 224
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If you aren't looking for any customization, just use the `from_pretrained` method to load a model's default image processor parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Modify any of the [`ViTImageProcessor`] parameters to create your custom image processor:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import ViTImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_vit_extractor = ViTImageProcessor(resample="PIL.Image.BOX", do_normalize=False, image_mean=[0.3, 0.3, 0.3])
|
||||
>>> print(my_vit_extractor)
|
||||
ViTImageProcessor {
|
||||
"do_normalize": false,
|
||||
"do_resize": true,
|
||||
"feature_extractor_type": "ViTImageProcessor",
|
||||
"image_mean": [
|
||||
0.3,
|
||||
0.3,
|
||||
0.3
|
||||
],
|
||||
"image_std": [
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5
|
||||
],
|
||||
"resample": "PIL.Image.BOX",
|
||||
"size": 224
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Feature Extractor
|
||||
|
||||
A feature extractor processes audio inputs. It inherits from the base [`~feature_extraction_utils.FeatureExtractionMixin`] class, and may also inherit from the [`SequenceFeatureExtractor`] class for processing audio inputs.
|
||||
|
||||
To use, create a feature extractor associated with the model you're using. For example, create a default [`Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor`] if you are using [Wav2Vec2](model_doc/wav2vec2) for audio classification:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> w2v2_extractor = Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor()
|
||||
>>> print(w2v2_extractor)
|
||||
Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor {
|
||||
"do_normalize": true,
|
||||
"feature_extractor_type": "Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor",
|
||||
"feature_size": 1,
|
||||
"padding_side": "right",
|
||||
"padding_value": 0.0,
|
||||
"return_attention_mask": false,
|
||||
"sampling_rate": 16000
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If you aren't looking for any customization, just use the `from_pretrained` method to load a model's default feature extractor parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Modify any of the [`Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor`] parameters to create your custom feature extractor:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> w2v2_extractor = Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor(sampling_rate=8000, do_normalize=False)
|
||||
>>> print(w2v2_extractor)
|
||||
Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor {
|
||||
"do_normalize": false,
|
||||
"feature_extractor_type": "Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor",
|
||||
"feature_size": 1,
|
||||
"padding_side": "right",
|
||||
"padding_value": 0.0,
|
||||
"return_attention_mask": false,
|
||||
"sampling_rate": 8000
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Processor
|
||||
|
||||
For models that support multimodal tasks, 🤗 Transformers offers a processor class that conveniently wraps processing classes such as a feature extractor and a tokenizer into a single object. For example, let's use the [`Wav2Vec2Processor`] for an automatic speech recognition task (ASR). ASR transcribes audio to text, so you will need a feature extractor and a tokenizer.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a feature extractor to handle the audio inputs:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> feature_extractor = Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor(padding_value=1.0, do_normalize=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a tokenizer to handle the text inputs:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2CTCTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = Wav2Vec2CTCTokenizer(vocab_file="my_vocab_file.txt")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Combine the feature extractor and tokenizer in [`Wav2Vec2Processor`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2Processor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> processor = Wav2Vec2Processor(feature_extractor=feature_extractor, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With two basic classes - configuration and model - and an additional preprocessing class (tokenizer, image processor, feature extractor, or processor), you can create any of the models supported by 🤗 Transformers. Each of these base classes are configurable, allowing you to use the specific attributes you want. You can easily setup a model for training or modify an existing pretrained model to fine-tune.
|
||||
@ -1,385 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a custom architecture
|
||||
|
||||
An [`AutoClass`](model_doc/auto) automatically infers the model architecture and downloads pretrained configuration and weights. Generally, we recommend using an `AutoClass` to produce checkpoint-agnostic code. But users who want more control over specific model parameters can create a custom 🤗 Transformers model from just a few base classes. This could be particularly useful for anyone who is interested in studying, training or experimenting with a 🤗 Transformers model. In this guide, dive deeper into creating a custom model without an `AutoClass`. Learn how to:
|
||||
|
||||
- Load and customize a model configuration.
|
||||
- Create a model architecture.
|
||||
- Create a slow and fast tokenizer for text.
|
||||
- Create an image processor for vision tasks.
|
||||
- Create a feature extractor for audio tasks.
|
||||
- Create a processor for multimodal tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
A [configuration](main_classes/configuration) refers to a model's specific attributes. Each model configuration has different attributes; for instance, all NLP models have the `hidden_size`, `num_attention_heads`, `num_hidden_layers` and `vocab_size` attributes in common. These attributes specify the number of attention heads or hidden layers to construct a model with.
|
||||
|
||||
Get a closer look at [DistilBERT](model_doc/distilbert) by accessing [`DistilBertConfig`] to inspect it's attributes:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> config = DistilBertConfig()
|
||||
>>> print(config)
|
||||
DistilBertConfig {
|
||||
"activation": "gelu",
|
||||
"attention_dropout": 0.1,
|
||||
"dim": 768,
|
||||
"dropout": 0.1,
|
||||
"hidden_dim": 3072,
|
||||
"initializer_range": 0.02,
|
||||
"max_position_embeddings": 512,
|
||||
"model_type": "distilbert",
|
||||
"n_heads": 12,
|
||||
"n_layers": 6,
|
||||
"pad_token_id": 0,
|
||||
"qa_dropout": 0.1,
|
||||
"seq_classif_dropout": 0.2,
|
||||
"sinusoidal_pos_embds": false,
|
||||
"transformers_version": "4.16.2",
|
||||
"vocab_size": 30522
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[`DistilBertConfig`] displays all the default attributes used to build a base [`DistilBertModel`]. All attributes are customizable, creating space for experimentation. For example, you can customize a default model to:
|
||||
|
||||
- Try a different activation function with the `activation` parameter.
|
||||
- Use a higher dropout ratio for the attention probabilities with the `attention_dropout` parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> my_config = DistilBertConfig(activation="relu", attention_dropout=0.4)
|
||||
>>> print(my_config)
|
||||
DistilBertConfig {
|
||||
"activation": "relu",
|
||||
"attention_dropout": 0.4,
|
||||
"dim": 768,
|
||||
"dropout": 0.1,
|
||||
"hidden_dim": 3072,
|
||||
"initializer_range": 0.02,
|
||||
"max_position_embeddings": 512,
|
||||
"model_type": "distilbert",
|
||||
"n_heads": 12,
|
||||
"n_layers": 6,
|
||||
"pad_token_id": 0,
|
||||
"qa_dropout": 0.1,
|
||||
"seq_classif_dropout": 0.2,
|
||||
"sinusoidal_pos_embds": false,
|
||||
"transformers_version": "4.16.2",
|
||||
"vocab_size": 30522
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Pretrained model attributes can be modified in the [`~PretrainedConfig.from_pretrained`] function:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> my_config = DistilBertConfig.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased", activation="relu", attention_dropout=0.4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once you are satisfied with your model configuration, you can save it with [`~PretrainedConfig.save_pretrained`]. Your configuration file is stored as a JSON file in the specified save directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> my_config.save_pretrained(save_directory="./your_model_save_path")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To reuse the configuration file, load it with [`~PretrainedConfig.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> my_config = DistilBertConfig.from_pretrained("./your_model_save_path/config.json")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
You can also save your configuration file as a dictionary or even just the difference between your custom configuration attributes and the default configuration attributes! See the [configuration](main_classes/configuration) documentation for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Model
|
||||
|
||||
The next step is to create a [model](main_classes/models). The model - also loosely referred to as the architecture - defines what each layer is doing and what operations are happening. Attributes like `num_hidden_layers` from the configuration are used to define the architecture. Every model shares the base class [`PreTrainedModel`] and a few common methods like resizing input embeddings and pruning self-attention heads. In addition, all models are also either a [`torch.nn.Module`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Module.html), [`tf.keras.Model`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/Model) or [`flax.linen.Module`](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/flax.linen.html#module) subclass. This means models are compatible with each of their respective framework's usage.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Load your custom configuration attributes into the model:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_config = DistilBertConfig.from_pretrained("./your_model_save_path/config.json")
|
||||
>>> model = DistilBertModel(my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This creates a model with random values instead of pretrained weights. You won't be able to use this model for anything useful yet until you train it. Training is a costly and time-consuming process. It is generally better to use a pretrained model to obtain better results faster, while using only a fraction of the resources required for training.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a pretrained model with [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model = DistilBertModel.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When you load pretrained weights, the default model configuration is automatically loaded if the model is provided by 🤗 Transformers. However, you can still replace - some or all of - the default model configuration attributes with your own if you'd like:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model = DistilBertModel.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased", config=my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Load your custom configuration attributes into the model:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFDistilBertModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_config = DistilBertConfig.from_pretrained("./your_model_save_path/my_config.json")
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertModel(my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This creates a model with random values instead of pretrained weights. You won't be able to use this model for anything useful yet until you train it. Training is a costly and time-consuming process. It is generally better to use a pretrained model to obtain better results faster, while using only a fraction of the resources required for training.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a pretrained model with [`~TFPreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertModel.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When you load pretrained weights, the default model configuration is automatically loaded if the model is provided by 🤗 Transformers. However, you can still replace - some or all of - the default model configuration attributes with your own if you'd like:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertModel.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased", config=my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
### Model heads
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, you have a base DistilBERT model which outputs the *hidden states*. The hidden states are passed as inputs to a model head to produce the final output. 🤗 Transformers provides a different model head for each task as long as a model supports the task (i.e., you can't use DistilBERT for a sequence-to-sequence task like translation).
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
For example, [`DistilBertForSequenceClassification`] is a base DistilBERT model with a sequence classification head. The sequence classification head is a linear layer on top of the pooled outputs.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = DistilBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Easily reuse this checkpoint for another task by switching to a different model head. For a question answering task, you would use the [`DistilBertForQuestionAnswering`] model head. The question answering head is similar to the sequence classification head except it is a linear layer on top of the hidden states output.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = DistilBertForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
For example, [`TFDistilBertForSequenceClassification`] is a base DistilBERT model with a sequence classification head. The sequence classification head is a linear layer on top of the pooled outputs.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFDistilBertForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Easily reuse this checkpoint for another task by switching to a different model head. For a question answering task, you would use the [`TFDistilBertForQuestionAnswering`] model head. The question answering head is similar to the sequence classification head except it is a linear layer on top of the hidden states output.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFDistilBertForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Tokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
The last base class you need before using a model for textual data is a [tokenizer](main_classes/tokenizer) to convert raw text to tensors. There are two types of tokenizers you can use with 🤗 Transformers:
|
||||
|
||||
- [`PreTrainedTokenizer`]: a Python implementation of a tokenizer.
|
||||
- [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`]: a tokenizer from our Rust-based [🤗 Tokenizer](https://huggingface.co/docs/tokenizers/python/latest/) library. This tokenizer type is significantly faster - especially during batch tokenization - due to it's Rust implementation. The fast tokenizer also offers additional methods like *offset mapping* which maps tokens to their original words or characters.
|
||||
|
||||
Both tokenizers support common methods such as encoding and decoding, adding new tokens, and managing special tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Not every model supports a fast tokenizer. Take a look at this [table](index#supported-frameworks) to check if a model has fast tokenizer support.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If you trained your own tokenizer, you can create one from your *vocabulary* file:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizer(vocab_file="my_vocab_file.txt", do_lower_case=False, padding_side="left")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is important to remember the vocabulary from a custom tokenizer will be different from the vocabulary generated by a pretrained model's tokenizer. You need to use a pretrained model's vocabulary if you are using a pretrained model, otherwise the inputs won't make sense. Create a tokenizer with a pretrained model's vocabulary with the [`DistilBertTokenizer`] class:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> slow_tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizer.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a fast tokenizer with the [`DistilBertTokenizerFast`] class:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
>>> fast_tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
By default, [`AutoTokenizer`] will try to load a fast tokenizer. You can disable this behavior by setting `use_fast=False` in `from_pretrained`.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Image Processor
|
||||
|
||||
An image processor processes vision inputs. It inherits from the base [`~image_processing_utils.ImageProcessingMixin`] class.
|
||||
|
||||
To use, create an image processor associated with the model you're using. For example, create a default [`ViTImageProcessor`] if you are using [ViT](model_doc/vit) for image classification:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import ViTImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> vit_extractor = ViTImageProcessor()
|
||||
>>> print(vit_extractor)
|
||||
ViTImageProcessor {
|
||||
"do_normalize": true,
|
||||
"do_resize": true,
|
||||
"feature_extractor_type": "ViTImageProcessor",
|
||||
"image_mean": [
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5
|
||||
],
|
||||
"image_std": [
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5
|
||||
],
|
||||
"resample": 2,
|
||||
"size": 224
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If you aren't looking for any customization, just use the `from_pretrained` method to load a model's default image processor parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Modify any of the [`ViTImageProcessor`] parameters to create your custom image processor:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import ViTImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_vit_extractor = ViTImageProcessor(resample="PIL.Image.BOX", do_normalize=False, image_mean=[0.3, 0.3, 0.3])
|
||||
>>> print(my_vit_extractor)
|
||||
ViTImageProcessor {
|
||||
"do_normalize": false,
|
||||
"do_resize": true,
|
||||
"feature_extractor_type": "ViTImageProcessor",
|
||||
"image_mean": [
|
||||
0.3,
|
||||
0.3,
|
||||
0.3
|
||||
],
|
||||
"image_std": [
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5
|
||||
],
|
||||
"resample": "PIL.Image.BOX",
|
||||
"size": 224
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Feature Extractor
|
||||
|
||||
A feature extractor processes audio inputs. It inherits from the base [`~feature_extraction_utils.FeatureExtractionMixin`] class, and may also inherit from the [`SequenceFeatureExtractor`] class for processing audio inputs.
|
||||
|
||||
To use, create a feature extractor associated with the model you're using. For example, create a default [`Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor`] if you are using [Wav2Vec2](model_doc/wav2vec2) for audio classification:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> w2v2_extractor = Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor()
|
||||
>>> print(w2v2_extractor)
|
||||
Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor {
|
||||
"do_normalize": true,
|
||||
"feature_extractor_type": "Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor",
|
||||
"feature_size": 1,
|
||||
"padding_side": "right",
|
||||
"padding_value": 0.0,
|
||||
"return_attention_mask": false,
|
||||
"sampling_rate": 16000
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If you aren't looking for any customization, just use the `from_pretrained` method to load a model's default feature extractor parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Modify any of the [`Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor`] parameters to create your custom feature extractor:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> w2v2_extractor = Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor(sampling_rate=8000, do_normalize=False)
|
||||
>>> print(w2v2_extractor)
|
||||
Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor {
|
||||
"do_normalize": false,
|
||||
"feature_extractor_type": "Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor",
|
||||
"feature_size": 1,
|
||||
"padding_side": "right",
|
||||
"padding_value": 0.0,
|
||||
"return_attention_mask": false,
|
||||
"sampling_rate": 8000
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Processor
|
||||
|
||||
For models that support multimodal tasks, 🤗 Transformers offers a processor class that conveniently wraps processing classes such as a feature extractor and a tokenizer into a single object. For example, let's use the [`Wav2Vec2Processor`] for an automatic speech recognition task (ASR). ASR transcribes audio to text, so you will need a feature extractor and a tokenizer.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a feature extractor to handle the audio inputs:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> feature_extractor = Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor(padding_value=1.0, do_normalize=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a tokenizer to handle the text inputs:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2CTCTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = Wav2Vec2CTCTokenizer(vocab_file="my_vocab_file.txt")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Combine the feature extractor and tokenizer in [`Wav2Vec2Processor`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2Processor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> processor = Wav2Vec2Processor(feature_extractor=feature_extractor, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With two basic classes - configuration and model - and an additional preprocessing class (tokenizer, image processor, feature extractor, or processor), you can create any of the models supported by 🤗 Transformers. Each of these base classes are configurable, allowing you to use the specific attributes you want. You can easily setup a model for training or modify an existing pretrained model to fine-tune.
|
||||
356
docs/source/en/custom_models.md
Normal file
356
docs/source/en/custom_models.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,356 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Sharing custom models
|
||||
|
||||
The 🤗 Transformers library is designed to be easily extensible. Every model is fully coded in a given subfolder
|
||||
of the repository with no abstraction, so you can easily copy a modeling file and tweak it to your needs.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are writing a brand new model, it might be easier to start from scratch. In this tutorial, we will show you
|
||||
how to write a custom model and its configuration so it can be used inside Transformers, and how you can share it
|
||||
with the community (with the code it relies on) so that anyone can use it, even if it's not present in the 🤗
|
||||
Transformers library.
|
||||
|
||||
We will illustrate all of this on a ResNet model, by wrapping the ResNet class of the
|
||||
[timm library](https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models) into a [`PreTrainedModel`].
|
||||
|
||||
## Writing a custom configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Before we dive into the model, let's first write its configuration. The configuration of a model is an object that
|
||||
will contain all the necessary information to build the model. As we will see in the next section, the model can only
|
||||
take a `config` to be initialized, so we really need that object to be as complete as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
In our example, we will take a couple of arguments of the ResNet class that we might want to tweak. Different
|
||||
configurations will then give us the different types of ResNets that are possible. We then just store those arguments,
|
||||
after checking the validity of a few of them.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import PretrainedConfig
|
||||
from typing import List
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ResnetConfig(PretrainedConfig):
|
||||
model_type = "resnet"
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
block_type="bottleneck",
|
||||
layers: List[int] = [3, 4, 6, 3],
|
||||
num_classes: int = 1000,
|
||||
input_channels: int = 3,
|
||||
cardinality: int = 1,
|
||||
base_width: int = 64,
|
||||
stem_width: int = 64,
|
||||
stem_type: str = "",
|
||||
avg_down: bool = False,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
):
|
||||
if block_type not in ["basic", "bottleneck"]:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`block_type` must be 'basic' or bottleneck', got {block_type}.")
|
||||
if stem_type not in ["", "deep", "deep-tiered"]:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`stem_type` must be '', 'deep' or 'deep-tiered', got {stem_type}.")
|
||||
|
||||
self.block_type = block_type
|
||||
self.layers = layers
|
||||
self.num_classes = num_classes
|
||||
self.input_channels = input_channels
|
||||
self.cardinality = cardinality
|
||||
self.base_width = base_width
|
||||
self.stem_width = stem_width
|
||||
self.stem_type = stem_type
|
||||
self.avg_down = avg_down
|
||||
super().__init__(**kwargs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The three important things to remember when writing you own configuration are the following:
|
||||
- you have to inherit from `PretrainedConfig`,
|
||||
- the `__init__` of your `PretrainedConfig` must accept any kwargs,
|
||||
- those `kwargs` need to be passed to the superclass `__init__`.
|
||||
|
||||
The inheritance is to make sure you get all the functionality from the 🤗 Transformers library, while the two other
|
||||
constraints come from the fact a `PretrainedConfig` has more fields than the ones you are setting. When reloading a
|
||||
config with the `from_pretrained` method, those fields need to be accepted by your config and then sent to the
|
||||
superclass.
|
||||
|
||||
Defining a `model_type` for your configuration (here `model_type="resnet"`) is not mandatory, unless you want to
|
||||
register your model with the auto classes (see last section).
|
||||
|
||||
With this done, you can easily create and save your configuration like you would do with any other model config of the
|
||||
library. Here is how we can create a resnet50d config and save it:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d_config = ResnetConfig(block_type="bottleneck", stem_width=32, stem_type="deep", avg_down=True)
|
||||
resnet50d_config.save_pretrained("custom-resnet")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will save a file named `config.json` inside the folder `custom-resnet`. You can then reload your config with the
|
||||
`from_pretrained` method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d_config = ResnetConfig.from_pretrained("custom-resnet")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use any other method of the [`PretrainedConfig`] class, like [`~PretrainedConfig.push_to_hub`] to
|
||||
directly upload your config to the Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
## Writing a custom model
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we have our ResNet configuration, we can go on writing the model. We will actually write two: one that
|
||||
extracts the hidden features from a batch of images (like [`BertModel`]) and one that is suitable for image
|
||||
classification (like [`BertForSequenceClassification`]).
|
||||
|
||||
As we mentioned before, we'll only write a loose wrapper of the model to keep it simple for this example. The only
|
||||
thing we need to do before writing this class is a map between the block types and actual block classes. Then the
|
||||
model is defined from the configuration by passing everything to the `ResNet` class:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import PreTrainedModel
|
||||
from timm.models.resnet import BasicBlock, Bottleneck, ResNet
|
||||
from .configuration_resnet import ResnetConfig
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
BLOCK_MAPPING = {"basic": BasicBlock, "bottleneck": Bottleneck}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ResnetModel(PreTrainedModel):
|
||||
config_class = ResnetConfig
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__(config)
|
||||
block_layer = BLOCK_MAPPING[config.block_type]
|
||||
self.model = ResNet(
|
||||
block_layer,
|
||||
config.layers,
|
||||
num_classes=config.num_classes,
|
||||
in_chans=config.input_channels,
|
||||
cardinality=config.cardinality,
|
||||
base_width=config.base_width,
|
||||
stem_width=config.stem_width,
|
||||
stem_type=config.stem_type,
|
||||
avg_down=config.avg_down,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, tensor):
|
||||
return self.model.forward_features(tensor)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the model that will classify images, we just change the forward method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ResnetModelForImageClassification(PreTrainedModel):
|
||||
config_class = ResnetConfig
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__(config)
|
||||
block_layer = BLOCK_MAPPING[config.block_type]
|
||||
self.model = ResNet(
|
||||
block_layer,
|
||||
config.layers,
|
||||
num_classes=config.num_classes,
|
||||
in_chans=config.input_channels,
|
||||
cardinality=config.cardinality,
|
||||
base_width=config.base_width,
|
||||
stem_width=config.stem_width,
|
||||
stem_type=config.stem_type,
|
||||
avg_down=config.avg_down,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, tensor, labels=None):
|
||||
logits = self.model(tensor)
|
||||
if labels is not None:
|
||||
loss = torch.nn.cross_entropy(logits, labels)
|
||||
return {"loss": loss, "logits": logits}
|
||||
return {"logits": logits}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In both cases, notice how we inherit from `PreTrainedModel` and call the superclass initialization with the `config`
|
||||
(a bit like when you write a regular `torch.nn.Module`). The line that sets the `config_class` is not mandatory, unless
|
||||
you want to register your model with the auto classes (see last section).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If your model is very similar to a model inside the library, you can re-use the same configuration as this model.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
You can have your model return anything you want, but returning a dictionary like we did for
|
||||
`ResnetModelForImageClassification`, with the loss included when labels are passed, will make your model directly
|
||||
usable inside the [`Trainer`] class. Using another output format is fine as long as you are planning on using your own
|
||||
training loop or another library for training.
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we have our model class, let's create one:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d = ResnetModelForImageClassification(resnet50d_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Again, you can use any of the methods of [`PreTrainedModel`], like [`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] or
|
||||
[`~PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`]. We will use the second in the next section, and see how to push the model weights
|
||||
with the code of our model. But first, let's load some pretrained weights inside our model.
|
||||
|
||||
In your own use case, you will probably be training your custom model on your own data. To go fast for this tutorial,
|
||||
we will use the pretrained version of the resnet50d. Since our model is just a wrapper around it, it's going to be
|
||||
easy to transfer those weights:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import timm
|
||||
|
||||
pretrained_model = timm.create_model("resnet50d", pretrained=True)
|
||||
resnet50d.model.load_state_dict(pretrained_model.state_dict())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's see how to make sure that when we do [`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] or [`~PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`], the
|
||||
code of the model is saved.
|
||||
|
||||
## Sending the code to the Hub
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
This API is experimental and may have some slight breaking changes in the next releases.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
First, make sure your model is fully defined in a `.py` file. It can rely on relative imports to some other files as
|
||||
long as all the files are in the same directory (we don't support submodules for this feature yet). For our example,
|
||||
we'll define a `modeling_resnet.py` file and a `configuration_resnet.py` file in a folder of the current working
|
||||
directory named `resnet_model`. The configuration file contains the code for `ResnetConfig` and the modeling file
|
||||
contains the code of `ResnetModel` and `ResnetModelForImageClassification`.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
└── resnet_model
|
||||
├── __init__.py
|
||||
├── configuration_resnet.py
|
||||
└── modeling_resnet.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `__init__.py` can be empty, it's just there so that Python detects `resnet_model` can be use as a module.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
If copying a modeling files from the library, you will need to replace all the relative imports at the top of the file
|
||||
to import from the `transformers` package.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you can re-use (or subclass) an existing configuration/model.
|
||||
|
||||
To share your model with the community, follow those steps: first import the ResNet model and config from the newly
|
||||
created files:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from resnet_model.configuration_resnet import ResnetConfig
|
||||
from resnet_model.modeling_resnet import ResnetModel, ResnetModelForImageClassification
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you have to tell the library you want to copy the code files of those objects when using the `save_pretrained`
|
||||
method and properly register them with a given Auto class (especially for models), just run:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
ResnetConfig.register_for_auto_class()
|
||||
ResnetModel.register_for_auto_class("AutoModel")
|
||||
ResnetModelForImageClassification.register_for_auto_class("AutoModelForImageClassification")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that there is no need to specify an auto class for the configuration (there is only one auto class for them,
|
||||
[`AutoConfig`]) but it's different for models. Your custom model could be suitable for many different tasks, so you
|
||||
have to specify which one of the auto classes is the correct one for your model.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, let's create the config and models as we did before:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d_config = ResnetConfig(block_type="bottleneck", stem_width=32, stem_type="deep", avg_down=True)
|
||||
resnet50d = ResnetModelForImageClassification(resnet50d_config)
|
||||
|
||||
pretrained_model = timm.create_model("resnet50d", pretrained=True)
|
||||
resnet50d.model.load_state_dict(pretrained_model.state_dict())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now to send the model to the Hub, make sure you are logged in. Either run in your terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
huggingface-cli login
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or from a notebook:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
|
||||
|
||||
notebook_login()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can then push to your own namespace (or an organization you are a member of) like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d.push_to_hub("custom-resnet50d")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
On top of the modeling weights and the configuration in json format, this also copied the modeling and
|
||||
configuration `.py` files in the folder `custom-resnet50d` and uploaded the result to the Hub. You can check the result
|
||||
in this [model repo](https://huggingface.co/sgugger/custom-resnet50d).
|
||||
|
||||
See the [sharing tutorial](model_sharing) for more information on the push to Hub method.
|
||||
|
||||
## Using a model with custom code
|
||||
|
||||
You can use any configuration, model or tokenizer with custom code files in its repository with the auto-classes and
|
||||
the `from_pretrained` method. All files and code uploaded to the Hub are scanned for malware (refer to the [Hub security](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security#malware-scanning) documentation for more information), but you should still
|
||||
review the model code and author to avoid executing malicious code on your machine. Set `trust_remote_code=True` to use
|
||||
a model with custom code:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained("sgugger/custom-resnet50d", trust_remote_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is also strongly encouraged to pass a commit hash as a `revision` to make sure the author of the models did not
|
||||
update the code with some malicious new lines (unless you fully trust the authors of the models).
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
commit_hash = "ed94a7c6247d8aedce4647f00f20de6875b5b292"
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"sgugger/custom-resnet50d", trust_remote_code=True, revision=commit_hash
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that when browsing the commit history of the model repo on the Hub, there is a button to easily copy the commit
|
||||
hash of any commit.
|
||||
|
||||
## Registering a model with custom code to the auto classes
|
||||
|
||||
If you are writing a library that extends 🤗 Transformers, you may want to extend the auto classes to include your own
|
||||
model. This is different from pushing the code to the Hub in the sense that users will need to import your library to
|
||||
get the custom models (contrarily to automatically downloading the model code from the Hub).
|
||||
|
||||
As long as your config has a `model_type` attribute that is different from existing model types, and that your model
|
||||
classes have the right `config_class` attributes, you can just add them to the auto classes likes this:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoConfig, AutoModel, AutoModelForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
AutoConfig.register("resnet", ResnetConfig)
|
||||
AutoModel.register(ResnetConfig, ResnetModel)
|
||||
AutoModelForImageClassification.register(ResnetConfig, ResnetModelForImageClassification)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the first argument used when registering your custom config to [`AutoConfig`] needs to match the `model_type`
|
||||
of your custom config, and the first argument used when registering your custom models to any auto model class needs
|
||||
to match the `config_class` of those models.
|
||||
@ -1,352 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Sharing custom models
|
||||
|
||||
The 🤗 Transformers library is designed to be easily extensible. Every model is fully coded in a given subfolder
|
||||
of the repository with no abstraction, so you can easily copy a modeling file and tweak it to your needs.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are writing a brand new model, it might be easier to start from scratch. In this tutorial, we will show you
|
||||
how to write a custom model and its configuration so it can be used inside Transformers, and how you can share it
|
||||
with the community (with the code it relies on) so that anyone can use it, even if it's not present in the 🤗
|
||||
Transformers library.
|
||||
|
||||
We will illustrate all of this on a ResNet model, by wrapping the ResNet class of the
|
||||
[timm library](https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models) into a [`PreTrainedModel`].
|
||||
|
||||
## Writing a custom configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Before we dive into the model, let's first write its configuration. The configuration of a model is an object that
|
||||
will contain all the necessary information to build the model. As we will see in the next section, the model can only
|
||||
take a `config` to be initialized, so we really need that object to be as complete as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
In our example, we will take a couple of arguments of the ResNet class that we might want to tweak. Different
|
||||
configurations will then give us the different types of ResNets that are possible. We then just store those arguments,
|
||||
after checking the validity of a few of them.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import PretrainedConfig
|
||||
from typing import List
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ResnetConfig(PretrainedConfig):
|
||||
model_type = "resnet"
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
block_type="bottleneck",
|
||||
layers: List[int] = [3, 4, 6, 3],
|
||||
num_classes: int = 1000,
|
||||
input_channels: int = 3,
|
||||
cardinality: int = 1,
|
||||
base_width: int = 64,
|
||||
stem_width: int = 64,
|
||||
stem_type: str = "",
|
||||
avg_down: bool = False,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
):
|
||||
if block_type not in ["basic", "bottleneck"]:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`block_type` must be 'basic' or bottleneck', got {block_type}.")
|
||||
if stem_type not in ["", "deep", "deep-tiered"]:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`stem_type` must be '', 'deep' or 'deep-tiered', got {stem_type}.")
|
||||
|
||||
self.block_type = block_type
|
||||
self.layers = layers
|
||||
self.num_classes = num_classes
|
||||
self.input_channels = input_channels
|
||||
self.cardinality = cardinality
|
||||
self.base_width = base_width
|
||||
self.stem_width = stem_width
|
||||
self.stem_type = stem_type
|
||||
self.avg_down = avg_down
|
||||
super().__init__(**kwargs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The three important things to remember when writing you own configuration are the following:
|
||||
- you have to inherit from `PretrainedConfig`,
|
||||
- the `__init__` of your `PretrainedConfig` must accept any kwargs,
|
||||
- those `kwargs` need to be passed to the superclass `__init__`.
|
||||
|
||||
The inheritance is to make sure you get all the functionality from the 🤗 Transformers library, while the two other
|
||||
constraints come from the fact a `PretrainedConfig` has more fields than the ones you are setting. When reloading a
|
||||
config with the `from_pretrained` method, those fields need to be accepted by your config and then sent to the
|
||||
superclass.
|
||||
|
||||
Defining a `model_type` for your configuration (here `model_type="resnet"`) is not mandatory, unless you want to
|
||||
register your model with the auto classes (see last section).
|
||||
|
||||
With this done, you can easily create and save your configuration like you would do with any other model config of the
|
||||
library. Here is how we can create a resnet50d config and save it:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d_config = ResnetConfig(block_type="bottleneck", stem_width=32, stem_type="deep", avg_down=True)
|
||||
resnet50d_config.save_pretrained("custom-resnet")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will save a file named `config.json` inside the folder `custom-resnet`. You can then reload your config with the
|
||||
`from_pretrained` method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d_config = ResnetConfig.from_pretrained("custom-resnet")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use any other method of the [`PretrainedConfig`] class, like [`~PretrainedConfig.push_to_hub`] to
|
||||
directly upload your config to the Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
## Writing a custom model
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we have our ResNet configuration, we can go on writing the model. We will actually write two: one that
|
||||
extracts the hidden features from a batch of images (like [`BertModel`]) and one that is suitable for image
|
||||
classification (like [`BertForSequenceClassification`]).
|
||||
|
||||
As we mentioned before, we'll only write a loose wrapper of the model to keep it simple for this example. The only
|
||||
thing we need to do before writing this class is a map between the block types and actual block classes. Then the
|
||||
model is defined from the configuration by passing everything to the `ResNet` class:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import PreTrainedModel
|
||||
from timm.models.resnet import BasicBlock, Bottleneck, ResNet
|
||||
from .configuration_resnet import ResnetConfig
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
BLOCK_MAPPING = {"basic": BasicBlock, "bottleneck": Bottleneck}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ResnetModel(PreTrainedModel):
|
||||
config_class = ResnetConfig
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__(config)
|
||||
block_layer = BLOCK_MAPPING[config.block_type]
|
||||
self.model = ResNet(
|
||||
block_layer,
|
||||
config.layers,
|
||||
num_classes=config.num_classes,
|
||||
in_chans=config.input_channels,
|
||||
cardinality=config.cardinality,
|
||||
base_width=config.base_width,
|
||||
stem_width=config.stem_width,
|
||||
stem_type=config.stem_type,
|
||||
avg_down=config.avg_down,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, tensor):
|
||||
return self.model.forward_features(tensor)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the model that will classify images, we just change the forward method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ResnetModelForImageClassification(PreTrainedModel):
|
||||
config_class = ResnetConfig
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__(config)
|
||||
block_layer = BLOCK_MAPPING[config.block_type]
|
||||
self.model = ResNet(
|
||||
block_layer,
|
||||
config.layers,
|
||||
num_classes=config.num_classes,
|
||||
in_chans=config.input_channels,
|
||||
cardinality=config.cardinality,
|
||||
base_width=config.base_width,
|
||||
stem_width=config.stem_width,
|
||||
stem_type=config.stem_type,
|
||||
avg_down=config.avg_down,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, tensor, labels=None):
|
||||
logits = self.model(tensor)
|
||||
if labels is not None:
|
||||
loss = torch.nn.cross_entropy(logits, labels)
|
||||
return {"loss": loss, "logits": logits}
|
||||
return {"logits": logits}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In both cases, notice how we inherit from `PreTrainedModel` and call the superclass initialization with the `config`
|
||||
(a bit like when you write a regular `torch.nn.Module`). The line that sets the `config_class` is not mandatory, unless
|
||||
you want to register your model with the auto classes (see last section).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If your model is very similar to a model inside the library, you can re-use the same configuration as this model.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
You can have your model return anything you want, but returning a dictionary like we did for
|
||||
`ResnetModelForImageClassification`, with the loss included when labels are passed, will make your model directly
|
||||
usable inside the [`Trainer`] class. Using another output format is fine as long as you are planning on using your own
|
||||
training loop or another library for training.
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we have our model class, let's create one:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d = ResnetModelForImageClassification(resnet50d_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Again, you can use any of the methods of [`PreTrainedModel`], like [`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] or
|
||||
[`~PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`]. We will use the second in the next section, and see how to push the model weights
|
||||
with the code of our model. But first, let's load some pretrained weights inside our model.
|
||||
|
||||
In your own use case, you will probably be training your custom model on your own data. To go fast for this tutorial,
|
||||
we will use the pretrained version of the resnet50d. Since our model is just a wrapper around it, it's going to be
|
||||
easy to transfer those weights:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import timm
|
||||
|
||||
pretrained_model = timm.create_model("resnet50d", pretrained=True)
|
||||
resnet50d.model.load_state_dict(pretrained_model.state_dict())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's see how to make sure that when we do [`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] or [`~PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`], the
|
||||
code of the model is saved.
|
||||
|
||||
## Sending the code to the Hub
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
This API is experimental and may have some slight breaking changes in the next releases.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
First, make sure your model is fully defined in a `.py` file. It can rely on relative imports to some other files as
|
||||
long as all the files are in the same directory (we don't support submodules for this feature yet). For our example,
|
||||
we'll define a `modeling_resnet.py` file and a `configuration_resnet.py` file in a folder of the current working
|
||||
directory named `resnet_model`. The configuration file contains the code for `ResnetConfig` and the modeling file
|
||||
contains the code of `ResnetModel` and `ResnetModelForImageClassification`.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
└── resnet_model
|
||||
├── __init__.py
|
||||
├── configuration_resnet.py
|
||||
└── modeling_resnet.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `__init__.py` can be empty, it's just there so that Python detects `resnet_model` can be use as a module.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
If copying a modeling files from the library, you will need to replace all the relative imports at the top of the file
|
||||
to import from the `transformers` package.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you can re-use (or subclass) an existing configuration/model.
|
||||
|
||||
To share your model with the community, follow those steps: first import the ResNet model and config from the newly
|
||||
created files:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from resnet_model.configuration_resnet import ResnetConfig
|
||||
from resnet_model.modeling_resnet import ResnetModel, ResnetModelForImageClassification
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you have to tell the library you want to copy the code files of those objects when using the `save_pretrained`
|
||||
method and properly register them with a given Auto class (especially for models), just run:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
ResnetConfig.register_for_auto_class()
|
||||
ResnetModel.register_for_auto_class("AutoModel")
|
||||
ResnetModelForImageClassification.register_for_auto_class("AutoModelForImageClassification")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that there is no need to specify an auto class for the configuration (there is only one auto class for them,
|
||||
[`AutoConfig`]) but it's different for models. Your custom model could be suitable for many different tasks, so you
|
||||
have to specify which one of the auto classes is the correct one for your model.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, let's create the config and models as we did before:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d_config = ResnetConfig(block_type="bottleneck", stem_width=32, stem_type="deep", avg_down=True)
|
||||
resnet50d = ResnetModelForImageClassification(resnet50d_config)
|
||||
|
||||
pretrained_model = timm.create_model("resnet50d", pretrained=True)
|
||||
resnet50d.model.load_state_dict(pretrained_model.state_dict())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now to send the model to the Hub, make sure you are logged in. Either run in your terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
huggingface-cli login
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or from a notebook:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
|
||||
|
||||
notebook_login()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can then push to your own namespace (or an organization you are a member of) like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d.push_to_hub("custom-resnet50d")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
On top of the modeling weights and the configuration in json format, this also copied the modeling and
|
||||
configuration `.py` files in the folder `custom-resnet50d` and uploaded the result to the Hub. You can check the result
|
||||
in this [model repo](https://huggingface.co/sgugger/custom-resnet50d).
|
||||
|
||||
See the [sharing tutorial](model_sharing) for more information on the push to Hub method.
|
||||
|
||||
## Using a model with custom code
|
||||
|
||||
You can use any configuration, model or tokenizer with custom code files in its repository with the auto-classes and
|
||||
the `from_pretrained` method. All files and code uploaded to the Hub are scanned for malware (refer to the [Hub security](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security#malware-scanning) documentation for more information), but you should still
|
||||
review the model code and author to avoid executing malicious code on your machine. Set `trust_remote_code=True` to use
|
||||
a model with custom code:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained("sgugger/custom-resnet50d", trust_remote_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It is also strongly encouraged to pass a commit hash as a `revision` to make sure the author of the models did not
|
||||
update the code with some malicious new lines (unless you fully trust the authors of the models).
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
commit_hash = "ed94a7c6247d8aedce4647f00f20de6875b5b292"
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"sgugger/custom-resnet50d", trust_remote_code=True, revision=commit_hash
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that when browsing the commit history of the model repo on the Hub, there is a button to easily copy the commit
|
||||
hash of any commit.
|
||||
|
||||
## Registering a model with custom code to the auto classes
|
||||
|
||||
If you are writing a library that extends 🤗 Transformers, you may want to extend the auto classes to include your own
|
||||
model. This is different from pushing the code to the Hub in the sense that users will need to import your library to
|
||||
get the custom models (contrarily to automatically downloading the model code from the Hub).
|
||||
|
||||
As long as your config has a `model_type` attribute that is different from existing model types, and that your model
|
||||
classes have the right `config_class` attributes, you can just add them to the auto classes likes this:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoConfig, AutoModel, AutoModelForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
AutoConfig.register("resnet", ResnetConfig)
|
||||
AutoModel.register(ResnetConfig, ResnetModel)
|
||||
AutoModelForImageClassification.register(ResnetConfig, ResnetModelForImageClassification)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the first argument used when registering your custom config to [`AutoConfig`] needs to match the `model_type`
|
||||
of your custom config, and the first argument used when registering your custom models to any auto model class needs
|
||||
to match the `config_class` of those models.
|
||||
789
docs/source/en/custom_tools.md
Normal file
789
docs/source/en/custom_tools.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,789 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Custom Tools and Prompts
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If you are not aware of what tools and agents are in the context of transformers, we recommend you read the
|
||||
[Transformers Agents](transformers_agents) page first.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers Agent is an experimental API that is subject to change at any time. Results returned by the agents
|
||||
can vary as the APIs or underlying models are prone to change.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Creating and using custom tools and prompts is paramount to empowering the agent and having it perform new tasks.
|
||||
In this guide we'll take a look at:
|
||||
|
||||
- How to customize the prompt
|
||||
- How to use custom tools
|
||||
- How to create custom tools
|
||||
|
||||
## Customizing the prompt
|
||||
|
||||
As explained in [Transformers Agents](transformers_agents) agents can run in [`~Agent.run`] and [`~Agent.chat`] mode.
|
||||
Both the `run` and `chat` modes underlie the same logic. The language model powering the agent is conditioned on a long
|
||||
prompt and completes the prompt by generating the next tokens until the stop token is reached.
|
||||
The only difference between the two modes is that during the `chat` mode the prompt is extended with
|
||||
previous user inputs and model generations. This allows the agent to have access to past interactions,
|
||||
seemingly giving the agent some kind of memory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Structure of the prompt
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take a closer look at how the prompt is structured to understand how it can be best customized.
|
||||
The prompt is structured broadly into four parts.
|
||||
|
||||
- 1. Introduction: how the agent should behave, explanation of the concept of tools.
|
||||
- 2. Description of all the tools. This is defined by a `<<all_tools>>` token that is dynamically replaced at runtime with the tools defined/chosen by the user.
|
||||
- 3. A set of examples of tasks and their solution
|
||||
- 4. Current example, and request for solution.
|
||||
|
||||
To better understand each part, let's look at a shortened version of how the `run` prompt can look like:
|
||||
|
||||
````text
|
||||
I will ask you to perform a task, your job is to come up with a series of simple commands in Python that will perform the task.
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
You can print intermediate results if it makes sense to do so.
|
||||
|
||||
Tools:
|
||||
- document_qa: This is a tool that answers a question about a document (pdf). It takes an input named `document` which should be the document containing the information, as well as a `question` that is the question about the document. It returns a text that contains the answer to the question.
|
||||
- image_captioner: This is a tool that generates a description of an image. It takes an input named `image` which should be the image to the caption and returns a text that contains the description in English.
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
|
||||
Task: "Answer the question in the variable `question` about the image stored in the variable `image`. The question is in French."
|
||||
|
||||
I will use the following tools: `translator` to translate the question into English and then `image_qa` to answer the question on the input image.
|
||||
|
||||
Answer:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
translated_question = translator(question=question, src_lang="French", tgt_lang="English")
|
||||
print(f"The translated question is {translated_question}.")
|
||||
answer = image_qa(image=image, question=translated_question)
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Task: "Identify the oldest person in the `document` and create an image showcasing the result as a banner."
|
||||
|
||||
I will use the following tools: `document_qa` to find the oldest person in the document, then `image_generator` to generate an image according to the answer.
|
||||
|
||||
Answer:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
answer = document_qa(document, question="What is the oldest person?")
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator("A banner showing " + answer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
|
||||
Task: "Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes"
|
||||
|
||||
I will use the following
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
The introduction (the text before *"Tools:"*) explains precisely how the model shall behave and what it should do.
|
||||
This part most likely does not need to be customized as the agent shall always behave the same way.
|
||||
|
||||
The second part (the bullet points below *"Tools"*) is dynamically added upon calling `run` or `chat`. There are
|
||||
exactly as many bullet points as there are tools in `agent.toolbox` and each bullet point consists of the name
|
||||
and description of the tool:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
- <tool.name>: <tool.description>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let's verify this quickly by loading the document_qa tool and printing out the name and description.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
document_qa = load_tool("document-question-answering")
|
||||
print(f"- {document_qa.name}: {document_qa.description}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which gives:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
- document_qa: This is a tool that answers a question about a document (pdf). It takes an input named `document` which should be the document containing the information, as well as a `question` that is the question about the document. It returns a text that contains the answer to the question.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can see that the tool name is short and precise. The description includes two parts, the first explaining
|
||||
what the tool does and the second states what input arguments and return values are expected.
|
||||
|
||||
A good tool name and tool description are very important for the agent to correctly use it. Note that the only
|
||||
information the agent has about the tool is its name and description, so one should make sure that both
|
||||
are precisely written and match the style of the existing tools in the toolbox. In particular make sure the description
|
||||
mentions all the arguments expected by name in code-style, along with the expected type and a description of what they
|
||||
are.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Check the naming and description of the curated Transformers tools to better understand what name and
|
||||
description a tool is expected to have. You can see all tools with the [`Agent.toolbox`] property.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The third part includes a set of curated examples that show the agent exactly what code it should produce
|
||||
for what kind of user request. The large language models empowering the agent are extremely good at
|
||||
recognizing patterns in a prompt and repeating the pattern with new data. Therefore, it is very important
|
||||
that the examples are written in a way that maximizes the likelihood of the agent to generating correct,
|
||||
executable code in practice.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's have a look at one example:
|
||||
|
||||
````text
|
||||
Task: "Identify the oldest person in the `document` and create an image showcasing the result as a banner."
|
||||
|
||||
I will use the following tools: `document_qa` to find the oldest person in the document, then `image_generator` to generate an image according to the answer.
|
||||
|
||||
Answer:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
answer = document_qa(document, question="What is the oldest person?")
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator("A banner showing " + answer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
The pattern the model is prompted to repeat has three parts: The task statement, the agent's explanation of
|
||||
what it intends to do, and finally the generated code. Every example that is part of the prompt has this exact
|
||||
pattern, thus making sure that the agent will reproduce exactly the same pattern when generating new tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
The prompt examples are curated by the Transformers team and rigorously evaluated on a set of
|
||||
[problem statements](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/tools/evaluate_agent.py)
|
||||
to ensure that the agent's prompt is as good as possible to solve real use cases of the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
The final part of the prompt corresponds to:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Task: "Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes"
|
||||
|
||||
I will use the following
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
is a final and unfinished example that the agent is tasked to complete. The unfinished example
|
||||
is dynamically created based on the actual user input. For the above example, the user ran:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The user input - *a.k.a* the task: *"Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes"* is cast into the
|
||||
prompt template: "Task: <task> \n\n I will use the following". This sentence makes up the final lines of the
|
||||
prompt the agent is conditioned on, therefore strongly influencing the agent to finish the example
|
||||
exactly in the same way it was previously done in the examples.
|
||||
|
||||
Without going into too much detail, the chat template has the same prompt structure with the
|
||||
examples having a slightly different style, *e.g.*:
|
||||
|
||||
````text
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
|
||||
=====
|
||||
|
||||
Human: Answer the question in the variable `question` about the image stored in the variable `image`.
|
||||
|
||||
Assistant: I will use the tool `image_qa` to answer the question on the input image.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
answer = image_qa(text=question, image=image)
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Human: I tried this code, it worked but didn't give me a good result. The question is in French
|
||||
|
||||
Assistant: In this case, the question needs to be translated first. I will use the tool `translator` to do this.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
translated_question = translator(question=question, src_lang="French", tgt_lang="English")
|
||||
print(f"The translated question is {translated_question}.")
|
||||
answer = image_qa(text=translated_question, image=image)
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=====
|
||||
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
Contrary, to the examples of the `run` prompt, each `chat` prompt example has one or more exchanges between the
|
||||
*Human* and the *Assistant*. Every exchange is structured similarly to the example of the `run` prompt.
|
||||
The user's input is appended to behind *Human:* and the agent is prompted to first generate what needs to be done
|
||||
before generating code. An exchange can be based on previous exchanges, therefore allowing the user to refer
|
||||
to past exchanges as is done *e.g.* above by the user's input of "I tried **this** code" refers to the
|
||||
previously generated code of the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
Upon running `.chat`, the user's input or *task* is cast into an unfinished example of the form:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Human: <user-input>\n\nAssistant:
|
||||
```
|
||||
which the agent completes. Contrary to the `run` command, the `chat` command then appends the completed example
|
||||
to the prompt, thus giving the agent more context for the next `chat` turn.
|
||||
|
||||
Great now that we know how the prompt is structured, let's see how we can customize it!
|
||||
|
||||
### Writing good user inputs
|
||||
|
||||
While large language models are getting better and better at understanding users' intentions, it helps
|
||||
enormously to be as precise as possible to help the agent pick the correct task. What does it mean to be
|
||||
as precise as possible?
|
||||
|
||||
The agent sees a list of tool names and their description in its prompt. The more tools are added the
|
||||
more difficult it becomes for the agent to choose the correct tool and it's even more difficult to choose
|
||||
the correct sequences of tools to run. Let's look at a common failure case, here we will only return
|
||||
the code to analyze it.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder")
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Show me a tree", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
gives:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tool: `image_segmenter` to create a segmentation mask for the image.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
mask = image_segmenter(image, prompt="tree")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which is probably not what we wanted. Instead, it is more likely that we want an image of a tree to be generated.
|
||||
To steer the agent more towards using a specific tool it can therefore be very helpful to use important keywords that
|
||||
are present in the tool's name and description. Let's have a look.
