# AWQ
Try AWQ quantization with this [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1HzZH89yAXJaZgwJDhQj9LqSBux932BvY)!
[Activation-aware Weight Quantization (AWQ)](https://hf.co/papers/2306.00978) doesn't quantize all the weights in a model, and instead, it preserves a small percentage of weights that are important for LLM performance. This significantly reduces quantization loss such that you can run models in 4-bit precision without experiencing any performance degradation.
There are several libraries for quantizing models with the AWQ algorithm, such as [llm-awq](https://github.com/mit-han-lab/llm-awq), [autoawq](https://github.com/casper-hansen/AutoAWQ) or [optimum-intel](https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/main/en/intel/optimization_inc). Transformers supports loading models quantized with the llm-awq and autoawq libraries. This guide will show you how to load models quantized with autoawq, but the process is similar for llm-awq quantized models.
Make sure you have autoawq installed:
```bash
pip install autoawq
```
AWQ-quantized models can be identified by checking the `quantization_config` attribute in the model's [config.json](https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/zephyr-7B-alpha-AWQ/blob/main/config.json) file:
```json
{
"_name_or_path": "/workspace/process/huggingfaceh4_zephyr-7b-alpha/source",
"architectures": [
"MistralForCausalLM"
],
...
...
...
"quantization_config": {
"quant_method": "awq",
"zero_point": true,
"group_size": 128,
"bits": 4,
"version": "gemm"
}
}
```
A quantized model is loaded with the [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] method. If you loaded your model on the CPU, make sure to move it to a GPU device first. Use the `device_map` parameter to specify where to place the model:
```py
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_id = "TheBloke/zephyr-7B-alpha-AWQ"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, device_map="cuda:0")
```
Loading an AWQ-quantized model automatically sets other weights to fp16 by default for performance reasons. If you want to load these other weights in a different format, use the `torch_dtype` parameter:
```py
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_id = "TheBloke/zephyr-7B-alpha-AWQ"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float32)
```
AWQ quantization can also be combined with [FlashAttention-2](../perf_infer_gpu_one#flashattention-2) to further accelerate inference:
```py
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("TheBloke/zephyr-7B-alpha-AWQ", attn_implementation="flash_attention_2", device_map="cuda:0")
```
## Fused modules
Fused modules offers improved accuracy and performance and it is supported out-of-the-box for AWQ modules for [Llama](https://huggingface.co/meta-llama) and [Mistral](https://huggingface.co/mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1) architectures, but you can also fuse AWQ modules for unsupported architectures.
Fused modules cannot be combined with other optimization techniques such as FlashAttention-2.
To enable fused modules for supported architectures, create an [`AwqConfig`] and set the parameters `fuse_max_seq_len` and `do_fuse=True`. The `fuse_max_seq_len` parameter is the total sequence length and it should include the context length and the expected generation length. You can set it to a larger value to be safe.
For example, to fuse the AWQ modules of the [TheBloke/Mistral-7B-OpenOrca-AWQ](https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/Mistral-7B-OpenOrca-AWQ) model.
```python
import torch
from transformers import AwqConfig, AutoModelForCausalLM
model_id = "TheBloke/Mistral-7B-OpenOrca-AWQ"
quantization_config = AwqConfig(
bits=4,
fuse_max_seq_len=512,
do_fuse=True,
)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, quantization_config=quantization_config).to(0)
```
The [TheBloke/Mistral-7B-OpenOrca-AWQ](https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/Mistral-7B-OpenOrca-AWQ) model was benchmarked with `batch_size=1` with and without fused modules.
Unfused module
| Batch Size | Prefill Length | Decode Length | Prefill tokens/s | Decode tokens/s | Memory (VRAM) |
|-------------:|-----------------:|----------------:|-------------------:|------------------:|:----------------|
| 1 | 32 | 32 | 60.0984 | 38.4537 | 4.50 GB (5.68%) |
| 1 | 64 | 64 | 1333.67 | 31.6604 | 4.50 GB (5.68%) |
| 1 | 128 | 128 | 2434.06 | 31.6272 | 4.50 GB (5.68%) |
| 1 | 256 | 256 | 3072.26 | 38.1731 | 4.50 GB (5.68%) |
| 1 | 512 | 512 | 3184.74 | 31.6819 | 4.59 GB (5.80%) |
| 1 | 1024 | 1024 | 3148.18 | 36.8031 | 4.81 GB (6.07%) |
| 1 | 2048 | 2048 | 2927.33 | 35.2676 | 5.73 GB (7.23%) |
Fused module
| Batch Size | Prefill Length | Decode Length | Prefill tokens/s | Decode tokens/s | Memory (VRAM) |
|-------------:|-----------------:|----------------:|-------------------:|------------------:|:----------------|
| 1 | 32 | 32 | 81.4899 | 80.2569 | 4.00 GB (5.05%) |
| 1 | 64 | 64 | 1756.1 | 106.26 | 4.00 GB (5.05%) |
| 1 | 128 | 128 | 2479.32 | 105.631 | 4.00 GB (5.06%) |
| 1 | 256 | 256 | 1813.6 | 85.7485 | 4.01 GB (5.06%) |
| 1 | 512 | 512 | 2848.9 | 97.701 | 4.11 GB (5.19%) |
| 1 | 1024 | 1024 | 3044.35 | 87.7323 | 4.41 GB (5.57%) |
| 1 | 2048 | 2048 | 2715.11 | 89.4709 | 5.57 GB (7.04%) |
The speed and throughput of fused and unfused modules were also tested with the [optimum-benchmark](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-benchmark) library.
