mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
synced 2025-07-03 21:00:08 +06:00
Add TAPEX (#16473)
* Add TapexTokenizer * Improve docstrings and provide option to provide answer * Remove option for pretokenized inputs * Add TAPEX to README * Fix copies * Remove option for pretokenized inputs * Initial commit: add tapex fine-tuning examples on both table-based question answering and table-based fact verification. * - Draft a README file for running the script and introducing some background. - Remove unused code lines in tabfact script. - Disable the deafult `pad_to_max_length` option which is memory-consuming. * * Support `as_target_tokenizer` function for TapexTokenizer. * Fix the do_lower_case behaviour of TapexTokenizer. * Add unit tests for target scenarios and cased/uncased scenarios for both source and target. * * Replace the label BartTokenizer with TapexTokenizer's as_target_tokenizer function. * Fix typos in tapex example README. * * fix the evaluation script - remove the property `task_name` * * Make the label space more clear for tabfact tasks * * Using a new fine-tuning script for tapex-base on tabfact. * * Remove the lowercase code outside the tokenizer - we use the tokenizer to control whether do_lower_case * Guarantee the hyper-parameter can be run without out-of-memory on 16GB card and report the new reproduced number on wikisql * * Remove the default tokenizer_name option. * Provide evaluation command. * * Support for WikiTableQuestion dataset. * Fix a typo in README. * * Fix the datasets's key name in WikiTableQuestions * Run make fixup and move test to folder * Fix quality * Apply suggestions from code review * Apply suggestions from code review Co-authored-by: Suraj Patil <surajp815@gmail.com> * Apply suggestions from code review * Apply suggestions from code review Co-authored-by: Sylvain Gugger <35901082+sgugger@users.noreply.github.com> * Apply some more suggestions from code review * Improve docstrings * Overwrite failing test * Improve comment in example scripts * Fix rebase * Add TAPEX to Auto mapping * Add TAPEX to auto config mappings * Put TAPEX higher than BART in auto mapping * Add TAPEX to doc tests Co-authored-by: Niels Rogge <nielsrogge@Nielss-MBP.localdomain> Co-authored-by: SivilTaram <qianlxc@outlook.com> Co-authored-by: Niels Rogge <nielsrogge@nielss-mbp.home> Co-authored-by: Suraj Patil <surajp815@gmail.com> Co-authored-by: Sylvain Gugger <35901082+sgugger@users.noreply.github.com> Co-authored-by: Niels Rogge <nielsrogge@Nielss-MacBook-Pro.local>
This commit is contained in:
parent
33cb21150c
commit
4ef0abb738
@ -318,6 +318,7 @@ Min, Patrick Lewis, Ledell Wu, Sergey Edunov, Danqi Chen, and Wen-tau Yih.
|
||||
1. **[T5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10683) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[T5v1.1](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5v1.1)** (from Google AI) released in the repository [google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer](https://github.com/google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer/blob/main/released_checkpoints.md#t511) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[TAPAS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/tapas)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [TAPAS: Weakly Supervised Table Parsing via Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02349) by Jonathan Herzig, Paweł Krzysztof Nowak, Thomas Müller, Francesco Piccinno and Julian Martin Eisenschlos.
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/tapex)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou.
|
||||
1. **[Transformer-XL](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/transfo-xl)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860) by Zihang Dai*, Zhilin Yang*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Quoc V. Le, Ruslan Salakhutdinov.
|
||||
1. **[TrOCR](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/trocr)** (from Microsoft), released together with the paper [TrOCR: Transformer-based Optical Character Recognition with Pre-trained Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.10282) by Minghao Li, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Zhoujun Li, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeech](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/unispeech)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.07597) by Chengyi Wang, Yu Wu, Yao Qian, Kenichi Kumatani, Shujie Liu, Furu Wei, Michael Zeng, Xuedong Huang.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -297,6 +297,7 @@ Flax, PyTorch, TensorFlow 설치 페이지에서 이들을 conda로 설치하는
|
||||
1. **[T5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10683) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[T5v1.1](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5v1.1)** (from Google AI) released in the repository [google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer](https://github.com/google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer/blob/main/released_checkpoints.md#t511) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[TAPAS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/tapas)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [TAPAS: Weakly Supervised Table Parsing via Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02349) by Jonathan Herzig, Paweł Krzysztof Nowak, Thomas Müller, Francesco Piccinno and Julian Martin Eisenschlos.
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/tapex)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou.
|
||||
1. **[Transformer-XL](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/transfo-xl)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860) by Zihang Dai*, Zhilin Yang*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Quoc V. Le, Ruslan Salakhutdinov.
|
||||
1. **[TrOCR](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/trocr)** (from Microsoft), released together with the paper [TrOCR: Transformer-based Optical Character Recognition with Pre-trained Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.10282) by Minghao Li, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Zhoujun Li, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeech](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/unispeech)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.07597) by Chengyi Wang, Yu Wu, Yao Qian, Kenichi Kumatani, Shujie Liu, Furu Wei, Michael Zeng, Xuedong Huang.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -321,6 +321,7 @@ conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
1. **[T5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5)** (来自 Google AI) 伴随论文 [Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10683) 由 Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu 发布。
|
||||
1. **[T5v1.1](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5v1.1)** (来自 Google AI) 伴随论文 [google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer](https://github.com/google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer/blob/main/released_checkpoints.md#t511) 由 Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu 发布。
|
||||
1. **[TAPAS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/tapas)** (来自 Google AI) 伴随论文 [TAPAS: Weakly Supervised Table Parsing via Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02349) 由 Jonathan Herzig, Paweł Krzysztof Nowak, Thomas Müller, Francesco Piccinno and Julian Martin Eisenschlos 发布。
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/tapex)** (来自 Microsoft Research) 伴随论文 [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) 由 Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Transformer-XL](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/transfo-xl)** (来自 Google/CMU) 伴随论文 [Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860) 由 Zihang Dai*, Zhilin Yang*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Quoc V. Le, Ruslan Salakhutdinov 发布。
|
||||
1. **[TrOCR](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/trocr)** (来自 Microsoft) 伴随论文 [TrOCR: Transformer-based Optical Character Recognition with Pre-trained Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.10282) 由 Minghao Li, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Zhoujun Li, Furu Wei 发布。
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeech](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/unispeech)** (来自 Microsoft Research) 伴随论文 [UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.07597) 由 Chengyi Wang, Yu Wu, Yao Qian, Kenichi Kumatani, Shujie Liu, Furu Wei, Michael Zeng, Xuedong Huang 发布。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -333,6 +333,7 @@ conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
1. **[T5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10683) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[T5v1.1](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5v1.1)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer](https://github.com/google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer/blob/main/released_checkpoints.md#t511) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[TAPAS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/tapas)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [TAPAS: Weakly Supervised Table Parsing via Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02349) by Jonathan Herzig, Paweł Krzysztof Nowak, Thomas Müller, Francesco Piccinno and Julian Martin Eisenschlos.
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/tapex)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou.
|
||||
1. **[Transformer-XL](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/transfo-xl)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860) by Zihang Dai*, Zhilin Yang*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Quoc V. Le, Ruslan Salakhutdinov.
|
||||
1. **[TrOCR](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/trocr)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [TrOCR: Transformer-based Optical Character Recognition with Pre-trained Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.10282) by Minghao Li, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Zhoujun Li, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeech](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/unispeech)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.07597) by Chengyi Wang, Yu Wu, Yao Qian, Kenichi Kumatani, Shujie Liu, Furu Wei, Michael Zeng, Xuedong Huang.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -330,6 +330,8 @@
|
||||
title: T5v1.1
|
||||
- local: model_doc/tapas
|
||||
title: TAPAS
|
||||
- local: model_doc/tapex
|
||||
title: TAPEX
|
||||
- local: model_doc/transfo-xl
|
||||
title: Transformer XL
|
||||
- local: model_doc/trocr
|
||||
|
||||
@ -139,6 +139,7 @@ The library currently contains JAX, PyTorch and TensorFlow implementations, pret
|
||||
1. **[T5](model_doc/t5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10683) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[T5v1.1](model_doc/t5v1.1)** (from Google AI) released in the repository [google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer](https://github.com/google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer/blob/main/released_checkpoints.md#t511) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[TAPAS](model_doc/tapas)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [TAPAS: Weakly Supervised Table Parsing via Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02349) by Jonathan Herzig, Paweł Krzysztof Nowak, Thomas Müller, Francesco Piccinno and Julian Martin Eisenschlos.
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](model_doc/tapex)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou.
|
||||
1. **[Transformer-XL](model_doc/transfo-xl)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860) by Zihang Dai*, Zhilin Yang*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Quoc V. Le, Ruslan Salakhutdinov.
|
||||
1. **[TrOCR](model_doc/trocr)** (from Microsoft), released together with the paper [TrOCR: Transformer-based Optical Character Recognition with Pre-trained Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.10282) by Minghao Li, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Zhoujun Li, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeech](model_doc/unispeech)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.07597) by Chengyi Wang, Yu Wu, Yao Qian, Kenichi Kumatani, Shujie Liu, Furu Wei, Michael Zeng, Xuedong Huang.
|
||||
@ -252,6 +253,7 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| Swin | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| T5 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| TAPAS | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TAPEX | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Transformer-XL | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TrOCR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| UniSpeech | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
|
||||
130
docs/source/en/model_doc/tapex.mdx
Normal file
130
docs/source/en/model_doc/tapex.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# TAPEX
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The TAPEX model was proposed in [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu,
|
||||
Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou. TAPEX pre-trains a BART model to solve synthetic SQL queries, after
|
||||
which it can be fine-tuned to answer natural language questions related to tabular data, as well as performing table fact checking.
|
||||
|
||||
TAPEX has been fine-tuned on several datasets:
|
||||
- [SQA](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=54253) (Sequential Question Answering by Microsoft)
|
||||
- [WTQ](https://github.com/ppasupat/WikiTableQuestions) (Wiki Table Questions by Stanford University)
|
||||
- [WikiSQL](https://github.com/salesforce/WikiSQL) (by Salesforce)
|
||||
- [TabFact](https://tabfact.github.io/) (by USCB NLP Lab).
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Recent progress in language model pre-training has achieved a great success via leveraging large-scale unstructured textual data. However, it is
|
||||
still a challenge to apply pre-training on structured tabular data due to the absence of large-scale high-quality tabular data. In this paper, we
|
||||
propose TAPEX to show that table pre-training can be achieved by learning a neural SQL executor over a synthetic corpus, which is obtained by automatically
|
||||
synthesizing executable SQL queries and their execution outputs. TAPEX addresses the data scarcity challenge via guiding the language model to mimic a SQL
|
||||
executor on the diverse, large-scale and high-quality synthetic corpus. We evaluate TAPEX on four benchmark datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that
|
||||
TAPEX outperforms previous table pre-training approaches by a large margin and achieves new state-of-the-art results on all of them. This includes improvements
|
||||
on the weakly-supervised WikiSQL denotation accuracy to 89.5% (+2.3%), the WikiTableQuestions denotation accuracy to 57.5% (+4.8%), the SQA denotation accuracy
|
||||
to 74.5% (+3.5%), and the TabFact accuracy to 84.2% (+3.2%). To our knowledge, this is the first work to exploit table pre-training via synthetic executable programs
|
||||
and to achieve new state-of-the-art results on various downstream tasks.*
|
||||
|
||||
Tips:
|
||||
|
||||
- TAPEX is a generative (seq2seq) model. One can directly plug in the weights of TAPEX into a BART model.
|
||||
- TAPEX has checkpoints on the hub that are either pre-trained only, or fine-tuned on WTQ, SQA, WikiSQL and TabFact.
|
||||
- Sentences + tables are presented to the model as `sentence + " " + linearized table`. The linearized table has the following format:
|
||||
`col: col1 | col2 | col 3 row 1 : val1 | val2 | val3 row 2 : ...`.
|
||||
- TAPEX has its own tokenizer, that allows to prepare all data for the model easily. One can pass Pandas DataFrames and strings to the tokenizer,
|
||||
and it will automatically create the `input_ids` and `attention_mask` (as shown in the usage examples below).
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage: inference
|
||||
|
||||
Below, we illustrate how to use TAPEX for table question answering. As one can see, one can directly plug in the weights of TAPEX into a BART model.
|
||||
We use the [Auto API](auto), which will automatically instantiate the appropriate tokenizer ([`TapexTokenizer`]) and model ([`BartForConditionalGeneration`]) for us,
|
||||
based on the configuration file of the checkpoint on the hub.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
>>> import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("microsoft/tapex-large-finetuned-wtq")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("microsoft/tapex-large-finetuned-wtq")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # prepare table + question
|
||||
>>> data = {"Actors": ["Brad Pitt", "Leonardo Di Caprio", "George Clooney"], "Number of movies": ["87", "53", "69"]}
|
||||
>>> table = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(data)
|
||||
>>> question = "how many movies does Leonardo Di Caprio have?"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> encoding = tokenizer(table, question, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # let the model generate an answer autoregressively
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**encoding)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # decode back to text
|
||||
>>> predicted_answer = tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
|
||||
>>> print(predicted_answer)
|
||||
53
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that [`TapexTokenizer`] also supports batched inference. Hence, one can provide a batch of different tables/questions, or a batch of a single table
|
||||
and multiple questions, or a batch of a single query and multiple tables. Let's illustrate this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> # prepare table + question
|
||||
>>> data = {"Actors": ["Brad Pitt", "Leonardo Di Caprio", "George Clooney"], "Number of movies": ["87", "53", "69"]}
|
||||
>>> table = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(data)
|
||||
>>> questions = [
|
||||
... "how many movies does Leonardo Di Caprio have?",
|
||||
... "which actor has 69 movies?",
|
||||
... "what's the first name of the actor who has 87 movies?",
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
>>> encoding = tokenizer(table, questions, padding=True, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # let the model generate an answer autoregressively
|
||||
>>> outputs = model.generate(**encoding)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # decode back to text
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
[' 53', ' george clooney', ' brad pitt']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In case one wants to do table verification (i.e. the task of determining whether a given sentence is supported or refuted by the contents
|
||||
of a table), one can instantiate a [`BartForSequenceClassification`] model. TAPEX has checkpoints on the hub fine-tuned on TabFact, an important
|
||||
benchmark for table fact checking (it achieves 84% accuracy). The code example below again leverages the [Auto API](auto).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("microsoft/tapex-large-finetuned-tabfact")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("microsoft/tapex-large-finetuned-tabfact")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # prepare table + sentence
|
||||
>>> data = {"Actors": ["Brad Pitt", "Leonardo Di Caprio", "George Clooney"], "Number of movies": ["87", "53", "69"]}
|
||||
>>> table = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(data)
|
||||
>>> sentence = "George Clooney has 30 movies"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> encoding = tokenizer(table, sentence, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # forward pass
|
||||
>>> outputs = model(**encoding)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # print prediction
|
||||
>>> predicted_class_idx = outputs.logits[0].argmax(dim=0).item()
|
||||
>>> print(model.config.id2label[predicted_class_idx])
|
||||
Refused
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## TapexTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TapexTokenizer
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- save_vocabulary
|
||||
@ -67,6 +67,7 @@ Ready-made configurations include the following architectures:
|
||||
- PLBart
|
||||
- RoBERTa
|
||||
- T5
|
||||
- TAPEX
|
||||
- ViT
|
||||
- XLM-RoBERTa
|
||||
- XLM-RoBERTa-XL
|
||||
|
||||
288
examples/research_projects/tapex/README.md
Normal file
288
examples/research_projects/tapex/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,288 @@
|
||||
<!---
|
||||
Copyright 2022 The Microsoft Inc. and The HuggingFace Inc. Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Run Table Tasks with TAPEX
|
||||
|
||||
TAPEX is a table pre-training approach for table-related tasks. By learning a neural SQL executor over a synthetic corpus based on generative language models (e.g., BART), it achieves state-of-the-art performance on several table-based question answering benchmarks and table-based fact verification benchmark. More details can be found in the original paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2107.07653.pdf).
|
||||
|
||||
> If you are also familiar with [fairseq](https://github.com/pytorch/fairseq), you may also find [the official implementation](https://github.com/microsoft/Table-Pretraining) useful, which leverages the framework.
|
||||
|
||||
## Table Question Answering Tasks
|
||||
|
||||
### What is Table Question Answering
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The task of Table Question Answering (TableQA) is to empower machines to answer users' questions over a given table. The resulting answer(s) can be a region in the table, or a number calculated by applying aggregation operators to a specific region.
|
||||
|
||||
### What Questions Can be Answered
|
||||
|
||||
Benefiting from the powerfulness of generative models, TAPEX can deal with almost all kinds of questions over tables (if there is training data). Below are some typical question and their answers taken from [WikiTableQuestion](https://nlp.stanford.edu/blog/wikitablequestions-a-complex-real-world-question-understanding-dataset).
|
||||
|
||||
| Question | Answer |
|
||||
| :---: | :---: |
|
||||
| What is the years won for each team? | 2004, 2008, 2012 |
|
||||
| How long did Taiki Tsuchiya last? | 4:27 |
|
||||
| What is the total amount of matches drawn? | 1 |
|
||||
| Besides Tiger Woods, what other player won between 2007 and 2009? | Camilo Villegas |
|
||||
| What was the last Baekje Temple? | Uija |
|
||||
| What is the difference between White voters and Black voters in 1948? | 0 |
|
||||
| What is the average number of sailors for each country during the worlds qualification tournament? | 2 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Fine-tune TAPEX on TableQA
|
||||
|
||||
We provide a fine-tuning script of tapex for TableQA on the WikiSQL benchmark: [WikiSQL](https://github.com/salesforce/WikiSQL).
|
||||
This script is customized for tapex models, and can be easily adapted to other benchmarks such as WikiTableQuestion
|
||||
(only some tweaks in the function `preprocess_tableqa_function`).