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.toolbox["image_generator"].description
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
'This is a tool that creates an image according to a prompt, which is a text description. It takes an input named `prompt` which contains the image description and outputs an image.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The name and description make use of the keywords "image", "prompt", "create" and "generate". Using these words will most likely work better here. Let's refine our prompt a bit.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Create an image of a tree", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
gives:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tool `image_generator` to generate an image of a tree.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt="tree")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Much better! That looks more like what we want. In short, when you notice that the agent struggles to
|
||||
correctly map your task to the correct tools, try looking up the most pertinent keywords of the tool's name
|
||||
and description and try refining your task request with it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Customizing the tool descriptions
|
||||
|
||||
As we've seen before the agent has access to each of the tools' names and descriptions. The base tools
|
||||
should have very precise names and descriptions, however, you might find that it could help to change the
|
||||
the description or name of a tool for your specific use case. This might become especially important
|
||||
when you've added multiple tools that are very similar or if you want to use your agent only for a certain
|
||||
domain, *e.g.* image generation and transformations.
|
||||
|
||||
A common problem is that the agent confuses image generation with image transformation/modification when
|
||||
used a lot for image generation tasks, *e.g.*
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Make an image of a house and a car", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
returns
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tools `image_generator` to generate an image of a house and `image_transformer` to transform the image of a car into the image of a house.
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
house_image = image_generator(prompt="A house")
|
||||
car_image = image_generator(prompt="A car")
|
||||
house_car_image = image_transformer(image=car_image, prompt="A house")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which is probably not exactly what we want here. It seems like the agent has a difficult time
|
||||
to understand the difference between `image_generator` and `image_transformer` and often uses the two together.
|
||||
|
||||
We can help the agent here by changing the tool name and description of `image_transformer`. Let's instead call it `modifier`
|
||||
to disassociate it a bit from "image" and "prompt":
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.toolbox["modifier"] = agent.toolbox.pop("image_transformer")
|
||||
agent.toolbox["modifier"].description = agent.toolbox["modifier"].description.replace(
|
||||
"transforms an image according to a prompt", "modifies an image"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now "modify" is a strong cue to use the new image processor which should help with the above prompt. Let's run it again.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Make an image of a house and a car", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now we're getting:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tools: `image_generator` to generate an image of a house, then `image_generator` to generate an image of a car.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
house_image = image_generator(prompt="A house")
|
||||
car_image = image_generator(prompt="A car")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which is definitely closer to what we had in mind! However, we want to have both the house and car in the same image. Steering the task more toward single image generation should help:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Create image: 'A house and car'", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tool: `image_generator` to generate an image.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt="A house and car")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Agents are still brittle for many use cases, especially when it comes to
|
||||
slightly more complex use cases like generating an image of multiple objects.
|
||||
Both the agent itself and the underlying prompt will be further improved in the coming
|
||||
months making sure that agents become more robust to a variety of user inputs.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Customizing the whole prompt
|
||||
|
||||
To give the user maximum flexibility, the whole prompt template as explained in [above](#structure-of-the-prompt)
|
||||
can be overwritten by the user. In this case make sure that your custom prompt includes an introduction section,
|
||||
a tool section, an example section, and an unfinished example section. If you want to overwrite the `run` prompt template,
|
||||
you can do as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
template = """ [...] """
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent(your_endpoint, run_prompt_template=template)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Please make sure to have the `<<all_tools>>` string and the `<<prompt>>` defined somewhere in the `template` so that the agent can be aware
|
||||
of the tools, it has available to it as well as correctly insert the user's prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, one can overwrite the `chat` prompt template. Note that the `chat` mode always uses the following format for the exchanges:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Human: <<task>>
|
||||
|
||||
Assistant:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore it is important that the examples of the custom `chat` prompt template also make use of this format.
|
||||
You can overwrite the `chat` template at instantiation as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
template = """ [...] """
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent(url_endpoint=your_endpoint, chat_prompt_template=template)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Please make sure to have the `<<all_tools>>` string defined somewhere in the `template` so that the agent can be aware
|
||||
of the tools, it has available to it.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In both cases, you can pass a repo ID instead of the prompt template if you would like to use a template hosted by someone in the community. The default prompts live in [this repo](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface-tools/default-prompts) as an example.
|
||||
|
||||
To upload your custom prompt on a repo on the Hub and share it with the community just make sure:
|
||||
- to use a dataset repository
|
||||
- to put the prompt template for the `run` command in a file named `run_prompt_template.txt`
|
||||
- to put the prompt template for the `chat` command in a file named `chat_prompt_template.txt`
|
||||
|
||||
## Using custom tools
|
||||
|
||||
In this section, we'll be leveraging two existing custom tools that are specific to image generation:
|
||||
|
||||
- We replace [huggingface-tools/image-transformation](https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface-tools/image-transformation),
|
||||
with [diffusers/controlnet-canny-tool](https://huggingface.co/spaces/diffusers/controlnet-canny-tool)
|
||||
to allow for more image modifications.
|
||||
- We add a new tool for image upscaling to the default toolbox:
|
||||
[diffusers/latent-upscaler-tool](https://huggingface.co/spaces/diffusers/latent-upscaler-tool) replace the existing image-transformation tool.
|
||||
|
||||
We'll start by loading the custom tools with the convenient [`load_tool`] function:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
controlnet_transformer = load_tool("diffusers/controlnet-canny-tool")
|
||||
upscaler = load_tool("diffusers/latent-upscaler-tool")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Upon adding custom tools to an agent, the tools' descriptions and names are automatically
|
||||
included in the agents' prompts. Thus, it is imperative that custom tools have
|
||||
a well-written description and name in order for the agent to understand how to use them.
|
||||
Let's take a look at the description and name of `controlnet_transformer`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
print(f"Description: '{controlnet_transformer.description}'")
|
||||
print(f"Name: '{controlnet_transformer.name}'")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
gives
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Description: 'This is a tool that transforms an image with ControlNet according to a prompt.
|
||||
It takes two inputs: `image`, which should be the image to transform, and `prompt`, which should be the prompt to use to change it. It returns the modified image.'
|
||||
Name: 'image_transformer'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The name and description are accurate and fit the style of the [curated set of tools](./transformers_agents#a-curated-set-of-tools).
|
||||
Next, let's instantiate an agent with `controlnet_transformer` and `upscaler`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
tools = [controlnet_transformer, upscaler]
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder", additional_tools=tools)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This command should give you the following info:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
image_transformer has been replaced by <transformers_modules.diffusers.controlnet-canny-tool.bd76182c7777eba9612fc03c0
|
||||
8718a60c0aa6312.image_transformation.ControlNetTransformationTool object at 0x7f1d3bfa3a00> as provided in `additional_tools`
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The set of curated tools already has an `image_transformer` tool which is hereby replaced with our custom tool.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Overwriting existing tools can be beneficial if we want to use a custom tool exactly for the same task as an existing tool
|
||||
because the agent is well-versed in using the specific task. Beware that the custom tool should follow the exact same API
|
||||
as the overwritten tool in this case, or you should adapt the prompt template to make sure all examples using that
|
||||
tool are updated.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The upscaler tool was given the name `image_upscaler` which is not yet present in the default toolbox and is therefore simply added to the list of tools.
|
||||
You can always have a look at the toolbox that is currently available to the agent via the `agent.toolbox` attribute:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
print("\n".join([f"- {a}" for a in agent.toolbox.keys()]))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
- document_qa
|
||||
- image_captioner
|
||||
- image_qa
|
||||
- image_segmenter
|
||||
- transcriber
|
||||
- summarizer
|
||||
- text_classifier
|
||||
- text_qa
|
||||
- text_reader
|
||||
- translator
|
||||
- image_transformer
|
||||
- text_downloader
|
||||
- image_generator
|
||||
- video_generator
|
||||
- image_upscaler
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note how `image_upscaler` is now part of the agents' toolbox.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's now try out the new tools! We will re-use the image we generated in [Transformers Agents Quickstart](./transformers_agents#single-execution-run).
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
image = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
Let's transform the image into a beautiful winter landscape:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = agent.run("Transform the image: 'A frozen lake and snowy forest'", image=image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tool: `image_transformer` to transform the image.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
image = image_transformer(image, prompt="A frozen lake and snowy forest")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes_winter.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
The new image processing tool is based on ControlNet which can make very strong modifications to the image.
|
||||
By default the image processing tool returns an image of size 512x512 pixels. Let's see if we can upscale it.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = agent.run("Upscale the image", image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tool: `image_upscaler` to upscale the image.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
upscaled_image = image_upscaler(image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes_winter_upscale.png" width=400>
|
||||
|
||||
The agent automatically mapped our prompt "Upscale the image" to the just added upscaler tool purely based on the description and name of the upscaler tool
|
||||
and was able to correctly run it.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, let's have a look at how you can create a new custom tool.
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding new tools
|
||||
|
||||
In this section, we show how to create a new tool that can be added to the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Creating a new tool
|
||||
|
||||
We'll first start by creating a tool. We'll add the not-so-useful yet fun task of fetching the model on the Hugging Face
|
||||
Hub with the most downloads for a given task.
|
||||
|
||||
We can do that with the following code:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
task = "text-classification"
|
||||
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
print(model.id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the task `text-classification`, this returns `'facebook/bart-large-mnli'`, for `translation` it returns `'t5-base`.
|
||||
|
||||
How do we convert this to a tool that the agent can leverage? All tools depend on the superclass `Tool` that holds the
|
||||
main attributes necessary. We'll create a class that inherits from it:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import Tool
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class HFModelDownloadsTool(Tool):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This class has a few needs:
|
||||
- An attribute `name`, which corresponds to the name of the tool itself. To be in tune with other tools which have a
|
||||
performative name, we'll name it `model_download_counter`.
|
||||
- An attribute `description`, which will be used to populate the prompt of the agent.
|
||||
- `inputs` and `outputs` attributes. Defining this will help the python interpreter make educated choices about types,
|
||||
and will allow for a gradio-demo to be spawned when we push our tool to the Hub. They're both a list of expected
|
||||
values, which can be `text`, `image`, or `audio`.
|
||||
- A `__call__` method which contains the inference code. This is the code we've played with above!
|
||||
|
||||
Here's what our class looks like now:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import Tool
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class HFModelDownloadsTool(Tool):
|
||||
name = "model_download_counter"
|
||||
description = (
|
||||
"This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub. "
|
||||
"It takes the name of the category (such as text-classification, depth-estimation, etc), and "
|
||||
"returns the name of the checkpoint."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = ["text"]
|
||||
outputs = ["text"]
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, task: str):
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
return model.id
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We now have our tool handy. Save it in a file and import it from your main script. Let's name this file
|
||||
`model_downloads.py`, so the resulting import code looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from model_downloads import HFModelDownloadsTool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = HFModelDownloadsTool()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In order to let others benefit from it and for simpler initialization, we recommend pushing it to the Hub under your
|
||||
namespace. To do so, just call `push_to_hub` on the `tool` variable:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tool.push_to_hub("hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You now have your code on the Hub! Let's take a look at the final step, which is to have the agent use it.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Having the agent use the tool
|
||||
|
||||
We now have our tool that lives on the Hub which can be instantiated as such (change the user name for your tool):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = load_tool("lysandre/hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In order to use it in the agent, simply pass it in the `additional_tools` parameter of the agent initialization method:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder", additional_tools=[tool])
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Can you read out loud the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
which outputs the following:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
model = model_download_counter(task="text-to-video")
|
||||
print(f"The model with the most downloads is {model}.")
|
||||
audio_model = text_reader(model)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Result==
|
||||
The model with the most downloads is damo-vilab/text-to-video-ms-1.7b.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and generates the following audio.
|
||||
|
||||
| **Audio** |
|
||||
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| <audio controls><source src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/damo.wav" type="audio/wav"/> |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on the LLM, some are quite brittle and require very exact prompts in order to work well. Having a well-defined
|
||||
name and description of the tool is paramount to having it be leveraged by the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Replacing existing tools
|
||||
|
||||
Replacing existing tools can be done simply by assigning a new item to the agent's toolbox. Here's how one would do so:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent, load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder")
|
||||
agent.toolbox["image-transformation"] = load_tool("diffusers/controlnet-canny-tool")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Beware when replacing tools with others! This will also adjust the agent's prompt. This can be good if you have a better
|
||||
prompt suited for the task, but it can also result in your tool being selected way more than others or for other
|
||||
tools to be selected instead of the one you have defined.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Leveraging gradio-tools
|
||||
|
||||
[gradio-tools](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools) is a powerful library that allows using Hugging
|
||||
Face Spaces as tools. It supports many existing Spaces as well as custom Spaces to be designed with it.
|
||||
|
||||
We offer support for `gradio_tools` by using the `Tool.from_gradio` method. For example, we want to take
|
||||
advantage of the `StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool` tool offered in the `gradio-tools` toolkit so as to
|
||||
improve our prompts and generate better images.
|
||||
|
||||
We first import the tool from `gradio_tools` and instantiate it:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from gradio_tools import StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool
|
||||
|
||||
gradio_tool = StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We pass that instance to the `Tool.from_gradio` method:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import Tool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = Tool.from_gradio(gradio_tool)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can manage it exactly as we would a usual custom tool. We leverage it to improve our prompt
|
||||
` a rabbit wearing a space suit`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder", additional_tools=[tool])
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Generate an image of the `prompt` after improving it.", prompt="A rabbit wearing a space suit")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The model adequately leverages the tool:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tools: `StableDiffusionPromptGenerator` to improve the prompt, then `image_generator` to generate an image according to the improved prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
improved_prompt = StableDiffusionPromptGenerator(prompt)
|
||||
print(f"The improved prompt is {improved_prompt}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator(improved_prompt)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Before finally generating the image:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rabbit.png">
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
gradio-tools requires *textual* inputs and outputs, even when working with different modalities. This implementation
|
||||
works with image and audio objects. The two are currently incompatible, but will rapidly become compatible as we
|
||||
work to improve the support.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Future compatibility with Langchain
|
||||
|
||||
We love Langchain and think it has a very compelling suite of tools. In order to handle these tools,
|
||||
Langchain requires *textual* inputs and outputs, even when working with different modalities.
|
||||
This is often the serialized version (i.e., saved to disk) of the objects.
|
||||
|
||||
This difference means that multi-modality isn't handled between transformers-agents and langchain.
|
||||
We aim for this limitation to be resolved in future versions, and welcome any help from avid langchain
|
||||
users to help us achieve this compatibility.
|
||||
|
||||
We would love to have better support. If you would like to help, please
|
||||
[open an issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/new) and share what you have in mind.
|
||||
@ -1,785 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Custom Tools and Prompts
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If you are not aware of what tools and agents are in the context of transformers, we recommend you read the
|
||||
[Transformers Agents](transformers_agents) page first.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers Agent is an experimental API that is subject to change at any time. Results returned by the agents
|
||||
can vary as the APIs or underlying models are prone to change.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Creating and using custom tools and prompts is paramount to empowering the agent and having it perform new tasks.
|
||||
In this guide we'll take a look at:
|
||||
|
||||
- How to customize the prompt
|
||||
- How to use custom tools
|
||||
- How to create custom tools
|
||||
|
||||
## Customizing the prompt
|
||||
|
||||
As explained in [Transformers Agents](transformers_agents) agents can run in [`~Agent.run`] and [`~Agent.chat`] mode.
|
||||
Both the `run` and `chat` modes underlie the same logic. The language model powering the agent is conditioned on a long
|
||||
prompt and completes the prompt by generating the next tokens until the stop token is reached.
|
||||
The only difference between the two modes is that during the `chat` mode the prompt is extended with
|
||||
previous user inputs and model generations. This allows the agent to have access to past interactions,
|
||||
seemingly giving the agent some kind of memory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Structure of the prompt
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take a closer look at how the prompt is structured to understand how it can be best customized.
|
||||
The prompt is structured broadly into four parts.
|
||||
|
||||
- 1. Introduction: how the agent should behave, explanation of the concept of tools.
|
||||
- 2. Description of all the tools. This is defined by a `<<all_tools>>` token that is dynamically replaced at runtime with the tools defined/chosen by the user.
|
||||
- 3. A set of examples of tasks and their solution
|
||||
- 4. Current example, and request for solution.
|
||||
|
||||
To better understand each part, let's look at a shortened version of how the `run` prompt can look like:
|
||||
|
||||
````text
|
||||
I will ask you to perform a task, your job is to come up with a series of simple commands in Python that will perform the task.
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
You can print intermediate results if it makes sense to do so.
|
||||
|
||||
Tools:
|
||||
- document_qa: This is a tool that answers a question about a document (pdf). It takes an input named `document` which should be the document containing the information, as well as a `question` that is the question about the document. It returns a text that contains the answer to the question.
|
||||
- image_captioner: This is a tool that generates a description of an image. It takes an input named `image` which should be the image to the caption and returns a text that contains the description in English.
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
|
||||
Task: "Answer the question in the variable `question` about the image stored in the variable `image`. The question is in French."
|
||||
|
||||
I will use the following tools: `translator` to translate the question into English and then `image_qa` to answer the question on the input image.
|
||||
|
||||
Answer:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
translated_question = translator(question=question, src_lang="French", tgt_lang="English")
|
||||
print(f"The translated question is {translated_question}.")
|
||||
answer = image_qa(image=image, question=translated_question)
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Task: "Identify the oldest person in the `document` and create an image showcasing the result as a banner."
|
||||
|
||||
I will use the following tools: `document_qa` to find the oldest person in the document, then `image_generator` to generate an image according to the answer.
|
||||
|
||||
Answer:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
answer = document_qa(document, question="What is the oldest person?")
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator("A banner showing " + answer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
|
||||
Task: "Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes"
|
||||
|
||||
I will use the following
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
The introduction (the text before *"Tools:"*) explains precisely how the model shall behave and what it should do.
|
||||
This part most likely does not need to be customized as the agent shall always behave the same way.
|
||||
|
||||
The second part (the bullet points below *"Tools"*) is dynamically added upon calling `run` or `chat`. There are
|
||||
exactly as many bullet points as there are tools in `agent.toolbox` and each bullet point consists of the name
|
||||
and description of the tool:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
- <tool.name>: <tool.description>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let's verify this quickly by loading the document_qa tool and printing out the name and description.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
document_qa = load_tool("document-question-answering")
|
||||
print(f"- {document_qa.name}: {document_qa.description}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which gives:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
- document_qa: This is a tool that answers a question about a document (pdf). It takes an input named `document` which should be the document containing the information, as well as a `question` that is the question about the document. It returns a text that contains the answer to the question.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can see that the tool name is short and precise. The description includes two parts, the first explaining
|
||||
what the tool does and the second states what input arguments and return values are expected.
|
||||
|
||||
A good tool name and tool description are very important for the agent to correctly use it. Note that the only
|
||||
information the agent has about the tool is its name and description, so one should make sure that both
|
||||
are precisely written and match the style of the existing tools in the toolbox. In particular make sure the description
|
||||
mentions all the arguments expected by name in code-style, along with the expected type and a description of what they
|
||||
are.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Check the naming and description of the curated Transformers tools to better understand what name and
|
||||
description a tool is expected to have. You can see all tools with the [`Agent.toolbox`] property.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The third part includes a set of curated examples that show the agent exactly what code it should produce
|
||||
for what kind of user request. The large language models empowering the agent are extremely good at
|
||||
recognizing patterns in a prompt and repeating the pattern with new data. Therefore, it is very important
|
||||
that the examples are written in a way that maximizes the likelihood of the agent to generating correct,
|
||||
executable code in practice.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's have a look at one example:
|
||||
|
||||
````text
|
||||
Task: "Identify the oldest person in the `document` and create an image showcasing the result as a banner."
|
||||
|
||||
I will use the following tools: `document_qa` to find the oldest person in the document, then `image_generator` to generate an image according to the answer.
|
||||
|
||||
Answer:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
answer = document_qa(document, question="What is the oldest person?")
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator("A banner showing " + answer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
The pattern the model is prompted to repeat has three parts: The task statement, the agent's explanation of
|
||||
what it intends to do, and finally the generated code. Every example that is part of the prompt has this exact
|
||||
pattern, thus making sure that the agent will reproduce exactly the same pattern when generating new tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
The prompt examples are curated by the Transformers team and rigorously evaluated on a set of
|
||||
[problem statements](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/tools/evaluate_agent.py)
|
||||
to ensure that the agent's prompt is as good as possible to solve real use cases of the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
The final part of the prompt corresponds to:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Task: "Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes"
|
||||
|
||||
I will use the following
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
is a final and unfinished example that the agent is tasked to complete. The unfinished example
|
||||
is dynamically created based on the actual user input. For the above example, the user ran:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The user input - *a.k.a* the task: *"Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes"* is cast into the
|
||||
prompt template: "Task: <task> \n\n I will use the following". This sentence makes up the final lines of the
|
||||
prompt the agent is conditioned on, therefore strongly influencing the agent to finish the example
|
||||
exactly in the same way it was previously done in the examples.
|
||||
|
||||
Without going into too much detail, the chat template has the same prompt structure with the
|
||||
examples having a slightly different style, *e.g.*:
|
||||
|
||||
````text
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
|
||||
=====
|
||||
|
||||
Human: Answer the question in the variable `question` about the image stored in the variable `image`.
|
||||
|
||||
Assistant: I will use the tool `image_qa` to answer the question on the input image.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
answer = image_qa(text=question, image=image)
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Human: I tried this code, it worked but didn't give me a good result. The question is in French
|
||||
|
||||
Assistant: In this case, the question needs to be translated first. I will use the tool `translator` to do this.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
translated_question = translator(question=question, src_lang="French", tgt_lang="English")
|
||||
print(f"The translated question is {translated_question}.")
|
||||
answer = image_qa(text=translated_question, image=image)
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=====
|
||||
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
Contrary, to the examples of the `run` prompt, each `chat` prompt example has one or more exchanges between the
|
||||
*Human* and the *Assistant*. Every exchange is structured similarly to the example of the `run` prompt.
|
||||
The user's input is appended to behind *Human:* and the agent is prompted to first generate what needs to be done
|
||||
before generating code. An exchange can be based on previous exchanges, therefore allowing the user to refer
|
||||
to past exchanges as is done *e.g.* above by the user's input of "I tried **this** code" refers to the
|
||||
previously generated code of the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
Upon running `.chat`, the user's input or *task* is cast into an unfinished example of the form:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Human: <user-input>\n\nAssistant:
|
||||
```
|
||||
which the agent completes. Contrary to the `run` command, the `chat` command then appends the completed example
|
||||
to the prompt, thus giving the agent more context for the next `chat` turn.
|
||||
|
||||
Great now that we know how the prompt is structured, let's see how we can customize it!
|
||||
|
||||
### Writing good user inputs
|
||||
|
||||
While large language models are getting better and better at understanding users' intentions, it helps
|
||||
enormously to be as precise as possible to help the agent pick the correct task. What does it mean to be
|
||||
as precise as possible?
|
||||
|
||||
The agent sees a list of tool names and their description in its prompt. The more tools are added the
|
||||
more difficult it becomes for the agent to choose the correct tool and it's even more difficult to choose
|
||||
the correct sequences of tools to run. Let's look at a common failure case, here we will only return
|
||||
the code to analyze it.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder")
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Show me a tree", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
gives:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tool: `image_segmenter` to create a segmentation mask for the image.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
mask = image_segmenter(image, prompt="tree")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which is probably not what we wanted. Instead, it is more likely that we want an image of a tree to be generated.
|
||||
To steer the agent more towards using a specific tool it can therefore be very helpful to use important keywords that
|
||||
are present in the tool's name and description. Let's have a look.
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.toolbox["image_generator"].description
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
'This is a tool that creates an image according to a prompt, which is a text description. It takes an input named `prompt` which contains the image description and outputs an image.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The name and description make use of the keywords "image", "prompt", "create" and "generate". Using these words will most likely work better here. Let's refine our prompt a bit.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Create an image of a tree", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
gives:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tool `image_generator` to generate an image of a tree.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt="tree")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Much better! That looks more like what we want. In short, when you notice that the agent struggles to
|
||||
correctly map your task to the correct tools, try looking up the most pertinent keywords of the tool's name
|
||||
and description and try refining your task request with it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Customizing the tool descriptions
|
||||
|
||||
As we've seen before the agent has access to each of the tools' names and descriptions. The base tools
|
||||
should have very precise names and descriptions, however, you might find that it could help to change the
|
||||
the description or name of a tool for your specific use case. This might become especially important
|
||||
when you've added multiple tools that are very similar or if you want to use your agent only for a certain
|
||||
domain, *e.g.* image generation and transformations.
|
||||
|
||||
A common problem is that the agent confuses image generation with image transformation/modification when
|
||||
used a lot for image generation tasks, *e.g.*
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Make an image of a house and a car", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
returns
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tools `image_generator` to generate an image of a house and `image_transformer` to transform the image of a car into the image of a house.
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
house_image = image_generator(prompt="A house")
|
||||
car_image = image_generator(prompt="A car")
|
||||
house_car_image = image_transformer(image=car_image, prompt="A house")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which is probably not exactly what we want here. It seems like the agent has a difficult time
|
||||
to understand the difference between `image_generator` and `image_transformer` and often uses the two together.
|
||||
|
||||
We can help the agent here by changing the tool name and description of `image_transformer`. Let's instead call it `modifier`
|
||||
to disassociate it a bit from "image" and "prompt":
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.toolbox["modifier"] = agent.toolbox.pop("image_transformer")
|
||||
agent.toolbox["modifier"].description = agent.toolbox["modifier"].description.replace(
|
||||
"transforms an image according to a prompt", "modifies an image"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now "modify" is a strong cue to use the new image processor which should help with the above prompt. Let's run it again.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Make an image of a house and a car", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now we're getting:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tools: `image_generator` to generate an image of a house, then `image_generator` to generate an image of a car.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
house_image = image_generator(prompt="A house")
|
||||
car_image = image_generator(prompt="A car")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which is definitely closer to what we had in mind! However, we want to have both the house and car in the same image. Steering the task more toward single image generation should help:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Create image: 'A house and car'", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tool: `image_generator` to generate an image.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt="A house and car")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Agents are still brittle for many use cases, especially when it comes to
|
||||
slightly more complex use cases like generating an image of multiple objects.
|
||||
Both the agent itself and the underlying prompt will be further improved in the coming
|
||||
months making sure that agents become more robust to a variety of user inputs.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Customizing the whole prompt
|
||||
|
||||
To give the user maximum flexibility, the whole prompt template as explained in [above](#structure-of-the-prompt)
|
||||
can be overwritten by the user. In this case make sure that your custom prompt includes an introduction section,
|
||||
a tool section, an example section, and an unfinished example section. If you want to overwrite the `run` prompt template,
|
||||
you can do as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
template = """ [...] """
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent(your_endpoint, run_prompt_template=template)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Please make sure to have the `<<all_tools>>` string and the `<<prompt>>` defined somewhere in the `template` so that the agent can be aware
|
||||
of the tools, it has available to it as well as correctly insert the user's prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, one can overwrite the `chat` prompt template. Note that the `chat` mode always uses the following format for the exchanges:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Human: <<task>>
|
||||
|
||||
Assistant:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore it is important that the examples of the custom `chat` prompt template also make use of this format.
|
||||
You can overwrite the `chat` template at instantiation as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
template = """ [...] """
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent(url_endpoint=your_endpoint, chat_prompt_template=template)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Please make sure to have the `<<all_tools>>` string defined somewhere in the `template` so that the agent can be aware
|
||||
of the tools, it has available to it.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In both cases, you can pass a repo ID instead of the prompt template if you would like to use a template hosted by someone in the community. The default prompts live in [this repo](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface-tools/default-prompts) as an example.
|
||||
|
||||
To upload your custom prompt on a repo on the Hub and share it with the community just make sure:
|
||||
- to use a dataset repository
|
||||
- to put the prompt template for the `run` command in a file named `run_prompt_template.txt`
|
||||
- to put the prompt template for the `chat` command in a file named `chat_prompt_template.txt`
|
||||
|
||||
## Using custom tools
|
||||
|
||||
In this section, we'll be leveraging two existing custom tools that are specific to image generation:
|
||||
|
||||
- We replace [huggingface-tools/image-transformation](https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface-tools/image-transformation),
|
||||
with [diffusers/controlnet-canny-tool](https://huggingface.co/spaces/diffusers/controlnet-canny-tool)
|
||||
to allow for more image modifications.
|
||||
- We add a new tool for image upscaling to the default toolbox:
|
||||
[diffusers/latent-upscaler-tool](https://huggingface.co/spaces/diffusers/latent-upscaler-tool) replace the existing image-transformation tool.
|
||||
|
||||
We'll start by loading the custom tools with the convenient [`load_tool`] function:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
controlnet_transformer = load_tool("diffusers/controlnet-canny-tool")
|
||||
upscaler = load_tool("diffusers/latent-upscaler-tool")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Upon adding custom tools to an agent, the tools' descriptions and names are automatically
|
||||
included in the agents' prompts. Thus, it is imperative that custom tools have
|
||||
a well-written description and name in order for the agent to understand how to use them.
|
||||
Let's take a look at the description and name of `controlnet_transformer`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
print(f"Description: '{controlnet_transformer.description}'")
|
||||
print(f"Name: '{controlnet_transformer.name}'")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
gives
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Description: 'This is a tool that transforms an image with ControlNet according to a prompt.
|
||||
It takes two inputs: `image`, which should be the image to transform, and `prompt`, which should be the prompt to use to change it. It returns the modified image.'
|
||||
Name: 'image_transformer'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The name and description are accurate and fit the style of the [curated set of tools](./transformers_agents#a-curated-set-of-tools).
|
||||
Next, let's instantiate an agent with `controlnet_transformer` and `upscaler`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
tools = [controlnet_transformer, upscaler]
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder", additional_tools=tools)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This command should give you the following info:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
image_transformer has been replaced by <transformers_modules.diffusers.controlnet-canny-tool.bd76182c7777eba9612fc03c0
|
||||
8718a60c0aa6312.image_transformation.ControlNetTransformationTool object at 0x7f1d3bfa3a00> as provided in `additional_tools`
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The set of curated tools already has an `image_transformer` tool which is hereby replaced with our custom tool.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Overwriting existing tools can be beneficial if we want to use a custom tool exactly for the same task as an existing tool
|
||||
because the agent is well-versed in using the specific task. Beware that the custom tool should follow the exact same API
|
||||
as the overwritten tool in this case, or you should adapt the prompt template to make sure all examples using that
|
||||
tool are updated.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The upscaler tool was given the name `image_upscaler` which is not yet present in the default toolbox and is therefore simply added to the list of tools.
|
||||
You can always have a look at the toolbox that is currently available to the agent via the `agent.toolbox` attribute:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
print("\n".join([f"- {a}" for a in agent.toolbox.keys()]))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
- document_qa
|
||||
- image_captioner
|
||||
- image_qa
|
||||
- image_segmenter
|
||||
- transcriber
|
||||
- summarizer
|
||||
- text_classifier
|
||||
- text_qa
|
||||
- text_reader
|
||||
- translator
|
||||
- image_transformer
|
||||
- text_downloader
|
||||
- image_generator
|
||||
- video_generator
|
||||
- image_upscaler
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note how `image_upscaler` is now part of the agents' toolbox.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's now try out the new tools! We will re-use the image we generated in [Transformers Agents Quickstart](./transformers_agents#single-execution-run).
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
image = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
Let's transform the image into a beautiful winter landscape:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = agent.run("Transform the image: 'A frozen lake and snowy forest'", image=image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tool: `image_transformer` to transform the image.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
image = image_transformer(image, prompt="A frozen lake and snowy forest")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes_winter.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
The new image processing tool is based on ControlNet which can make very strong modifications to the image.
|
||||
By default the image processing tool returns an image of size 512x512 pixels. Let's see if we can upscale it.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = agent.run("Upscale the image", image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tool: `image_upscaler` to upscale the image.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
upscaled_image = image_upscaler(image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes_winter_upscale.png" width=400>
|
||||
|
||||
The agent automatically mapped our prompt "Upscale the image" to the just added upscaler tool purely based on the description and name of the upscaler tool
|
||||
and was able to correctly run it.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, let's have a look at how you can create a new custom tool.
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding new tools
|
||||
|
||||
In this section, we show how to create a new tool that can be added to the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Creating a new tool
|
||||
|
||||
We'll first start by creating a tool. We'll add the not-so-useful yet fun task of fetching the model on the Hugging Face
|
||||
Hub with the most downloads for a given task.
|
||||
|
||||
We can do that with the following code:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
task = "text-classification"
|
||||
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
print(model.id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the task `text-classification`, this returns `'facebook/bart-large-mnli'`, for `translation` it returns `'t5-base`.
|
||||
|
||||
How do we convert this to a tool that the agent can leverage? All tools depend on the superclass `Tool` that holds the
|
||||
main attributes necessary. We'll create a class that inherits from it:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import Tool
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class HFModelDownloadsTool(Tool):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This class has a few needs:
|
||||
- An attribute `name`, which corresponds to the name of the tool itself. To be in tune with other tools which have a
|
||||
performative name, we'll name it `model_download_counter`.
|
||||
- An attribute `description`, which will be used to populate the prompt of the agent.
|
||||
- `inputs` and `outputs` attributes. Defining this will help the python interpreter make educated choices about types,
|
||||
and will allow for a gradio-demo to be spawned when we push our tool to the Hub. They're both a list of expected
|
||||
values, which can be `text`, `image`, or `audio`.
|
||||
- A `__call__` method which contains the inference code. This is the code we've played with above!
|
||||
|
||||
Here's what our class looks like now:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import Tool
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class HFModelDownloadsTool(Tool):
|
||||
name = "model_download_counter"
|
||||
description = (
|
||||
"This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub. "
|
||||
"It takes the name of the category (such as text-classification, depth-estimation, etc), and "
|
||||
"returns the name of the checkpoint."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = ["text"]
|
||||
outputs = ["text"]
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, task: str):
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
return model.id
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We now have our tool handy. Save it in a file and import it from your main script. Let's name this file
|
||||
`model_downloads.py`, so the resulting import code looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from model_downloads import HFModelDownloadsTool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = HFModelDownloadsTool()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In order to let others benefit from it and for simpler initialization, we recommend pushing it to the Hub under your
|
||||
namespace. To do so, just call `push_to_hub` on the `tool` variable:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tool.push_to_hub("hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You now have your code on the Hub! Let's take a look at the final step, which is to have the agent use it.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Having the agent use the tool
|
||||
|
||||
We now have our tool that lives on the Hub which can be instantiated as such (change the user name for your tool):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = load_tool("lysandre/hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In order to use it in the agent, simply pass it in the `additional_tools` parameter of the agent initialization method:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder", additional_tools=[tool])
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Can you read out loud the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
which outputs the following:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
model = model_download_counter(task="text-to-video")
|
||||
print(f"The model with the most downloads is {model}.")
|
||||
audio_model = text_reader(model)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Result==
|
||||
The model with the most downloads is damo-vilab/text-to-video-ms-1.7b.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and generates the following audio.
|
||||
|
||||
| **Audio** |
|
||||
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| <audio controls><source src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/damo.wav" type="audio/wav"/> |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on the LLM, some are quite brittle and require very exact prompts in order to work well. Having a well-defined
|
||||
name and description of the tool is paramount to having it be leveraged by the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Replacing existing tools
|
||||
|
||||
Replacing existing tools can be done simply by assigning a new item to the agent's toolbox. Here's how one would do so:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent, load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder")
|
||||
agent.toolbox["image-transformation"] = load_tool("diffusers/controlnet-canny-tool")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Beware when replacing tools with others! This will also adjust the agent's prompt. This can be good if you have a better
|
||||
prompt suited for the task, but it can also result in your tool being selected way more than others or for other
|
||||
tools to be selected instead of the one you have defined.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Leveraging gradio-tools
|
||||
|
||||
[gradio-tools](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools) is a powerful library that allows using Hugging
|
||||
Face Spaces as tools. It supports many existing Spaces as well as custom Spaces to be designed with it.
|
||||
|
||||
We offer support for `gradio_tools` by using the `Tool.from_gradio` method. For example, we want to take
|
||||
advantage of the `StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool` tool offered in the `gradio-tools` toolkit so as to
|
||||
improve our prompts and generate better images.
|
||||
|
||||
We first import the tool from `gradio_tools` and instantiate it:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from gradio_tools import StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool
|
||||
|
||||
gradio_tool = StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We pass that instance to the `Tool.from_gradio` method:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import Tool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = Tool.from_gradio(gradio_tool)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can manage it exactly as we would a usual custom tool. We leverage it to improve our prompt
|
||||
` a rabbit wearing a space suit`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder", additional_tools=[tool])
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Generate an image of the `prompt` after improving it.", prompt="A rabbit wearing a space suit")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The model adequately leverages the tool:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tools: `StableDiffusionPromptGenerator` to improve the prompt, then `image_generator` to generate an image according to the improved prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
improved_prompt = StableDiffusionPromptGenerator(prompt)
|
||||
print(f"The improved prompt is {improved_prompt}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator(improved_prompt)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Before finally generating the image:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rabbit.png">
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
gradio-tools requires *textual* inputs and outputs, even when working with different modalities. This implementation
|
||||
works with image and audio objects. The two are currently incompatible, but will rapidly become compatible as we
|
||||
work to improve the support.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Future compatibility with Langchain
|
||||
|
||||
We love Langchain and think it has a very compelling suite of tools. In order to handle these tools,
|
||||
Langchain requires *textual* inputs and outputs, even when working with different modalities.
|
||||
This is often the serialized version (i.e., saved to disk) of the objects.
|
||||
|
||||
This difference means that multi-modality isn't handled between transformers-agents and langchain.
|
||||
We aim for this limitation to be resolved in future versions, and welcome any help from avid langchain
|
||||
users to help us achieve this compatibility.
|
||||
|
||||
We would love to have better support. If you would like to help, please
|
||||
[open an issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/new) and share what you have in mind.
|
||||
339
docs/source/en/debugging.md
Normal file
339
docs/source/en/debugging.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,339 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Debugging
|
||||
|
||||
## Multi-GPU Network Issues Debug
|
||||
|
||||
When training or inferencing with `DistributedDataParallel` and multiple GPU, if you run into issue of inter-communication between processes and/or nodes, you can use the following script to diagnose network issues.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/huggingface/transformers/main/scripts/distributed/torch-distributed-gpu-test.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For example to test how 2 GPUs interact do:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node 2 --nnodes 1 torch-distributed-gpu-test.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
If both processes can talk to each and allocate GPU memory each will print an OK status.
|
||||
|
||||
For more GPUs or nodes adjust the arguments in the script.
|
||||
|
||||
You will find a lot more details inside the diagnostics script and even a recipe to how you could run it in a SLURM environment.
|
||||
|
||||
An additional level of debug is to add `NCCL_DEBUG=INFO` environment variable as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
NCCL_DEBUG=INFO python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node 2 --nnodes 1 torch-distributed-gpu-test.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will dump a lot of NCCL-related debug information, which you can then search online if you find that some problems are reported. Or if you're not sure how to interpret the output you can share the log file in an Issue.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Underflow and Overflow Detection
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
This feature is currently available for PyTorch-only.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For multi-GPU training it requires DDP (`torch.distributed.launch`).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
This feature can be used with any `nn.Module`-based model.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If you start getting `loss=NaN` or the model inhibits some other abnormal behavior due to `inf` or `nan` in
|
||||
activations or weights one needs to discover where the first underflow or overflow happens and what led to it. Luckily
|
||||
you can accomplish that easily by activating a special module that will do the detection automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're using [`Trainer`], you just need to add:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--debug underflow_overflow
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
to the normal command line arguments, or pass `debug="underflow_overflow"` when creating the
|
||||
[`TrainingArguments`] object.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're using your own training loop or another Trainer you can accomplish the same with:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers.debug_utils import DebugUnderflowOverflow
|
||||
|
||||
debug_overflow = DebugUnderflowOverflow(model)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[`~debug_utils.DebugUnderflowOverflow`] inserts hooks into the model that immediately after each
|
||||
forward call will test input and output variables and also the corresponding module's weights. As soon as `inf` or
|
||||
`nan` is detected in at least one element of the activations or weights, the program will assert and print a report
|
||||
like this (this was caught with `google/mt5-small` under fp16 mixed precision):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Detected inf/nan during batch_number=0
|
||||
Last 21 forward frames:
|
||||
abs min abs max metadata
|
||||
encoder.block.1.layer.1.DenseReluDense.dropout Dropout
|
||||
0.00e+00 2.57e+02 input[0]
|
||||
0.00e+00 2.85e+02 output
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.0 T5LayerSelfAttention
|
||||
6.78e-04 3.15e+03 input[0]
|
||||
2.65e-04 3.42e+03 output[0]
|
||||
None output[1]
|
||||
2.25e-01 1.00e+04 output[2]
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.layer_norm T5LayerNorm
|
||||
8.69e-02 4.18e-01 weight
|
||||
2.65e-04 3.42e+03 input[0]
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi_0 Linear
|
||||
2.17e-07 4.50e+00 weight
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
|
||||
2.68e-06 3.70e+01 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi_1 Linear
|
||||
8.08e-07 2.66e+01 weight
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
|
||||
1.27e-04 2.37e+02 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.dropout Dropout
|
||||
0.00e+00 8.76e+03 input[0]
|
||||
0.00e+00 9.74e+03 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wo Linear
|
||||
1.01e-06 6.44e+00 weight
|
||||
0.00e+00 9.74e+03 input[0]
|
||||
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense T5DenseGatedGeluDense
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
|
||||
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.dropout Dropout
|
||||
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 input[0]
|
||||
0.00e+00 inf output
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The example output has been trimmed in the middle for brevity.
|
||||
|
||||
The second column shows the value of the absolute largest element, so if you have a closer look at the last few frames,
|
||||
the inputs and outputs were in the range of `1e4`. So when this training was done under fp16 mixed precision the very
|
||||
last step overflowed (since under `fp16` the largest number before `inf` is `64e3`). To avoid overflows under
|
||||
`fp16` the activations must remain way below `1e4`, because `1e4 * 1e4 = 1e8` so any matrix multiplication with
|
||||
large activations is going to lead to a numerical overflow condition.
|
||||
|
||||
At the very start of the trace you can discover at which batch number the problem occurred (here `Detected inf/nan during batch_number=0` means the problem occurred on the first batch).
|
||||
|
||||
Each reported frame starts by declaring the fully qualified entry for the corresponding module this frame is reporting
|
||||
for. If we look just at this frame:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.layer_norm T5LayerNorm
|
||||
8.69e-02 4.18e-01 weight
|
||||
2.65e-04 3.42e+03 input[0]
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 output
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here, `encoder.block.2.layer.1.layer_norm` indicates that it was a layer norm for the first layer, of the second
|
||||
block of the encoder. And the specific calls of the `forward` is `T5LayerNorm`.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's look at the last few frames of that report:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Detected inf/nan during batch_number=0
|
||||
Last 21 forward frames:
|
||||
abs min abs max metadata
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi_0 Linear
|
||||
2.17e-07 4.50e+00 weight
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
|
||||
2.68e-06 3.70e+01 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi_1 Linear
|
||||
8.08e-07 2.66e+01 weight
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
|
||||
1.27e-04 2.37e+02 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wo Linear
|
||||
1.01e-06 6.44e+00 weight
|
||||
0.00e+00 9.74e+03 input[0]
|
||||
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense T5DenseGatedGeluDense
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
|
||||
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.dropout Dropout
|
||||
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 input[0]
|
||||
0.00e+00 inf output
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The last frame reports for `Dropout.forward` function with the first entry for the only input and the second for the
|
||||
only output. You can see that it was called from an attribute `dropout` inside `DenseReluDense` class. We can see
|
||||
that it happened during the first layer, of the 2nd block, during the very first batch. Finally, the absolute largest
|
||||
input elements was `6.27e+04` and same for the output was `inf`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can see here, that `T5DenseGatedGeluDense.forward` resulted in output activations, whose absolute max value was
|
||||
around 62.7K, which is very close to fp16's top limit of 64K. In the next frame we have `Dropout` which renormalizes
|
||||
the weights, after it zeroed some of the elements, which pushes the absolute max value to more than 64K, and we get an
|
||||
overflow (`inf`).
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see it's the previous frames that we need to look into when the numbers start going into very large for fp16
|
||||
numbers.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's match the report to the code from `models/t5/modeling_t5.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class T5DenseGatedGeluDense(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.wi_0 = nn.Linear(config.d_model, config.d_ff, bias=False)
|
||||
self.wi_1 = nn.Linear(config.d_model, config.d_ff, bias=False)
|
||||
self.wo = nn.Linear(config.d_ff, config.d_model, bias=False)
|
||||
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout_rate)
|
||||
self.gelu_act = ACT2FN["gelu_new"]
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, hidden_states):
|
||||
hidden_gelu = self.gelu_act(self.wi_0(hidden_states))
|
||||
hidden_linear = self.wi_1(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = hidden_gelu * hidden_linear
|
||||
hidden_states = self.dropout(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = self.wo(hidden_states)
|
||||
return hidden_states
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now it's easy to see the `dropout` call, and all the previous calls as well.
|
||||
|
||||
Since the detection is happening in a forward hook, these reports are printed immediately after each `forward`
|
||||
returns.
|
||||
|
||||
Going back to the full report, to act on it and to fix the problem, we need to go a few frames up where the numbers
|
||||
started to go up and most likely switch to the `fp32` mode here, so that the numbers don't overflow when multiplied
|
||||
or summed up. Of course, there might be other solutions. For example, we could turn off `amp` temporarily if it's
|
||||
enabled, after moving the original `forward` into a helper wrapper, like so:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def _forward(self, hidden_states):
|
||||
hidden_gelu = self.gelu_act(self.wi_0(hidden_states))
|
||||
hidden_linear = self.wi_1(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = hidden_gelu * hidden_linear
|
||||
hidden_states = self.dropout(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = self.wo(hidden_states)
|
||||
return hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, hidden_states):
|
||||
if torch.is_autocast_enabled():
|
||||
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast(enabled=False):
|
||||
return self._forward(hidden_states)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return self._forward(hidden_states)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Since the automatic detector only reports on inputs and outputs of full frames, once you know where to look, you may
|
||||
want to analyse the intermediary stages of any specific `forward` function as well. In such a case you can use the
|
||||
`detect_overflow` helper function to inject the detector where you want it, for example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from debug_utils import detect_overflow
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class T5LayerFF(nn.Module):
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, hidden_states):
|
||||
forwarded_states = self.layer_norm(hidden_states)
|
||||
detect_overflow(forwarded_states, "after layer_norm")
|
||||
forwarded_states = self.DenseReluDense(forwarded_states)
|
||||
detect_overflow(forwarded_states, "after DenseReluDense")
|
||||
return hidden_states + self.dropout(forwarded_states)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can see that we added 2 of these and now we track if `inf` or `nan` for `forwarded_states` was detected
|
||||
somewhere in between.
|
||||
|
||||
Actually, the detector already reports these because each of the calls in the example above is a `nn.Module`, but
|
||||
let's say if you had some local direct calculations this is how you'd do that.