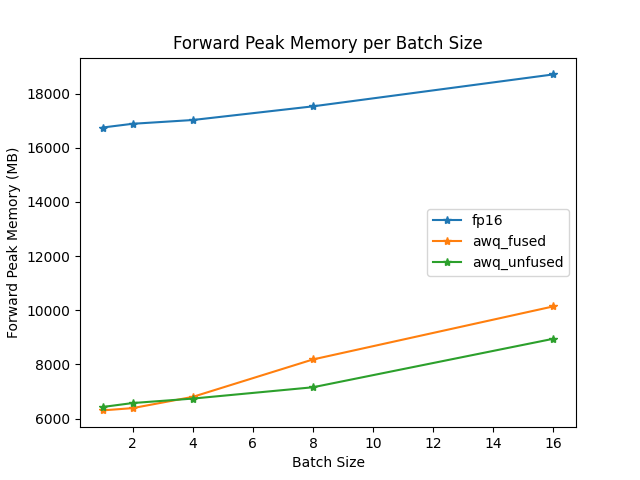 forward peak memory/batch size
forward peak memory/batch size
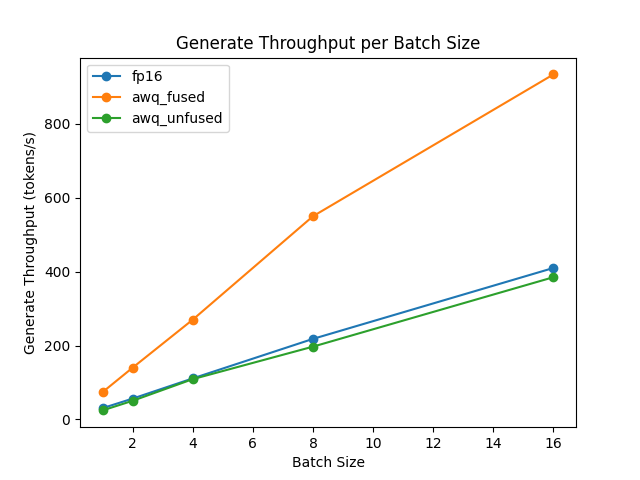 generate throughput/batch size
generate throughput/batch size
For architectures that don't support fused modules yet, you need to create a custom fusing mapping to define which modules need to be fused with the `modules_to_fuse` parameter. For example, to fuse the AWQ modules of the [TheBloke/Yi-34B-AWQ](https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/Yi-34B-AWQ) model.
```python
import torch
from transformers import AwqConfig, AutoModelForCausalLM
model_id = "TheBloke/Yi-34B-AWQ"
quantization_config = AwqConfig(
bits=4,
fuse_max_seq_len=512,
modules_to_fuse={
"attention": ["q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj"],
"layernorm": ["ln1", "ln2", "norm"],
"mlp": ["gate_proj", "up_proj", "down_proj"],
"use_alibi": False,
"num_attention_heads": 56,
"num_key_value_heads": 8,
"hidden_size": 7168
}
)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, quantization_config=quantization_config).to(0)
```
The parameter `modules_to_fuse` should include:
- `"attention"`: The names of the attention layers to fuse in the following order: query, key, value and output projection layer. If you don't want to fuse these layers, pass an empty list.
- `"layernorm"`: The names of all the LayerNorm layers you want to replace with a custom fused LayerNorm. If you don't want to fuse these layers, pass an empty list.
- `"mlp"`: The names of the MLP layers you want to fuse into a single MLP layer in the order: (gate (dense, layer, post-attention) / up / down layers).
- `"use_alibi"`: If your model uses ALiBi positional embedding.
- `"num_attention_heads"`: The number of attention heads.
- `"num_key_value_heads"`: The number of key value heads that should be used to implement Grouped Query Attention (GQA). If `num_key_value_heads=num_attention_heads`, the model will use Multi Head Attention (MHA), if `num_key_value_heads=1` the model will use Multi Query Attention (MQA), otherwise GQA is used.
- `"hidden_size"`: The dimension of the hidden representations.
## ExLlama-v2 support
Recent versions of `autoawq` supports ExLlama-v2 kernels for faster prefill and decoding. To get started, first install the latest version of `autoawq` by running:
```bash
pip install git+https://github.com/casper-hansen/AutoAWQ.git
```
Get started by passing an `AwqConfig()` with `version="exllama"`.
```python
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, AwqConfig
quantization_config = AwqConfig(version="exllama")
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"TheBloke/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1-AWQ",
quantization_config=quantization_config,
device_map="auto",
)
input_ids = torch.randint(0, 100, (1, 128), dtype=torch.long, device="cuda")
output = model(input_ids)
print(output.logits)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("TheBloke/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1-AWQ")
input_ids = tokenizer.encode("How to make a cake", return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
output = model.generate(input_ids, do_sample=True, max_length=50, pad_token_id=50256)
print(tokenizer.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
```
Note this feature is supported on AMD GPUs.
## CPU support
Recent versions of `autoawq` supports CPU with ipex op optimizations. To get started, first install the latest version of `autoawq` by running:
```bash
pip install intel-extension-for-pytorch
pip install git+https://github.com/casper-hansen/AutoAWQ.git
```
Get started by passing an `AwqConfig()` with `version="ipex"`.
```python
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, AwqConfig
quantization_config = AwqConfig(version="ipex")
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
"TheBloke/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v0.3-AWQ",
quantization_config=quantization_config,
device_map="cpu",
)
input_ids = torch.randint(0, 100, (1, 128), dtype=torch.long, device="cpu")
output = model(input_ids)
print(output.logits)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("TheBloke/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v0.3-AWQ")
input_ids = tokenizer.encode("How to make a cake", return_tensors="pt")
pad_token_id = tokenizer.eos_token_id
output = model.generate(input_ids, do_sample=True, max_length=50, pad_token_id=pad_token_id)
print(tokenizer.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
```
Note this feature is supported on Intel CPUs.