|
||||
|
||||
#### TAPEX-Base on WikiSQL
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how to run the script on the WikiSQL with `tapex-base`:
|
||||
> The default hyper-parameter may allow you to reproduce our reported tapex-base results within the memory budget of 16GB and 1 GPU card. If you have more GPU cards, you could reduce `gradient_accumulation_steps` accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export EXP_NAME=wikisql_tapex_base
|
||||
|
||||
python run_wikisql_with_tapex.py \
|
||||
--do_train \
|
||||
--do_eval \
|
||||
--output_dir $EXP_NAME \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path microsoft/tapex-base \
|
||||
--overwrite_output_dir \
|
||||
--per_device_train_batch_size 4 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps 8 \
|
||||
--per_device_eval_batch_size 4 \
|
||||
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
|
||||
--logging_steps 10 \
|
||||
--eval_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--save_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--warmup_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--evaluation_strategy steps \
|
||||
--predict_with_generate \
|
||||
--num_beams 5 \
|
||||
--weight_decay 1e-2 \
|
||||
--label_smoothing_factor 0.1 \
|
||||
--max_steps 20000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### TAPEX-Large on WikiSQL
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how to run the script on the WikiSQL with `tapex-large`:
|
||||
> The default hyper-parameter may allow you to reproduce our reported tapex-large results within the memory budget of 16GB and 1 GPU card with fp16. If you have more GPU cards, you could reduce `gradient_accumulation_steps` accordingly. If you do not install apex or other mixed-precision-training libs, you could disable the `predict_with_generate` option to save GPU memory and manually evaluate the model once the fine-tuning finished. Or just pick up the last checkpoint, which usually performs good enough on the dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export EXP_NAME=wikisql_tapex_large
|
||||
|
||||
python run_wikisql_with_tapex.py \
|
||||
--do_train \
|
||||
--do_eval \
|
||||
--output_dir $EXP_NAME \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path microsoft/tapex-large \
|
||||
--overwrite_output_dir \
|
||||
--per_device_train_batch_size 1 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps 32 \
|
||||
--per_device_eval_batch_size 4 \
|
||||
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
|
||||
--logging_steps 10 \
|
||||
--eval_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--save_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--warmup_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--evaluation_strategy steps \
|
||||
--predict_with_generate \
|
||||
--num_beams 5 \
|
||||
--weight_decay 1e-2 \
|
||||
--label_smoothing_factor 0.1 \
|
||||
--max_steps 20000 \
|
||||
--fp16
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### TAPEX-Base on WikiTableQuestions
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how to run the script on the WikiTableQuestions with `tapex-base`:
|
||||
> The default hyper-parameter may allow you to reproduce our reported tapex-base results within the memory budget of 16GB and 1 GPU card. If you have more GPU cards, you could reduce `gradient_accumulation_steps` accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export EXP_NAME=wikitablequestions_tapex_base
|
||||
|
||||
python run_wikitablequestions_with_tapex.py \
|
||||
--do_train \
|
||||
--do_eval \
|
||||
--output_dir $EXP_NAME \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path microsoft/tapex-base \
|
||||
--overwrite_output_dir \
|
||||
--per_device_train_batch_size 4 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps 8 \
|
||||
--per_device_eval_batch_size 4 \
|
||||
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
|
||||
--logging_steps 10 \
|
||||
--eval_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--save_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--warmup_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--evaluation_strategy steps \
|
||||
--predict_with_generate \
|
||||
--num_beams 5 \
|
||||
--weight_decay 1e-2 \
|
||||
--label_smoothing_factor 0.1 \
|
||||
--max_steps 20000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### TAPEX-Large on WikiTableQuestions
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how to run the script on the WikiTableQuestions with `tapex-large`:
|
||||
> The default hyper-parameter may allow you to reproduce our reported tapex-large results within the memory budget of 16GB and 1 GPU card with fp16. If you have more GPU cards, you could reduce `gradient_accumulation_steps` accordingly. If you do not install apex or other mixed-precision-training libs, you could reduce the `per_device_train_batch_size` and `per_device_eval_batch_size` and have another try. Or you could disable the `predict_with_generate` option to save GPU memory and manually evaluate the model once the fine-tuning finished. Or just pick up the last checkpoint, which usually performs good enough on the dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export EXP_NAME=wikitablequestions_tapex_large
|
||||
|
||||
python run_wikitablequestions_with_tapex.py \
|
||||
--do_train \
|
||||
--do_eval \
|
||||
--output_dir $EXP_NAME \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path microsoft/tapex-large \
|
||||
--overwrite_output_dir \
|
||||
--per_device_train_batch_size 2 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps 12 \
|
||||
--per_device_eval_batch_size 4 \
|
||||
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
|
||||
--logging_steps 10 \
|
||||
--eval_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--save_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--warmup_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--evaluation_strategy steps \
|
||||
--predict_with_generate \
|
||||
--num_beams 5 \
|
||||
--weight_decay 1e-2 \
|
||||
--label_smoothing_factor 0.1 \
|
||||
--max_steps 20000 \
|
||||
--fp16
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Evaluate TAPEX Fine-tuned Models on TableQA
|
||||
|
||||
We provide fine-tuned model weights to reproduce our results. You can evaluate them using the following command:
|
||||
> You can also replace `microsoft/tapex-base-finetuned-wikisql` with your local directory to evaluate your fine-tuned models. Notice that if the model has a larger size, you should reduce `per_device_eval_batch_size` to fit the memory requirement.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export EXP_NAME=wikisql_tapex_base_eval
|
||||
|
||||
python run_wikisql_with_tapex.py \
|
||||
--do_eval \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path microsoft/tapex-base-finetuned-wikisql \
|
||||
--output_dir $EXP_NAME \
|
||||
--per_device_eval_batch_size 4 \
|
||||
--predict_with_generate \
|
||||
--num_beams 5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Table Fact Verification Tasks
|
||||
|
||||
### What is Table Fact Verification
|
||||
|
||||
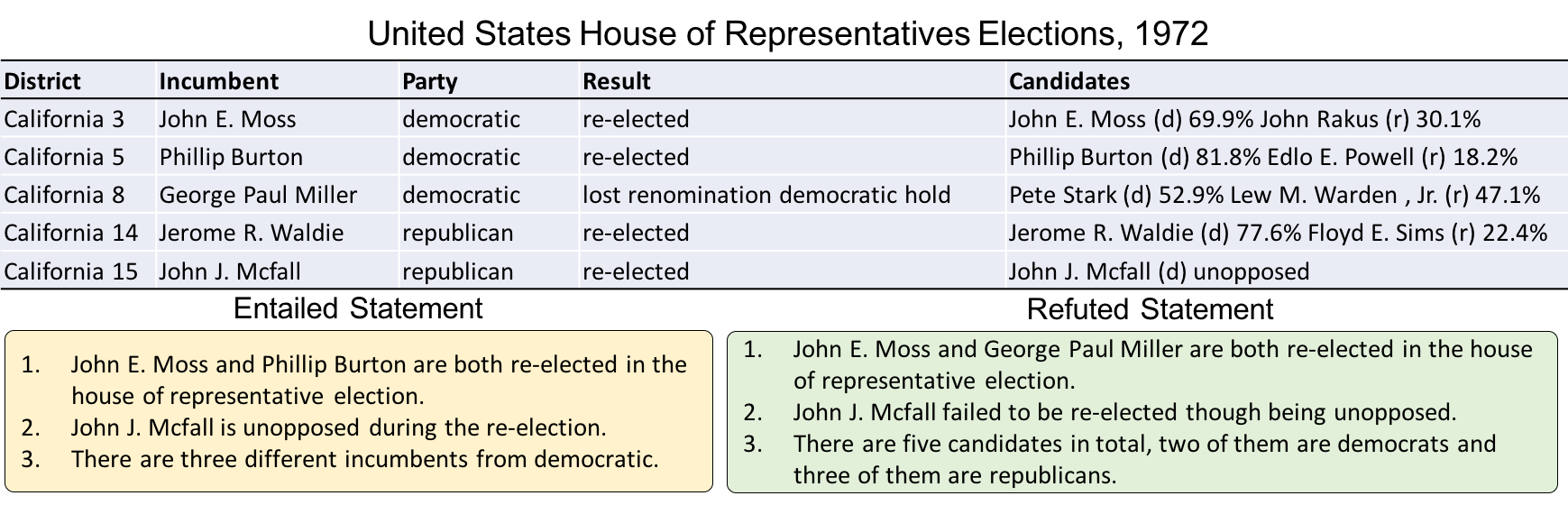
|
||||
|
||||
The task of Table Fact Verification (TableFV) is to empower machines to justify if a statement follows facts in a given table. The result is a binary classification belonging to `1` (entailed) or `0` (refused).
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Fine-tune TAPEX on TableFV
|
||||
|
||||
#### TAPEX-Base on TabFact
|
||||
|
||||
We provide a fine-tuning script of tapex for TableFV on the TabFact benchmark: [TabFact](https://github.com/wenhuchen/Table-Fact-Checking).
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how to run the script on the TabFact:
|
||||
> The default hyper-parameter may allow you to reproduce our reported tapex-base results within the memory budget of 16GB and 1 GPU card. If you have more GPU cards, you could reduce `gradient_accumulation_steps` accordingly. Note that the `eval_accumulation_steps` is necessary, otherwise GPU memory leaks will occur during the evaluation.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export EXP_NAME=tabfact_tapex_base
|
||||
|
||||
python run_tabfact_with_tapex.py \
|
||||
--do_train \
|
||||
--do_eval \
|
||||
--output_dir $EXP_NAME \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path microsoft/tapex-base \
|
||||
--overwrite_output_dir \
|
||||
--per_device_train_batch_size 3 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps 16 \
|
||||
--per_device_eval_batch_size 12 \
|
||||
--eval_accumulation_steps 6 \
|
||||
--warm_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--logging_steps 10 \
|
||||
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
|
||||
--eval_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--save_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--evaluation_strategy steps \
|
||||
--weight_decay 1e-2 \
|
||||
--max_steps 30000 \
|
||||
--max_grad_norm 0.1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### TAPEX-Large on TabFact
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how to run the script on the TabFact:
|
||||
> The default hyper-parameter may allow you to reproduce our reported tapex-base results within the memory budget of 24GB and 1 GPU card. Sorry we cannot reduce the memory consumption since the model input in TabFact usually contains nearly ~1000 tokens. If you have more GPU cards, you could reduce `gradient_accumulation_steps` accordingly. Note that the `eval_accumulation_steps` is necessary, otherwise GPU memory leaks will occur during the evaluation.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export EXP_NAME=tabfact_tapex_large
|
||||
|
||||
python run_tabfact_with_tapex.py \
|
||||
--do_train \
|
||||
--do_eval \
|
||||
--output_dir $EXP_NAME \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path microsoft/tapex-large \
|
||||
--overwrite_output_dir \
|
||||
--per_device_train_batch_size 2 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps 18 \
|
||||
--per_device_eval_batch_size 4 \
|
||||
--eval_accumulation_steps 12 \
|
||||
--warm_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--logging_steps 10 \
|
||||
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
|
||||
--eval_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--save_steps 1000 \
|
||||
--evaluation_strategy steps \
|
||||
--weight_decay 1e-2 \
|
||||
--max_steps 30000 \
|
||||
--max_grad_norm 0.1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Evaluate TAPEX Fine-tuned Models on TableFV
|
||||
|
||||
We provide fine-tuned model weights to reproduce our results. You can evaluate them using the following command:
|
||||
> You can also replace `microsoft/tapex-base-finetuned-tabfact` with your local directory to evaluate your fine-tuned models. Notice that if the model has a larger size, you should reduce `per_device_eval_batch_size` to fit the memory requirement.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export EXP_NAME=tabfact_tapex_base_eval
|
||||
|
||||
python run_tabfact_with_tapex.py \
|
||||
--do_eval \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path microsoft/tapex-base-finetuned-tabfact \
|
||||
--output_dir $EXP_NAME \
|
||||
--per_device_eval_batch_size 12 \
|
||||
--eval_accumulation_steps 6
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Reproduced Results
|
||||
|
||||
We get the following results on the dev set of the benchmark with the previous commands:
|
||||
|
||||
| Task | Model Size | Metric | Result |
|
||||
|:---:|:---:|:---:|:---:|
|
||||
| WikiSQL (Weak) | Base | Denotation Accuracy | 88.1 |
|
||||
| WikiSQL (Weak) | Large | Denotation Accuracy | 89.5 |
|
||||
| WikiTableQuestion | Base | Denotation Accuracy | 47.1 |
|
||||
| WikiTableQuestion | Large | Denotation Accuracy | 57.2 |
|
||||
| TabFact | Base | Accuracy | 78.7 |
|
||||
| TabFact | Large | Accuracy | 83.6 |
|
||||
4
examples/research_projects/tapex/requirements.txt
Normal file
4
examples/research_projects/tapex/requirements.txt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
numpy
|
||||
datasets
|
||||
pandas
|
||||
nltk
|
||||
459
examples/research_projects/tapex/run_tabfact_with_tapex.py
Normal file
459
examples/research_projects/tapex/run_tabfact_with_tapex.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,459 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
# Copyright 2022 The Microsoft and The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Fine-tuning the library models for tapex on table-based fact verification tasks.
|
||||
Adapted from script: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/master/examples/pytorch/text-classification/run_glue.py
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
import datasets
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
import transformers
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
AutoConfig,
|
||||
BartForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
DataCollatorWithPadding,
|
||||
EvalPrediction,
|
||||
HfArgumentParser,
|
||||
TapexTokenizer,
|
||||
Trainer,
|
||||
TrainingArguments,
|
||||
default_data_collator,
|
||||
set_seed,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from transformers.trainer_utils import get_last_checkpoint
|
||||
from transformers.utils import check_min_version
|
||||
from transformers.utils.versions import require_version
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.17.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
require_version("datasets>=1.8.0", "To fix: pip install -r examples/pytorch/text-classification/requirements.txt")
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class DataTrainingArguments:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Arguments pertaining to what data we are going to input our model for training and eval.
|
||||
|
||||
Using `HfArgumentParser` we can turn this class
|
||||
into argparse arguments to be able to specify them on
|
||||
the command line.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
dataset_name: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default="tab_fact", metadata={"help": "The name of the dataset to use (via the datasets library)."}
|
||||
)
|
||||
dataset_config_name: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default="tab_fact",
|
||||
metadata={"help": "The configuration name of the dataset to use (via the datasets library)."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_seq_length: int = field(
|
||||
default=1024,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "The maximum total input sequence length after tokenization. Sequences longer "
|
||||
"than this will be truncated, sequences shorter will be padded."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
overwrite_cache: bool = field(
|
||||
default=False, metadata={"help": "Overwrite the cached preprocessed datasets or not."}
|
||||
)
|
||||
pad_to_max_length: bool = field(
|
||||
default=False,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Whether to pad all samples to `max_seq_length`. "
|
||||
"If False, will pad the samples dynamically when batching to the maximum length in the batch."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_train_samples: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "For debugging purposes or quicker training, truncate the number of training examples to this "
|
||||
"value if set."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_eval_samples: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "For debugging purposes or quicker training, truncate the number of evaluation examples to this "
|
||||
"value if set."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_predict_samples: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "For debugging purposes or quicker training, truncate the number of prediction examples to this "
|
||||
"value if set."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
train_file: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None, metadata={"help": "A csv or a json file containing the training data."}
|
||||
)
|
||||
validation_file: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None, metadata={"help": "A csv or a json file containing the validation data."}
|
||||
)
|
||||
test_file: Optional[str] = field(default=None, metadata={"help": "A csv or a json file containing the test data."})
|
||||
|
||||
def __post_init__(self):
|
||||
if self.dataset_name is not None:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
elif self.train_file is None or self.validation_file is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Need either a GLUE task, a training/validation file or a dataset name.")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
train_extension = self.train_file.split(".")[-1]
|
||||
assert train_extension in ["csv", "json"], "`train_file` should be a csv or a json file."
|
||||
validation_extension = self.validation_file.split(".")[-1]
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
validation_extension == train_extension
|
||||
), "`validation_file` should have the same extension (csv or json) as `train_file`."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class ModelArguments:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Arguments pertaining to which model/config/tokenizer we are going to fine-tune from.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
model_name_or_path: str = field(
|
||||
default=None, metadata={"help": "Path to pretrained model or model identifier from huggingface.co/models"}
|
||||
)
|
||||
config_name: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None, metadata={"help": "Pretrained config name or path if not the same as model_name"}
|
||||
)
|
||||
tokenizer_name: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None, metadata={"help": "Pretrained tokenizer name or path if not the same as model_name"}
|
||||
)
|
||||
cache_dir: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Where do you want to store the pretrained models downloaded from huggingface.co"},
|
||||
)
|
||||
use_fast_tokenizer: bool = field(
|
||||
default=True,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Whether to use one of the fast tokenizer (backed by the tokenizers library) or not."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
model_revision: str = field(
|
||||
default="main",
|
||||
metadata={"help": "The specific model version to use (can be a branch name, tag name or commit id)."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
use_auth_token: bool = field(
|
||||
default=False,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Will use the token generated when running `transformers-cli login` (necessary to use this script "
|
||||
"with private models)."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
# See all possible arguments in src/transformers/training_args.py
|
||||
# or by passing the --help flag to this script.
|
||||
# We now keep distinct sets of args, for a cleaner separation of concerns.
|
||||
|
||||
parser = HfArgumentParser((ModelArguments, DataTrainingArguments, TrainingArguments))
|
||||
if len(sys.argv) == 2 and sys.argv[1].endswith(".json"):
|
||||
# If we pass only one argument to the script and it's the path to a json file,
|
||||
# let's parse it to get our arguments.
|
||||
model_args, data_args, training_args = parser.parse_json_file(json_file=os.path.abspath(sys.argv[1]))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
model_args, data_args, training_args = parser.parse_args_into_dataclasses()
|
||||
|
||||
# Setup logging
|
||||
logging.basicConfig(
|
||||
format="%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(name)s - %(message)s",
|
||||
datefmt="%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S",
|
||||
handlers=[logging.StreamHandler(sys.stdout)],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
log_level = training_args.get_process_log_level()
|
||||
logger.setLevel(log_level)
|
||||
datasets.utils.logging.set_verbosity(log_level)
|
||||
transformers.utils.logging.set_verbosity(log_level)
|
||||
transformers.utils.logging.enable_default_handler()
|
||||
transformers.utils.logging.enable_explicit_format()
|
||||
|
||||
# Log on each process the small summary:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"Process rank: {training_args.local_rank}, device: {training_args.device}, n_gpu: {training_args.n_gpu}"
|
||||
+ f"distributed training: {bool(training_args.local_rank != -1)}, 16-bits training: {training_args.fp16}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Training/evaluation parameters {training_args}")
|
||||
|
||||
# Detecting last checkpoint.
|
||||
last_checkpoint = None
|
||||
if os.path.isdir(training_args.output_dir) and training_args.do_train and not training_args.overwrite_output_dir:
|
||||
last_checkpoint = get_last_checkpoint(training_args.output_dir)
|
||||
if last_checkpoint is None and len(os.listdir(training_args.output_dir)) > 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Output directory ({training_args.output_dir}) already exists and is not empty. "
|
||||
"Use --overwrite_output_dir to overcome."