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, if you're instantiating the debugger in your own code, you can adjust the number of frames printed from
|
||||
its default, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers.debug_utils import DebugUnderflowOverflow
|
||||
|
||||
debug_overflow = DebugUnderflowOverflow(model, max_frames_to_save=100)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Specific batch absolute min and max value tracing
|
||||
|
||||
The same debugging class can be used for per-batch tracing with the underflow/overflow detection feature turned off.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's say you want to watch the absolute min and max values for all the ingredients of each `forward` call of a given
|
||||
batch, and only do that for batches 1 and 3. Then you instantiate this class as:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
debug_overflow = DebugUnderflowOverflow(model, trace_batch_nums=[1, 3])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And now full batches 1 and 3 will be traced using the same format as the underflow/overflow detector does.
|
||||
|
||||
Batches are 0-indexed.
|
||||
|
||||
This is helpful if you know that the program starts misbehaving after a certain batch number, so you can fast-forward
|
||||
right to that area. Here is a sample truncated output for such configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
*** Starting batch number=1 ***
|
||||
abs min abs max metadata
|
||||
shared Embedding
|
||||
1.01e-06 7.92e+02 weight
|
||||
0.00e+00 2.47e+04 input[0]
|
||||
5.36e-05 7.92e+02 output
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
decoder.dropout Dropout
|
||||
1.60e-07 2.27e+01 input[0]
|
||||
0.00e+00 2.52e+01 output
|
||||
decoder T5Stack
|
||||
not a tensor output
|
||||
lm_head Linear
|
||||
1.01e-06 7.92e+02 weight
|
||||
0.00e+00 1.11e+00 input[0]
|
||||
6.06e-02 8.39e+01 output
|
||||
T5ForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
not a tensor output
|
||||
|
||||
*** Starting batch number=3 ***
|
||||
abs min abs max metadata
|
||||
shared Embedding
|
||||
1.01e-06 7.92e+02 weight
|
||||
0.00e+00 2.78e+04 input[0]
|
||||
5.36e-05 7.92e+02 output
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here you will get a huge number of frames dumped - as many as there were forward calls in your model, so it may or may
|
||||
not what you want, but sometimes it can be easier to use for debugging purposes than a normal debugger. For example, if
|
||||
a problem starts happening at batch number 150. So you can dump traces for batches 149 and 150 and compare where
|
||||
numbers started to diverge.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also specify the batch number after which to stop the training, with:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
debug_overflow = DebugUnderflowOverflow(model, trace_batch_nums=[1, 3], abort_after_batch_num=3)
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,335 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Debugging
|
||||
|
||||
## Multi-GPU Network Issues Debug
|
||||
|
||||
When training or inferencing with `DistributedDataParallel` and multiple GPU, if you run into issue of inter-communication between processes and/or nodes, you can use the following script to diagnose network issues.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/huggingface/transformers/main/scripts/distributed/torch-distributed-gpu-test.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For example to test how 2 GPUs interact do:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node 2 --nnodes 1 torch-distributed-gpu-test.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
If both processes can talk to each and allocate GPU memory each will print an OK status.
|
||||
|
||||
For more GPUs or nodes adjust the arguments in the script.
|
||||
|
||||
You will find a lot more details inside the diagnostics script and even a recipe to how you could run it in a SLURM environment.
|
||||
|
||||
An additional level of debug is to add `NCCL_DEBUG=INFO` environment variable as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
NCCL_DEBUG=INFO python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node 2 --nnodes 1 torch-distributed-gpu-test.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will dump a lot of NCCL-related debug information, which you can then search online if you find that some problems are reported. Or if you're not sure how to interpret the output you can share the log file in an Issue.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Underflow and Overflow Detection
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
This feature is currently available for PyTorch-only.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For multi-GPU training it requires DDP (`torch.distributed.launch`).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
This feature can be used with any `nn.Module`-based model.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If you start getting `loss=NaN` or the model inhibits some other abnormal behavior due to `inf` or `nan` in
|
||||
activations or weights one needs to discover where the first underflow or overflow happens and what led to it. Luckily
|
||||
you can accomplish that easily by activating a special module that will do the detection automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're using [`Trainer`], you just need to add:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
--debug underflow_overflow
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
to the normal command line arguments, or pass `debug="underflow_overflow"` when creating the
|
||||
[`TrainingArguments`] object.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're using your own training loop or another Trainer you can accomplish the same with:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers.debug_utils import DebugUnderflowOverflow
|
||||
|
||||
debug_overflow = DebugUnderflowOverflow(model)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[`~debug_utils.DebugUnderflowOverflow`] inserts hooks into the model that immediately after each
|
||||
forward call will test input and output variables and also the corresponding module's weights. As soon as `inf` or
|
||||
`nan` is detected in at least one element of the activations or weights, the program will assert and print a report
|
||||
like this (this was caught with `google/mt5-small` under fp16 mixed precision):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Detected inf/nan during batch_number=0
|
||||
Last 21 forward frames:
|
||||
abs min abs max metadata
|
||||
encoder.block.1.layer.1.DenseReluDense.dropout Dropout
|
||||
0.00e+00 2.57e+02 input[0]
|
||||
0.00e+00 2.85e+02 output
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.0 T5LayerSelfAttention
|
||||
6.78e-04 3.15e+03 input[0]
|
||||
2.65e-04 3.42e+03 output[0]
|
||||
None output[1]
|
||||
2.25e-01 1.00e+04 output[2]
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.layer_norm T5LayerNorm
|
||||
8.69e-02 4.18e-01 weight
|
||||
2.65e-04 3.42e+03 input[0]
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi_0 Linear
|
||||
2.17e-07 4.50e+00 weight
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
|
||||
2.68e-06 3.70e+01 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi_1 Linear
|
||||
8.08e-07 2.66e+01 weight
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
|
||||
1.27e-04 2.37e+02 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.dropout Dropout
|
||||
0.00e+00 8.76e+03 input[0]
|
||||
0.00e+00 9.74e+03 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wo Linear
|
||||
1.01e-06 6.44e+00 weight
|
||||
0.00e+00 9.74e+03 input[0]
|
||||
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense T5DenseGatedGeluDense
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
|
||||
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.dropout Dropout
|
||||
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 input[0]
|
||||
0.00e+00 inf output
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The example output has been trimmed in the middle for brevity.
|
||||
|
||||
The second column shows the value of the absolute largest element, so if you have a closer look at the last few frames,
|
||||
the inputs and outputs were in the range of `1e4`. So when this training was done under fp16 mixed precision the very
|
||||
last step overflowed (since under `fp16` the largest number before `inf` is `64e3`). To avoid overflows under
|
||||
`fp16` the activations must remain way below `1e4`, because `1e4 * 1e4 = 1e8` so any matrix multiplication with
|
||||
large activations is going to lead to a numerical overflow condition.
|
||||
|
||||
At the very start of the trace you can discover at which batch number the problem occurred (here `Detected inf/nan during batch_number=0` means the problem occurred on the first batch).
|
||||
|
||||
Each reported frame starts by declaring the fully qualified entry for the corresponding module this frame is reporting
|
||||
for. If we look just at this frame:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.layer_norm T5LayerNorm
|
||||
8.69e-02 4.18e-01 weight
|
||||
2.65e-04 3.42e+03 input[0]
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 output
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here, `encoder.block.2.layer.1.layer_norm` indicates that it was a layer norm for the first layer, of the second
|
||||
block of the encoder. And the specific calls of the `forward` is `T5LayerNorm`.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's look at the last few frames of that report:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Detected inf/nan during batch_number=0
|
||||
Last 21 forward frames:
|
||||
abs min abs max metadata
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi_0 Linear
|
||||
2.17e-07 4.50e+00 weight
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
|
||||
2.68e-06 3.70e+01 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi_1 Linear
|
||||
8.08e-07 2.66e+01 weight
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
|
||||
1.27e-04 2.37e+02 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wo Linear
|
||||
1.01e-06 6.44e+00 weight
|
||||
0.00e+00 9.74e+03 input[0]
|
||||
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.DenseReluDense T5DenseGatedGeluDense
|
||||
1.79e-06 4.65e+00 input[0]
|
||||
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 output
|
||||
encoder.block.2.layer.1.dropout Dropout
|
||||
3.18e-04 6.27e+04 input[0]
|
||||
0.00e+00 inf output
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The last frame reports for `Dropout.forward` function with the first entry for the only input and the second for the
|
||||
only output. You can see that it was called from an attribute `dropout` inside `DenseReluDense` class. We can see
|
||||
that it happened during the first layer, of the 2nd block, during the very first batch. Finally, the absolute largest
|
||||
input elements was `6.27e+04` and same for the output was `inf`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can see here, that `T5DenseGatedGeluDense.forward` resulted in output activations, whose absolute max value was
|
||||
around 62.7K, which is very close to fp16's top limit of 64K. In the next frame we have `Dropout` which renormalizes
|
||||
the weights, after it zeroed some of the elements, which pushes the absolute max value to more than 64K, and we get an
|
||||
overflow (`inf`).
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see it's the previous frames that we need to look into when the numbers start going into very large for fp16
|
||||
numbers.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's match the report to the code from `models/t5/modeling_t5.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class T5DenseGatedGeluDense(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.wi_0 = nn.Linear(config.d_model, config.d_ff, bias=False)
|
||||
self.wi_1 = nn.Linear(config.d_model, config.d_ff, bias=False)
|
||||
self.wo = nn.Linear(config.d_ff, config.d_model, bias=False)
|
||||
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.dropout_rate)
|
||||
self.gelu_act = ACT2FN["gelu_new"]
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, hidden_states):
|
||||
hidden_gelu = self.gelu_act(self.wi_0(hidden_states))
|
||||
hidden_linear = self.wi_1(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = hidden_gelu * hidden_linear
|
||||
hidden_states = self.dropout(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = self.wo(hidden_states)
|
||||
return hidden_states
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now it's easy to see the `dropout` call, and all the previous calls as well.
|
||||
|
||||
Since the detection is happening in a forward hook, these reports are printed immediately after each `forward`
|
||||
returns.
|
||||
|
||||
Going back to the full report, to act on it and to fix the problem, we need to go a few frames up where the numbers
|
||||
started to go up and most likely switch to the `fp32` mode here, so that the numbers don't overflow when multiplied
|
||||
or summed up. Of course, there might be other solutions. For example, we could turn off `amp` temporarily if it's
|
||||
enabled, after moving the original `forward` into a helper wrapper, like so:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def _forward(self, hidden_states):
|
||||
hidden_gelu = self.gelu_act(self.wi_0(hidden_states))
|
||||
hidden_linear = self.wi_1(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = hidden_gelu * hidden_linear
|
||||
hidden_states = self.dropout(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = self.wo(hidden_states)
|
||||
return hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, hidden_states):
|
||||
if torch.is_autocast_enabled():
|
||||
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast(enabled=False):
|
||||
return self._forward(hidden_states)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return self._forward(hidden_states)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Since the automatic detector only reports on inputs and outputs of full frames, once you know where to look, you may
|
||||
want to analyse the intermediary stages of any specific `forward` function as well. In such a case you can use the
|
||||
`detect_overflow` helper function to inject the detector where you want it, for example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from debug_utils import detect_overflow
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class T5LayerFF(nn.Module):
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, hidden_states):
|
||||
forwarded_states = self.layer_norm(hidden_states)
|
||||
detect_overflow(forwarded_states, "after layer_norm")
|
||||
forwarded_states = self.DenseReluDense(forwarded_states)
|
||||
detect_overflow(forwarded_states, "after DenseReluDense")
|
||||
return hidden_states + self.dropout(forwarded_states)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can see that we added 2 of these and now we track if `inf` or `nan` for `forwarded_states` was detected
|
||||
somewhere in between.
|
||||
|
||||
Actually, the detector already reports these because each of the calls in the example above is a `nn.Module`, but
|
||||
let's say if you had some local direct calculations this is how you'd do that.
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, if you're instantiating the debugger in your own code, you can adjust the number of frames printed from
|
||||
its default, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers.debug_utils import DebugUnderflowOverflow
|
||||
|
||||
debug_overflow = DebugUnderflowOverflow(model, max_frames_to_save=100)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Specific batch absolute min and max value tracing
|
||||
|
||||
The same debugging class can be used for per-batch tracing with the underflow/overflow detection feature turned off.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's say you want to watch the absolute min and max values for all the ingredients of each `forward` call of a given
|
||||
batch, and only do that for batches 1 and 3. Then you instantiate this class as:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
debug_overflow = DebugUnderflowOverflow(model, trace_batch_nums=[1, 3])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And now full batches 1 and 3 will be traced using the same format as the underflow/overflow detector does.
|
||||
|
||||
Batches are 0-indexed.
|
||||
|
||||
This is helpful if you know that the program starts misbehaving after a certain batch number, so you can fast-forward
|
||||
right to that area. Here is a sample truncated output for such configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
*** Starting batch number=1 ***
|
||||
abs min abs max metadata
|
||||
shared Embedding
|
||||
1.01e-06 7.92e+02 weight
|
||||
0.00e+00 2.47e+04 input[0]
|
||||
5.36e-05 7.92e+02 output
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
decoder.dropout Dropout
|
||||
1.60e-07 2.27e+01 input[0]
|
||||
0.00e+00 2.52e+01 output
|
||||
decoder T5Stack
|
||||
not a tensor output
|
||||
lm_head Linear
|
||||
1.01e-06 7.92e+02 weight
|
||||
0.00e+00 1.11e+00 input[0]
|
||||
6.06e-02 8.39e+01 output
|
||||
T5ForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
not a tensor output
|
||||
|
||||
*** Starting batch number=3 ***
|
||||
abs min abs max metadata
|
||||
shared Embedding
|
||||
1.01e-06 7.92e+02 weight
|
||||
0.00e+00 2.78e+04 input[0]
|
||||
5.36e-05 7.92e+02 output
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here you will get a huge number of frames dumped - as many as there were forward calls in your model, so it may or may
|
||||
not what you want, but sometimes it can be easier to use for debugging purposes than a normal debugger. For example, if
|
||||
a problem starts happening at batch number 150. So you can dump traces for batches 149 and 150 and compare where
|
||||
numbers started to diverge.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also specify the batch number after which to stop the training, with:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
debug_overflow = DebugUnderflowOverflow(model, trace_batch_nums=[1, 3], abort_after_batch_num=3)
|
||||
```
|
||||
74
docs/source/en/fast_tokenizers.md
Normal file
74
docs/source/en/fast_tokenizers.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Use tokenizers from 🤗 Tokenizers
|
||||
|
||||
The [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`] depends on the [🤗 Tokenizers](https://huggingface.co/docs/tokenizers) library. The tokenizers obtained from the 🤗 Tokenizers library can be
|
||||
loaded very simply into 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
Before getting in the specifics, let's first start by creating a dummy tokenizer in a few lines:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from tokenizers import Tokenizer
|
||||
>>> from tokenizers.models import BPE
|
||||
>>> from tokenizers.trainers import BpeTrainer
|
||||
>>> from tokenizers.pre_tokenizers import Whitespace
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = Tokenizer(BPE(unk_token="[UNK]"))
|
||||
>>> trainer = BpeTrainer(special_tokens=["[UNK]", "[CLS]", "[SEP]", "[PAD]", "[MASK]"])
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.pre_tokenizer = Whitespace()
|
||||
>>> files = [...]
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.train(files, trainer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We now have a tokenizer trained on the files we defined. We can either continue using it in that runtime, or save it to
|
||||
a JSON file for future re-use.
|
||||
|
||||
## Loading directly from the tokenizer object
|
||||
|
||||
Let's see how to leverage this tokenizer object in the 🤗 Transformers library. The
|
||||
[`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`] class allows for easy instantiation, by accepting the instantiated
|
||||
*tokenizer* object as an argument:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PreTrainedTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
>>> fast_tokenizer = PreTrainedTokenizerFast(tokenizer_object=tokenizer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This object can now be used with all the methods shared by the 🤗 Transformers tokenizers! Head to [the tokenizer
|
||||
page](main_classes/tokenizer) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
## Loading from a JSON file
|
||||
|
||||
In order to load a tokenizer from a JSON file, let's first start by saving our tokenizer:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.save("tokenizer.json")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The path to which we saved this file can be passed to the [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`] initialization
|
||||
method using the `tokenizer_file` parameter:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PreTrainedTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
>>> fast_tokenizer = PreTrainedTokenizerFast(tokenizer_file="tokenizer.json")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This object can now be used with all the methods shared by the 🤗 Transformers tokenizers! Head to [the tokenizer
|
||||
page](main_classes/tokenizer) for more information.
|
||||
@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Use tokenizers from 🤗 Tokenizers
|
||||
|
||||
The [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`] depends on the [🤗 Tokenizers](https://huggingface.co/docs/tokenizers) library. The tokenizers obtained from the 🤗 Tokenizers library can be
|
||||
loaded very simply into 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
Before getting in the specifics, let's first start by creating a dummy tokenizer in a few lines:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from tokenizers import Tokenizer
|
||||
>>> from tokenizers.models import BPE
|
||||
>>> from tokenizers.trainers import BpeTrainer
|
||||
>>> from tokenizers.pre_tokenizers import Whitespace
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = Tokenizer(BPE(unk_token="[UNK]"))
|
||||
>>> trainer = BpeTrainer(special_tokens=["[UNK]", "[CLS]", "[SEP]", "[PAD]", "[MASK]"])
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.pre_tokenizer = Whitespace()
|
||||
>>> files = [...]
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.train(files, trainer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We now have a tokenizer trained on the files we defined. We can either continue using it in that runtime, or save it to
|
||||
a JSON file for future re-use.
|
||||
|
||||
## Loading directly from the tokenizer object
|
||||
|
||||
Let's see how to leverage this tokenizer object in the 🤗 Transformers library. The
|
||||
[`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`] class allows for easy instantiation, by accepting the instantiated
|
||||
*tokenizer* object as an argument:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PreTrainedTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
>>> fast_tokenizer = PreTrainedTokenizerFast(tokenizer_object=tokenizer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This object can now be used with all the methods shared by the 🤗 Transformers tokenizers! Head to [the tokenizer
|
||||
page](main_classes/tokenizer) for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
## Loading from a JSON file
|
||||
|
||||
In order to load a tokenizer from a JSON file, let's first start by saving our tokenizer:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.save("tokenizer.json")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The path to which we saved this file can be passed to the [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`] initialization
|
||||
method using the `tokenizer_file` parameter:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PreTrainedTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
>>> fast_tokenizer = PreTrainedTokenizerFast(tokenizer_file="tokenizer.json")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This object can now be used with all the methods shared by the 🤗 Transformers tokenizers! Head to [the tokenizer
|
||||
page](main_classes/tokenizer) for more information.
|
||||
385
docs/source/en/generation_strategies.md
Normal file
385
docs/source/en/generation_strategies.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,385 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Text generation strategies
|
||||
|
||||
Text generation is essential to many NLP tasks, such as open-ended text generation, summarization, translation, and
|
||||
more. It also plays a role in a variety of mixed-modality applications that have text as an output like speech-to-text
|
||||
and vision-to-text. Some of the models that can generate text include
|
||||
GPT2, XLNet, OpenAI GPT, CTRL, TransformerXL, XLM, Bart, T5, GIT, Whisper.
|
||||
|
||||
Check out a few examples that use [`~transformers.generation_utils.GenerationMixin.generate`] method to produce
|
||||
text outputs for different tasks:
|
||||
* [Text summarization](./tasks/summarization#inference)
|
||||
* [Image captioning](./model_doc/git#transformers.GitForCausalLM.forward.example)
|
||||
* [Audio transcription](./model_doc/whisper#transformers.WhisperForConditionalGeneration.forward.example)
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the inputs to the generate method depend on the model's modality. They are returned by the model's preprocessor
|
||||
class, such as AutoTokenizer or AutoProcessor. If a model's preprocessor creates more than one kind of input, pass all
|
||||
the inputs to generate(). You can learn more about the individual model's preprocessor in the corresponding model's documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
The process of selecting output tokens to generate text is known as decoding, and you can customize the decoding strategy
|
||||
that the `generate()` method will use. Modifying a decoding strategy does not change the values of any trainable parameters.
|
||||
However, it can have a noticeable impact on the quality of the generated output. It can help reduce repetition in the text
|
||||
and make it more coherent.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide describes:
|
||||
* default generation configuration
|
||||
* common decoding strategies and their main parameters
|
||||
* saving and sharing custom generation configurations with your fine-tuned model on 🤗 Hub
|
||||
|
||||
## Default text generation configuration
|
||||
|
||||
A decoding strategy for a model is defined in its generation configuration. When using pre-trained models for inference
|
||||
within a [`pipeline`], the models call the `PreTrainedModel.generate()` method that applies a default generation
|
||||
configuration under the hood. The default configuration is also used when no custom configuration has been saved with
|
||||
the model.
|
||||
|
||||
When you load a model explicitly, you can inspect the generation configuration that comes with it through
|
||||
`model.generation_config`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("distilgpt2")
|
||||
>>> model.generation_config
|
||||
GenerationConfig {
|
||||
"_from_model_config": true,
|
||||
"bos_token_id": 50256,
|
||||
"eos_token_id": 50256,
|
||||
"transformers_version": "4.26.0.dev0"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Printing out the `model.generation_config` reveals only the values that are different from the default generation
|
||||
configuration, and does not list any of the default values.
|
||||
|
||||
The default generation configuration limits the size of the output combined with the input prompt to a maximum of 20
|
||||
tokens to avoid running into resource limitations. The default decoding strategy is greedy search, which is the simplest decoding strategy that picks a token with the highest probability as the next token. For many tasks
|
||||
and small output sizes this works well. However, when used to generate longer outputs, greedy search can start
|
||||
producing highly repetitive results.
|
||||
|
||||
## Customize text generation
|
||||
|
||||
You can override any `generation_config` by passing the parameters and their values directly to the [`generate`] method:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> my_model.generate(**inputs, num_beams=4, do_sample=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Even if the default decoding strategy mostly works for your task, you can still tweak a few things. Some of the
|
||||
commonly adjusted parameters include:
|
||||
|
||||
- `max_new_tokens`: the maximum number of tokens to generate. In other words, the size of the output sequence, not
|
||||
including the tokens in the prompt.
|
||||
- `num_beams`: by specifying a number of beams higher than 1, you are effectively switching from greedy search to
|
||||
beam search. This strategy evaluates several hypotheses at each time step and eventually chooses the hypothesis that
|
||||
has the overall highest probability for the entire sequence. This has the advantage of identifying high-probability
|
||||
sequences that start with a lower probability initial tokens and would've been ignored by the greedy search.
|
||||
- `do_sample`: if set to `True`, this parameter enables decoding strategies such as multinomial sampling, beam-search
|
||||
multinomial sampling, Top-K sampling and Top-p sampling. All these strategies select the next token from the probability
|
||||
distribution over the entire vocabulary with various strategy-specific adjustments.
|
||||
- `num_return_sequences`: the number of sequence candidates to return for each input. This options is only available for
|
||||
the decoding strategies that support multiple sequence candidates, e.g. variations of beam search and sampling. Decoding
|
||||
strategies like greedy search and contrastive search return a single output sequence.
|
||||
|
||||
## Save a custom decoding strategy with your model
|
||||
|
||||
If you would like to share your fine-tuned model with a specific generation configuration, you can:
|
||||
* Create a [`GenerationConfig`] class instance
|
||||
* Specify the decoding strategy parameters
|
||||
* Save your generation configuration with [`GenerationConfig.save_pretrained`], making sure to leave its `config_file_name` argument empty
|
||||
* Set `push_to_hub` to `True` to upload your config to the model's repo
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, GenerationConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("my_account/my_model")
|
||||
>>> generation_config = GenerationConfig(
|
||||
... max_new_tokens=50, do_sample=True, top_k=50, eos_token_id=model.config.eos_token_id
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> generation_config.save_pretrained("my_account/my_model", push_to_hub=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also store several generation configurations in a single directory, making use of the `config_file_name`
|
||||
argument in [`GenerationConfig.save_pretrained`]. You can later instantiate them with [`GenerationConfig.from_pretrained`]. This is useful if you want to
|
||||
store several generation configurations for a single model (e.g. one for creative text generation with sampling, and
|
||||
one for summarization with beam search). You must have the right Hub permissions to add configuration files to a model.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer, GenerationConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("t5-small")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("t5-small")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> translation_generation_config = GenerationConfig(
|
||||
... num_beams=4,
|
||||
... early_stopping=True,
|
||||
... decoder_start_token_id=0,
|
||||
... eos_token_id=model.config.eos_token_id,
|
||||
... pad_token=model.config.pad_token_id,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
|
||||
>>> translation_generation_config.save_pretrained("t5-small", "translation_generation_config.json", push_to_hub=True)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # You could then use the named generation config file to parameterize generation
|
||||
>>> generation_config = GenerationConfig.from_pretrained("t5-small", "translation_generation_config.json")
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer("translate English to French: Configuration files are easy to use!", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, generation_config=generation_config)
|
||||
>>> print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
['Les fichiers de configuration sont faciles à utiliser !']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Streaming
|
||||
|
||||
The `generate()` supports streaming, through its `streamer` input. The `streamer` input is compatible any instance
|
||||
from a class that has the following methods: `put()` and `end()`. Internally, `put()` is used to push new tokens and
|
||||
`end()` is used to flag the end of text generation.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
The API for the streamer classes is still under development and may change in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In practice, you can craft your own streaming class for all sorts of purposes! We also have basic streaming classes
|
||||
ready for you to use. For example, you can use the [`TextStreamer`] class to stream the output of `generate()` into
|
||||
your screen, one word at a time:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, TextStreamer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tok = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("gpt2")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("gpt2")
|
||||
>>> inputs = tok(["An increasing sequence: one,"], return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> streamer = TextStreamer(tok)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # Despite returning the usual output, the streamer will also print the generated text to stdout.
|
||||
>>> _ = model.generate(**inputs, streamer=streamer, max_new_tokens=20)
|
||||
An increasing sequence: one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, nine, ten, eleven,
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Decoding strategies
|
||||
|
||||
Certain combinations of the `generate()` parameters, and ultimately `generation_config`, can be used to enable specific
|
||||
decoding strategies. If you are new to this concept, we recommend reading [this blog post that illustrates how common decoding strategies work](https://huggingface.co/blog/how-to-generate).
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we'll show some of the parameters that control the decoding strategies and illustrate how you can use them.
|
||||
|
||||
### Greedy Search
|
||||
|
||||
[`generate`] uses greedy search decoding by default so you don't have to pass any parameters to enable it. This means the parameters `num_beams` is set to 1 and `do_sample=False`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "I look forward to"
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "distilgpt2"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
['I look forward to seeing you all again!\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Contrastive search
|
||||
|
||||
The contrastive search decoding strategy was proposed in the 2022 paper [A Contrastive Framework for Neural Text Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.06417).
|
||||
It demonstrates superior results for generating non-repetitive yet coherent long outputs. To learn how contrastive search
|
||||
works, check out [this blog post](https://huggingface.co/blog/introducing-csearch).
|
||||
The two main parameters that enable and control the behavior of contrastive search are `penalty_alpha` and `top_k`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "gpt2-large"
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "Hugging Face Company is"
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, penalty_alpha=0.6, top_k=4, max_new_tokens=100)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
['Hugging Face Company is a family owned and operated business. \
|
||||
We pride ourselves on being the best in the business and our customer service is second to none.\
|
||||
\n\nIf you have any questions about our products or services, feel free to contact us at any time.\
|
||||
We look forward to hearing from you!']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Multinomial sampling
|
||||
|
||||
As opposed to greedy search that always chooses a token with the highest probability as the
|
||||
next token, multinomial sampling (also called ancestral sampling) randomly selects the next token based on the probability distribution over the entire
|
||||
vocabulary given by the model. Every token with a non-zero probability has a chance of being selected, thus reducing the
|
||||
risk of repetition.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable multinomial sampling set `do_sample=True` and `num_beams=1`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "gpt2-large"
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "Today was an amazing day because"
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, do_sample=True, num_beams=1, max_new_tokens=100)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
['Today was an amazing day because we are now in the final stages of our trip to New York City which was very tough. \
|
||||
It is a difficult schedule and a challenging part of the year but still worth it. I have been taking things easier and \
|
||||
I feel stronger and more motivated to be out there on their tour. Hopefully, that experience is going to help them with \
|
||||
their upcoming events which are currently scheduled in Australia.\n\nWe love that they are here. They want to make a \
|
||||
name for themselves and become famous for what they']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Beam-search decoding
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike greedy search, beam-search decoding keeps several hypotheses at each time step and eventually chooses
|
||||
the hypothesis that has the overall highest probability for the entire sequence. This has the advantage of identifying high-probability
|
||||
sequences that start with lower probability initial tokens and would've been ignored by the greedy search.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable this decoding strategy, specify the `num_beams` (aka number of hypotheses to keep track of) that is greater than 1.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "It is astonishing how one can"
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "gpt2-medium"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, num_beams=5, max_new_tokens=50)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
['It is astonishing how one can have such a profound impact on the lives of so many people in such a short period of \
|
||||
time."\n\nHe added: "I am very proud of the work I have been able to do in the last few years.\n\n"I have']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Beam-search multinomial sampling
|
||||
|
||||
As the name implies, this decoding strategy combines beam search with multinomial sampling. You need to specify
|
||||
the `num_beams` greater than 1, and set `do_sample=True` to use this decoding strategy.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "translate English to German: The house is wonderful."
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "t5-small"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, num_beams=5, do_sample=True)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
'Das Haus ist wunderbar.'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Diverse beam search decoding
|
||||
|
||||
The diverse beam search decoding strategy is an extension of the beam search strategy that allows for generating a more diverse
|
||||
set of beam sequences to choose from. To learn how it works, refer to [Diverse Beam Search: Decoding Diverse Solutions from Neural Sequence Models](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1610.02424.pdf).
|
||||
This approach has two main parameters: `num_beams` and `num_beam_groups`.
|
||||
The groups are selected to ensure they are distinct enough compared to the others, and regular beam search is used within each group.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "google/pegasus-xsum"
|
||||
>>> prompt = "The Permaculture Design Principles are a set of universal design principles \
|
||||
>>> that can be applied to any location, climate and culture, and they allow us to design \
|
||||
>>> the most efficient and sustainable human habitation and food production systems. \
|
||||
>>> Permaculture is a design system that encompasses a wide variety of disciplines, such \
|
||||
>>> as ecology, landscape design, environmental science and energy conservation, and the \
|
||||
>>> Permaculture design principles are drawn from these various disciplines. Each individual \
|
||||
>>> design principle itself embodies a complete conceptual framework based on sound \
|
||||
>>> scientific principles. When we bring all these separate principles together, we can \
|
||||
>>> create a design system that both looks at whole systems, the parts that these systems \
|
||||
>>> consist of, and how those parts interact with each other to create a complex, dynamic, \
|
||||
>>> living system. Each design principle serves as a tool that allows us to integrate all \
|
||||
>>> the separate parts of a design, referred to as elements, into a functional, synergistic, \
|
||||
>>> whole system, where the elements harmoniously interact and work together in the most \
|
||||
>>> efficient way possible."
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, num_beams=5, num_beam_groups=5, max_new_tokens=30)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
'The Design Principles are a set of universal design principles that can be applied to any location, climate and culture, and they allow us to design the most efficient and sustainable human habitation and food production systems.'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This guide illustrates the main parameters that enable various decoding strategies. More advanced parameters exist for the
|
||||
[`generate`] method, which gives you even further control over the [`generate`] method's behavior.
|
||||
For the complete list of the available parameters, refer to the [API documentation](./main_classes/text_generation.md).
|
||||
|
||||
### Assisted Decoding
|
||||
|
||||
Assisted decoding is a modification of the decoding strategies above that uses an assistant model with the same
|
||||
tokenizer (ideally a much smaller model) to greedily generate a few candidate tokens. The main model then validates
|
||||
the candidate tokens in a single forward pass, which speeds up the decoding process. Currently, only greedy search
|
||||
and sampling are supported with assisted decoding, and doesn't support batched inputs. To learn more about assisted
|
||||
decoding, check [this blog post](https://huggingface.co/blog/assisted-generation).
|
||||
|
||||
To enable assisted decoding, set the `assistant_model` argument with a model.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "Alice and Bob"
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "EleutherAI/pythia-1.4b-deduped"
|
||||
>>> assistant_checkpoint = "EleutherAI/pythia-160m-deduped"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> assistant_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(assistant_checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, assistant_model=assistant_model)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
['Alice and Bob are sitting in a bar. Alice is drinking a beer and Bob is drinking a']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When using assisted decoding with sampling methods, you can use the `temperarure` argument to control the randomness
|
||||
just like in multinomial sampling. However, in assisted decoding, reducing the temperature will help improving latency.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "Alice and Bob"
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "EleutherAI/pythia-1.4b-deduped"
|
||||
>>> assistant_checkpoint = "EleutherAI/pythia-160m-deduped"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> assistant_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(assistant_checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, assistant_model=assistant_model, do_sample=True, temperature=0.5)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
["Alice and Bob are sitting on the sofa. Alice says, 'I'm going to my room"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,381 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Text generation strategies
|
||||
|
||||
Text generation is essential to many NLP tasks, such as open-ended text generation, summarization, translation, and
|
||||
more. It also plays a role in a variety of mixed-modality applications that have text as an output like speech-to-text
|
||||
and vision-to-text. Some of the models that can generate text include
|
||||
GPT2, XLNet, OpenAI GPT, CTRL, TransformerXL, XLM, Bart, T5, GIT, Whisper.
|
||||
|
||||
Check out a few examples that use [`~transformers.generation_utils.GenerationMixin.generate`] method to produce
|
||||
text outputs for different tasks:
|
||||
* [Text summarization](./tasks/summarization#inference)
|
||||
* [Image captioning](./model_doc/git#transformers.GitForCausalLM.forward.example)
|
||||
* [Audio transcription](./model_doc/whisper#transformers.WhisperForConditionalGeneration.forward.example)
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the inputs to the generate method depend on the model's modality. They are returned by the model's preprocessor
|
||||
class, such as AutoTokenizer or AutoProcessor. If a model's preprocessor creates more than one kind of input, pass all
|
||||
the inputs to generate(). You can learn more about the individual model's preprocessor in the corresponding model's documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
The process of selecting output tokens to generate text is known as decoding, and you can customize the decoding strategy
|
||||
that the `generate()` method will use. Modifying a decoding strategy does not change the values of any trainable parameters.
|
||||
However, it can have a noticeable impact on the quality of the generated output. It can help reduce repetition in the text
|
||||
and make it more coherent.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide describes:
|
||||
* default generation configuration
|
||||
* common decoding strategies and their main parameters
|
||||
* saving and sharing custom generation configurations with your fine-tuned model on 🤗 Hub
|
||||
|
||||
## Default text generation configuration
|
||||
|
||||
A decoding strategy for a model is defined in its generation configuration. When using pre-trained models for inference
|
||||
within a [`pipeline`], the models call the `PreTrainedModel.generate()` method that applies a default generation
|
||||
configuration under the hood. The default configuration is also used when no custom configuration has been saved with
|
||||
the model.
|
||||
|
||||
When you load a model explicitly, you can inspect the generation configuration that comes with it through
|
||||
`model.generation_config`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("distilgpt2")
|
||||
>>> model.generation_config
|
||||
GenerationConfig {
|
||||
"_from_model_config": true,
|
||||
"bos_token_id": 50256,
|
||||
"eos_token_id": 50256,
|
||||
"transformers_version": "4.26.0.dev0"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Printing out the `model.generation_config` reveals only the values that are different from the default generation
|
||||
configuration, and does not list any of the default values.
|
||||
|
||||
The default generation configuration limits the size of the output combined with the input prompt to a maximum of 20
|
||||
tokens to avoid running into resource limitations. The default decoding strategy is greedy search, which is the simplest decoding strategy that picks a token with the highest probability as the next token. For many tasks
|
||||
and small output sizes this works well. However, when used to generate longer outputs, greedy search can start
|
||||
producing highly repetitive results.
|
||||
|
||||
## Customize text generation
|
||||
|
||||
You can override any `generation_config` by passing the parameters and their values directly to the [`generate`] method:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> my_model.generate(**inputs, num_beams=4, do_sample=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Even if the default decoding strategy mostly works for your task, you can still tweak a few things. Some of the
|
||||
commonly adjusted parameters include:
|
||||
|
||||
- `max_new_tokens`: the maximum number of tokens to generate. In other words, the size of the output sequence, not
|
||||
including the tokens in the prompt.
|
||||
- `num_beams`: by specifying a number of beams higher than 1, you are effectively switching from greedy search to
|
||||
beam search. This strategy evaluates several hypotheses at each time step and eventually chooses the hypothesis that
|
||||
has the overall highest probability for the entire sequence. This has the advantage of identifying high-probability
|
||||
sequences that start with a lower probability initial tokens and would've been ignored by the greedy search.
|
||||
- `do_sample`: if set to `True`, this parameter enables decoding strategies such as multinomial sampling, beam-search
|
||||
multinomial sampling, Top-K sampling and Top-p sampling. All these strategies select the next token from the probability
|
||||
distribution over the entire vocabulary with various strategy-specific adjustments.
|
||||
- `num_return_sequences`: the number of sequence candidates to return for each input. This options is only available for
|
||||
the decoding strategies that support multiple sequence candidates, e.g. variations of beam search and sampling. Decoding
|
||||
strategies like greedy search and contrastive search return a single output sequence.
|
||||
|
||||
## Save a custom decoding strategy with your model
|
||||
|
||||
If you would like to share your fine-tuned model with a specific generation configuration, you can:
|
||||
* Create a [`GenerationConfig`] class instance
|
||||
* Specify the decoding strategy parameters
|
||||
* Save your generation configuration with [`GenerationConfig.save_pretrained`], making sure to leave its `config_file_name` argument empty
|
||||
* Set `push_to_hub` to `True` to upload your config to the model's repo
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, GenerationConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("my_account/my_model")
|
||||
>>> generation_config = GenerationConfig(
|
||||
... max_new_tokens=50, do_sample=True, top_k=50, eos_token_id=model.config.eos_token_id
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> generation_config.save_pretrained("my_account/my_model", push_to_hub=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also store several generation configurations in a single directory, making use of the `config_file_name`
|
||||
argument in [`GenerationConfig.save_pretrained`]. You can later instantiate them with [`GenerationConfig.from_pretrained`]. This is useful if you want to
|
||||
store several generation configurations for a single model (e.g. one for creative text generation with sampling, and
|
||||
one for summarization with beam search). You must have the right Hub permissions to add configuration files to a model.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer, GenerationConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("t5-small")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("t5-small")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> translation_generation_config = GenerationConfig(
|
||||
... num_beams=4,
|
||||
... early_stopping=True,
|
||||
... decoder_start_token_id=0,
|
||||
... eos_token_id=model.config.eos_token_id,
|
||||
... pad_token=model.config.pad_token_id,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
|
||||
>>> translation_generation_config.save_pretrained("t5-small", "translation_generation_config.json", push_to_hub=True)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # You could then use the named generation config file to parameterize generation
|
||||
>>> generation_config = GenerationConfig.from_pretrained("t5-small", "translation_generation_config.json")
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer("translate English to French: Configuration files are easy to use!", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, generation_config=generation_config)
|
||||
>>> print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
['Les fichiers de configuration sont faciles à utiliser !']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Streaming
|
||||
|
||||
The `generate()` supports streaming, through its `streamer` input. The `streamer` input is compatible any instance
|
||||
from a class that has the following methods: `put()` and `end()`. Internally, `put()` is used to push new tokens and
|
||||
`end()` is used to flag the end of text generation.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
The API for the streamer classes is still under development and may change in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In practice, you can craft your own streaming class for all sorts of purposes! We also have basic streaming classes
|
||||
ready for you to use. For example, you can use the [`TextStreamer`] class to stream the output of `generate()` into
|
||||
your screen, one word at a time:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, TextStreamer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tok = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("gpt2")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("gpt2")
|
||||
>>> inputs = tok(["An increasing sequence: one,"], return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> streamer = TextStreamer(tok)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # Despite returning the usual output, the streamer will also print the generated text to stdout.
|
||||
>>> _ = model.generate(**inputs, streamer=streamer, max_new_tokens=20)
|
||||
An increasing sequence: one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, nine, ten, eleven,
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Decoding strategies
|
||||
|
||||
Certain combinations of the `generate()` parameters, and ultimately `generation_config`, can be used to enable specific
|
||||
decoding strategies. If you are new to this concept, we recommend reading [this blog post that illustrates how common decoding strategies work](https://huggingface.co/blog/how-to-generate).
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we'll show some of the parameters that control the decoding strategies and illustrate how you can use them.
|
||||
|
||||
### Greedy Search
|
||||
|
||||
[`generate`] uses greedy search decoding by default so you don't have to pass any parameters to enable it. This means the parameters `num_beams` is set to 1 and `do_sample=False`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "I look forward to"
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "distilgpt2"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
['I look forward to seeing you all again!\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Contrastive search
|
||||
|
||||
The contrastive search decoding strategy was proposed in the 2022 paper [A Contrastive Framework for Neural Text Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.06417).
|
||||
It demonstrates superior results for generating non-repetitive yet coherent long outputs. To learn how contrastive search
|
||||
works, check out [this blog post](https://huggingface.co/blog/introducing-csearch).
|
||||
The two main parameters that enable and control the behavior of contrastive search are `penalty_alpha` and `top_k`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "gpt2-large"
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "Hugging Face Company is"
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, penalty_alpha=0.6, top_k=4, max_new_tokens=100)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
['Hugging Face Company is a family owned and operated business. \
|
||||
We pride ourselves on being the best in the business and our customer service is second to none.\
|
||||
\n\nIf you have any questions about our products or services, feel free to contact us at any time.\
|
||||
We look forward to hearing from you!']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Multinomial sampling
|
||||
|
||||
As opposed to greedy search that always chooses a token with the highest probability as the
|
||||
next token, multinomial sampling (also called ancestral sampling) randomly selects the next token based on the probability distribution over the entire
|
||||
vocabulary given by the model. Every token with a non-zero probability has a chance of being selected, thus reducing the
|
||||
risk of repetition.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable multinomial sampling set `do_sample=True` and `num_beams=1`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "gpt2-large"
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "Today was an amazing day because"
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, do_sample=True, num_beams=1, max_new_tokens=100)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
['Today was an amazing day because we are now in the final stages of our trip to New York City which was very tough. \
|
||||
It is a difficult schedule and a challenging part of the year but still worth it. I have been taking things easier and \
|
||||
I feel stronger and more motivated to be out there on their tour. Hopefully, that experience is going to help them with \
|
||||
their upcoming events which are currently scheduled in Australia.\n\nWe love that they are here. They want to make a \
|
||||
name for themselves and become famous for what they']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Beam-search decoding
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike greedy search, beam-search decoding keeps several hypotheses at each time step and eventually chooses
|
||||
the hypothesis that has the overall highest probability for the entire sequence. This has the advantage of identifying high-probability
|
||||
sequences that start with lower probability initial tokens and would've been ignored by the greedy search.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable this decoding strategy, specify the `num_beams` (aka number of hypotheses to keep track of) that is greater than 1.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "It is astonishing how one can"
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "gpt2-medium"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, num_beams=5, max_new_tokens=50)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
['It is astonishing how one can have such a profound impact on the lives of so many people in such a short period of \
|
||||
time."\n\nHe added: "I am very proud of the work I have been able to do in the last few years.\n\n"I have']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Beam-search multinomial sampling
|
||||
|
||||
As the name implies, this decoding strategy combines beam search with multinomial sampling. You need to specify
|
||||
the `num_beams` greater than 1, and set `do_sample=True` to use this decoding strategy.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "translate English to German: The house is wonderful."
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "t5-small"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, num_beams=5, do_sample=True)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
'Das Haus ist wunderbar.'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Diverse beam search decoding
|
||||
|
||||
The diverse beam search decoding strategy is an extension of the beam search strategy that allows for generating a more diverse
|
||||
set of beam sequences to choose from. To learn how it works, refer to [Diverse Beam Search: Decoding Diverse Solutions from Neural Sequence Models](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1610.02424.pdf).
|
||||
This approach has two main parameters: `num_beams` and `num_beam_groups`.
|
||||
The groups are selected to ensure they are distinct enough compared to the others, and regular beam search is used within each group.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "google/pegasus-xsum"
|
||||
>>> prompt = "The Permaculture Design Principles are a set of universal design principles \
|
||||
>>> that can be applied to any location, climate and culture, and they allow us to design \
|
||||
>>> the most efficient and sustainable human habitation and food production systems. \
|
||||
>>> Permaculture is a design system that encompasses a wide variety of disciplines, such \
|
||||
>>> as ecology, landscape design, environmental science and energy conservation, and the \
|
||||
>>> Permaculture design principles are drawn from these various disciplines. Each individual \
|
||||
>>> design principle itself embodies a complete conceptual framework based on sound \
|
||||
>>> scientific principles. When we bring all these separate principles together, we can \
|
||||
>>> create a design system that both looks at whole systems, the parts that these systems \
|
||||
>>> consist of, and how those parts interact with each other to create a complex, dynamic, \
|
||||
>>> living system. Each design principle serves as a tool that allows us to integrate all \
|
||||
>>> the separate parts of a design, referred to as elements, into a functional, synergistic, \
|
||||
>>> whole system, where the elements harmoniously interact and work together in the most \
|
||||
>>> efficient way possible."
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, num_beams=5, num_beam_groups=5, max_new_tokens=30)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.decode(outputs[0], skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
'The Design Principles are a set of universal design principles that can be applied to any location, climate and culture, and they allow us to design the most efficient and sustainable human habitation and food production systems.'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This guide illustrates the main parameters that enable various decoding strategies. More advanced parameters exist for the
|
||||
[`generate`] method, which gives you even further control over the [`generate`] method's behavior.
|
||||
For the complete list of the available parameters, refer to the [API documentation](./main_classes/text_generation.mdx).
|
||||
|
||||
### Assisted Decoding
|
||||
|
||||
Assisted decoding is a modification of the decoding strategies above that uses an assistant model with the same
|
||||
tokenizer (ideally a much smaller model) to greedily generate a few candidate tokens. The main model then validates
|
||||
the candidate tokens in a single forward pass, which speeds up the decoding process. Currently, only greedy search
|
||||
and sampling are supported with assisted decoding, and doesn't support batched inputs. To learn more about assisted
|
||||
decoding, check [this blog post](https://huggingface.co/blog/assisted-generation).
|
||||
|
||||
To enable assisted decoding, set the `assistant_model` argument with a model.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "Alice and Bob"
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "EleutherAI/pythia-1.4b-deduped"
|
||||
>>> assistant_checkpoint = "EleutherAI/pythia-160m-deduped"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> assistant_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(assistant_checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, assistant_model=assistant_model)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
['Alice and Bob are sitting in a bar. Alice is drinking a beer and Bob is drinking a']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When using assisted decoding with sampling methods, you can use the `temperarure` argument to control the randomness
|
||||
just like in multinomial sampling. However, in assisted decoding, reducing the temperature will help improving latency.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "Alice and Bob"
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "EleutherAI/pythia-1.4b-deduped"
|
||||
>>> assistant_checkpoint = "EleutherAI/pythia-160m-deduped"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> assistant_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(assistant_checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**inputs, assistant_model=assistant_model, do_sample=True, temperature=0.5)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
["Alice and Bob are sitting on the sofa. Alice says, 'I'm going to my room"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
491
docs/source/en/glossary.md
Normal file
491
docs/source/en/glossary.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,491 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Glossary
|
||||
|
||||
This glossary defines general machine learning and 🤗 Transformers terms to help you better understand the
|
||||
documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
## A
|
||||
|
||||
### attention mask
|
||||
|
||||
The attention mask is an optional argument used when batching sequences together.