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif last_checkpoint is not None and training_args.resume_from_checkpoint is None:
|
||||
logger.info(
|
||||
f"Checkpoint detected, resuming training at {last_checkpoint}. To avoid this behavior, change "
|
||||
"the `--output_dir` or add `--overwrite_output_dir` to train from scratch."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Set seed before initializing model.
|
||||
set_seed(training_args.seed)
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the datasets: you can either provide your own CSV/JSON training and evaluation files (see below)
|
||||
# or specify a GLUE benchmark task (the dataset will be downloaded automatically from the datasets Hub).
|
||||
#
|
||||
# For JSON files, this script will use the `question` column for the input question and `table` column for the corresponding table.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# If the CSVs/JSONs contain only one non-label column, the script does single sentence classification on this
|
||||
# single column. You can easily tweak this behavior (see below)
|
||||
#
|
||||
# In distributed training, the load_dataset function guarantee that only one local process can concurrently
|
||||
# download the dataset.
|
||||
if data_args.dataset_name is not None:
|
||||
# Downloading and loading a dataset from the hub.
|
||||
raw_datasets = load_dataset(
|
||||
data_args.dataset_name, data_args.dataset_config_name, cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Loading a dataset from your local files.
|
||||
# CSV/JSON training and evaluation files are needed.
|
||||
data_files = {"train": data_args.train_file, "validation": data_args.validation_file}
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the test dataset: you can provide your own CSV/JSON test file (see below)
|
||||
# when you use `do_predict` without specifying a GLUE benchmark task.
|
||||
if training_args.do_predict:
|
||||
if data_args.test_file is not None:
|
||||
train_extension = data_args.train_file.split(".")[-1]
|
||||
test_extension = data_args.test_file.split(".")[-1]
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
test_extension == train_extension
|
||||
), "`test_file` should have the same extension (csv or json) as `train_file`."
|
||||
data_files["test"] = data_args.test_file
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Need either a GLUE task or a test file for `do_predict`.")
|
||||
|
||||
for key in data_files.keys():
|
||||
logger.info(f"load a local file for {key}: {data_files[key]}")
|
||||
|
||||
if data_args.train_file.endswith(".csv"):
|
||||
# Loading a dataset from local csv files
|
||||
raw_datasets = load_dataset("csv", data_files=data_files, cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Loading a dataset from local json files
|
||||
raw_datasets = load_dataset("json", data_files=data_files, cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir)
|
||||
# See more about loading any type of standard or custom dataset at
|
||||
# https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/loading_datasets.html.
|
||||
|
||||
# Labels
|
||||
label_list = raw_datasets["train"].features["label"].names
|
||||
num_labels = len(label_list)
|
||||
|
||||
# Load pretrained model and tokenizer
|
||||
#
|
||||
# In distributed training, the .from_pretrained methods guarantee that only one local process can concurrently
|
||||
# download model & vocab.
|
||||
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_args.config_name if model_args.config_name else model_args.model_name_or_path,
|
||||
num_labels=num_labels,
|
||||
cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir,
|
||||
revision=model_args.model_revision,
|
||||
use_auth_token=True if model_args.use_auth_token else None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
# load tapex tokenizer
|
||||
tokenizer = TapexTokenizer.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_args.tokenizer_name if model_args.tokenizer_name else model_args.model_name_or_path,
|
||||
cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir,
|
||||
use_fast=model_args.use_fast_tokenizer,
|
||||
revision=model_args.model_revision,
|
||||
use_auth_token=True if model_args.use_auth_token else None,
|
||||
add_prefix_space=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
model = BartForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_args.model_name_or_path,
|
||||
from_tf=bool(".ckpt" in model_args.model_name_or_path),
|
||||
config=config,
|
||||
cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir,
|
||||
revision=model_args.model_revision,
|
||||
use_auth_token=True if model_args.use_auth_token else None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Padding strategy
|
||||
if data_args.pad_to_max_length:
|
||||
padding = "max_length"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# We will pad later, dynamically at batch creation, to the max sequence length in each batch
|
||||
padding = False
|
||||
|
||||
# Some models have set the order of the labels to use, so let's make sure we do use it.
|
||||
model.config.label2id = {"Refused": 0, "Entailed": 1}
|
||||
model.config.id2label = {0: "Refused", 1: "Entailed"}
|
||||
|
||||
if data_args.max_seq_length > tokenizer.model_max_length:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"The max_seq_length passed ({data_args.max_seq_length}) is larger than the maximum length for the"
|
||||
f"model ({tokenizer.model_max_length}). Using max_seq_length={tokenizer.model_max_length}."
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_seq_length = min(data_args.max_seq_length, tokenizer.model_max_length)
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess_tabfact_function(examples):
|
||||
# Tokenize the texts
|
||||
def _convert_table_text_to_pandas(_table_text):
|
||||
"""Runs the structured pandas table object for _table_text.
|
||||
An example _table_text can be: round#clubs remaining\nfirst round#156\n
|
||||
"""
|
||||
_table_content = [_table_row.split("#") for _table_row in _table_text.strip("\n").split("\n")]
|
||||
_table_pd = pd.DataFrame.from_records(_table_content[1:], columns=_table_content[0])
|
||||
return _table_pd
|
||||
|
||||
questions = examples["statement"]
|
||||
tables = list(map(_convert_table_text_to_pandas, examples["table_text"]))
|
||||
result = tokenizer(tables, questions, padding=padding, max_length=max_seq_length, truncation=True)
|
||||
|
||||
result["label"] = examples["label"]
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
with training_args.main_process_first(desc="dataset map pre-processing"):
|
||||
raw_datasets = raw_datasets.map(
|
||||
preprocess_tabfact_function,
|
||||
batched=True,
|
||||
load_from_cache_file=not data_args.overwrite_cache,
|
||||
desc="Running tokenizer on dataset",
|
||||
)
|
||||
if training_args.do_train:
|
||||
if "train" not in raw_datasets:
|
||||
raise ValueError("--do_train requires a train dataset")
|
||||
train_dataset = raw_datasets["train"]
|
||||
if data_args.max_train_samples is not None:
|
||||
train_dataset = train_dataset.select(range(data_args.max_train_samples))
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.do_eval:
|
||||
if "validation" not in raw_datasets and "validation_matched" not in raw_datasets:
|
||||
raise ValueError("--do_eval requires a validation dataset")
|
||||
eval_dataset = raw_datasets["validation"]
|
||||
if data_args.max_eval_samples is not None:
|
||||
eval_dataset = eval_dataset.select(range(data_args.max_eval_samples))
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.do_predict or data_args.test_file is not None:
|
||||
if "test" not in raw_datasets and "test_matched" not in raw_datasets:
|
||||
raise ValueError("--do_predict requires a test dataset")
|
||||
predict_dataset = raw_datasets["test"]
|
||||
if data_args.max_predict_samples is not None:
|
||||
predict_dataset = predict_dataset.select(range(data_args.max_predict_samples))
|
||||
|
||||
# Log a few random samples from the training set:
|
||||
if training_args.do_train:
|
||||
for index in random.sample(range(len(train_dataset)), 3):
|
||||
logger.info(f"Sample {index} of the training set: {train_dataset[index]}.")
|
||||
|
||||
# You can define your custom compute_metrics function. It takes an `EvalPrediction` object (a namedtuple with a
|
||||
# predictions and label_ids field) and has to return a dictionary string to float.
|
||||
def compute_metrics(p: EvalPrediction):
|
||||
preds = p.predictions[0] if isinstance(p.predictions, tuple) else p.predictions
|
||||
preds = np.argmax(preds, axis=1)
|
||||
return {"accuracy": (preds == p.label_ids).astype(np.float32).mean().item()}
|
||||
|
||||
# Data collator will default to DataCollatorWithPadding, so we change it if we already did the padding.
|
||||
if data_args.pad_to_max_length:
|
||||
data_collator = default_data_collator
|
||||
elif training_args.fp16:
|
||||
data_collator = DataCollatorWithPadding(tokenizer, pad_to_multiple_of=8)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
data_collator = None
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize our Trainer
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=train_dataset if training_args.do_train else None,
|
||||
eval_dataset=eval_dataset if training_args.do_eval else None,
|
||||
compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
|
||||
tokenizer=tokenizer,
|
||||
data_collator=data_collator,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Training
|
||||
if training_args.do_train:
|
||||
checkpoint = None
|
||||
if training_args.resume_from_checkpoint is not None:
|
||||
checkpoint = training_args.resume_from_checkpoint
|
||||
elif last_checkpoint is not None:
|
||||
checkpoint = last_checkpoint
|
||||
train_result = trainer.train(resume_from_checkpoint=checkpoint)
|
||||
metrics = train_result.metrics
|
||||
max_train_samples = (
|
||||
data_args.max_train_samples if data_args.max_train_samples is not None else len(train_dataset)
|
||||
)
|
||||
metrics["train_samples"] = min(max_train_samples, len(train_dataset))
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.save_model() # Saves the tokenizer too for easy upload
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.log_metrics("train", metrics)
|
||||
trainer.save_metrics("train", metrics)
|
||||
trainer.save_state()
|
||||
|
||||
# Evaluation
|
||||
if training_args.do_eval:
|
||||
logger.info("*** Evaluate ***")
|
||||
|
||||
metrics = trainer.evaluate(eval_dataset=eval_dataset)
|
||||
max_eval_samples = data_args.max_eval_samples if data_args.max_eval_samples is not None else len(eval_dataset)
|
||||
metrics["eval_samples"] = min(max_eval_samples, len(eval_dataset))
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.log_metrics("eval", metrics)
|
||||
trainer.save_metrics("eval", metrics)
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.do_predict:
|
||||
logger.info("*** Predict ***")
|
||||
|
||||
# Removing the `label` columns because it contains -1 and Trainer won't like that.
|
||||
predict_dataset = predict_dataset.remove_columns("label")
|
||||
predictions = trainer.predict(predict_dataset, metric_key_prefix="predict").predictions
|
||||
predictions = np.argmax(predictions, axis=1)
|
||||
|
||||
output_predict_file = os.path.join(training_args.output_dir, "predict_results_tabfact.txt")
|
||||
if trainer.is_world_process_zero():
|
||||
with open(output_predict_file, "w") as writer:
|
||||
logger.info("***** Predict Results *****")
|
||||
writer.write("index\tprediction\n")
|
||||
for index, item in enumerate(predictions):
|
||||
item = label_list[item]
|
||||
writer.write(f"{index}\t{item}\n")
|
||||
|
||||
kwargs = {"finetuned_from": model_args.model_name_or_path, "tasks": "text-classification"}
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.push_to_hub:
|
||||
trainer.push_to_hub(**kwargs)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
trainer.create_model_card(**kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _mp_fn(index):
|
||||
# For xla_spawn (TPUs)
|
||||
main()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
629
examples/research_projects/tapex/run_wikisql_with_tapex.py
Normal file
629
examples/research_projects/tapex/run_wikisql_with_tapex.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,629 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
# Copyright 2022 The Microsoft and The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Fine-tuning the library models for tapex on table-based question answering tasks.
|
||||
Adapted from script: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/master/examples/pytorch/summarization/run_summarization.py
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from collections import defaultdict
|
||||
from copy import deepcopy
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from functools import partial
|
||||
from typing import List, Optional
|
||||
|
||||
import nltk # Here to have a nice missing dependency error message early on
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
import transformers
|
||||
from filelock import FileLock
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
AutoConfig,
|
||||
BartForConditionalGeneration,
|
||||
DataCollatorForSeq2Seq,
|
||||
HfArgumentParser,
|
||||
Seq2SeqTrainer,
|
||||
Seq2SeqTrainingArguments,
|
||||
TapexTokenizer,
|
||||
set_seed,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from transformers.file_utils import is_offline_mode
|
||||
from transformers.trainer_utils import get_last_checkpoint, is_main_process
|
||||
from transformers.utils import check_min_version
|
||||
from wikisql_utils import _TYPE_CONVERTER, retrieve_wikisql_query_answer_tapas
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.17.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
nltk.data.find("tokenizers/punkt")
|
||||
except (LookupError, OSError):
|
||||
if is_offline_mode():
|
||||
raise LookupError(
|
||||
"Offline mode: run this script without TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE first to download nltk data files"
|
||||
)
|
||||
with FileLock(".lock") as lock:
|
||||
nltk.download("punkt", quiet=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class ModelArguments:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Arguments pertaining to which model/config/tokenizer we are going to fine-tune from.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
model_name_or_path: str = field(
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Path to pretrained model or model identifier from huggingface.co/models"},
|
||||
)
|
||||
config_name: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None, metadata={"help": "Pretrained config name or path if not the same as model_name"}
|
||||
)
|
||||
tokenizer_name: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Pretrained tokenizer name or path if not the same as model_name. "
|
||||
"By default we use BART-large tokenizer for TAPEX-large."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
cache_dir: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Where to store the pretrained models downloaded from huggingface.co"},
|
||||
)
|
||||
use_fast_tokenizer: bool = field(
|
||||
default=True,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Whether to use one of the fast tokenizer (backed by the tokenizers library) or not."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
model_revision: str = field(
|
||||
default="main",
|
||||
metadata={"help": "The specific model version to use (can be a branch name, tag name or commit id)."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
use_auth_token: bool = field(
|
||||
default=False,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Will use the token generated when running `transformers-cli login` (necessary to use this script "
|
||||
"with private models)."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class DataTrainingArguments:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Arguments pertaining to what data we are going to input our model for training and eval.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
dataset_name: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default="wikisql", metadata={"help": "The name of the dataset to use (via the datasets library)."}
|
||||
)
|
||||
dataset_config_name: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None, metadata={"help": "The configuration name of the dataset to use (via the datasets library)."}
|
||||
)
|
||||
train_file: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None, metadata={"help": "The input training data file (a jsonlines or csv file)."}
|
||||
)
|
||||
validation_file: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "An optional input evaluation data file to evaluate the metrics (rouge) on "
|
||||
"(a jsonlines or csv file)."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
test_file: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "An optional input test data file to evaluate the metrics (rouge) on " "(a jsonlines or csv file)."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
overwrite_cache: bool = field(
|
||||
default=False, metadata={"help": "Overwrite the cached training and evaluation sets"}
|
||||
)
|
||||
preprocessing_num_workers: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "The number of processes to use for the preprocessing."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_source_length: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=1024,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "The maximum total input sequence length after tokenization. Sequences longer "
|
||||
"than this will be truncated, sequences shorter will be padded."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_target_length: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=128,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "The maximum total sequence length for target text after tokenization. Sequences longer "
|
||||
"than this will be truncated, sequences shorter will be padded."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
val_max_target_length: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "The maximum total sequence length for validation target text after tokenization. Sequences longer "
|
||||
"than this will be truncated, sequences shorter will be padded. Will default to `max_target_length`."
|
||||
"This argument is also used to override the ``max_length`` param of ``model.generate``, which is used "
|
||||
"during ``evaluate`` and ``predict``."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
pad_to_max_length: bool = field(
|
||||
default=False,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Whether to pad all samples to model maximum sentence length. "
|
||||
"If False, will pad the samples dynamically when batching to the maximum length in the batch. More "
|
||||
"efficient on GPU but very bad for TPU."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_train_samples: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "For debugging purposes or quicker training, truncate the number of training examples to this "
|
||||
"value if set."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_eval_samples: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "For debugging purposes or quicker training, truncate the number of evaluation examples to this "
|
||||
"value if set."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_predict_samples: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "For debugging purposes or quicker training, truncate the number of prediction examples to this "
|
||||
"value if set."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
num_beams: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Number of beams to use for evaluation. This argument will be passed to ``model.generate``, "
|
||||
"which is used during ``evaluate`` and ``predict``."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
ignore_pad_token_for_loss: bool = field(
|
||||
default=True,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Whether to ignore the tokens corresponding to padded labels in the loss computation or not."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def __post_init__(self):
|
||||
if self.dataset_name is None and self.train_file is None and self.validation_file is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Need either a dataset name or a training/validation file.")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if self.train_file is not None:
|
||||
extension = self.train_file.split(".")[-1]
|
||||
assert extension in ["csv", "json"], "`train_file` should be a csv or a json file."
|
||||
if self.validation_file is not None:
|
||||
extension = self.validation_file.split(".")[-1]
|
||||
assert extension in ["csv", "json"], "`validation_file` should be a csv or a json file."
|
||||
if self.val_max_target_length is None:
|
||||
self.val_max_target_length = self.max_target_length
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
# See all possible arguments in src/transformers/training_args.py
|
||||
# or by passing the --help flag to this script.
|
||||
# We now keep distinct sets of args, for a cleaner separation of concerns.
|
||||
|
||||
parser = HfArgumentParser((ModelArguments, DataTrainingArguments, Seq2SeqTrainingArguments))
|
||||
if len(sys.argv) == 2 and sys.argv[1].endswith(".json"):
|
||||
# If we pass only one argument to the script and it's the path to a json file,
|
||||
# let's parse it to get our arguments.
|
||||
model_args, data_args, training_args = parser.parse_json_file(json_file=os.path.abspath(sys.argv[1]))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
model_args, data_args, training_args = parser.parse_args_into_dataclasses()
|
||||
|
||||
# Detecting last checkpoint.
|
||||
last_checkpoint = None
|
||||
if os.path.isdir(training_args.output_dir) and training_args.do_train and not training_args.overwrite_output_dir:
|
||||
last_checkpoint = get_last_checkpoint(training_args.output_dir)
|
||||
if last_checkpoint is None and len(os.listdir(training_args.output_dir)) > 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Output directory ({training_args.output_dir}) already exists and is not empty. "
|
||||
"Use --overwrite_output_dir to overcome."
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif last_checkpoint is not None and training_args.resume_from_checkpoint is None:
|
||||
logger.info(
|
||||
f"Checkpoint detected, resuming training at {last_checkpoint}. To avoid this behavior, change "
|
||||
"the `--output_dir` or add `--overwrite_output_dir` to train from scratch."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Setup logging
|
||||
logging.basicConfig(
|
||||
format="%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(name)s - %(message)s",
|
||||
datefmt="%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S",
|
||||
handlers=[logging.StreamHandler(sys.stdout)],
|
||||
)
|
||||
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO if is_main_process(training_args.local_rank) else logging.WARN)
|
||||
|
||||
# Log on each process the small summary:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"Process rank: {training_args.local_rank}, device: {training_args.device}, n_gpu: {training_args.n_gpu}"
|
||||
+ f"distributed training: {bool(training_args.local_rank != -1)}, 16-bits training: {training_args.fp16}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Set the verbosity to info of the Transformers logger (on main process only):
|
||||
if is_main_process(training_args.local_rank):
|
||||
transformers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_info()
|
||||
logger.info(f"Training/evaluation parameters {training_args}")
|
||||
|
||||
# Set seed before initializing model.
|
||||
set_seed(training_args.seed)
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the datasets: you can either provide your own CSV/JSON training and evaluation files (see below)
|
||||
# or just provide the name of one of the public datasets available on the hub at https://huggingface.co/datasets/
|
||||
# (the dataset will be downloaded automatically from the datasets Hub).
|
||||
#
|
||||
# For JSON files, this script will use the `question` column for the input question and `table` column for the corresponding table.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# In distributed training, the load_dataset function guarantee that only one local process can concurrently
|
||||
# download the dataset.
|
||||
if data_args.dataset_name is not None:
|
||||
# Downloading and loading a dataset from the hub.
|
||||
datasets = load_dataset(data_args.dataset_name, data_args.dataset_config_name, cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
data_files = {}
|
||||
if data_args.train_file is not None:
|
||||
data_files["train"] = data_args.train_file
|
||||
extension = data_args.train_file.split(".")[-1]
|
||||
if data_args.validation_file is not None:
|
||||
data_files["validation"] = data_args.validation_file
|
||||
extension = data_args.validation_file.split(".")[-1]
|
||||
if data_args.test_file is not None:
|
||||
data_files["test"] = data_args.test_file
|
||||
extension = data_args.test_file.split(".")[-1]
|
||||
datasets = load_dataset(extension, data_files=data_files, cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
# See more about loading any type of standard or custom dataset (from files, python dict, pandas DataFrame, etc) at
|
||||
# https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/loading_datasets.html.
|
||||
|
||||
# Load pretrained model and tokenizer
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Distributed training:
|
||||
# The .from_pretrained methods guarantee that only one local process can concurrently
|
||||
# download model & vocab.
|
||||
|
||||
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_args.config_name if model_args.config_name else model_args.model_name_or_path,
|
||||
cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir,
|
||||
revision=model_args.model_revision,
|
||||
use_auth_token=True if model_args.use_auth_token else None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# IMPORTANT: the initial BART model's decoding is penalized by no_repeat_ngram_size, and thus
|
||||
# we should disable it here to avoid problematic generation
|
||||
config.no_repeat_ngram_size = 0
|
||||
config.max_length = 1024
|
||||
config.early_stopping = False
|
||||
|
||||
# load tapex tokenizer
|
||||
tokenizer = TapexTokenizer.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_args.tokenizer_name if model_args.tokenizer_name else model_args.model_name_or_path,
|
||||
cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir,
|
||||
use_fast=model_args.use_fast_tokenizer,
|
||||
revision=model_args.model_revision,
|
||||
use_auth_token=True if model_args.use_auth_token else None,
|
||||
add_prefix_space=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# load Bart based Tapex model (default tapex-large)
|
||||
model = BartForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_args.model_name_or_path,
|
||||
from_tf=bool(".ckpt" in model_args.model_name_or_path),
|
||||
config=config,
|
||||
cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir,
|
||||
revision=model_args.model_revision,
|
||||
use_auth_token=True if model_args.use_auth_token else None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if model.config.decoder_start_token_id is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Make sure that `config.decoder_start_token_id` is correctly defined")
|
||||
|
||||
# Preprocessing the datasets.
|
||||
# We need to tokenize inputs and targets.
|
||||
if training_args.do_train:
|
||||
column_names = datasets["train"].column_names
|
||||
elif training_args.do_eval:
|
||||
column_names = datasets["validation"].column_names
|
||||
elif training_args.do_predict:
|
||||
column_names = datasets["test"].column_names
|
||||
else:
|
||||
logger.info("There is nothing to do. Please pass `do_train`, `do_eval` and/or `do_predict`.")
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
# Temporarily set max_target_length for training.
|
||||
max_target_length = data_args.max_target_length
|
||||
padding = "max_length" if data_args.pad_to_max_length else False
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.label_smoothing_factor > 0 and not hasattr(model, "prepare_decoder_input_ids_from_labels"):
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
"label_smoothing is enabled but the `prepare_decoder_input_ids_from_labels` method is not defined for"
|
||||
f"`{model.__class__.__name__}`. This will lead to loss being calculated twice and will take up more memory"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess_tableqa_function(examples, is_training=False):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
The is_training FLAG is used to identify if we could use the supervision
|
||||
to truncate the table content if it is required.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# this function is specific for WikiSQL since the util function need the data structure
|
||||
# to retrieve the WikiSQL answer for each question
|
||||
def _convert_table_types(_table):
|
||||
"""Runs the type converter over the table cells."""
|
||||
ret_table = deepcopy(_table)
|
||||
types = ret_table["types"]
|
||||
ret_table["real_rows"] = ret_table["rows"]
|
||||
typed_rows = []
|
||||
for row in ret_table["rows"]:
|
||||
typed_row = []
|
||||
for column, cell_value in enumerate(row):
|
||||
typed_row.append(_TYPE_CONVERTER[types[column]](cell_value))
|
||||
typed_rows.append(typed_row)
|
||||
ret_table["rows"] = typed_rows
|
||||
return ret_table
|
||||
|
||||
questions = [question.lower() for question in examples["question"]]
|
||||
example_tables = examples["table"]
|
||||
example_sqls = examples["sql"]
|
||||
tables = [
|
||||
pd.DataFrame.from_records(example_table["rows"], columns=example_table["header"])
|
||||
for example_table in example_tables
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# using tapas utils to obtain wikisql answer
|
||||
answers = []
|
||||
for example_sql, example_table in zip(example_sqls, example_tables):
|
||||
tapas_table = _convert_table_types(example_table)
|
||||
answer_list: List[str] = retrieve_wikisql_query_answer_tapas(tapas_table, example_sql)
|
||||
# you can choose other delimiters to split each answer
|
||||
answers.append(answer_list)
|
||||
|
||||
# IMPORTANT: we cannot pass by answers during evaluation, answers passed during training are used to
|
||||
# truncate large tables in the train set!
|
||||
if is_training:
|
||||
model_inputs = tokenizer(
|
||||
table=tables,
|
||||
query=questions,
|
||||
answer=answers,
|
||||
max_length=data_args.max_source_length,
|
||||
padding=padding,
|
||||
truncation=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
model_inputs = tokenizer(
|
||||
table=tables, query=questions, max_length=data_args.max_source_length, padding=padding, truncation=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with tokenizer.as_target_tokenizer():
|
||||
labels = tokenizer(
|
||||
answer=[", ".join(answer) for answer in answers],
|
||||
max_length=max_target_length,
|
||||
padding=padding,
|
||||
truncation=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# If we are padding here, replace all tokenizer.pad_token_id in the labels by -100 when we want to ignore
|
||||
# padding in the loss.
|
||||
if padding == "max_length" and data_args.ignore_pad_token_for_loss:
|
||||
labels["input_ids"] = [
|
||||
[(l if l != tokenizer.pad_token_id else -100) for l in label] for label in labels["input_ids"]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
model_inputs["labels"] = labels["input_ids"]
|
||||
|
||||
return model_inputs
|
||||
|
||||
# in training, we can use the answer as extra information to truncate large tables
|
||||
preprocess_tableqa_function_training = partial(preprocess_tableqa_function, is_training=True)
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.do_train:
|
||||
if "train" not in datasets:
|
||||
raise ValueError("--do_train requires a train dataset")
|
||||
train_dataset = datasets["train"]
|
||||
if data_args.max_train_samples is not None:
|
||||
train_dataset = train_dataset.select(range(data_args.max_train_samples))
|
||||
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(
|
||||
preprocess_tableqa_function_training,
|
||||
batched=True,
|
||||
num_proc=data_args.preprocessing_num_workers,
|
||||
remove_columns=column_names,
|
||||
load_from_cache_file=not data_args.overwrite_cache,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.do_eval:
|
||||
max_target_length = data_args.val_max_target_length
|
||||
if "validation" not in datasets:
|
||||
raise ValueError("--do_eval requires a validation dataset")
|
||||
eval_dataset = datasets["validation"]
|
||||
if data_args.max_eval_samples is not None:
|
||||
eval_dataset = eval_dataset.select(range(data_args.max_eval_samples))
|
||||
eval_dataset = eval_dataset.map(
|
||||
preprocess_tableqa_function,
|
||||
batched=True,
|
||||
num_proc=data_args.preprocessing_num_workers,
|
||||
remove_columns=column_names,
|
||||
load_from_cache_file=not data_args.overwrite_cache,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.do_predict:
|
||||
max_target_length = data_args.val_max_target_length
|
||||
if "test" not in datasets:
|
||||
raise ValueError("--do_predict requires a test dataset")
|
||||
predict_dataset = datasets["test"]
|
||||
if data_args.max_predict_samples is not None:
|
||||
predict_dataset = predict_dataset.select(range(data_args.max_predict_samples))
|
||||
predict_dataset = predict_dataset.map(
|
||||
preprocess_tableqa_function,
|
||||
batched=True,
|
||||
num_proc=data_args.preprocessing_num_workers,
|
||||
remove_columns=column_names,
|
||||
load_from_cache_file=not data_args.overwrite_cache,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Data collator
|
||||
label_pad_token_id = -100 if data_args.ignore_pad_token_for_loss else tokenizer.pad_token_id
|
||||
data_collator = DataCollatorForSeq2Seq(
|
||||
tokenizer,
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
label_pad_token_id=label_pad_token_id,
|
||||
pad_to_multiple_of=8 if training_args.fp16 else None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def postprocess_text(preds, labels):
|
||||
preds = [pred.strip() for pred in preds]
|
||||
labels = [label.strip() for label in labels]
|
||||
|
||||
return preds, labels
|
||||
|
||||
def compute_metrics(eval_preds):
|
||||
preds, labels = eval_preds
|
||||
if isinstance(preds, tuple):
|
||||
preds = preds[0]
|
||||
decoded_preds = tokenizer.batch_decode(preds, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
if data_args.ignore_pad_token_for_loss:
|
||||
# Replace -100 in the labels as we can't decode them.
|
||||
labels = np.where(labels != -100, labels, tokenizer.pad_token_id)
|
||||
decoded_labels = tokenizer.batch_decode(labels, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Some simple post-processing
|
||||
decoded_preds, decoded_labels = postprocess_text(decoded_preds, decoded_labels)
|
||||
|
||||
delimiter = ", "
|
||||
|
||||
# define example evaluation
|
||||
def evaluate_example(predict_str: str, ground_str: str):
|
||||
predict_spans = predict_str.split(delimiter)
|
||||
ground_spans = ground_str.split(delimiter)
|
||||
predict_values = defaultdict(lambda: 0)
|
||||
ground_values = defaultdict(lambda: 0)
|
||||
for span in predict_spans:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
predict_values[float(span)] += 1
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
predict_values[span.strip()] += 1
|
||||
for span in ground_spans:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
ground_values[float(span)] += 1
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
ground_values[span.strip()] += 1
|
||||
is_correct = predict_values == ground_values
|
||||
return is_correct
|
||||
|
||||
def get_denotation_accuracy(predictions: List[str], references: List[str]):
|
||||
assert len(predictions) == len(references)
|
||||
correct_num = 0
|
||||
for predict_str, ground_str in zip(predictions, references):
|
||||
is_correct = evaluate_example(predict_str.lower(), ground_str.lower())
|
||||
if is_correct:
|
||||
correct_num += 1
|
||||
return correct_num / len(predictions)
|
||||
|
||||
accuracy = get_denotation_accuracy(decoded_preds, decoded_labels)
|
||||
result = {"denotation_accuracy": accuracy}
|
||||
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize our Trainer
|
||||
trainer = Seq2SeqTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=train_dataset if training_args.do_train else None,
|
||||
eval_dataset=eval_dataset if training_args.do_eval else None,
|
||||
tokenizer=tokenizer,
|
||||
data_collator=data_collator,
|
||||
compute_metrics=compute_metrics if training_args.predict_with_generate else None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.do_train:
|
||||
checkpoint = None
|
||||
if training_args.resume_from_checkpoint is not None:
|
||||
checkpoint = training_args.resume_from_checkpoint
|
||||
elif last_checkpoint is not None:
|
||||
checkpoint = last_checkpoint
|
||||
train_result = trainer.train(resume_from_checkpoint=checkpoint)
|
||||
trainer.save_model() # Saves the tokenizer too for easy upload
|
||||
|
||||
metrics = train_result.metrics
|
||||
max_train_samples = (
|
||||
data_args.max_train_samples if data_args.max_train_samples is not None else len(train_dataset)
|
||||
)
|
||||
metrics["train_samples"] = min(max_train_samples, len(train_dataset))
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.log_metrics("train", metrics)
|
||||
trainer.save_metrics("train", metrics)
|
||||
trainer.save_state()
|
||||
|
||||
# Evaluation
|
||||
results = {}
|
||||
if training_args.do_eval:
|
||||
logger.info("*** Evaluate ***")
|
||||
|
||||
metrics = trainer.evaluate(
|
||||
max_length=data_args.val_max_target_length, num_beams=data_args.num_beams, metric_key_prefix="eval"
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_eval_samples = data_args.max_eval_samples if data_args.max_eval_samples is not None else len(eval_dataset)
|
||||
metrics["eval_samples"] = min(max_eval_samples, len(eval_dataset))
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.log_metrics("eval", metrics)
|
||||
trainer.save_metrics("eval", metrics)
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.do_predict:
|
||||
logger.info("*** Predict ***")
|
||||
|
||||
predict_results = trainer.predict(
|
||||
predict_dataset,
|
||||
metric_key_prefix="predict",
|
||||
max_length=data_args.val_max_target_length,
|
||||
num_beams=data_args.num_beams,
|
||||
)
|
||||
metrics = predict_results.metrics
|
||||
max_predict_samples = (
|
||||
data_args.max_predict_samples if data_args.max_predict_samples is not None else len(predict_dataset)
|
||||
)
|
||||
metrics["predict_samples"] = min(max_predict_samples, len(predict_dataset))
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.log_metrics("predict", metrics)
|
||||
trainer.save_metrics("predict", metrics)
|
||||
|
||||
if trainer.is_world_process_zero():
|
||||
if training_args.predict_with_generate:
|
||||
predictions = tokenizer.batch_decode(
|
||||
predict_results.predictions, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
predictions = [pred.strip() for pred in predictions]
|
||||
output_prediction_file = os.path.join(training_args.output_dir, "tapex_predictions.txt")
|
||||
with open(output_prediction_file, "w") as writer:
|
||||
writer.write("\n".join(predictions))
|
||||
|
||||
return results
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _mp_fn(index):
|
||||
# For xla_spawn (TPUs)
|
||||
main()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,605 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
# Copyright 2022 The Microsoft and The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Fine-tuning the library models for tapex on table-based question answering tasks.