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="M6adb1j2jPI"/>
|
||||
|
||||
This argument indicates to the model which tokens should be attended to, and which should not.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, consider these two sequences:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import BertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> sequence_a = "This is a short sequence."
|
||||
>>> sequence_b = "This is a rather long sequence. It is at least longer than the sequence A."
|
||||
|
||||
>>> encoded_sequence_a = tokenizer(sequence_a)["input_ids"]
|
||||
>>> encoded_sequence_b = tokenizer(sequence_b)["input_ids"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The encoded versions have different lengths:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> len(encoded_sequence_a), len(encoded_sequence_b)
|
||||
(8, 19)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, we can't put them together in the same tensor as-is. The first sequence needs to be padded up to the length
|
||||
of the second one, or the second one needs to be truncated down to the length of the first one.
|
||||
|
||||
In the first case, the list of IDs will be extended by the padding indices. We can pass a list to the tokenizer and ask
|
||||
it to pad like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> padded_sequences = tokenizer([sequence_a, sequence_b], padding=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can see that 0s have been added on the right of the first sentence to make it the same length as the second one:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> padded_sequences["input_ids"]
|
||||
[[101, 1188, 1110, 170, 1603, 4954, 119, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [101, 1188, 1110, 170, 1897, 1263, 4954, 119, 1135, 1110, 1120, 1655, 2039, 1190, 1103, 4954, 138, 119, 102]]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This can then be converted into a tensor in PyTorch or TensorFlow. The attention mask is a binary tensor indicating the
|
||||
position of the padded indices so that the model does not attend to them. For the [`BertTokenizer`], `1` indicates a
|
||||
value that should be attended to, while `0` indicates a padded value. This attention mask is in the dictionary returned
|
||||
by the tokenizer under the key "attention_mask":
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> padded_sequences["attention_mask"]
|
||||
[[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### autoencoding models
|
||||
|
||||
See [encoder models](#encoder-models) and [masked language modeling](#masked-language-modeling-mlm)
|
||||
|
||||
### autoregressive models
|
||||
|
||||
See [causal language modeling](#causal-language-modeling) and [decoder models](#decoder-models)
|
||||
|
||||
## B
|
||||
|
||||
### backbone
|
||||
|
||||
The backbone is the network (embeddings and layers) that outputs the raw hidden states or features. It is usually connected to a [head](#head) which accepts the features as its input to make a prediction. For example, [`ViTModel`] is a backbone without a specific head on top. Other models can also use [`VitModel`] as a backbone such as [DPT](model_doc/dpt).
|
||||
|
||||
## C
|
||||
|
||||
### causal language modeling
|
||||
|
||||
A pretraining task where the model reads the texts in order and has to predict the next word. It's usually done by
|
||||
reading the whole sentence but using a mask inside the model to hide the future tokens at a certain timestep.
|
||||
|
||||
### channel
|
||||
|
||||
Color images are made up of some combination of values in three channels - red, green, and blue (RGB) - and grayscale images only have one channel. In 🤗 Transformers, the channel can be the first or last dimension of an image's tensor: [`n_channels`, `height`, `width`] or [`height`, `width`, `n_channels`].
|
||||
|
||||
### connectionist temporal classification (CTC)
|
||||
|
||||
An algorithm which allows a model to learn without knowing exactly how the input and output are aligned; CTC calculates the distribution of all possible outputs for a given input and chooses the most likely output from it. CTC is commonly used in speech recognition tasks because speech doesn't always cleanly align with the transcript for a variety of reasons such as a speaker's different speech rates.
|
||||
|
||||
### convolution
|
||||
|
||||
A type of layer in a neural network where the input matrix is multiplied element-wise by a smaller matrix (kernel or filter) and the values are summed up in a new matrix. This is known as a convolutional operation which is repeated over the entire input matrix. Each operation is applied to a different segment of the input matrix. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are commonly used in computer vision.
|
||||
|
||||
## D
|
||||
|
||||
### decoder input IDs
|
||||
|
||||
This input is specific to encoder-decoder models, and contains the input IDs that will be fed to the decoder. These
|
||||
inputs should be used for sequence to sequence tasks, such as translation or summarization, and are usually built in a
|
||||
way specific to each model.
|
||||
|
||||
Most encoder-decoder models (BART, T5) create their `decoder_input_ids` on their own from the `labels`. In such models,
|
||||
passing the `labels` is the preferred way to handle training.
|
||||
|
||||
Please check each model's docs to see how they handle these input IDs for sequence to sequence training.
|
||||
|
||||
### decoder models
|
||||
|
||||
Also referred to as autoregressive models, decoder models involve a pretraining task (called causal language modeling) where the model reads the texts in order and has to predict the next word. It's usually done by
|
||||
reading the whole sentence with a mask to hide future tokens at a certain timestep.
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="d_ixlCubqQw"/>
|
||||
|
||||
### deep learning (DL)
|
||||
|
||||
Machine learning algorithms which uses neural networks with several layers.
|
||||
|
||||
## E
|
||||
|
||||
### encoder models
|
||||
|
||||
Also known as autoencoding models, encoder models take an input (such as text or images) and transform them into a condensed numerical representation called an embedding. Oftentimes, encoder models are pretrained using techniques like [masked language modeling](#masked-language-modeling-mlm), which masks parts of the input sequence and forces the model to create more meaningful representations.
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="H39Z_720T5s"/>
|
||||
|
||||
## F
|
||||
|
||||
### feature extraction
|
||||
|
||||
The process of selecting and transforming raw data into a set of features that are more informative and useful for machine learning algorithms. Some examples of feature extraction include transforming raw text into word embeddings and extracting important features such as edges or shapes from image/video data.
|
||||
|
||||
### feed forward chunking
|
||||
|
||||
In each residual attention block in transformers the self-attention layer is usually followed by 2 feed forward layers.
|
||||
The intermediate embedding size of the feed forward layers is often bigger than the hidden size of the model (e.g., for
|
||||
`bert-base-uncased`).
|
||||
|
||||
For an input of size `[batch_size, sequence_length]`, the memory required to store the intermediate feed forward
|
||||
embeddings `[batch_size, sequence_length, config.intermediate_size]` can account for a large fraction of the memory
|
||||
use. The authors of [Reformer: The Efficient Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04451) noticed that since the
|
||||
computation is independent of the `sequence_length` dimension, it is mathematically equivalent to compute the output
|
||||
embeddings of both feed forward layers `[batch_size, config.hidden_size]_0, ..., [batch_size, config.hidden_size]_n`
|
||||
individually and concat them afterward to `[batch_size, sequence_length, config.hidden_size]` with `n =
|
||||
sequence_length`, which trades increased computation time against reduced memory use, but yields a mathematically
|
||||
**equivalent** result.
|
||||
|
||||
For models employing the function [`apply_chunking_to_forward`], the `chunk_size` defines the number of output
|
||||
embeddings that are computed in parallel and thus defines the trade-off between memory and time complexity. If
|
||||
`chunk_size` is set to 0, no feed forward chunking is done.
|
||||
|
||||
### finetuned models
|
||||
|
||||
Finetuning is a form of transfer learning which involves taking a pretrained model, freezing its weights, and replacing the output layer with a newly added [model head](#head). The model head is trained on your target dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
See the [Fine-tune a pretrained model](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/training) tutorial for more details, and learn how to fine-tune models with 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
## H
|
||||
|
||||
### head
|
||||
|
||||
The model head refers to the last layer of a neural network that accepts the raw hidden states and projects them onto a different dimension. There is a different model head for each task. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
* [`GPT2ForSequenceClassification`] is a sequence classification head - a linear layer - on top of the base [`GPT2Model`].
|
||||
* [`ViTForImageClassification`] is an image classification head - a linear layer on top of the final hidden state of the `CLS` token - on top of the base [`ViTModel`].
|
||||
* [`Wav2Vec2ForCTC`] ia a language modeling head with [CTC](#connectionist-temporal-classification-(CTC)) on top of the base [`Wav2Vec2Model`].
|
||||
|
||||
## I
|
||||
|
||||
### image patch
|
||||
|
||||
Vision-based Transformers models split an image into smaller patches which are linearly embedded, and then passed as a sequence to the model. You can find the `patch_size` - or resolution - of the model in it's configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
### inference
|
||||
|
||||
Inference is the process of evaluating a model on new data after training is complete. See the [Pipeline for inference](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/pipeline_tutorial) tutorial to learn how to perform inference with 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
### input IDs
|
||||
|
||||
The input ids are often the only required parameters to be passed to the model as input. They are token indices,
|
||||
numerical representations of tokens building the sequences that will be used as input by the model.
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="VFp38yj8h3A"/>
|
||||
|
||||
Each tokenizer works differently but the underlying mechanism remains the same. Here's an example using the BERT
|
||||
tokenizer, which is a [WordPiece](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1609.08144.pdf) tokenizer:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import BertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> sequence = "A Titan RTX has 24GB of VRAM"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The tokenizer takes care of splitting the sequence into tokens available in the tokenizer vocabulary.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> tokenized_sequence = tokenizer.tokenize(sequence)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The tokens are either words or subwords. Here for instance, "VRAM" wasn't in the model vocabulary, so it's been split
|
||||
in "V", "RA" and "M". To indicate those tokens are not separate words but parts of the same word, a double-hash prefix
|
||||
is added for "RA" and "M":
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> print(tokenized_sequence)
|
||||
['A', 'Titan', 'R', '##T', '##X', 'has', '24', '##GB', 'of', 'V', '##RA', '##M']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
These tokens can then be converted into IDs which are understandable by the model. This can be done by directly feeding
|
||||
the sentence to the tokenizer, which leverages the Rust implementation of [🤗
|
||||
Tokenizers](https://github.com/huggingface/tokenizers) for peak performance.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(sequence)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The tokenizer returns a dictionary with all the arguments necessary for its corresponding model to work properly. The
|
||||
token indices are under the key `input_ids`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> encoded_sequence = inputs["input_ids"]
|
||||
>>> print(encoded_sequence)
|
||||
[101, 138, 18696, 155, 1942, 3190, 1144, 1572, 13745, 1104, 159, 9664, 2107, 102]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the tokenizer automatically adds "special tokens" (if the associated model relies on them) which are special
|
||||
IDs the model sometimes uses.
|
||||
|
||||
If we decode the previous sequence of ids,
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> decoded_sequence = tokenizer.decode(encoded_sequence)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
we will see
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> print(decoded_sequence)
|
||||
[CLS] A Titan RTX has 24GB of VRAM [SEP]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
because this is the way a [`BertModel`] is going to expect its inputs.
|
||||
|
||||
## L
|
||||
|
||||
### labels
|
||||
|
||||
The labels are an optional argument which can be passed in order for the model to compute the loss itself. These labels
|
||||
should be the expected prediction of the model: it will use the standard loss in order to compute the loss between its
|
||||
predictions and the expected value (the label).
|
||||
|
||||
These labels are different according to the model head, for example:
|
||||
|
||||
- For sequence classification models, ([`BertForSequenceClassification`]), the model expects a tensor of dimension
|
||||
`(batch_size)` with each value of the batch corresponding to the expected label of the entire sequence.
|
||||
- For token classification models, ([`BertForTokenClassification`]), the model expects a tensor of dimension
|
||||
`(batch_size, seq_length)` with each value corresponding to the expected label of each individual token.
|
||||
- For masked language modeling, ([`BertForMaskedLM`]), the model expects a tensor of dimension `(batch_size,
|
||||
seq_length)` with each value corresponding to the expected label of each individual token: the labels being the token
|
||||
ID for the masked token, and values to be ignored for the rest (usually -100).
|
||||
- For sequence to sequence tasks, ([`BartForConditionalGeneration`], [`MBartForConditionalGeneration`]), the model
|
||||
expects a tensor of dimension `(batch_size, tgt_seq_length)` with each value corresponding to the target sequences
|
||||
associated with each input sequence. During training, both BART and T5 will make the appropriate
|
||||
`decoder_input_ids` and decoder attention masks internally. They usually do not need to be supplied. This does not
|
||||
apply to models leveraging the Encoder-Decoder framework.
|
||||
- For image classification models, ([`ViTForImageClassification`]), the model expects a tensor of dimension
|
||||
`(batch_size)` with each value of the batch corresponding to the expected label of each individual image.
|
||||
- For semantic segmentation models, ([`SegformerForSemanticSegmentation`]), the model expects a tensor of dimension
|
||||
`(batch_size, height, width)` with each value of the batch corresponding to the expected label of each individual pixel.
|
||||
- For object detection models, ([`DetrForObjectDetection`]), the model expects a list of dictionaries with a
|
||||
`class_labels` and `boxes` key where each value of the batch corresponds to the expected label and number of bounding boxes of each individual image.
|
||||
- For automatic speech recognition models, ([`Wav2Vec2ForCTC`]), the model expects a tensor of dimension `(batch_size,
|
||||
target_length)` with each value corresponding to the expected label of each individual token.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Each model's labels may be different, so be sure to always check the documentation of each model for more information
|
||||
about their specific labels!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The base models ([`BertModel`]) do not accept labels, as these are the base transformer models, simply outputting
|
||||
features.
|
||||
|
||||
### large language models (LLM)
|
||||
|
||||
A generic term that refers to transformer language models (GPT-3, BLOOM, OPT) that were trained on a large quantity of data. These models also tend to have a large number of learnable parameters (e.g. 175 billion for GPT-3).
|
||||
|
||||
## M
|
||||
|
||||
### masked language modeling (MLM)
|
||||
|
||||
A pretraining task where the model sees a corrupted version of the texts, usually done by
|
||||
masking some tokens randomly, and has to predict the original text.
|
||||
|
||||
### multimodal
|
||||
|
||||
A task that combines texts with another kind of inputs (for instance images).
|
||||
|
||||
## N
|
||||
|
||||
### Natural language generation (NLG)
|
||||
|
||||
All tasks related to generating text (for instance, [Write With Transformers](https://transformer.huggingface.co/), translation).
|
||||
|
||||
### Natural language processing (NLP)
|
||||
|
||||
A generic way to say "deal with texts".
|
||||
|
||||
### Natural language understanding (NLU)
|
||||
|
||||
All tasks related to understanding what is in a text (for instance classifying the
|
||||
whole text, individual words).
|
||||
|
||||
## P
|
||||
|
||||
### pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
A pipeline in 🤗 Transformers is an abstraction referring to a series of steps that are executed in a specific order to preprocess and transform data and return a prediction from a model. Some example stages found in a pipeline might be data preprocessing, feature extraction, and normalization.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, see [Pipelines for inference](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/pipeline_tutorial).
|
||||
|
||||
### pixel values
|
||||
|
||||
A tensor of the numerical representations of an image that is passed to a model. The pixel values have a shape of [`batch_size`, `num_channels`, `height`, `width`], and are generated from an image processor.
|
||||
|
||||
### pooling
|
||||
|
||||
An operation that reduces a matrix into a smaller matrix, either by taking the maximum or average of the pooled dimension(s). Pooling layers are commonly found between convolutional layers to downsample the feature representation.
|
||||
|
||||
### position IDs
|
||||
|
||||
Contrary to RNNs that have the position of each token embedded within them, transformers are unaware of the position of
|
||||
each token. Therefore, the position IDs (`position_ids`) are used by the model to identify each token's position in the
|
||||
list of tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
They are an optional parameter. If no `position_ids` are passed to the model, the IDs are automatically created as
|
||||
absolute positional embeddings.
|
||||
|
||||
Absolute positional embeddings are selected in the range `[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1]`. Some models use
|
||||
other types of positional embeddings, such as sinusoidal position embeddings or relative position embeddings.
|
||||
|
||||
### preprocessing
|
||||
|
||||
The task of preparing raw data into a format that can be easily consumed by machine learning models. For example, text is typically preprocessed by tokenization. To gain a better idea of what preprocessing looks like for other input types, check out the [Preprocess](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/preprocessing) tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
### pretrained model
|
||||
|
||||
A model that has been pretrained on some data (for instance all of Wikipedia). Pretraining methods involve a
|
||||
self-supervised objective, which can be reading the text and trying to predict the next word (see [causal language
|
||||
modeling](#causal-language-modeling)) or masking some words and trying to predict them (see [masked language
|
||||
modeling](#masked-language-modeling-mlm)).
|
||||
|
||||
Speech and vision models have their own pretraining objectives. For example, Wav2Vec2 is a speech model pretrained on a contrastive task which requires the model to identify the "true" speech representation from a set of "false" speech representations. On the other hand, BEiT is a vision model pretrained on a masked image modeling task which masks some of the image patches and requires the model to predict the masked patches (similar to the masked language modeling objective).
|
||||
|
||||
## R
|
||||
|
||||
### recurrent neural network (RNN)
|
||||
|
||||
A type of model that uses a loop over a layer to process texts.
|
||||
|
||||
### representation learning
|
||||
|
||||
A subfield of machine learning which focuses on learning meaningful representations of raw data. Some examples of representation learning techniques include word embeddings, autoencoders, and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs).
|
||||
|
||||
## S
|
||||
|
||||
### sampling rate
|
||||
|
||||
A measurement in hertz of the number of samples (the audio signal) taken per second. The sampling rate is a result of discretizing a continuous signal such as speech.
|
||||
|
||||
### self-attention
|
||||
|
||||
Each element of the input finds out which other elements of the input they should attend to.
|
||||
|
||||
### self-supervised learning
|
||||
|
||||
A category of machine learning techniques in which a model creates its own learning objective from unlabeled data. It differs from [unsupervised learning](#unsupervised-learning) and [supervised learning](#supervised-learning) in that the learning process is supervised, but not explicitly from the user.
|
||||
|
||||
One example of self-supervised learning is [masked language modeling](#masked-language-modeling-mlm), where a model is passed sentences with a proportion of its tokens removed and learns to predict the missing tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
### semi-supervised learning
|
||||
|
||||
A broad category of machine learning training techniques that leverages a small amount of labeled data with a larger quantity of unlabeled data to improve the accuracy of a model, unlike [supervised learning](#supervised-learning) and [unsupervised learning](#unsupervised-learning).
|
||||
|
||||
An example of a semi-supervised learning approach is "self-training", in which a model is trained on labeled data, and then used to make predictions on the unlabeled data. The portion of the unlabeled data that the model predicts with the most confidence gets added to the labeled dataset and used to retrain the model.
|
||||
|
||||
### sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq)
|
||||
|
||||
Models that generate a new sequence from an input, like translation models, or summarization models (such as
|
||||
[Bart](model_doc/bart) or [T5](model_doc/t5)).
|
||||
|
||||
### stride
|
||||
|
||||
In [convolution](#convolution) or [pooling](#pooling), the stride refers to the distance the kernel is moved over a matrix. A stride of 1 means the kernel is moved one pixel over at a time, and a stride of 2 means the kernel is moved two pixels over at a time.
|
||||
|
||||
### supervised learning
|
||||
|
||||
A form of model training that directly uses labeled data to correct and instruct model performance. Data is fed into the model being trained, and its predictions are compared to the known labels. The model updates its weights based on how incorrect its predictions were, and the process is repeated to optimize model performance.
|
||||
|
||||
## T
|
||||
|
||||
### token
|
||||
|
||||
A part of a sentence, usually a word, but can also be a subword (non-common words are often split in subwords) or a
|
||||
punctuation symbol.
|
||||
|
||||
### token Type IDs
|
||||
|
||||
Some models' purpose is to do classification on pairs of sentences or question answering.
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="0u3ioSwev3s"/>
|
||||
|
||||
These require two different sequences to be joined in a single "input_ids" entry, which usually is performed with the
|
||||
help of special tokens, such as the classifier (`[CLS]`) and separator (`[SEP]`) tokens. For example, the BERT model
|
||||
builds its two sequence input as such:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> # [CLS] SEQUENCE_A [SEP] SEQUENCE_B [SEP]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can use our tokenizer to automatically generate such a sentence by passing the two sequences to `tokenizer` as two
|
||||
arguments (and not a list, like before) like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import BertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
>>> sequence_a = "HuggingFace is based in NYC"
|
||||
>>> sequence_b = "Where is HuggingFace based?"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> encoded_dict = tokenizer(sequence_a, sequence_b)
|
||||
>>> decoded = tokenizer.decode(encoded_dict["input_ids"])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which will return:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> print(decoded)
|
||||
[CLS] HuggingFace is based in NYC [SEP] Where is HuggingFace based? [SEP]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This is enough for some models to understand where one sequence ends and where another begins. However, other models,
|
||||
such as BERT, also deploy token type IDs (also called segment IDs). They are represented as a binary mask identifying
|
||||
the two types of sequence in the model.
|
||||
|
||||
The tokenizer returns this mask as the "token_type_ids" entry:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> encoded_dict["token_type_ids"]
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The first sequence, the "context" used for the question, has all its tokens represented by a `0`, whereas the second
|
||||
sequence, corresponding to the "question", has all its tokens represented by a `1`.
|
||||
|
||||
Some models, like [`XLNetModel`] use an additional token represented by a `2`.
|
||||
|
||||
### transfer learning
|
||||
|
||||
A technique that involves taking a pretrained model and adapting it to a dataset specific to your task. Instead of training a model from scratch, you can leverage knowledge obtained from an existing model as a starting point. This speeds up the learning process and reduces the amount of training data needed.
|
||||
|
||||
### transformer
|
||||
|
||||
Self-attention based deep learning model architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
## U
|
||||
|
||||
### unsupervised learning
|
||||
|
||||
A form of model training in which data provided to the model is not labeled. Unsupervised learning techniques leverage statistical information of the data distribution to find patterns useful for the task at hand.
|
||||
@ -1,487 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Glossary
|
||||
|
||||
This glossary defines general machine learning and 🤗 Transformers terms to help you better understand the
|
||||
documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
## A
|
||||
|
||||
### attention mask
|
||||
|
||||
The attention mask is an optional argument used when batching sequences together.
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="M6adb1j2jPI"/>
|
||||
|
||||
This argument indicates to the model which tokens should be attended to, and which should not.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, consider these two sequences:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import BertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> sequence_a = "This is a short sequence."
|
||||
>>> sequence_b = "This is a rather long sequence. It is at least longer than the sequence A."
|
||||
|
||||
>>> encoded_sequence_a = tokenizer(sequence_a)["input_ids"]
|
||||
>>> encoded_sequence_b = tokenizer(sequence_b)["input_ids"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The encoded versions have different lengths:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> len(encoded_sequence_a), len(encoded_sequence_b)
|
||||
(8, 19)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, we can't put them together in the same tensor as-is. The first sequence needs to be padded up to the length
|
||||
of the second one, or the second one needs to be truncated down to the length of the first one.
|
||||
|
||||
In the first case, the list of IDs will be extended by the padding indices. We can pass a list to the tokenizer and ask
|
||||
it to pad like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> padded_sequences = tokenizer([sequence_a, sequence_b], padding=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can see that 0s have been added on the right of the first sentence to make it the same length as the second one:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> padded_sequences["input_ids"]
|
||||
[[101, 1188, 1110, 170, 1603, 4954, 119, 102, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [101, 1188, 1110, 170, 1897, 1263, 4954, 119, 1135, 1110, 1120, 1655, 2039, 1190, 1103, 4954, 138, 119, 102]]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This can then be converted into a tensor in PyTorch or TensorFlow. The attention mask is a binary tensor indicating the
|
||||
position of the padded indices so that the model does not attend to them. For the [`BertTokenizer`], `1` indicates a
|
||||
value that should be attended to, while `0` indicates a padded value. This attention mask is in the dictionary returned
|
||||
by the tokenizer under the key "attention_mask":
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> padded_sequences["attention_mask"]
|
||||
[[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### autoencoding models
|
||||
|
||||
See [encoder models](#encoder-models) and [masked language modeling](#masked-language-modeling-mlm)
|
||||
|
||||
### autoregressive models
|
||||
|
||||
See [causal language modeling](#causal-language-modeling) and [decoder models](#decoder-models)
|
||||
|
||||
## B
|
||||
|
||||
### backbone
|
||||
|
||||
The backbone is the network (embeddings and layers) that outputs the raw hidden states or features. It is usually connected to a [head](#head) which accepts the features as its input to make a prediction. For example, [`ViTModel`] is a backbone without a specific head on top. Other models can also use [`VitModel`] as a backbone such as [DPT](model_doc/dpt).
|
||||
|
||||
## C
|
||||
|
||||
### causal language modeling
|
||||
|
||||
A pretraining task where the model reads the texts in order and has to predict the next word. It's usually done by
|
||||
reading the whole sentence but using a mask inside the model to hide the future tokens at a certain timestep.
|
||||
|
||||
### channel
|
||||
|
||||
Color images are made up of some combination of values in three channels - red, green, and blue (RGB) - and grayscale images only have one channel. In 🤗 Transformers, the channel can be the first or last dimension of an image's tensor: [`n_channels`, `height`, `width`] or [`height`, `width`, `n_channels`].
|
||||
|
||||
### connectionist temporal classification (CTC)
|
||||
|
||||
An algorithm which allows a model to learn without knowing exactly how the input and output are aligned; CTC calculates the distribution of all possible outputs for a given input and chooses the most likely output from it. CTC is commonly used in speech recognition tasks because speech doesn't always cleanly align with the transcript for a variety of reasons such as a speaker's different speech rates.
|
||||
|
||||
### convolution
|
||||
|
||||
A type of layer in a neural network where the input matrix is multiplied element-wise by a smaller matrix (kernel or filter) and the values are summed up in a new matrix. This is known as a convolutional operation which is repeated over the entire input matrix. Each operation is applied to a different segment of the input matrix. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are commonly used in computer vision.
|
||||
|
||||
## D
|
||||
|
||||
### decoder input IDs
|
||||
|
||||
This input is specific to encoder-decoder models, and contains the input IDs that will be fed to the decoder. These
|
||||
inputs should be used for sequence to sequence tasks, such as translation or summarization, and are usually built in a
|
||||
way specific to each model.
|
||||
|
||||
Most encoder-decoder models (BART, T5) create their `decoder_input_ids` on their own from the `labels`. In such models,
|
||||
passing the `labels` is the preferred way to handle training.
|
||||
|
||||
Please check each model's docs to see how they handle these input IDs for sequence to sequence training.
|
||||
|
||||
### decoder models
|
||||
|
||||
Also referred to as autoregressive models, decoder models involve a pretraining task (called causal language modeling) where the model reads the texts in order and has to predict the next word. It's usually done by
|
||||
reading the whole sentence with a mask to hide future tokens at a certain timestep.
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="d_ixlCubqQw"/>
|
||||
|
||||
### deep learning (DL)
|
||||
|
||||
Machine learning algorithms which uses neural networks with several layers.
|
||||
|
||||
## E
|
||||
|
||||
### encoder models
|
||||
|
||||
Also known as autoencoding models, encoder models take an input (such as text or images) and transform them into a condensed numerical representation called an embedding. Oftentimes, encoder models are pretrained using techniques like [masked language modeling](#masked-language-modeling-mlm), which masks parts of the input sequence and forces the model to create more meaningful representations.
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="H39Z_720T5s"/>
|
||||
|
||||
## F
|
||||
|
||||
### feature extraction
|
||||
|
||||
The process of selecting and transforming raw data into a set of features that are more informative and useful for machine learning algorithms. Some examples of feature extraction include transforming raw text into word embeddings and extracting important features such as edges or shapes from image/video data.
|
||||
|
||||
### feed forward chunking
|
||||
|
||||
In each residual attention block in transformers the self-attention layer is usually followed by 2 feed forward layers.
|
||||
The intermediate embedding size of the feed forward layers is often bigger than the hidden size of the model (e.g., for
|
||||
`bert-base-uncased`).
|
||||
|
||||
For an input of size `[batch_size, sequence_length]`, the memory required to store the intermediate feed forward
|
||||
embeddings `[batch_size, sequence_length, config.intermediate_size]` can account for a large fraction of the memory
|
||||
use. The authors of [Reformer: The Efficient Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04451) noticed that since the
|
||||
computation is independent of the `sequence_length` dimension, it is mathematically equivalent to compute the output
|
||||
embeddings of both feed forward layers `[batch_size, config.hidden_size]_0, ..., [batch_size, config.hidden_size]_n`
|
||||
individually and concat them afterward to `[batch_size, sequence_length, config.hidden_size]` with `n =
|
||||
sequence_length`, which trades increased computation time against reduced memory use, but yields a mathematically
|
||||
**equivalent** result.
|
||||
|
||||
For models employing the function [`apply_chunking_to_forward`], the `chunk_size` defines the number of output
|
||||
embeddings that are computed in parallel and thus defines the trade-off between memory and time complexity. If
|
||||
`chunk_size` is set to 0, no feed forward chunking is done.
|
||||
|
||||
### finetuned models
|
||||
|
||||
Finetuning is a form of transfer learning which involves taking a pretrained model, freezing its weights, and replacing the output layer with a newly added [model head](#head). The model head is trained on your target dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
See the [Fine-tune a pretrained model](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/training) tutorial for more details, and learn how to fine-tune models with 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
## H
|
||||
|
||||
### head
|
||||
|
||||
The model head refers to the last layer of a neural network that accepts the raw hidden states and projects them onto a different dimension. There is a different model head for each task. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
* [`GPT2ForSequenceClassification`] is a sequence classification head - a linear layer - on top of the base [`GPT2Model`].
|
||||
* [`ViTForImageClassification`] is an image classification head - a linear layer on top of the final hidden state of the `CLS` token - on top of the base [`ViTModel`].
|
||||
* [`Wav2Vec2ForCTC`] ia a language modeling head with [CTC](#connectionist-temporal-classification-(CTC)) on top of the base [`Wav2Vec2Model`].
|
||||
|
||||
## I
|
||||
|
||||
### image patch
|
||||
|
||||
Vision-based Transformers models split an image into smaller patches which are linearly embedded, and then passed as a sequence to the model. You can find the `patch_size` - or resolution - of the model in it's configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
### inference
|
||||
|
||||
Inference is the process of evaluating a model on new data after training is complete. See the [Pipeline for inference](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/pipeline_tutorial) tutorial to learn how to perform inference with 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
### input IDs
|
||||
|
||||
The input ids are often the only required parameters to be passed to the model as input. They are token indices,
|
||||
numerical representations of tokens building the sequences that will be used as input by the model.
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="VFp38yj8h3A"/>
|
||||
|
||||
Each tokenizer works differently but the underlying mechanism remains the same. Here's an example using the BERT
|
||||
tokenizer, which is a [WordPiece](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1609.08144.pdf) tokenizer:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import BertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> sequence = "A Titan RTX has 24GB of VRAM"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The tokenizer takes care of splitting the sequence into tokens available in the tokenizer vocabulary.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> tokenized_sequence = tokenizer.tokenize(sequence)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The tokens are either words or subwords. Here for instance, "VRAM" wasn't in the model vocabulary, so it's been split
|
||||
in "V", "RA" and "M". To indicate those tokens are not separate words but parts of the same word, a double-hash prefix
|
||||
is added for "RA" and "M":
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> print(tokenized_sequence)
|
||||
['A', 'Titan', 'R', '##T', '##X', 'has', '24', '##GB', 'of', 'V', '##RA', '##M']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
These tokens can then be converted into IDs which are understandable by the model. This can be done by directly feeding
|
||||
the sentence to the tokenizer, which leverages the Rust implementation of [🤗
|
||||
Tokenizers](https://github.com/huggingface/tokenizers) for peak performance.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(sequence)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The tokenizer returns a dictionary with all the arguments necessary for its corresponding model to work properly. The
|
||||
token indices are under the key `input_ids`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> encoded_sequence = inputs["input_ids"]
|
||||
>>> print(encoded_sequence)
|
||||
[101, 138, 18696, 155, 1942, 3190, 1144, 1572, 13745, 1104, 159, 9664, 2107, 102]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the tokenizer automatically adds "special tokens" (if the associated model relies on them) which are special
|
||||
IDs the model sometimes uses.
|
||||
|
||||
If we decode the previous sequence of ids,
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> decoded_sequence = tokenizer.decode(encoded_sequence)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
we will see
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> print(decoded_sequence)
|
||||
[CLS] A Titan RTX has 24GB of VRAM [SEP]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
because this is the way a [`BertModel`] is going to expect its inputs.
|
||||
|
||||
## L
|
||||
|
||||
### labels
|
||||
|
||||
The labels are an optional argument which can be passed in order for the model to compute the loss itself. These labels
|
||||
should be the expected prediction of the model: it will use the standard loss in order to compute the loss between its
|
||||
predictions and the expected value (the label).
|
||||
|
||||
These labels are different according to the model head, for example:
|
||||
|
||||
- For sequence classification models, ([`BertForSequenceClassification`]), the model expects a tensor of dimension
|
||||
`(batch_size)` with each value of the batch corresponding to the expected label of the entire sequence.
|
||||
- For token classification models, ([`BertForTokenClassification`]), the model expects a tensor of dimension
|
||||
`(batch_size, seq_length)` with each value corresponding to the expected label of each individual token.
|
||||
- For masked language modeling, ([`BertForMaskedLM`]), the model expects a tensor of dimension `(batch_size,
|
||||
seq_length)` with each value corresponding to the expected label of each individual token: the labels being the token
|
||||
ID for the masked token, and values to be ignored for the rest (usually -100).
|
||||
- For sequence to sequence tasks, ([`BartForConditionalGeneration`], [`MBartForConditionalGeneration`]), the model
|
||||
expects a tensor of dimension `(batch_size, tgt_seq_length)` with each value corresponding to the target sequences
|
||||
associated with each input sequence. During training, both BART and T5 will make the appropriate
|
||||
`decoder_input_ids` and decoder attention masks internally. They usually do not need to be supplied. This does not
|
||||
apply to models leveraging the Encoder-Decoder framework.
|
||||
- For image classification models, ([`ViTForImageClassification`]), the model expects a tensor of dimension
|
||||
`(batch_size)` with each value of the batch corresponding to the expected label of each individual image.
|
||||
- For semantic segmentation models, ([`SegformerForSemanticSegmentation`]), the model expects a tensor of dimension
|
||||
`(batch_size, height, width)` with each value of the batch corresponding to the expected label of each individual pixel.
|
||||
- For object detection models, ([`DetrForObjectDetection`]), the model expects a list of dictionaries with a
|
||||
`class_labels` and `boxes` key where each value of the batch corresponds to the expected label and number of bounding boxes of each individual image.
|
||||
- For automatic speech recognition models, ([`Wav2Vec2ForCTC`]), the model expects a tensor of dimension `(batch_size,
|
||||
target_length)` with each value corresponding to the expected label of each individual token.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Each model's labels may be different, so be sure to always check the documentation of each model for more information
|
||||
about their specific labels!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The base models ([`BertModel`]) do not accept labels, as these are the base transformer models, simply outputting
|
||||
features.
|
||||
|
||||
### large language models (LLM)
|
||||
|
||||
A generic term that refers to transformer language models (GPT-3, BLOOM, OPT) that were trained on a large quantity of data. These models also tend to have a large number of learnable parameters (e.g. 175 billion for GPT-3).
|
||||
|
||||
## M
|
||||
|
||||
### masked language modeling (MLM)
|
||||
|
||||
A pretraining task where the model sees a corrupted version of the texts, usually done by
|
||||
masking some tokens randomly, and has to predict the original text.
|
||||
|
||||
### multimodal
|
||||
|
||||
A task that combines texts with another kind of inputs (for instance images).
|
||||
|
||||
## N
|
||||
|
||||
### Natural language generation (NLG)
|
||||
|
||||
All tasks related to generating text (for instance, [Write With Transformers](https://transformer.huggingface.co/), translation).
|
||||
|
||||
### Natural language processing (NLP)
|
||||
|
||||
A generic way to say "deal with texts".
|
||||
|
||||
### Natural language understanding (NLU)
|
||||
|
||||
All tasks related to understanding what is in a text (for instance classifying the
|
||||
whole text, individual words).
|
||||
|
||||
## P
|
||||
|
||||
### pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
A pipeline in 🤗 Transformers is an abstraction referring to a series of steps that are executed in a specific order to preprocess and transform data and return a prediction from a model. Some example stages found in a pipeline might be data preprocessing, feature extraction, and normalization.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, see [Pipelines for inference](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/pipeline_tutorial).
|
||||
|
||||
### pixel values
|
||||
|
||||
A tensor of the numerical representations of an image that is passed to a model. The pixel values have a shape of [`batch_size`, `num_channels`, `height`, `width`], and are generated from an image processor.
|
||||
|
||||
### pooling
|
||||
|
||||
An operation that reduces a matrix into a smaller matrix, either by taking the maximum or average of the pooled dimension(s). Pooling layers are commonly found between convolutional layers to downsample the feature representation.
|
||||
|
||||
### position IDs
|
||||
|
||||
Contrary to RNNs that have the position of each token embedded within them, transformers are unaware of the position of
|
||||
each token. Therefore, the position IDs (`position_ids`) are used by the model to identify each token's position in the
|
||||
list of tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
They are an optional parameter. If no `position_ids` are passed to the model, the IDs are automatically created as
|
||||
absolute positional embeddings.
|
||||
|
||||
Absolute positional embeddings are selected in the range `[0, config.max_position_embeddings - 1]`. Some models use
|
||||
other types of positional embeddings, such as sinusoidal position embeddings or relative position embeddings.
|
||||
|
||||
### preprocessing
|
||||
|
||||
The task of preparing raw data into a format that can be easily consumed by machine learning models. For example, text is typically preprocessed by tokenization. To gain a better idea of what preprocessing looks like for other input types, check out the [Preprocess](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/preprocessing) tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
### pretrained model
|
||||
|
||||
A model that has been pretrained on some data (for instance all of Wikipedia). Pretraining methods involve a
|
||||
self-supervised objective, which can be reading the text and trying to predict the next word (see [causal language
|
||||
modeling](#causal-language-modeling)) or masking some words and trying to predict them (see [masked language
|
||||
modeling](#masked-language-modeling-mlm)).
|
||||
|
||||
Speech and vision models have their own pretraining objectives. For example, Wav2Vec2 is a speech model pretrained on a contrastive task which requires the model to identify the "true" speech representation from a set of "false" speech representations. On the other hand, BEiT is a vision model pretrained on a masked image modeling task which masks some of the image patches and requires the model to predict the masked patches (similar to the masked language modeling objective).
|
||||
|
||||
## R
|
||||
|
||||
### recurrent neural network (RNN)
|
||||
|
||||
A type of model that uses a loop over a layer to process texts.
|
||||
|
||||
### representation learning
|
||||
|
||||
A subfield of machine learning which focuses on learning meaningful representations of raw data. Some examples of representation learning techniques include word embeddings, autoencoders, and Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs).
|
||||
|
||||
## S
|
||||
|
||||
### sampling rate
|
||||
|
||||
A measurement in hertz of the number of samples (the audio signal) taken per second. The sampling rate is a result of discretizing a continuous signal such as speech.
|
||||
|
||||
### self-attention
|
||||
|
||||
Each element of the input finds out which other elements of the input they should attend to.
|
||||
|
||||
### self-supervised learning
|
||||
|
||||
A category of machine learning techniques in which a model creates its own learning objective from unlabeled data. It differs from [unsupervised learning](#unsupervised-learning) and [supervised learning](#supervised-learning) in that the learning process is supervised, but not explicitly from the user.
|
||||
|
||||
One example of self-supervised learning is [masked language modeling](#masked-language-modeling-mlm), where a model is passed sentences with a proportion of its tokens removed and learns to predict the missing tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
### semi-supervised learning
|
||||
|
||||
A broad category of machine learning training techniques that leverages a small amount of labeled data with a larger quantity of unlabeled data to improve the accuracy of a model, unlike [supervised learning](#supervised-learning) and [unsupervised learning](#unsupervised-learning).
|
||||
|
||||
An example of a semi-supervised learning approach is "self-training", in which a model is trained on labeled data, and then used to make predictions on the unlabeled data. The portion of the unlabeled data that the model predicts with the most confidence gets added to the labeled dataset and used to retrain the model.
|
||||
|
||||
### sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq)
|
||||
|
||||
Models that generate a new sequence from an input, like translation models, or summarization models (such as
|
||||
[Bart](model_doc/bart) or [T5](model_doc/t5)).
|
||||
|
||||
### stride
|
||||
|
||||
In [convolution](#convolution) or [pooling](#pooling), the stride refers to the distance the kernel is moved over a matrix. A stride of 1 means the kernel is moved one pixel over at a time, and a stride of 2 means the kernel is moved two pixels over at a time.
|
||||
|
||||
### supervised learning
|
||||
|
||||
A form of model training that directly uses labeled data to correct and instruct model performance. Data is fed into the model being trained, and its predictions are compared to the known labels. The model updates its weights based on how incorrect its predictions were, and the process is repeated to optimize model performance.
|
||||
|
||||
## T
|
||||
|
||||
### token
|
||||
|
||||
A part of a sentence, usually a word, but can also be a subword (non-common words are often split in subwords) or a
|
||||
punctuation symbol.
|
||||
|
||||
### token Type IDs
|
||||
|
||||
Some models' purpose is to do classification on pairs of sentences or question answering.
|
||||
|
||||
<Youtube id="0u3ioSwev3s"/>
|
||||
|
||||
These require two different sequences to be joined in a single "input_ids" entry, which usually is performed with the
|
||||
help of special tokens, such as the classifier (`[CLS]`) and separator (`[SEP]`) tokens. For example, the BERT model
|
||||
builds its two sequence input as such:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> # [CLS] SEQUENCE_A [SEP] SEQUENCE_B [SEP]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can use our tokenizer to automatically generate such a sentence by passing the two sequences to `tokenizer` as two
|
||||
arguments (and not a list, like before) like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import BertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased")
|
||||
>>> sequence_a = "HuggingFace is based in NYC"
|
||||
>>> sequence_b = "Where is HuggingFace based?"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> encoded_dict = tokenizer(sequence_a, sequence_b)
|
||||
>>> decoded = tokenizer.decode(encoded_dict["input_ids"])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which will return:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> print(decoded)
|
||||
[CLS] HuggingFace is based in NYC [SEP] Where is HuggingFace based? [SEP]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This is enough for some models to understand where one sequence ends and where another begins. However, other models,
|
||||
such as BERT, also deploy token type IDs (also called segment IDs). They are represented as a binary mask identifying
|
||||
the two types of sequence in the model.
|
||||
|
||||
The tokenizer returns this mask as the "token_type_ids" entry:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> encoded_dict["token_type_ids"]
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The first sequence, the "context" used for the question, has all its tokens represented by a `0`, whereas the second
|
||||
sequence, corresponding to the "question", has all its tokens represented by a `1`.
|
||||
|
||||
Some models, like [`XLNetModel`] use an additional token represented by a `2`.
|
||||
|
||||
### transfer learning
|
||||
|
||||
A technique that involves taking a pretrained model and adapting it to a dataset specific to your task. Instead of training a model from scratch, you can leverage knowledge obtained from an existing model as a starting point. This speeds up the learning process and reduces the amount of training data needed.
|
||||
|
||||
### transformer
|
||||
|
||||
Self-attention based deep learning model architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
## U
|
||||
|
||||
### unsupervised learning
|
||||
|
||||
A form of model training in which data provided to the model is not labeled. Unsupervised learning techniques leverage statistical information of the data distribution to find patterns useful for the task at hand.
|
||||
124
docs/source/en/hpo_train.md
Normal file
124
docs/source/en/hpo_train.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,124 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Hyperparameter Search using Trainer API
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers provides a [`Trainer`] class optimized for training 🤗 Transformers models, making it easier to start training without manually writing your own training loop. The [`Trainer`] provides API for hyperparameter search. This doc shows how to enable it in example.
|
||||
|
||||
## Hyperparameter Search backend
|
||||
|
||||
[`Trainer`] supports four hyperparameter search backends currently:
|
||||
[optuna](https://optuna.org/), [sigopt](https://sigopt.com/), [raytune](https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/index.html) and [wandb](https://wandb.ai/site/sweeps).
|
||||
|
||||
you should install them before using them as the hyperparameter search backend
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install optuna/sigopt/wandb/ray[tune]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## How to enable Hyperparameter search in example
|
||||
|
||||
Define the hyperparameter search space, different backends need different format.
|
||||
|
||||
For sigopt, see sigopt [object_parameter](https://docs.sigopt.com/ai-module-api-references/api_reference/objects/object_parameter), it's like following:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def sigopt_hp_space(trial):
|
||||
... return [
|
||||
... {"bounds": {"min": 1e-6, "max": 1e-4}, "name": "learning_rate", "type": "double"},
|
||||
... {
|
||||
... "categorical_values": ["16", "32", "64", "128"],
|
||||
... "name": "per_device_train_batch_size",
|
||||
... "type": "categorical",
|
||||
... },
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For optuna, see optuna [object_parameter](https://optuna.readthedocs.io/en/stable/tutorial/10_key_features/002_configurations.html#sphx-glr-tutorial-10-key-features-002-configurations-py), it's like following:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def optuna_hp_space(trial):
|
||||
... return {
|
||||
... "learning_rate": trial.suggest_float("learning_rate", 1e-6, 1e-4, log=True),
|
||||
... "per_device_train_batch_size": trial.suggest_categorical("per_device_train_batch_size", [16, 32, 64, 128]),
|
||||
... }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For raytune, see raytune [object_parameter](https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/api_docs/search_space.html), it's like following:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def ray_hp_space(trial):
|
||||
... return {
|
||||
... "learning_rate": tune.loguniform(1e-6, 1e-4),
|
||||
... "per_device_train_batch_size": tune.choice([16, 32, 64, 128]),
|
||||
... }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For wandb, see wandb [object_parameter](https://docs.wandb.ai/guides/sweeps/configuration), it's like following:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def wandb_hp_space(trial):
|
||||
... return {
|
||||
... "method": "random",
|
||||
... "metric": {"name": "objective", "goal": "minimize"},
|
||||
... "parameters": {
|
||||
... "learning_rate": {"distribution": "uniform", "min": 1e-6, "max": 1e-4},
|
||||
... "per_device_train_batch_size": {"values": [16, 32, 64, 128]},
|
||||
... },
|
||||
... }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Define a `model_init` function and pass it to the [`Trainer`], as an example:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def model_init(trial):
|
||||
... return AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
|
||||
... model_args.model_name_or_path,
|
||||
... from_tf=bool(".ckpt" in model_args.model_name_or_path),
|
||||
... config=config,
|
||||
... cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir,
|
||||
... revision=model_args.model_revision,
|
||||
... use_auth_token=True if model_args.use_auth_token else None,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a [`Trainer`] with your `model_init` function, training arguments, training and test datasets, and evaluation function:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> trainer = Trainer(
|
||||
... model=None,
|
||||
... args=training_args,
|
||||
... train_dataset=small_train_dataset,
|
||||
... eval_dataset=small_eval_dataset,
|
||||
... compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
|
||||
... tokenizer=tokenizer,
|
||||
... model_init=model_init,
|
||||
... data_collator=data_collator,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Call hyperparameter search, get the best trial parameters, backend could be `"optuna"`/`"sigopt"`/`"wandb"`/`"ray"`. direction can be`"minimize"` or `"maximize"`, which indicates whether to optimize greater or lower objective.
|
||||
|
||||
You could define your own compute_objective function, if not defined, the default compute_objective will be called, and the sum of eval metric like f1 is returned as objective value.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> best_trial = trainer.hyperparameter_search(
|
||||
... direction="maximize",
|
||||
... backend="optuna",
|
||||
... hp_space=optuna_hp_space,
|
||||
... n_trials=20,
|
||||
... compute_objective=compute_objective,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Hyperparameter search For DDP finetune
|
||||
Currently, Hyperparameter search for DDP is enabled for optuna and sigopt. Only the rank-zero process will generate the search trial and pass the argument to other ranks.
|
||||
@ -1,120 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Hyperparameter Search using Trainer API
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers provides a [`Trainer`] class optimized for training 🤗 Transformers models, making it easier to start training without manually writing your own training loop. The [`Trainer`] provides API for hyperparameter search. This doc shows how to enable it in example.
|
||||
|
||||
## Hyperparameter Search backend
|
||||
|
||||
[`Trainer`] supports four hyperparameter search backends currently:
|
||||
[optuna](https://optuna.org/), [sigopt](https://sigopt.com/), [raytune](https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/index.html) and [wandb](https://wandb.ai/site/sweeps).
|
||||
|
||||
you should install them before using them as the hyperparameter search backend
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install optuna/sigopt/wandb/ray[tune]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## How to enable Hyperparameter search in example
|
||||
|
||||
Define the hyperparameter search space, different backends need different format.
|
||||
|
||||
For sigopt, see sigopt [object_parameter](https://docs.sigopt.com/ai-module-api-references/api_reference/objects/object_parameter), it's like following:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def sigopt_hp_space(trial):
|
||||
... return [
|
||||
... {"bounds": {"min": 1e-6, "max": 1e-4}, "name": "learning_rate", "type": "double"},
|
||||
... {
|
||||
... "categorical_values": ["16", "32", "64", "128"],
|
||||
... "name": "per_device_train_batch_size",
|
||||
... "type": "categorical",
|
||||
... },
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For optuna, see optuna [object_parameter](https://optuna.readthedocs.io/en/stable/tutorial/10_key_features/002_configurations.html#sphx-glr-tutorial-10-key-features-002-configurations-py), it's like following:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def optuna_hp_space(trial):
|
||||
... return {
|
||||
... "learning_rate": trial.suggest_float("learning_rate", 1e-6, 1e-4, log=True),
|
||||
... "per_device_train_batch_size": trial.suggest_categorical("per_device_train_batch_size", [16, 32, 64, 128]),
|
||||
... }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For raytune, see raytune [object_parameter](https://docs.ray.io/en/latest/tune/api_docs/search_space.html), it's like following:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def ray_hp_space(trial):
|
||||
... return {
|
||||
... "learning_rate": tune.loguniform(1e-6, 1e-4),
|
||||
... "per_device_train_batch_size": tune.choice([16, 32, 64, 128]),
|
||||
... }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For wandb, see wandb [object_parameter](https://docs.wandb.ai/guides/sweeps/configuration), it's like following:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def wandb_hp_space(trial):
|
||||
... return {
|
||||
... "method": "random",
|
||||
... "metric": {"name": "objective", "goal": "minimize"},
|
||||
... "parameters": {
|
||||
... "learning_rate": {"distribution": "uniform", "min": 1e-6, "max": 1e-4},
|
||||
... "per_device_train_batch_size": {"values": [16, 32, 64, 128]},
|
||||
... },
|
||||
... }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Define a `model_init` function and pass it to the [`Trainer`], as an example:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> def model_init(trial):
|
||||
... return AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
|
||||
... model_args.model_name_or_path,
|
||||
... from_tf=bool(".ckpt" in model_args.model_name_or_path),
|
||||
... config=config,
|
||||
... cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir,
|
||||
... revision=model_args.model_revision,
|
||||
... use_auth_token=True if model_args.use_auth_token else None,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a [`Trainer`] with your `model_init` function, training arguments, training and test datasets, and evaluation function:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> trainer = Trainer(
|
||||
... model=None,
|
||||
... args=training_args,
|
||||
... train_dataset=small_train_dataset,
|
||||
... eval_dataset=small_eval_dataset,
|
||||
... compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
|
||||
... tokenizer=tokenizer,
|
||||
... model_init=model_init,
|
||||
... data_collator=data_collator,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Call hyperparameter search, get the best trial parameters, backend could be `"optuna"`/`"sigopt"`/`"wandb"`/`"ray"`. direction can be`"minimize"` or `"maximize"`, which indicates whether to optimize greater or lower objective.
|
||||
|
||||
You could define your own compute_objective function, if not defined, the default compute_objective will be called, and the sum of eval metric like f1 is returned as objective value.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> best_trial = trainer.hyperparameter_search(
|
||||
... direction="maximize",
|
||||
... backend="optuna",
|
||||
... hp_space=optuna_hp_space,
|
||||
... n_trials=20,
|
||||
... compute_objective=compute_objective,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Hyperparameter search For DDP finetune
|
||||
Currently, Hyperparameter search for DDP is enabled for optuna and sigopt. Only the rank-zero process will generate the search trial and pass the argument to other ranks.
|
||||
465
docs/source/en/index.md
Normal file
465
docs/source/en/index.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,465 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
State-of-the-art Machine Learning for [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/), and [JAX](https://jax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/).
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers provides APIs and tools to easily download and train state-of-the-art pretrained models. Using pretrained models can reduce your compute costs, carbon footprint, and save you the time and resources required to train a model from scratch. These models support common tasks in different modalities, such as:
|
||||
|
||||
📝 **Natural Language Processing**: text classification, named entity recognition, question answering, language modeling, summarization, translation, multiple choice, and text generation.<br>
|
||||
🖼️ **Computer Vision**: image classification, object detection, and segmentation.<br>
|
||||
🗣️ **Audio**: automatic speech recognition and audio classification.<br>
|
||||
🐙 **Multimodal**: table question answering, optical character recognition, information extraction from scanned documents, video classification, and visual question answering.
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers support framework interoperability between PyTorch, TensorFlow, and JAX. This provides the flexibility to use a different framework at each stage of a model's life; train a model in three lines of code in one framework, and load it for inference in another. Models can also be exported to a format like ONNX and TorchScript for deployment in production environments.
|
||||
|
||||
Join the growing community on the [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models), [forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/), or [Discord](https://discord.com/invite/JfAtkvEtRb) today!
|
||||
|
||||
## If you are looking for custom support from the Hugging Face team
|
||||
|
||||
<a target="_blank" href="https://huggingface.co/support">
|
||||
<img alt="HuggingFace Expert Acceleration Program" src="https://cdn-media.huggingface.co/marketing/transformers/new-support-improved.png" style="width: 100%; max-width: 600px; border: 1px solid #eee; border-radius: 4px; box-shadow: 0 1px 2px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Contents
|
||||
|
||||
The documentation is organized into five sections:
|
||||
|
||||
- **GET STARTED** provides a quick tour of the library and installation instructions to get up and running.
|
||||
- **TUTORIALS** are a great place to start if you're a beginner. This section will help you gain the basic skills you need to start using the library.
|
||||
- **HOW-TO GUIDES** show you how to achieve a specific goal, like finetuning a pretrained model for language modeling or how to write and share a custom model.
|
||||
- **CONCEPTUAL GUIDES** offers more discussion and explanation of the underlying concepts and ideas behind models, tasks, and the design philosophy of 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
- **API** describes all classes and functions:
|
||||
|
||||
- **MAIN CLASSES** details the most important classes like configuration, model, tokenizer, and pipeline.
|
||||
- **MODELS** details the classes and functions related to each model implemented in the library.
|
||||
- **INTERNAL HELPERS** details utility classes and functions used internally.
|
||||
|
||||
### Supported models
|
||||
|
||||
<!--This list is updated automatically from the README with _make fix-copies_. Do not update manually! -->
|
||||
|
||||
1. **[ALBERT](model_doc/albert)** (from Google Research and the Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago) released with the paper [ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-supervised Learning of Language Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.11942), by Zhenzhong Lan, Mingda Chen, Sebastian Goodman, Kevin Gimpel, Piyush Sharma, Radu Soricut.
|
||||
1. **[ALIGN](model_doc/align)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Scaling Up Visual and Vision-Language Representation Learning With Noisy Text Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.05918) by Chao Jia, Yinfei Yang, Ye Xia, Yi-Ting Chen, Zarana Parekh, Hieu Pham, Quoc V. Le, Yunhsuan Sung, Zhen Li, Tom Duerig.
|
||||
1. **[AltCLIP](model_doc/altclip)** (from BAAI) released with the paper [AltCLIP: Altering the Language Encoder in CLIP for Extended Language Capabilities](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06679) by Chen, Zhongzhi and Liu, Guang and Zhang, Bo-Wen and Ye, Fulong and Yang, Qinghong and Wu, Ledell.
|
||||
1. **[Audio Spectrogram Transformer](model_doc/audio-spectrogram-transformer)** (from MIT) released with the paper [AST: Audio Spectrogram Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01778) by Yuan Gong, Yu-An Chung, James Glass.
|
||||
1. **[Autoformer](model_doc/autoformer)** (from Tsinghua University) released with the paper [Autoformer: Decomposition Transformers with Auto-Correlation for Long-Term Series Forecasting](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.13008) by Haixu Wu, Jiehui Xu, Jianmin Wang, Mingsheng Long.
|
||||
1. **[BART](model_doc/bart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [BART: Denoising Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training for Natural Language Generation, Translation, and Comprehension](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.13461) by Mike Lewis, Yinhan Liu, Naman Goyal, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Omer Levy, Ves Stoyanov and Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[BARThez](model_doc/barthez)** (from École polytechnique) released with the paper [BARThez: a Skilled Pretrained French Sequence-to-Sequence Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.12321) by Moussa Kamal Eddine, Antoine J.-P. Tixier, Michalis Vazirgiannis.
|
||||
1. **[BARTpho](model_doc/bartpho)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [BARTpho: Pre-trained Sequence-to-Sequence Models for Vietnamese](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.09701) by Nguyen Luong Tran, Duong Minh Le and Dat Quoc Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[BEiT](model_doc/beit)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [BEiT: BERT Pre-Training of Image Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.08254) by Hangbo Bao, Li Dong, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[BERT](model_doc/bert)** (from Google) released with the paper [BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805) by Jacob Devlin, Ming-Wei Chang, Kenton Lee and Kristina Toutanova.
|
||||
1. **[BERT For Sequence Generation](model_doc/bert-generation)** (from Google) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[BERTweet](model_doc/bertweet)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [BERTweet: A pre-trained language model for English Tweets](https://aclanthology.org/2020.emnlp-demos.2/) by Dat Quoc Nguyen, Thanh Vu and Anh Tuan Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-Pegasus](model_doc/bigbird_pegasus)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-RoBERTa](model_doc/big_bird)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[BioGpt](model_doc/biogpt)** (from Microsoft Research AI4Science) released with the paper [BioGPT: generative pre-trained transformer for biomedical text generation and mining](https://academic.oup.com/bib/advance-article/doi/10.1093/bib/bbac409/6713511?guestAccessKey=a66d9b5d-4f83-4017-bb52-405815c907b9) by Renqian Luo, Liai Sun, Yingce Xia, Tao Qin, Sheng Zhang, Hoifung Poon and Tie-Yan Liu.
|
||||
1. **[BiT](model_doc/bit)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Big Transfer (BiT): General Visual Representation Learning](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.11370) by Alexander Kolesnikov, Lucas Beyer, Xiaohua Zhai, Joan Puigcerver, Jessica Yung, Sylvain Gelly, Neil Houlsby.
|
||||
1. **[Blenderbot](model_doc/blenderbot)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BlenderbotSmall](model_doc/blenderbot-small)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BLIP](model_doc/blip)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [BLIP: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training for Unified Vision-Language Understanding and Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.12086) by Junnan Li, Dongxu Li, Caiming Xiong, Steven Hoi.
|
||||
1. **[BLIP-2](model_doc/blip-2)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [BLIP-2: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training with Frozen Image Encoders and Large Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12597) by Junnan Li, Dongxu Li, Silvio Savarese, Steven Hoi.
|
||||
1. **[BLOOM](model_doc/bloom)** (from BigScience workshop) released by the [BigScience Workshop](https://bigscience.huggingface.co/).
|
||||
1. **[BORT](model_doc/bort)** (from Alexa) released with the paper [Optimal Subarchitecture Extraction For BERT](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.10499) by Adrian de Wynter and Daniel J. Perry.
|
||||
1. **[BridgeTower](model_doc/bridgetower)** (from Harbin Institute of Technology/Microsoft Research Asia/Intel Labs) released with the paper [BridgeTower: Building Bridges Between Encoders in Vision-Language Representation Learning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08657) by Xiao Xu, Chenfei Wu, Shachar Rosenman, Vasudev Lal, Wanxiang Che, Nan Duan.
|
||||
1. **[ByT5](model_doc/byt5)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [ByT5: Towards a token-free future with pre-trained byte-to-byte models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.13626) by Linting Xue, Aditya Barua, Noah Constant, Rami Al-Rfou, Sharan Narang, Mihir Kale, Adam Roberts, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[CamemBERT](model_doc/camembert)** (from Inria/Facebook/Sorbonne) released with the paper [CamemBERT: a Tasty French Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.03894) by Louis Martin*, Benjamin Muller*, Pedro Javier Ortiz Suárez*, Yoann Dupont, Laurent Romary, Éric Villemonte de la Clergerie, Djamé Seddah and Benoît Sagot.
|
||||
1. **[CANINE](model_doc/canine)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [CANINE: Pre-training an Efficient Tokenization-Free Encoder for Language Representation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06874) by Jonathan H. Clark, Dan Garrette, Iulia Turc, John Wieting.
|
||||
1. **[Chinese-CLIP](model_doc/chinese_clip)** (from OFA-Sys) released with the paper [Chinese CLIP: Contrastive Vision-Language Pretraining in Chinese](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.01335) by An Yang, Junshu Pan, Junyang Lin, Rui Men, Yichang Zhang, Jingren Zhou, Chang Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[CLAP](model_doc/clap)** (from LAION-AI) released with the paper [Large-scale Contrastive Language-Audio Pretraining with Feature Fusion and Keyword-to-Caption Augmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06687) by Yusong Wu, Ke Chen, Tianyu Zhang, Yuchen Hui, Taylor Berg-Kirkpatrick, Shlomo Dubnov.
|
||||
1. **[CLIP](model_doc/clip)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020) by Alec Radford, Jong Wook Kim, Chris Hallacy, Aditya Ramesh, Gabriel Goh, Sandhini Agarwal, Girish Sastry, Amanda Askell, Pamela Mishkin, Jack Clark, Gretchen Krueger, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[CLIPSeg](model_doc/clipseg)** (from University of Göttingen) released with the paper [Image Segmentation Using Text and Image Prompts](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10003) by Timo Lüddecke and Alexander Ecker.
|
||||
1. **[CodeGen](model_doc/codegen)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [A Conversational Paradigm for Program Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.13474) by Erik Nijkamp, Bo Pang, Hiroaki Hayashi, Lifu Tu, Huan Wang, Yingbo Zhou, Silvio Savarese, Caiming Xiong.
|
||||
1. **[Conditional DETR](model_doc/conditional_detr)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [Conditional DETR for Fast Training Convergence](https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.06152) by Depu Meng, Xiaokang Chen, Zejia Fan, Gang Zeng, Houqiang Li, Yuhui Yuan, Lei Sun, Jingdong Wang.
|
||||
1. **[ConvBERT](model_doc/convbert)** (from YituTech) released with the paper [ConvBERT: Improving BERT with Span-based Dynamic Convolution](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.02496) by Zihang Jiang, Weihao Yu, Daquan Zhou, Yunpeng Chen, Jiashi Feng, Shuicheng Yan.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXT](model_doc/convnext)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [A ConvNet for the 2020s](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545) by Zhuang Liu, Hanzi Mao, Chao-Yuan Wu, Christoph Feichtenhofer, Trevor Darrell, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXTV2](model_doc/convnextv2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [ConvNeXt V2: Co-designing and Scaling ConvNets with Masked Autoencoders](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.00808) by Sanghyun Woo, Shoubhik Debnath, Ronghang Hu, Xinlei Chen, Zhuang Liu, In So Kweon, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[CPM](model_doc/cpm)** (from Tsinghua University) released with the paper [CPM: A Large-scale Generative Chinese Pre-trained Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.00413) by Zhengyan Zhang, Xu Han, Hao Zhou, Pei Ke, Yuxian Gu, Deming Ye, Yujia Qin, Yusheng Su, Haozhe Ji, Jian Guan, Fanchao Qi, Xiaozhi Wang, Yanan Zheng, Guoyang Zeng, Huanqi Cao, Shengqi Chen, Daixuan Li, Zhenbo Sun, Zhiyuan Liu, Minlie Huang, Wentao Han, Jie Tang, Juanzi Li, Xiaoyan Zhu, Maosong Sun.
|
||||
1. **[CPM-Ant](model_doc/cpmant)** (from OpenBMB) released by the [OpenBMB](https://www.openbmb.org/).
|
||||
1. **[CTRL](model_doc/ctrl)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [CTRL: A Conditional Transformer Language Model for Controllable Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.05858) by Nitish Shirish Keskar*, Bryan McCann*, Lav R. Varshney, Caiming Xiong and Richard Socher.
|
||||
1. **[CvT](model_doc/cvt)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [CvT: Introducing Convolutions to Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.15808) by Haiping Wu, Bin Xiao, Noel Codella, Mengchen Liu, Xiyang Dai, Lu Yuan, Lei Zhang.
|
||||
1. **[Data2Vec](model_doc/data2vec)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Data2Vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.03555) by Alexei Baevski, Wei-Ning Hsu, Qiantong Xu, Arun Babu, Jiatao Gu, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa](model_doc/deberta)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa-v2](model_doc/deberta-v2)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[Decision Transformer](model_doc/decision_transformer)** (from Berkeley/Facebook/Google) released with the paper [Decision Transformer: Reinforcement Learning via Sequence Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.01345) by Lili Chen, Kevin Lu, Aravind Rajeswaran, Kimin Lee, Aditya Grover, Michael Laskin, Pieter Abbeel, Aravind Srinivas, Igor Mordatch.
|
||||
1. **[Deformable DETR](model_doc/deformable_detr)** (from SenseTime Research) released with the paper [Deformable DETR: Deformable Transformers for End-to-End Object Detection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.04159) by Xizhou Zhu, Weijie Su, Lewei Lu, Bin Li, Xiaogang Wang, Jifeng Dai.
|
||||
1. **[DeiT](model_doc/deit)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.12877) by Hugo Touvron, Matthieu Cord, Matthijs Douze, Francisco Massa, Alexandre Sablayrolles, Hervé Jégou.
|
||||
1. **[DePlot](model_doc/deplot)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [DePlot: One-shot visual language reasoning by plot-to-table translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.10505) by Fangyu Liu, Julian Martin Eisenschlos, Francesco Piccinno, Syrine Krichene, Chenxi Pang, Kenton Lee, Mandar Joshi, Wenhu Chen, Nigel Collier, Yasemin Altun.
|
||||
1. **[DETA](model_doc/deta)** (from The University of Texas at Austin) released with the paper [NMS Strikes Back](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.06137) by Jeffrey Ouyang-Zhang, Jang Hyun Cho, Xingyi Zhou, Philipp Krähenbühl.
|
||||
1. **[DETR](model_doc/detr)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.12872) by Nicolas Carion, Francisco Massa, Gabriel Synnaeve, Nicolas Usunier, Alexander Kirillov, Sergey Zagoruyko.
|
||||
1. **[DialoGPT](model_doc/dialogpt)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [DialoGPT: Large-Scale Generative Pre-training for Conversational Response Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.00536) by Yizhe Zhang, Siqi Sun, Michel Galley, Yen-Chun Chen, Chris Brockett, Xiang Gao, Jianfeng Gao, Jingjing Liu, Bill Dolan.
|
||||
1. **[DiNAT](model_doc/dinat)** (from SHI Labs) released with the paper [Dilated Neighborhood Attention Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.15001) by Ali Hassani and Humphrey Shi.
|
||||
1. **[DistilBERT](model_doc/distilbert)** (from HuggingFace), released together with the paper [DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.01108) by Victor Sanh, Lysandre Debut and Thomas Wolf. The same method has been applied to compress GPT2 into [DistilGPT2](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation), RoBERTa into [DistilRoBERTa](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation), Multilingual BERT into [DistilmBERT](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation) and a German version of DistilBERT.
|
||||
1. **[DiT](model_doc/dit)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [DiT: Self-supervised Pre-training for Document Image Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.02378) by Junlong Li, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[Donut](model_doc/donut)** (from NAVER), released together with the paper [OCR-free Document Understanding Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.15664) by Geewook Kim, Teakgyu Hong, Moonbin Yim, Jeongyeon Nam, Jinyoung Park, Jinyeong Yim, Wonseok Hwang, Sangdoo Yun, Dongyoon Han, Seunghyun Park.
|
||||
1. **[DPR](model_doc/dpr)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Dense Passage Retrieval for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.04906) by Vladimir Karpukhin, Barlas Oğuz, Sewon Min, Patrick Lewis, Ledell Wu, Sergey Edunov, Danqi Chen, and Wen-tau Yih.
|
||||
1. **[DPT](master/model_doc/dpt)** (from Intel Labs) released with the paper [Vision Transformers for Dense Prediction](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13413) by René Ranftl, Alexey Bochkovskiy, Vladlen Koltun.
|
||||
1. **[EfficientFormer](model_doc/efficientformer)** (from Snap Research) released with the paper [EfficientFormer: Vision Transformers at MobileNetSpeed](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.01191) by Yanyu Li, Geng Yuan, Yang Wen, Ju Hu, Georgios Evangelidis, Sergey Tulyakov, Yanzhi Wang, Jian Ren.
|
||||
1. **[EfficientNet](model_doc/efficientnet)** (from Google Brain) released with the paper [EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946) by Mingxing Tan, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[ELECTRA](model_doc/electra)** (from Google Research/Stanford University) released with the paper [ELECTRA: Pre-training text encoders as discriminators rather than generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10555) by Kevin Clark, Minh-Thang Luong, Quoc V. Le, Christopher D. Manning.
|
||||
1. **[EnCodec](model_doc/encodec)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [High Fidelity Neural Audio Compression](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.13438) by Alexandre Défossez, Jade Copet, Gabriel Synnaeve, Yossi Adi.
|
||||
1. **[EncoderDecoder](model_doc/encoder-decoder)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[ERNIE](model_doc/ernie)** (from Baidu) released with the paper [ERNIE: Enhanced Representation through Knowledge Integration](https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.09223) by Yu Sun, Shuohuan Wang, Yukun Li, Shikun Feng, Xuyi Chen, Han Zhang, Xin Tian, Danxiang Zhu, Hao Tian, Hua Wu.
|
||||
1. **[ErnieM](model_doc/ernie_m)** (from Baidu) released with the paper [ERNIE-M: Enhanced Multilingual Representation by Aligning Cross-lingual Semantics with Monolingual Corpora](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.15674) by Xuan Ouyang, Shuohuan Wang, Chao Pang, Yu Sun, Hao Tian, Hua Wu, Haifeng Wang.
|
||||
1. **[ESM](model_doc/esm)** (from Meta AI) are transformer protein language models. **ESM-1b** was released with the paper [Biological structure and function emerge from scaling unsupervised learning to 250 million protein sequences](https://www.pnas.org/content/118/15/e2016239118) by Alexander Rives, Joshua Meier, Tom Sercu, Siddharth Goyal, Zeming Lin, Jason Liu, Demi Guo, Myle Ott, C. Lawrence Zitnick, Jerry Ma, and Rob Fergus. **ESM-1v** was released with the paper [Language models enable zero-shot prediction of the effects of mutations on protein function](https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.09.450648) by Joshua Meier, Roshan Rao, Robert Verkuil, Jason Liu, Tom Sercu and Alexander Rives. **ESM-2 and ESMFold** were released with the paper [Language models of protein sequences at the scale of evolution enable accurate structure prediction](https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.20.500902) by Zeming Lin, Halil Akin, Roshan Rao, Brian Hie, Zhongkai Zhu, Wenting Lu, Allan dos Santos Costa, Maryam Fazel-Zarandi, Tom Sercu, Sal Candido, Alexander Rives.
|
||||
1. **[FLAN-T5](model_doc/flan-t5)** (from Google AI) released in the repository [google-research/t5x](https://github.com/google-research/t5x/blob/main/docs/models.md#flan-t5-checkpoints) by Hyung Won Chung, Le Hou, Shayne Longpre, Barret Zoph, Yi Tay, William Fedus, Eric Li, Xuezhi Wang, Mostafa Dehghani, Siddhartha Brahma, Albert Webson, Shixiang Shane Gu, Zhuyun Dai, Mirac Suzgun, Xinyun Chen, Aakanksha Chowdhery, Sharan Narang, Gaurav Mishra, Adams Yu, Vincent Zhao, Yanping Huang, Andrew Dai, Hongkun Yu, Slav Petrov, Ed H. Chi, Jeff Dean, Jacob Devlin, Adam Roberts, Denny Zhou, Quoc V. Le, and Jason Wei
|
||||
1. **[FLAN-UL2](model_doc/flan-ul2)** (from Google AI) released in the repository [google-research/t5x](https://github.com/google-research/t5x/blob/main/docs/models.md#flan-ul2-checkpoints) by Hyung Won Chung, Le Hou, Shayne Longpre, Barret Zoph, Yi Tay, William Fedus, Eric Li, Xuezhi Wang, Mostafa Dehghani, Siddhartha Brahma, Albert Webson, Shixiang Shane Gu, Zhuyun Dai, Mirac Suzgun, Xinyun Chen, Aakanksha Chowdhery, Sharan Narang, Gaurav Mishra, Adams Yu, Vincent Zhao, Yanping Huang, Andrew Dai, Hongkun Yu, Slav Petrov, Ed H. Chi, Jeff Dean, Jacob Devlin, Adam Roberts, Denny Zhou, Quoc V. Le, and Jason Wei
|
||||
1. **[FlauBERT](model_doc/flaubert)** (from CNRS) released with the paper [FlauBERT: Unsupervised Language Model Pre-training for French](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.05372) by Hang Le, Loïc Vial, Jibril Frej, Vincent Segonne, Maximin Coavoux, Benjamin Lecouteux, Alexandre Allauzen, Benoît Crabbé, Laurent Besacier, Didier Schwab.
|
||||
1. **[FLAVA](model_doc/flava)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FLAVA: A Foundational Language And Vision Alignment Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.04482) by Amanpreet Singh, Ronghang Hu, Vedanuj Goswami, Guillaume Couairon, Wojciech Galuba, Marcus Rohrbach, and Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[FNet](model_doc/fnet)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [FNet: Mixing Tokens with Fourier Transforms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.03824) by James Lee-Thorp, Joshua Ainslie, Ilya Eckstein, Santiago Ontanon.
|
||||
1. **[FocalNet](model_doc/focalnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [Focal Modulation Networks](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.11926) by Jianwei Yang, Chunyuan Li, Xiyang Dai, Lu Yuan, Jianfeng Gao.
|
||||
1. **[Funnel Transformer](model_doc/funnel)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [Funnel-Transformer: Filtering out Sequential Redundancy for Efficient Language Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03236) by Zihang Dai, Guokun Lai, Yiming Yang, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[GIT](model_doc/git)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [GIT: A Generative Image-to-text Transformer for Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14100) by Jianfeng Wang, Zhengyuan Yang, Xiaowei Hu, Linjie Li, Kevin Lin, Zhe Gan, Zicheng Liu, Ce Liu, Lijuan Wang.
|
||||
1. **[GLPN](model_doc/glpn)** (from KAIST) released with the paper [Global-Local Path Networks for Monocular Depth Estimation with Vertical CutDepth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.07436) by Doyeon Kim, Woonghyun Ga, Pyungwhan Ahn, Donggyu Joo, Sehwan Chun, Junmo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[GPT](model_doc/openai-gpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training](https://blog.openai.com/language-unsupervised/) by Alec Radford, Karthik Narasimhan, Tim Salimans and Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[GPT Neo](model_doc/gpt_neo)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [EleutherAI/gpt-neo](https://github.com/EleutherAI/gpt-neo) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Leo Gao, Phil Wang and Connor Leahy.
|
||||
1. **[GPT NeoX](model_doc/gpt_neox)** (from EleutherAI) released with the paper [GPT-NeoX-20B: An Open-Source Autoregressive Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06745) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Eric Hallahan, Quentin Anthony, Leo Gao, Laurence Golding, Horace He, Connor Leahy, Kyle McDonell, Jason Phang, Michael Pieler, USVSN Sai Prashanth, Shivanshu Purohit, Laria Reynolds, Jonathan Tow, Ben Wang, Samuel Weinbach
|
||||
1. **[GPT NeoX Japanese](model_doc/gpt_neox_japanese)** (from ABEJA) released by Shinya Otani, Takayoshi Makabe, Anuj Arora, and Kyo Hattori.
|
||||
1. **[GPT-2](model_doc/gpt2)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners](https://blog.openai.com/better-language-models/) by Alec Radford*, Jeffrey Wu*, Rewon Child, David Luan, Dario Amodei** and Ilya Sutskever**.
|
||||
1. **[GPT-J](model_doc/gptj)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax](https://github.com/kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax/) by Ben Wang and Aran Komatsuzaki.
|
||||
1. **[GPT-Sw3](model_doc/gpt-sw3)** (from AI-Sweden) released with the paper [Lessons Learned from GPT-SW3: Building the First Large-Scale Generative Language Model for Swedish](http://www.lrec-conf.org/proceedings/lrec2022/pdf/2022.lrec-1.376.pdf) by Ariel Ekgren, Amaru Cuba Gyllensten, Evangelia Gogoulou, Alice Heiman, Severine Verlinden, Joey Öhman, Fredrik Carlsson, Magnus Sahlgren.
|
||||
1. **[GPTBigCode](model_doc/gpt_bigcode)** (from BigCode) released with the paper [SantaCoder: don't reach for the stars!](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.03988) by Loubna Ben Allal, Raymond Li, Denis Kocetkov, Chenghao Mou, Christopher Akiki, Carlos Munoz Ferrandis, Niklas Muennighoff, Mayank Mishra, Alex Gu, Manan Dey, Logesh Kumar Umapathi, Carolyn Jane Anderson, Yangtian Zi, Joel Lamy Poirier, Hailey Schoelkopf, Sergey Troshin, Dmitry Abulkhanov, Manuel Romero, Michael Lappert, Francesco De Toni, Bernardo García del Río, Qian Liu, Shamik Bose, Urvashi Bhattacharyya, Terry Yue Zhuo, Ian Yu, Paulo Villegas, Marco Zocca, Sourab Mangrulkar, David Lansky, Huu Nguyen, Danish Contractor, Luis Villa, Jia Li, Dzmitry Bahdanau, Yacine Jernite, Sean Hughes, Daniel Fried, Arjun Guha, Harm de Vries, Leandro von Werra.
|
||||
1. **[GPTSAN-japanese](model_doc/gptsan-japanese)** released in the repository [tanreinama/GPTSAN](https://github.com/tanreinama/GPTSAN/blob/main/report/model.md) by Toshiyuki Sakamoto(tanreinama).
|
||||
1. **[Graphormer](model_doc/graphormer)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [Do Transformers Really Perform Bad for Graph Representation?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.05234) by Chengxuan Ying, Tianle Cai, Shengjie Luo, Shuxin Zheng, Guolin Ke, Di He, Yanming Shen, Tie-Yan Liu.
|
||||
1. **[GroupViT](model_doc/groupvit)** (from UCSD, NVIDIA) released with the paper [GroupViT: Semantic Segmentation Emerges from Text Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.11094) by Jiarui Xu, Shalini De Mello, Sifei Liu, Wonmin Byeon, Thomas Breuel, Jan Kautz, Xiaolong Wang.
|
||||
1. **[Hubert](model_doc/hubert)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [HuBERT: Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning by Masked Prediction of Hidden Units](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.07447) by Wei-Ning Hsu, Benjamin Bolte, Yao-Hung Hubert Tsai, Kushal Lakhotia, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Abdelrahman Mohamed.
|
||||
1. **[I-BERT](model_doc/ibert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [I-BERT: Integer-only BERT Quantization](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.01321) by Sehoon Kim, Amir Gholami, Zhewei Yao, Michael W. Mahoney, Kurt Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[ImageGPT](model_doc/imagegpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Generative Pretraining from Pixels](https://openai.com/blog/image-gpt/) by Mark Chen, Alec Radford, Rewon Child, Jeffrey Wu, Heewoo Jun, David Luan, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[Informer](model_doc/informer)** (from Beihang University, UC Berkeley, Rutgers University, SEDD Company) released with the paper [Informer: Beyond Efficient Transformer for Long Sequence Time-Series Forecasting](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.07436) by Haoyi Zhou, Shanghang Zhang, Jieqi Peng, Shuai Zhang, Jianxin Li, Hui Xiong, and Wancai Zhang.
|
||||
1. **[Jukebox](model_doc/jukebox)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Jukebox: A Generative Model for Music](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2005.00341.pdf) by Prafulla Dhariwal, Heewoo Jun, Christine Payne, Jong Wook Kim, Alec Radford, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLM](model_doc/layoutlm)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLM: Pre-training of Text and Layout for Document Image Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.13318) by Yiheng Xu, Minghao Li, Lei Cui, Shaohan Huang, Furu Wei, Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv2](model_doc/layoutlmv2)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv2: Multi-modal Pre-training for Visually-Rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.14740) by Yang Xu, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Furu Wei, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Wanxiang Che, Min Zhang, Lidong Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv3](model_doc/layoutlmv3)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv3: Pre-training for Document AI with Unified Text and Image Masking](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.08387) by Yupan Huang, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yutong Lu, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutXLM](model_doc/layoutxlm)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutXLM: Multimodal Pre-training for Multilingual Visually-rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.08836) by Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LED](model_doc/led)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LeViT](model_doc/levit)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [LeViT: A Vision Transformer in ConvNet's Clothing for Faster Inference](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01136) by Ben Graham, Alaaeldin El-Nouby, Hugo Touvron, Pierre Stock, Armand Joulin, Hervé Jégou, Matthijs Douze.
|
||||
1. **[LiLT](model_doc/lilt)** (from South China University of Technology) released with the paper [LiLT: A Simple yet Effective Language-Independent Layout Transformer for Structured Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.13669) by Jiapeng Wang, Lianwen Jin, Kai Ding.
|
||||
1. **[LLaMA](model_doc/llama)** (from The FAIR team of Meta AI) released with the paper [LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.13971) by Hugo Touvron, Thibaut Lavril, Gautier Izacard, Xavier Martinet, Marie-Anne Lachaux, Timothée Lacroix, Baptiste Rozière, Naman Goyal, Eric Hambro, Faisal Azhar, Aurelien Rodriguez, Armand Joulin, Edouard Grave, Guillaume Lample.
|
||||
1. **[Longformer](model_doc/longformer)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LongT5](model_doc/longt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [LongT5: Efficient Text-To-Text Transformer for Long Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.07916) by Mandy Guo, Joshua Ainslie, David Uthus, Santiago Ontanon, Jianmo Ni, Yun-Hsuan Sung, Yinfei Yang.
|
||||
1. **[LUKE](model_doc/luke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [LUKE: Deep Contextualized Entity Representations with Entity-aware Self-attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.01057) by Ikuya Yamada, Akari Asai, Hiroyuki Shindo, Hideaki Takeda, Yuji Matsumoto.
|
||||
1. **[LXMERT](model_doc/lxmert)** (from UNC Chapel Hill) released with the paper [LXMERT: Learning Cross-Modality Encoder Representations from Transformers for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.07490) by Hao Tan and Mohit Bansal.
|
||||
1. **[M-CTC-T](model_doc/mctct)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Pseudo-Labeling For Massively Multilingual Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.00161) by Loren Lugosch, Tatiana Likhomanenko, Gabriel Synnaeve, and Ronan Collobert.
|
||||
1. **[M2M100](model_doc/m2m_100)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Beyond English-Centric Multilingual Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11125) by Angela Fan, Shruti Bhosale, Holger Schwenk, Zhiyi Ma, Ahmed El-Kishky, Siddharth Goyal, Mandeep Baines, Onur Celebi, Guillaume Wenzek, Vishrav Chaudhary, Naman Goyal, Tom Birch, Vitaliy Liptchinsky, Sergey Edunov, Edouard Grave, Michael Auli, Armand Joulin.
|
||||
1. **[MarianMT](model_doc/marian)** Machine translation models trained using [OPUS](http://opus.nlpl.eu/) data by Jörg Tiedemann. The [Marian Framework](https://marian-nmt.github.io/) is being developed by the Microsoft Translator Team.
|
||||
1. **[MarkupLM](model_doc/markuplm)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [MarkupLM: Pre-training of Text and Markup Language for Visually-rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.08518) by Junlong Li, Yiheng Xu, Lei Cui, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[Mask2Former](model_doc/mask2former)** (from FAIR and UIUC) released with the paper [Masked-attention Mask Transformer for Universal Image Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.01527) by Bowen Cheng, Ishan Misra, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov, Rohit Girdhar.
|
||||
1. **[MaskFormer](model_doc/maskformer)** (from Meta and UIUC) released with the paper [Per-Pixel Classification is Not All You Need for Semantic Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.06278) by Bowen Cheng, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov.
|
||||
1. **[MatCha](model_doc/matcha)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [MatCha: Enhancing Visual Language Pretraining with Math Reasoning and Chart Derendering](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.09662) by Fangyu Liu, Francesco Piccinno, Syrine Krichene, Chenxi Pang, Kenton Lee, Mandar Joshi, Yasemin Altun, Nigel Collier, Julian Martin Eisenschlos.
|
||||
1. **[mBART](model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08210) by Yinhan Liu, Jiatao Gu, Naman Goyal, Xian Li, Sergey Edunov, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[mBART-50](model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Translation with Extensible Multilingual Pretraining and Finetuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00401) by Yuqing Tang, Chau Tran, Xian Li, Peng-Jen Chen, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Jiatao Gu, Angela Fan.
|
||||
1. **[MEGA](model_doc/mega)** (from Meta/USC/CMU/SJTU) released with the paper [Mega: Moving Average Equipped Gated Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.10655) by Xuezhe Ma, Chunting Zhou, Xiang Kong, Junxian He, Liangke Gui, Graham Neubig, Jonathan May, and Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-BERT](model_doc/megatron-bert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-GPT2](model_doc/megatron_gpt2)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[MGP-STR](model_doc/mgp-str)** (from Alibaba Research) released with the paper [Multi-Granularity Prediction for Scene Text Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.03592) by Peng Wang, Cheng Da, and Cong Yao.
|
||||
1. **[mLUKE](model_doc/mluke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [mLUKE: The Power of Entity Representations in Multilingual Pretrained Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.08151) by Ryokan Ri, Ikuya Yamada, and Yoshimasa Tsuruoka.
|
||||
1. **[MMS](model_doc/mms)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Scaling Speech Technology to 1,000+ Languages](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.13516) by Vineel Pratap, Andros Tjandra, Bowen Shi, Paden Tomasello, Arun Babu, Sayani Kundu, Ali Elkahky, Zhaoheng Ni, Apoorv Vyas, Maryam Fazel-Zarandi, Alexei Baevski, Yossi Adi, Xiaohui Zhang, Wei-Ning Hsu, Alexis Conneau, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[MobileBERT](model_doc/mobilebert)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [MobileBERT: a Compact Task-Agnostic BERT for Resource-Limited Devices](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02984) by Zhiqing Sun, Hongkun Yu, Xiaodan Song, Renjie Liu, Yiming Yang, and Denny Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[MobileNetV1](model_doc/mobilenet_v1)** (from Google Inc.) released with the paper [MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications](https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861) by Andrew G. Howard, Menglong Zhu, Bo Chen, Dmitry Kalenichenko, Weijun Wang, Tobias Weyand, Marco Andreetto, Hartwig Adam.
|
||||
1. **[MobileNetV2](model_doc/mobilenet_v2)** (from Google Inc.) released with the paper [MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.04381) by Mark Sandler, Andrew Howard, Menglong Zhu, Andrey Zhmoginov, Liang-Chieh Chen.
|
||||
1. **[MobileViT](model_doc/mobilevit)** (from Apple) released with the paper [MobileViT: Light-weight, General-purpose, and Mobile-friendly Vision Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.02178) by Sachin Mehta and Mohammad Rastegari.
|
||||
1. **[MobileViTV2](model_doc/mobilevitv2)** (from Apple) released with the paper [Separable Self-attention for Mobile Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.02680) by Sachin Mehta and Mohammad Rastegari.
|
||||
1. **[MPNet](model_doc/mpnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [MPNet: Masked and Permuted Pre-training for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09297) by Kaitao Song, Xu Tan, Tao Qin, Jianfeng Lu, Tie-Yan Liu.
|
||||
1. **[MT5](model_doc/mt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [mT5: A massively multilingual pre-trained text-to-text transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11934) by Linting Xue, Noah Constant, Adam Roberts, Mihir Kale, Rami Al-Rfou, Aditya Siddhant, Aditya Barua, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[MVP](model_doc/mvp)** (from RUC AI Box) released with the paper [MVP: Multi-task Supervised Pre-training for Natural Language Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.12131) by Tianyi Tang, Junyi Li, Wayne Xin Zhao and Ji-Rong Wen.
|
||||
1. **[NAT](model_doc/nat)** (from SHI Labs) released with the paper [Neighborhood Attention Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.07143) by Ali Hassani, Steven Walton, Jiachen Li, Shen Li, and Humphrey Shi.
|
||||
1. **[Nezha](model_doc/nezha)** (from Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab) released with the paper [NEZHA: Neural Contextualized Representation for Chinese Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.00204) by Junqiu Wei, Xiaozhe Ren, Xiaoguang Li, Wenyong Huang, Yi Liao, Yasheng Wang, Jiashu Lin, Xin Jiang, Xiao Chen and Qun Liu.
|
||||
1. **[NLLB](model_doc/nllb)** (from Meta) released with the paper [No Language Left Behind: Scaling Human-Centered Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.04672) by the NLLB team.
|
||||
1. **[NLLB-MOE](model_doc/nllb-moe)** (from Meta) released with the paper [No Language Left Behind: Scaling Human-Centered Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.04672) by the NLLB team.
|
||||
1. **[Nyströmformer](model_doc/nystromformer)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [Nyströmformer: A Nyström-Based Algorithm for Approximating Self-Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03902) by Yunyang Xiong, Zhanpeng Zeng, Rudrasis Chakraborty, Mingxing Tan, Glenn Fung, Yin Li, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
1. **[OneFormer](model_doc/oneformer)** (from SHI Labs) released with the paper [OneFormer: One Transformer to Rule Universal Image Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06220) by Jitesh Jain, Jiachen Li, MangTik Chiu, Ali Hassani, Nikita Orlov, Humphrey Shi.
|
||||
1. **[OpenLlama](model_doc/open-llama)** (from [s-JoL](https://huggingface.co/s-JoL)) released in [Open-Llama](https://github.com/s-JoL/Open-Llama).
|
||||
1. **[OPT](master/model_doc/opt)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [OPT: Open Pre-trained Transformer Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.01068) by Susan Zhang, Stephen Roller, Naman Goyal, Mikel Artetxe, Moya Chen, Shuohui Chen et al.
|
||||
1. **[OWL-ViT](model_doc/owlvit)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Simple Open-Vocabulary Object Detection with Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.06230) by Matthias Minderer, Alexey Gritsenko, Austin Stone, Maxim Neumann, Dirk Weissenborn, Alexey Dosovitskiy, Aravindh Mahendran, Anurag Arnab, Mostafa Dehghani, Zhuoran Shen, Xiao Wang, Xiaohua Zhai, Thomas Kipf, and Neil Houlsby.
|
||||
1. **[Pegasus](model_doc/pegasus)** (from Google) released with the paper [PEGASUS: Pre-training with Extracted Gap-sentences for Abstractive Summarization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.08777) by Jingqing Zhang, Yao Zhao, Mohammad Saleh and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[PEGASUS-X](model_doc/pegasus_x)** (from Google) released with the paper [Investigating Efficiently Extending Transformers for Long Input Summarization](https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.04347) by Jason Phang, Yao Zhao, and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[Perceiver IO](model_doc/perceiver)** (from Deepmind) released with the paper [Perceiver IO: A General Architecture for Structured Inputs & Outputs](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.14795) by Andrew Jaegle, Sebastian Borgeaud, Jean-Baptiste Alayrac, Carl Doersch, Catalin Ionescu, David Ding, Skanda Koppula, Daniel Zoran, Andrew Brock, Evan Shelhamer, Olivier Hénaff, Matthew M. Botvinick, Andrew Zisserman, Oriol Vinyals, João Carreira.
|
||||
1. **[PhoBERT](model_doc/phobert)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [PhoBERT: Pre-trained language models for Vietnamese](https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.findings-emnlp.92/) by Dat Quoc Nguyen and Anh Tuan Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[Pix2Struct](model_doc/pix2struct)** (from Google) released with the paper [Pix2Struct: Screenshot Parsing as Pretraining for Visual Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.03347) by Kenton Lee, Mandar Joshi, Iulia Turc, Hexiang Hu, Fangyu Liu, Julian Eisenschlos, Urvashi Khandelwal, Peter Shaw, Ming-Wei Chang, Kristina Toutanova.
|
||||
1. **[PLBart](model_doc/plbart)** (from UCLA NLP) released with the paper [Unified Pre-training for Program Understanding and Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06333) by Wasi Uddin Ahmad, Saikat Chakraborty, Baishakhi Ray, Kai-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[PoolFormer](model_doc/poolformer)** (from Sea AI Labs) released with the paper [MetaFormer is Actually What You Need for Vision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.11418) by Yu, Weihao and Luo, Mi and Zhou, Pan and Si, Chenyang and Zhou, Yichen and Wang, Xinchao and Feng, Jiashi and Yan, Shuicheng.
|
||||
1. **[ProphetNet](model_doc/prophetnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [ProphetNet: Predicting Future N-gram for Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04063) by Yu Yan, Weizhen Qi, Yeyun Gong, Dayiheng Liu, Nan Duan, Jiusheng Chen, Ruofei Zhang and Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[QDQBert](model_doc/qdqbert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Integer Quantization for Deep Learning Inference: Principles and Empirical Evaluation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09602) by Hao Wu, Patrick Judd, Xiaojie Zhang, Mikhail Isaev and Paulius Micikevicius.
|
||||
1. **[RAG](model_doc/rag)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11401) by Patrick Lewis, Ethan Perez, Aleksandara Piktus, Fabio Petroni, Vladimir Karpukhin, Naman Goyal, Heinrich Küttler, Mike Lewis, Wen-tau Yih, Tim Rocktäschel, Sebastian Riedel, Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[REALM](model_doc/realm.html)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [REALM: Retrieval-Augmented Language Model Pre-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.08909) by Kelvin Guu, Kenton Lee, Zora Tung, Panupong Pasupat and Ming-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[Reformer](model_doc/reformer)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Reformer: The Efficient Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04451) by Nikita Kitaev, Łukasz Kaiser, Anselm Levskaya.
|
||||
1. **[RegNet](model_doc/regnet)** (from META Platforms) released with the paper [Designing Network Design Space](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.13678) by Ilija Radosavovic, Raj Prateek Kosaraju, Ross Girshick, Kaiming He, Piotr Dollár.
|
||||
1. **[RemBERT](model_doc/rembert)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Rethinking embedding coupling in pre-trained language models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.12821) by Hyung Won Chung, Thibault Févry, Henry Tsai, M. Johnson, Sebastian Ruder.
|
||||
1. **[ResNet](model_doc/resnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385) by Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun.
|
||||
1. **[RoBERTa](model_doc/roberta)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692) by Yinhan Liu, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Mandar Joshi, Danqi Chen, Omer Levy, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer, Veselin Stoyanov.
|
||||
1. **[RoBERTa-PreLayerNorm](model_doc/roberta-prelayernorm)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [fairseq: A Fast, Extensible Toolkit for Sequence Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.01038) by Myle Ott, Sergey Edunov, Alexei Baevski, Angela Fan, Sam Gross, Nathan Ng, David Grangier, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[RoCBert](model_doc/roc_bert)** (from WeChatAI) released with the paper [RoCBert: Robust Chinese Bert with Multimodal Contrastive Pretraining](https://aclanthology.org/2022.acl-long.65.pdf) by HuiSu, WeiweiShi, XiaoyuShen, XiaoZhou, TuoJi, JiaruiFang, JieZhou.
|
||||
1. **[RoFormer](model_doc/roformer)** (from ZhuiyiTechnology), released together with the paper [RoFormer: Enhanced Transformer with Rotary Position Embedding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.09864) by Jianlin Su and Yu Lu and Shengfeng Pan and Bo Wen and Yunfeng Liu.
|
||||
1. **[RWKV](model_doc/rwkv)** (from Bo Peng), released on [this repo](https://github.com/BlinkDL/RWKV-LM) by Bo Peng.
|
||||
1. **[SegFormer](model_doc/segformer)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [SegFormer: Simple and Efficient Design for Semantic Segmentation with Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.15203) by Enze Xie, Wenhai Wang, Zhiding Yu, Anima Anandkumar, Jose M. Alvarez, Ping Luo.
|
||||
1. **[Segment Anything](model_doc/sam)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Segment Anything](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.02643v1.pdf) by Alexander Kirillov, Eric Mintun, Nikhila Ravi, Hanzi Mao, Chloe Rolland, Laura Gustafson, Tete Xiao, Spencer Whitehead, Alex Berg, Wan-Yen Lo, Piotr Dollar, Ross Girshick.
|
||||
1. **[SEW](model_doc/sew)** (from ASAPP) released with the paper [Performance-Efficiency Trade-offs in Unsupervised Pre-training for Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.06870) by Felix Wu, Kwangyoun Kim, Jing Pan, Kyu Han, Kilian Q. Weinberger, Yoav Artzi.
|
||||
1. **[SEW-D](model_doc/sew_d)** (from ASAPP) released with the paper [Performance-Efficiency Trade-offs in Unsupervised Pre-training for Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.06870) by Felix Wu, Kwangyoun Kim, Jing Pan, Kyu Han, Kilian Q. Weinberger, Yoav Artzi.
|
||||
1. **[SpeechT5](model_doc/speecht5)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [SpeechT5: Unified-Modal Encoder-Decoder Pre-Training for Spoken Language Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.07205) by Junyi Ao, Rui Wang, Long Zhou, Chengyi Wang, Shuo Ren, Yu Wu, Shujie Liu, Tom Ko, Qing Li, Yu Zhang, Zhihua Wei, Yao Qian, Jinyu Li, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer](model_doc/speech_to_text)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [fairseq S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with fairseq](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer2](model_doc/speech_to_text_2)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [Large-Scale Self- and Semi-Supervised Learning for Speech Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.06678) by Changhan Wang, Anne Wu, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli, Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[Splinter](model_doc/splinter)** (from Tel Aviv University), released together with the paper [Few-Shot Question Answering by Pretraining Span Selection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.00438) by Ori Ram, Yuval Kirstain, Jonathan Berant, Amir Globerson, Omer Levy.
|
||||
1. **[SqueezeBERT](model_doc/squeezebert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [SqueezeBERT: What can computer vision teach NLP about efficient neural networks?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11316) by Forrest N. Iandola, Albert E. Shaw, Ravi Krishna, and Kurt W. Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[SwiftFormer](model_doc/swiftformer)** (from MBZUAI) released with the paper [SwiftFormer: Efficient Additive Attention for Transformer-based Real-time Mobile Vision Applications](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.15446) by Abdelrahman Shaker, Muhammad Maaz, Hanoona Rasheed, Salman Khan, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Fahad Shahbaz Khan.
|
||||
1. **[Swin Transformer](model_doc/swin)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14030) by Ze Liu, Yutong Lin, Yue Cao, Han Hu, Yixuan Wei, Zheng Zhang, Stephen Lin, Baining Guo.
|
||||
1. **[Swin Transformer V2](model_doc/swinv2)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [Swin Transformer V2: Scaling Up Capacity and Resolution](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09883) by Ze Liu, Han Hu, Yutong Lin, Zhuliang Yao, Zhenda Xie, Yixuan Wei, Jia Ning, Yue Cao, Zheng Zhang, Li Dong, Furu Wei, Baining Guo.
|
||||
1. **[Swin2SR](model_doc/swin2sr)** (from University of Würzburg) released with the paper [Swin2SR: SwinV2 Transformer for Compressed Image Super-Resolution and Restoration](https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.11345) by Marcos V. Conde, Ui-Jin Choi, Maxime Burchi, Radu Timofte.
|
||||
1. **[SwitchTransformers](model_doc/switch_transformers)** (from Google) released with the paper [Switch Transformers: Scaling to Trillion Parameter Models with Simple and Efficient Sparsity](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.03961) by William Fedus, Barret Zoph, Noam Shazeer.
|
||||
1. **[T5](model_doc/t5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10683) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[T5v1.1](model_doc/t5v1.1)** (from Google AI) released in the repository [google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer](https://github.com/google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer/blob/main/released_checkpoints.md#t511) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[Table Transformer](model_doc/table-transformer)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [PubTables-1M: Towards Comprehensive Table Extraction From Unstructured Documents](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.00061) by Brandon Smock, Rohith Pesala, Robin Abraham.
|
||||
1. **[TAPAS](model_doc/tapas)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [TAPAS: Weakly Supervised Table Parsing via Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02349) by Jonathan Herzig, Paweł Krzysztof Nowak, Thomas Müller, Francesco Piccinno and Julian Martin Eisenschlos.