|
||||
Adapted from script: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/master/examples/pytorch/summarization/run_summarization.py
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from collections import defaultdict
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from functools import partial
|
||||
from typing import List, Optional
|
||||
|
||||
import nltk # Here to have a nice missing dependency error message early on
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
import transformers
|
||||
from filelock import FileLock
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
AutoConfig,
|
||||
BartForConditionalGeneration,
|
||||
DataCollatorForSeq2Seq,
|
||||
HfArgumentParser,
|
||||
Seq2SeqTrainer,
|
||||
Seq2SeqTrainingArguments,
|
||||
TapexTokenizer,
|
||||
set_seed,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from transformers.file_utils import is_offline_mode
|
||||
from transformers.trainer_utils import get_last_checkpoint, is_main_process
|
||||
from transformers.utils import check_min_version
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.17.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
nltk.data.find("tokenizers/punkt")
|
||||
except (LookupError, OSError):
|
||||
if is_offline_mode():
|
||||
raise LookupError(
|
||||
"Offline mode: run this script without TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE first to download nltk data files"
|
||||
)
|
||||
with FileLock(".lock") as lock:
|
||||
nltk.download("punkt", quiet=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class ModelArguments:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Arguments pertaining to which model/config/tokenizer we are going to fine-tune from.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
model_name_or_path: str = field(
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Path to pretrained model or model identifier from huggingface.co/models"},
|
||||
)
|
||||
config_name: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None, metadata={"help": "Pretrained config name or path if not the same as model_name"}
|
||||
)
|
||||
tokenizer_name: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Pretrained tokenizer name or path if not the same as model_name. "
|
||||
"By default we use BART-large tokenizer for TAPEX-large."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
cache_dir: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Where to store the pretrained models downloaded from huggingface.co"},
|
||||
)
|
||||
use_fast_tokenizer: bool = field(
|
||||
default=True,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Whether to use one of the fast tokenizer (backed by the tokenizers library) or not."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
model_revision: str = field(
|
||||
default="main",
|
||||
metadata={"help": "The specific model version to use (can be a branch name, tag name or commit id)."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
use_auth_token: bool = field(
|
||||
default=False,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Will use the token generated when running `transformers-cli login` (necessary to use this script "
|
||||
"with private models)."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class DataTrainingArguments:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Arguments pertaining to what data we are going to input our model for training and eval.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
dataset_name: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default="wikitablequestions", metadata={"help": "The name of the dataset to use (via the datasets library)."}
|
||||
)
|
||||
dataset_config_name: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None, metadata={"help": "The configuration name of the dataset to use (via the datasets library)."}
|
||||
)
|
||||
train_file: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None, metadata={"help": "The input training data file (a jsonlines or csv file)."}
|
||||
)
|
||||
validation_file: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "An optional input evaluation data file to evaluate the metrics (rouge) on "
|
||||
"(a jsonlines or csv file)."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
test_file: Optional[str] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "An optional input test data file to evaluate the metrics (rouge) on " "(a jsonlines or csv file)."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
overwrite_cache: bool = field(
|
||||
default=False, metadata={"help": "Overwrite the cached training and evaluation sets"}
|
||||
)
|
||||
preprocessing_num_workers: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "The number of processes to use for the preprocessing."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_source_length: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=1024,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "The maximum total input sequence length after tokenization. Sequences longer "
|
||||
"than this will be truncated, sequences shorter will be padded."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_target_length: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=128,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "The maximum total sequence length for target text after tokenization. Sequences longer "
|
||||
"than this will be truncated, sequences shorter will be padded."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
val_max_target_length: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "The maximum total sequence length for validation target text after tokenization. Sequences longer "
|
||||
"than this will be truncated, sequences shorter will be padded. Will default to `max_target_length`."
|
||||
"This argument is also used to override the ``max_length`` param of ``model.generate``, which is used "
|
||||
"during ``evaluate`` and ``predict``."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
pad_to_max_length: bool = field(
|
||||
default=False,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Whether to pad all samples to model maximum sentence length. "
|
||||
"If False, will pad the samples dynamically when batching to the maximum length in the batch. More "
|
||||
"efficient on GPU but very bad for TPU."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_train_samples: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "For debugging purposes or quicker training, truncate the number of training examples to this "
|
||||
"value if set."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_eval_samples: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "For debugging purposes or quicker training, truncate the number of evaluation examples to this "
|
||||
"value if set."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_predict_samples: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "For debugging purposes or quicker training, truncate the number of prediction examples to this "
|
||||
"value if set."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
num_beams: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Number of beams to use for evaluation. This argument will be passed to ``model.generate``, "
|
||||
"which is used during ``evaluate`` and ``predict``."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
ignore_pad_token_for_loss: bool = field(
|
||||
default=True,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Whether to ignore the tokens corresponding to padded labels in the loss computation or not."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def __post_init__(self):
|
||||
if self.dataset_name is None and self.train_file is None and self.validation_file is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Need either a dataset name or a training/validation file.")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if self.train_file is not None:
|
||||
extension = self.train_file.split(".")[-1]
|
||||
assert extension in ["csv", "json"], "`train_file` should be a csv or a json file."
|
||||
if self.validation_file is not None:
|
||||
extension = self.validation_file.split(".")[-1]
|
||||
assert extension in ["csv", "json"], "`validation_file` should be a csv or a json file."
|
||||
if self.val_max_target_length is None:
|
||||
self.val_max_target_length = self.max_target_length
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
# See all possible arguments in src/transformers/training_args.py
|
||||
# or by passing the --help flag to this script.
|
||||
# We now keep distinct sets of args, for a cleaner separation of concerns.
|
||||
|
||||
parser = HfArgumentParser((ModelArguments, DataTrainingArguments, Seq2SeqTrainingArguments))
|
||||
if len(sys.argv) == 2 and sys.argv[1].endswith(".json"):
|
||||
# If we pass only one argument to the script and it's the path to a json file,
|
||||
# let's parse it to get our arguments.
|
||||
model_args, data_args, training_args = parser.parse_json_file(json_file=os.path.abspath(sys.argv[1]))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
model_args, data_args, training_args = parser.parse_args_into_dataclasses()
|
||||
|
||||
# Detecting last checkpoint.
|
||||
last_checkpoint = None
|
||||
if os.path.isdir(training_args.output_dir) and training_args.do_train and not training_args.overwrite_output_dir:
|
||||
last_checkpoint = get_last_checkpoint(training_args.output_dir)
|
||||
if last_checkpoint is None and len(os.listdir(training_args.output_dir)) > 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Output directory ({training_args.output_dir}) already exists and is not empty. "
|
||||
"Use --overwrite_output_dir to overcome."
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif last_checkpoint is not None and training_args.resume_from_checkpoint is None:
|
||||
logger.info(
|
||||
f"Checkpoint detected, resuming training at {last_checkpoint}. To avoid this behavior, change "
|
||||
"the `--output_dir` or add `--overwrite_output_dir` to train from scratch."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Setup logging
|
||||
logging.basicConfig(
|
||||
format="%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(name)s - %(message)s",
|
||||
datefmt="%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S",
|
||||
handlers=[logging.StreamHandler(sys.stdout)],
|
||||
)
|
||||
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO if is_main_process(training_args.local_rank) else logging.WARN)
|
||||
|
||||
# Log on each process the small summary:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"Process rank: {training_args.local_rank}, device: {training_args.device}, n_gpu: {training_args.n_gpu}"
|
||||
+ f"distributed training: {bool(training_args.local_rank != -1)}, 16-bits training: {training_args.fp16}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Set the verbosity to info of the Transformers logger (on main process only):
|
||||
if is_main_process(training_args.local_rank):
|
||||
transformers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_info()
|
||||
logger.info(f"Training/evaluation parameters {training_args}")
|
||||
|
||||
# Set seed before initializing model.
|
||||
set_seed(training_args.seed)
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the datasets: you can either provide your own CSV/JSON training and evaluation files (see below)
|
||||
# or just provide the name of one of the public datasets available on the hub at https://huggingface.co/datasets/
|
||||
# (the dataset will be downloaded automatically from the datasets Hub).
|
||||
#
|
||||
# For JSON files, this script will use the `question` column for the input question and `table` column for the corresponding table.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# In distributed training, the load_dataset function guarantee that only one local process can concurrently
|
||||
# download the dataset.
|
||||
if data_args.dataset_name is not None:
|
||||
# Downloading and loading a dataset from the hub.
|
||||
datasets = load_dataset(data_args.dataset_name, data_args.dataset_config_name, cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
data_files = {}
|
||||
if data_args.train_file is not None:
|
||||
data_files["train"] = data_args.train_file
|
||||
extension = data_args.train_file.split(".")[-1]
|
||||
if data_args.validation_file is not None:
|
||||
data_files["validation"] = data_args.validation_file
|
||||
extension = data_args.validation_file.split(".")[-1]
|
||||
if data_args.test_file is not None:
|
||||
data_files["test"] = data_args.test_file
|
||||
extension = data_args.test_file.split(".")[-1]
|
||||
datasets = load_dataset(extension, data_files=data_files, cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
# See more about loading any type of standard or custom dataset (from files, python dict, pandas DataFrame, etc) at
|
||||
# https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/loading_datasets.html.
|
||||
|
||||
# Load pretrained model and tokenizer
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Distributed training:
|
||||
# The .from_pretrained methods guarantee that only one local process can concurrently
|
||||
# download model & vocab.
|
||||
|
||||
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_args.config_name if model_args.config_name else model_args.model_name_or_path,
|
||||
cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir,
|
||||
revision=model_args.model_revision,
|
||||
use_auth_token=True if model_args.use_auth_token else None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# IMPORTANT: the initial BART model's decoding is penalized by no_repeat_ngram_size, and thus
|
||||
# we should disable it here to avoid problematic generation
|
||||
config.no_repeat_ngram_size = 0
|
||||
config.max_length = 1024
|
||||
config.early_stopping = False
|
||||
|
||||
# load tapex tokenizer
|
||||
tokenizer = TapexTokenizer.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_args.tokenizer_name if model_args.tokenizer_name else model_args.model_name_or_path,
|
||||
cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir,
|
||||
use_fast=model_args.use_fast_tokenizer,
|
||||
revision=model_args.model_revision,
|
||||
use_auth_token=True if model_args.use_auth_token else None,
|
||||
add_prefix_space=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# load Bart based Tapex model (default tapex-large)
|
||||
model = BartForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_args.model_name_or_path,
|
||||
from_tf=bool(".ckpt" in model_args.model_name_or_path),
|
||||
config=config,
|
||||
cache_dir=model_args.cache_dir,
|
||||
revision=model_args.model_revision,
|
||||
use_auth_token=True if model_args.use_auth_token else None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if model.config.decoder_start_token_id is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Make sure that `config.decoder_start_token_id` is correctly defined")
|
||||
|
||||
# Preprocessing the datasets.
|
||||
# We need to tokenize inputs and targets.
|
||||
if training_args.do_train:
|
||||
column_names = datasets["train"].column_names
|
||||
elif training_args.do_eval:
|
||||
column_names = datasets["validation"].column_names
|
||||
elif training_args.do_predict:
|
||||
column_names = datasets["test"].column_names
|
||||
else:
|
||||
logger.info("There is nothing to do. Please pass `do_train`, `do_eval` and/or `do_predict`.")
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
# Temporarily set max_target_length for training.
|
||||
max_target_length = data_args.max_target_length
|
||||
padding = "max_length" if data_args.pad_to_max_length else False
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.label_smoothing_factor > 0 and not hasattr(model, "prepare_decoder_input_ids_from_labels"):
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
"label_smoothing is enabled but the `prepare_decoder_input_ids_from_labels` method is not defined for"
|
||||
f"`{model.__class__.__name__}`. This will lead to loss being calculated twice and will take up more memory"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess_tableqa_function(examples, is_training=False):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
The is_training FLAG is used to identify if we could use the supervision
|
||||
to truncate the table content if it is required.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
questions = [question.lower() for question in examples["question"]]
|
||||
example_tables = examples["table"]
|
||||
tables = [
|
||||
pd.DataFrame.from_records(example_table["rows"], columns=example_table["header"])
|
||||
for example_table in example_tables
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# using wikitablequestion's answer set
|
||||
answers = examples["answers"]
|
||||
|
||||
# IMPORTANT: we cannot pass by answers during evaluation, answers passed during training are used to
|
||||
# truncate large tables in the train set!
|
||||
if is_training:
|
||||
model_inputs = tokenizer(
|
||||
table=tables,
|
||||
query=questions,
|
||||
answer=answers,
|
||||
max_length=data_args.max_source_length,
|
||||
padding=padding,
|
||||
truncation=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
model_inputs = tokenizer(
|
||||
table=tables, query=questions, max_length=data_args.max_source_length, padding=padding, truncation=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with tokenizer.as_target_tokenizer():
|
||||
labels = tokenizer(
|
||||
answer=[", ".join(answer) for answer in answers],
|
||||
max_length=max_target_length,
|
||||
padding=padding,
|
||||
truncation=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# If we are padding here, replace all tokenizer.pad_token_id in the labels by -100 when we want to ignore
|
||||
# padding in the loss.
|
||||
if padding == "max_length" and data_args.ignore_pad_token_for_loss:
|
||||
labels["input_ids"] = [
|
||||
[(l if l != tokenizer.pad_token_id else -100) for l in label] for label in labels["input_ids"]
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
model_inputs["labels"] = labels["input_ids"]
|
||||
|
||||
return model_inputs
|
||||
|
||||
# in training, we can use the answer as extra information to truncate large tables
|
||||
preprocess_tableqa_function_training = partial(preprocess_tableqa_function, is_training=True)
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.do_train:
|
||||
if "train" not in datasets:
|
||||
raise ValueError("--do_train requires a train dataset")
|
||||
train_dataset = datasets["train"]
|
||||
if data_args.max_train_samples is not None:
|
||||
train_dataset = train_dataset.select(range(data_args.max_train_samples))
|
||||
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(
|
||||
preprocess_tableqa_function_training,
|
||||
batched=True,
|
||||
num_proc=data_args.preprocessing_num_workers,
|
||||
remove_columns=column_names,
|
||||
load_from_cache_file=not data_args.overwrite_cache,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.do_eval:
|
||||
max_target_length = data_args.val_max_target_length
|
||||
if "validation" not in datasets:
|
||||
raise ValueError("--do_eval requires a validation dataset")
|
||||
eval_dataset = datasets["validation"]
|
||||
if data_args.max_eval_samples is not None:
|
||||
eval_dataset = eval_dataset.select(range(data_args.max_eval_samples))
|
||||
eval_dataset = eval_dataset.map(
|
||||
preprocess_tableqa_function,
|
||||
batched=True,
|
||||
num_proc=data_args.preprocessing_num_workers,
|
||||
remove_columns=column_names,
|
||||
load_from_cache_file=not data_args.overwrite_cache,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.do_predict:
|
||||
max_target_length = data_args.val_max_target_length
|
||||
if "test" not in datasets:
|
||||
raise ValueError("--do_predict requires a test dataset")
|
||||
predict_dataset = datasets["test"]
|
||||
if data_args.max_predict_samples is not None:
|
||||
predict_dataset = predict_dataset.select(range(data_args.max_predict_samples))
|
||||
predict_dataset = predict_dataset.map(
|
||||
preprocess_tableqa_function,
|
||||
batched=True,
|
||||
num_proc=data_args.preprocessing_num_workers,
|
||||
remove_columns=column_names,
|
||||
load_from_cache_file=not data_args.overwrite_cache,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Data collator
|
||||
label_pad_token_id = -100 if data_args.ignore_pad_token_for_loss else tokenizer.pad_token_id
|
||||
data_collator = DataCollatorForSeq2Seq(
|
||||
tokenizer,
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
label_pad_token_id=label_pad_token_id,
|
||||
pad_to_multiple_of=8 if training_args.fp16 else None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def postprocess_text(preds, labels):
|
||||
preds = [pred.strip() for pred in preds]
|
||||
labels = [label.strip() for label in labels]
|
||||
|
||||
return preds, labels
|
||||
|
||||
def compute_metrics(eval_preds):
|
||||
preds, labels = eval_preds
|
||||
if isinstance(preds, tuple):
|
||||
preds = preds[0]
|
||||
decoded_preds = tokenizer.batch_decode(preds, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
if data_args.ignore_pad_token_for_loss:
|
||||
# Replace -100 in the labels as we can't decode them.
|
||||
labels = np.where(labels != -100, labels, tokenizer.pad_token_id)
|
||||
decoded_labels = tokenizer.batch_decode(labels, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Some simple post-processing
|
||||
decoded_preds, decoded_labels = postprocess_text(decoded_preds, decoded_labels)
|
||||
|
||||
delimiter = ", "
|
||||
|
||||
# define example evaluation
|
||||
def evaluate_example(predict_str: str, ground_str: str):
|
||||
predict_spans = predict_str.split(delimiter)
|
||||
ground_spans = ground_str.split(delimiter)
|
||||
predict_values = defaultdict(lambda: 0)
|
||||
ground_values = defaultdict(lambda: 0)
|
||||
for span in predict_spans:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
predict_values[float(span)] += 1
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
predict_values[span.strip()] += 1
|
||||
for span in ground_spans:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
ground_values[float(span)] += 1
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
ground_values[span.strip()] += 1
|
||||
_is_correct = predict_values == ground_values
|
||||
return _is_correct
|
||||
|
||||
def get_denotation_accuracy(predictions: List[str], references: List[str]):
|
||||
assert len(predictions) == len(references)
|
||||
correct_num = 0
|
||||
for predict_str, ground_str in zip(predictions, references):
|
||||
is_correct = evaluate_example(predict_str.lower(), ground_str.lower())
|
||||
if is_correct:
|
||||
correct_num += 1
|
||||
return correct_num / len(predictions)
|
||||
|
||||
accuracy = get_denotation_accuracy(decoded_preds, decoded_labels)
|
||||
result = {"denotation_accuracy": accuracy}
|
||||
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize our Trainer
|
||||
trainer = Seq2SeqTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=train_dataset if training_args.do_train else None,
|
||||
eval_dataset=eval_dataset if training_args.do_eval else None,
|
||||
tokenizer=tokenizer,
|
||||
data_collator=data_collator,
|
||||
compute_metrics=compute_metrics if training_args.predict_with_generate else None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.do_train:
|
||||
checkpoint = None
|
||||
if training_args.resume_from_checkpoint is not None:
|
||||
checkpoint = training_args.resume_from_checkpoint
|
||||
elif last_checkpoint is not None:
|
||||
checkpoint = last_checkpoint
|
||||
train_result = trainer.train(resume_from_checkpoint=checkpoint)
|
||||
trainer.save_model() # Saves the tokenizer too for easy upload
|
||||
|
||||
metrics = train_result.metrics
|
||||
max_train_samples = (
|
||||
data_args.max_train_samples if data_args.max_train_samples is not None else len(train_dataset)
|
||||
)
|
||||
metrics["train_samples"] = min(max_train_samples, len(train_dataset))
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.log_metrics("train", metrics)
|
||||
trainer.save_metrics("train", metrics)
|
||||
trainer.save_state()
|
||||
|
||||
# Evaluation
|
||||
results = {}
|
||||
if training_args.do_eval:
|
||||
logger.info("*** Evaluate ***")
|
||||
|
||||
metrics = trainer.evaluate(
|
||||
max_length=data_args.val_max_target_length, num_beams=data_args.num_beams, metric_key_prefix="eval"
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_eval_samples = data_args.max_eval_samples if data_args.max_eval_samples is not None else len(eval_dataset)
|
||||
metrics["eval_samples"] = min(max_eval_samples, len(eval_dataset))
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.log_metrics("eval", metrics)
|
||||
trainer.save_metrics("eval", metrics)
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.do_predict:
|
||||
logger.info("*** Predict ***")
|
||||
|
||||
predict_results = trainer.predict(
|
||||
predict_dataset,
|
||||
metric_key_prefix="predict",
|
||||
max_length=data_args.val_max_target_length,
|
||||
num_beams=data_args.num_beams,
|
||||
)
|
||||
metrics = predict_results.metrics
|
||||
max_predict_samples = (
|
||||
data_args.max_predict_samples if data_args.max_predict_samples is not None else len(predict_dataset)
|
||||
)
|
||||
metrics["predict_samples"] = min(max_predict_samples, len(predict_dataset))
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.log_metrics("predict", metrics)
|
||||
trainer.save_metrics("predict", metrics)
|
||||
|
||||
if trainer.is_world_process_zero():
|
||||
if training_args.predict_with_generate:
|
||||
predictions = tokenizer.batch_decode(
|
||||
predict_results.predictions, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
predictions = [pred.strip() for pred in predictions]
|
||||
output_prediction_file = os.path.join(training_args.output_dir, "tapex_predictions.txt")
|
||||
with open(output_prediction_file, "w") as writer:
|
||||
writer.write("\n".join(predictions))
|
||||
|
||||
return results
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _mp_fn(index):
|
||||
# For xla_spawn (TPUs)
|
||||
main()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
259
examples/research_projects/tapex/wikisql_utils.py
Normal file
259
examples/research_projects/tapex/wikisql_utils.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,259 @@
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
# Copyright 2022 The Microsoft, The Google and The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import dataclasses
|
||||
import enum
|
||||
import functools
|
||||
import math
|
||||
import re
|
||||
|
||||
# The following script is adapted from the script of TaPas.
|
||||
# Original: https://github.com/google-research/tapas/master/wikisql_utils.py
|
||||
from typing import Any, List, Text
|
||||
|
||||
import six
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
EMPTY_ANSWER = "none"
|
||||
EMPTY_ANSWER_AGG = "none"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _split_thousands(delimiter, value):
|
||||
split = value.split(delimiter)
|
||||
return len(split) > 1 and any(map(lambda x: len(x) == 3, split))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def convert_to_float(value):
|
||||
"""Converts value to a float using a series of increasingly complex heuristics.