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](model_doc/tapex)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou.
|
||||
1. **[Time Series Transformer](model_doc/time_series_transformer)** (from HuggingFace).
|
||||
1. **[TimeSformer](model_doc/timesformer)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Is Space-Time Attention All You Need for Video Understanding?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.05095) by Gedas Bertasius, Heng Wang, Lorenzo Torresani.
|
||||
1. **[Trajectory Transformer](model_doc/trajectory_transformers)** (from the University of California at Berkeley) released with the paper [Offline Reinforcement Learning as One Big Sequence Modeling Problem](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.02039) by Michael Janner, Qiyang Li, Sergey Levine
|
||||
1. **[Transformer-XL](model_doc/transfo-xl)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860) by Zihang Dai*, Zhilin Yang*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Quoc V. Le, Ruslan Salakhutdinov.
|
||||
1. **[TrOCR](model_doc/trocr)** (from Microsoft), released together with the paper [TrOCR: Transformer-based Optical Character Recognition with Pre-trained Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.10282) by Minghao Li, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Zhoujun Li, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[TVLT](model_doc/tvlt)** (from UNC Chapel Hill) released with the paper [TVLT: Textless Vision-Language Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.14156) by Zineng Tang, Jaemin Cho, Yixin Nie, Mohit Bansal.
|
||||
1. **[UL2](model_doc/ul2)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Unifying Language Learning Paradigms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.05131v1) by Yi Tay, Mostafa Dehghani, Vinh Q. Tran, Xavier Garcia, Dara Bahri, Tal Schuster, Huaixiu Steven Zheng, Neil Houlsby, Donald Metzler
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeech](model_doc/unispeech)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.07597) by Chengyi Wang, Yu Wu, Yao Qian, Kenichi Kumatani, Shujie Liu, Furu Wei, Michael Zeng, Xuedong Huang.
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeechSat](model_doc/unispeech-sat)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UNISPEECH-SAT: UNIVERSAL SPEECH REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH SPEAKER AWARE PRE-TRAINING](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.05752) by Sanyuan Chen, Yu Wu, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Zhuo Chen, Shujie Liu, Jian Wu, Yao Qian, Furu Wei, Jinyu Li, Xiangzhan Yu.
|
||||
1. **[UPerNet](model_doc/upernet)** (from Peking University) released with the paper [Unified Perceptual Parsing for Scene Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.10221) by Tete Xiao, Yingcheng Liu, Bolei Zhou, Yuning Jiang, Jian Sun.
|
||||
1. **[VAN](model_doc/van)** (from Tsinghua University and Nankai University) released with the paper [Visual Attention Network](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.09741) by Meng-Hao Guo, Cheng-Ze Lu, Zheng-Ning Liu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Shi-Min Hu.
|
||||
1. **[VideoMAE](model_doc/videomae)** (from Multimedia Computing Group, Nanjing University) released with the paper [VideoMAE: Masked Autoencoders are Data-Efficient Learners for Self-Supervised Video Pre-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.12602) by Zhan Tong, Yibing Song, Jue Wang, Limin Wang.
|
||||
1. **[ViLT](model_doc/vilt)** (from NAVER AI Lab/Kakao Enterprise/Kakao Brain) released with the paper [ViLT: Vision-and-Language Transformer Without Convolution or Region Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03334) by Wonjae Kim, Bokyung Son, Ildoo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[Vision Transformer (ViT)](model_doc/vit)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929) by Alexey Dosovitskiy, Lucas Beyer, Alexander Kolesnikov, Dirk Weissenborn, Xiaohua Zhai, Thomas Unterthiner, Mostafa Dehghani, Matthias Minderer, Georg Heigold, Sylvain Gelly, Jakob Uszkoreit, Neil Houlsby.
|
||||
1. **[VisualBERT](model_doc/visual_bert)** (from UCLA NLP) released with the paper [VisualBERT: A Simple and Performant Baseline for Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.03557) by Liunian Harold Li, Mark Yatskar, Da Yin, Cho-Jui Hsieh, Kai-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[ViT Hybrid](model_doc/vit_hybrid)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929) by Alexey Dosovitskiy, Lucas Beyer, Alexander Kolesnikov, Dirk Weissenborn, Xiaohua Zhai, Thomas Unterthiner, Mostafa Dehghani, Matthias Minderer, Georg Heigold, Sylvain Gelly, Jakob Uszkoreit, Neil Houlsby.
|
||||
1. **[ViTMAE](model_doc/vit_mae)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.06377) by Kaiming He, Xinlei Chen, Saining Xie, Yanghao Li, Piotr Dollár, Ross Girshick.
|
||||
1. **[ViTMSN](model_doc/vit_msn)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Masked Siamese Networks for Label-Efficient Learning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.07141) by Mahmoud Assran, Mathilde Caron, Ishan Misra, Piotr Bojanowski, Florian Bordes, Pascal Vincent, Armand Joulin, Michael Rabbat, Nicolas Ballas.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2](model_doc/wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [wav2vec 2.0: A Framework for Self-Supervised Learning of Speech Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11477) by Alexei Baevski, Henry Zhou, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2-Conformer](model_doc/wav2vec2-conformer)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FAIRSEQ S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with FAIRSEQ](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Sravya Popuri, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2Phoneme](model_doc/wav2vec2_phoneme)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Simple and Effective Zero-shot Cross-lingual Phoneme Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.11680) by Qiantong Xu, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[WavLM](model_doc/wavlm)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [WavLM: Large-Scale Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Full Stack Speech Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.13900) by Sanyuan Chen, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Yu Wu, Shujie Liu, Zhuo Chen, Jinyu Li, Naoyuki Kanda, Takuya Yoshioka, Xiong Xiao, Jian Wu, Long Zhou, Shuo Ren, Yanmin Qian, Yao Qian, Jian Wu, Michael Zeng, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[Whisper](model_doc/whisper)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Robust Speech Recognition via Large-Scale Weak Supervision](https://cdn.openai.com/papers/whisper.pdf) by Alec Radford, Jong Wook Kim, Tao Xu, Greg Brockman, Christine McLeavey, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[X-CLIP](model_doc/xclip)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [Expanding Language-Image Pretrained Models for General Video Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.02816) by Bolin Ni, Houwen Peng, Minghao Chen, Songyang Zhang, Gaofeng Meng, Jianlong Fu, Shiming Xiang, Haibin Ling.
|
||||
1. **[X-MOD](model_doc/xmod)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Lifting the Curse of Multilinguality by Pre-training Modular Transformers](http://dx.doi.org/10.18653/v1/2022.naacl-main.255) by Jonas Pfeiffer, Naman Goyal, Xi Lin, Xian Li, James Cross, Sebastian Riedel, Mikel Artetxe.
|
||||
1. **[XGLM](model_doc/xglm)** (From Facebook AI) released with the paper [Few-shot Learning with Multilingual Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10668) by Xi Victoria Lin, Todor Mihaylov, Mikel Artetxe, Tianlu Wang, Shuohui Chen, Daniel Simig, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Shruti Bhosale, Jingfei Du, Ramakanth Pasunuru, Sam Shleifer, Punit Singh Koura, Vishrav Chaudhary, Brian O'Horo, Jeff Wang, Luke Zettlemoyer, Zornitsa Kozareva, Mona Diab, Veselin Stoyanov, Xian Li.
|
||||
1. **[XLM](model_doc/xlm)** (from Facebook) released together with the paper [Cross-lingual Language Model Pretraining](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.07291) by Guillaume Lample and Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-ProphetNet](model_doc/xlm-prophetnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [ProphetNet: Predicting Future N-gram for Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04063) by Yu Yan, Weizhen Qi, Yeyun Gong, Dayiheng Liu, Nan Duan, Jiusheng Chen, Ruofei Zhang and Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-RoBERTa](model_doc/xlm-roberta)** (from Facebook AI), released together with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-lingual Representation Learning at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.02116) by Alexis Conneau*, Kartikay Khandelwal*, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Guillaume Wenzek, Francisco Guzmán, Edouard Grave, Myle Ott, Luke Zettlemoyer and Veselin Stoyanov.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-RoBERTa-XL](model_doc/xlm-roberta-xl)** (from Facebook AI), released together with the paper [Larger-Scale Transformers for Multilingual Masked Language Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.00572) by Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Myle Ott, Giri Anantharaman, Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-V](model_doc/xlm-v)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [XLM-V: Overcoming the Vocabulary Bottleneck in Multilingual Masked Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.10472) by Davis Liang, Hila Gonen, Yuning Mao, Rui Hou, Naman Goyal, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Luke Zettlemoyer, Madian Khabsa.
|
||||
1. **[XLNet](model_doc/xlnet)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [XLNet: Generalized Autoregressive Pretraining for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.08237) by Zhilin Yang*, Zihang Dai*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[XLS-R](model_doc/xls_r)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [XLS-R: Self-supervised Cross-lingual Speech Representation Learning at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09296) by Arun Babu, Changhan Wang, Andros Tjandra, Kushal Lakhotia, Qiantong Xu, Naman Goyal, Kritika Singh, Patrick von Platen, Yatharth Saraf, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Alexis Conneau, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[XLSR-Wav2Vec2](model_doc/xlsr_wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-Lingual Representation Learning For Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.13979) by Alexis Conneau, Alexei Baevski, Ronan Collobert, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[YOLOS](model_doc/yolos)** (from Huazhong University of Science & Technology) released with the paper [You Only Look at One Sequence: Rethinking Transformer in Vision through Object Detection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00666) by Yuxin Fang, Bencheng Liao, Xinggang Wang, Jiemin Fang, Jiyang Qi, Rui Wu, Jianwei Niu, Wenyu Liu.
|
||||
1. **[YOSO](model_doc/yoso)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [You Only Sample (Almost) Once: Linear Cost Self-Attention Via Bernoulli Sampling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09714) by Zhanpeng Zeng, Yunyang Xiong, Sathya N. Ravi, Shailesh Acharya, Glenn Fung, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Supported frameworks
|
||||
|
||||
The table below represents the current support in the library for each of those models, whether they have a Python
|
||||
tokenizer (called "slow"). A "fast" tokenizer backed by the 🤗 Tokenizers library, whether they have support in Jax (via
|
||||
Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
|
||||
<!--This table is updated automatically from the auto modules with _make fix-copies_. Do not update manually!-->
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Tokenizer slow | Tokenizer fast | PyTorch support | TensorFlow support | Flax Support |
|
||||
|:-----------------------------:|:--------------:|:--------------:|:---------------:|:------------------:|:------------:|
|
||||
| ALBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| ALIGN | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| AltCLIP | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Audio Spectrogram Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Autoformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BART | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BEiT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Bert Generation | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BigBird | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BigBird-Pegasus | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BioGpt | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BiT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Blenderbot | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BlenderbotSmall | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BLIP | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BLIP-2 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BLOOM | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BridgeTower | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CamemBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CANINE | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Chinese-CLIP | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CLAP | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CLIP | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| CLIPSeg | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CodeGen | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Conditional DETR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ConvBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ConvNeXT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ConvNeXTV2 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CPM-Ant | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CTRL | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CvT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Data2VecAudio | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Data2VecText | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Data2VecVision | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeBERTa-v2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Decision Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Deformable DETR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeiT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DETA | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DETR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DiNAT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DistilBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| DonutSwin | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DPR | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| EfficientFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| EfficientNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ELECTRA | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| EnCodec | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Encoder decoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| ERNIE | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ErnieM | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ESM | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FairSeq Machine-Translation | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FlauBERT | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FLAVA | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FNet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FocalNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Funnel Transformer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GIT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GLPN | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GPT Neo | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GPT NeoX | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GPT NeoX Japanese | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GPT-J | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GPT-Sw3 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GPTBigCode | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GPTSAN-japanese | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Graphormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GroupViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Hubert | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| I-BERT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ImageGPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Informer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Jukebox | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LayoutLM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LayoutLMv2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LayoutLMv3 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LED | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LeViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LiLT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LLaMA | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Longformer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LongT5 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| LUKE | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LXMERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| M-CTC-T | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| M2M100 | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Marian | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| MarkupLM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Mask2Former | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MaskFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MaskFormerSwin | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| mBART | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| MEGA | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Megatron-BERT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MGP-STR | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileNetV1 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileNetV2 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileViTV2 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MPNet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MT5 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| MVP | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| NAT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Nezha | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| NLLB-MOE | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Nyströmformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| OneFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| OpenAI GPT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| OpenAI GPT-2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| OpenLlama | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| OPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| OWL-ViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Pegasus | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| PEGASUS-X | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Perceiver | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Pix2Struct | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| PLBart | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| PoolFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ProphetNet | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| QDQBert | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RAG | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| REALM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Reformer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RegNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RemBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ResNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RetriBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RoBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RoBERTa-PreLayerNorm | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RoCBert | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RoFormer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RWKV | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SAM | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SegFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SEW | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SEW-D | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Speech Encoder decoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Speech2Text | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Speech2Text2 | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SpeechT5 | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Splinter | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SqueezeBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SwiftFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Swin Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Swin Transformer V2 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Swin2SR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SwitchTransformers | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| T5 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Table Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TAPAS | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Time Series Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TimeSformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TimmBackbone | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Trajectory Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Transformer-XL | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TrOCR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TVLT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| UniSpeech | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| UniSpeechSat | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| UPerNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| VAN | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| VideoMAE | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ViLT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Vision Encoder decoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| VisionTextDualEncoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| VisualBERT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| ViT Hybrid | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ViTMAE | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ViTMSN | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Wav2Vec2 | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Wav2Vec2-Conformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| WavLM | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Whisper | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| X-CLIP | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| X-MOD | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XGLM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| XLM | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLM-ProphetNet | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLM-RoBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| XLM-RoBERTa-XL | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLNet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| YOLOS | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| YOSO | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- End table-->
|
||||
@ -1,462 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
State-of-the-art Machine Learning for [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/), [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/), and [JAX](https://jax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/).
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers provides APIs and tools to easily download and train state-of-the-art pretrained models. Using pretrained models can reduce your compute costs, carbon footprint, and save you the time and resources required to train a model from scratch. These models support common tasks in different modalities, such as:
|
||||
|
||||
📝 **Natural Language Processing**: text classification, named entity recognition, question answering, language modeling, summarization, translation, multiple choice, and text generation.<br>
|
||||
🖼️ **Computer Vision**: image classification, object detection, and segmentation.<br>
|
||||
🗣️ **Audio**: automatic speech recognition and audio classification.<br>
|
||||
🐙 **Multimodal**: table question answering, optical character recognition, information extraction from scanned documents, video classification, and visual question answering.
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers support framework interoperability between PyTorch, TensorFlow, and JAX. This provides the flexibility to use a different framework at each stage of a model's life; train a model in three lines of code in one framework, and load it for inference in another. Models can also be exported to a format like ONNX and TorchScript for deployment in production environments.
|
||||
|
||||
Join the growing community on the [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models), [forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/), or [Discord](https://discord.com/invite/JfAtkvEtRb) today!
|
||||
|
||||
## If you are looking for custom support from the Hugging Face team
|
||||
|
||||
<a target="_blank" href="https://huggingface.co/support">
|
||||
<img alt="HuggingFace Expert Acceleration Program" src="https://cdn-media.huggingface.co/marketing/transformers/new-support-improved.png" style="width: 100%; max-width: 600px; border: 1px solid #eee; border-radius: 4px; box-shadow: 0 1px 2px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
|
||||
## Contents
|
||||
|
||||
The documentation is organized into five sections:
|
||||
|
||||
- **GET STARTED** provides a quick tour of the library and installation instructions to get up and running.
|
||||
- **TUTORIALS** are a great place to start if you're a beginner. This section will help you gain the basic skills you need to start using the library.
|
||||
- **HOW-TO GUIDES** show you how to achieve a specific goal, like finetuning a pretrained model for language modeling or how to write and share a custom model.
|
||||
- **CONCEPTUAL GUIDES** offers more discussion and explanation of the underlying concepts and ideas behind models, tasks, and the design philosophy of 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
- **API** describes all classes and functions:
|
||||
|
||||
- **MAIN CLASSES** details the most important classes like configuration, model, tokenizer, and pipeline.
|
||||
- **MODELS** details the classes and functions related to each model implemented in the library.
|
||||
- **INTERNAL HELPERS** details utility classes and functions used internally.
|
||||
|
||||
### Supported models
|
||||
|
||||
<!--This list is updated automatically from the README with _make fix-copies_. Do not update manually! -->
|
||||
|
||||
1. **[ALBERT](model_doc/albert)** (from Google Research and the Toyota Technological Institute at Chicago) released with the paper [ALBERT: A Lite BERT for Self-supervised Learning of Language Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.11942), by Zhenzhong Lan, Mingda Chen, Sebastian Goodman, Kevin Gimpel, Piyush Sharma, Radu Soricut.
|
||||
1. **[ALIGN](model_doc/align)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Scaling Up Visual and Vision-Language Representation Learning With Noisy Text Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.05918) by Chao Jia, Yinfei Yang, Ye Xia, Yi-Ting Chen, Zarana Parekh, Hieu Pham, Quoc V. Le, Yunhsuan Sung, Zhen Li, Tom Duerig.
|
||||
1. **[AltCLIP](model_doc/altclip)** (from BAAI) released with the paper [AltCLIP: Altering the Language Encoder in CLIP for Extended Language Capabilities](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06679) by Chen, Zhongzhi and Liu, Guang and Zhang, Bo-Wen and Ye, Fulong and Yang, Qinghong and Wu, Ledell.
|
||||
1. **[Audio Spectrogram Transformer](model_doc/audio-spectrogram-transformer)** (from MIT) released with the paper [AST: Audio Spectrogram Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01778) by Yuan Gong, Yu-An Chung, James Glass.
|
||||
1. **[Autoformer](model_doc/autoformer)** (from Tsinghua University) released with the paper [Autoformer: Decomposition Transformers with Auto-Correlation for Long-Term Series Forecasting](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.13008) by Haixu Wu, Jiehui Xu, Jianmin Wang, Mingsheng Long.
|
||||
1. **[BART](model_doc/bart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [BART: Denoising Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training for Natural Language Generation, Translation, and Comprehension](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.13461) by Mike Lewis, Yinhan Liu, Naman Goyal, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Omer Levy, Ves Stoyanov and Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[BARThez](model_doc/barthez)** (from École polytechnique) released with the paper [BARThez: a Skilled Pretrained French Sequence-to-Sequence Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.12321) by Moussa Kamal Eddine, Antoine J.-P. Tixier, Michalis Vazirgiannis.
|
||||
1. **[BARTpho](model_doc/bartpho)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [BARTpho: Pre-trained Sequence-to-Sequence Models for Vietnamese](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.09701) by Nguyen Luong Tran, Duong Minh Le and Dat Quoc Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[BEiT](model_doc/beit)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [BEiT: BERT Pre-Training of Image Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.08254) by Hangbo Bao, Li Dong, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[BERT](model_doc/bert)** (from Google) released with the paper [BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805) by Jacob Devlin, Ming-Wei Chang, Kenton Lee and Kristina Toutanova.
|
||||
1. **[BERT For Sequence Generation](model_doc/bert-generation)** (from Google) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[BERTweet](model_doc/bertweet)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [BERTweet: A pre-trained language model for English Tweets](https://aclanthology.org/2020.emnlp-demos.2/) by Dat Quoc Nguyen, Thanh Vu and Anh Tuan Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-Pegasus](model_doc/bigbird_pegasus)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-RoBERTa](model_doc/big_bird)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[BioGpt](model_doc/biogpt)** (from Microsoft Research AI4Science) released with the paper [BioGPT: generative pre-trained transformer for biomedical text generation and mining](https://academic.oup.com/bib/advance-article/doi/10.1093/bib/bbac409/6713511?guestAccessKey=a66d9b5d-4f83-4017-bb52-405815c907b9) by Renqian Luo, Liai Sun, Yingce Xia, Tao Qin, Sheng Zhang, Hoifung Poon and Tie-Yan Liu.
|
||||
1. **[BiT](model_doc/bit)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Big Transfer (BiT): General Visual Representation Learning](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.11370) by Alexander Kolesnikov, Lucas Beyer, Xiaohua Zhai, Joan Puigcerver, Jessica Yung, Sylvain Gelly, Neil Houlsby.
|
||||
1. **[Blenderbot](model_doc/blenderbot)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BlenderbotSmall](model_doc/blenderbot-small)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BLIP](model_doc/blip)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [BLIP: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training for Unified Vision-Language Understanding and Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.12086) by Junnan Li, Dongxu Li, Caiming Xiong, Steven Hoi.
|
||||
1. **[BLIP-2](model_doc/blip-2)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [BLIP-2: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training with Frozen Image Encoders and Large Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12597) by Junnan Li, Dongxu Li, Silvio Savarese, Steven Hoi.
|
||||
1. **[BLOOM](model_doc/bloom)** (from BigScience workshop) released by the [BigScience Workshop](https://bigscience.huggingface.co/).
|
||||
1. **[BORT](model_doc/bort)** (from Alexa) released with the paper [Optimal Subarchitecture Extraction For BERT](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.10499) by Adrian de Wynter and Daniel J. Perry.
|
||||
1. **[BridgeTower](model_doc/bridgetower)** (from Harbin Institute of Technology/Microsoft Research Asia/Intel Labs) released with the paper [BridgeTower: Building Bridges Between Encoders in Vision-Language Representation Learning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08657) by Xiao Xu, Chenfei Wu, Shachar Rosenman, Vasudev Lal, Wanxiang Che, Nan Duan.
|
||||
1. **[ByT5](model_doc/byt5)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [ByT5: Towards a token-free future with pre-trained byte-to-byte models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.13626) by Linting Xue, Aditya Barua, Noah Constant, Rami Al-Rfou, Sharan Narang, Mihir Kale, Adam Roberts, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[CamemBERT](model_doc/camembert)** (from Inria/Facebook/Sorbonne) released with the paper [CamemBERT: a Tasty French Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.03894) by Louis Martin*, Benjamin Muller*, Pedro Javier Ortiz Suárez*, Yoann Dupont, Laurent Romary, Éric Villemonte de la Clergerie, Djamé Seddah and Benoît Sagot.
|
||||
1. **[CANINE](model_doc/canine)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [CANINE: Pre-training an Efficient Tokenization-Free Encoder for Language Representation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06874) by Jonathan H. Clark, Dan Garrette, Iulia Turc, John Wieting.
|
||||
1. **[Chinese-CLIP](model_doc/chinese_clip)** (from OFA-Sys) released with the paper [Chinese CLIP: Contrastive Vision-Language Pretraining in Chinese](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.01335) by An Yang, Junshu Pan, Junyang Lin, Rui Men, Yichang Zhang, Jingren Zhou, Chang Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[CLAP](model_doc/clap)** (from LAION-AI) released with the paper [Large-scale Contrastive Language-Audio Pretraining with Feature Fusion and Keyword-to-Caption Augmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06687) by Yusong Wu, Ke Chen, Tianyu Zhang, Yuchen Hui, Taylor Berg-Kirkpatrick, Shlomo Dubnov.
|
||||
1. **[CLIP](model_doc/clip)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020) by Alec Radford, Jong Wook Kim, Chris Hallacy, Aditya Ramesh, Gabriel Goh, Sandhini Agarwal, Girish Sastry, Amanda Askell, Pamela Mishkin, Jack Clark, Gretchen Krueger, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[CLIPSeg](model_doc/clipseg)** (from University of Göttingen) released with the paper [Image Segmentation Using Text and Image Prompts](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10003) by Timo Lüddecke and Alexander Ecker.
|
||||
1. **[CodeGen](model_doc/codegen)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [A Conversational Paradigm for Program Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.13474) by Erik Nijkamp, Bo Pang, Hiroaki Hayashi, Lifu Tu, Huan Wang, Yingbo Zhou, Silvio Savarese, Caiming Xiong.
|
||||
1. **[Conditional DETR](model_doc/conditional_detr)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [Conditional DETR for Fast Training Convergence](https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.06152) by Depu Meng, Xiaokang Chen, Zejia Fan, Gang Zeng, Houqiang Li, Yuhui Yuan, Lei Sun, Jingdong Wang.
|
||||
1. **[ConvBERT](model_doc/convbert)** (from YituTech) released with the paper [ConvBERT: Improving BERT with Span-based Dynamic Convolution](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.02496) by Zihang Jiang, Weihao Yu, Daquan Zhou, Yunpeng Chen, Jiashi Feng, Shuicheng Yan.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXT](model_doc/convnext)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [A ConvNet for the 2020s](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545) by Zhuang Liu, Hanzi Mao, Chao-Yuan Wu, Christoph Feichtenhofer, Trevor Darrell, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXTV2](model_doc/convnextv2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [ConvNeXt V2: Co-designing and Scaling ConvNets with Masked Autoencoders](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.00808) by Sanghyun Woo, Shoubhik Debnath, Ronghang Hu, Xinlei Chen, Zhuang Liu, In So Kweon, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[CPM](model_doc/cpm)** (from Tsinghua University) released with the paper [CPM: A Large-scale Generative Chinese Pre-trained Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.00413) by Zhengyan Zhang, Xu Han, Hao Zhou, Pei Ke, Yuxian Gu, Deming Ye, Yujia Qin, Yusheng Su, Haozhe Ji, Jian Guan, Fanchao Qi, Xiaozhi Wang, Yanan Zheng, Guoyang Zeng, Huanqi Cao, Shengqi Chen, Daixuan Li, Zhenbo Sun, Zhiyuan Liu, Minlie Huang, Wentao Han, Jie Tang, Juanzi Li, Xiaoyan Zhu, Maosong Sun.
|
||||
1. **[CPM-Ant](model_doc/cpmant)** (from OpenBMB) released by the [OpenBMB](https://www.openbmb.org/).
|
||||
1. **[CTRL](model_doc/ctrl)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [CTRL: A Conditional Transformer Language Model for Controllable Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.05858) by Nitish Shirish Keskar*, Bryan McCann*, Lav R. Varshney, Caiming Xiong and Richard Socher.
|
||||
1. **[CvT](model_doc/cvt)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [CvT: Introducing Convolutions to Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.15808) by Haiping Wu, Bin Xiao, Noel Codella, Mengchen Liu, Xiyang Dai, Lu Yuan, Lei Zhang.
|
||||
1. **[Data2Vec](model_doc/data2vec)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Data2Vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.03555) by Alexei Baevski, Wei-Ning Hsu, Qiantong Xu, Arun Babu, Jiatao Gu, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa](model_doc/deberta)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa-v2](model_doc/deberta-v2)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[Decision Transformer](model_doc/decision_transformer)** (from Berkeley/Facebook/Google) released with the paper [Decision Transformer: Reinforcement Learning via Sequence Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.01345) by Lili Chen, Kevin Lu, Aravind Rajeswaran, Kimin Lee, Aditya Grover, Michael Laskin, Pieter Abbeel, Aravind Srinivas, Igor Mordatch.
|
||||
1. **[Deformable DETR](model_doc/deformable_detr)** (from SenseTime Research) released with the paper [Deformable DETR: Deformable Transformers for End-to-End Object Detection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.04159) by Xizhou Zhu, Weijie Su, Lewei Lu, Bin Li, Xiaogang Wang, Jifeng Dai.
|
||||
1. **[DeiT](model_doc/deit)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.12877) by Hugo Touvron, Matthieu Cord, Matthijs Douze, Francisco Massa, Alexandre Sablayrolles, Hervé Jégou.
|
||||
1. **[DePlot](model_doc/deplot)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [DePlot: One-shot visual language reasoning by plot-to-table translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.10505) by Fangyu Liu, Julian Martin Eisenschlos, Francesco Piccinno, Syrine Krichene, Chenxi Pang, Kenton Lee, Mandar Joshi, Wenhu Chen, Nigel Collier, Yasemin Altun.
|
||||
1. **[DETA](model_doc/deta)** (from The University of Texas at Austin) released with the paper [NMS Strikes Back](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.06137) by Jeffrey Ouyang-Zhang, Jang Hyun Cho, Xingyi Zhou, Philipp Krähenbühl.
|
||||
1. **[DETR](model_doc/detr)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.12872) by Nicolas Carion, Francisco Massa, Gabriel Synnaeve, Nicolas Usunier, Alexander Kirillov, Sergey Zagoruyko.
|
||||
1. **[DialoGPT](model_doc/dialogpt)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [DialoGPT: Large-Scale Generative Pre-training for Conversational Response Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.00536) by Yizhe Zhang, Siqi Sun, Michel Galley, Yen-Chun Chen, Chris Brockett, Xiang Gao, Jianfeng Gao, Jingjing Liu, Bill Dolan.
|
||||
1. **[DiNAT](model_doc/dinat)** (from SHI Labs) released with the paper [Dilated Neighborhood Attention Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.15001) by Ali Hassani and Humphrey Shi.
|
||||
1. **[DistilBERT](model_doc/distilbert)** (from HuggingFace), released together with the paper [DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.01108) by Victor Sanh, Lysandre Debut and Thomas Wolf. The same method has been applied to compress GPT2 into [DistilGPT2](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation), RoBERTa into [DistilRoBERTa](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation), Multilingual BERT into [DistilmBERT](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation) and a German version of DistilBERT.
|
||||
1. **[DiT](model_doc/dit)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [DiT: Self-supervised Pre-training for Document Image Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.02378) by Junlong Li, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[Donut](model_doc/donut)** (from NAVER), released together with the paper [OCR-free Document Understanding Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.15664) by Geewook Kim, Teakgyu Hong, Moonbin Yim, Jeongyeon Nam, Jinyoung Park, Jinyeong Yim, Wonseok Hwang, Sangdoo Yun, Dongyoon Han, Seunghyun Park.
|
||||
1. **[DPR](model_doc/dpr)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Dense Passage Retrieval for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.04906) by Vladimir Karpukhin, Barlas Oğuz, Sewon Min, Patrick Lewis, Ledell Wu, Sergey Edunov, Danqi Chen, and Wen-tau Yih.
|
||||
1. **[DPT](master/model_doc/dpt)** (from Intel Labs) released with the paper [Vision Transformers for Dense Prediction](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13413) by René Ranftl, Alexey Bochkovskiy, Vladlen Koltun.
|
||||
1. **[EfficientFormer](model_doc/efficientformer)** (from Snap Research) released with the paper [EfficientFormer: Vision Transformers at MobileNetSpeed](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.01191) by Yanyu Li, Geng Yuan, Yang Wen, Ju Hu, Georgios Evangelidis, Sergey Tulyakov, Yanzhi Wang, Jian Ren.
|
||||
1. **[EfficientNet](model_doc/efficientnet)** (from Google Brain) released with the paper [EfficientNet: Rethinking Model Scaling for Convolutional Neural Networks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11946) by Mingxing Tan, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[ELECTRA](model_doc/electra)** (from Google Research/Stanford University) released with the paper [ELECTRA: Pre-training text encoders as discriminators rather than generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10555) by Kevin Clark, Minh-Thang Luong, Quoc V. Le, Christopher D. Manning.
|
||||
1. **[EnCodec](model_doc/encodec)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [High Fidelity Neural Audio Compression](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.13438) by Alexandre Défossez, Jade Copet, Gabriel Synnaeve, Yossi Adi.
|
||||
1. **[EncoderDecoder](model_doc/encoder-decoder)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[ERNIE](model_doc/ernie)** (from Baidu) released with the paper [ERNIE: Enhanced Representation through Knowledge Integration](https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.09223) by Yu Sun, Shuohuan Wang, Yukun Li, Shikun Feng, Xuyi Chen, Han Zhang, Xin Tian, Danxiang Zhu, Hao Tian, Hua Wu.
|
||||
1. **[ErnieM](model_doc/ernie_m)** (from Baidu) released with the paper [ERNIE-M: Enhanced Multilingual Representation by Aligning Cross-lingual Semantics with Monolingual Corpora](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.15674) by Xuan Ouyang, Shuohuan Wang, Chao Pang, Yu Sun, Hao Tian, Hua Wu, Haifeng Wang.
|
||||
1. **[ESM](model_doc/esm)** (from Meta AI) are transformer protein language models. **ESM-1b** was released with the paper [Biological structure and function emerge from scaling unsupervised learning to 250 million protein sequences](https://www.pnas.org/content/118/15/e2016239118) by Alexander Rives, Joshua Meier, Tom Sercu, Siddharth Goyal, Zeming Lin, Jason Liu, Demi Guo, Myle Ott, C. Lawrence Zitnick, Jerry Ma, and Rob Fergus. **ESM-1v** was released with the paper [Language models enable zero-shot prediction of the effects of mutations on protein function](https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.07.09.450648) by Joshua Meier, Roshan Rao, Robert Verkuil, Jason Liu, Tom Sercu and Alexander Rives. **ESM-2 and ESMFold** were released with the paper [Language models of protein sequences at the scale of evolution enable accurate structure prediction](https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.07.20.500902) by Zeming Lin, Halil Akin, Roshan Rao, Brian Hie, Zhongkai Zhu, Wenting Lu, Allan dos Santos Costa, Maryam Fazel-Zarandi, Tom Sercu, Sal Candido, Alexander Rives.
|
||||
1. **[FLAN-T5](model_doc/flan-t5)** (from Google AI) released in the repository [google-research/t5x](https://github.com/google-research/t5x/blob/main/docs/models.md#flan-t5-checkpoints) by Hyung Won Chung, Le Hou, Shayne Longpre, Barret Zoph, Yi Tay, William Fedus, Eric Li, Xuezhi Wang, Mostafa Dehghani, Siddhartha Brahma, Albert Webson, Shixiang Shane Gu, Zhuyun Dai, Mirac Suzgun, Xinyun Chen, Aakanksha Chowdhery, Sharan Narang, Gaurav Mishra, Adams Yu, Vincent Zhao, Yanping Huang, Andrew Dai, Hongkun Yu, Slav Petrov, Ed H. Chi, Jeff Dean, Jacob Devlin, Adam Roberts, Denny Zhou, Quoc V. Le, and Jason Wei
|
||||
1. **[FLAN-UL2](model_doc/flan-ul2)** (from Google AI) released in the repository [google-research/t5x](https://github.com/google-research/t5x/blob/main/docs/models.md#flan-ul2-checkpoints) by Hyung Won Chung, Le Hou, Shayne Longpre, Barret Zoph, Yi Tay, William Fedus, Eric Li, Xuezhi Wang, Mostafa Dehghani, Siddhartha Brahma, Albert Webson, Shixiang Shane Gu, Zhuyun Dai, Mirac Suzgun, Xinyun Chen, Aakanksha Chowdhery, Sharan Narang, Gaurav Mishra, Adams Yu, Vincent Zhao, Yanping Huang, Andrew Dai, Hongkun Yu, Slav Petrov, Ed H. Chi, Jeff Dean, Jacob Devlin, Adam Roberts, Denny Zhou, Quoc V. Le, and Jason Wei
|
||||
1. **[FlauBERT](model_doc/flaubert)** (from CNRS) released with the paper [FlauBERT: Unsupervised Language Model Pre-training for French](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.05372) by Hang Le, Loïc Vial, Jibril Frej, Vincent Segonne, Maximin Coavoux, Benjamin Lecouteux, Alexandre Allauzen, Benoît Crabbé, Laurent Besacier, Didier Schwab.
|
||||
1. **[FLAVA](model_doc/flava)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FLAVA: A Foundational Language And Vision Alignment Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.04482) by Amanpreet Singh, Ronghang Hu, Vedanuj Goswami, Guillaume Couairon, Wojciech Galuba, Marcus Rohrbach, and Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[FNet](model_doc/fnet)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [FNet: Mixing Tokens with Fourier Transforms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.03824) by James Lee-Thorp, Joshua Ainslie, Ilya Eckstein, Santiago Ontanon.
|
||||
1. **[FocalNet](model_doc/focalnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [Focal Modulation Networks](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.11926) by Jianwei Yang, Chunyuan Li, Xiyang Dai, Lu Yuan, Jianfeng Gao.
|
||||
1. **[Funnel Transformer](model_doc/funnel)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [Funnel-Transformer: Filtering out Sequential Redundancy for Efficient Language Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03236) by Zihang Dai, Guokun Lai, Yiming Yang, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[GIT](model_doc/git)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [GIT: A Generative Image-to-text Transformer for Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14100) by Jianfeng Wang, Zhengyuan Yang, Xiaowei Hu, Linjie Li, Kevin Lin, Zhe Gan, Zicheng Liu, Ce Liu, Lijuan Wang.
|
||||
1. **[GLPN](model_doc/glpn)** (from KAIST) released with the paper [Global-Local Path Networks for Monocular Depth Estimation with Vertical CutDepth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.07436) by Doyeon Kim, Woonghyun Ga, Pyungwhan Ahn, Donggyu Joo, Sehwan Chun, Junmo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[GPT](model_doc/openai-gpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training](https://blog.openai.com/language-unsupervised/) by Alec Radford, Karthik Narasimhan, Tim Salimans and Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[GPT Neo](model_doc/gpt_neo)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [EleutherAI/gpt-neo](https://github.com/EleutherAI/gpt-neo) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Leo Gao, Phil Wang and Connor Leahy.
|
||||
1. **[GPT NeoX](model_doc/gpt_neox)** (from EleutherAI) released with the paper [GPT-NeoX-20B: An Open-Source Autoregressive Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06745) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Eric Hallahan, Quentin Anthony, Leo Gao, Laurence Golding, Horace He, Connor Leahy, Kyle McDonell, Jason Phang, Michael Pieler, USVSN Sai Prashanth, Shivanshu Purohit, Laria Reynolds, Jonathan Tow, Ben Wang, Samuel Weinbach
|
||||
1. **[GPT NeoX Japanese](model_doc/gpt_neox_japanese)** (from ABEJA) released by Shinya Otani, Takayoshi Makabe, Anuj Arora, and Kyo Hattori.
|
||||
1. **[GPT-2](model_doc/gpt2)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners](https://blog.openai.com/better-language-models/) by Alec Radford*, Jeffrey Wu*, Rewon Child, David Luan, Dario Amodei** and Ilya Sutskever**.
|
||||
1. **[GPT-J](model_doc/gptj)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax](https://github.com/kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax/) by Ben Wang and Aran Komatsuzaki.
|
||||
1. **[GPT-Sw3](model_doc/gpt-sw3)** (from AI-Sweden) released with the paper [Lessons Learned from GPT-SW3: Building the First Large-Scale Generative Language Model for Swedish](http://www.lrec-conf.org/proceedings/lrec2022/pdf/2022.lrec-1.376.pdf) by Ariel Ekgren, Amaru Cuba Gyllensten, Evangelia Gogoulou, Alice Heiman, Severine Verlinden, Joey Öhman, Fredrik Carlsson, Magnus Sahlgren.
|
||||
1. **[GPTBigCode](model_doc/gpt_bigcode)** (from BigCode) released with the paper [SantaCoder: don't reach for the stars!](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.03988) by Loubna Ben Allal, Raymond Li, Denis Kocetkov, Chenghao Mou, Christopher Akiki, Carlos Munoz Ferrandis, Niklas Muennighoff, Mayank Mishra, Alex Gu, Manan Dey, Logesh Kumar Umapathi, Carolyn Jane Anderson, Yangtian Zi, Joel Lamy Poirier, Hailey Schoelkopf, Sergey Troshin, Dmitry Abulkhanov, Manuel Romero, Michael Lappert, Francesco De Toni, Bernardo García del Río, Qian Liu, Shamik Bose, Urvashi Bhattacharyya, Terry Yue Zhuo, Ian Yu, Paulo Villegas, Marco Zocca, Sourab Mangrulkar, David Lansky, Huu Nguyen, Danish Contractor, Luis Villa, Jia Li, Dzmitry Bahdanau, Yacine Jernite, Sean Hughes, Daniel Fried, Arjun Guha, Harm de Vries, Leandro von Werra.
|
||||
1. **[GPTSAN-japanese](model_doc/gptsan-japanese)** released in the repository [tanreinama/GPTSAN](https://github.com/tanreinama/GPTSAN/blob/main/report/model.md) by Toshiyuki Sakamoto(tanreinama).
|
||||
1. **[Graphormer](model_doc/graphormer)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [Do Transformers Really Perform Bad for Graph Representation?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.05234) by Chengxuan Ying, Tianle Cai, Shengjie Luo, Shuxin Zheng, Guolin Ke, Di He, Yanming Shen, Tie-Yan Liu.
|
||||
1. **[GroupViT](model_doc/groupvit)** (from UCSD, NVIDIA) released with the paper [GroupViT: Semantic Segmentation Emerges from Text Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.11094) by Jiarui Xu, Shalini De Mello, Sifei Liu, Wonmin Byeon, Thomas Breuel, Jan Kautz, Xiaolong Wang.
|
||||
1. **[Hubert](model_doc/hubert)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [HuBERT: Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning by Masked Prediction of Hidden Units](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.07447) by Wei-Ning Hsu, Benjamin Bolte, Yao-Hung Hubert Tsai, Kushal Lakhotia, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Abdelrahman Mohamed.
|
||||
1. **[I-BERT](model_doc/ibert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [I-BERT: Integer-only BERT Quantization](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.01321) by Sehoon Kim, Amir Gholami, Zhewei Yao, Michael W. Mahoney, Kurt Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[ImageGPT](model_doc/imagegpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Generative Pretraining from Pixels](https://openai.com/blog/image-gpt/) by Mark Chen, Alec Radford, Rewon Child, Jeffrey Wu, Heewoo Jun, David Luan, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[Informer](model_doc/informer)** (from Beihang University, UC Berkeley, Rutgers University, SEDD Company) released with the paper [Informer: Beyond Efficient Transformer for Long Sequence Time-Series Forecasting](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.07436) by Haoyi Zhou, Shanghang Zhang, Jieqi Peng, Shuai Zhang, Jianxin Li, Hui Xiong, and Wancai Zhang.
|
||||
1. **[Jukebox](model_doc/jukebox)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Jukebox: A Generative Model for Music](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2005.00341.pdf) by Prafulla Dhariwal, Heewoo Jun, Christine Payne, Jong Wook Kim, Alec Radford, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLM](model_doc/layoutlm)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLM: Pre-training of Text and Layout for Document Image Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.13318) by Yiheng Xu, Minghao Li, Lei Cui, Shaohan Huang, Furu Wei, Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv2](model_doc/layoutlmv2)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv2: Multi-modal Pre-training for Visually-Rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.14740) by Yang Xu, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Furu Wei, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Wanxiang Che, Min Zhang, Lidong Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv3](model_doc/layoutlmv3)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv3: Pre-training for Document AI with Unified Text and Image Masking](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.08387) by Yupan Huang, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yutong Lu, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutXLM](model_doc/layoutxlm)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutXLM: Multimodal Pre-training for Multilingual Visually-rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.08836) by Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LED](model_doc/led)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LeViT](model_doc/levit)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [LeViT: A Vision Transformer in ConvNet's Clothing for Faster Inference](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01136) by Ben Graham, Alaaeldin El-Nouby, Hugo Touvron, Pierre Stock, Armand Joulin, Hervé Jégou, Matthijs Douze.
|
||||
1. **[LiLT](model_doc/lilt)** (from South China University of Technology) released with the paper [LiLT: A Simple yet Effective Language-Independent Layout Transformer for Structured Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.13669) by Jiapeng Wang, Lianwen Jin, Kai Ding.
|
||||
1. **[LLaMA](model_doc/llama)** (from The FAIR team of Meta AI) released with the paper [LLaMA: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.13971) by Hugo Touvron, Thibaut Lavril, Gautier Izacard, Xavier Martinet, Marie-Anne Lachaux, Timothée Lacroix, Baptiste Rozière, Naman Goyal, Eric Hambro, Faisal Azhar, Aurelien Rodriguez, Armand Joulin, Edouard Grave, Guillaume Lample.
|
||||
1. **[Longformer](model_doc/longformer)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LongT5](model_doc/longt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [LongT5: Efficient Text-To-Text Transformer for Long Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.07916) by Mandy Guo, Joshua Ainslie, David Uthus, Santiago Ontanon, Jianmo Ni, Yun-Hsuan Sung, Yinfei Yang.
|
||||
1. **[LUKE](model_doc/luke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [LUKE: Deep Contextualized Entity Representations with Entity-aware Self-attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.01057) by Ikuya Yamada, Akari Asai, Hiroyuki Shindo, Hideaki Takeda, Yuji Matsumoto.
|
||||
1. **[LXMERT](model_doc/lxmert)** (from UNC Chapel Hill) released with the paper [LXMERT: Learning Cross-Modality Encoder Representations from Transformers for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.07490) by Hao Tan and Mohit Bansal.
|
||||
1. **[M-CTC-T](model_doc/mctct)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Pseudo-Labeling For Massively Multilingual Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.00161) by Loren Lugosch, Tatiana Likhomanenko, Gabriel Synnaeve, and Ronan Collobert.
|
||||
1. **[M2M100](model_doc/m2m_100)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Beyond English-Centric Multilingual Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11125) by Angela Fan, Shruti Bhosale, Holger Schwenk, Zhiyi Ma, Ahmed El-Kishky, Siddharth Goyal, Mandeep Baines, Onur Celebi, Guillaume Wenzek, Vishrav Chaudhary, Naman Goyal, Tom Birch, Vitaliy Liptchinsky, Sergey Edunov, Edouard Grave, Michael Auli, Armand Joulin.
|
||||
1. **[MarianMT](model_doc/marian)** Machine translation models trained using [OPUS](http://opus.nlpl.eu/) data by Jörg Tiedemann. The [Marian Framework](https://marian-nmt.github.io/) is being developed by the Microsoft Translator Team.
|
||||
1. **[MarkupLM](model_doc/markuplm)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [MarkupLM: Pre-training of Text and Markup Language for Visually-rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.08518) by Junlong Li, Yiheng Xu, Lei Cui, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[Mask2Former](model_doc/mask2former)** (from FAIR and UIUC) released with the paper [Masked-attention Mask Transformer for Universal Image Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.01527) by Bowen Cheng, Ishan Misra, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov, Rohit Girdhar.
|
||||
1. **[MaskFormer](model_doc/maskformer)** (from Meta and UIUC) released with the paper [Per-Pixel Classification is Not All You Need for Semantic Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.06278) by Bowen Cheng, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov.
|
||||
1. **[MatCha](model_doc/matcha)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [MatCha: Enhancing Visual Language Pretraining with Math Reasoning and Chart Derendering](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.09662) by Fangyu Liu, Francesco Piccinno, Syrine Krichene, Chenxi Pang, Kenton Lee, Mandar Joshi, Yasemin Altun, Nigel Collier, Julian Martin Eisenschlos.
|
||||
1. **[mBART](model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08210) by Yinhan Liu, Jiatao Gu, Naman Goyal, Xian Li, Sergey Edunov, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[mBART-50](model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Translation with Extensible Multilingual Pretraining and Finetuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00401) by Yuqing Tang, Chau Tran, Xian Li, Peng-Jen Chen, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Jiatao Gu, Angela Fan.
|
||||
1. **[MEGA](model_doc/mega)** (from Meta/USC/CMU/SJTU) released with the paper [Mega: Moving Average Equipped Gated Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.10655) by Xuezhe Ma, Chunting Zhou, Xiang Kong, Junxian He, Liangke Gui, Graham Neubig, Jonathan May, and Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-BERT](model_doc/megatron-bert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-GPT2](model_doc/megatron_gpt2)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[MGP-STR](model_doc/mgp-str)** (from Alibaba Research) released with the paper [Multi-Granularity Prediction for Scene Text Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.03592) by Peng Wang, Cheng Da, and Cong Yao.
|
||||
1. **[mLUKE](model_doc/mluke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [mLUKE: The Power of Entity Representations in Multilingual Pretrained Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.08151) by Ryokan Ri, Ikuya Yamada, and Yoshimasa Tsuruoka.
|
||||
1. **[MMS](model_doc/mms)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Scaling Speech Technology to 1,000+ Languages](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.13516) by Vineel Pratap, Andros Tjandra, Bowen Shi, Paden Tomasello, Arun Babu, Sayani Kundu, Ali Elkahky, Zhaoheng Ni, Apoorv Vyas, Maryam Fazel-Zarandi, Alexei Baevski, Yossi Adi, Xiaohui Zhang, Wei-Ning Hsu, Alexis Conneau, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[MobileBERT](model_doc/mobilebert)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [MobileBERT: a Compact Task-Agnostic BERT for Resource-Limited Devices](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02984) by Zhiqing Sun, Hongkun Yu, Xiaodan Song, Renjie Liu, Yiming Yang, and Denny Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[MobileNetV1](model_doc/mobilenet_v1)** (from Google Inc.) released with the paper [MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications](https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861) by Andrew G. Howard, Menglong Zhu, Bo Chen, Dmitry Kalenichenko, Weijun Wang, Tobias Weyand, Marco Andreetto, Hartwig Adam.
|
||||
1. **[MobileNetV2](model_doc/mobilenet_v2)** (from Google Inc.) released with the paper [MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.04381) by Mark Sandler, Andrew Howard, Menglong Zhu, Andrey Zhmoginov, Liang-Chieh Chen.
|
||||
1. **[MobileViT](model_doc/mobilevit)** (from Apple) released with the paper [MobileViT: Light-weight, General-purpose, and Mobile-friendly Vision Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.02178) by Sachin Mehta and Mohammad Rastegari.
|
||||
1. **[MobileViTV2](model_doc/mobilevitv2)** (from Apple) released with the paper [Separable Self-attention for Mobile Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.02680) by Sachin Mehta and Mohammad Rastegari.
|
||||
1. **[MPNet](model_doc/mpnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [MPNet: Masked and Permuted Pre-training for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09297) by Kaitao Song, Xu Tan, Tao Qin, Jianfeng Lu, Tie-Yan Liu.
|
||||
1. **[MT5](model_doc/mt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [mT5: A massively multilingual pre-trained text-to-text transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11934) by Linting Xue, Noah Constant, Adam Roberts, Mihir Kale, Rami Al-Rfou, Aditya Siddhant, Aditya Barua, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[MVP](model_doc/mvp)** (from RUC AI Box) released with the paper [MVP: Multi-task Supervised Pre-training for Natural Language Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.12131) by Tianyi Tang, Junyi Li, Wayne Xin Zhao and Ji-Rong Wen.
|
||||
1. **[NAT](model_doc/nat)** (from SHI Labs) released with the paper [Neighborhood Attention Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.07143) by Ali Hassani, Steven Walton, Jiachen Li, Shen Li, and Humphrey Shi.
|
||||
1. **[Nezha](model_doc/nezha)** (from Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab) released with the paper [NEZHA: Neural Contextualized Representation for Chinese Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.00204) by Junqiu Wei, Xiaozhe Ren, Xiaoguang Li, Wenyong Huang, Yi Liao, Yasheng Wang, Jiashu Lin, Xin Jiang, Xiao Chen and Qun Liu.
|
||||
1. **[NLLB](model_doc/nllb)** (from Meta) released with the paper [No Language Left Behind: Scaling Human-Centered Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.04672) by the NLLB team.
|
||||
1. **[NLLB-MOE](model_doc/nllb-moe)** (from Meta) released with the paper [No Language Left Behind: Scaling Human-Centered Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.04672) by the NLLB team.
|
||||
1. **[Nyströmformer](model_doc/nystromformer)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [Nyströmformer: A Nyström-Based Algorithm for Approximating Self-Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03902) by Yunyang Xiong, Zhanpeng Zeng, Rudrasis Chakraborty, Mingxing Tan, Glenn Fung, Yin Li, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
1. **[OneFormer](model_doc/oneformer)** (from SHI Labs) released with the paper [OneFormer: One Transformer to Rule Universal Image Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06220) by Jitesh Jain, Jiachen Li, MangTik Chiu, Ali Hassani, Nikita Orlov, Humphrey Shi.
|
||||
1. **[OpenLlama](model_doc/open-llama)** (from [s-JoL](https://huggingface.co/s-JoL)) released in [Open-Llama](https://github.com/s-JoL/Open-Llama).
|
||||
1. **[OPT](master/model_doc/opt)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [OPT: Open Pre-trained Transformer Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.01068) by Susan Zhang, Stephen Roller, Naman Goyal, Mikel Artetxe, Moya Chen, Shuohui Chen et al.
|
||||
1. **[OWL-ViT](model_doc/owlvit)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Simple Open-Vocabulary Object Detection with Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.06230) by Matthias Minderer, Alexey Gritsenko, Austin Stone, Maxim Neumann, Dirk Weissenborn, Alexey Dosovitskiy, Aravindh Mahendran, Anurag Arnab, Mostafa Dehghani, Zhuoran Shen, Xiao Wang, Xiaohua Zhai, Thomas Kipf, and Neil Houlsby.
|
||||
1. **[Pegasus](model_doc/pegasus)** (from Google) released with the paper [PEGASUS: Pre-training with Extracted Gap-sentences for Abstractive Summarization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.08777) by Jingqing Zhang, Yao Zhao, Mohammad Saleh and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[PEGASUS-X](model_doc/pegasus_x)** (from Google) released with the paper [Investigating Efficiently Extending Transformers for Long Input Summarization](https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.04347) by Jason Phang, Yao Zhao, and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[Perceiver IO](model_doc/perceiver)** (from Deepmind) released with the paper [Perceiver IO: A General Architecture for Structured Inputs & Outputs](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.14795) by Andrew Jaegle, Sebastian Borgeaud, Jean-Baptiste Alayrac, Carl Doersch, Catalin Ionescu, David Ding, Skanda Koppula, Daniel Zoran, Andrew Brock, Evan Shelhamer, Olivier Hénaff, Matthew M. Botvinick, Andrew Zisserman, Oriol Vinyals, João Carreira.
|
||||
1. **[PhoBERT](model_doc/phobert)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [PhoBERT: Pre-trained language models for Vietnamese](https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.findings-emnlp.92/) by Dat Quoc Nguyen and Anh Tuan Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[Pix2Struct](model_doc/pix2struct)** (from Google) released with the paper [Pix2Struct: Screenshot Parsing as Pretraining for Visual Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.03347) by Kenton Lee, Mandar Joshi, Iulia Turc, Hexiang Hu, Fangyu Liu, Julian Eisenschlos, Urvashi Khandelwal, Peter Shaw, Ming-Wei Chang, Kristina Toutanova.
|
||||
1. **[PLBart](model_doc/plbart)** (from UCLA NLP) released with the paper [Unified Pre-training for Program Understanding and Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06333) by Wasi Uddin Ahmad, Saikat Chakraborty, Baishakhi Ray, Kai-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[PoolFormer](model_doc/poolformer)** (from Sea AI Labs) released with the paper [MetaFormer is Actually What You Need for Vision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.11418) by Yu, Weihao and Luo, Mi and Zhou, Pan and Si, Chenyang and Zhou, Yichen and Wang, Xinchao and Feng, Jiashi and Yan, Shuicheng.
|
||||
1. **[ProphetNet](model_doc/prophetnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [ProphetNet: Predicting Future N-gram for Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04063) by Yu Yan, Weizhen Qi, Yeyun Gong, Dayiheng Liu, Nan Duan, Jiusheng Chen, Ruofei Zhang and Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[QDQBert](model_doc/qdqbert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Integer Quantization for Deep Learning Inference: Principles and Empirical Evaluation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09602) by Hao Wu, Patrick Judd, Xiaojie Zhang, Mikhail Isaev and Paulius Micikevicius.
|
||||
1. **[RAG](model_doc/rag)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11401) by Patrick Lewis, Ethan Perez, Aleksandara Piktus, Fabio Petroni, Vladimir Karpukhin, Naman Goyal, Heinrich Küttler, Mike Lewis, Wen-tau Yih, Tim Rocktäschel, Sebastian Riedel, Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[REALM](model_doc/realm.html)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [REALM: Retrieval-Augmented Language Model Pre-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.08909) by Kelvin Guu, Kenton Lee, Zora Tung, Panupong Pasupat and Ming-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[Reformer](model_doc/reformer)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Reformer: The Efficient Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04451) by Nikita Kitaev, Łukasz Kaiser, Anselm Levskaya.
|
||||
1. **[RegNet](model_doc/regnet)** (from META Platforms) released with the paper [Designing Network Design Space](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.13678) by Ilija Radosavovic, Raj Prateek Kosaraju, Ross Girshick, Kaiming He, Piotr Dollár.
|
||||
1. **[RemBERT](model_doc/rembert)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Rethinking embedding coupling in pre-trained language models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.12821) by Hyung Won Chung, Thibault Févry, Henry Tsai, M. Johnson, Sebastian Ruder.
|
||||
1. **[ResNet](model_doc/resnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385) by Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun.
|
||||
1. **[RoBERTa](model_doc/roberta)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692) by Yinhan Liu, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Mandar Joshi, Danqi Chen, Omer Levy, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer, Veselin Stoyanov.
|
||||
1. **[RoBERTa-PreLayerNorm](model_doc/roberta-prelayernorm)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [fairseq: A Fast, Extensible Toolkit for Sequence Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.01038) by Myle Ott, Sergey Edunov, Alexei Baevski, Angela Fan, Sam Gross, Nathan Ng, David Grangier, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[RoCBert](model_doc/roc_bert)** (from WeChatAI) released with the paper [RoCBert: Robust Chinese Bert with Multimodal Contrastive Pretraining](https://aclanthology.org/2022.acl-long.65.pdf) by HuiSu, WeiweiShi, XiaoyuShen, XiaoZhou, TuoJi, JiaruiFang, JieZhou.
|
||||
1. **[RoFormer](model_doc/roformer)** (from ZhuiyiTechnology), released together with the paper [RoFormer: Enhanced Transformer with Rotary Position Embedding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.09864) by Jianlin Su and Yu Lu and Shengfeng Pan and Bo Wen and Yunfeng Liu.
|
||||
1. **[RWKV](model_doc/rwkv)** (from Bo Peng), released on [this repo](https://github.com/BlinkDL/RWKV-LM) by Bo Peng.
|
||||
1. **[SegFormer](model_doc/segformer)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [SegFormer: Simple and Efficient Design for Semantic Segmentation with Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.15203) by Enze Xie, Wenhai Wang, Zhiding Yu, Anima Anandkumar, Jose M. Alvarez, Ping Luo.
|
||||
1. **[Segment Anything](model_doc/sam)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Segment Anything](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.02643v1.pdf) by Alexander Kirillov, Eric Mintun, Nikhila Ravi, Hanzi Mao, Chloe Rolland, Laura Gustafson, Tete Xiao, Spencer Whitehead, Alex Berg, Wan-Yen Lo, Piotr Dollar, Ross Girshick.
|
||||
1. **[SEW](model_doc/sew)** (from ASAPP) released with the paper [Performance-Efficiency Trade-offs in Unsupervised Pre-training for Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.06870) by Felix Wu, Kwangyoun Kim, Jing Pan, Kyu Han, Kilian Q. Weinberger, Yoav Artzi.
|
||||
1. **[SEW-D](model_doc/sew_d)** (from ASAPP) released with the paper [Performance-Efficiency Trade-offs in Unsupervised Pre-training for Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.06870) by Felix Wu, Kwangyoun Kim, Jing Pan, Kyu Han, Kilian Q. Weinberger, Yoav Artzi.
|
||||
1. **[SpeechT5](model_doc/speecht5)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [SpeechT5: Unified-Modal Encoder-Decoder Pre-Training for Spoken Language Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.07205) by Junyi Ao, Rui Wang, Long Zhou, Chengyi Wang, Shuo Ren, Yu Wu, Shujie Liu, Tom Ko, Qing Li, Yu Zhang, Zhihua Wei, Yao Qian, Jinyu Li, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer](model_doc/speech_to_text)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [fairseq S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with fairseq](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer2](model_doc/speech_to_text_2)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [Large-Scale Self- and Semi-Supervised Learning for Speech Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.06678) by Changhan Wang, Anne Wu, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli, Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[Splinter](model_doc/splinter)** (from Tel Aviv University), released together with the paper [Few-Shot Question Answering by Pretraining Span Selection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.00438) by Ori Ram, Yuval Kirstain, Jonathan Berant, Amir Globerson, Omer Levy.
|
||||
1. **[SqueezeBERT](model_doc/squeezebert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [SqueezeBERT: What can computer vision teach NLP about efficient neural networks?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11316) by Forrest N. Iandola, Albert E. Shaw, Ravi Krishna, and Kurt W. Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[SwiftFormer](model_doc/swiftformer)** (from MBZUAI) released with the paper [SwiftFormer: Efficient Additive Attention for Transformer-based Real-time Mobile Vision Applications](https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.15446) by Abdelrahman Shaker, Muhammad Maaz, Hanoona Rasheed, Salman Khan, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Fahad Shahbaz Khan.
|
||||
1. **[Swin Transformer](model_doc/swin)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14030) by Ze Liu, Yutong Lin, Yue Cao, Han Hu, Yixuan Wei, Zheng Zhang, Stephen Lin, Baining Guo.
|
||||
1. **[Swin Transformer V2](model_doc/swinv2)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [Swin Transformer V2: Scaling Up Capacity and Resolution](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09883) by Ze Liu, Han Hu, Yutong Lin, Zhuliang Yao, Zhenda Xie, Yixuan Wei, Jia Ning, Yue Cao, Zheng Zhang, Li Dong, Furu Wei, Baining Guo.
|
||||
1. **[Swin2SR](model_doc/swin2sr)** (from University of Würzburg) released with the paper [Swin2SR: SwinV2 Transformer for Compressed Image Super-Resolution and Restoration](https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.11345) by Marcos V. Conde, Ui-Jin Choi, Maxime Burchi, Radu Timofte.
|
||||
1. **[SwitchTransformers](model_doc/switch_transformers)** (from Google) released with the paper [Switch Transformers: Scaling to Trillion Parameter Models with Simple and Efficient Sparsity](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.03961) by William Fedus, Barret Zoph, Noam Shazeer.
|
||||
1. **[T5](model_doc/t5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10683) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[T5v1.1](model_doc/t5v1.1)** (from Google AI) released in the repository [google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer](https://github.com/google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer/blob/main/released_checkpoints.md#t511) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[Table Transformer](model_doc/table-transformer)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [PubTables-1M: Towards Comprehensive Table Extraction From Unstructured Documents](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.00061) by Brandon Smock, Rohith Pesala, Robin Abraham.
|
||||
1. **[TAPAS](model_doc/tapas)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [TAPAS: Weakly Supervised Table Parsing via Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02349) by Jonathan Herzig, Paweł Krzysztof Nowak, Thomas Müller, Francesco Piccinno and Julian Martin Eisenschlos.
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](model_doc/tapex)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou.
|
||||
1. **[Time Series Transformer](model_doc/time_series_transformer)** (from HuggingFace).
|
||||
1. **[TimeSformer](model_doc/timesformer)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Is Space-Time Attention All You Need for Video Understanding?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.05095) by Gedas Bertasius, Heng Wang, Lorenzo Torresani.
|
||||
1. **[Trajectory Transformer](model_doc/trajectory_transformers)** (from the University of California at Berkeley) released with the paper [Offline Reinforcement Learning as One Big Sequence Modeling Problem](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.02039) by Michael Janner, Qiyang Li, Sergey Levine
|
||||
1. **[Transformer-XL](model_doc/transfo-xl)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860) by Zihang Dai*, Zhilin Yang*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Quoc V. Le, Ruslan Salakhutdinov.
|
||||
1. **[TrOCR](model_doc/trocr)** (from Microsoft), released together with the paper [TrOCR: Transformer-based Optical Character Recognition with Pre-trained Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.10282) by Minghao Li, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Zhoujun Li, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[TVLT](model_doc/tvlt)** (from UNC Chapel Hill) released with the paper [TVLT: Textless Vision-Language Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.14156) by Zineng Tang, Jaemin Cho, Yixin Nie, Mohit Bansal.
|
||||
1. **[UL2](model_doc/ul2)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Unifying Language Learning Paradigms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.05131v1) by Yi Tay, Mostafa Dehghani, Vinh Q. Tran, Xavier Garcia, Dara Bahri, Tal Schuster, Huaixiu Steven Zheng, Neil Houlsby, Donald Metzler
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeech](model_doc/unispeech)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.07597) by Chengyi Wang, Yu Wu, Yao Qian, Kenichi Kumatani, Shujie Liu, Furu Wei, Michael Zeng, Xuedong Huang.
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeechSat](model_doc/unispeech-sat)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UNISPEECH-SAT: UNIVERSAL SPEECH REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH SPEAKER AWARE PRE-TRAINING](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.05752) by Sanyuan Chen, Yu Wu, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Zhuo Chen, Shujie Liu, Jian Wu, Yao Qian, Furu Wei, Jinyu Li, Xiangzhan Yu.
|
||||
1. **[UPerNet](model_doc/upernet)** (from Peking University) released with the paper [Unified Perceptual Parsing for Scene Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1807.10221) by Tete Xiao, Yingcheng Liu, Bolei Zhou, Yuning Jiang, Jian Sun.
|
||||
1. **[VAN](model_doc/van)** (from Tsinghua University and Nankai University) released with the paper [Visual Attention Network](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.09741) by Meng-Hao Guo, Cheng-Ze Lu, Zheng-Ning Liu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Shi-Min Hu.
|
||||
1. **[VideoMAE](model_doc/videomae)** (from Multimedia Computing Group, Nanjing University) released with the paper [VideoMAE: Masked Autoencoders are Data-Efficient Learners for Self-Supervised Video Pre-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.12602) by Zhan Tong, Yibing Song, Jue Wang, Limin Wang.
|
||||
1. **[ViLT](model_doc/vilt)** (from NAVER AI Lab/Kakao Enterprise/Kakao Brain) released with the paper [ViLT: Vision-and-Language Transformer Without Convolution or Region Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03334) by Wonjae Kim, Bokyung Son, Ildoo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[Vision Transformer (ViT)](model_doc/vit)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929) by Alexey Dosovitskiy, Lucas Beyer, Alexander Kolesnikov, Dirk Weissenborn, Xiaohua Zhai, Thomas Unterthiner, Mostafa Dehghani, Matthias Minderer, Georg Heigold, Sylvain Gelly, Jakob Uszkoreit, Neil Houlsby.
|
||||
1. **[VisualBERT](model_doc/visual_bert)** (from UCLA NLP) released with the paper [VisualBERT: A Simple and Performant Baseline for Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.03557) by Liunian Harold Li, Mark Yatskar, Da Yin, Cho-Jui Hsieh, Kai-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[ViT Hybrid](model_doc/vit_hybrid)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929) by Alexey Dosovitskiy, Lucas Beyer, Alexander Kolesnikov, Dirk Weissenborn, Xiaohua Zhai, Thomas Unterthiner, Mostafa Dehghani, Matthias Minderer, Georg Heigold, Sylvain Gelly, Jakob Uszkoreit, Neil Houlsby.
|
||||
1. **[ViTMAE](model_doc/vit_mae)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.06377) by Kaiming He, Xinlei Chen, Saining Xie, Yanghao Li, Piotr Dollár, Ross Girshick.
|
||||
1. **[ViTMSN](model_doc/vit_msn)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Masked Siamese Networks for Label-Efficient Learning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.07141) by Mahmoud Assran, Mathilde Caron, Ishan Misra, Piotr Bojanowski, Florian Bordes, Pascal Vincent, Armand Joulin, Michael Rabbat, Nicolas Ballas.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2](model_doc/wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [wav2vec 2.0: A Framework for Self-Supervised Learning of Speech Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11477) by Alexei Baevski, Henry Zhou, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2-Conformer](model_doc/wav2vec2-conformer)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FAIRSEQ S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with FAIRSEQ](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Sravya Popuri, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2Phoneme](model_doc/wav2vec2_phoneme)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Simple and Effective Zero-shot Cross-lingual Phoneme Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.11680) by Qiantong Xu, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[WavLM](model_doc/wavlm)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [WavLM: Large-Scale Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Full Stack Speech Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.13900) by Sanyuan Chen, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Yu Wu, Shujie Liu, Zhuo Chen, Jinyu Li, Naoyuki Kanda, Takuya Yoshioka, Xiong Xiao, Jian Wu, Long Zhou, Shuo Ren, Yanmin Qian, Yao Qian, Jian Wu, Michael Zeng, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[Whisper](model_doc/whisper)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Robust Speech Recognition via Large-Scale Weak Supervision](https://cdn.openai.com/papers/whisper.pdf) by Alec Radford, Jong Wook Kim, Tao Xu, Greg Brockman, Christine McLeavey, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[X-CLIP](model_doc/xclip)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [Expanding Language-Image Pretrained Models for General Video Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.02816) by Bolin Ni, Houwen Peng, Minghao Chen, Songyang Zhang, Gaofeng Meng, Jianlong Fu, Shiming Xiang, Haibin Ling.
|
||||
1. **[X-MOD](model_doc/xmod)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Lifting the Curse of Multilinguality by Pre-training Modular Transformers](http://dx.doi.org/10.18653/v1/2022.naacl-main.255) by Jonas Pfeiffer, Naman Goyal, Xi Lin, Xian Li, James Cross, Sebastian Riedel, Mikel Artetxe.
|
||||
1. **[XGLM](model_doc/xglm)** (From Facebook AI) released with the paper [Few-shot Learning with Multilingual Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10668) by Xi Victoria Lin, Todor Mihaylov, Mikel Artetxe, Tianlu Wang, Shuohui Chen, Daniel Simig, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Shruti Bhosale, Jingfei Du, Ramakanth Pasunuru, Sam Shleifer, Punit Singh Koura, Vishrav Chaudhary, Brian O'Horo, Jeff Wang, Luke Zettlemoyer, Zornitsa Kozareva, Mona Diab, Veselin Stoyanov, Xian Li.
|
||||
1. **[XLM](model_doc/xlm)** (from Facebook) released together with the paper [Cross-lingual Language Model Pretraining](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.07291) by Guillaume Lample and Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-ProphetNet](model_doc/xlm-prophetnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [ProphetNet: Predicting Future N-gram for Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04063) by Yu Yan, Weizhen Qi, Yeyun Gong, Dayiheng Liu, Nan Duan, Jiusheng Chen, Ruofei Zhang and Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-RoBERTa](model_doc/xlm-roberta)** (from Facebook AI), released together with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-lingual Representation Learning at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.02116) by Alexis Conneau*, Kartikay Khandelwal*, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Guillaume Wenzek, Francisco Guzmán, Edouard Grave, Myle Ott, Luke Zettlemoyer and Veselin Stoyanov.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-RoBERTa-XL](model_doc/xlm-roberta-xl)** (from Facebook AI), released together with the paper [Larger-Scale Transformers for Multilingual Masked Language Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.00572) by Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Myle Ott, Giri Anantharaman, Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-V](model_doc/xlm-v)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [XLM-V: Overcoming the Vocabulary Bottleneck in Multilingual Masked Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.10472) by Davis Liang, Hila Gonen, Yuning Mao, Rui Hou, Naman Goyal, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Luke Zettlemoyer, Madian Khabsa.
|
||||
1. **[XLNet](model_doc/xlnet)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [XLNet: Generalized Autoregressive Pretraining for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.08237) by Zhilin Yang*, Zihang Dai*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[XLS-R](model_doc/xls_r)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [XLS-R: Self-supervised Cross-lingual Speech Representation Learning at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09296) by Arun Babu, Changhan Wang, Andros Tjandra, Kushal Lakhotia, Qiantong Xu, Naman Goyal, Kritika Singh, Patrick von Platen, Yatharth Saraf, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Alexis Conneau, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[XLSR-Wav2Vec2](model_doc/xlsr_wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-Lingual Representation Learning For Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.13979) by Alexis Conneau, Alexei Baevski, Ronan Collobert, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[YOLOS](model_doc/yolos)** (from Huazhong University of Science & Technology) released with the paper [You Only Look at One Sequence: Rethinking Transformer in Vision through Object Detection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00666) by Yuxin Fang, Bencheng Liao, Xinggang Wang, Jiemin Fang, Jiyang Qi, Rui Wu, Jianwei Niu, Wenyu Liu.
|
||||
1. **[YOSO](model_doc/yoso)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [You Only Sample (Almost) Once: Linear Cost Self-Attention Via Bernoulli Sampling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09714) by Zhanpeng Zeng, Yunyang Xiong, Sathya N. Ravi, Shailesh Acharya, Glenn Fung, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Supported frameworks
|
||||
|
||||
The table below represents the current support in the library for each of those models, whether they have a Python
|
||||
tokenizer (called "slow"). A "fast" tokenizer backed by the 🤗 Tokenizers library, whether they have support in Jax (via
|
||||
Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
|
||||
<!--This table is updated automatically from the auto modules with _make fix-copies_. Do not update manually!-->
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Tokenizer slow | Tokenizer fast | PyTorch support | TensorFlow support | Flax Support |
|
||||
|:-----------------------------:|:--------------:|:--------------:|:---------------:|:------------------:|:------------:|
|
||||
| ALBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| ALIGN | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| AltCLIP | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Audio Spectrogram Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Autoformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BART | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BEiT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Bert Generation | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BigBird | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BigBird-Pegasus | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BioGpt | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BiT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Blenderbot | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BlenderbotSmall | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BLIP | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BLIP-2 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BLOOM | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BridgeTower | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CamemBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CANINE | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Chinese-CLIP | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CLAP | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CLIP | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| CLIPSeg | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CodeGen | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Conditional DETR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ConvBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ConvNeXT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ConvNeXTV2 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CPM-Ant | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CTRL | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CvT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Data2VecAudio | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Data2VecText | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Data2VecVision | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeBERTa-v2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Decision Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Deformable DETR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeiT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DETA | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DETR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DiNAT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DistilBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| DonutSwin | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DPR | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| EfficientFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| EfficientNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ELECTRA | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| EnCodec | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Encoder decoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| ERNIE | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ErnieM | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ESM | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FairSeq Machine-Translation | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FlauBERT | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FLAVA | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FNet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FocalNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Funnel Transformer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GIT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GLPN | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GPT Neo | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GPT NeoX | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GPT NeoX Japanese | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GPT-J | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GPT-Sw3 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GPTBigCode | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GPTSAN-japanese | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Graphormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GroupViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Hubert | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| I-BERT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ImageGPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Informer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Jukebox | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LayoutLM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LayoutLMv2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LayoutLMv3 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LED | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LeViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LiLT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LLaMA | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Longformer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LongT5 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| LUKE | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LXMERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| M-CTC-T | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| M2M100 | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Marian | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| MarkupLM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Mask2Former | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MaskFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MaskFormerSwin | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| mBART | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| MEGA | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Megatron-BERT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MGP-STR | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileNetV1 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileNetV2 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileViTV2 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MPNet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MT5 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| MVP | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| NAT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Nezha | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| NLLB-MOE | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Nyströmformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| OneFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| OpenAI GPT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| OpenAI GPT-2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| OpenLlama | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| OPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| OWL-ViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Pegasus | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| PEGASUS-X | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Perceiver | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Pix2Struct | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| PLBart | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| PoolFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ProphetNet | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| QDQBert | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RAG | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| REALM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Reformer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RegNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RemBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ResNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RetriBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RoBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RoBERTa-PreLayerNorm | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RoCBert | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RoFormer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RWKV | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SAM | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SegFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SEW | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SEW-D | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Speech Encoder decoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Speech2Text | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Speech2Text2 | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SpeechT5 | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Splinter | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SqueezeBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SwiftFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Swin Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Swin Transformer V2 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Swin2SR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SwitchTransformers | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| T5 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Table Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TAPAS | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Time Series Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TimeSformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TimmBackbone | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Trajectory Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Transformer-XL | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TrOCR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TVLT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| UniSpeech | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| UniSpeechSat | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| UPerNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| VAN | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| VideoMAE | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ViLT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Vision Encoder decoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| VisionTextDualEncoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| VisualBERT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| ViT Hybrid | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ViTMAE | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ViTMSN | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Wav2Vec2 | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Wav2Vec2-Conformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| WavLM | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Whisper | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| X-CLIP | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| X-MOD | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XGLM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| XLM | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLM-ProphetNet | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLM-RoBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| XLM-RoBERTa-XL | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLNet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| YOLOS | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| YOSO | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
|
||||
<!-- End table-->
|
||||
256
docs/source/en/installation.md
Normal file
256
docs/source/en/installation.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,256 @@
|
||||
<!---
|
||||
Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Install 🤗 Transformers for whichever deep learning library you're working with, setup your cache, and optionally configure 🤗 Transformers to run offline.
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers is tested on Python 3.6+, PyTorch 1.1.0+, TensorFlow 2.0+, and Flax. Follow the installation instructions below for the deep learning library you are using:
|
||||
|
||||
* [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/) installation instructions.
|
||||
* [TensorFlow 2.0](https://www.tensorflow.org/install/pip) installation instructions.
|
||||
* [Flax](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) installation instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
## Install with pip
|
||||
|
||||
You should install 🤗 Transformers in a [virtual environment](https://docs.python.org/3/library/venv.html). If you're unfamiliar with Python virtual environments, take a look at this [guide](https://packaging.python.org/guides/installing-using-pip-and-virtual-environments/). A virtual environment makes it easier to manage different projects, and avoid compatibility issues between dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
Start by creating a virtual environment in your project directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m venv .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Activate the virtual environment. On Linux and MacOs:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
source .env/bin/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
Activate Virtual environment on Windows
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
.env/Scripts/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you're ready to install 🤗 Transformers with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For CPU-support only, you can conveniently install 🤗 Transformers and a deep learning library in one line. For example, install 🤗 Transformers and PyTorch with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install 'transformers[torch]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers and TensorFlow 2.0:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install 'transformers[tf-cpu]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
M1 / ARM Users
|
||||
|
||||
You will need to install the following before installing TensorFLow 2.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
brew install cmake
|
||||
brew install pkg-config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers and Flax:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install 'transformers[flax]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, check if 🤗 Transformers has been properly installed by running the following command. It will download a pretrained model:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -c "from transformers import pipeline; print(pipeline('sentiment-analysis')('we love you'))"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then print out the label and score:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
[{'label': 'POSITIVE', 'score': 0.9998704791069031}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Install from source
|
||||
|
||||
Install 🤗 Transformers from source with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This command installs the bleeding edge `main` version rather than the latest `stable` version. The `main` version is useful for staying up-to-date with the latest developments. For instance, if a bug has been fixed since the last official release but a new release hasn't been rolled out yet. However, this means the `main` version may not always be stable. We strive to keep the `main` version operational, and most issues are usually resolved within a few hours or a day. If you run into a problem, please open an [Issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues) so we can fix it even sooner!
|
||||
|
||||
Check if 🤗 Transformers has been properly installed by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -c "from transformers import pipeline; print(pipeline('sentiment-analysis')('I love you'))"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Editable install
|
||||
|
||||
You will need an editable install if you'd like to:
|
||||
|
||||
* Use the `main` version of the source code.
|
||||
* Contribute to 🤗 Transformers and need to test changes in the code.
|
||||
|
||||
Clone the repository and install 🤗 Transformers with the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
|
||||
cd transformers
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
These commands will link the folder you cloned the repository to and your Python library paths. Python will now look inside the folder you cloned to in addition to the normal library paths. For example, if your Python packages are typically installed in `~/anaconda3/envs/main/lib/python3.7/site-packages/`, Python will also search the folder you cloned to: `~/transformers/`.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
You must keep the `transformers` folder if you want to keep using the library.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can easily update your clone to the latest version of 🤗 Transformers with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ~/transformers/
|
||||
git pull
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Your Python environment will find the `main` version of 🤗 Transformers on the next run.
|
||||
|
||||
## Install with conda
|
||||
|
||||
Install from the conda channel `huggingface`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Cache setup
|
||||
|
||||
Pretrained models are downloaded and locally cached at: `~/.cache/huggingface/hub`. This is the default directory given by the shell environment variable `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`. On Windows, the default directory is given by `C:\Users\username\.cache\huggingface\hub`. You can change the shell environment variables shown below - in order of priority - to specify a different cache directory:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Shell environment variable (default): `HUGGINGFACE_HUB_CACHE` or `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
2. Shell environment variable: `HF_HOME`.
|
||||
3. Shell environment variable: `XDG_CACHE_HOME` + `/huggingface`.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers will use the shell environment variables `PYTORCH_TRANSFORMERS_CACHE` or `PYTORCH_PRETRAINED_BERT_CACHE` if you are coming from an earlier iteration of this library and have set those environment variables, unless you specify the shell environment variable `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Offline mode
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers is able to run in a firewalled or offline environment by only using local files. Set the environment variable `TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE=1` to enable this behavior.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Add [🤗 Datasets](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/) to your offline training workflow by setting the environment variable `HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE=1`.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you would typically run a program on a normal network firewalled to external instances with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py --model_name_or_path t5-small --dataset_name wmt16 --dataset_config ro-en ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run this same program in an offline instance with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE=1 TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE=1 \
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py --model_name_or_path t5-small --dataset_name wmt16 --dataset_config ro-en ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The script should now run without hanging or waiting to timeout because it knows it should only look for local files.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fetch models and tokenizers to use offline
|
||||
|
||||
Another option for using 🤗 Transformers offline is to download the files ahead of time, and then point to their local path when you need to use them offline. There are three ways to do this:
|
||||
|
||||
* Download a file through the user interface on the [Model Hub](https://huggingface.co/models) by clicking on the ↓ icon.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Use the [`PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] and [`PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] workflow:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Download your files ahead of time with [`PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0_3B")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0_3B")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Save your files to a specified directory with [`PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.save_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
>>> model.save_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Now when you're offline, reload your files with [`PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] from the specified directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Programmatically download files with the [huggingface_hub](https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface_hub/tree/main/src/huggingface_hub) library:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install the `huggingface_hub` library in your virtual environment:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m pip install huggingface_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Use the [`hf_hub_download`](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/adding-a-library#download-files-from-the-hub) function to download a file to a specific path. For example, the following command downloads the `config.json` file from the [T0](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/T0_3B) model to your desired path:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
|
||||
|
||||
>>> hf_hub_download(repo_id="bigscience/T0_3B", filename="config.json", cache_dir="./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once your file is downloaded and locally cached, specify it's local path to load and use it:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0/config.json")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
See the [How to download files from the Hub](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/how-to-downstream) section for more details on downloading files stored on the Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
@ -1,252 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!---
|
||||
Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Install 🤗 Transformers for whichever deep learning library you're working with, setup your cache, and optionally configure 🤗 Transformers to run offline.
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers is tested on Python 3.6+, PyTorch 1.1.0+, TensorFlow 2.0+, and Flax. Follow the installation instructions below for the deep learning library you are using:
|
||||
|
||||
* [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/) installation instructions.
|
||||
* [TensorFlow 2.0](https://www.tensorflow.org/install/pip) installation instructions.
|
||||
* [Flax](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) installation instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
## Install with pip
|
||||
|
||||
You should install 🤗 Transformers in a [virtual environment](https://docs.python.org/3/library/venv.html). If you're unfamiliar with Python virtual environments, take a look at this [guide](https://packaging.python.org/guides/installing-using-pip-and-virtual-environments/). A virtual environment makes it easier to manage different projects, and avoid compatibility issues between dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
Start by creating a virtual environment in your project directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m venv .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Activate the virtual environment. On Linux and MacOs:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
source .env/bin/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
Activate Virtual environment on Windows
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
.env/Scripts/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you're ready to install 🤗 Transformers with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For CPU-support only, you can conveniently install 🤗 Transformers and a deep learning library in one line. For example, install 🤗 Transformers and PyTorch with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install 'transformers[torch]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers and TensorFlow 2.0:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install 'transformers[tf-cpu]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
M1 / ARM Users
|
||||
|
||||
You will need to install the following before installing TensorFLow 2.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
brew install cmake
|
||||
brew install pkg-config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers and Flax:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install 'transformers[flax]'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, check if 🤗 Transformers has been properly installed by running the following command. It will download a pretrained model:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -c "from transformers import pipeline; print(pipeline('sentiment-analysis')('we love you'))"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then print out the label and score:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
[{'label': 'POSITIVE', 'score': 0.9998704791069031}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Install from source
|
||||
|
||||
Install 🤗 Transformers from source with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This command installs the bleeding edge `main` version rather than the latest `stable` version. The `main` version is useful for staying up-to-date with the latest developments. For instance, if a bug has been fixed since the last official release but a new release hasn't been rolled out yet. However, this means the `main` version may not always be stable. We strive to keep the `main` version operational, and most issues are usually resolved within a few hours or a day. If you run into a problem, please open an [Issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues) so we can fix it even sooner!
|
||||
|
||||
Check if 🤗 Transformers has been properly installed by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -c "from transformers import pipeline; print(pipeline('sentiment-analysis')('I love you'))"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Editable install
|
||||
|
||||
You will need an editable install if you'd like to:
|
||||
|
||||
* Use the `main` version of the source code.
|
||||
* Contribute to 🤗 Transformers and need to test changes in the code.
|
||||
|
||||
Clone the repository and install 🤗 Transformers with the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
|
||||
cd transformers
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
These commands will link the folder you cloned the repository to and your Python library paths. Python will now look inside the folder you cloned to in addition to the normal library paths. For example, if your Python packages are typically installed in `~/anaconda3/envs/main/lib/python3.7/site-packages/`, Python will also search the folder you cloned to: `~/transformers/`.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
You must keep the `transformers` folder if you want to keep using the library.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can easily update your clone to the latest version of 🤗 Transformers with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ~/transformers/
|
||||
git pull
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Your Python environment will find the `main` version of 🤗 Transformers on the next run.
|
||||
|
||||
## Install with conda
|
||||
|
||||
Install from the conda channel `huggingface`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Cache setup
|
||||
|
||||
Pretrained models are downloaded and locally cached at: `~/.cache/huggingface/hub`. This is the default directory given by the shell environment variable `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`. On Windows, the default directory is given by `C:\Users\username\.cache\huggingface\hub`. You can change the shell environment variables shown below - in order of priority - to specify a different cache directory:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Shell environment variable (default): `HUGGINGFACE_HUB_CACHE` or `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
2. Shell environment variable: `HF_HOME`.
|
||||
3. Shell environment variable: `XDG_CACHE_HOME` + `/huggingface`.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers will use the shell environment variables `PYTORCH_TRANSFORMERS_CACHE` or `PYTORCH_PRETRAINED_BERT_CACHE` if you are coming from an earlier iteration of this library and have set those environment variables, unless you specify the shell environment variable `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Offline mode
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers is able to run in a firewalled or offline environment by only using local files. Set the environment variable `TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE=1` to enable this behavior.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Add [🤗 Datasets](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/) to your offline training workflow by setting the environment variable `HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE=1`.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you would typically run a program on a normal network firewalled to external instances with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py --model_name_or_path t5-small --dataset_name wmt16 --dataset_config ro-en ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run this same program in an offline instance with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE=1 TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE=1 \
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py --model_name_or_path t5-small --dataset_name wmt16 --dataset_config ro-en ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The script should now run without hanging or waiting to timeout because it knows it should only look for local files.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fetch models and tokenizers to use offline
|
||||
|
||||
Another option for using 🤗 Transformers offline is to download the files ahead of time, and then point to their local path when you need to use them offline. There are three ways to do this:
|
||||
|
||||
* Download a file through the user interface on the [Model Hub](https://huggingface.co/models) by clicking on the ↓ icon.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
* Use the [`PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] and [`PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] workflow:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Download your files ahead of time with [`PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0_3B")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0_3B")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Save your files to a specified directory with [`PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.save_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
>>> model.save_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. Now when you're offline, reload your files with [`PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] from the specified directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Programmatically download files with the [huggingface_hub](https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface_hub/tree/main/src/huggingface_hub) library:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install the `huggingface_hub` library in your virtual environment:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m pip install huggingface_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Use the [`hf_hub_download`](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/adding-a-library#download-files-from-the-hub) function to download a file to a specific path. For example, the following command downloads the `config.json` file from the [T0](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/T0_3B) model to your desired path:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
|
||||
|
||||
>>> hf_hub_download(repo_id="bigscience/T0_3B", filename="config.json", cache_dir="./your/path/bigscience_t0")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once your file is downloaded and locally cached, specify it's local path to load and use it:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0/config.json")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
See the [How to download files from the Hub](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/how-to-downstream) section for more details on downloading files stored on the Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
39
docs/source/en/internal/audio_utils.md
Normal file
39
docs/source/en/internal/audio_utils.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Utilities for `FeatureExtractors`
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the utility functions that can be used by the audio [`FeatureExtractor`] in order to compute special features from a raw audio using common algorithms such as *Short Time Fourier Transform* or *log mel spectrogram*.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the audio processors in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
## Audio Transformations
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.hertz_to_mel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.mel_to_hertz
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.mel_filter_bank
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.optimal_fft_length
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.window_function
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.spectrogram
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.power_to_db
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.amplitude_to_db
|
||||
@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Utilities for `FeatureExtractors`
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the utility functions that can be used by the audio [`FeatureExtractor`] in order to compute special features from a raw audio using common algorithms such as *Short Time Fourier Transform* or *log mel spectrogram*.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the audio processors in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
## Audio Transformations
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.hertz_to_mel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.mel_to_hertz
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.mel_filter_bank
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.optimal_fft_length
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.window_function
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.spectrogram
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.power_to_db
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] audio_utils.amplitude_to_db
|
||||
50
docs/source/en/internal/file_utils.md
Normal file
50
docs/source/en/internal/file_utils.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# General Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all of Transformers general utility functions that are found in the file `utils.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the general code in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Enums and namedtuples
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.ExplicitEnum
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.PaddingStrategy
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.TensorType
|
||||
|
||||
## Special Decorators
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.add_start_docstrings
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.add_end_docstrings
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.add_code_sample_docstrings
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.replace_return_docstrings
|
||||
|
||||
## Special Properties
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.cached_property
|
||||
|
||||
## Other Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils._LazyModule
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# General Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all of Transformers general utility functions that are found in the file `utils.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the general code in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Enums and namedtuples
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.ExplicitEnum
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.PaddingStrategy
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.TensorType
|
||||
|
||||
## Special Decorators
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.add_start_docstrings
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.add_end_docstrings
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.add_code_sample_docstrings
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.replace_return_docstrings
|
||||
|
||||
## Special Properties
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.cached_property
|
||||
|
||||
## Other Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils._LazyModule
|
||||
277
docs/source/en/internal/generation_utils.md
Normal file
277
docs/source/en/internal/generation_utils.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,277 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Utilities for Generation
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the utility functions used by [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`],
|
||||
[`~generation.GenerationMixin.greedy_search`],
|
||||
[`~generation.GenerationMixin.contrastive_search`],
|
||||
[`~generation.GenerationMixin.sample`],
|
||||
[`~generation.GenerationMixin.beam_search`],
|
||||
[`~generation.GenerationMixin.beam_sample`],
|
||||
[`~generation.GenerationMixin.group_beam_search`], and
|
||||
[`~generation.GenerationMixin.constrained_beam_search`].
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the generate methods in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
## Generate Outputs
|
||||
|
||||
The output of [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`] is an instance of a subclass of
|
||||
[`~utils.ModelOutput`]. This output is a data structure containing all the information returned
|
||||
by [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`], but that can also be used as tuple or dictionary.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import GPT2Tokenizer, GPT2LMHeadModel
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained("gpt2")
|
||||
model = GPT2LMHeadModel.from_pretrained("gpt2")
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer("Hello, my dog is cute and ", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
generation_output = model.generate(**inputs, return_dict_in_generate=True, output_scores=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `generation_output` object is a [`~generation.GreedySearchDecoderOnlyOutput`], as we can
|
||||
see in the documentation of that class below, it means it has the following attributes:
|
||||
|
||||
- `sequences`: the generated sequences of tokens
|
||||
- `scores` (optional): the prediction scores of the language modelling head, for each generation step
|
||||
- `hidden_states` (optional): the hidden states of the model, for each generation step
|
||||
- `attentions` (optional): the attention weights of the model, for each generation step
|
||||
|
||||
Here we have the `scores` since we passed along `output_scores=True`, but we don't have `hidden_states` and
|
||||
`attentions` because we didn't pass `output_hidden_states=True` or `output_attentions=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can access each attribute as you would usually do, and if that attribute has not been returned by the model, you
|
||||
will get `None`. Here for instance `generation_output.scores` are all the generated prediction scores of the
|
||||
language modeling head, and `generation_output.attentions` is `None`.
|
||||
|
||||
When using our `generation_output` object as a tuple, it only keeps the attributes that don't have `None` values.
|
||||
Here, for instance, it has two elements, `loss` then `logits`, so
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
generation_output[:2]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
will return the tuple `(generation_output.sequences, generation_output.scores)` for instance.
|
||||
|
||||
When using our `generation_output` object as a dictionary, it only keeps the attributes that don't have `None`
|
||||
values. Here, for instance, it has two keys that are `sequences` and `scores`.
|
||||
|
||||
We document here all output types.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### GreedySearchOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.GreedySearchDecoderOnlyOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.GreedySearchEncoderDecoderOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.FlaxGreedySearchOutput
|
||||
|
||||
### SampleOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.SampleDecoderOnlyOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.SampleEncoderDecoderOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.FlaxSampleOutput
|
||||
|
||||
### BeamSearchOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.BeamSearchDecoderOnlyOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.BeamSearchEncoderDecoderOutput
|
||||
|
||||
### BeamSampleOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.BeamSampleDecoderOnlyOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.BeamSampleEncoderDecoderOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## LogitsProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
A [`LogitsProcessor`] can be used to modify the prediction scores of a language model head for
|
||||
generation.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LogitsProcessorList
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MinLengthLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MinNewTokensLengthLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TemperatureLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] RepetitionPenaltyLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TopPLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TopKLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TypicalLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NoRepeatNGramLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NoBadWordsLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PrefixConstrainedLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HammingDiversityLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ForcedBOSTokenLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ForcedEOSTokenLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] InfNanRemoveLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFLogitsProcessorList
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFTemperatureLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFTopPLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFTopKLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFMinLengthLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFNoBadWordsLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFNoRepeatNGramLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFRepetitionPenaltyLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFForcedBOSTokenLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFForcedEOSTokenLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxLogitsProcessorList
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxTemperatureLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxTopPLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxTopKLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxForcedBOSTokenLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxForcedEOSTokenLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxMinLengthLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## StoppingCriteria
|
||||
|
||||
A [`StoppingCriteria`] can be used to change when to stop generation (other than EOS token).