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
value: object that needs to be converted. Allowed types include
|
||||
float/int/strings.
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
A float interpretation of value.
|
||||
Raises:
|
||||
ValueError if the float conversion of value fails.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if isinstance(value, float):
|
||||
return value
|
||||
if isinstance(value, int):
|
||||
return float(value)
|
||||
if not isinstance(value, six.string_types):
|
||||
raise ValueError("Argument value is not a string. Can't parse it as float")
|
||||
sanitized = value
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# Example: 1,000.7
|
||||
if "." in sanitized and "," in sanitized:
|
||||
return float(sanitized.replace(",", ""))
|
||||
# 1,000
|
||||
if "," in sanitized and _split_thousands(",", sanitized):
|
||||
return float(sanitized.replace(",", ""))
|
||||
# 5,5556
|
||||
if "," in sanitized and sanitized.count(",") == 1 and not _split_thousands(",", sanitized):
|
||||
return float(sanitized.replace(",", "."))
|
||||
# 0.0.0.1
|
||||
if sanitized.count(".") > 1:
|
||||
return float(sanitized.replace(".", ""))
|
||||
# 0,0,0,1
|
||||
if sanitized.count(",") > 1:
|
||||
return float(sanitized.replace(",", ""))
|
||||
return float(sanitized)
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
# Avoid adding the sanitized value in the error message.
|
||||
raise ValueError("Unable to convert value to float")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _normalize_float(answer):
|
||||
if answer is None:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
try:
|
||||
value = convert_to_float(answer)
|
||||
if isinstance(value, float) and math.isnan(value):
|
||||
return None
|
||||
return value
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
return answer.lower()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
_TYPE_CONVERTER = {
|
||||
"text": lambda x: x,
|
||||
"real": convert_to_float,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class _Aggregation(enum.Enum):
|
||||
"""Aggregations as defined by WikiSQL. Indexes match the data."""
|
||||
|
||||
NONE = 0
|
||||
MAX = 1
|
||||
MIN = 2
|
||||
COUNT = 3
|
||||
SUM = 4
|
||||
AVERAGE = 5
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class _Operator(enum.Enum):
|
||||
"""The boolean operators used by WikiSQL. Indexes match the data."""
|
||||
|
||||
EQUALS = 0
|
||||
GREATER = 1
|
||||
LESSER = 2
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclasses.dataclass
|
||||
class _Condition:
|
||||
"""Represents an SQL where clauses (e.g A = "a" or B > 5)."""
|
||||
|
||||
column: Text
|
||||
operator: _Operator
|
||||
cmp_value: Any
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
_TOKENIZER = re.compile(r"\w+|[^\w\s]+", re.UNICODE | re.MULTILINE | re.DOTALL)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _normalize_for_match(x):
|
||||
return [t for t in _TOKENIZER.findall(x.lower())]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _compare(operator, src, tgt):
|
||||
if operator == _Operator.EQUALS:
|
||||
return src == tgt
|
||||
elif operator == _Operator.GREATER:
|
||||
return src > tgt
|
||||
elif operator == _Operator.LESSER:
|
||||
return src < tgt
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Unknown operator: {operator}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _parse_value(table, column, cell_value):
|
||||
"""Convert numeric values to floats and keeps everything else as string."""
|
||||
types = table["types"]
|
||||
return _TYPE_CONVERTER[types[column]](cell_value)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _is_string(x):
|
||||
return isinstance(x, str)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _respect_conditions(table, row, conditions):
|
||||
"""True if 'row' satisfies all 'conditions'."""
|
||||
for cond in conditions:
|
||||
table_value = row[cond.column]
|
||||
|
||||
cmp_value = _parse_value(table, cond.column, cond.cmp_value)
|
||||
|
||||
if _is_string(table_value) and _is_string(cmp_value):
|
||||
table_value = _normalize_for_match(table_value)
|
||||
cmp_value = _normalize_for_match(cmp_value)
|
||||
|
||||
if not isinstance(table_value, type(cmp_value)):
|
||||
raise ValueError("Type difference {} != {}".format(type(table_value), type(cmp_value)))
|
||||
|
||||
if not _compare(cond.operator, table_value, cmp_value):
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_float_answer(table, answer_coordinates, aggregation_op):
|
||||
"""Applies operation to produce reference float answer."""
|
||||
if not answer_coordinates:
|
||||
if aggregation_op == _Aggregation.COUNT:
|
||||
return 0.0
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return EMPTY_ANSWER_AGG
|
||||
|
||||
# Count can support non numeric answers.
|
||||
if aggregation_op == _Aggregation.COUNT:
|
||||
return float(len(answer_coordinates))
|
||||
|
||||
# If we have just one answer, if float returns it or try a conversion.
|
||||
values = [table["rows"][i][j] for (i, j) in answer_coordinates]
|
||||
if len(answer_coordinates) == 1:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return convert_to_float(values[0])
|
||||
except ValueError as e:
|
||||
if aggregation_op != _Aggregation.NONE:
|
||||
raise e
|
||||
|
||||
if aggregation_op == _Aggregation.NONE:
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
# Other aggregation only support numeric values. Bail out if we have strings.
|
||||
if not all((isinstance(v, (int, float)) for v in values)):
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
if aggregation_op == _Aggregation.SUM:
|
||||
return float(sum(values))
|
||||
elif aggregation_op == _Aggregation.AVERAGE:
|
||||
return sum(values) / len(answer_coordinates)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Unknown aggregation: {aggregation_op}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_answer_coordinates(table, sql_query):
|
||||
"""Retrieves references coordinates by executing SQL."""
|
||||
# MAX and MIN are automatically supported by the model.
|
||||
aggregation_op_index = sql_query["agg"]
|
||||
if aggregation_op_index >= 3:
|
||||
aggregation_op = _Aggregation(aggregation_op_index)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
aggregation_op = _Aggregation.NONE
|
||||
|
||||
target_column = sql_query["sel"]
|
||||
conditions = [
|
||||
_Condition(column, _Operator(operator), cmp_value)
|
||||
for column, operator, cmp_value in zip(
|
||||
sql_query["conds"]["column_index"], sql_query["conds"]["operator_index"], sql_query["conds"]["condition"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
indices = []
|
||||
for row in range(len(table["rows"])):
|
||||
if _respect_conditions(table, table["rows"][row], conditions):
|
||||
indices.append((row, target_column))
|
||||
|
||||
if not indices:
|
||||
return [], aggregation_op
|
||||
|
||||
if len(indices) == 1:
|
||||
return indices, aggregation_op
|
||||
|
||||
# Parsing of MIN/MAX.
|
||||
if aggregation_op_index in (1, 2):
|
||||
operators = {2: min, 1: max}
|
||||
values = [(table["rows"][i][j], index) for index, (i, j) in enumerate(indices)]
|
||||
reduced = functools.reduce(operators[sql_query["agg"]], values)
|
||||
|
||||
ret = [indices[reduced[1]]]
|
||||
return ret, _Aggregation.NONE
|
||||
|
||||
return indices, aggregation_op
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_answer_text(table, answer_coordinates, float_answer):
|
||||
if float_answer is not None:
|
||||
return [str(float_answer)]
|
||||
return [str(table["real_rows"][r][c]) for r, c in answer_coordinates]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def retrieve_wikisql_query_answer_tapas(table, example) -> List:
|
||||
answer_coordinates, aggregation_op = _get_answer_coordinates(table, example)
|
||||
float_answer = _get_float_answer(table, answer_coordinates, aggregation_op)
|
||||
answer_text = _get_answer_text(table, answer_coordinates, float_answer)
|
||||
# keep the original data the same with TaPas
|
||||
if len(answer_text) == 0:
|
||||
answer_text = [EMPTY_ANSWER]
|
||||
return answer_text
|
||||
@ -267,6 +267,7 @@ _import_structure = {
|
||||
"models.swin": ["SWIN_PRETRAINED_CONFIG_ARCHIVE_MAP", "SwinConfig"],
|
||||
"models.t5": ["T5_PRETRAINED_CONFIG_ARCHIVE_MAP", "T5Config"],
|
||||
"models.tapas": ["TAPAS_PRETRAINED_CONFIG_ARCHIVE_MAP", "TapasConfig", "TapasTokenizer"],
|
||||
"models.tapex": ["TapexTokenizer"],
|
||||
"models.transfo_xl": [
|
||||
"TRANSFO_XL_PRETRAINED_CONFIG_ARCHIVE_MAP",
|
||||
"TransfoXLConfig",
|
||||
@ -2643,6 +2644,7 @@ if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
from .models.swin import SWIN_PRETRAINED_CONFIG_ARCHIVE_MAP, SwinConfig
|
||||
from .models.t5 import T5_PRETRAINED_CONFIG_ARCHIVE_MAP, T5Config
|
||||
from .models.tapas import TAPAS_PRETRAINED_CONFIG_ARCHIVE_MAP, TapasConfig, TapasTokenizer
|
||||
from .models.tapex import TapexTokenizer
|
||||
from .models.transfo_xl import (
|
||||
TRANSFO_XL_PRETRAINED_CONFIG_ARCHIVE_MAP,
|
||||
TransfoXLConfig,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -113,6 +113,7 @@ from . import (
|
||||
swin,
|
||||
t5,
|
||||
tapas,
|
||||
tapex,
|
||||
transfo_xl,
|
||||
trocr,
|
||||
unispeech,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -29,6 +29,7 @@ logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
CONFIG_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
[
|
||||
# Add configs here
|
||||
("tapex", "BartConfig"),
|
||||
("dpt", "DPTConfig"),
|
||||
("decision_transformer", "DecisionTransformerConfig"),
|
||||
("glpn", "GLPNConfig"),
|
||||
@ -135,7 +136,7 @@ CONFIG_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
|
||||
CONFIG_ARCHIVE_MAP_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
[
|
||||
# Add archive maps here
|
||||
# Add archive maps here)
|
||||
("dpt", "DPT_PRETRAINED_CONFIG_ARCHIVE_MAP"),
|
||||
("glpn", "GLPN_PRETRAINED_CONFIG_ARCHIVE_MAP"),
|
||||
("maskformer", "MASKFORMER_PRETRAINED_CONFIG_ARCHIVE_MAP"),
|
||||
@ -228,6 +229,7 @@ CONFIG_ARCHIVE_MAP_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
MODEL_NAMES_MAPPING = OrderedDict(
|
||||
[
|
||||
# Add full (and cased) model names here
|
||||
("tapex", "TAPEX"),
|
||||
("dpt", "DPT"),
|
||||
("decision_transformer", "Decision Transformer"),
|
||||
("glpn", "GLPN"),
|
||||
|
||||
@ -390,6 +390,7 @@ MODEL_FOR_OBJECT_DETECTION_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_SEQ_TO_SEQ_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
[
|
||||
# Model for Seq2Seq Causal LM mapping
|
||||
("tapex", "BartForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("plbart", "PLBartForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("bigbird_pegasus", "BigBirdPegasusForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("m2m_100", "M2M100ForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
@ -419,6 +420,7 @@ MODEL_FOR_SPEECH_SEQ_2_SEQ_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
MODEL_FOR_SEQUENCE_CLASSIFICATION_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
[
|
||||
# Model for Sequence Classification mapping
|
||||
("tapex", "BartForSequenceClassification"),
|
||||
("yoso", "YosoForSequenceClassification"),
|
||||
("nystromformer", "NystromformerForSequenceClassification"),
|
||||
("plbart", "PLBartForSequenceClassification"),
|
||||
|
||||
@ -105,6 +105,7 @@ else:
|
||||
("marian", ("MarianTokenizer" if is_sentencepiece_available() else None, None)),
|
||||
("blenderbot-small", ("BlenderbotSmallTokenizer", None)),
|
||||
("blenderbot", ("BlenderbotTokenizer", "BlenderbotTokenizerFast")),
|
||||
("tapex", ("TapexTokenizer", None)),
|
||||
("bart", ("BartTokenizer", "BartTokenizerFast")),
|
||||
("longformer", ("LongformerTokenizer", "LongformerTokenizerFast" if is_tokenizers_available() else None)),
|
||||
("roberta", ("RobertaTokenizer", "RobertaTokenizerFast" if is_tokenizers_available() else None)),
|
||||
|
||||
36
src/transformers/models/tapex/__init__.py
Normal file
36
src/transformers/models/tapex/__init__.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
# flake8: noqa
|
||||
# There's no way to ignore "F401 '...' imported but unused" warnings in this
|
||||
# module, but to preserve other warnings. So, don't check this module at all.
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
|
||||
|
||||
# rely on isort to merge the imports
|
||||
from ...file_utils import _LazyModule
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
_import_structure = {
|
||||
"tokenization_tapex": ["TapexTokenizer"],
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
from .tokenization_tapex import TapexTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
|
||||
sys.modules[__name__] = _LazyModule(__name__, globals()["__file__"], _import_structure)
|
||||
1512
src/transformers/models/tapex/tokenization_tapex.py
Normal file
1512
src/transformers/models/tapex/tokenization_tapex.py
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
0
tests/tapex/__init__.py
Normal file
0
tests/tapex/__init__.py
Normal file
909
tests/tapex/test_tokenization_tapex.py
Normal file
909
tests/tapex/test_tokenization_tapex.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,909 @@
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
# Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import shutil
|
||||
import tempfile
|
||||
import unittest
|
||||
from typing import List
|
||||
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers import AddedToken, TapexTokenizer
|
||||
from transformers.models.tapex.tokenization_tapex import VOCAB_FILES_NAMES
|
||||
from transformers.testing_utils import is_pt_tf_cross_test, require_pandas, slow
|
||||
|
||||
from ..test_tokenization_common import TokenizerTesterMixin
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@require_pandas
|
||||
class TapexTokenizationTest(TokenizerTesterMixin, unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
tokenizer_class = TapexTokenizer
|
||||
test_rust_tokenizer = False
|
||||
from_pretrained_kwargs = {"cls_token": "<s>"}
|
||||
test_seq2seq = False
|
||||
|
||||
def setUp(self):
|
||||
super().setUp()
|
||||
|
||||
# Adapted from Sennrich et al. 2015 and https://github.com/rsennrich/subword-nmt
|
||||
# fmt: off
|
||||
vocab = ["l", "o", "w", "e", "r", "s", "t", "i", "d", "n", "\u0120", "\u0120l", "\u0120n", "\u0120lo", "\u0120low", "er", "\u0120lowest", "\u0120newer", "\u0120wider", "<unk>"] # noqa: E231
|
||||
# fmt: on
|
||||
vocab_tokens = dict(zip(vocab, range(len(vocab))))
|
||||
merges = ["#version: 0.2", "\u0120 l", "\u0120l o", "\u0120lo w", "e r", ""]
|
||||
self.special_tokens_map = {"unk_token": "<unk>"}
|
||||
|
||||
self.vocab_file = os.path.join(self.tmpdirname, VOCAB_FILES_NAMES["vocab_file"])
|
||||
self.merges_file = os.path.join(self.tmpdirname, VOCAB_FILES_NAMES["merges_file"])
|
||||
with open(self.vocab_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fp:
|
||||
fp.write(json.dumps(vocab_tokens) + "\n")
|
||||
with open(self.merges_file, "w", encoding="utf-8") as fp:
|
||||
fp.write("\n".join(merges))
|
||||
|
||||
def get_table(self, tokenizer, length=5):
|
||||
toks = [tokenizer.decode([i], clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False) for i in range(len(tokenizer))]
|
||||
|
||||
if length == 0:
|
||||
data = {}
|
||||
else:
|
||||
data = {toks[0]: [toks[tok] for tok in range(1, length)]}
|
||||
|
||||
table = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(data)
|
||||
|
||||
return table
|
||||
|
||||
def get_table_and_query(self, tokenizer, length=5):
|
||||
toks = [tokenizer.decode([i], clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False) for i in range(len(tokenizer))]
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=length - 3)
|
||||
query = " ".join(toks[:3])
|
||||
|
||||
return table, query
|
||||
|
||||
def get_clean_sequence(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
tokenizer,
|
||||
with_prefix_space=False,
|
||||
max_length=20,
|
||||
min_length=5,
|
||||
empty_table: bool = False,
|
||||
add_special_tokens: bool = True,
|
||||
return_table_and_query: bool = False,
|
||||
):
|
||||
|
||||
toks = [tokenizer.decode([i], clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False) for i in range(len(tokenizer))]
|
||||
|
||||
if empty_table:
|
||||
table = pd.DataFrame.from_dict({})
|
||||
query = " ".join(toks[:min_length])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
data = {toks[0]: [toks[tok] for tok in range(1, min_length - 3)]}
|
||||
table = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(data)
|
||||
query = " ".join(toks[:3])
|
||||
|
||||
output_ids = tokenizer.encode(table, query, add_special_tokens=add_special_tokens)
|
||||
output_txt = tokenizer.decode(output_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
if len(output_ids) < min_length:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Update the code to generate the sequences so that they are larger")
|
||||
if len(output_ids) > max_length:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Update the code to generate the sequences so that they are smaller")
|
||||
|
||||
if return_table_and_query:
|
||||
return output_txt, output_ids, table, query
|
||||
|
||||
return output_txt, output_ids
|
||||
|
||||
def get_tokenizer(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
kwargs.update(self.special_tokens_map)
|
||||
return self.tokenizer_class.from_pretrained(self.tmpdirname, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def get_input_output_texts(self, tokenizer):
|
||||
input_text = "lower newer"
|
||||
output_text = "lower newer"
|
||||
return input_text, output_text
|
||||
|
||||
def test_full_tokenizer_roberta(self):
|
||||
tokenizer = self.tokenizer_class(self.vocab_file, self.merges_file, **self.special_tokens_map)
|
||||
text = "lower newer"
|
||||
bpe_tokens = ["l", "o", "w", "er", "\u0120", "n", "e", "w", "er"]
|
||||
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(text)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(tokens, bpe_tokens)
|
||||
|
||||
input_tokens = tokens + [tokenizer.unk_token]
|
||||
input_bpe_tokens = [0, 1, 2, 15, 10, 9, 3, 2, 15, 19]
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(input_tokens), input_bpe_tokens)
|
||||
|
||||
def roberta_dict_integration_testing(self):
|
||||
tokenizer = self.get_tokenizer()
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(tokenizer.encode("Hello world!", add_special_tokens=False), [0, 31414, 232, 328, 2])
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(
|
||||
tokenizer.encode("Hello world! cécé herlolip 418", add_special_tokens=False),
|
||||
[0, 31414, 232, 328, 740, 1140, 12695, 69, 46078, 1588, 2],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_add_tokens_tokenizer(self):
|
||||
tokenizers: List[TapexTokenizer] = self.get_tokenizers(do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
vocab_size = tokenizer.vocab_size
|
||||
all_size = len(tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertNotEqual(vocab_size, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
# We usually have added tokens from the start in tests because our vocab fixtures are
|
||||
# smaller than the original vocabs - let's not assert this
|
||||
# self.assertEqual(vocab_size, all_size)
|
||||
|
||||
new_toks = ["aaaaa bbbbbb", "cccccccccdddddddd"]
|
||||
added_toks = tokenizer.add_tokens(new_toks)
|
||||
vocab_size_2 = tokenizer.vocab_size
|
||||
all_size_2 = len(tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertNotEqual(vocab_size_2, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(vocab_size, vocab_size_2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(added_toks, len(new_toks))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(all_size_2, all_size + len(new_toks))
|
||||
|
||||
tokens = tokenizer.encode(table, "aaaaa bbbbbb low cccccccccdddddddd l", add_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertGreaterEqual(len(tokens), 4)
|
||||
self.assertGreater(tokens[0], tokenizer.vocab_size - 1)
|
||||
self.assertGreater(tokens[-2], tokenizer.vocab_size - 1)
|
||||
|
||||
new_toks_2 = {"eos_token": ">>>>|||<||<<|<<", "pad_token": "<<<<<|||>|>>>>|>"}
|
||||
added_toks_2 = tokenizer.add_special_tokens(new_toks_2)
|
||||
vocab_size_3 = tokenizer.vocab_size
|
||||
all_size_3 = len(tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertNotEqual(vocab_size_3, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(vocab_size, vocab_size_3)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(added_toks_2, len(new_toks_2))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(all_size_3, all_size_2 + len(new_toks_2))
|
||||
|
||||
tokens = tokenizer.encode(
|
||||
table,
|
||||
">>>>|||<||<<|<< aaaaabbbbbb low cccccccccdddddddd <<<<<|||>|>>>>|> l",
|
||||
add_special_tokens=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertGreaterEqual(len(tokens), 6)
|
||||
self.assertGreater(tokens[0], tokenizer.vocab_size - 1)
|
||||
self.assertGreater(tokens[0], tokens[1])
|
||||
self.assertGreater(tokens[-2], tokenizer.vocab_size - 1)
|
||||
self.assertGreater(tokens[-2], tokens[-3])
|
||||
self.assertEqual(tokens[0], tokenizer.eos_token_id)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(tokens[-2], tokenizer.pad_token_id)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_token_type_ids(self):
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers()
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
empty_table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
seq_0 = "Test this method."
|
||||
|
||||
# We want to have sequence 0 and sequence 1 are tagged
|
||||
# respectively with 0 and 1 token_ids
|
||||
# (regardless of whether the model use token type ids)
|
||||
# We use this assumption in the QA pipeline among other place
|
||||
output = tokenizer(empty_table, seq_0, return_token_type_ids=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Assert that the token type IDs have the same length as the input IDs
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(output["token_type_ids"]), len(output["input_ids"]))
|
||||
self.assertIn(0, output["token_type_ids"])
|
||||
|
||||
def test_add_special_tokens(self):
|
||||
tokenizers: List[TapexTokenizer] = self.get_tokenizers(do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
input_table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
|
||||
special_token = "[SPECIAL_TOKEN]"
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer.add_special_tokens({"cls_token": special_token})
|
||||
encoded_special_token = tokenizer.encode(input_table, special_token, add_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(encoded_special_token), 1)
|
||||
|
||||
decoded = tokenizer.decode(encoded_special_token, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(special_token not in decoded)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_batch_encode_plus_overflowing_tokens(self):
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers(do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=10)
|
||||
string_sequences = ["Testing the prepare_for_model method.", "Test"]
|
||||
|
||||
if tokenizer.pad_token is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.add_special_tokens({"pad_token": "[PAD]"})
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(
|
||||
table, string_sequences, return_overflowing_tokens=True, truncation=True, padding=True, max_length=3
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@is_pt_tf_cross_test
|
||||
def test_batch_encode_plus_tensors(self):
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers(do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
sequences = [
|
||||
"Testing batch encode plus",
|
||||
"Testing batch encode plus with different sequence lengths",
|
||||
"Testing batch encode plus with different sequence lengths correctly pads",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
|
||||
# A Tensor cannot be build by sequences which are not the same size
|
||||
self.assertRaises(ValueError, tokenizer.batch_encode_plus, table, sequences, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
self.assertRaises(ValueError, tokenizer.batch_encode_plus, table, sequences, return_tensors="tf")
|
||||
|
||||
if tokenizer.pad_token_id is None:
|
||||
self.assertRaises(
|
||||
ValueError,
|
||||
tokenizer.batch_encode_plus,
|
||||
table,
|
||||
sequences,
|
||||
padding=True,
|
||||
return_tensors="pt",
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.assertRaises(
|
||||
ValueError,
|
||||
tokenizer.batch_encode_plus,
|
||||
table,
|
||||
sequences,
|
||||
padding="longest",
|
||||
return_tensors="tf",
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
pytorch_tensor = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(table, sequences, padding=True, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
tensorflow_tensor = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(
|
||||
table, sequences, padding="longest", return_tensors="tf"
|
||||
)
|
||||
encoded_sequences = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(table, sequences, padding=True)
|
||||
|
||||
for key in encoded_sequences.keys():
|
||||
pytorch_value = pytorch_tensor[key].tolist()
|
||||
tensorflow_value = tensorflow_tensor[key].numpy().tolist()
|
||||
encoded_value = encoded_sequences[key]
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual(pytorch_value, tensorflow_value, encoded_value)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_call(self):
|
||||
# Tests that all call wrap to encode_plus and batch_encode_plus
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers(do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
sequences = [
|
||||
"Testing batch encode plus",
|
||||
"Testing batch encode plus with different sequence lengths",
|
||||
"Testing batch encode plus with different sequence lengths correctly pads",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# Test not batched
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
encoded_sequences_1 = tokenizer.encode_plus(table, sequences[0])
|
||||
encoded_sequences_2 = tokenizer(table, sequences[0])
|
||||
self.assertEqual(encoded_sequences_1, encoded_sequences_2)
|
||||
|
||||
# Test not batched pairs
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=10)
|
||||
encoded_sequences_1 = tokenizer.encode_plus(table, sequences[1])
|
||||
encoded_sequences_2 = tokenizer(table, sequences[1])
|
||||
self.assertEqual(encoded_sequences_1, encoded_sequences_2)
|
||||
|
||||
# Test batched
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
encoded_sequences_1 = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(table, sequences)
|
||||
encoded_sequences_2 = tokenizer(table, sequences)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(encoded_sequences_1, encoded_sequences_2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_internal_consistency(self):
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers()
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
input_text, output_text = self.get_input_output_texts(tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(input_text)
|
||||
ids = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens)
|
||||
ids_2 = tokenizer.encode(table, input_text, add_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(ids, ids_2)
|
||||
|
||||
tokens_2 = tokenizer.convert_ids_to_tokens(ids)
|
||||
self.assertNotEqual(len(tokens_2), 0)
|
||||
text_2 = tokenizer.decode(ids)
|
||||
self.assertIsInstance(text_2, str)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual(text_2, output_text)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_save_and_load_tokenizer(self):
|
||||
# safety check on max_len default value so we are sure the test works
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers()
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
self.assertNotEqual(tokenizer.model_max_length, 42)
|
||||
|
||||
# Now let's start the test
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers()
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
# Isolate this from the other tests because we save additional tokens/etc
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
tmpdirname = tempfile.mkdtemp()
|
||||
|
||||
sample_text = " He is very happy, UNwant\u00E9d,running"
|
||||
before_tokens = tokenizer.encode(table, sample_text, add_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
before_vocab = tokenizer.get_vocab()
|
||||
tokenizer.save_pretrained(tmpdirname)
|
||||
|
||||
after_tokenizer = tokenizer.__class__.from_pretrained(tmpdirname)
|
||||
after_tokens = after_tokenizer.encode(table, sample_text, add_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
after_vocab = after_tokenizer.get_vocab()
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(before_tokens, after_tokens)
|
||||
self.assertDictEqual(before_vocab, after_vocab)
|
||||
|
||||
shutil.rmtree(tmpdirname)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_number_of_added_tokens(self):
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers(do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
|
||||
table, query = self.get_table_and_query(tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
sequences = tokenizer.encode(table, query, add_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
attached_sequences = tokenizer.encode(table, query, add_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual(2, len(attached_sequences) - len(sequences))
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skip("TAPEX cannot handle `prepare_for_model` without passing by `encode_plus` or `batch_encode_plus`")
|
||||
def test_prepare_for_model(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skip("TAPEX tokenizer does not support pairs.")
|
||||
def test_maximum_encoding_length_pair_input(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skip("TAPEX tokenizer does not support pairs.")
|
||||
def test_maximum_encoding_length_single_input(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skip("Not implemented")
|
||||
def test_right_and_left_truncation(self):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
def test_encode_decode_with_spaces(self):
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers(do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
|
||||
new_toks = [AddedToken("[ABC]", normalized=False), AddedToken("[DEF]", normalized=False)]
|
||||
tokenizer.add_tokens(new_toks)
|
||||
input = "[ABC][DEF][ABC][DEF]"
|
||||
if self.space_between_special_tokens:
|
||||
output = "[ABC] [DEF] [ABC] [DEF]"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
output = input
|
||||
encoded = tokenizer.encode(table, input, add_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
decoded = tokenizer.decode(encoded, spaces_between_special_tokens=self.space_between_special_tokens)
|
||||
self.assertIn(decoded, [output, output.lower()])
|
||||
|
||||
def test_tokenize_special_tokens(self):
|
||||
"""Test `tokenize` with special tokens."""
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers(fast=True, do_lower_case=True)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
SPECIAL_TOKEN_1 = "[SPECIAL_TOKEN_1]"
|
||||
SPECIAL_TOKEN_2 = "[SPECIAL_TOKEN_2]"
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO:
|
||||
# Can we combine `unique_no_split_tokens` and `all_special_tokens`(and properties related to it)
|
||||
# with one variable(property) for a better maintainability?
|
||||
|
||||
# `add_tokens` method stores special tokens only in `tokenizer.unique_no_split_tokens`. (in tokenization_utils.py)
|
||||
tokenizer.add_tokens([SPECIAL_TOKEN_1], special_tokens=True)
|
||||
# `add_special_tokens` method stores special tokens in `tokenizer.additional_special_tokens`,
|
||||
# which also occur in `tokenizer.all_special_tokens`. (in tokenization_utils_base.py)
|
||||
tokenizer.add_special_tokens({"additional_special_tokens": [SPECIAL_TOKEN_2]})
|
||||
|
||||
token_1 = tokenizer.tokenize(SPECIAL_TOKEN_1)
|
||||
token_2 = tokenizer.tokenize(SPECIAL_TOKEN_2)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(token_1), 1)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(token_2), 1)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(token_1[0], SPECIAL_TOKEN_1)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(token_2[0], SPECIAL_TOKEN_2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_special_tokens_mask(self):
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers(do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
sequence_0 = "Encode this."