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] StoppingCriteria
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] StoppingCriteriaList
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MaxLengthCriteria
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MaxTimeCriteria
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## Constraints
|
||||
|
||||
A [`Constraint`] can be used to force the generation to include specific tokens or sequences in the output.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Constraint
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PhrasalConstraint
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DisjunctiveConstraint
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ConstraintListState
|
||||
|
||||
## BeamSearch
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BeamScorer
|
||||
- process
|
||||
- finalize
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BeamSearchScorer
|
||||
- process
|
||||
- finalize
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ConstrainedBeamSearchScorer
|
||||
- process
|
||||
- finalize
|
||||
|
||||
## Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] top_k_top_p_filtering
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tf_top_k_top_p_filtering
|
||||
|
||||
## Streamers
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TextStreamer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TextIteratorStreamer
|
||||
@ -1,273 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Utilities for Generation
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the utility functions used by [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`],
|
||||
[`~generation.GenerationMixin.greedy_search`],
|
||||
[`~generation.GenerationMixin.contrastive_search`],
|
||||
[`~generation.GenerationMixin.sample`],
|
||||
[`~generation.GenerationMixin.beam_search`],
|
||||
[`~generation.GenerationMixin.beam_sample`],
|
||||
[`~generation.GenerationMixin.group_beam_search`], and
|
||||
[`~generation.GenerationMixin.constrained_beam_search`].
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the generate methods in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
## Generate Outputs
|
||||
|
||||
The output of [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`] is an instance of a subclass of
|
||||
[`~utils.ModelOutput`]. This output is a data structure containing all the information returned
|
||||
by [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`], but that can also be used as tuple or dictionary.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import GPT2Tokenizer, GPT2LMHeadModel
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = GPT2Tokenizer.from_pretrained("gpt2")
|
||||
model = GPT2LMHeadModel.from_pretrained("gpt2")
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer("Hello, my dog is cute and ", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
generation_output = model.generate(**inputs, return_dict_in_generate=True, output_scores=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `generation_output` object is a [`~generation.GreedySearchDecoderOnlyOutput`], as we can
|
||||
see in the documentation of that class below, it means it has the following attributes:
|
||||
|
||||
- `sequences`: the generated sequences of tokens
|
||||
- `scores` (optional): the prediction scores of the language modelling head, for each generation step
|
||||
- `hidden_states` (optional): the hidden states of the model, for each generation step
|
||||
- `attentions` (optional): the attention weights of the model, for each generation step
|
||||
|
||||
Here we have the `scores` since we passed along `output_scores=True`, but we don't have `hidden_states` and
|
||||
`attentions` because we didn't pass `output_hidden_states=True` or `output_attentions=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can access each attribute as you would usually do, and if that attribute has not been returned by the model, you
|
||||
will get `None`. Here for instance `generation_output.scores` are all the generated prediction scores of the
|
||||
language modeling head, and `generation_output.attentions` is `None`.
|
||||
|
||||
When using our `generation_output` object as a tuple, it only keeps the attributes that don't have `None` values.
|
||||
Here, for instance, it has two elements, `loss` then `logits`, so
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
generation_output[:2]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
will return the tuple `(generation_output.sequences, generation_output.scores)` for instance.
|
||||
|
||||
When using our `generation_output` object as a dictionary, it only keeps the attributes that don't have `None`
|
||||
values. Here, for instance, it has two keys that are `sequences` and `scores`.
|
||||
|
||||
We document here all output types.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### GreedySearchOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.GreedySearchDecoderOnlyOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.GreedySearchEncoderDecoderOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.FlaxGreedySearchOutput
|
||||
|
||||
### SampleOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.SampleDecoderOnlyOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.SampleEncoderDecoderOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.FlaxSampleOutput
|
||||
|
||||
### BeamSearchOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.BeamSearchDecoderOnlyOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.BeamSearchEncoderDecoderOutput
|
||||
|
||||
### BeamSampleOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.BeamSampleDecoderOnlyOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.BeamSampleEncoderDecoderOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## LogitsProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
A [`LogitsProcessor`] can be used to modify the prediction scores of a language model head for
|
||||
generation.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LogitsProcessorList
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MinLengthLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MinNewTokensLengthLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TemperatureLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] RepetitionPenaltyLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TopPLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TopKLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TypicalLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NoRepeatNGramLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NoBadWordsLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PrefixConstrainedLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HammingDiversityLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ForcedBOSTokenLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ForcedEOSTokenLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] InfNanRemoveLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFLogitsProcessorList
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFTemperatureLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFTopPLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFTopKLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFMinLengthLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFNoBadWordsLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFNoRepeatNGramLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFRepetitionPenaltyLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFForcedBOSTokenLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFForcedEOSTokenLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxLogitsProcessorList
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxTemperatureLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxTopPLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxTopKLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxForcedBOSTokenLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxForcedEOSTokenLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxMinLengthLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## StoppingCriteria
|
||||
|
||||
A [`StoppingCriteria`] can be used to change when to stop generation (other than EOS token).
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] StoppingCriteria
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] StoppingCriteriaList
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MaxLengthCriteria
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MaxTimeCriteria
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## Constraints
|
||||
|
||||
A [`Constraint`] can be used to force the generation to include specific tokens or sequences in the output.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Constraint
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PhrasalConstraint
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DisjunctiveConstraint
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ConstraintListState
|
||||
|
||||
## BeamSearch
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BeamScorer
|
||||
- process
|
||||
- finalize
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BeamSearchScorer
|
||||
- process
|
||||
- finalize
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ConstrainedBeamSearchScorer
|
||||
- process
|
||||
- finalize
|
||||
|
||||
## Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] top_k_top_p_filtering
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tf_top_k_top_p_filtering
|
||||
|
||||
## Streamers
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TextStreamer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TextIteratorStreamer
|
||||
48
docs/source/en/internal/image_processing_utils.md
Normal file
48
docs/source/en/internal/image_processing_utils.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Utilities for Image Processors
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the utility functions used by the image processors, mainly the functional
|
||||
transformations used to process the images.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the image processors in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
## Image Transformations
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.center_crop
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.center_to_corners_format
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.corners_to_center_format
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.id_to_rgb
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.normalize
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.pad
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.rgb_to_id
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.rescale
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.resize
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.to_pil_image
|
||||
|
||||
## ImageProcessingMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_processing_utils.ImageProcessingMixin
|
||||
@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Utilities for Image Processors
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the utility functions used by the image processors, mainly the functional
|
||||
transformations used to process the images.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the image processors in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
## Image Transformations
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.center_crop
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.center_to_corners_format
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.corners_to_center_format
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.id_to_rgb
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.normalize
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.pad
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.rgb_to_id
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.rescale
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.resize
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_transforms.to_pil_image
|
||||
|
||||
## ImageProcessingMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_processing_utils.ImageProcessingMixin
|
||||
83
docs/source/en/internal/modeling_utils.md
Normal file
83
docs/source/en/internal/modeling_utils.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Custom Layers and Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the custom layers used by the library, as well as the utility functions it provides for modeling.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the models in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Pytorch custom modules
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pytorch_utils.Conv1D
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.PoolerStartLogits
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.PoolerEndLogits
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.PoolerAnswerClass
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.SquadHeadOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.SQuADHead
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.SequenceSummary
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## PyTorch Helper Functions
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pytorch_utils.apply_chunking_to_forward
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pytorch_utils.find_pruneable_heads_and_indices
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pytorch_utils.prune_layer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pytorch_utils.prune_conv1d_layer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pytorch_utils.prune_linear_layer
|
||||
|
||||
## TensorFlow custom layers
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFConv1D
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFSequenceSummary
|
||||
|
||||
## TensorFlow loss functions
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFCausalLanguageModelingLoss
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFMaskedLanguageModelingLoss
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFMultipleChoiceLoss
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFQuestionAnsweringLoss
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFSequenceClassificationLoss
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFTokenClassificationLoss
|
||||
|
||||
## TensorFlow Helper Functions
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.get_initializer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.keras_serializable
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.shape_list
|
||||
@ -1,79 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Custom Layers and Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the custom layers used by the library, as well as the utility functions it provides for modeling.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the models in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Pytorch custom modules
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pytorch_utils.Conv1D
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.PoolerStartLogits
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.PoolerEndLogits
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.PoolerAnswerClass
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.SquadHeadOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.SQuADHead
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.SequenceSummary
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## PyTorch Helper Functions
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pytorch_utils.apply_chunking_to_forward
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pytorch_utils.find_pruneable_heads_and_indices
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pytorch_utils.prune_layer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pytorch_utils.prune_conv1d_layer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pytorch_utils.prune_linear_layer
|
||||
|
||||
## TensorFlow custom layers
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFConv1D
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFSequenceSummary
|
||||
|
||||
## TensorFlow loss functions
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFCausalLanguageModelingLoss
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFMaskedLanguageModelingLoss
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFMultipleChoiceLoss
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFQuestionAnsweringLoss
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFSequenceClassificationLoss
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFTokenClassificationLoss
|
||||
|
||||
## TensorFlow Helper Functions
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.get_initializer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.keras_serializable
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.shape_list
|
||||
44
docs/source/en/internal/pipelines_utils.md
Normal file
44
docs/source/en/internal/pipelines_utils.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Utilities for pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the utility functions the library provides for pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the models in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Argument handling
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.ArgumentHandler
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.ZeroShotClassificationArgumentHandler
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.QuestionAnsweringArgumentHandler
|
||||
|
||||
## Data format
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.PipelineDataFormat
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.CsvPipelineDataFormat
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.JsonPipelineDataFormat
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.PipedPipelineDataFormat
|
||||
|
||||
## Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.PipelineException
|
||||
@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Utilities for pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the utility functions the library provides for pipelines.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the models in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Argument handling
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.ArgumentHandler
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.ZeroShotClassificationArgumentHandler
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.QuestionAnsweringArgumentHandler
|
||||
|
||||
## Data format
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.PipelineDataFormat
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.CsvPipelineDataFormat
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.JsonPipelineDataFormat
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.PipedPipelineDataFormat
|
||||
|
||||
## Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] pipelines.PipelineException
|
||||
29
docs/source/en/internal/time_series_utils.md
Normal file
29
docs/source/en/internal/time_series_utils.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Time Series Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the utility functions and classes that can be used for Time Series based models.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the time series models or you wish to add to the collection of distributional output classes.
|
||||
|
||||
## Distributional Output
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] time_series_utils.NormalOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] time_series_utils.StudentTOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] time_series_utils.NegativeBinomialOutput
|
||||
@ -1,25 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Time Series Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the utility functions and classes that can be used for Time Series based models.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the time series models or you wish to add to the collection of distributional output classes.
|
||||
|
||||
## Distributional Output
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] time_series_utils.NormalOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] time_series_utils.StudentTOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] time_series_utils.NegativeBinomialOutput
|
||||
42
docs/source/en/internal/tokenization_utils.md
Normal file
42
docs/source/en/internal/tokenization_utils.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Utilities for Tokenizers
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the utility functions used by the tokenizers, mainly the class
|
||||
[`~tokenization_utils_base.PreTrainedTokenizerBase`] that implements the common methods between
|
||||
[`PreTrainedTokenizer`] and [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`] and the mixin
|
||||
[`~tokenization_utils_base.SpecialTokensMixin`].
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the tokenizers in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
## PreTrainedTokenizerBase
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tokenization_utils_base.PreTrainedTokenizerBase
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## SpecialTokensMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tokenization_utils_base.SpecialTokensMixin
|
||||
|
||||
## Enums and namedtuples
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tokenization_utils_base.TruncationStrategy
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tokenization_utils_base.CharSpan
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tokenization_utils_base.TokenSpan
|
||||
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Utilities for Tokenizers
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the utility functions used by the tokenizers, mainly the class
|
||||
[`~tokenization_utils_base.PreTrainedTokenizerBase`] that implements the common methods between
|
||||
[`PreTrainedTokenizer`] and [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`] and the mixin
|
||||
[`~tokenization_utils_base.SpecialTokensMixin`].
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the tokenizers in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
## PreTrainedTokenizerBase
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tokenization_utils_base.PreTrainedTokenizerBase
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## SpecialTokensMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tokenization_utils_base.SpecialTokensMixin
|
||||
|
||||
## Enums and namedtuples
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tokenization_utils_base.TruncationStrategy
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tokenization_utils_base.CharSpan
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tokenization_utils_base.TokenSpan
|
||||
49
docs/source/en/internal/trainer_utils.md
Normal file
49
docs/source/en/internal/trainer_utils.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Utilities for Trainer
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the utility functions used by [`Trainer`].
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the Trainer in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
## Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] EvalPrediction
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] IntervalStrategy
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] enable_full_determinism
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] set_seed
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] torch_distributed_zero_first
|
||||
|
||||
## Callbacks internals
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] trainer_callback.CallbackHandler
|
||||
|
||||
## Distributed Evaluation
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] trainer_pt_utils.DistributedTensorGatherer
|
||||
|
||||
## Distributed Evaluation
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HfArgumentParser
|
||||
|
||||
## Debug Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] debug_utils.DebugUnderflowOverflow
|
||||
@ -1,45 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Utilities for Trainer
|
||||
|
||||
This page lists all the utility functions used by [`Trainer`].
|
||||
|
||||
Most of those are only useful if you are studying the code of the Trainer in the library.
|
||||
|
||||
## Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] EvalPrediction
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] IntervalStrategy
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] enable_full_determinism
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] set_seed
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] torch_distributed_zero_first
|
||||
|
||||
## Callbacks internals
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] trainer_callback.CallbackHandler
|
||||
|
||||
## Distributed Evaluation
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] trainer_pt_utils.DistributedTensorGatherer
|
||||
|
||||
## Distributed Evaluation
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HfArgumentParser
|
||||
|
||||
## Debug Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] debug_utils.DebugUnderflowOverflow
|
||||
105
docs/source/en/main_classes/agent.md
Normal file
105
docs/source/en/main_classes/agent.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Agents & Tools
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers Agent is an experimental API which is subject to change at any time. Results returned by the agents
|
||||
can vary as the APIs or underlying models are prone to change.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about agents and tools make sure to read the [introductory guide](../transformers_agents). This page
|
||||
contains the API docs for the underlying classes.
|
||||
|
||||
## Agents
|
||||
|
||||
We provide three types of agents: [`HfAgent`] uses inference endpoints for opensource models, [`LocalAgent`] uses a model of your choice locally and [`OpenAiAgent`] uses OpenAI closed models.
|
||||
|
||||
### HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### LocalAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LocalAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] OpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### AzureOpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AzureOpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### Agent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Agent
|
||||
- chat
|
||||
- run
|
||||
- prepare_for_new_chat
|
||||
|
||||
## Tools
|
||||
|
||||
### load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
### Tool
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Tool
|
||||
|
||||
### PipelineTool
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PipelineTool
|
||||
|
||||
### RemoteTool
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] RemoteTool
|
||||
|
||||
### launch_gradio_demo
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] launch_gradio_demo
|
||||
|
||||
## Agent Types
|
||||
|
||||
Agents can handle any type of object in-between tools; tools, being completely multimodal, can accept and return
|
||||
text, image, audio, video, among other types. In order to increase compatibility between tools, as well as to
|
||||
correctly render these returns in ipython (jupyter, colab, ipython notebooks, ...), we implement wrapper classes
|
||||
around these types.
|
||||
|
||||
The wrapped objects should continue behaving as initially; a text object should still behave as a string, an image
|
||||
object should still behave as a `PIL.Image`.
|
||||
|
||||
These types have three specific purposes:
|
||||
|
||||
- Calling `to_raw` on the type should return the underlying object
|
||||
- Calling `to_string` on the type should return the object as a string: that can be the string in case of an `AgentText`
|
||||
but will be the path of the serialized version of the object in other instances
|
||||
- Displaying it in an ipython kernel should display the object correctly
|
||||
|
||||
### AgentText
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.tools.agent_types.AgentText
|
||||
|
||||
### AgentImage
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.tools.agent_types.AgentImage
|
||||
|
||||
### AgentAudio
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.tools.agent_types.AgentAudio
|
||||
@ -1,101 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Agents & Tools
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers Agent is an experimental API which is subject to change at any time. Results returned by the agents
|
||||
can vary as the APIs or underlying models are prone to change.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about agents and tools make sure to read the [introductory guide](../transformers_agents). This page
|
||||
contains the API docs for the underlying classes.
|
||||
|
||||
## Agents
|
||||
|
||||
We provide three types of agents: [`HfAgent`] uses inference endpoints for opensource models, [`LocalAgent`] uses a model of your choice locally and [`OpenAiAgent`] uses OpenAI closed models.
|
||||
|
||||
### HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### LocalAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LocalAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] OpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### AzureOpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AzureOpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### Agent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Agent
|
||||
- chat
|
||||
- run
|
||||
- prepare_for_new_chat
|
||||
|
||||
## Tools
|
||||
|
||||
### load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
### Tool
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Tool
|
||||
|
||||
### PipelineTool
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PipelineTool
|
||||
|
||||
### RemoteTool
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] RemoteTool
|
||||
|
||||
### launch_gradio_demo
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] launch_gradio_demo
|
||||
|
||||
## Agent Types
|
||||
|
||||
Agents can handle any type of object in-between tools; tools, being completely multimodal, can accept and return
|
||||
text, image, audio, video, among other types. In order to increase compatibility between tools, as well as to
|
||||
correctly render these returns in ipython (jupyter, colab, ipython notebooks, ...), we implement wrapper classes
|
||||
around these types.
|
||||
|
||||
The wrapped objects should continue behaving as initially; a text object should still behave as a string, an image
|
||||
object should still behave as a `PIL.Image`.
|
||||
|
||||
These types have three specific purposes:
|
||||
|
||||
- Calling `to_raw` on the type should return the underlying object
|
||||
- Calling `to_string` on the type should return the object as a string: that can be the string in case of an `AgentText`
|
||||
but will be the path of the serialized version of the object in other instances
|
||||
- Displaying it in an ipython kernel should display the object correctly
|
||||
|
||||
### AgentText
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.tools.agent_types.AgentText
|
||||
|
||||
### AgentImage
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.tools.agent_types.AgentImage
|
||||
|
||||
### AgentAudio
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.tools.agent_types.AgentAudio
|
||||
127
docs/source/en/main_classes/callback.md
Normal file
127
docs/source/en/main_classes/callback.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Callbacks
|
||||
|
||||
Callbacks are objects that can customize the behavior of the training loop in the PyTorch
|
||||
[`Trainer`] (this feature is not yet implemented in TensorFlow) that can inspect the training loop
|
||||
state (for progress reporting, logging on TensorBoard or other ML platforms...) and take decisions (like early
|
||||
stopping).
|
||||
|
||||
Callbacks are "read only" pieces of code, apart from the [`TrainerControl`] object they return, they
|
||||
cannot change anything in the training loop. For customizations that require changes in the training loop, you should
|
||||
subclass [`Trainer`] and override the methods you need (see [trainer](trainer) for examples).
|
||||
|
||||
By default a [`Trainer`] will use the following callbacks:
|
||||
|
||||
- [`DefaultFlowCallback`] which handles the default behavior for logging, saving and evaluation.
|
||||
- [`PrinterCallback`] or [`ProgressCallback`] to display progress and print the
|
||||
logs (the first one is used if you deactivate tqdm through the [`TrainingArguments`], otherwise
|
||||
it's the second one).
|
||||
- [`~integrations.TensorBoardCallback`] if tensorboard is accessible (either through PyTorch >= 1.4
|
||||
or tensorboardX).
|
||||
- [`~integrations.WandbCallback`] if [wandb](https://www.wandb.com/) is installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.CometCallback`] if [comet_ml](https://www.comet.ml/site/) is installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.MLflowCallback`] if [mlflow](https://www.mlflow.org/) is installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.NeptuneCallback`] if [neptune](https://neptune.ai/) is installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.AzureMLCallback`] if [azureml-sdk](https://pypi.org/project/azureml-sdk/) is
|
||||
installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.CodeCarbonCallback`] if [codecarbon](https://pypi.org/project/codecarbon/) is
|
||||
installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.ClearMLCallback`] if [clearml](https://github.com/allegroai/clearml) is installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.DagsHubCallback`] if [dagshub](https://dagshub.com/) is installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.FlyteCallback`] if [flyte](https://flyte.org/) is installed.
|
||||
|
||||
The main class that implements callbacks is [`TrainerCallback`]. It gets the
|
||||
[`TrainingArguments`] used to instantiate the [`Trainer`], can access that
|
||||
Trainer's internal state via [`TrainerState`], and can take some actions on the training loop via
|
||||
[`TrainerControl`].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Callbacks
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the list of the available [`TrainerCallback`] in the library:
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.CometCallback
|
||||
- setup
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DefaultFlowCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PrinterCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ProgressCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] EarlyStoppingCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.TensorBoardCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.WandbCallback
|
||||
- setup
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.MLflowCallback
|
||||
- setup
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.AzureMLCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.CodeCarbonCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.NeptuneCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.ClearMLCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.DagsHubCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.FlyteCallback
|
||||
|
||||
## TrainerCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TrainerCallback
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of how to register a custom callback with the PyTorch [`Trainer`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class MyCallback(TrainerCallback):
|
||||
"A callback that prints a message at the beginning of training"
|
||||
|
||||
def on_train_begin(self, args, state, control, **kwargs):
|
||||
print("Starting training")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args,
|
||||
train_dataset=train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=eval_dataset,
|
||||
callbacks=[MyCallback], # We can either pass the callback class this way or an instance of it (MyCallback())
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to register a callback is to call `trainer.add_callback()` as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(...)
|
||||
trainer.add_callback(MyCallback)
|
||||
# Alternatively, we can pass an instance of the callback class
|
||||
trainer.add_callback(MyCallback())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TrainerState
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TrainerState
|
||||
|
||||
## TrainerControl
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TrainerControl
|
||||
@ -1,123 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Callbacks
|
||||
|
||||
Callbacks are objects that can customize the behavior of the training loop in the PyTorch
|
||||
[`Trainer`] (this feature is not yet implemented in TensorFlow) that can inspect the training loop
|
||||
state (for progress reporting, logging on TensorBoard or other ML platforms...) and take decisions (like early
|
||||
stopping).
|
||||
|
||||
Callbacks are "read only" pieces of code, apart from the [`TrainerControl`] object they return, they
|
||||
cannot change anything in the training loop. For customizations that require changes in the training loop, you should
|
||||
subclass [`Trainer`] and override the methods you need (see [trainer](trainer) for examples).
|
||||
|
||||
By default a [`Trainer`] will use the following callbacks:
|
||||
|
||||
- [`DefaultFlowCallback`] which handles the default behavior for logging, saving and evaluation.
|
||||
- [`PrinterCallback`] or [`ProgressCallback`] to display progress and print the
|
||||
logs (the first one is used if you deactivate tqdm through the [`TrainingArguments`], otherwise
|
||||
it's the second one).
|
||||
- [`~integrations.TensorBoardCallback`] if tensorboard is accessible (either through PyTorch >= 1.4
|
||||
or tensorboardX).
|
||||
- [`~integrations.WandbCallback`] if [wandb](https://www.wandb.com/) is installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.CometCallback`] if [comet_ml](https://www.comet.ml/site/) is installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.MLflowCallback`] if [mlflow](https://www.mlflow.org/) is installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.NeptuneCallback`] if [neptune](https://neptune.ai/) is installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.AzureMLCallback`] if [azureml-sdk](https://pypi.org/project/azureml-sdk/) is
|
||||
installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.CodeCarbonCallback`] if [codecarbon](https://pypi.org/project/codecarbon/) is
|
||||
installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.ClearMLCallback`] if [clearml](https://github.com/allegroai/clearml) is installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.DagsHubCallback`] if [dagshub](https://dagshub.com/) is installed.
|
||||
- [`~integrations.FlyteCallback`] if [flyte](https://flyte.org/) is installed.
|
||||
|
||||
The main class that implements callbacks is [`TrainerCallback`]. It gets the
|
||||
[`TrainingArguments`] used to instantiate the [`Trainer`], can access that
|
||||
Trainer's internal state via [`TrainerState`], and can take some actions on the training loop via
|
||||
[`TrainerControl`].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Available Callbacks
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the list of the available [`TrainerCallback`] in the library:
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.CometCallback
|
||||
- setup
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DefaultFlowCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PrinterCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ProgressCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] EarlyStoppingCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.TensorBoardCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.WandbCallback
|
||||
- setup
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.MLflowCallback
|
||||
- setup
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.AzureMLCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.CodeCarbonCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.NeptuneCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.ClearMLCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.DagsHubCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] integrations.FlyteCallback
|
||||
|
||||
## TrainerCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TrainerCallback
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of how to register a custom callback with the PyTorch [`Trainer`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class MyCallback(TrainerCallback):
|
||||
"A callback that prints a message at the beginning of training"
|
||||
|
||||
def on_train_begin(self, args, state, control, **kwargs):
|
||||
print("Starting training")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args,
|
||||
train_dataset=train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=eval_dataset,
|
||||
callbacks=[MyCallback], # We can either pass the callback class this way or an instance of it (MyCallback())
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to register a callback is to call `trainer.add_callback()` as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(...)
|
||||
trainer.add_callback(MyCallback)
|
||||
# Alternatively, we can pass an instance of the callback class
|
||||
trainer.add_callback(MyCallback())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TrainerState
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TrainerState
|
||||
|
||||
## TrainerControl
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TrainerControl
|
||||
32
docs/source/en/main_classes/configuration.md
Normal file
32
docs/source/en/main_classes/configuration.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
The base class [`PretrainedConfig`] implements the common methods for loading/saving a configuration
|
||||
either from a local file or directory, or from a pretrained model configuration provided by the library (downloaded
|
||||
from HuggingFace's AWS S3 repository).
|
||||
|
||||
Each derived config class implements model specific attributes. Common attributes present in all config classes are:
|
||||
`hidden_size`, `num_attention_heads`, and `num_hidden_layers`. Text models further implement:
|
||||
`vocab_size`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## PretrainedConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PretrainedConfig
|
||||
- push_to_hub
|
||||
- all
|
||||
@ -1,28 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
The base class [`PretrainedConfig`] implements the common methods for loading/saving a configuration
|
||||
either from a local file or directory, or from a pretrained model configuration provided by the library (downloaded
|
||||
from HuggingFace's AWS S3 repository).
|
||||
|
||||
Each derived config class implements model specific attributes. Common attributes present in all config classes are:
|
||||
`hidden_size`, `num_attention_heads`, and `num_hidden_layers`. Text models further implement:
|
||||
`vocab_size`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## PretrainedConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PretrainedConfig
|
||||
- push_to_hub
|
||||
- all
|
||||
68
docs/source/en/main_classes/data_collator.md
Normal file
68
docs/source/en/main_classes/data_collator.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Data Collator
|
||||
|
||||
Data collators are objects that will form a batch by using a list of dataset elements as input. These elements are of
|
||||
the same type as the elements of `train_dataset` or `eval_dataset`.
|
||||
|
||||
To be able to build batches, data collators may apply some processing (like padding). Some of them (like
|
||||
[`DataCollatorForLanguageModeling`]) also apply some random data augmentation (like random masking)
|
||||
on the formed batch.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples of use can be found in the [example scripts](../examples) or [example notebooks](../notebooks).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Default data collator
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.default_data_collator
|
||||
|
||||
## DefaultDataCollator
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.DefaultDataCollator
|
||||
|
||||
## DataCollatorWithPadding
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.DataCollatorWithPadding
|
||||
|
||||
## DataCollatorForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.DataCollatorForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
## DataCollatorForSeq2Seq
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.DataCollatorForSeq2Seq
|
||||
|
||||
## DataCollatorForLanguageModeling
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.DataCollatorForLanguageModeling
|
||||
- numpy_mask_tokens
|
||||
- tf_mask_tokens
|
||||
- torch_mask_tokens
|
||||
|
||||
## DataCollatorForWholeWordMask
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.DataCollatorForWholeWordMask
|
||||
- numpy_mask_tokens
|
||||
- tf_mask_tokens
|
||||
- torch_mask_tokens
|
||||
|
||||
## DataCollatorForPermutationLanguageModeling
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.DataCollatorForPermutationLanguageModeling
|
||||
- numpy_mask_tokens
|
||||
- tf_mask_tokens
|
||||
- torch_mask_tokens
|
||||
@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Data Collator
|
||||
|
||||
Data collators are objects that will form a batch by using a list of dataset elements as input. These elements are of
|
||||
the same type as the elements of `train_dataset` or `eval_dataset`.
|
||||
|
||||
To be able to build batches, data collators may apply some processing (like padding). Some of them (like
|
||||
[`DataCollatorForLanguageModeling`]) also apply some random data augmentation (like random masking)
|
||||
on the formed batch.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples of use can be found in the [example scripts](../examples) or [example notebooks](../notebooks).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Default data collator
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.default_data_collator
|
||||
|
||||
## DefaultDataCollator
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.DefaultDataCollator
|
||||
|
||||
## DataCollatorWithPadding
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.DataCollatorWithPadding
|
||||
|
||||
## DataCollatorForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.DataCollatorForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
## DataCollatorForSeq2Seq
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.DataCollatorForSeq2Seq
|
||||
|
||||
## DataCollatorForLanguageModeling
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.DataCollatorForLanguageModeling
|
||||
- numpy_mask_tokens
|
||||
- tf_mask_tokens
|
||||
- torch_mask_tokens
|
||||
|
||||
## DataCollatorForWholeWordMask
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.DataCollatorForWholeWordMask
|
||||
- numpy_mask_tokens
|
||||
- tf_mask_tokens
|
||||
- torch_mask_tokens
|
||||
|
||||
## DataCollatorForPermutationLanguageModeling
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] data.data_collator.DataCollatorForPermutationLanguageModeling
|
||||
- numpy_mask_tokens
|
||||
- tf_mask_tokens
|
||||
- torch_mask_tokens
|
||||
2316
docs/source/en/main_classes/deepspeed.md
Normal file
2316
docs/source/en/main_classes/deepspeed.md
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
42
docs/source/en/main_classes/feature_extractor.md
Normal file
42
docs/source/en/main_classes/feature_extractor.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Feature Extractor
|
||||
|
||||
A feature extractor is in charge of preparing input features for audio or vision models. This includes feature extraction
|
||||
from sequences, *e.g.*, pre-processing audio files to Log-Mel Spectrogram features, feature extraction from images
|
||||
*e.g.* cropping image image files, but also padding, normalization, and conversion to Numpy, PyTorch, and TensorFlow
|
||||
tensors.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## FeatureExtractionMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] feature_extraction_utils.FeatureExtractionMixin
|
||||
- from_pretrained
|
||||
- save_pretrained
|
||||
|
||||
## SequenceFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] SequenceFeatureExtractor
|
||||
- pad
|
||||
|
||||
## BatchFeature
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BatchFeature
|
||||
|
||||
## ImageFeatureExtractionMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_utils.ImageFeatureExtractionMixin
|
||||
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Feature Extractor
|
||||
|
||||
A feature extractor is in charge of preparing input features for audio or vision models. This includes feature extraction
|
||||
from sequences, *e.g.*, pre-processing audio files to Log-Mel Spectrogram features, feature extraction from images
|
||||
*e.g.* cropping image image files, but also padding, normalization, and conversion to Numpy, PyTorch, and TensorFlow
|
||||
tensors.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## FeatureExtractionMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] feature_extraction_utils.FeatureExtractionMixin
|
||||
- from_pretrained
|
||||
- save_pretrained
|
||||
|
||||
## SequenceFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] SequenceFeatureExtractor
|
||||
- pad
|
||||
|
||||
## BatchFeature
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BatchFeature
|
||||
|
||||
## ImageFeatureExtractionMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_utils.ImageFeatureExtractionMixin
|
||||
34
docs/source/en/main_classes/image_processor.md
Normal file
34
docs/source/en/main_classes/image_processor.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Image Processor
|
||||
|
||||
An image processor is in charge of preparing input features for vision models and post processing their outputs. This includes transformations such as resizing, normalization, and conversion to PyTorch, TensorFlow, Flax and Numpy tensors. It may also include model specific post-processing such as converting logits to segmentation masks.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## ImageProcessingMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_processing_utils.ImageProcessingMixin
|
||||
- from_pretrained
|
||||
- save_pretrained
|
||||
|
||||
## BatchFeature
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BatchFeature
|
||||
|
||||
## BaseImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_processing_utils.BaseImageProcessor
|
||||
@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Image Processor
|
||||
|
||||
An image processor is in charge of preparing input features for vision models and post processing their outputs. This includes transformations such as resizing, normalization, and conversion to PyTorch, TensorFlow, Flax and Numpy tensors. It may also include model specific post-processing such as converting logits to segmentation masks.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## ImageProcessingMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_processing_utils.ImageProcessingMixin
|
||||
- from_pretrained
|
||||
- save_pretrained
|
||||
|
||||
## BatchFeature
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BatchFeature
|
||||
|
||||
## BaseImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_processing_utils.BaseImageProcessor
|
||||
28
docs/source/en/main_classes/keras_callbacks.md
Normal file
28
docs/source/en/main_classes/keras_callbacks.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Keras callbacks
|
||||
|
||||
When training a Transformers model with Keras, there are some library-specific callbacks available to automate common
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
|
||||
## KerasMetricCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KerasMetricCallback
|
||||
|
||||
## PushToHubCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PushToHubCallback
|
||||
@ -1,24 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Keras callbacks
|
||||
|
||||
When training a Transformers model with Keras, there are some library-specific callbacks available to automate common
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
|
||||
## KerasMetricCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] KerasMetricCallback
|
||||
|
||||
## PushToHubCallback
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PushToHubCallback
|
||||
102
docs/source/en/main_classes/logging.md
Normal file
102
docs/source/en/main_classes/logging.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Logging
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers has a centralized logging system, so that you can setup the verbosity of the library easily.
|
||||
|
||||
Currently the default verbosity of the library is `WARNING`.
|
||||
|
||||
To change the level of verbosity, just use one of the direct setters. For instance, here is how to change the verbosity
|
||||
to the INFO level.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import transformers
|
||||
|
||||
transformers.logging.set_verbosity_info()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use the environment variable `TRANSFORMERS_VERBOSITY` to override the default verbosity. You can set it
|
||||
to one of the following: `debug`, `info`, `warning`, `error`, `critical`. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_VERBOSITY=error ./myprogram.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, some `warnings` can be disabled by setting the environment variable
|
||||
`TRANSFORMERS_NO_ADVISORY_WARNINGS` to a true value, like *1*. This will disable any warning that is logged using
|
||||
[`logger.warning_advice`]. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_NO_ADVISORY_WARNINGS=1 ./myprogram.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of how to use the same logger as the library in your own module or script:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers.utils import logging
|
||||
|
||||
logging.set_verbosity_info()
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger("transformers")
|
||||
logger.info("INFO")
|
||||
logger.warning("WARN")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
All the methods of this logging module are documented below, the main ones are
|
||||
[`logging.get_verbosity`] to get the current level of verbosity in the logger and
|
||||
[`logging.set_verbosity`] to set the verbosity to the level of your choice. In order (from the least
|
||||
verbose to the most verbose), those levels (with their corresponding int values in parenthesis) are:
|
||||
|
||||
- `transformers.logging.CRITICAL` or `transformers.logging.FATAL` (int value, 50): only report the most
|
||||
critical errors.
|
||||
- `transformers.logging.ERROR` (int value, 40): only report errors.
|
||||
- `transformers.logging.WARNING` or `transformers.logging.WARN` (int value, 30): only reports error and
|
||||
warnings. This the default level used by the library.
|
||||
- `transformers.logging.INFO` (int value, 20): reports error, warnings and basic information.
|
||||
- `transformers.logging.DEBUG` (int value, 10): report all information.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, `tqdm` progress bars will be displayed during model download. [`logging.disable_progress_bar`] and [`logging.enable_progress_bar`] can be used to suppress or unsuppress this behavior.
|
||||
|
||||
## Base setters
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.set_verbosity_error
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.set_verbosity_warning
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.set_verbosity_info
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.set_verbosity_debug
|
||||
|
||||
## Other functions
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.get_verbosity
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.set_verbosity
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.get_logger
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.enable_default_handler
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.disable_default_handler
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.enable_explicit_format
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.reset_format
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.enable_progress_bar
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.disable_progress_bar
|
||||
@ -1,98 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Logging
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers has a centralized logging system, so that you can setup the verbosity of the library easily.
|
||||
|
||||
Currently the default verbosity of the library is `WARNING`.
|
||||
|
||||
To change the level of verbosity, just use one of the direct setters. For instance, here is how to change the verbosity
|
||||
to the INFO level.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import transformers
|
||||
|
||||
transformers.logging.set_verbosity_info()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use the environment variable `TRANSFORMERS_VERBOSITY` to override the default verbosity. You can set it
|
||||
to one of the following: `debug`, `info`, `warning`, `error`, `critical`. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_VERBOSITY=error ./myprogram.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, some `warnings` can be disabled by setting the environment variable
|
||||
`TRANSFORMERS_NO_ADVISORY_WARNINGS` to a true value, like *1*. This will disable any warning that is logged using
|
||||
[`logger.warning_advice`]. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_NO_ADVISORY_WARNINGS=1 ./myprogram.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of how to use the same logger as the library in your own module or script:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers.utils import logging
|
||||
|
||||
logging.set_verbosity_info()
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger("transformers")
|
||||
logger.info("INFO")
|
||||
logger.warning("WARN")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
All the methods of this logging module are documented below, the main ones are
|
||||
[`logging.get_verbosity`] to get the current level of verbosity in the logger and
|
||||
[`logging.set_verbosity`] to set the verbosity to the level of your choice. In order (from the least
|
||||
verbose to the most verbose), those levels (with their corresponding int values in parenthesis) are:
|
||||
|
||||
- `transformers.logging.CRITICAL` or `transformers.logging.FATAL` (int value, 50): only report the most
|
||||
critical errors.
|
||||
- `transformers.logging.ERROR` (int value, 40): only report errors.
|
||||
- `transformers.logging.WARNING` or `transformers.logging.WARN` (int value, 30): only reports error and
|
||||
warnings. This the default level used by the library.
|
||||
- `transformers.logging.INFO` (int value, 20): reports error, warnings and basic information.
|
||||
- `transformers.logging.DEBUG` (int value, 10): report all information.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, `tqdm` progress bars will be displayed during model download. [`logging.disable_progress_bar`] and [`logging.enable_progress_bar`] can be used to suppress or unsuppress this behavior.
|
||||
|
||||
## Base setters
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.set_verbosity_error
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.set_verbosity_warning
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.set_verbosity_info
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.set_verbosity_debug
|
||||
|
||||
## Other functions
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.get_verbosity
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.set_verbosity
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.get_logger
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.enable_default_handler
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.disable_default_handler
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.enable_explicit_format
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.reset_format
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.enable_progress_bar
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.disable_progress_bar
|
||||
167
docs/source/en/main_classes/model.md
Normal file
167
docs/source/en/main_classes/model.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Models
|
||||
|
||||
The base classes [`PreTrainedModel`], [`TFPreTrainedModel`], and
|
||||
[`FlaxPreTrainedModel`] implement the common methods for loading/saving a model either from a local
|
||||
file or directory, or from a pretrained model configuration provided by the library (downloaded from HuggingFace's AWS
|
||||
S3 repository).
|
||||
|
||||
[`PreTrainedModel`] and [`TFPreTrainedModel`] also implement a few methods which
|
||||
are common among all the models to:
|
||||
|
||||
- resize the input token embeddings when new tokens are added to the vocabulary
|
||||
- prune the attention heads of the model.
|
||||
|
||||
The other methods that are common to each model are defined in [`~modeling_utils.ModuleUtilsMixin`]
|
||||
(for the PyTorch models) and [`~modeling_tf_utils.TFModuleUtilsMixin`] (for the TensorFlow models) or
|
||||
for text generation, [`~generation.GenerationMixin`] (for the PyTorch models),
|
||||
[`~generation.TFGenerationMixin`] (for the TensorFlow models) and
|
||||
[`~generation.FlaxGenerationMixin`] (for the Flax/JAX models).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## PreTrainedModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PreTrainedModel
|
||||
- push_to_hub
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
<a id='from_pretrained-torch-dtype'></a>
|
||||
|
||||
### Large model loading
|
||||
|
||||
In Transformers 4.20.0, the [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] method has been reworked to accommodate large models using [Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/big_modeling). This requires Accelerate >= 0.9.0 and PyTorch >= 1.9.0. Instead of creating the full model, then loading the pretrained weights inside it (which takes twice the size of the model in RAM, one for the randomly initialized model, one for the weights), there is an option to create the model as an empty shell, then only materialize its parameters when the pretrained weights are loaded.
|
||||
|
||||
This option can be activated with `low_cpu_mem_usage=True`. The model is first created on the Meta device (with empty weights) and the state dict is then loaded inside it (shard by shard in the case of a sharded checkpoint). This way the maximum RAM used is the full size of the model only.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
t0pp = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0pp", low_cpu_mem_usage=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Moreover, you can directly place the model on different devices if it doesn't fully fit in RAM (only works for inference for now). With `device_map="auto"`, Accelerate will determine where to put each layer to maximize the use of your fastest devices (GPUs) and offload the rest on the CPU, or even the hard drive if you don't have enough GPU RAM (or CPU RAM). Even if the model is split across several devices, it will run as you would normally expect.
|
||||
|
||||
When passing a `device_map`, `low_cpu_mem_usage` is automatically set to `True`, so you don't need to specify it:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
t0pp = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0pp", device_map="auto")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can inspect how the model was split across devices by looking at its `hf_device_map` attribute:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
t0pp.hf_device_map
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python out
|
||||
{'shared': 0,
|
||||
'decoder.embed_tokens': 0,
|
||||
'encoder': 0,
|
||||
'decoder.block.0': 0,
|
||||
'decoder.block.1': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.2': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.3': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.4': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.5': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.6': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.7': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.8': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.9': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.10': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.11': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.12': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.13': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.14': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.15': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.16': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.17': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.18': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.19': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.20': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.21': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.22': 'cpu',
|
||||
'decoder.block.23': 'cpu',
|
||||
'decoder.final_layer_norm': 'cpu',
|
||||
'decoder.dropout': 'cpu',
|
||||
'lm_head': 'cpu'}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also write your own device map following the same format (a dictionary layer name to device). It should map all parameters of the model to a given device, but you don't have to detail where all the submosules of one layer go if that layer is entirely on the same device. For instance, the following device map would work properly for T0pp (as long as you have the GPU memory):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
device_map = {"shared": 0, "encoder": 0, "decoder": 1, "lm_head": 1}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to minimize the memory impact of your model is to instantiate it at a lower precision dtype (like `torch.float16`) or use direct quantization techniques as described below.
|
||||
|
||||
### Model Instantiation dtype
|
||||
|
||||
Under Pytorch a model normally gets instantiated with `torch.float32` format. This can be an issue if one tries to
|
||||
load a model whose weights are in fp16, since it'd require twice as much memory. To overcome this limitation, you can
|
||||
either explicitly pass the desired `dtype` using `torch_dtype` argument:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("t5", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or, if you want the model to always load in the most optimal memory pattern, you can use the special value `"auto"`,
|
||||
and then `dtype` will be automatically derived from the model's weights:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("t5", torch_dtype="auto")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Models instantiated from scratch can also be told which `dtype` to use with:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
config = T5Config.from_pretrained("t5")
|
||||
model = AutoModel.from_config(config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Due to Pytorch design, this functionality is only available for floating dtypes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## ModuleUtilsMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.ModuleUtilsMixin
|
||||
|
||||
## TFPreTrainedModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFPreTrainedModel
|
||||
- push_to_hub
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## TFModelUtilsMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFModelUtilsMixin
|
||||
|
||||
## FlaxPreTrainedModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxPreTrainedModel
|
||||
- push_to_hub
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## Pushing to the Hub
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.PushToHubMixin
|
||||
|
||||
## Sharded checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.load_sharded_checkpoint
|
||||
@ -1,163 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Models
|
||||
|
||||
The base classes [`PreTrainedModel`], [`TFPreTrainedModel`], and
|
||||
[`FlaxPreTrainedModel`] implement the common methods for loading/saving a model either from a local
|
||||
file or directory, or from a pretrained model configuration provided by the library (downloaded from HuggingFace's AWS
|
||||
S3 repository).
|
||||
|
||||
[`PreTrainedModel`] and [`TFPreTrainedModel`] also implement a few methods which
|
||||
are common among all the models to:
|
||||
|
||||
- resize the input token embeddings when new tokens are added to the vocabulary
|
||||
- prune the attention heads of the model.
|
||||
|
||||
The other methods that are common to each model are defined in [`~modeling_utils.ModuleUtilsMixin`]
|
||||
(for the PyTorch models) and [`~modeling_tf_utils.TFModuleUtilsMixin`] (for the TensorFlow models) or
|
||||
for text generation, [`~generation.GenerationMixin`] (for the PyTorch models),
|
||||
[`~generation.TFGenerationMixin`] (for the TensorFlow models) and
|
||||
[`~generation.FlaxGenerationMixin`] (for the Flax/JAX models).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## PreTrainedModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PreTrainedModel
|
||||
- push_to_hub
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
<a id='from_pretrained-torch-dtype'></a>
|
||||
|
||||
### Large model loading
|
||||
|
||||
In Transformers 4.20.0, the [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] method has been reworked to accommodate large models using [Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/big_modeling). This requires Accelerate >= 0.9.0 and PyTorch >= 1.9.0. Instead of creating the full model, then loading the pretrained weights inside it (which takes twice the size of the model in RAM, one for the randomly initialized model, one for the weights), there is an option to create the model as an empty shell, then only materialize its parameters when the pretrained weights are loaded.
|
||||
|
||||
This option can be activated with `low_cpu_mem_usage=True`. The model is first created on the Meta device (with empty weights) and the state dict is then loaded inside it (shard by shard in the case of a sharded checkpoint). This way the maximum RAM used is the full size of the model only.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
t0pp = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0pp", low_cpu_mem_usage=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Moreover, you can directly place the model on different devices if it doesn't fully fit in RAM (only works for inference for now). With `device_map="auto"`, Accelerate will determine where to put each layer to maximize the use of your fastest devices (GPUs) and offload the rest on the CPU, or even the hard drive if you don't have enough GPU RAM (or CPU RAM). Even if the model is split across several devices, it will run as you would normally expect.
|
||||
|
||||
When passing a `device_map`, `low_cpu_mem_usage` is automatically set to `True`, so you don't need to specify it:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
t0pp = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0pp", device_map="auto")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can inspect how the model was split across devices by looking at its `hf_device_map` attribute:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
t0pp.hf_device_map
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python out
|
||||
{'shared': 0,
|
||||
'decoder.embed_tokens': 0,
|
||||
'encoder': 0,
|
||||
'decoder.block.0': 0,
|
||||
'decoder.block.1': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.2': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.3': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.4': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.5': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.6': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.7': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.8': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.9': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.10': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.11': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.12': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.13': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.14': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.15': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.16': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.17': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.18': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.19': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.20': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.21': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.22': 'cpu',
|
||||
'decoder.block.23': 'cpu',
|
||||
'decoder.final_layer_norm': 'cpu',
|
||||
'decoder.dropout': 'cpu',
|
||||
'lm_head': 'cpu'}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also write your own device map following the same format (a dictionary layer name to device). It should map all parameters of the model to a given device, but you don't have to detail where all the submosules of one layer go if that layer is entirely on the same device. For instance, the following device map would work properly for T0pp (as long as you have the GPU memory):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
device_map = {"shared": 0, "encoder": 0, "decoder": 1, "lm_head": 1}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to minimize the memory impact of your model is to instantiate it at a lower precision dtype (like `torch.float16`) or use direct quantization techniques as described below.
|
||||
|
||||
### Model Instantiation dtype
|
||||
|
||||
Under Pytorch a model normally gets instantiated with `torch.float32` format. This can be an issue if one tries to
|
||||
load a model whose weights are in fp16, since it'd require twice as much memory. To overcome this limitation, you can
|
||||
either explicitly pass the desired `dtype` using `torch_dtype` argument:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("t5", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
or, if you want the model to always load in the most optimal memory pattern, you can use the special value `"auto"`,
|
||||
and then `dtype` will be automatically derived from the model's weights:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("t5", torch_dtype="auto")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Models instantiated from scratch can also be told which `dtype` to use with:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
config = T5Config.from_pretrained("t5")
|
||||
model = AutoModel.from_config(config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Due to Pytorch design, this functionality is only available for floating dtypes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## ModuleUtilsMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.ModuleUtilsMixin
|
||||
|
||||
## TFPreTrainedModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFPreTrainedModel
|
||||
- push_to_hub
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## TFModelUtilsMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_utils.TFModelUtilsMixin
|
||||
|
||||
## FlaxPreTrainedModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxPreTrainedModel
|
||||
- push_to_hub
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## Pushing to the Hub
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.PushToHubMixin
|
||||
|
||||
## Sharded checkpoints
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_utils.load_sharded_checkpoint
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user