|
||||
# Testing single inputs
|
||||
encoded_sequence = tokenizer.encode(table, sequence_0, add_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
encoded_sequence_dict = tokenizer.encode_plus(
|
||||
table, sequence_0, add_special_tokens=True, return_special_tokens_mask=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
encoded_sequence_w_special = encoded_sequence_dict["input_ids"]
|
||||
special_tokens_mask = encoded_sequence_dict["special_tokens_mask"]
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(special_tokens_mask), len(encoded_sequence_w_special))
|
||||
|
||||
filtered_sequence = [x for i, x in enumerate(encoded_sequence_w_special) if not special_tokens_mask[i]]
|
||||
self.assertEqual(encoded_sequence, filtered_sequence)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_padding_to_max_length(self):
|
||||
"""We keep this test for backward compatibility but it should be removed when `pad_to_max_length` will be deprecated"""
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers(do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer)
|
||||
sequence = "Sequence"
|
||||
padding_size = 10
|
||||
|
||||
# check correct behaviour if no pad_token_id exists and add it eventually
|
||||
self._check_no_pad_token_padding(tokenizer, sequence)
|
||||
|
||||
padding_idx = tokenizer.pad_token_id
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that it correctly pads when a maximum length is specified along with the padding flag set to True
|
||||
tokenizer.padding_side = "right"
|
||||
encoded_sequence = tokenizer.encode(table, sequence)
|
||||
sequence_length = len(encoded_sequence)
|
||||
padded_sequence = tokenizer.encode(
|
||||
table,
|
||||
sequence,
|
||||
max_length=sequence_length + padding_size,
|
||||
pad_to_max_length=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
padded_sequence_length = len(padded_sequence)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(sequence_length + padding_size, padded_sequence_length)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(encoded_sequence + [padding_idx] * padding_size, padded_sequence)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that nothing is done when a maximum length is not specified
|
||||
encoded_sequence = tokenizer.encode(table, sequence)
|
||||
sequence_length = len(encoded_sequence)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer.padding_side = "right"
|
||||
padded_sequence_right = tokenizer.encode(table, sequence, pad_to_max_length=True)
|
||||
padded_sequence_right_length = len(padded_sequence_right)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(sequence_length, padded_sequence_right_length)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(encoded_sequence, padded_sequence_right)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_padding_to_multiple_of(self):
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers()
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
if tokenizer.pad_token is None:
|
||||
self.skipTest("No padding token.")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
empty_tokens = tokenizer(table, padding=True, pad_to_multiple_of=8)
|
||||
normal_tokens = tokenizer(table, "This is a sample input", padding=True, pad_to_multiple_of=8)
|
||||
for key, value in empty_tokens.items():
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(value) % 8, 0, f"BatchEncoding.{key} is not multiple of 8")
|
||||
for key, value in normal_tokens.items():
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(value) % 8, 0, f"BatchEncoding.{key} is not multiple of 8")
|
||||
|
||||
normal_tokens = tokenizer(table, "This", pad_to_multiple_of=8)
|
||||
for key, value in normal_tokens.items():
|
||||
self.assertNotEqual(len(value) % 8, 0, f"BatchEncoding.{key} is not multiple of 8")
|
||||
|
||||
# Should also work with truncation
|
||||
normal_tokens = tokenizer(table, "This", padding=True, truncation=True, pad_to_multiple_of=8)
|
||||
for key, value in normal_tokens.items():
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(value) % 8, 0, f"BatchEncoding.{key} is not multiple of 8")
|
||||
|
||||
def test_right_and_left_padding(self):
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers(do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
sequence = "Sequence"
|
||||
padding_size = 10
|
||||
|
||||
# check correct behaviour if no pad_token_id exists and add it eventually
|
||||
self._check_no_pad_token_padding(tokenizer, sequence)
|
||||
|
||||
padding_idx = tokenizer.pad_token_id
|
||||
|
||||
# RIGHT PADDING - Check that it correctly pads when a maximum length is specified along with the padding flag set to True
|
||||
tokenizer.padding_side = "right"
|
||||
encoded_sequence = tokenizer.encode(table, sequence)
|
||||
sequence_length = len(encoded_sequence)
|
||||
padded_sequence = tokenizer.encode(
|
||||
table, sequence, max_length=sequence_length + padding_size, padding="max_length"
|
||||
)
|
||||
padded_sequence_length = len(padded_sequence)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(sequence_length + padding_size, padded_sequence_length)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(encoded_sequence + [padding_idx] * padding_size, padded_sequence)
|
||||
|
||||
# LEFT PADDING - Check that it correctly pads when a maximum length is specified along with the padding flag set to True
|
||||
tokenizer.padding_side = "left"
|
||||
encoded_sequence = tokenizer.encode(table, sequence)
|
||||
sequence_length = len(encoded_sequence)
|
||||
padded_sequence = tokenizer.encode(
|
||||
table, sequence, max_length=sequence_length + padding_size, padding="max_length"
|
||||
)
|
||||
padded_sequence_length = len(padded_sequence)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(sequence_length + padding_size, padded_sequence_length)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual([padding_idx] * padding_size + encoded_sequence, padded_sequence)
|
||||
|
||||
# RIGHT & LEFT PADDING - Check that nothing is done for 'longest' and 'no_padding'
|
||||
encoded_sequence = tokenizer.encode(table, sequence)
|
||||
sequence_length = len(encoded_sequence)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer.padding_side = "right"
|
||||
padded_sequence_right = tokenizer.encode(table, sequence, padding=True)
|
||||
padded_sequence_right_length = len(padded_sequence_right)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(sequence_length, padded_sequence_right_length)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(encoded_sequence, padded_sequence_right)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer.padding_side = "left"
|
||||
padded_sequence_left = tokenizer.encode(table, sequence, padding="longest")
|
||||
padded_sequence_left_length = len(padded_sequence_left)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(sequence_length, padded_sequence_left_length)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(encoded_sequence, padded_sequence_left)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer.padding_side = "right"
|
||||
padded_sequence_right = tokenizer.encode(table, sequence)
|
||||
padded_sequence_right_length = len(padded_sequence_right)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(sequence_length, padded_sequence_right_length)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(encoded_sequence, padded_sequence_right)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer.padding_side = "left"
|
||||
padded_sequence_left = tokenizer.encode(table, sequence, padding=False)
|
||||
padded_sequence_left_length = len(padded_sequence_left)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(sequence_length, padded_sequence_left_length)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(encoded_sequence, padded_sequence_left)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_encode_plus_with_padding(self):
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers(do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
sequence = "Sequence"
|
||||
|
||||
# check correct behaviour if no pad_token_id exists and add it eventually
|
||||
self._check_no_pad_token_padding(tokenizer, sequence)
|
||||
|
||||
padding_size = 10
|
||||
padding_idx = tokenizer.pad_token_id
|
||||
token_type_padding_idx = tokenizer.pad_token_type_id
|
||||
|
||||
encoded_sequence = tokenizer.encode_plus(table, sequence, return_special_tokens_mask=True)
|
||||
input_ids = encoded_sequence["input_ids"]
|
||||
special_tokens_mask = encoded_sequence["special_tokens_mask"]
|
||||
sequence_length = len(input_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
# Test 'longest' and 'no_padding' don't do anything
|
||||
tokenizer.padding_side = "right"
|
||||
|
||||
not_padded_sequence = tokenizer.encode_plus(
|
||||
table,
|
||||
sequence,
|
||||
padding=False,
|
||||
return_special_tokens_mask=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
not_padded_input_ids = not_padded_sequence["input_ids"]
|
||||
|
||||
not_padded_special_tokens_mask = not_padded_sequence["special_tokens_mask"]
|
||||
not_padded_sequence_length = len(not_padded_input_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual(sequence_length, not_padded_sequence_length)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(input_ids, not_padded_input_ids)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(special_tokens_mask, not_padded_special_tokens_mask)
|
||||
|
||||
not_padded_sequence = tokenizer.encode_plus(
|
||||
table,
|
||||
sequence,
|
||||
padding=False,
|
||||
return_special_tokens_mask=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
not_padded_input_ids = not_padded_sequence["input_ids"]
|
||||
|
||||
not_padded_special_tokens_mask = not_padded_sequence["special_tokens_mask"]
|
||||
not_padded_sequence_length = len(not_padded_input_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual(sequence_length, not_padded_sequence_length)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(input_ids, not_padded_input_ids)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(special_tokens_mask, not_padded_special_tokens_mask)
|
||||
|
||||
# Test right padding
|
||||
tokenizer.padding_side = "right"
|
||||
|
||||
right_padded_sequence = tokenizer.encode_plus(
|
||||
table,
|
||||
sequence,
|
||||
max_length=sequence_length + padding_size,
|
||||
padding="max_length",
|
||||
return_special_tokens_mask=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
right_padded_input_ids = right_padded_sequence["input_ids"]
|
||||
|
||||
right_padded_special_tokens_mask = right_padded_sequence["special_tokens_mask"]
|
||||
right_padded_sequence_length = len(right_padded_input_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual(sequence_length + padding_size, right_padded_sequence_length)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(input_ids + [padding_idx] * padding_size, right_padded_input_ids)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(special_tokens_mask + [1] * padding_size, right_padded_special_tokens_mask)
|
||||
|
||||
# Test left padding
|
||||
tokenizer.padding_side = "left"
|
||||
left_padded_sequence = tokenizer.encode_plus(
|
||||
table,
|
||||
sequence,
|
||||
max_length=sequence_length + padding_size,
|
||||
padding="max_length",
|
||||
return_special_tokens_mask=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
left_padded_input_ids = left_padded_sequence["input_ids"]
|
||||
left_padded_special_tokens_mask = left_padded_sequence["special_tokens_mask"]
|
||||
left_padded_sequence_length = len(left_padded_input_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual(sequence_length + padding_size, left_padded_sequence_length)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual([padding_idx] * padding_size + input_ids, left_padded_input_ids)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual([1] * padding_size + special_tokens_mask, left_padded_special_tokens_mask)
|
||||
|
||||
if "token_type_ids" in tokenizer.model_input_names:
|
||||
token_type_ids = encoded_sequence["token_type_ids"]
|
||||
left_padded_token_type_ids = left_padded_sequence["token_type_ids"]
|
||||
right_padded_token_type_ids = right_padded_sequence["token_type_ids"]
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(
|
||||
(token_type_ids + [[token_type_padding_idx] * 7] * padding_size, right_padded_token_type_ids)
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(
|
||||
[[token_type_padding_idx] * 7] * padding_size + token_type_ids, left_padded_token_type_ids
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if "attention_mask" in tokenizer.model_input_names:
|
||||
attention_mask = encoded_sequence["attention_mask"]
|
||||
right_padded_attention_mask = right_padded_sequence["attention_mask"]
|
||||
left_padded_attention_mask = left_padded_sequence["attention_mask"]
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(attention_mask + [0] * padding_size, right_padded_attention_mask)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual([0] * padding_size + attention_mask, left_padded_attention_mask)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_batch_encode_plus_padding(self):
|
||||
# Test that padded sequences are equivalent between batch_encode_plus and encode_plus
|
||||
|
||||
# Right padding tests
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers(do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
sequences = [
|
||||
"Testing batch encode plus",
|
||||
"Testing batch encode plus with different sequence lengths",
|
||||
"Testing batch encode plus with different sequence lengths correctly pads",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
max_length = 100
|
||||
|
||||
# check correct behaviour if no pad_token_id exists and add it eventually
|
||||
self._check_no_pad_token_padding(tokenizer, sequences)
|
||||
|
||||
encoded_sequences = [
|
||||
tokenizer.encode_plus(table, sequence, max_length=max_length, padding="max_length")
|
||||
for sequence in sequences
|
||||
]
|
||||
encoded_sequences_batch = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(
|
||||
table, sequences, max_length=max_length, padding="max_length"
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(
|
||||
encoded_sequences, self.convert_batch_encode_plus_format_to_encode_plus(encoded_sequences_batch)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Left padding tests
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers(do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
tokenizer.padding_side = "left"
|
||||
sequences = [
|
||||
"Testing batch encode plus",
|
||||
"Testing batch encode plus with different sequence lengths",
|
||||
"Testing batch encode plus with different sequence lengths correctly pads",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
max_length = 100
|
||||
|
||||
# check correct behaviour if no pad_token_id exists and add it eventually
|
||||
self._check_no_pad_token_padding(tokenizer, sequences)
|
||||
|
||||
encoded_sequences = [
|
||||
tokenizer.encode_plus(table, sequence, max_length=max_length, padding="max_length")
|
||||
for sequence in sequences
|
||||
]
|
||||
encoded_sequences_batch = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(
|
||||
table, sequences, max_length=max_length, padding="max_length"
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(
|
||||
encoded_sequences, self.convert_batch_encode_plus_format_to_encode_plus(encoded_sequences_batch)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_batch_encode_plus_batch_sequence_length(self):
|
||||
# Tests that all encoded values have the correct size
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers(do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
sequences = [
|
||||
"Testing batch encode plus",
|
||||
"Testing batch encode plus with different sequence lengths",
|
||||
"Testing batch encode plus with different sequence lengths correctly pads",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
encoded_sequences = [tokenizer.encode_plus(table, sequence) for sequence in sequences]
|
||||
encoded_sequences_batch = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(table, sequences, padding=False)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(
|
||||
encoded_sequences, self.convert_batch_encode_plus_format_to_encode_plus(encoded_sequences_batch)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
maximum_length = len(
|
||||
max([encoded_sequence["input_ids"] for encoded_sequence in encoded_sequences], key=len)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# check correct behaviour if no pad_token_id exists and add it eventually
|
||||
self._check_no_pad_token_padding(tokenizer, sequences)
|
||||
|
||||
encoded_sequences_padded = [
|
||||
tokenizer.encode_plus(table, sequence, max_length=maximum_length, padding="max_length")
|
||||
for sequence in sequences
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
encoded_sequences_batch_padded = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(table, sequences, padding=True)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(
|
||||
encoded_sequences_padded,
|
||||
self.convert_batch_encode_plus_format_to_encode_plus(encoded_sequences_batch_padded),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# check 'longest' is unsensitive to a max length
|
||||
encoded_sequences_batch_padded_1 = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(table, sequences, padding=True)
|
||||
encoded_sequences_batch_padded_2 = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(
|
||||
table, sequences, max_length=maximum_length + 10, padding="longest"
|
||||
)
|
||||
for key in encoded_sequences_batch_padded_1.keys():
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(
|
||||
encoded_sequences_batch_padded_1[key],
|
||||
encoded_sequences_batch_padded_2[key],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# check 'no_padding' is unsensitive to a max length
|
||||
encoded_sequences_batch_padded_1 = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(table, sequences, padding=False)
|
||||
encoded_sequences_batch_padded_2 = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus(
|
||||
table, sequences, max_length=maximum_length + 10, padding=False
|
||||
)
|
||||
for key in encoded_sequences_batch_padded_1.keys():
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(
|
||||
encoded_sequences_batch_padded_1[key],
|
||||
encoded_sequences_batch_padded_2[key],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_special_tokens_mask_input_pairs(self):
|
||||
tokenizers = self.get_tokenizers(do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
for tokenizer in tokenizers:
|
||||
with self.subTest(f"{tokenizer.__class__.__name__}"):
|
||||
sequence_0 = "Encode this."
|
||||
empty_table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=0)
|
||||
table = self.get_table(tokenizer, length=10)
|
||||
encoded_sequence = tokenizer.encode(empty_table, sequence_0, add_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
number_of_tokens = len(encoded_sequence)
|
||||
encoded_sequence += tokenizer.encode(table, "", add_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
encoded_sequence_dict = tokenizer.encode_plus(
|
||||
table,
|
||||
sequence_0,
|
||||
add_special_tokens=True,
|
||||
return_special_tokens_mask=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
encoded_sequence_w_special = encoded_sequence_dict["input_ids"]
|
||||
special_tokens_mask = encoded_sequence_dict["special_tokens_mask"]
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(special_tokens_mask), len(encoded_sequence_w_special))
|
||||
|
||||
filtered_sequence = [
|
||||
(x if not special_tokens_mask[i] else None) for i, x in enumerate(encoded_sequence_w_special)
|
||||
]
|
||||
# NOTE: as TAPEX adds a space between a table and a sequence, we need to remove it
|
||||
# in order to have equivalent results with encoding an empty table or empty sequence
|
||||
del filtered_sequence[number_of_tokens + 1]
|
||||
filtered_sequence = [x for x in filtered_sequence if x is not None]
|
||||
print("Encoded sequence:", encoded_sequence)
|
||||
print("Filtered sequence:", filtered_sequence)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(encoded_sequence, filtered_sequence)
|
||||
|
||||
@slow
|
||||
def test_full_tokenizer(self):
|
||||
question = "Greece held its last Summer Olympics in 2004"
|
||||
table_dict = {
|
||||
"header": ["Year", "City", "Country", "Nations"],
|
||||
"rows": [
|
||||
[1896, "Athens", "Greece", 14],
|
||||
[1900, "Paris", "France", 24],
|
||||
[1904, "St. Louis", "USA", 12],
|
||||
[2004, "Athens", "Greece", 201],
|
||||
[2008, "Beijing", "China", 204],
|
||||
[2012, "London", "UK", 204],
|
||||
],
|
||||
}
|
||||
table = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(table_dict["rows"])
|
||||
table.columns = table_dict["header"]
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = TapexTokenizer.from_pretrained("microsoft/tapex-large-finetuned-wtq")
|
||||
encoding = tokenizer(table, question)
|
||||
|
||||
# fmt: off
|
||||
expected_results = {'input_ids': [0, 821, 5314, 1755, 547, 63, 94, 1035, 1021, 31434, 2857, 11, 4482, 11311, 4832, 76, 1721, 343, 1721, 247, 1721, 3949, 3236, 112, 4832, 42773, 1721, 23, 27859, 1721, 821, 5314, 1755, 1721, 501, 3236, 132, 4832, 23137, 1721, 2242, 354, 1721, 6664, 2389, 1721, 706, 3236, 155, 4832, 42224, 1721, 1690, 4, 26120, 354, 1721, 201, 102, 1721, 316, 3236, 204, 4832, 4482, 1721, 23, 27859, 1721, 821, 5314, 1755, 1721, 21458, 3236, 195, 4832, 2266, 1721, 28, 40049, 1721, 1855, 1243, 1721, 28325, 3236, 231, 4832, 1125, 1721, 784, 24639, 1721, 1717, 330, 1721, 28325, 2]}
|
||||
# fmt: on
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(encoding.input_ids, expected_results["input_ids"])
|
||||
|
||||
def test_tokenizer_as_target(self):
|
||||
# by default the tokenizer do_lower_case
|
||||
tokenizer = TapexTokenizer.from_pretrained("microsoft/tapex-base")
|
||||
answer_text = "tapex is a good model!"
|
||||
expected_src_tokens = [0, 90, 5776, 1178, 16, 10, 205, 1421, 328, 2]
|
||||
with tokenizer.as_target_tokenizer():
|
||||
answer_encoding = tokenizer(answer=answer_text)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(answer_encoding.input_ids, expected_src_tokens)
|
||||
|
||||
@slow
|
||||
def test_tokenizer_lower_case(self):
|
||||
cased_tokenizer = TapexTokenizer.from_pretrained("microsoft/tapex-base", do_lower_case=False)
|
||||
uncased_tokenizer = TapexTokenizer.from_pretrained("microsoft/tapex-base", do_lower_case=True)
|
||||
answer_text = "Beijing, London, Paris"
|
||||
answer_text_lower = "beijing, london, paris"
|
||||
|
||||
with cased_tokenizer.as_target_tokenizer():
|
||||
with uncased_tokenizer.as_target_tokenizer():
|
||||
self.assertNotEqual(
|
||||
cased_tokenizer(answer=answer_text).input_ids, uncased_tokenizer(answer=answer_text).input_ids
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(
|
||||
cased_tokenizer(answer=answer_text_lower).input_ids,
|
||||
uncased_tokenizer(answer=answer_text).input_ids,
|
||||
)
|
||||
# batched encoding assert
|
||||
self.assertNotEqual(
|
||||
cased_tokenizer(answer=[answer_text]).input_ids, uncased_tokenizer(answer=[answer_text]).input_ids
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(
|
||||
cased_tokenizer(answer=[answer_text_lower]).input_ids,
|
||||
uncased_tokenizer(answer=[answer_text]).input_ids,
|
||||
)
|
||||
# test input encoding lowercase
|
||||
question = "Greece held its last Summer Olympics in 2004"
|
||||
table_dict = {
|
||||
"header": ["Year", "City", "Country", "Nations"],
|
||||
"rows": [
|
||||
[1896, "Athens", "Greece", 14],
|
||||
[1900, "Paris", "France", 24],
|
||||
[1904, "St. Louis", "USA", 12],
|
||||
[2004, "Athens", "Greece", 201],
|
||||
[2008, "Beijing", "China", 204],
|
||||
[2012, "London", "UK", 204],
|
||||
],
|
||||
}
|
||||
table = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(table_dict["rows"])
|
||||
table.columns = table_dict["header"]
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertNotEqual(
|
||||
cased_tokenizer(table=table, query=question).input_ids,
|
||||
uncased_tokenizer(table=table, query=question).input_ids,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
docs/source/en/quicktour.mdx
|
||||
docs/source/en/task_summary.mdx
|
||||
docs/source/en/model_doc/speech_to_text.mdx
|
||||
docs/source/en/model_doc/tapex.mdx
|
||||
src/transformers/generation_utils.py
|
||||
src/transformers/models/bart/modeling_bart.py
|
||||
src/transformers/models/beit/modeling_beit.py
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user